ap bio unit 7
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Evolution
The gradual change of a species over time to better suit their environment.
The current accepted theory for evolution was created by Charles Darwin during the 1880s
Adaptation
An inherited trait that makes an organism more fit for its environment.
“Fitness” refers to an organism’s ability to reproduce
Example: large beaks are an adaptation of some finches, which allows them to crack open seeds
Niche
Refers to the role or function of an organism or species in an ecosystem.
Example: an organism’s food source, where it lives, what services it provides to an ecosystem, etc.
Organisms or species with overlapping niches leads to competition
Natural Selection
A process in which individuals with favorable inherited traits are more likely to survive and reproduce.
Natural selection is the mechanism, or driving force, of evolution
Artificial Selection
Where humans modify other species by selecting and breeding individuals with desired traits.
Key Features of Natural Selection
Members of a population often vary in their inherited traits
All species can produce more offspring than the environment can support, and many of these offspring fail to survive and reproduce.
Individuals whose inherited traits give them a higher probability of surviving and reproducing in a given environment tend to have more offspring than other individuals.
This unequal ability of individuals to survive and reproduce will lead to the accumulation of favorable traits in the population over generations.
Note that populations, not individuals, evolve over time
Natural selection can only increase or decrease existing heritable traits that vary in a population. It does not create new traits.
The traits that are adaptive will vary with different environments.
Requirements for natural selection to occur
Competition: More offspring must be produced than can be supported by the environment.
Variation: Offspring must be produced with traits that differ from one another.
Adaptation: Certain variations must be more advantageous than other variations. Some individuals must be more likely to survive and reproduce.
Heritability: The favorable trait, or adaptation, must be genetic and capable of being inherited by the next generation.
Homologies
Similarities between species resulting from common ancestry.
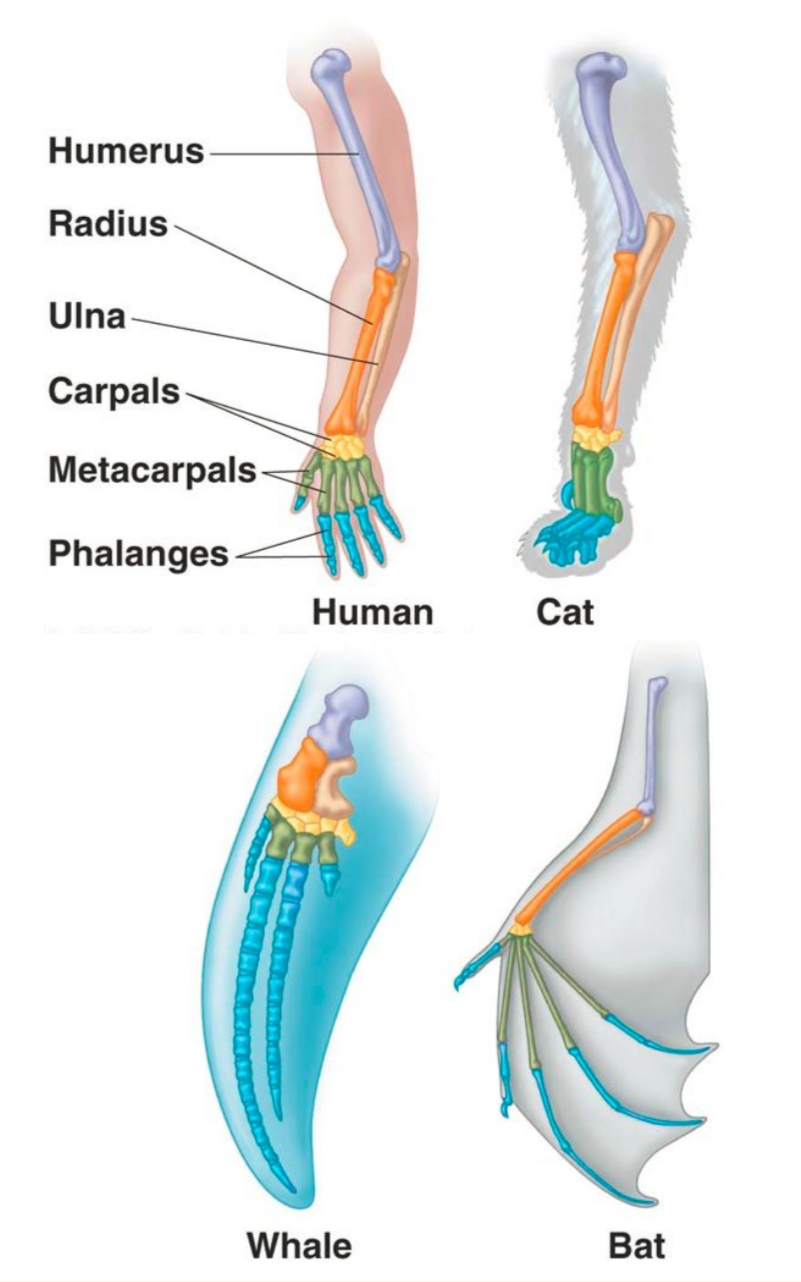
Homologous structures
Anatomical similarities between species that share a similar structure, but not necessarily the same function.
