Chem FINAL
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/99
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
1
New cards
decomposition
AB → A + B
2
New cards
Single Displacement
Element + Compound → Compound + Element
(A + BC → AC + B)
\
(Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2)
(A + BC → AC + B)
\
(Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2)
3
New cards
Ionic bonds
transfer of electrons
4
New cards
Covalent bonds
sharing of electrons
5
New cards
Anion
negative ions
* more negative because they **gain** electrons
* nonmetals
* end in -ide
* more negative because they **gain** electrons
* nonmetals
* end in -ide
6
New cards
Cation
Positive ions
* more positive because the **lose** electrons
* metals
* more positive because the **lose** electrons
* metals
7
New cards
Octet Rule definition
atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons in order to acquire eight valence electrons (noble gas configurations)
8
New cards
Non-metals tend to
gain electrons
9
New cards
Metals tend to
lose electrons
10
New cards
When two elements transfer electrons
Ionic bond is formed
11
New cards
Diatomic Molecules
N2, H2, O2, Cl2, F2, Br2, I2,
* forms a seven on the periodic table
* atoms are chemically bonded
* exist in nature
* two of the same types of atoms
* forms a seven on the periodic table
* atoms are chemically bonded
* exist in nature
* two of the same types of atoms
12
New cards
Alkali metals & Alkaline Earth Metals bond with
Halogens
13
New cards
Oxides
A metal forms a bond with oxygen
14
New cards
Binary Compounds
two elements
15
New cards
Monatomic
containing one atom
16
New cards
Polyatomic ions
Composed of *more than* two elements
17
New cards
Salt is formed
A non-metal and a metal
18
New cards
Properties of Ionic compounds
* hard but brittle
* high boiling and melting points
* __Solids__ **dont** conduct electricity
* __Liquids/Solutions__ conduct electricity
* high boiling and melting points
* __Solids__ **dont** conduct electricity
* __Liquids/Solutions__ conduct electricity
19
New cards
Diatomic molecules bond
Diatomic covalent bonding
20
New cards
Water
polar covalent compound
* oxygen has six valence electrons
* each hydrogen atom has one valence electron
* oxygen has six valence electrons
* each hydrogen atom has one valence electron
21
New cards
Types of Covalent Bonds
Single Bonds, Double Bonds, Triple Bonds
22
New cards
SIngle Bond
atoms share **one pair** of electrons **(2)**
23
New cards
Double Bonds
atoms share **two pairs** of electrons **(4)**
24
New cards
Triple Bonds
atoms share **three pairs** of electrons **(6)**
25
New cards
Lewis structures show
arrangements of electrons and bond
26
New cards
Strenght of a covalent bond is dependent on
bond length
27
New cards
Bond Length
the distance between two bonded nuclei
28
New cards
Bond-Dissociation energy
amount of energy needed to break bonds
* Inverse relationship between bond length and bond energy
* Inverse relationship between bond length and bond energy
29
New cards
Conversion for temperature (SI Unit)
273° K = 0° C
30
New cards
Lewis structures can predict
molecular shape
31
New cards
Unshared pairs of electrons can influence
molecular shape
32
New cards
Molecular orbital
the region of high probability that is occupied by an individual electron as it travels with the wavelike motion in the three-dimensional space around one of two or more associated nuclei
33
New cards
Dipole
has a slight negative and positive end
34
New cards
The symbol *𝛿*
shows partial negative or partial positive charge
35
New cards
Electronegativity
determines Bond Type
36
New cards
Polarity
related to Bond Strength
37
New cards
Reactions occur when
substances undergo changes
38
New cards
Bonds are ______,__ and new bonds are ____ in a chemical reaction
broken, formed
39
New cards
Combustion reactions always have
Water (H2O) and Carbon Dioxide (CO2) on the product side
40
New cards
△
heat has been added
41
New cards
Products
substances formed by reaction
* right of the arrow
* right of the arrow
42
New cards
States of matter
(s), (l), (g), or (aq)
43
New cards
Evidence of a Chemical Change
* color change
* evolution of a gas
* formation of a precipitate
* release or absorption of energy
* evolution of a gas
* formation of a precipitate
* release or absorption of energy
44
New cards
Endothermic
absorption of heat
45
New cards
exothermic
release of heat
46
New cards
What is the **study of quantitative relationships** between the amount of reactants used and the amounts of products formed by a chemical reaction
Stoichiometry
47
New cards
Percent Yield
Percent Yield = (Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield ) x 100
48
New cards
Stoichiometry is based on the law of. . .?
Conservation of mass
49
New cards
When atoms or ions are used in an equation what conversion factor must be used?
