LESSON 2 - DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
1/193
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
194 Terms
Identify the organ
Esophagus
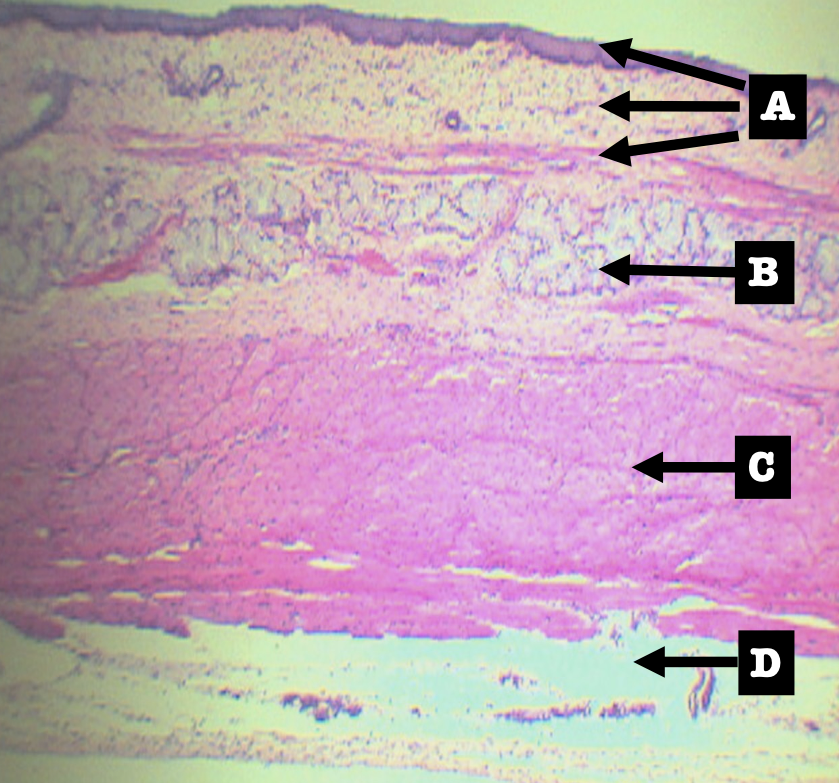
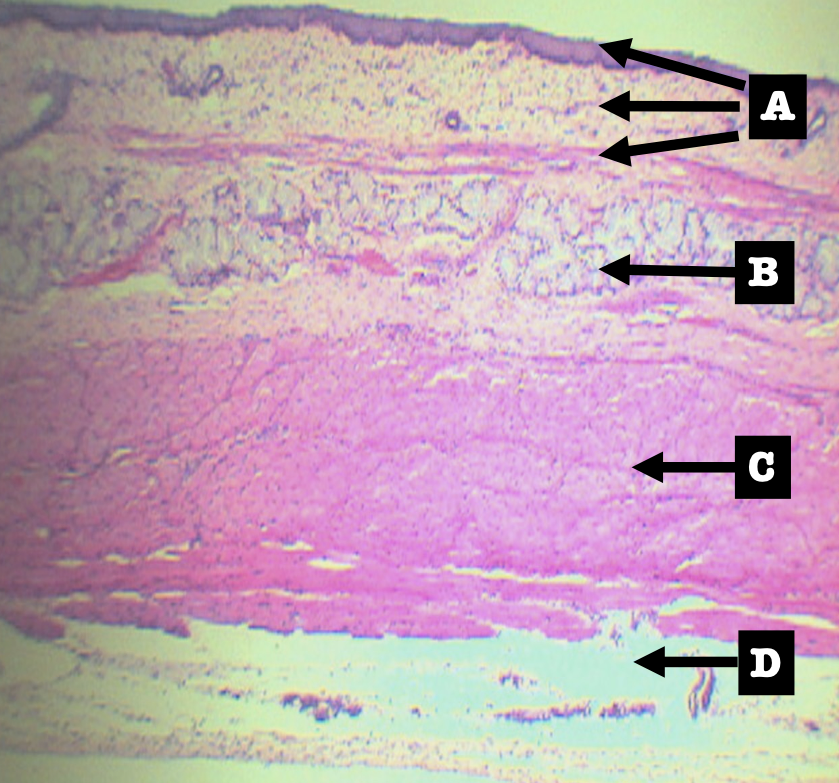
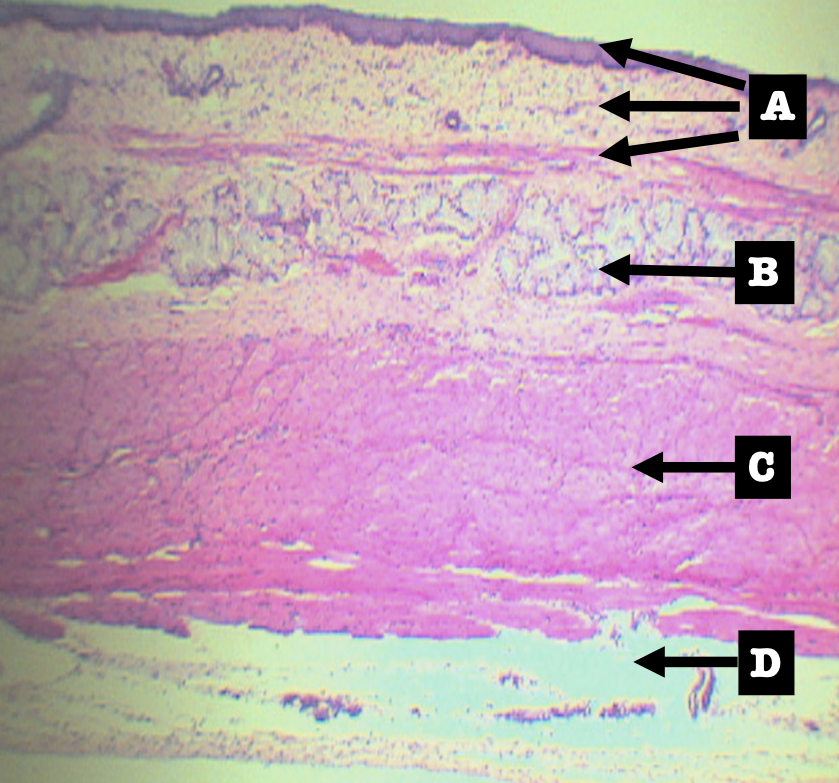
Identify the layers
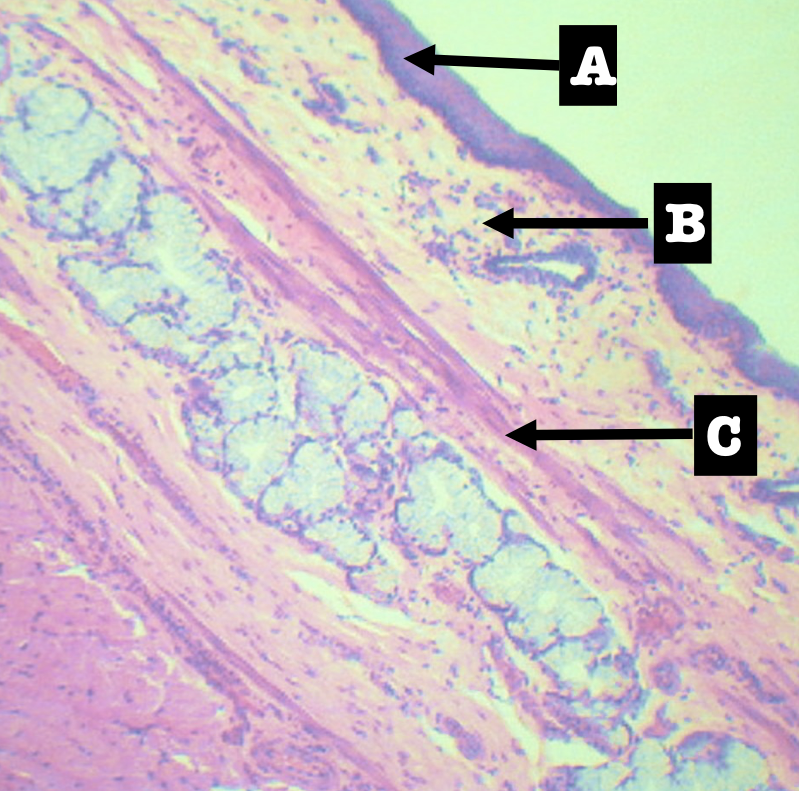
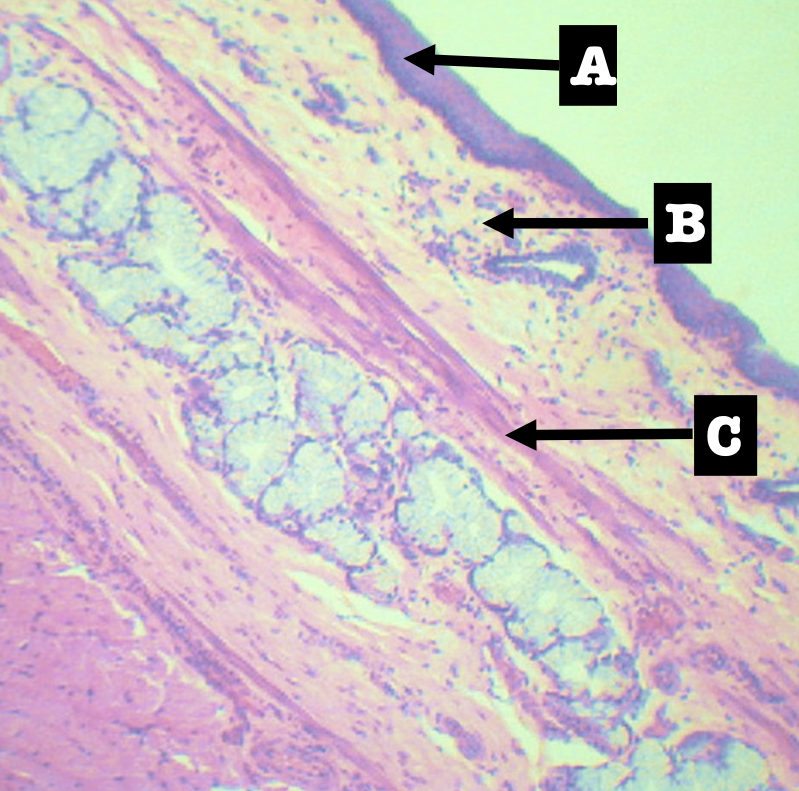
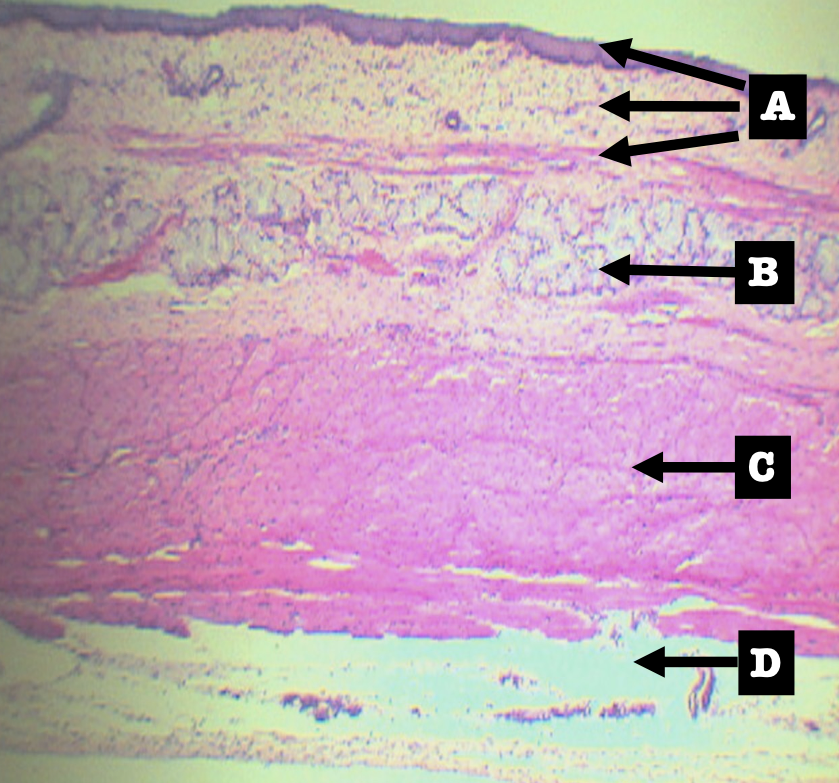
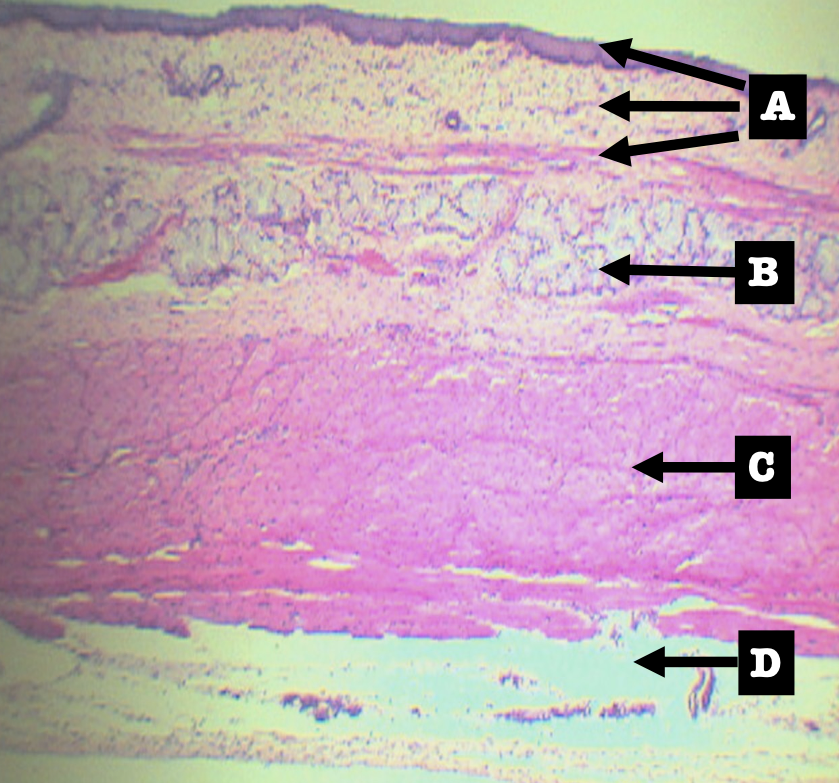
Layers of Esophagus
A. Mucosa
B. Submucosa
C. Tunica muscularis
D. Tunica adventita
The projected sublayers are sublayers of the ______?
Mucosa (A)
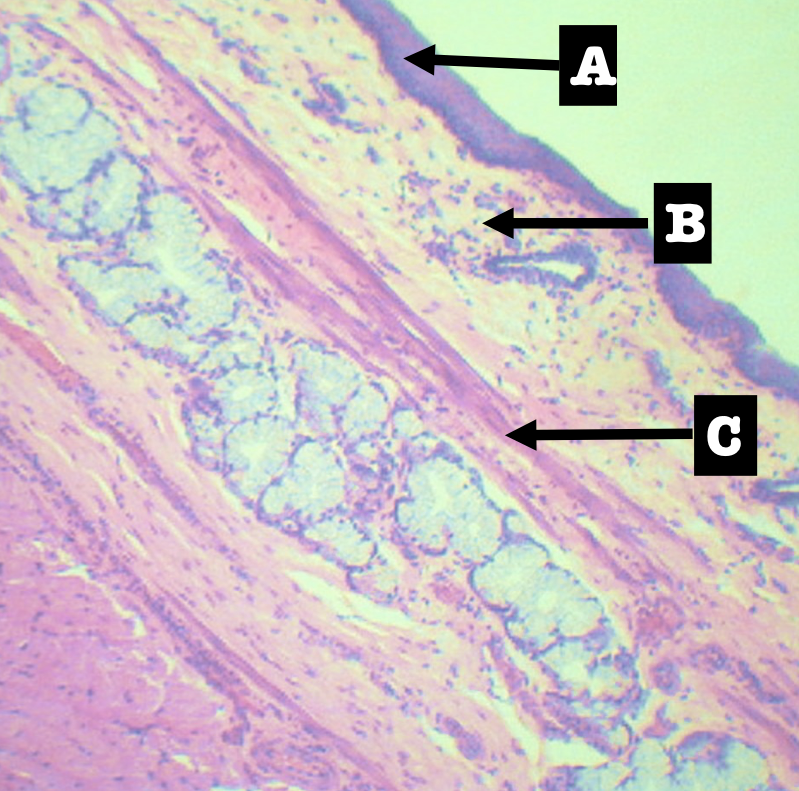
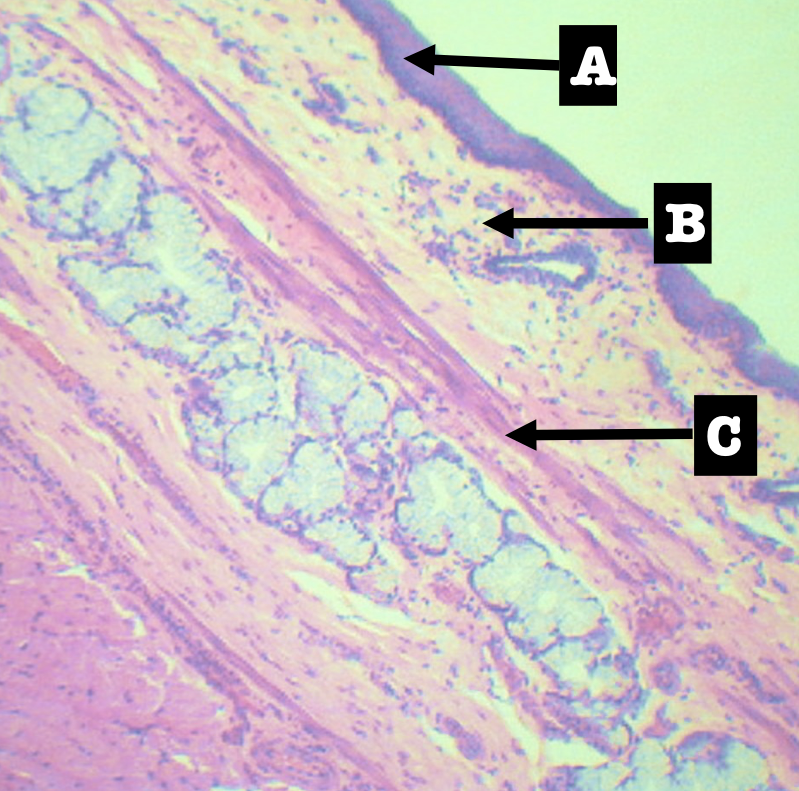
Identify the sublayers
A. Lining Epithelium
B. Lamina Propria
C. Muscularis mucosa
Lining Epithelium of the organ
Stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium
Lamina Propia of the organ
Loose Connective tissue with scattered lymphocytes
Muscularis mucosa of the organ