SIMILAR STRUCTURE, DIFFERENT FUNCTION
Example: The image shows these animals share the same basic structure of bones. However, the function of them are different.
Vestigial structure
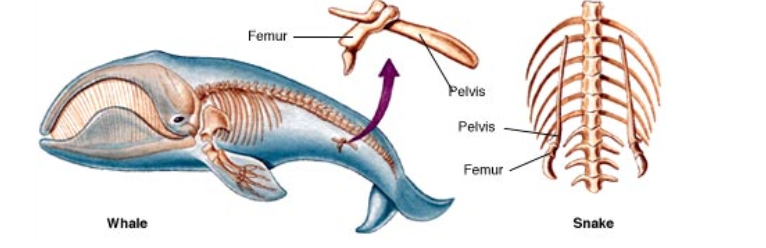
Structures that once have served important functions in ancestral species, but have lost most, or all, of their function in living species.
Examples: Humans, dogs, and cats all have similar pelvises, which are homologous structures (similar structure, different function) to a vestigial pair of bones that snakes and whales have. These bones are the last remains of a pelvis, with no legs to attach.
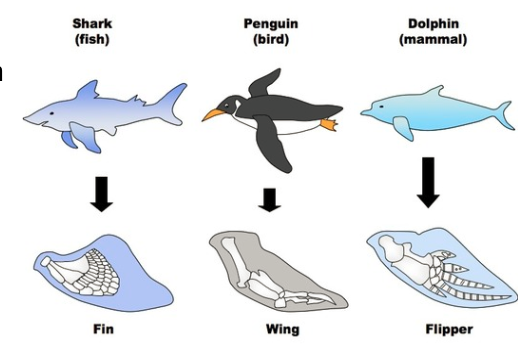
Analogous structures
Similar features found in different species that are NOT the result of recent common ancestry. These structures may serve similar functions but have different anatomical structures.
DIFFERENT STRUCTURE, SIMILAR FUNCTION
Example: A shark fin, penguin wing, and dolphin flipper have the same function but differ in their anatomical structure.
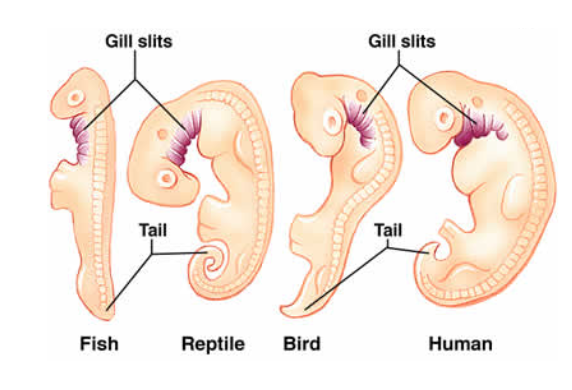
Comparative embryology
Reveals anatomical homologies (similarities between species resulting from common ancestry) not visible in adult organisms.
Example: Gill slits and tail bones found in the embryos of humans, reptiles, birds, and fish.
Fossil record
Provides evidence of:
The extinction of species
The origin of new groups
Changes within groups over time
Fossils can document important transitions.
Ex: the transition from land to sea in the ancestors of cetaceans
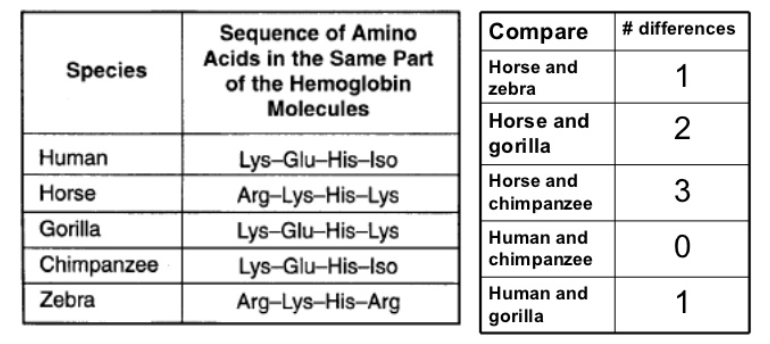
DNA Sequencing
Modern technological advances now allow scientists to sequence nucleotides in DNA and amino acids in proteins
By sequencing genes in different species, scientists can figure out what type of homologies exist between species on a molecular level.
