Biopsychology Y2
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
What is the CNS made up of
Brain and spine
What is the peripheral nervous system made of
Autonomic and somatic nervous system
Draw a synapse
yes
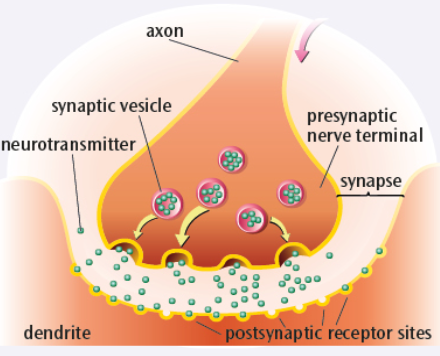
What is inhibition
Neuron becomes more negatively charged
Less likely to fire
What is excitation
Neuron becomes more positively charged
More likely to fire
What is summation
Excitatory and inhibatory influences summed before charge is passed
eg. if more inhibitory than excitatory, neuron does not fre
What is localisation of function
Idea that different parts of the brain perform different tasks
Where are the two hemispheres of the brain
Cerebrum
Label the brain structure
yes
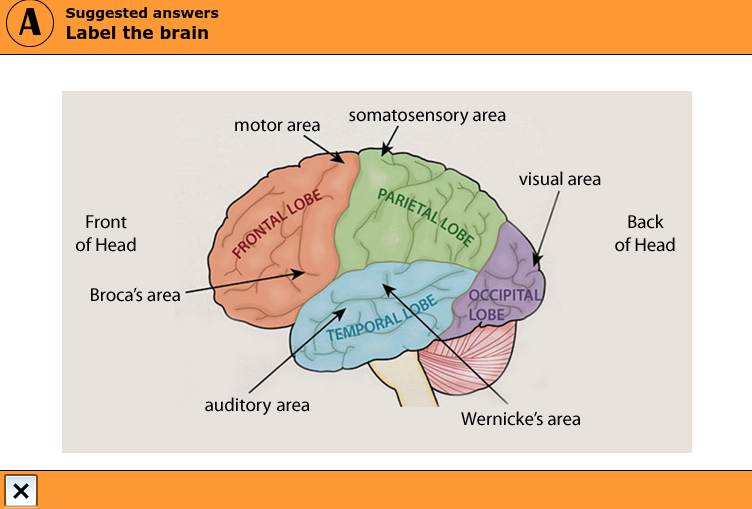
What is Broca’s area involved in
Language production
What is Wernicke’s area involved in
Language comprehension
Symptoms of Wernicke’s aphasia
Fluent yet senseless language - neologisms
Strengths for localisation of function
Dogherty et al found neurosurgery effective
Petersen et al found brain scans proved Wernicke’s area
Limitations for localisation of function
Lashley found no specific area of brain for rats to learn routes
Dick et al found modern researchers think language is not limited to Broca’s and Wernicke’s centres
Phineas Gage is case study
What does brain plasticity mean?
Brain is able to change throughout life
What is synaptic pruning?
Unused synapses are deleted
What did Maguire et al find in their study?
London taxi drivers had greater volume in posterior hippocampus than control group
What is functional recovery?
After brain damage, other areas of the brain can adapt and compensate for this
How does functional recovery work?
Axonal sprouting - new nerve endings grow to connect with other undamaged neurons
Denervation supersensitivity - axons become more aroused to send stronger signals to make up for lost neurons
Recruitment of homologous areas on opposite side of brain
Limitation of plasticity
Negative behavioural consequences - adaptation to drug use increases vulnerability to dementia
Who found adaptation to drug use increases vulnerability to dementia?
Medina et al
Strength of brain plasticity?
Life long ability - Bezzola et al found golf training at 60 increased motor cortex
Example of endogenous pacemaker
Superchiasmatic nucleus
What did Siffre find in the cave study?
Internal clock is around 25hours
Folkard et al findings
Little influence of exogenous zeitgeber on internal body sleep wake cycle
Strength of research into sleep wake cycle
Medical treatments
Can understand effects of desychnronisation
Who found 3x risk of heart disease when desycronisation?
Knutsson
Who found heart attacks are more common in the morning
Bonten et al
Limitations of research into circadian rhythmns
Individual differences (Czeisler et al) sleep wake hours vary from 13-36 hours
Who found evidence for menstruel synchronation?
Mclintock and Stern
Example of ultraradian rhythms
Sleep cycle
Strengths of mentstruel synchronisation study
Strong evolutionary basis
Limitations of mentstruel synchronisation study
Confounding variables - eg. diet and exercise
Real world applications of understanding ultraradian rhythms
ignore
Evidence for SCN
Decoursey found chipmunks with damaged SCNs died
Limitation of SCN research
SCN may obscure other body clocks - peripheral oscillators (Damiola)
May be interactionist system
Limitations of the effects of exogenous zeitebergers
Miles case study - blind boy was unaffected by any external factors
Where is Brocas’s area
Left frontal lobe
Where is Wernicke’s area
Right tempoural lobe
What side controls movement of each side
Contralateral wiring so right hand controls left hand side movement
Explain vision in terms of lateralisation
Left visual field goes to right hand and right visual field goes to left
What is each side in control of (in terms of Sperry)?
Right hand side can comprehend what is seen but cannot verbalise
Left hand side can verbalise
Describe Sperry experiment
11 split brain operated patients
Describe Sperry results
When RVF sees, LHS of brain can verbalise
When LVF sees, RHS cannot verbalise but can comprehend
Strength of lateralisation
Can be seen in connected brains - Fink et al found PET scans showed different sides for different tasks
Limitations of lateralisation
RH synthesiser and LH analyser may be wrong - Nielsen et al found no idea of dominance
Generalisation from Sperry questionable
fMRI
Detects changes in blood oxygenation and flow to produce 3D activation map
What device measures electrical activity and shows all waves
Electrocephalogram
Event related potential
Specific waves identified to events which trigger them
Post mortem brain examination
Comparison of dead brain to neurotypical brain
fMRI strengths
No radiation
High spatial resolution
fMRI limitations
5 sec lag means poor tempoural resolution
EEG strength
Used for sleep stages
High tempoural resolution
EEG limitations
Background information means stimuli and response can’t be detected
ERP strengths
More specific
High tempoural resolution
ERP limitations
Lack of standardisation in ERP methodology
Background noise elimination not always possible
Post mortem strengths
Foundation
Can be used in autopsy
Post mortem limitations
Ethics
Trauma and decay