Single layer of smooth muscles
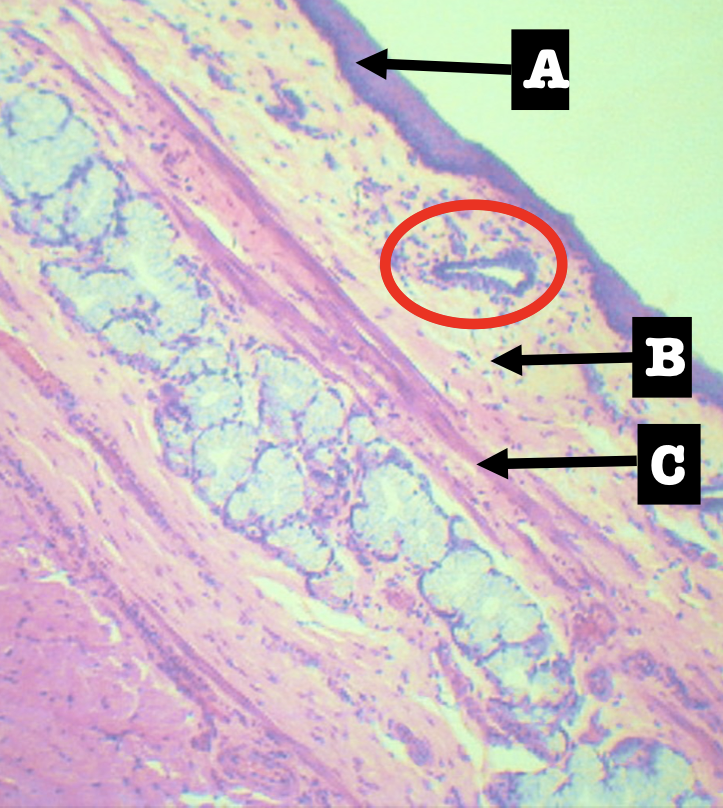
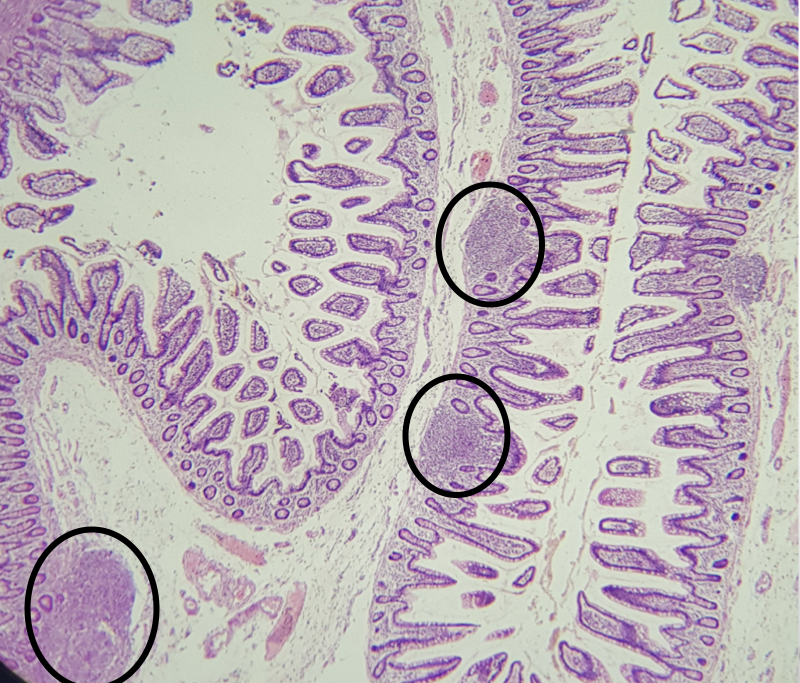
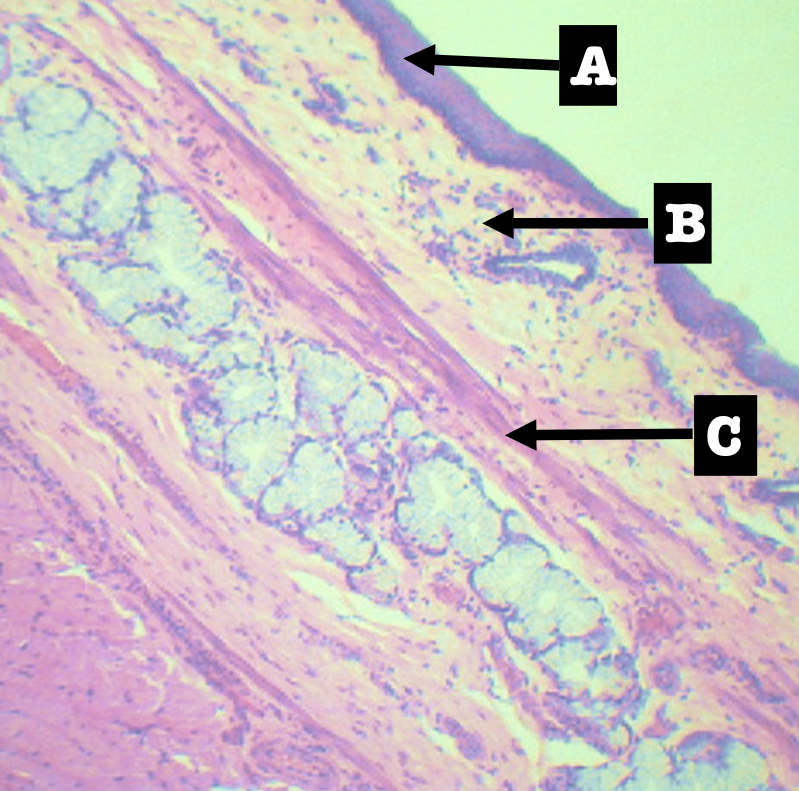
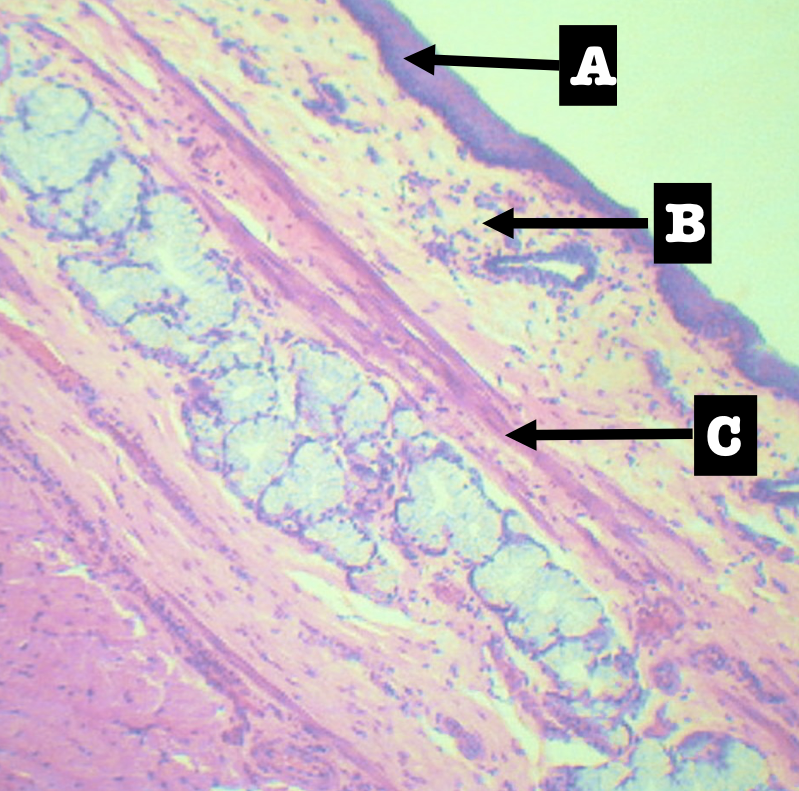
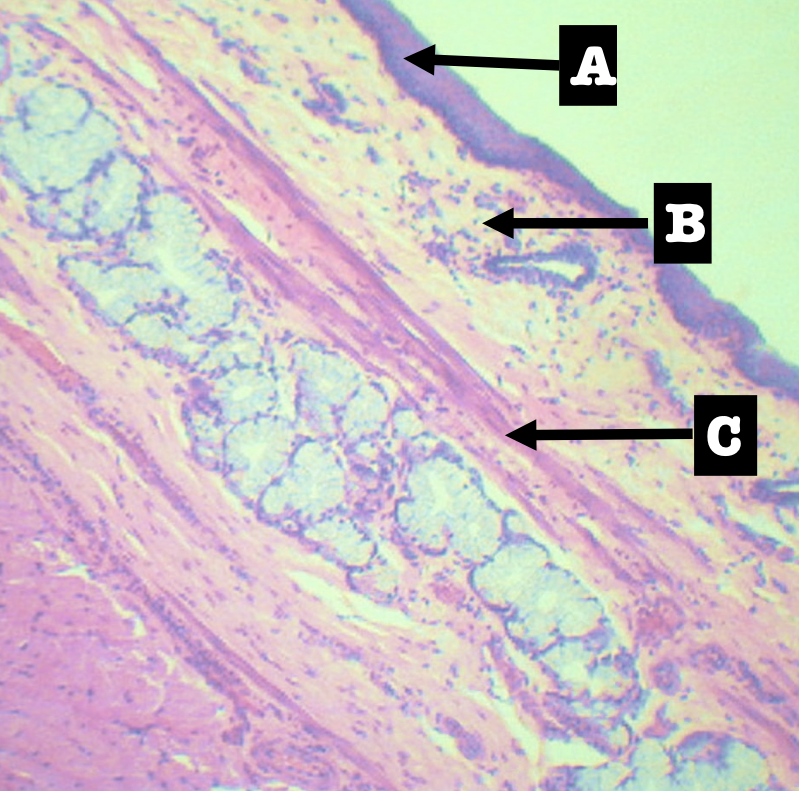
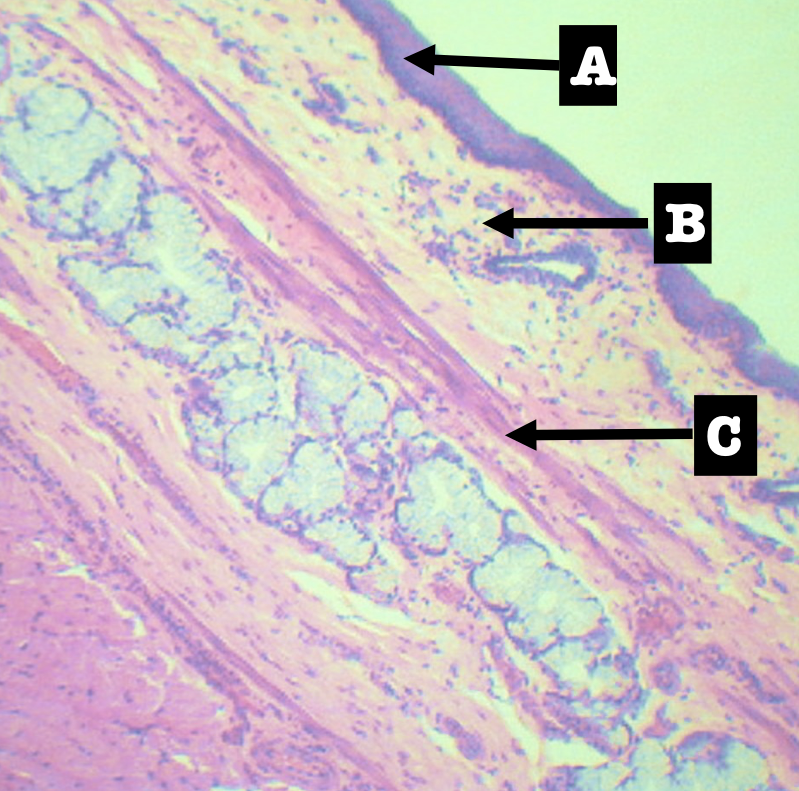
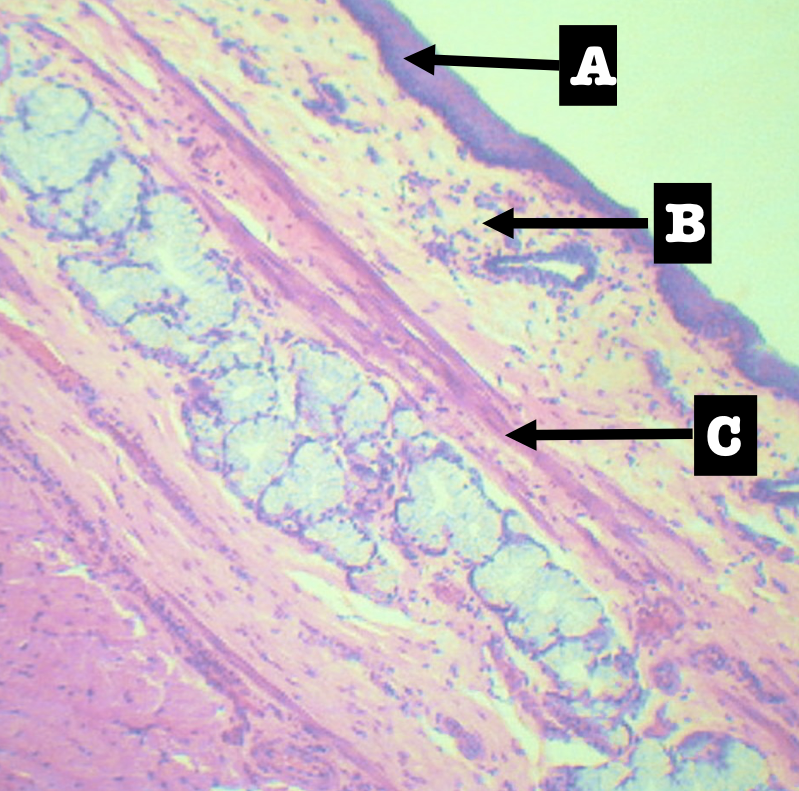
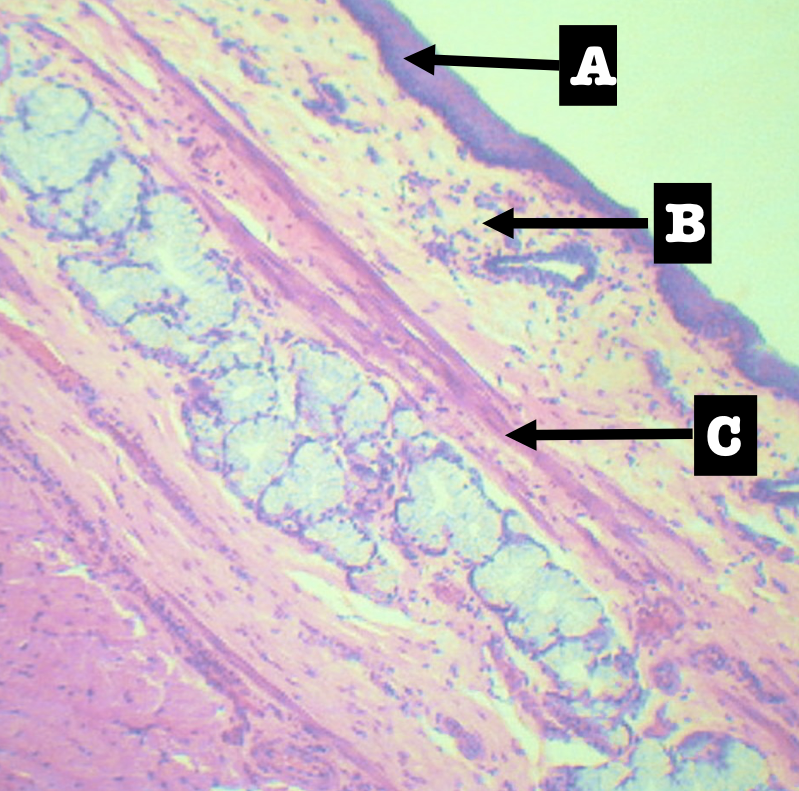
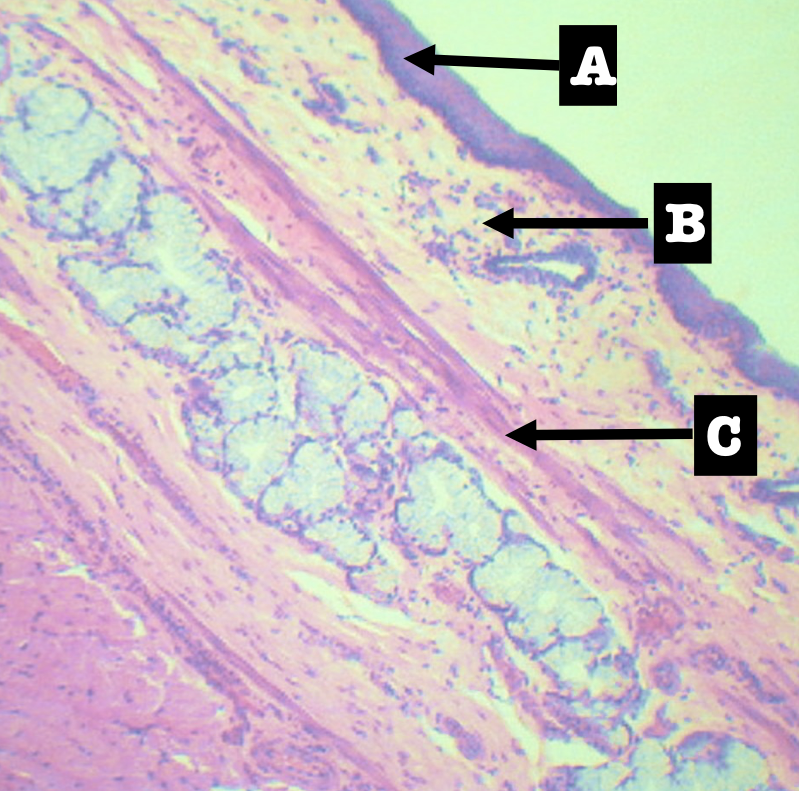
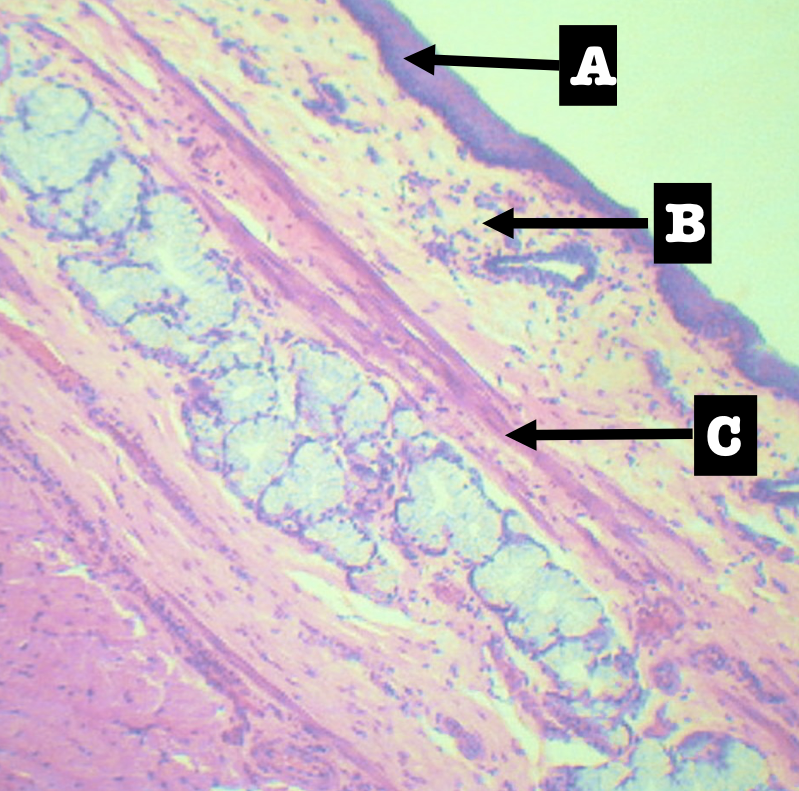
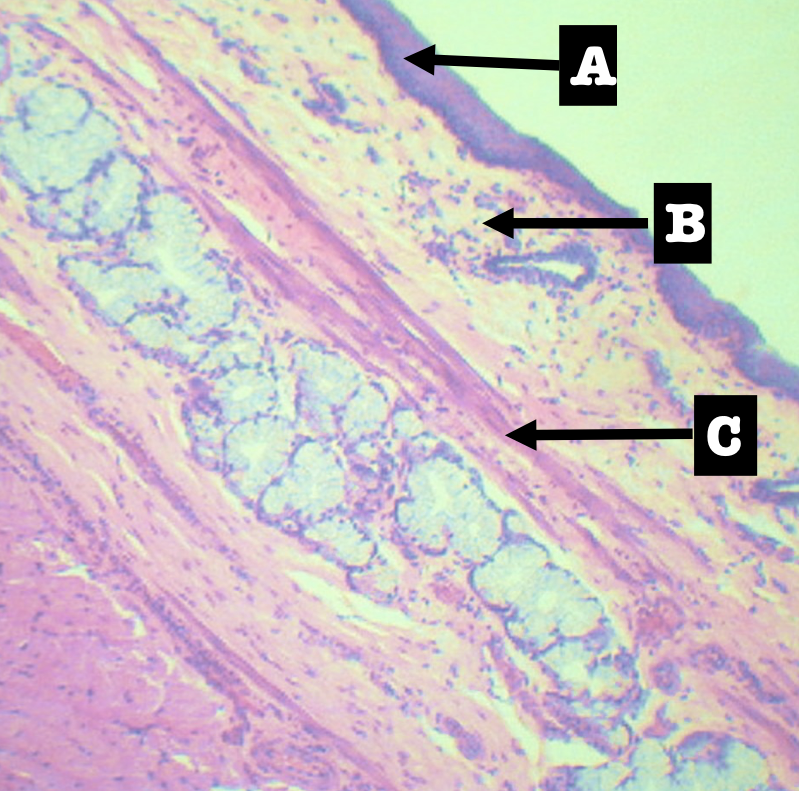
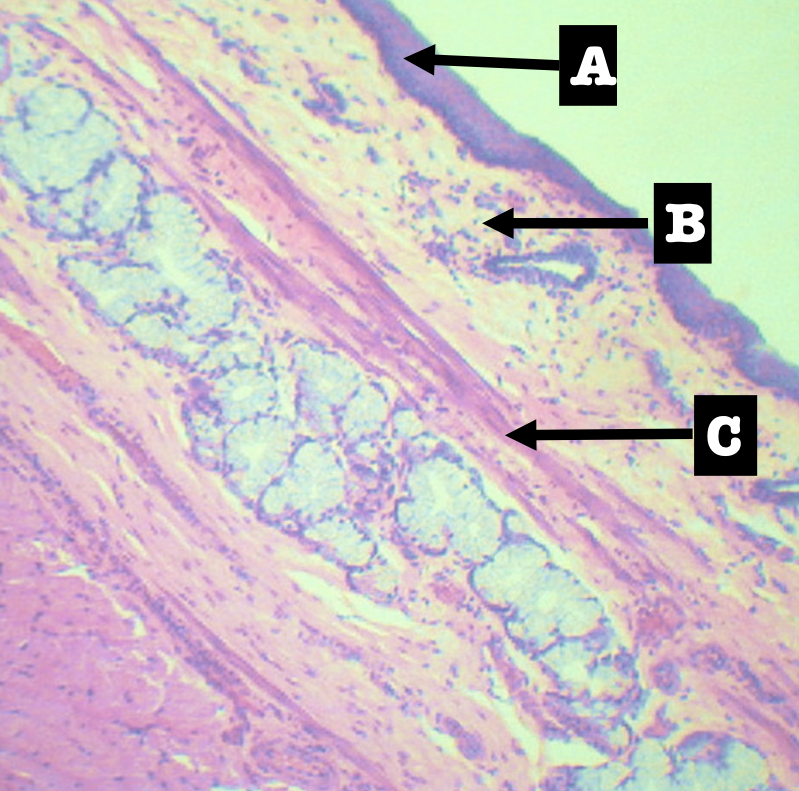
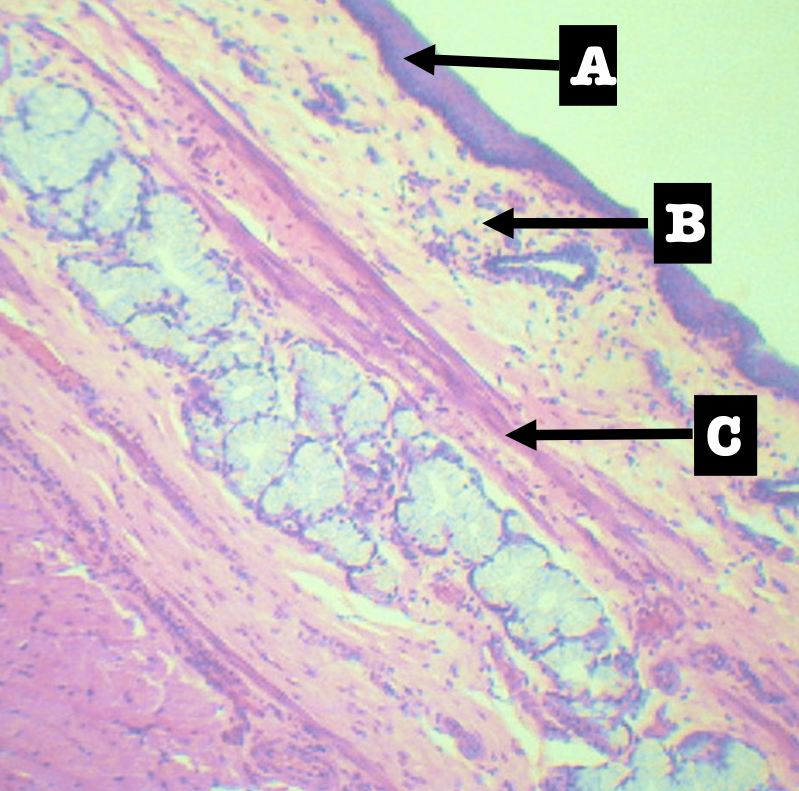
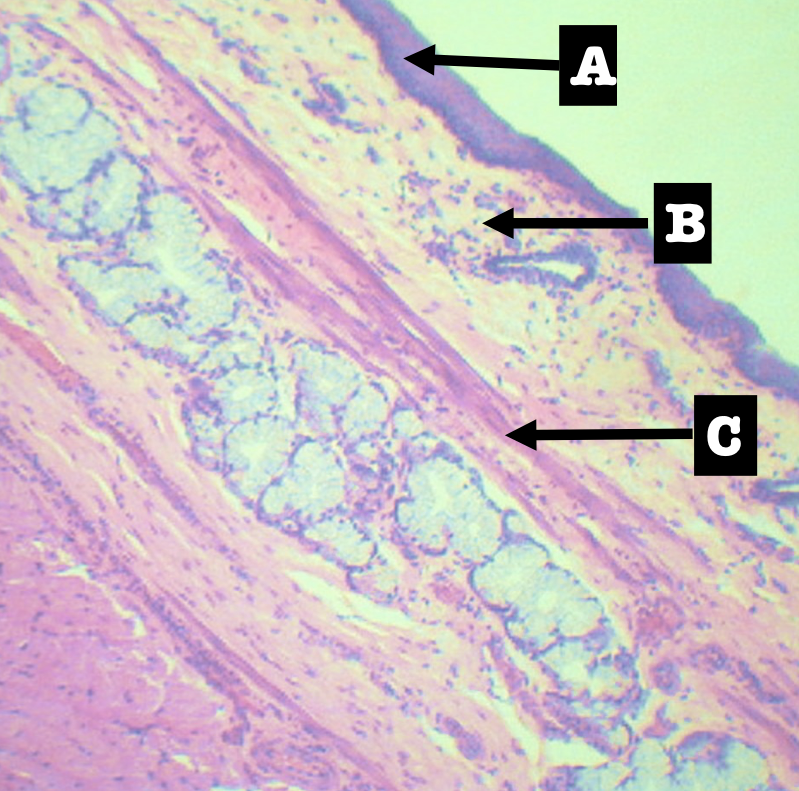
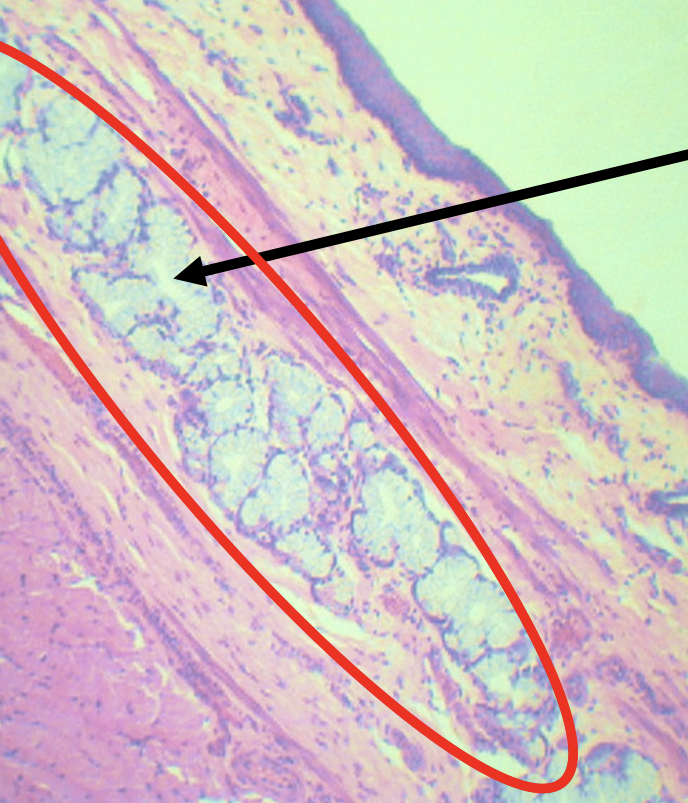
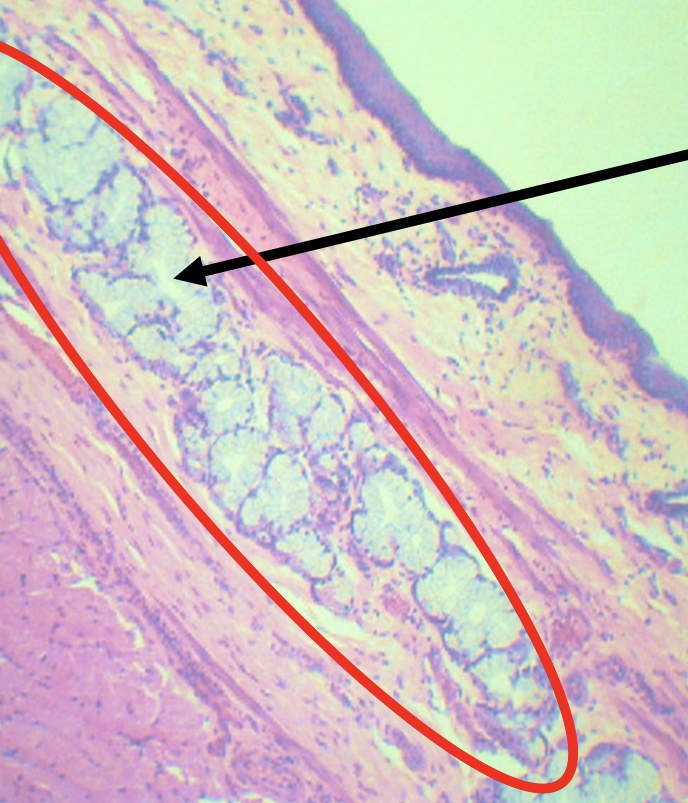
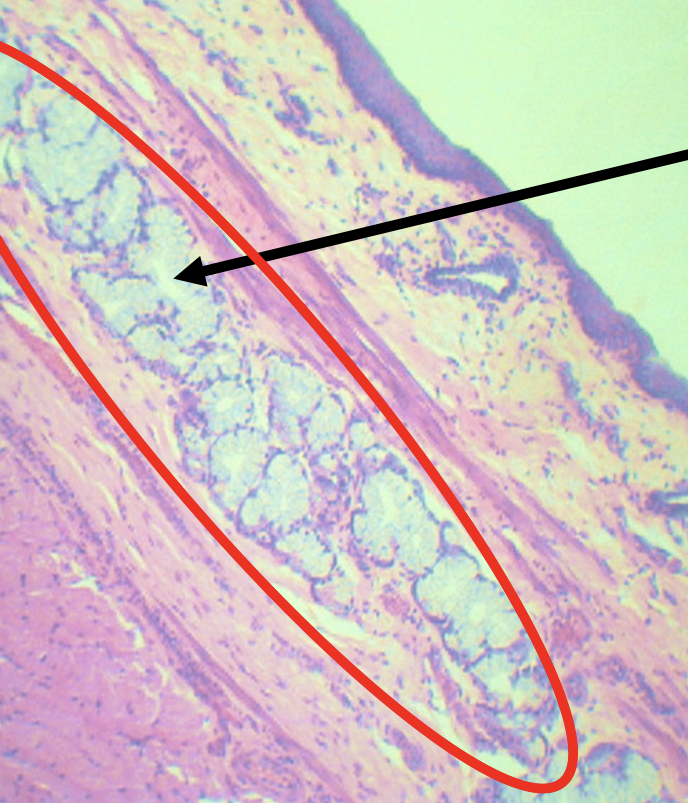
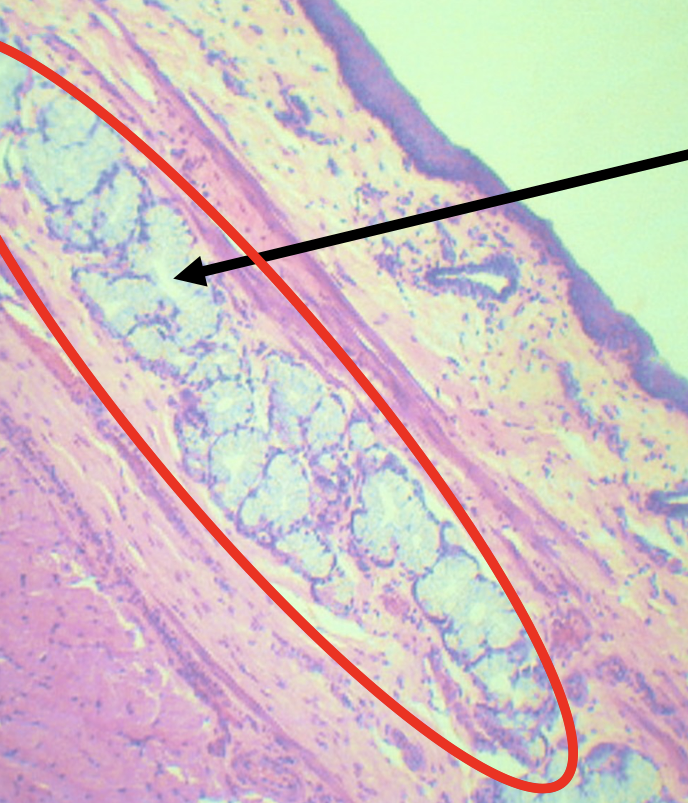
Identify the encircled structure
Superficial Esophageal glands
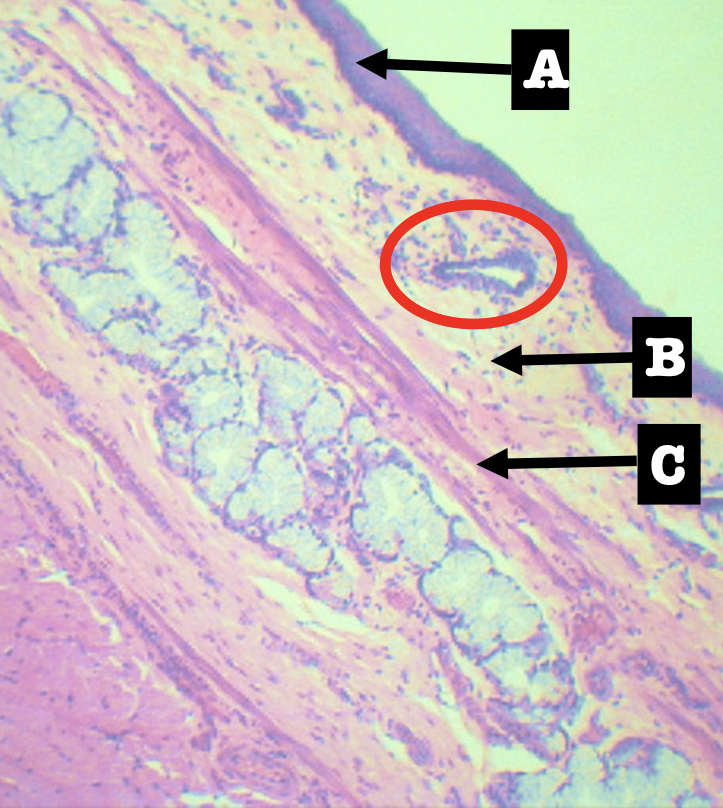
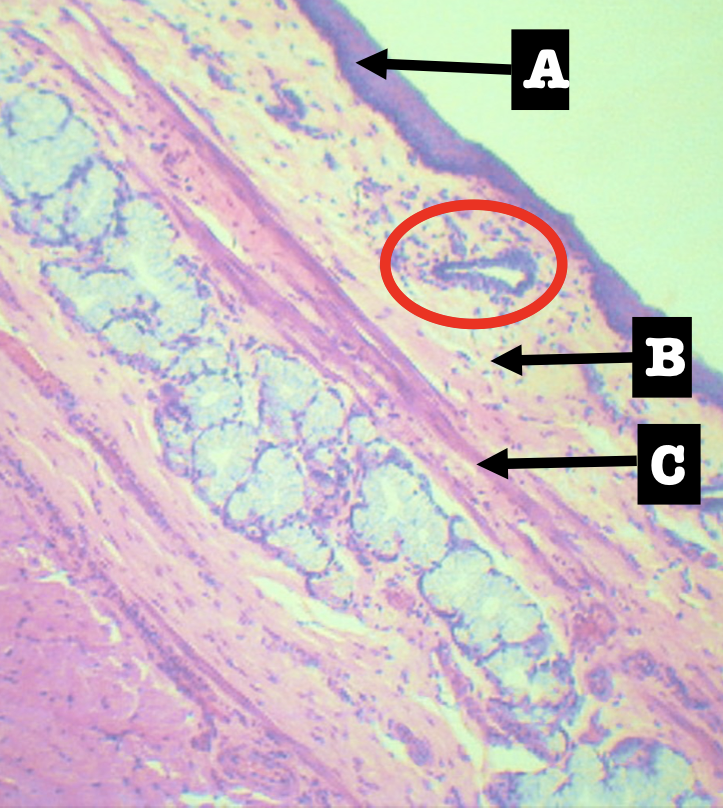
Identify the morphology of the encircled structure