Population
A localized group of individuals capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring.
Gene variation is required for a population to evolve, but does not guarantee that it will. One or more factors that cause evolution must be at work for a population to evolve.
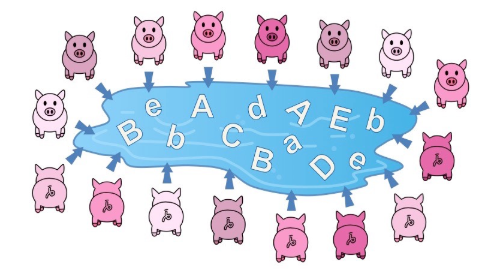
Gene pool
Refers to all the alleles, for every gene, present in individuals of a population.
Represents all the possible alleles that could be inherited by the next generation
Allele Frequencies
The frequency of an allele in a population can be calculated.
For diploid organisms, the total number of alleles at a locus (gene location on a chromosome) is the total number of individuals times 2
The total number of dominant alleles at a locus is 2 alleles for each homozygous dominant individual plus 1 allele for each heterozygous individual; the same logic applies for recessive alleles.
By convention, if there are 2 alleles at a locus, p and q are used to represent their frequencies.
p usually represents the frequency of dominant alleles, while q represents the frequency of recessive alleles.
The frequency of all alleles in a population will add up to 1
p + q = 1
The Hardy-Weinberg Equation
If p and q represent the frequencies of the only two possible alleles in a population at a particular locus, then p2 + 2pq +q2 = 1
p = frequency of dominant allele (usually)
q = frequency of recessive allele
p2 = frequency of homozygous dominant genotype
q2 = frequency of homozygous recessive genotype
2pq = frequency of heterozygous genotype
This is called the Hardy-Weinberg equation. It describes the genetic makeup expected for a population that is not evolving.
If the population is not evolving we say that the population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
The Hardy-Weinberg equation describes a hypothetical population that is not evolving.
Allele and genotype frequencies remain constant from generation to generation for a population in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
If the data observed for the population differ from the expected values, then the population may be evolving.
In real populations, allele and genotype frequencies usually change over time.
(If Hardy-Weinberg equation equals to 1, the population is not evolving. If it doesn’t equal to 1, the population is evolving because something is causing a change in allele frequencies like natural selection or a mutation).
Conditions needed for a population to be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium:
No mutations
Random mating (individuals do not pick mates based on traits)
No natural selection
Extremely large population size
No gene flow (no migration)
PKU
The occurrence of PKU (a recessive genetic disorder) is said to be in Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium for these reasons:
The PKU gene mutation rate is very low
Mate selection is random with respect to whether or not an individual is a carrier for the PKU allele
Natural selection can only act on rare homozygous individuals who do not follow dietary restrictions.
The population is large.
Migration has no effect, as many other populations have similar allele frequencies.
Microevolution
The change in allele frequencies in a population over many generations.
Three major factors alter allele frequencies and bring about most evolutionary change:
Genetic drift
Gene flow
Natural selection
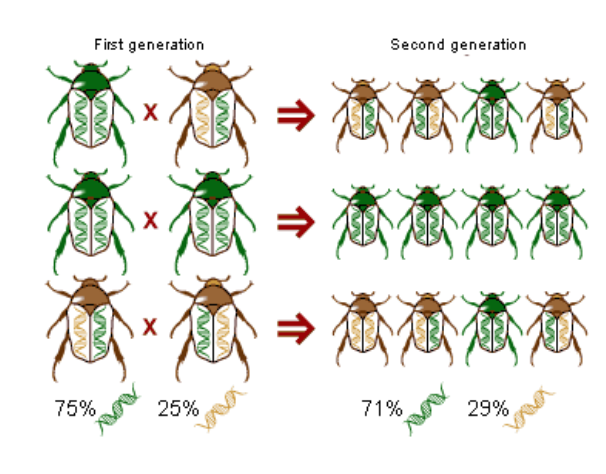
Genetic Drift
Occurs when allele frequencies in a population change by random chance, not because of natural selection.
The smaller a population, the more likely it is that chance alone will cause deviation from a predicted result.
Genetic drift tends to reduce genetic variation through losses of alleles, especially in small populations.
Two examples of genetic drift:
The founder effect
The bottleneck effect