Interest Rates & Banking Test #1
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
How to find the total amount of money borrowed
# of shares x price of shares = total price
total price x initial margin requirement = margin price
total price - margin price = amount to be borrowed
How to find the price when you receive a maintenance margin call
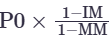
P0 = Initial price
IM = Initial margin
MM= Maintenance margin
How to find EAR
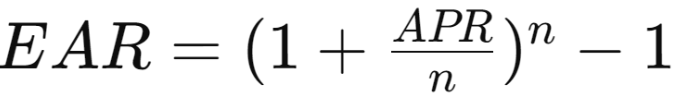
What is considered a banks assets and liabilities?
Assets:
cash, loans, investments in securities, mortgages
Liabilities:
deposits, money borrowed from other institutions
What is the main role of financial intermediaries and what are examples?
borrow funds from savers and lend them to borrowers
ex: banks
What is the Federal Reserve System?
the central bank of the United States
conducting monetary policy, supervising and regulating financial institutions, ensuring the safety and efficiency of payment systems, and promoting community development
Who carries out monetary policy?
the federal reserve system
M1 aggregate
representing "narrow money" and includes the most liquid components of the money supply used for everyday transactions: currency in circulation (physical cash and coins) and checkable deposits (such as checking and most savings accounts)
M2 Aggregrate
broader and slightly less liquid form of money M1
includes everything in the narrower M1 aggregate (currency in circulation, traveler's checks, demand and other checkable deposits)
plus savings deposits
small-denomination time deposits (like certificates of deposit under $100,000)
balances in retail money market funds
which aggregate includes money market mutual fund shares?
M2
What is the velocity of money?
the number of times each dollar in the money supply is used to buy goods and services included in GDP
What are all the financial assets?
Money
Bonds
Stocks
Foreign exchange
Securitization
What are examples of financial institutions?
commercial banks
brokerages
insurance companies
credit unions
What are the key functions of money?
-medium of exchange
-unit of measure
-store of value
-it offers a standard of deferred payment
what are examples of payment systems?
Automated clearing house (ACH)
Blockchain / bitcoin
CBCD
Spike
CLOVER
What is a margin call?
•Notification from broker that you must put up additional funds or have position liquidated
This happens when the value of your investments, bought with borrowed money (margin), falls below a certain threshold, meaning your account no longer has enough of your own money to cover the outstanding loan
What is the moral hazard problem?
•financial firms, especially large ones, make riskier investments if they believe the government will save them from bankruptcy
What are the four main sources of inefficiency in a barter economy?
double coincidence of wants increase the transactions costs
each good has many prices
a lack of standardization exists for goods and services
it is difficult to accumulate wealth
What does buying on margin mean?
using only a portion of the proceeds for an investment
borrow remaining component
margin arrangements differ for stocks and futures
What is the quantity of money theory?
a theory about the connection between money and prices that assumes that the velocity of money is determined mainly be institutional factors and so is roughly constant in the short run.
What are debt instruments
•methods of financing debt, including simple loans, discount bonds, coupon bonds, and fixed payment loans.
–also known as credit market instruments or fixed income assets
Explain the relationship between the yield to maturity on a bond and its price.
Bond price and yield to maturity (YTM) have an inverse relationship: when one goes up, the other goes down
What is a financial arbitrage?
is the process of buying and selling securities to profit from price changes over a brief period of time
What are the determinants of portfolio choice?
investors wealth
the expected rates of returns from different investments
the degrees of risk in different investments
the liquidity of different investments
the costs of acquiring information about different investments
Important factors for explaining shifts in the supply curve for bonds:
expected pretax profitability of physical capital investment
business taxes
expected inflation
government borrowing
The treasury yield curve
shows the relationship among the interest rates on treasury bonds with different maturities
upward sloping = short term rates lower than long term rates
downward sloping = short term rates are higher than long term interest rates
Why do banks have a maturity mismatch?
because they borrow short term from depositors and lend long term to households and firms
banks face a liquidity risk because they may be unable to meet their depositors’ withdrawals
How to fix maturity mismatch
immunization
intuition
duration matching
Expectations theory
1.Investors have the same investment objectives.
2.For a given holding period, investors view bonds of different maturities as being perfect substitutes for one another.
theory assumes that the returns from the two strategies must be the same
The liquidity premium theory
–Investors demand risk premium on long-term bonds
–fn must be > E(rN) to induce investment on the forward rate fn
–Liquidity premium
▪Extra expected return demanded by investors as compensation for greater risk of long-term bonds
–Spread between forward ROI and expected short sale
▪f_n=E(r_n )+Liquidity premium
The segmented markets theory of term structure
holds that the interest rate on a bond of a particular maturity is determined only by the demand and supply of bonds of that maturity
investors in the bond market do not all have the same objectives
.Investors do not see bonds of different maturities as being perfect substitutes for each other.
What is duration analysis?
an analysis of how sensitive a bank’s capital is to changes in market interest rates