Branched coiled glands
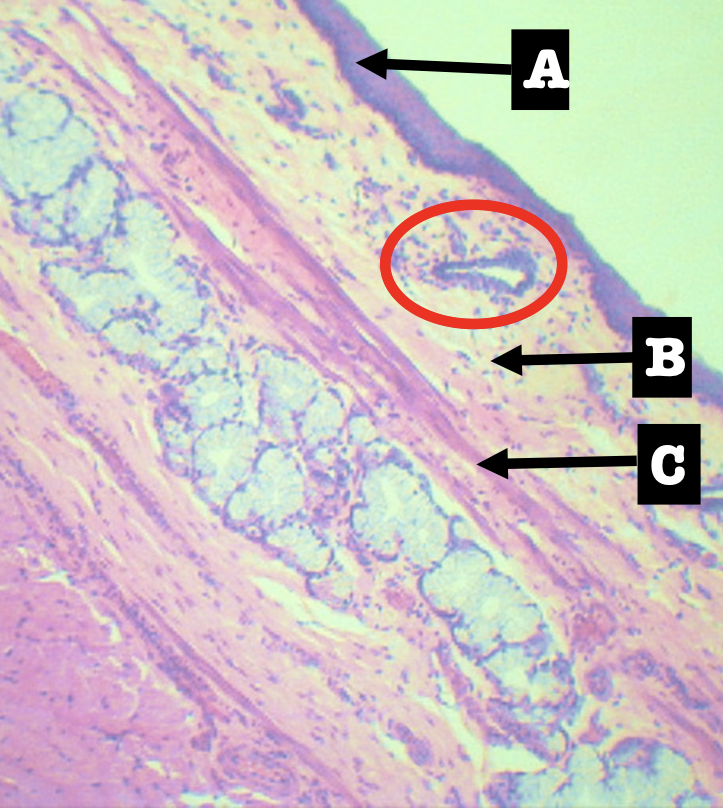
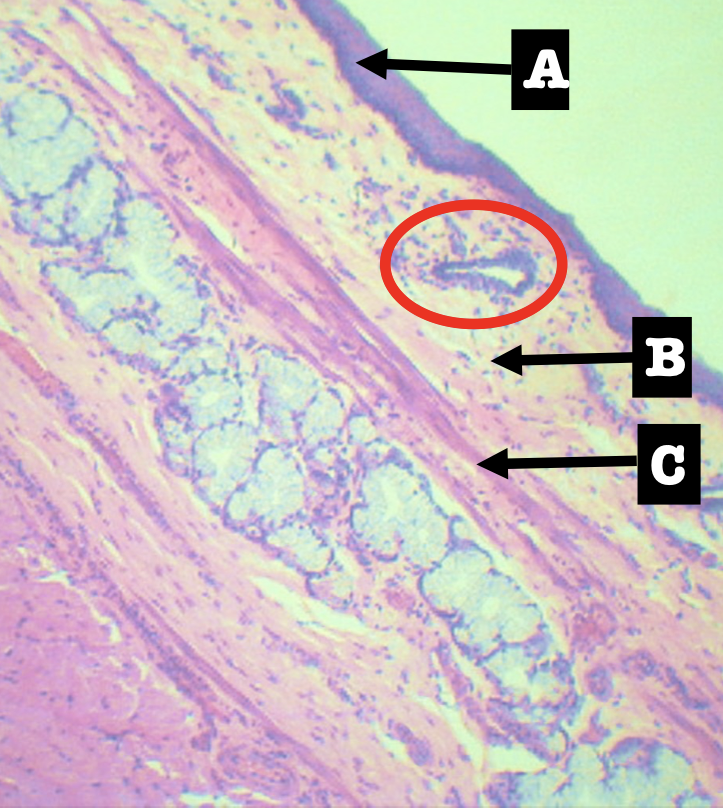
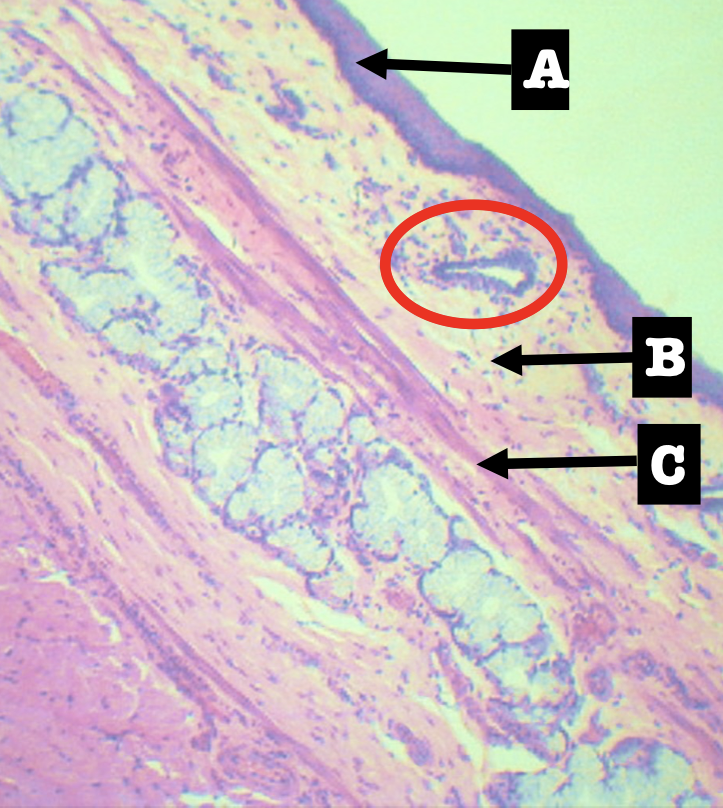
Identify the location of the encircled structure
Lower end of esophagus
Identify the fundamental type of tissue of B
Connective Tissue
Identify the subtype of B
Lymphatic Tissue or Connective Tissue Proper
Identify the specific subtype of B
Loose Lymphatic Tissue or Loose Connective Tissue
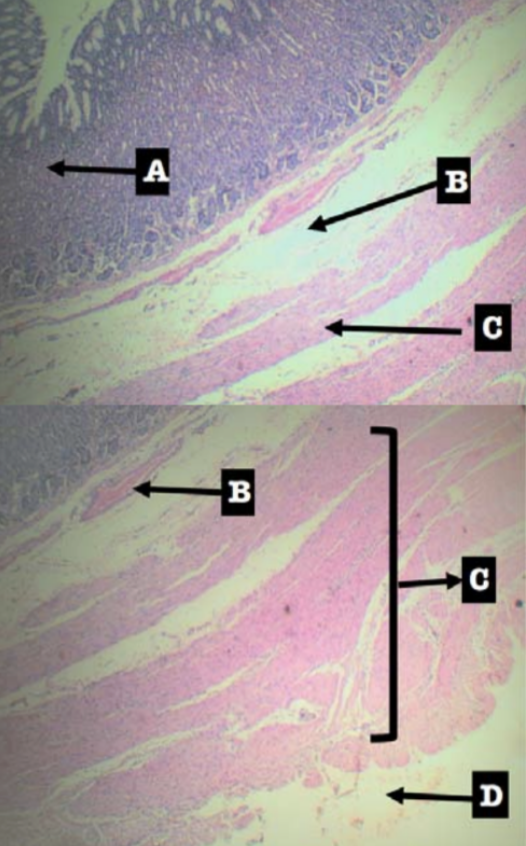
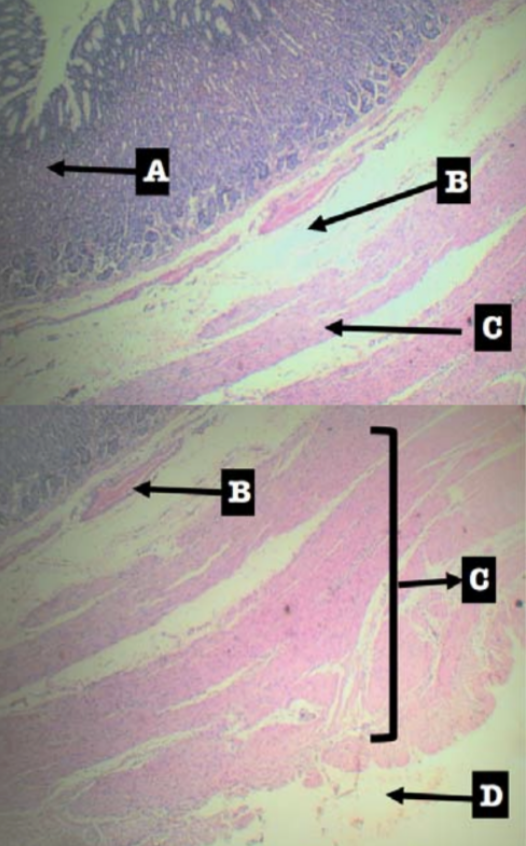
Divides the lamina propria from the submucosa
Muscularis mucosa (C)
Identify the pointed layer
Submucosa
Specific subtype of the pointed layer
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
Secretes mucus in the submucosa for lubrication to facilitate the passage of food
Meissner’s plexus
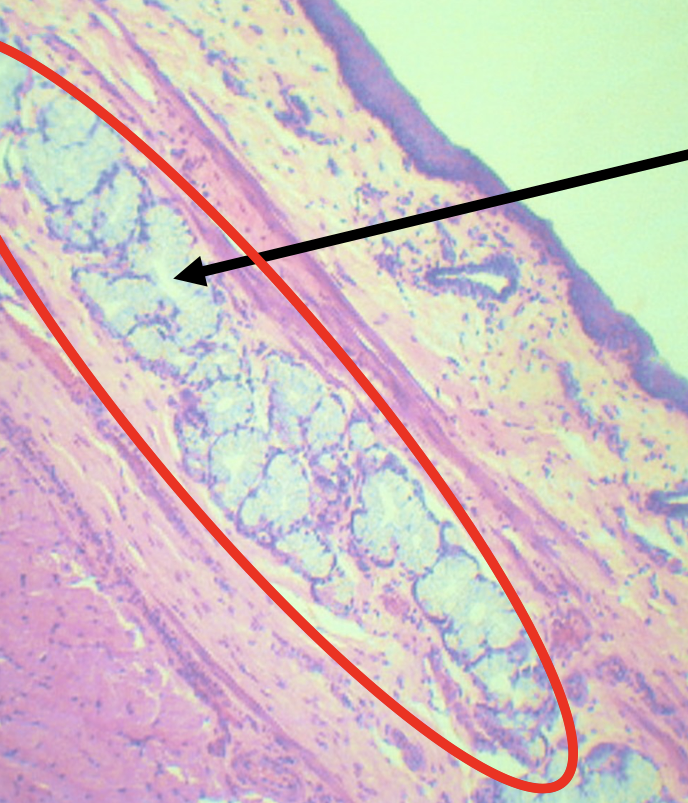
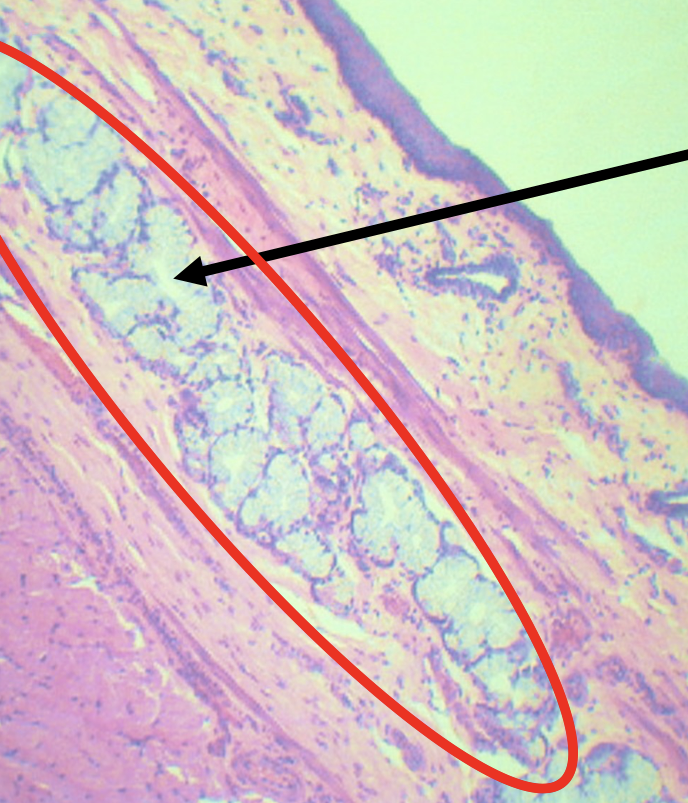
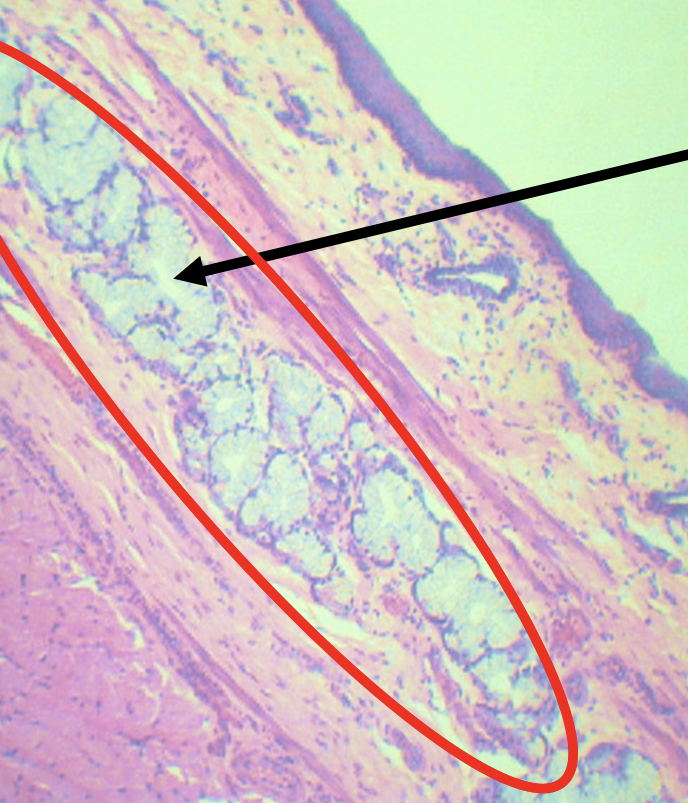
What is the encircled structure?