Avogadro’s Constant
50
New cards
What is always the first step in a stoichiometry problem
The given
51
New cards
Double Displacement
Compound + Compound → Compound + Compound
(AD+ BC → AC + BD)
\
(AgNO3 + NaCl → AgCl + NaNO3)
(\*metals go with nonmetals\*)
(AD+ BC → AC + BD)
\
(AgNO3 + NaCl → AgCl + NaNO3)
(\*metals go with nonmetals\*)
52
New cards
Combustion
compound/elements + O2 → products
(CH4 + **O2** → *CO2 + H2O*)
(CH4 + **O2** → *CO2 + H2O*)
53
New cards
Synthesis
A + B → AB
(Zn +I2 → ZnI2)
(Zn +I2 → ZnI2)
54
New cards
1
mono
55
New cards
6
hexa
56
New cards
0\.5 - 2.1
polar covalent
57
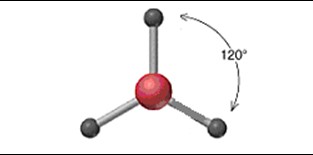
New cards
Linear
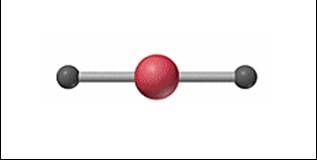
58
New cards
Trigonal Pyramidal
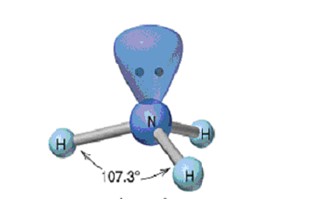
59
New cards
Which atom is most likely to form a triple covalent bond
Carbon
60
New cards
Bent
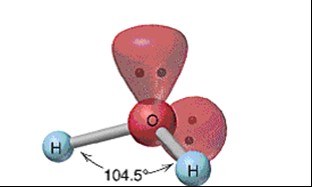
61
New cards
Tetrahedral
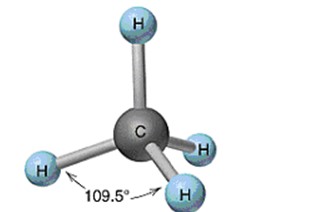
62
New cards
2
di
63
New cards
3
tri
64
New cards
4
tetra
65
New cards
5
penta
66
New cards
7
hepta
67
New cards
8
octa
68
New cards
9
nona
69
New cards
10
deca
70
New cards
Covalent bonds are between
two nonmetals
71
New cards
Bonds lengths ______ distances because bonds are ______
average, rigid
72
New cards
A gaseous substance with poor conductivity is most likely a(n) ________________.
A non-metal/molecular compound
73
New cards
Pt symbol
a catalyst
74
New cards
Ag(s) + NaCl(aq) →
Na(s) + AgCl(aq)
75
New cards
SI unit for amount
Mole/Mol
76
New cards
A mole is
the number of atoms in exactly 12 grams of carbon-12
77
New cards
number of particle in a mole is called
Avogadro’s Number
(6.022 x 10^23)
(6.022 x 10^23)
78
New cards
Mole ratio
the key in Stoichiometry
79
New cards
Mole ratio is
a ratio between the number of moles of any two substance in a balanced chemical equation
80
New cards
limiting reactant
determines the amount of product formed
* determines the theoretical yield
* the one that runs out first
* determines the theoretical yield
* the one that runs out first
81
New cards
excess reactant
the reactant that is left over
82
New cards
Theoretical Yield
the maximum amount of product that can be formed from a given reactant
* Theoretical Yield is higher than actual yield
* Theoretical Yield is higher than actual yield
83
New cards
Actual Yield
the amount of product produced in a chemical experiment
84
New cards
Percent Yield
the ratio of actual yield to theoretical yield
* describes the efficiency of a reaction
* describes the efficiency of a reaction
85
New cards
Precent Yield formula
Percent yield = actual/theoretical x 100
86
New cards
Coefficients in a chemical equations are used in which one of the following conversion factors?
mole ratios
87
New cards
In stoichiometric calculations, you should:
round off only the final answer
88
New cards
Boyle’s law
inverse relationship between volume and pressure
* “volume of a fixed amount of gas at constant temperature varies inversely with pressure”
* P1V1 = P2V2
* “volume of a fixed amount of gas at constant temperature varies inversely with pressure”
* P1V1 = P2V2
89
New cards
As volume increases
pressure decreases
90
New cards
As volume decreamses
pressure increases
91
New cards
Charles’ Law
Direct relationship between volume and temperature
* “the volume of a given amount of gas is directly proportional to the Kelvin temperature
* V1/T1 = V2/T2
* “the volume of a given amount of gas is directly proportional to the Kelvin temperature
* V1/T1 = V2/T2
92
New cards
As temperature increases
volume increases
93
New cards
As temperature decreases,
volume decreases
94
New cards
0° Celsius
273° Kelvin
* uses for all v/t equations
* used in p/t problems
* uses for all v/t equations
* used in p/t problems
95
New cards
Gay-Lussac’s law
Direct relationship between pressure and temperature
* “The pressure of a fixed amount of gas varies directly with Kelvin temperature when volume remains constant”
* P1/T1 = P2/T2 **OR** P/T = K
* “The pressure of a fixed amount of gas varies directly with Kelvin temperature when volume remains constant”
* P1/T1 = P2/T2 **OR** P/T = K
96
New cards
As temperature increases
pressure increases
97
New cards
As temperature decreases
pressure decreases
98
New cards
Which is **not** a unit which describes pressure?
Newton
99
New cards
Finding the Percent of an Element in a Compound Formula
element/compound x 100
100
New cards
Triagonal Planar