Deep Esophageal glands
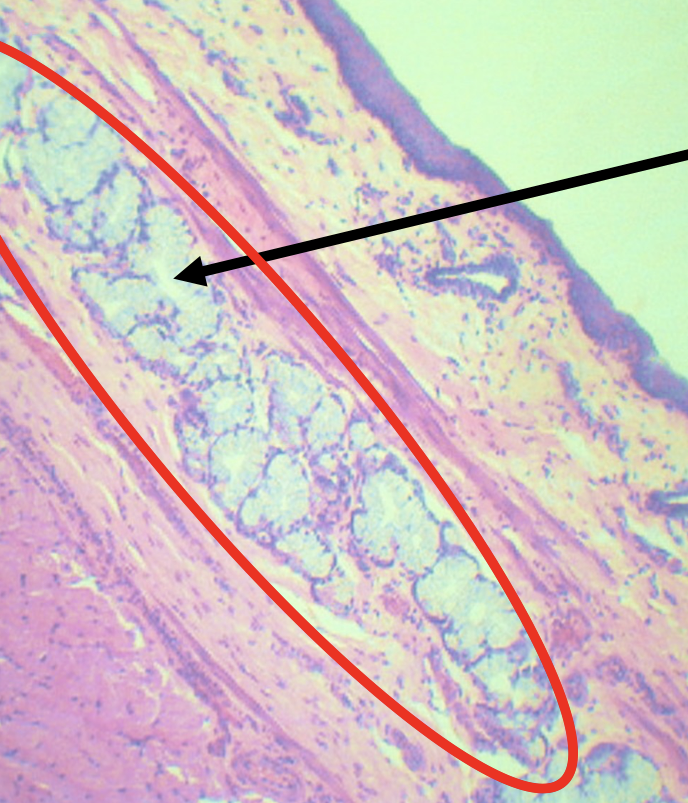
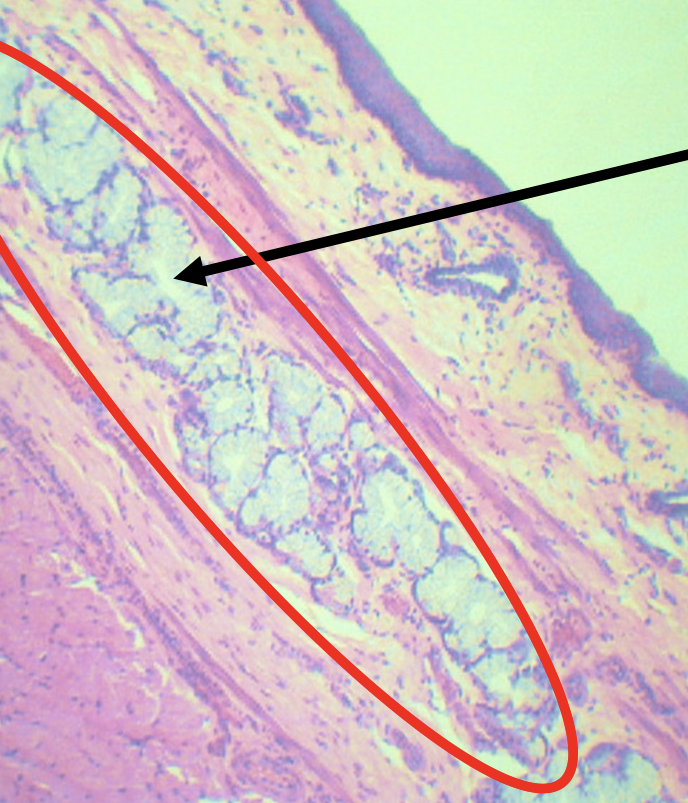
Function of the encircled structure
Mucus Secretion
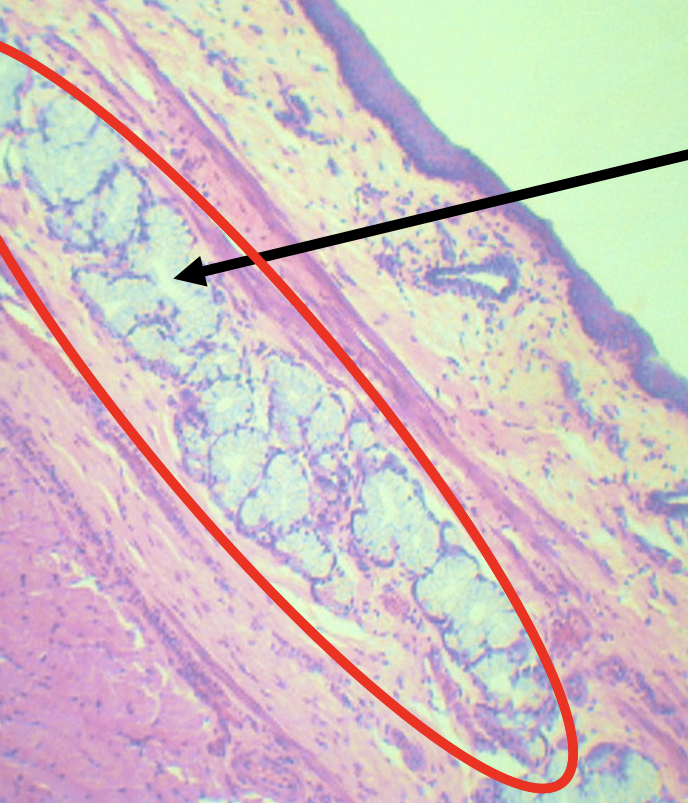
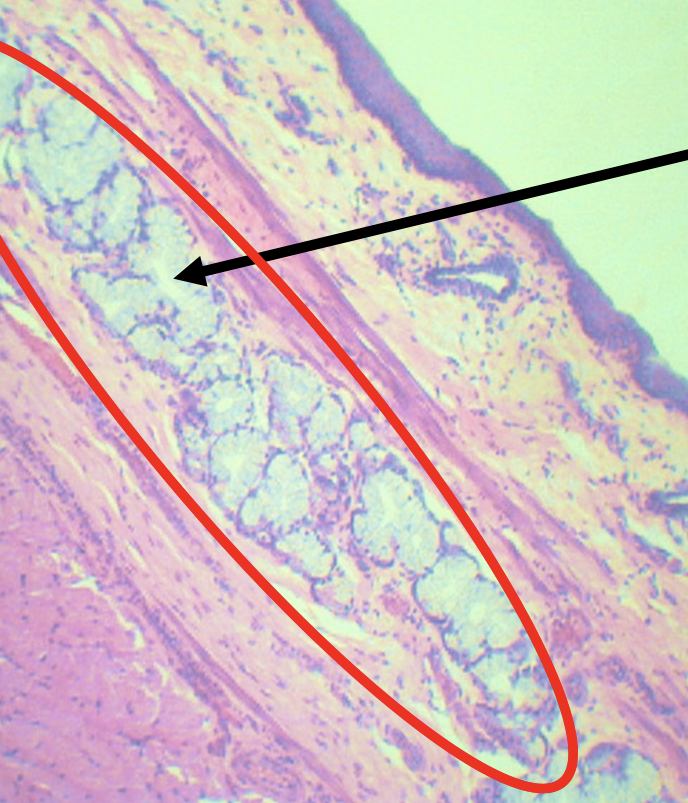
What nerves plexuses are found in this area?
Meissner’s plexus
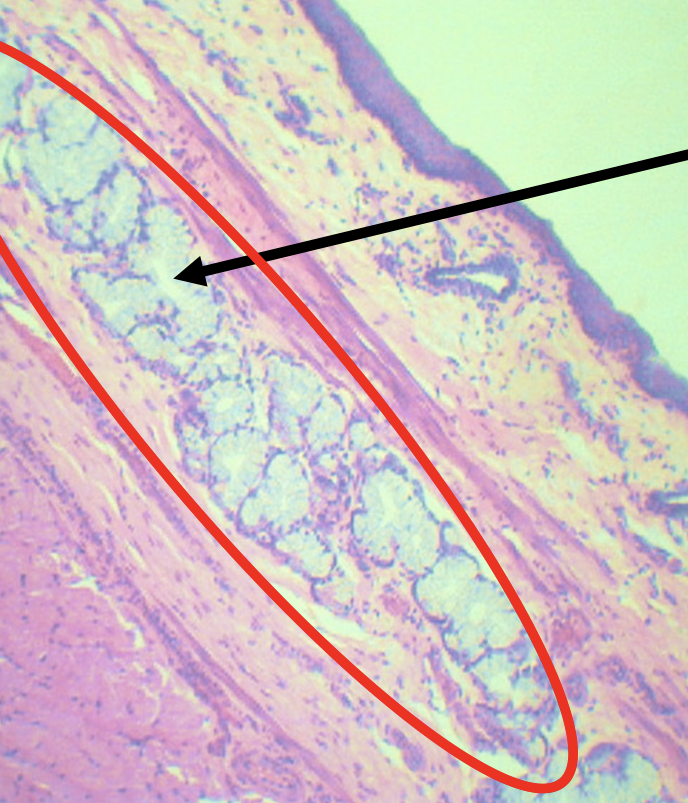
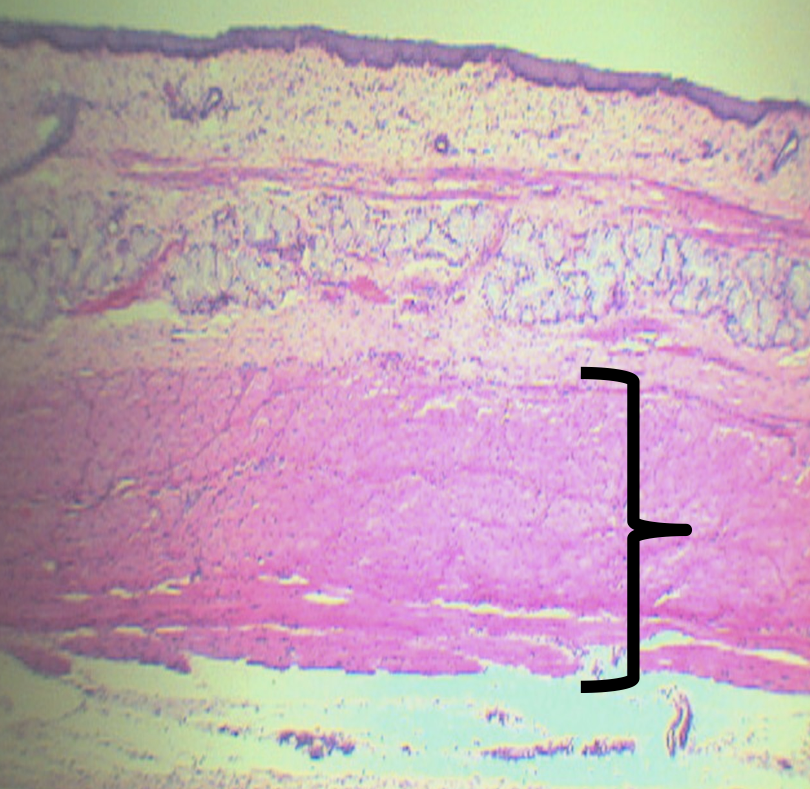
Identify the Layer
Tunica Muscularis (C)
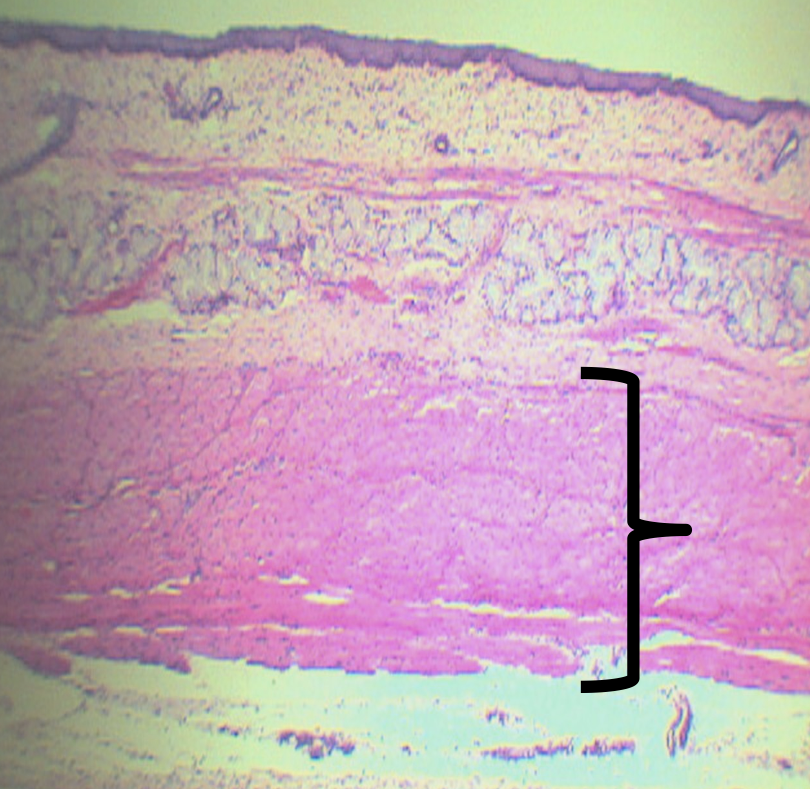
How is this layer arranged?
Inner Circular and Outer Longitudinal (ICOL)
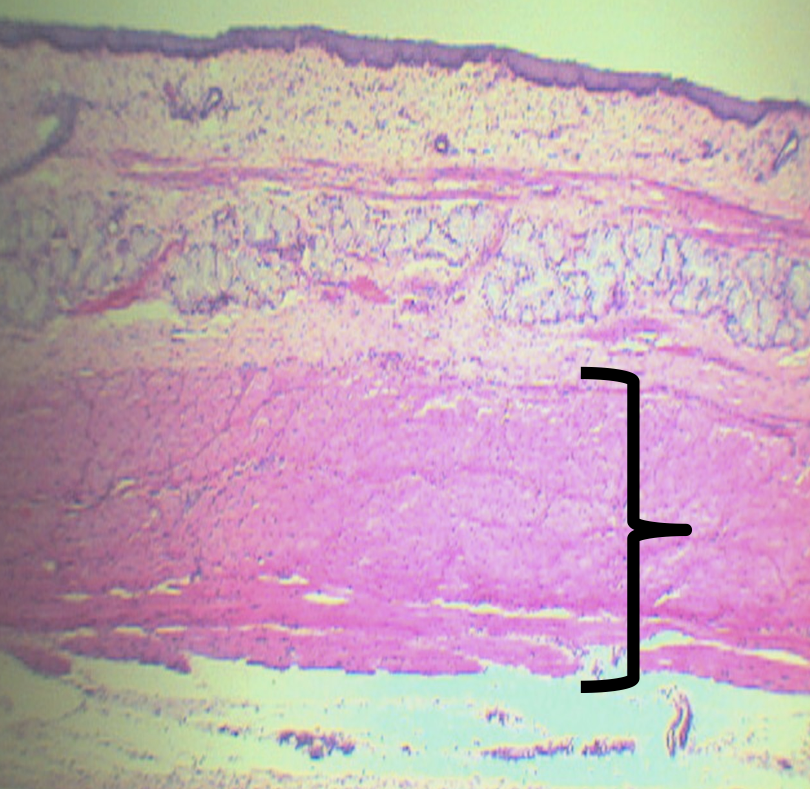
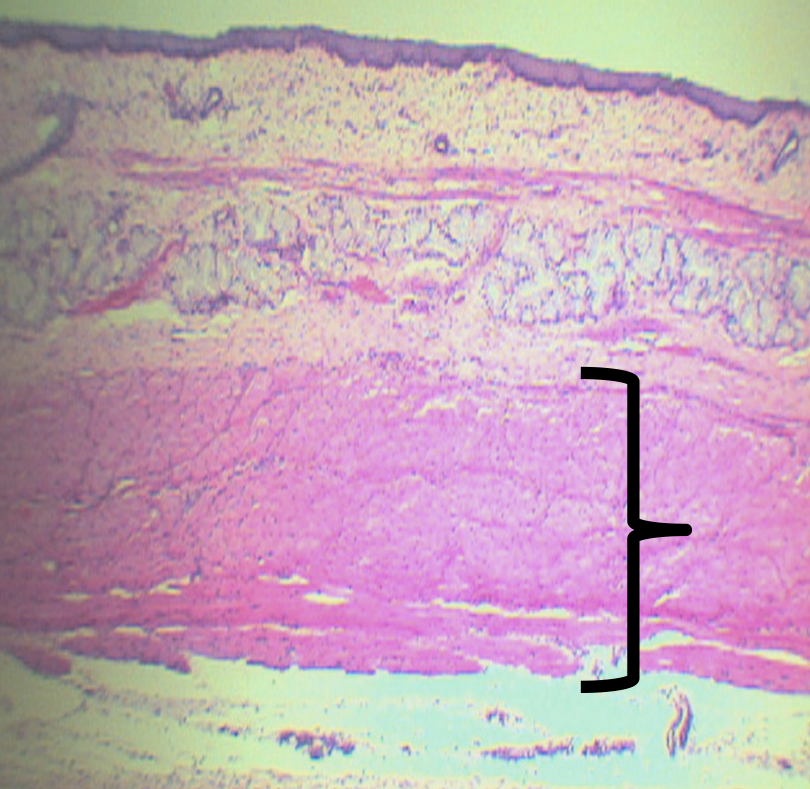
What is the upper third of this layer composed of?
Skeletal Muscles
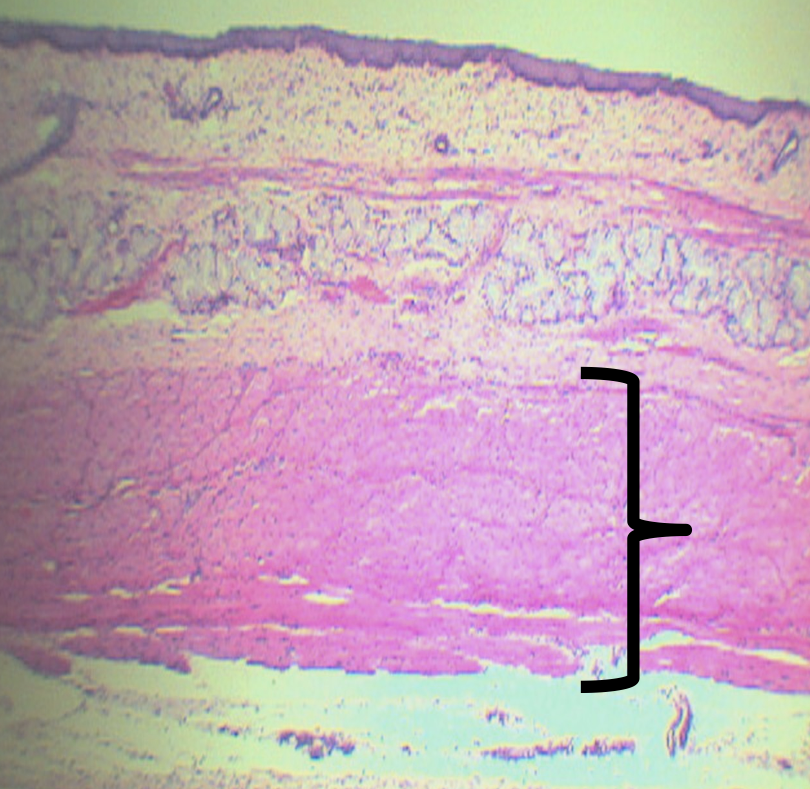
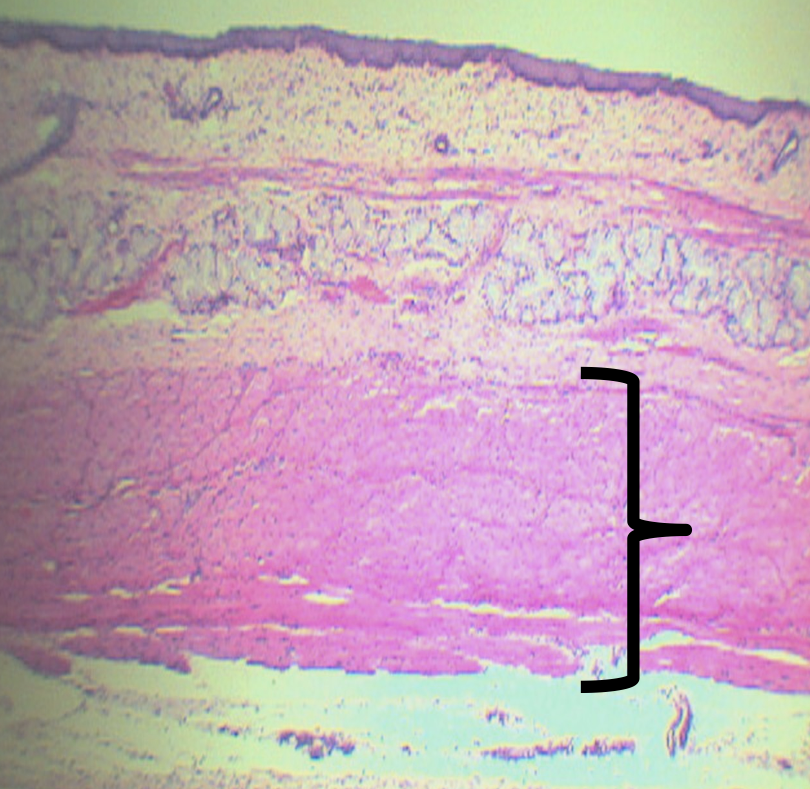
What is the middle third of this layer composed of?
Skeletal and Smooth Muscles
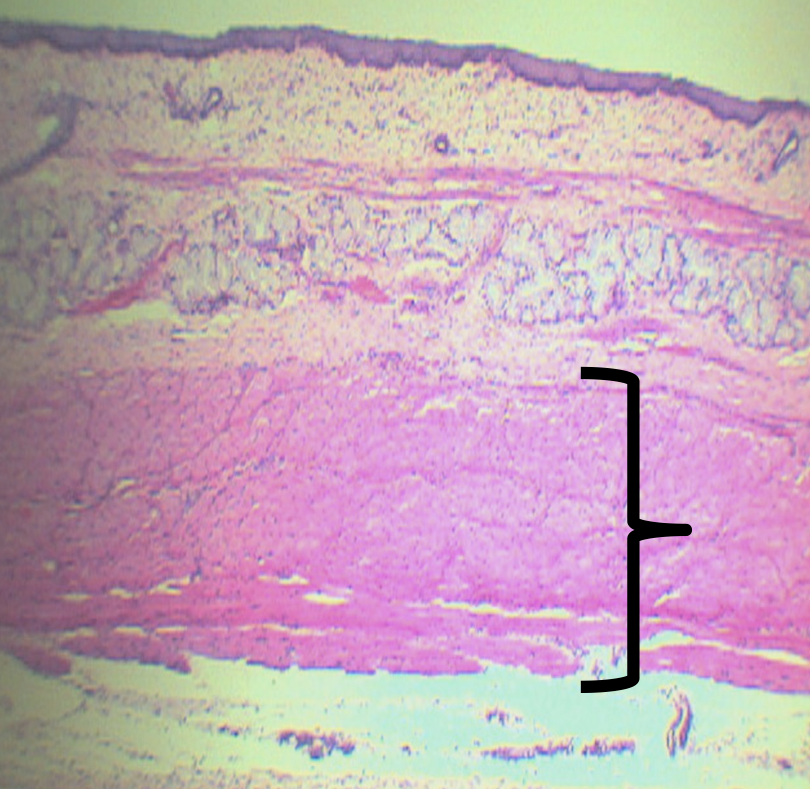
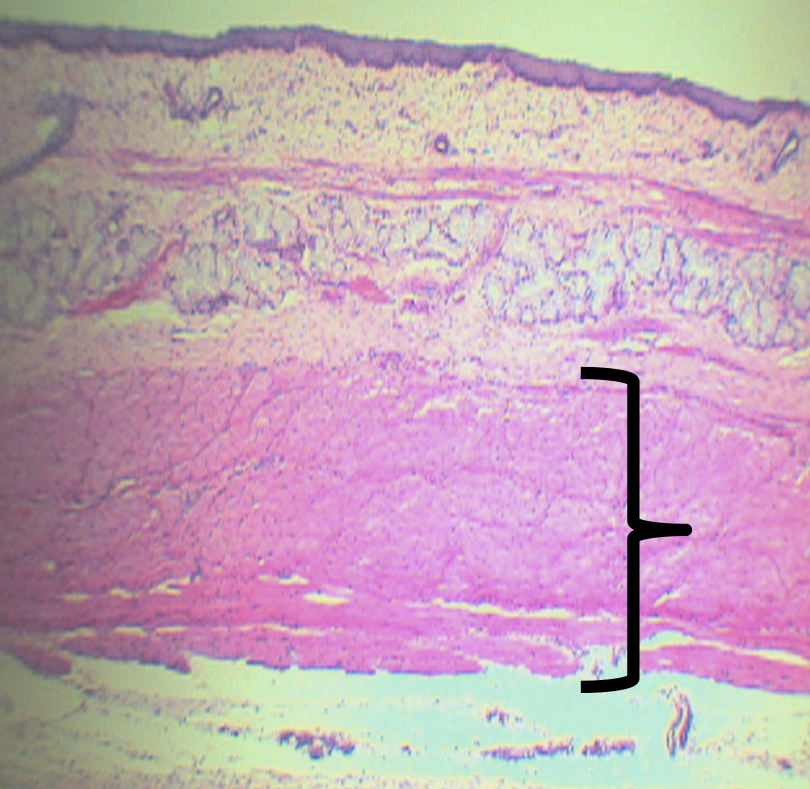
What is the lower third of this layer composed of?
Smooth Muscles
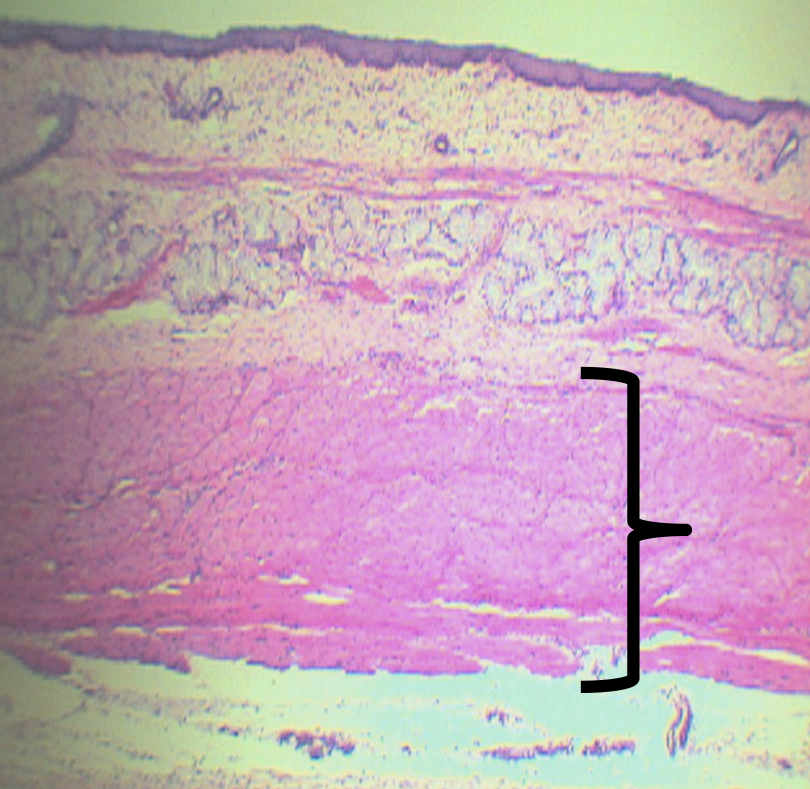
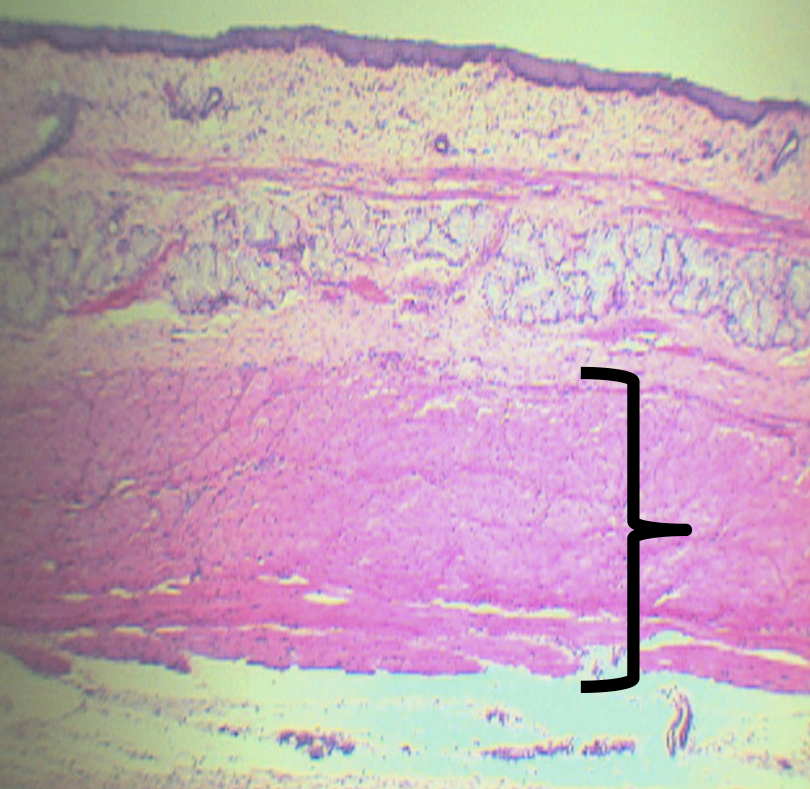
What is the name of the nerve plexuses found in this area?
Auerbach’s/ Myenteric plexus
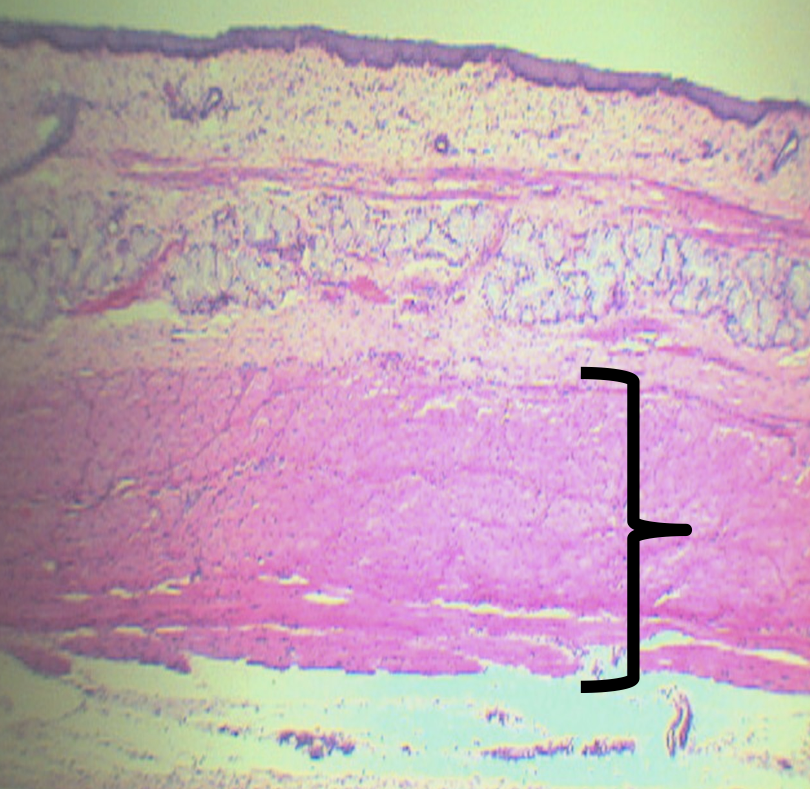
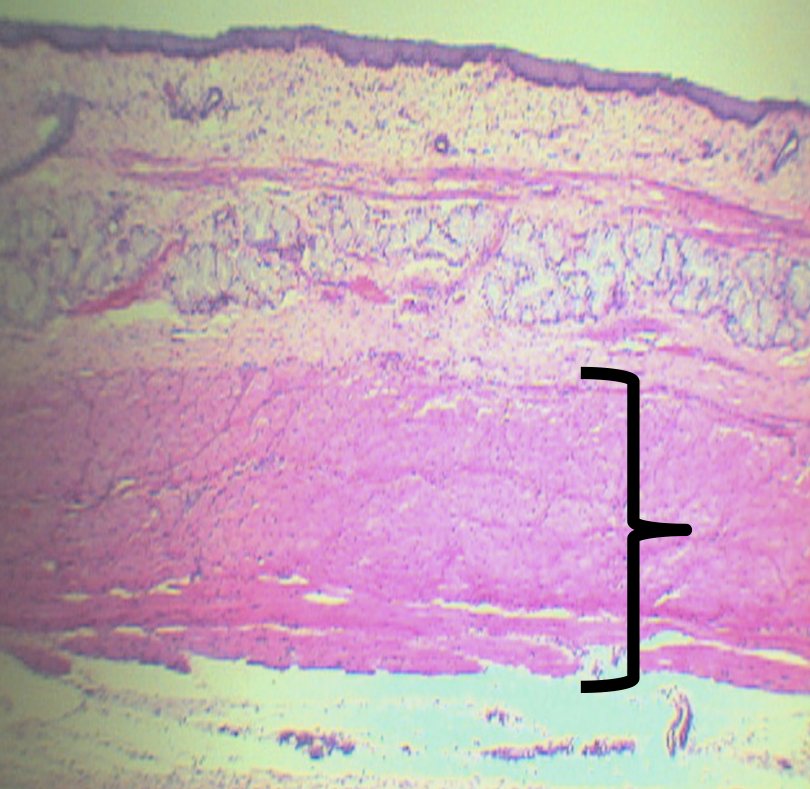
What is the function of the nerve plexuses found in this area?
Promotes motor/ peristaltic movement
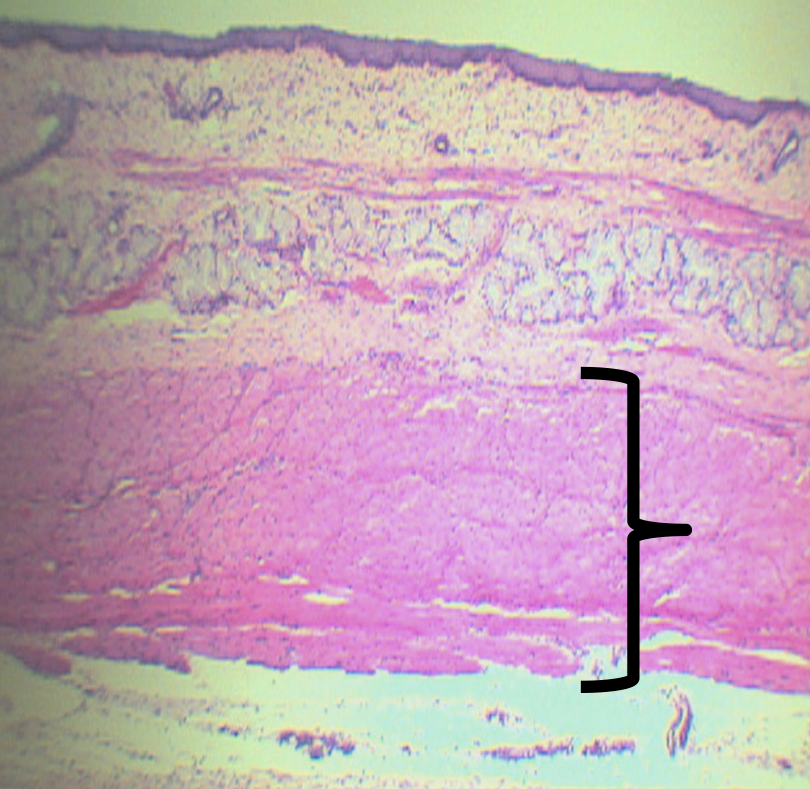
Identify the layer
Tunica Adventita (D)
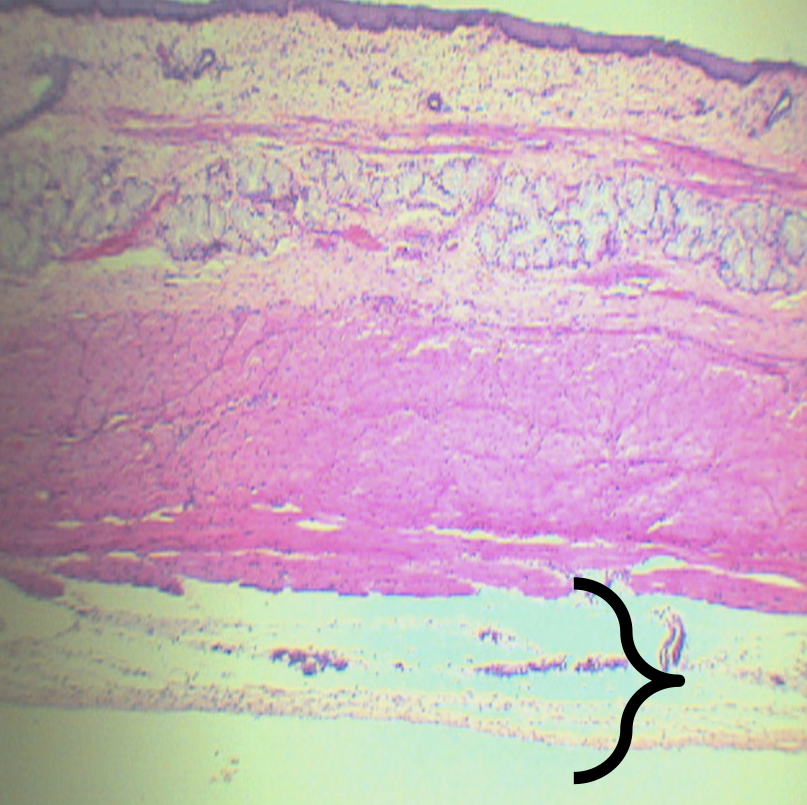
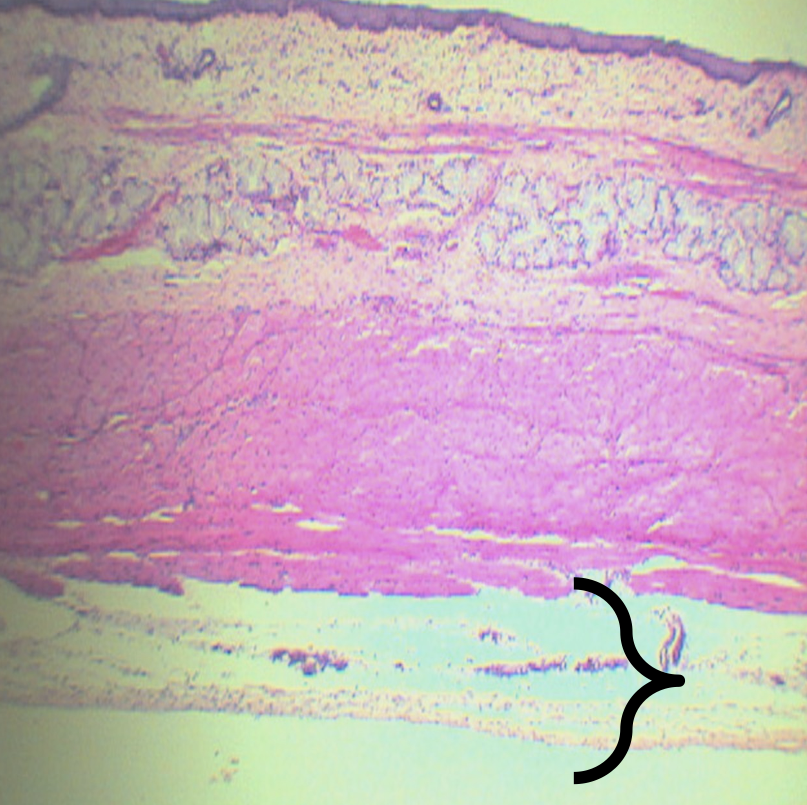
What is this structure composed of?
Loose Connective Tissue
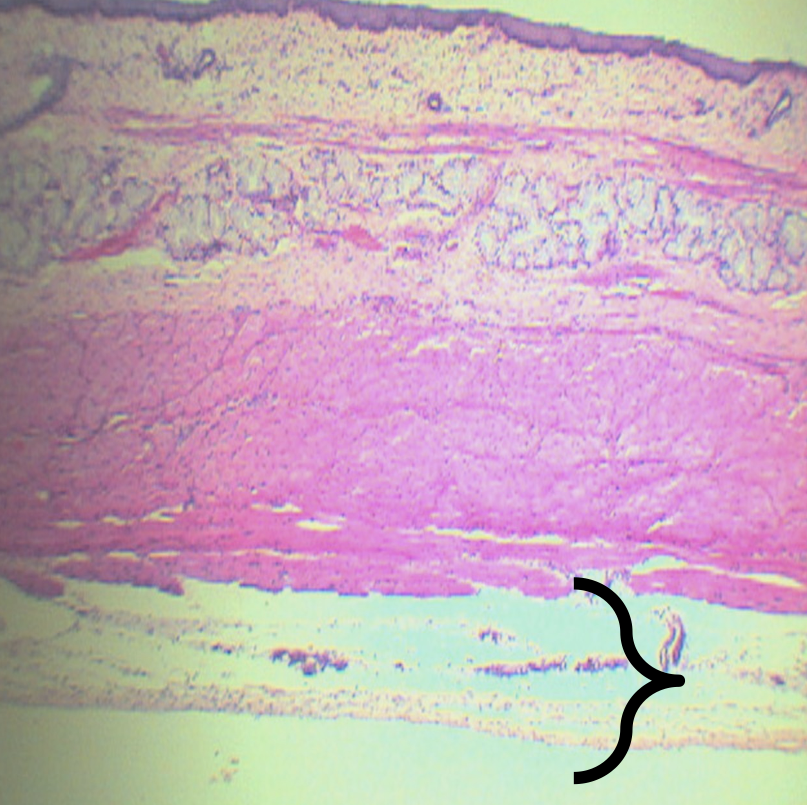
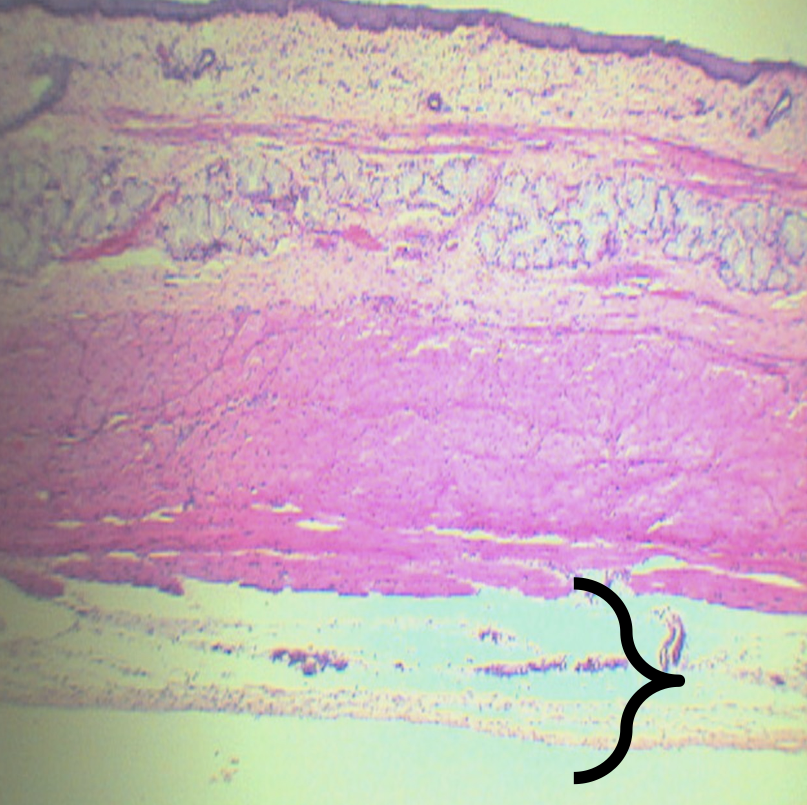
What is present in this structure?
Blood and lymphatic vessels
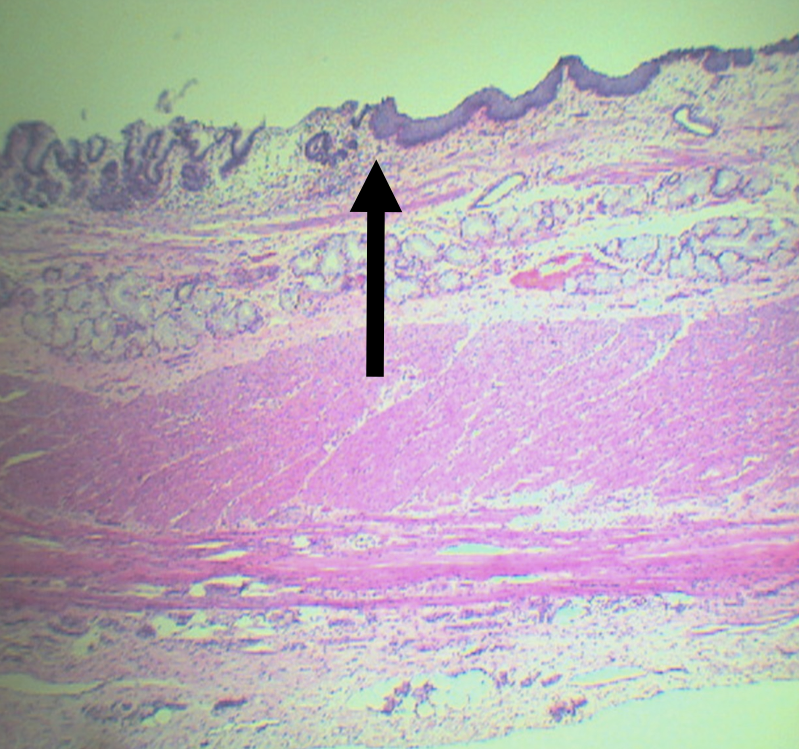
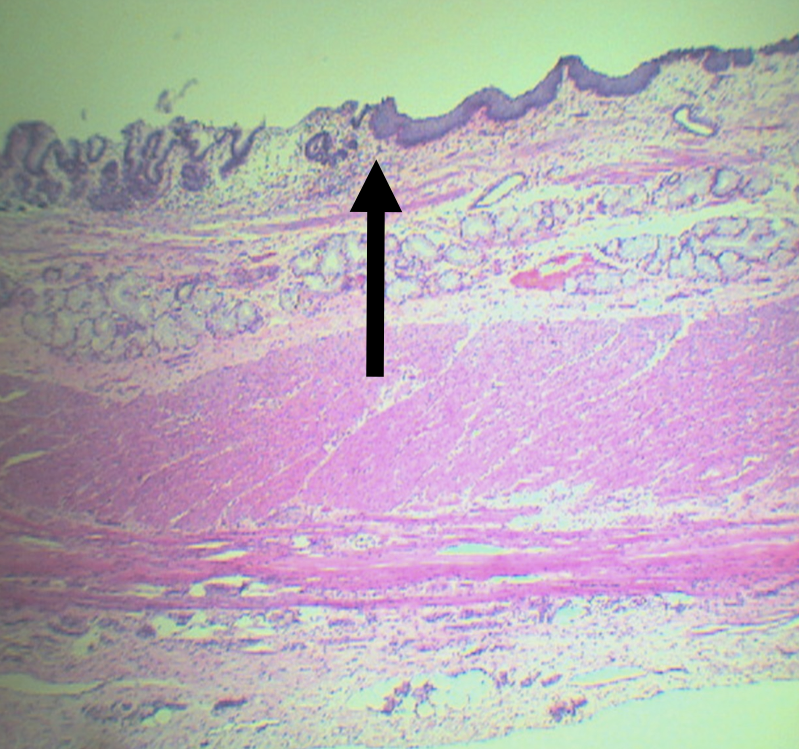
Identify the pointed structure
Gastroesophageal Junction
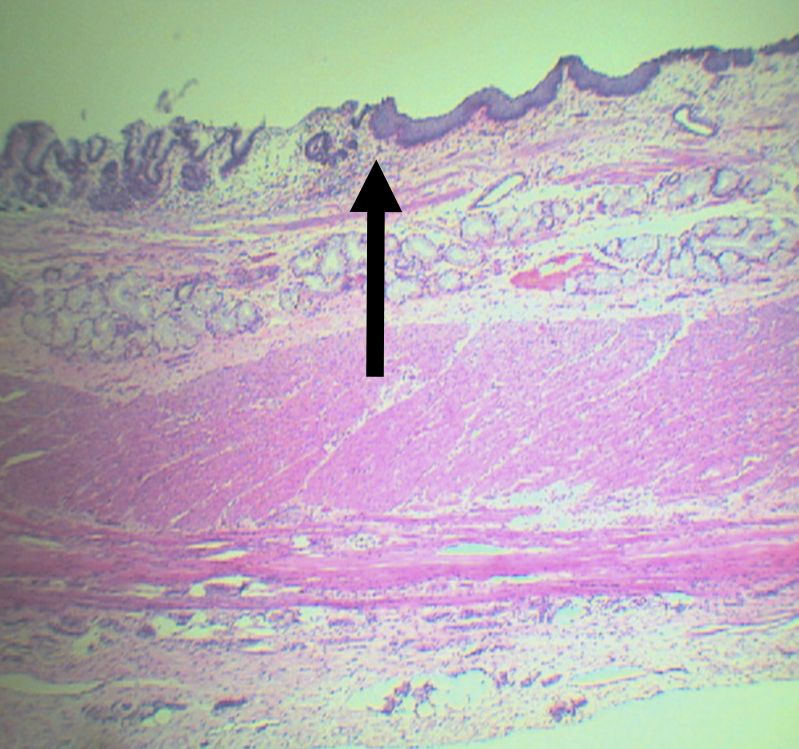
What is the junction between the esophagus and the stomach?
Gastroesophageal Junction
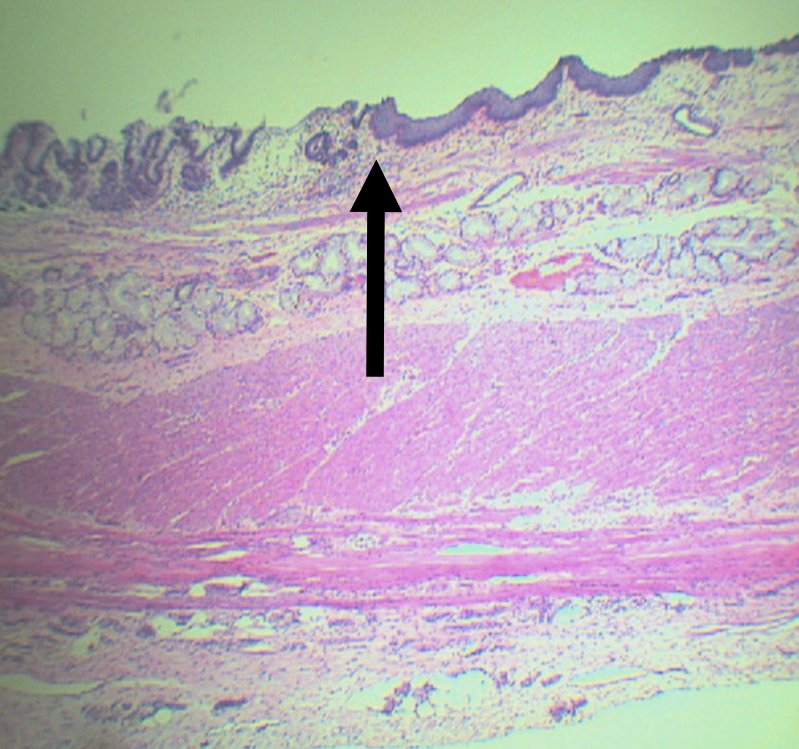
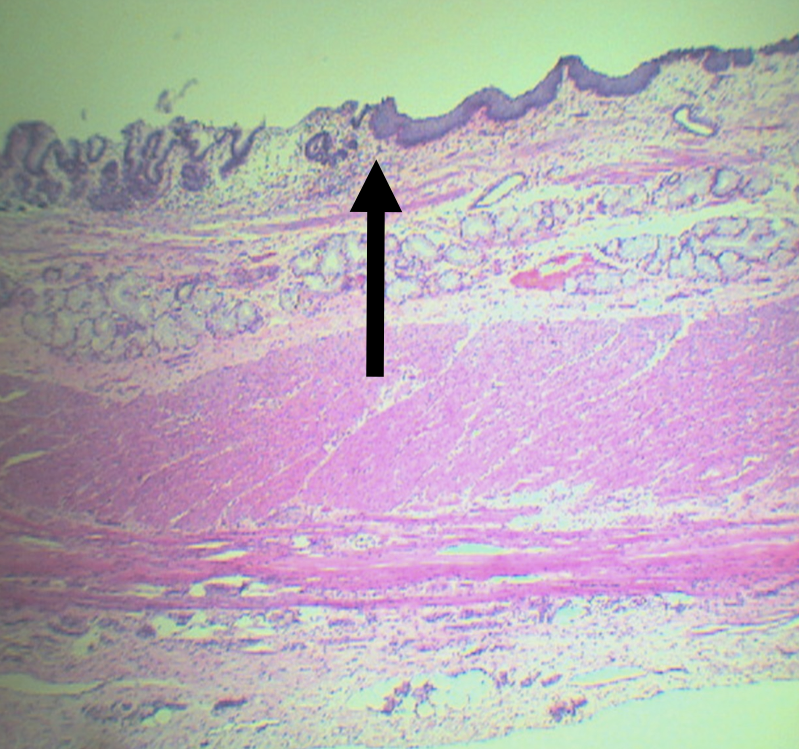
Lining epithelium of the left side of this structure
Simple Columnar non-cornified epithelium
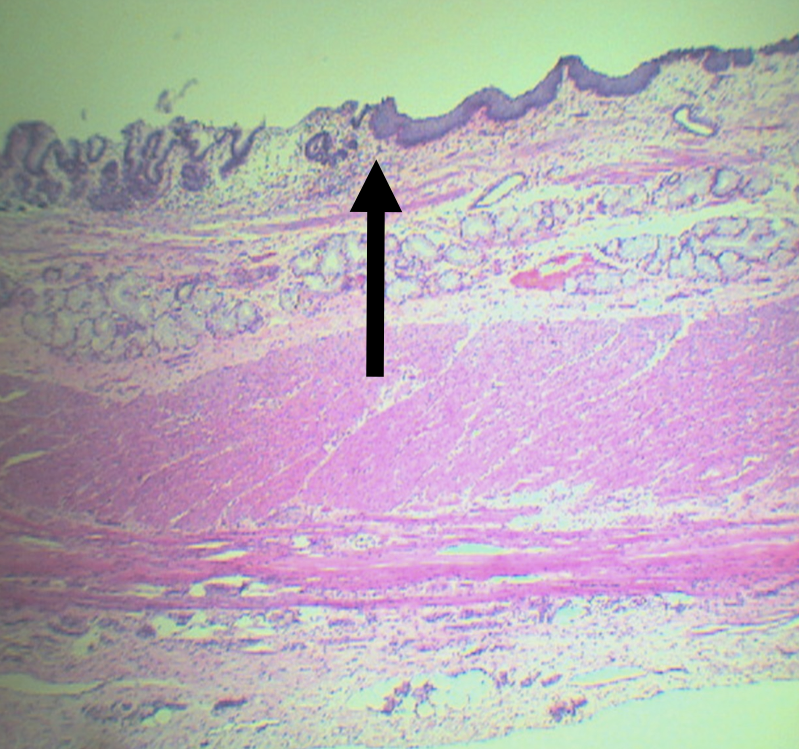
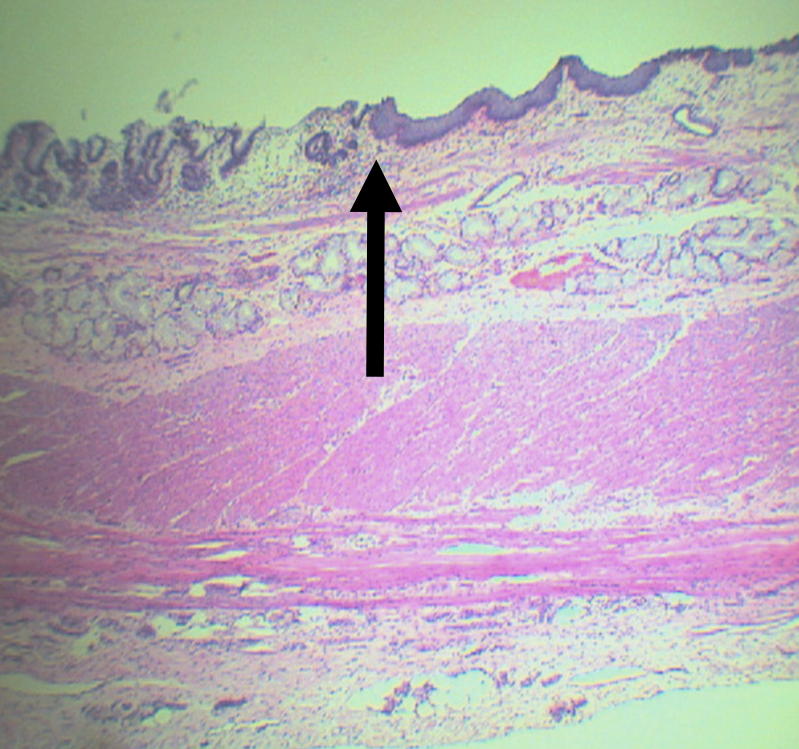
Lining epithelium of the right side of this structure
Stratified squamous non-cornified epithelium
Identify the Organ
Stomach
What does this organ produce to aid digestion
Digestive Enzymes
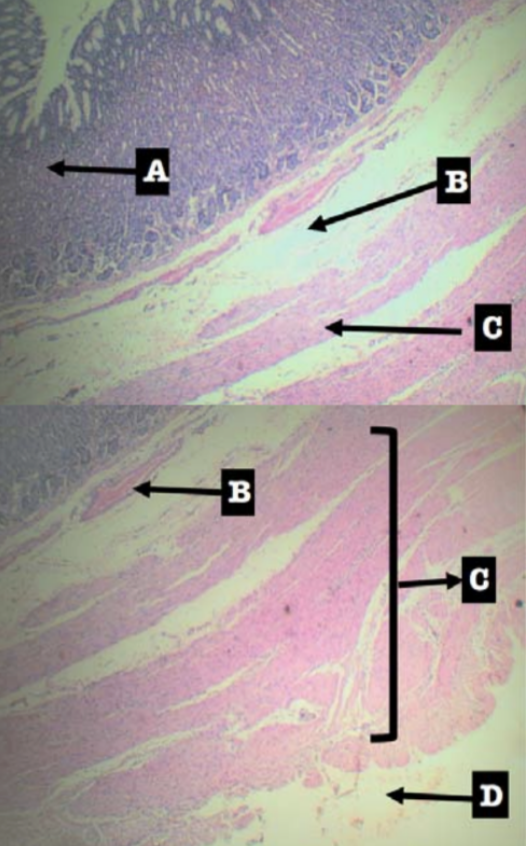
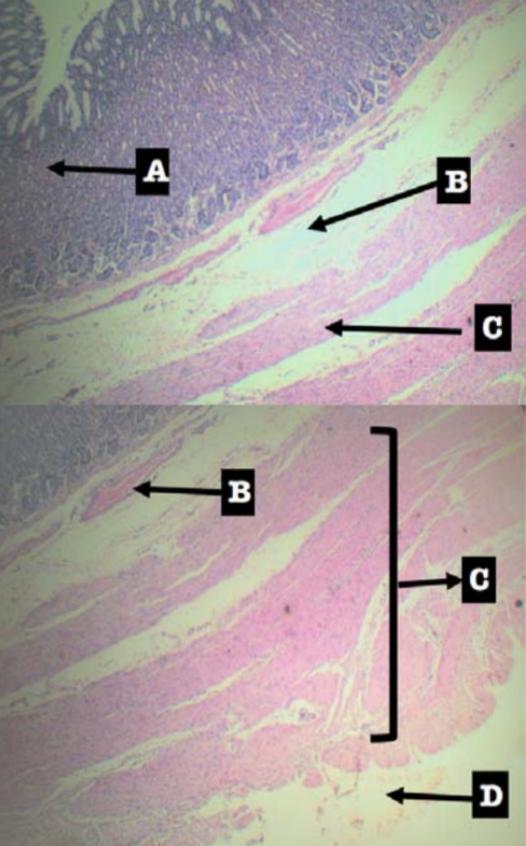
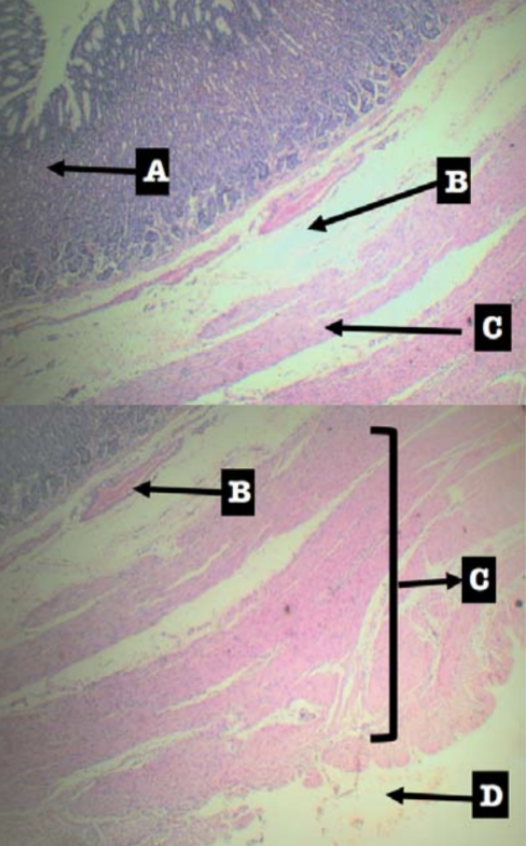
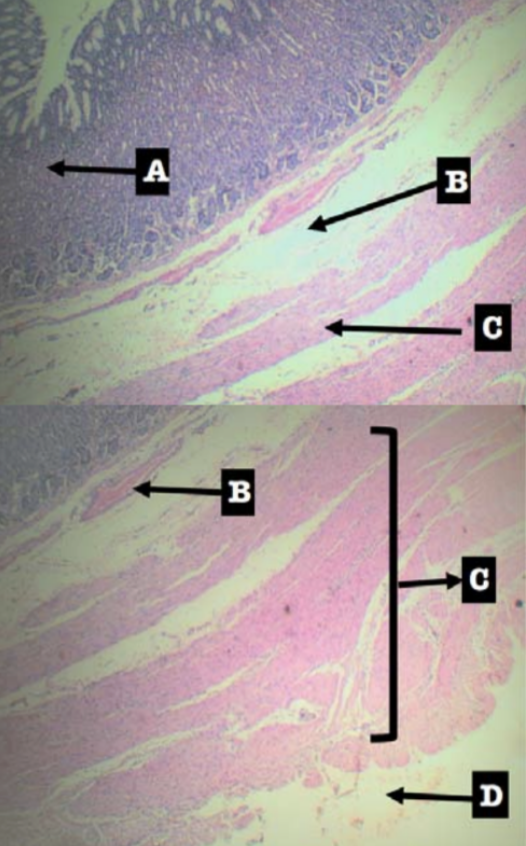
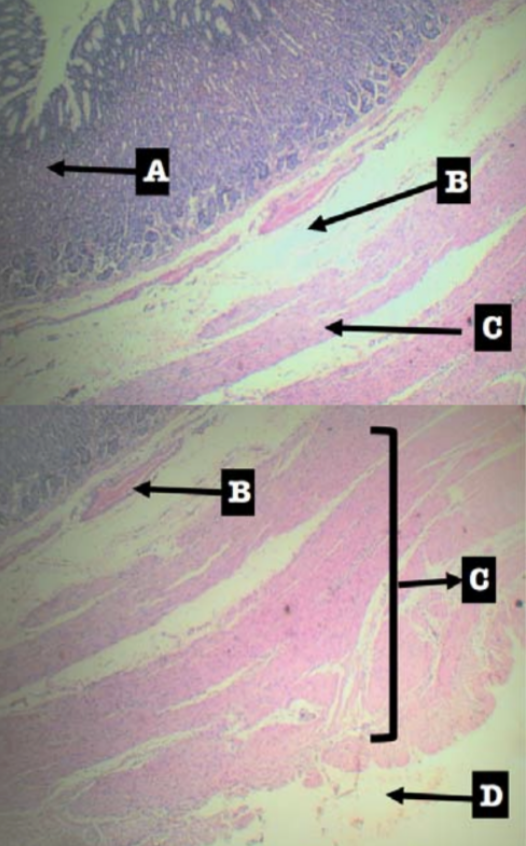
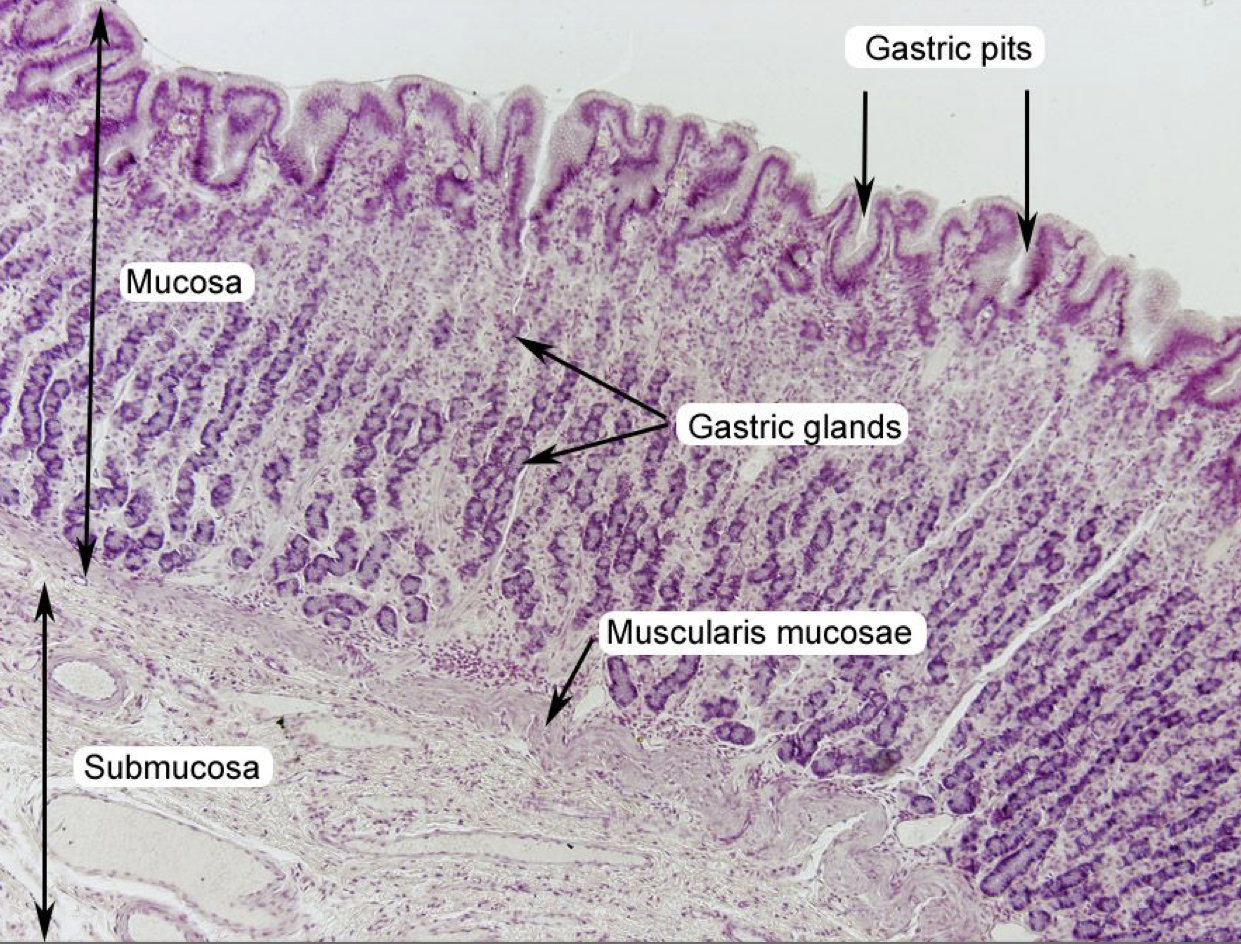
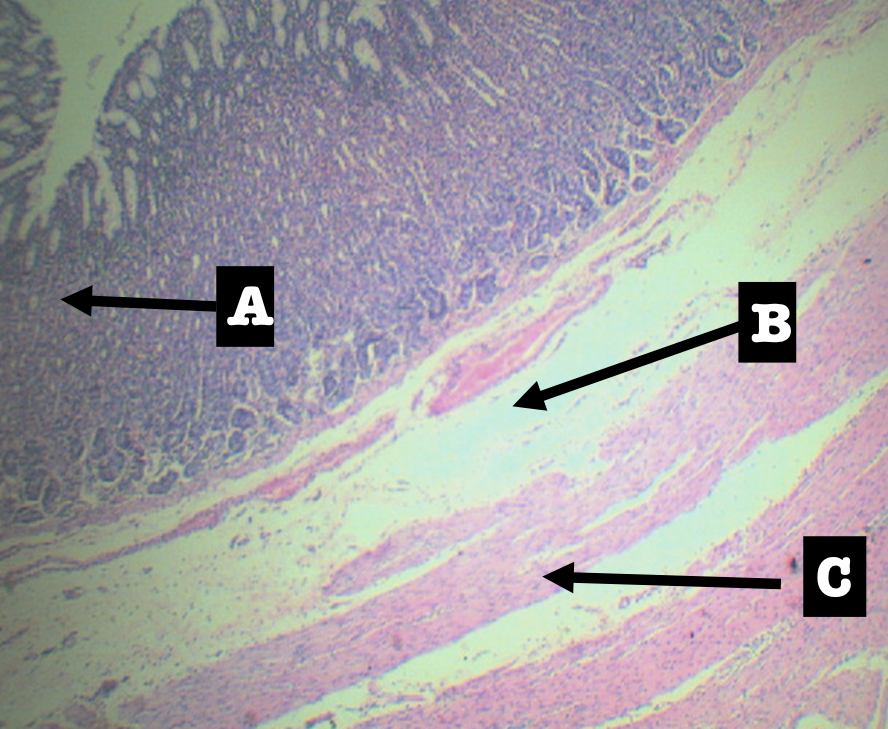
Label the layers of the organ
Layers of Stomach:
A. Mucosa
B. Submucosa
C. Tunica muscularis
D. Tunica serosa
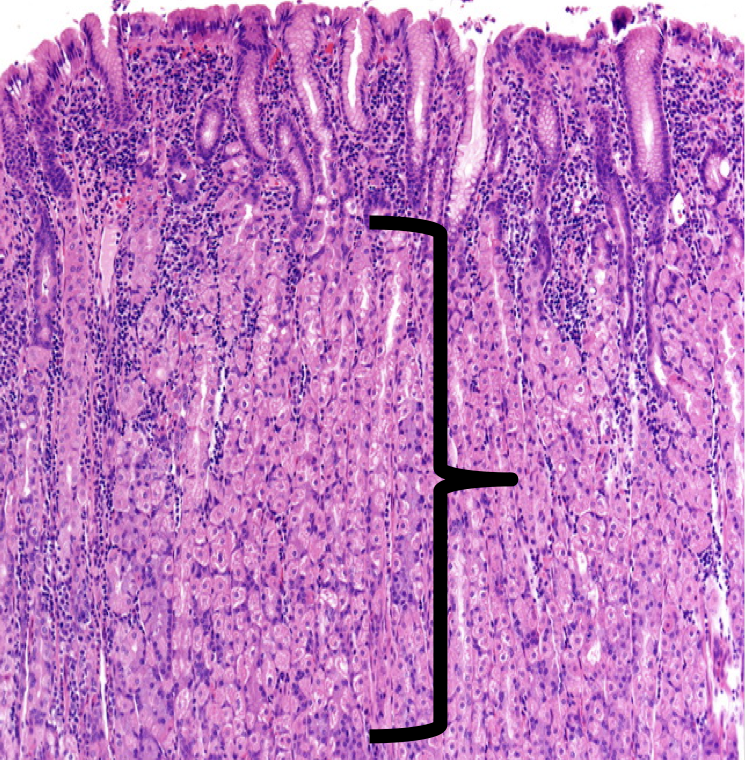
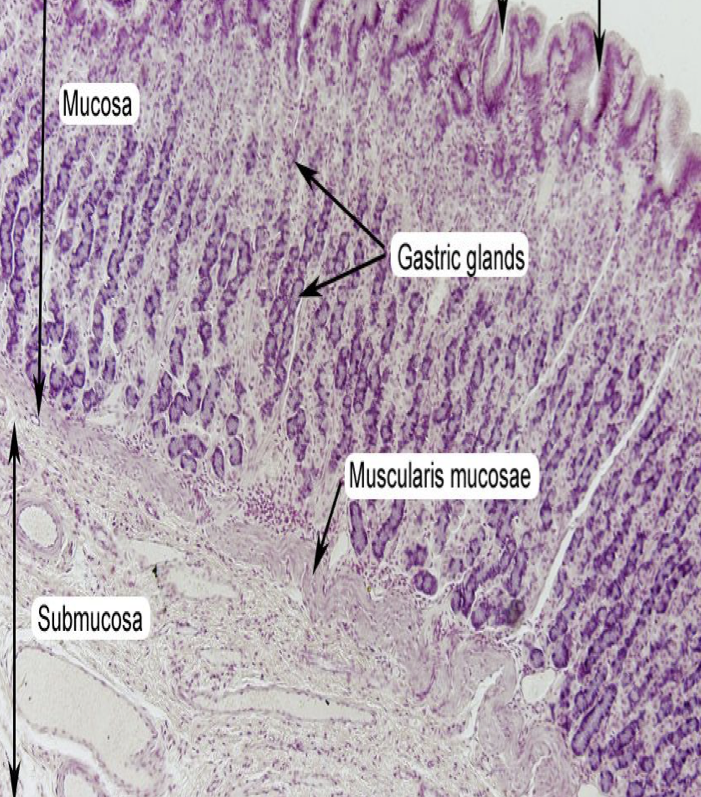
Where layer are the gastric organs of the stomach located
Mucosa; specifically the lamina propia
Label
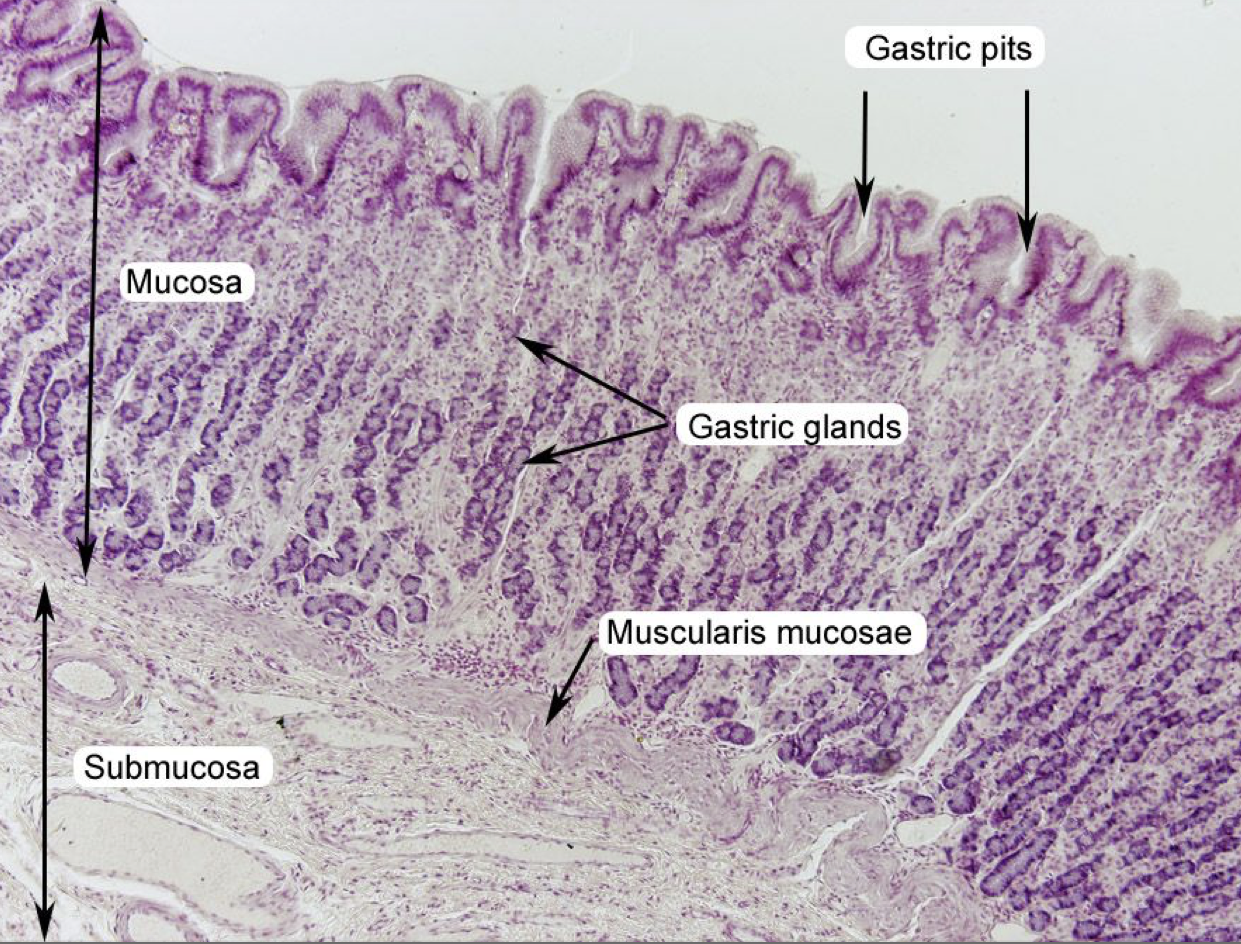
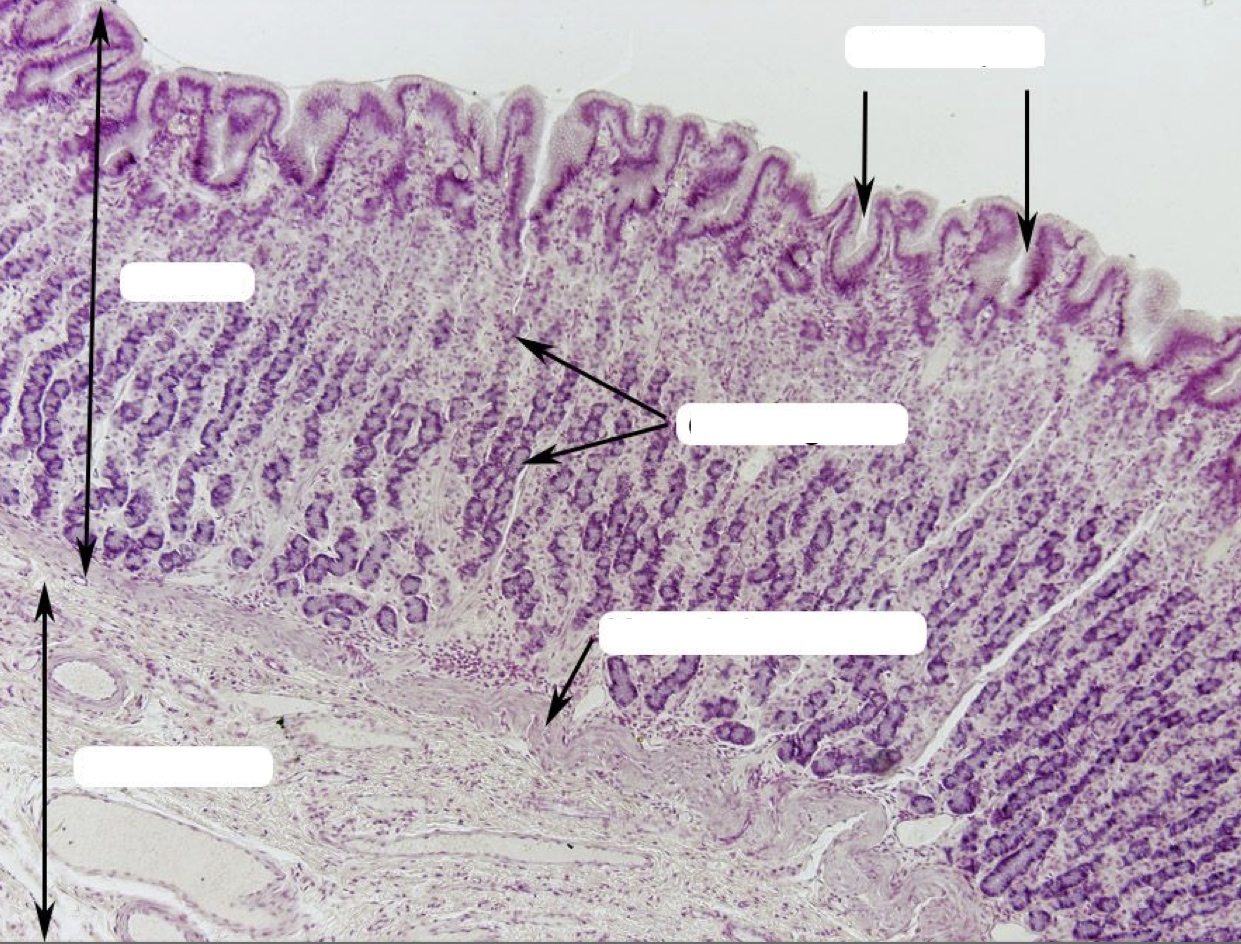
Where does the secretions of gastric glands come out?
Gastric Pits
Identify the layer
Mucosa (A)
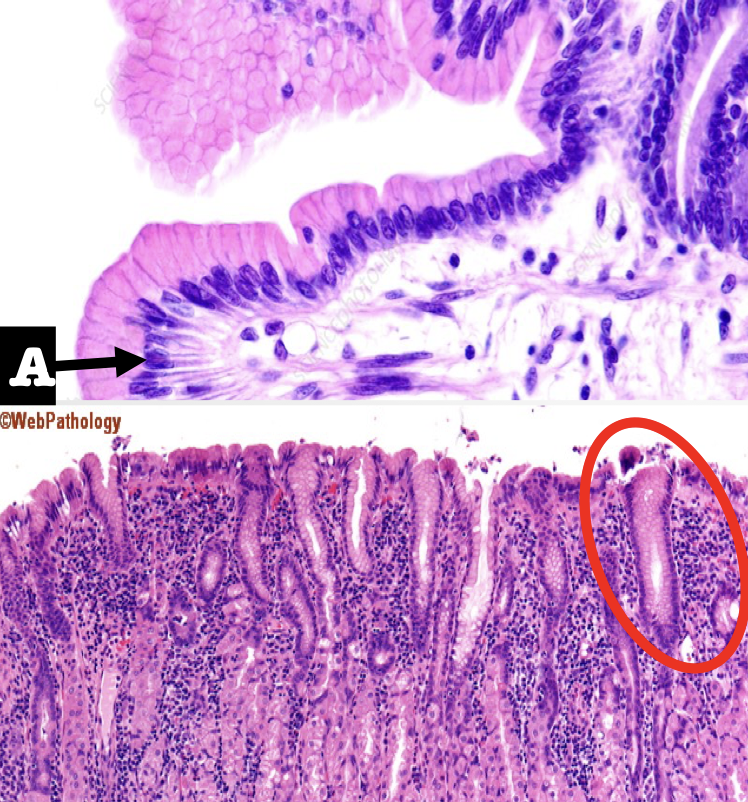
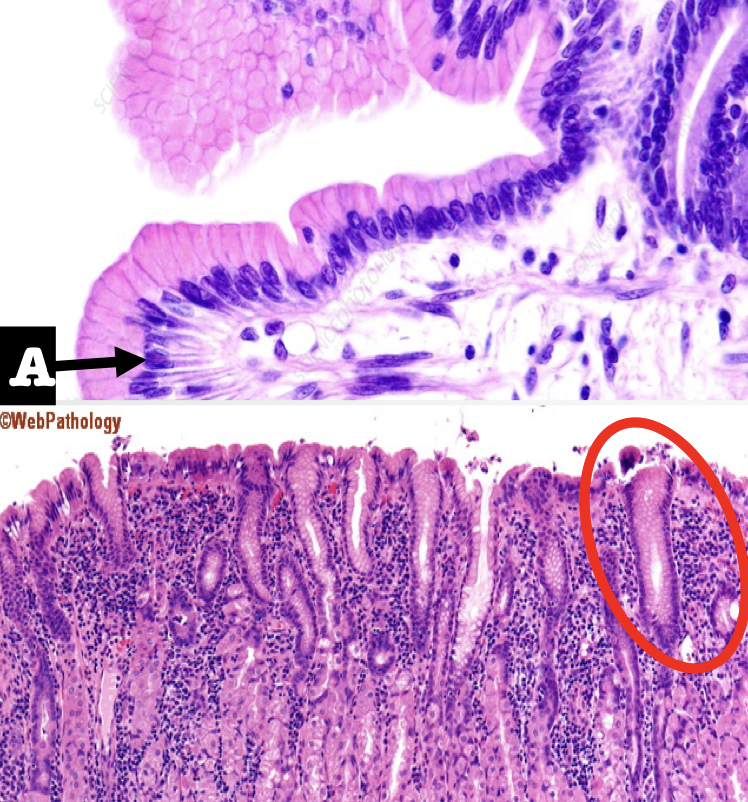
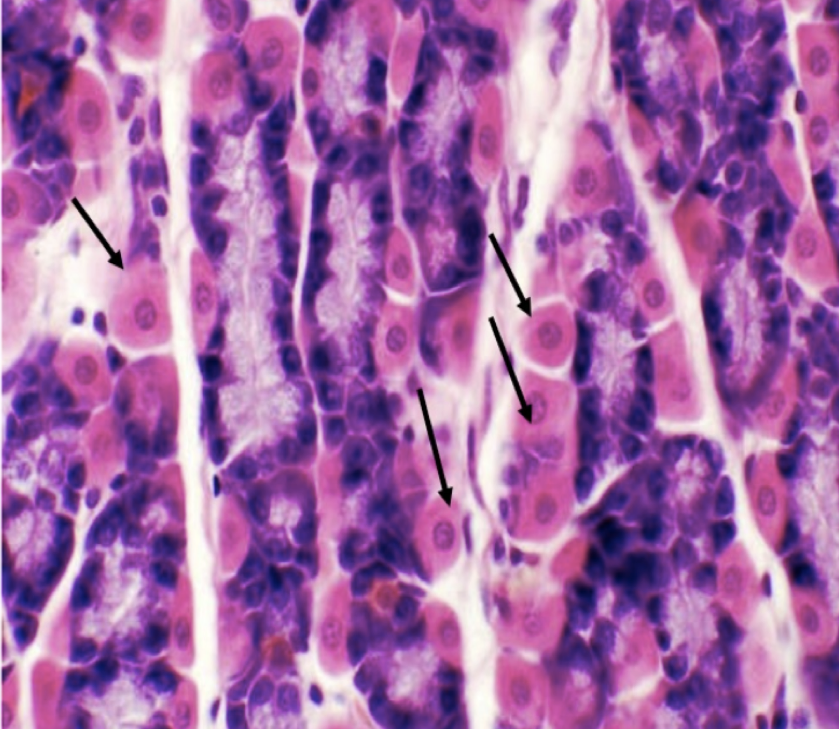
Identify the first two structures (A and encircled) of the mucosa
A: Lining Epithelium
Encircled: Mucous Neck Cells
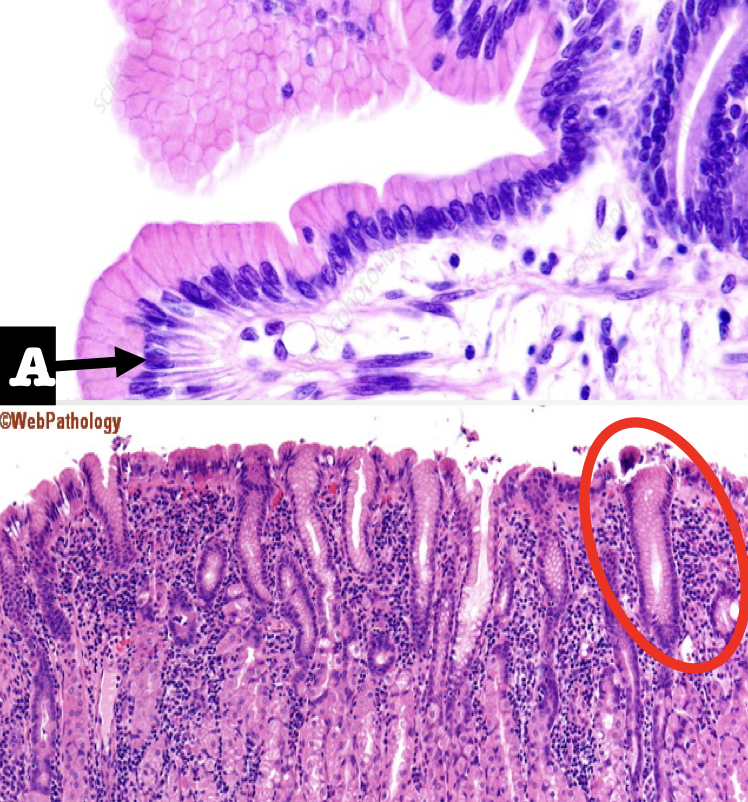
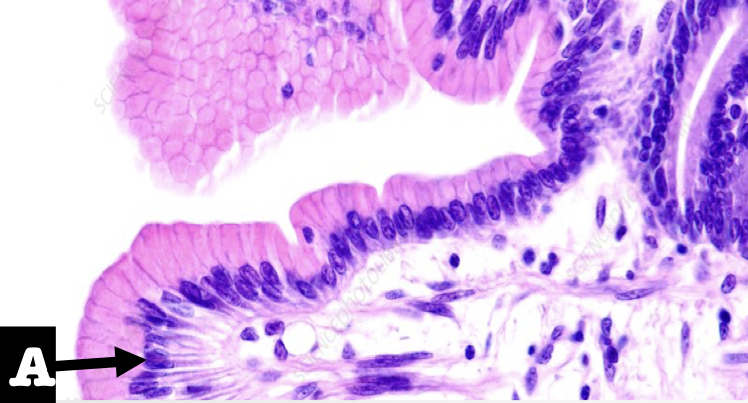
What is the lining epithelium of the organ?
Simple columnar epithelium without goblet cells
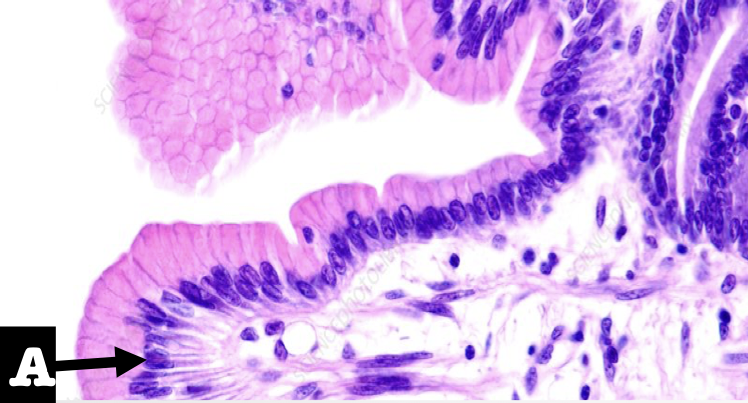
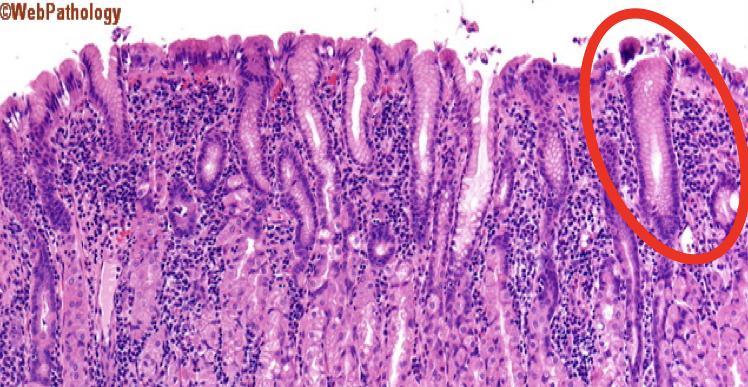
What is the encircled structure?
Mucous Neck Cells
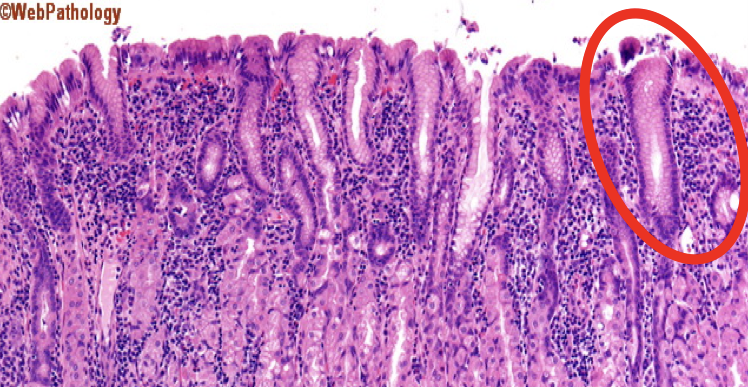
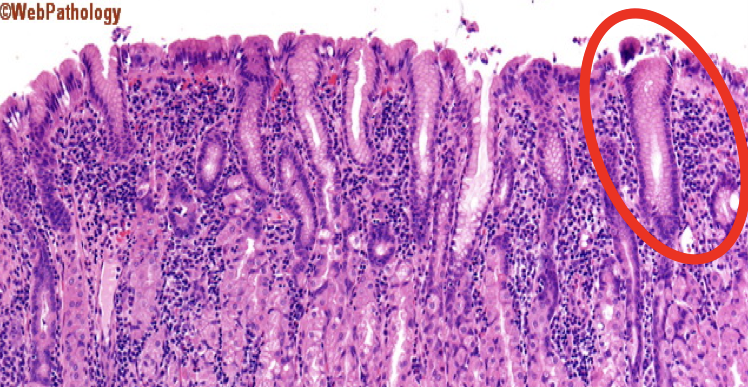
What is the function of the encircled structure?
Produce a thick coating of mucus that protects the gastric mucosa from acid and enzyme secretion
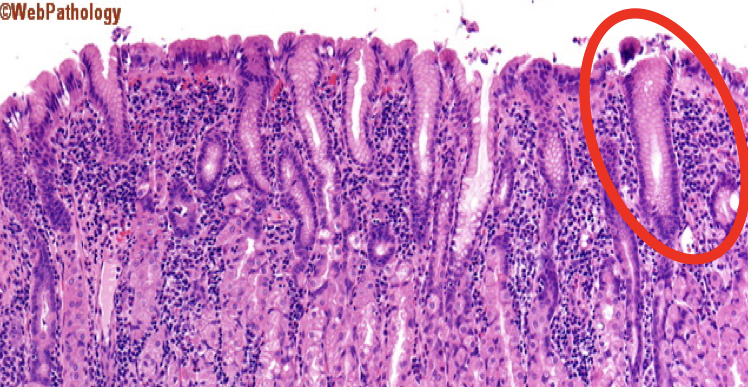
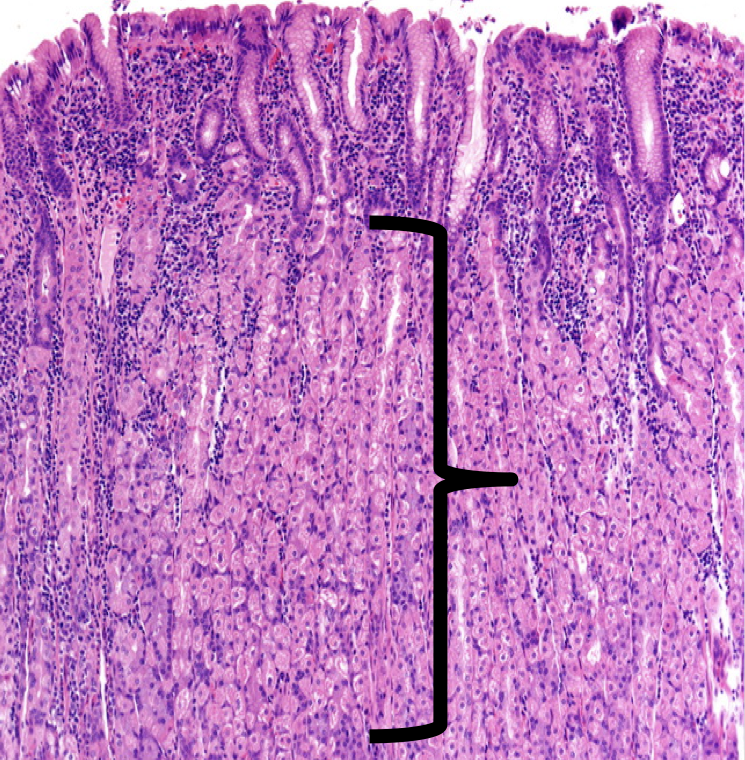
Identify
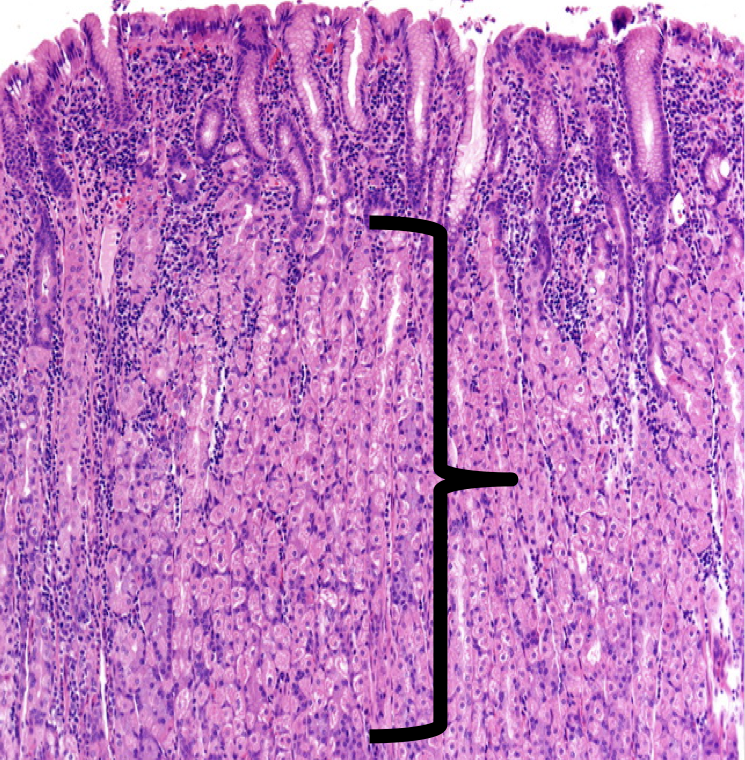
Lamina Propia
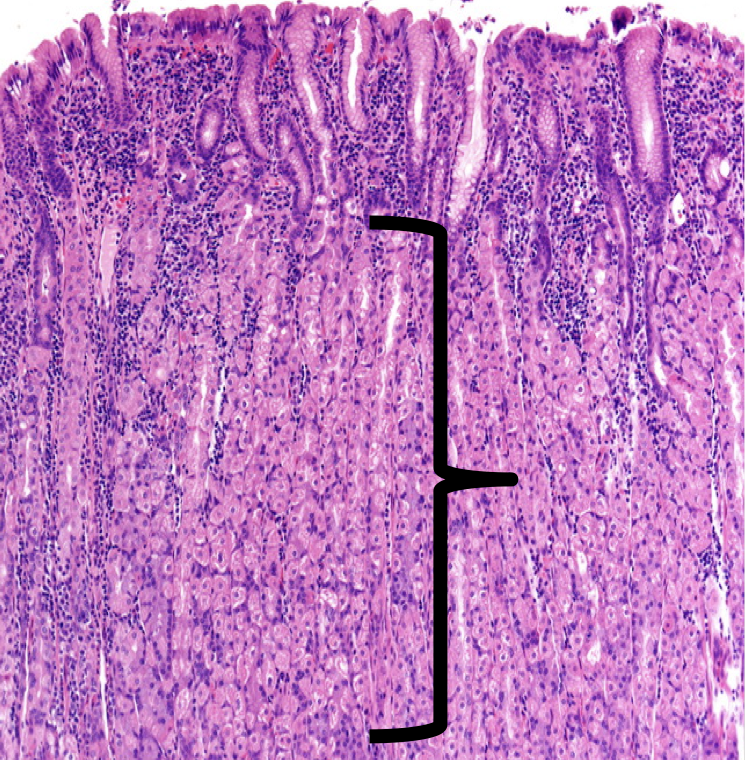
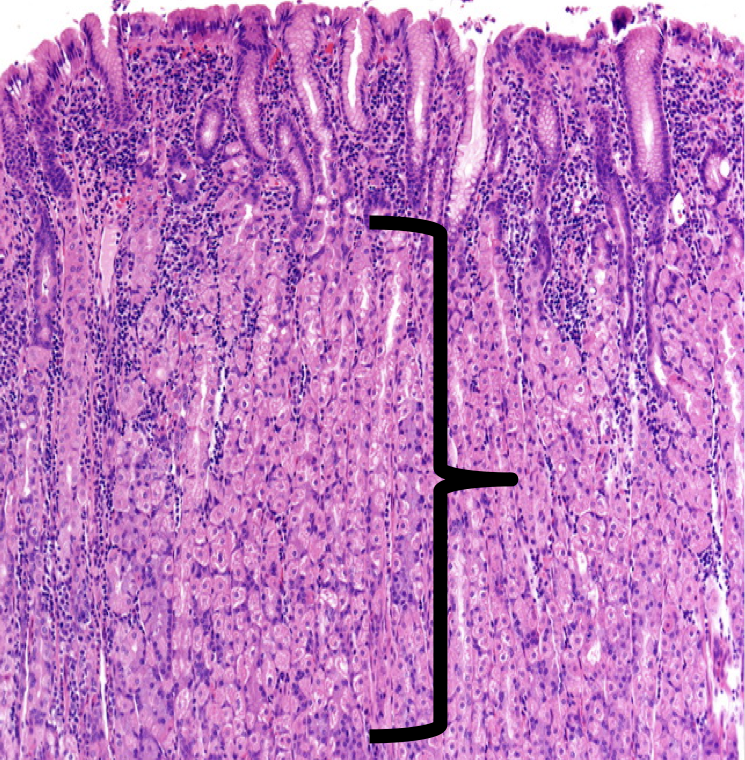
The shown layer produces _______ occupying the entire thickness which opens into the bases of the gastric pits.
Gastric glands
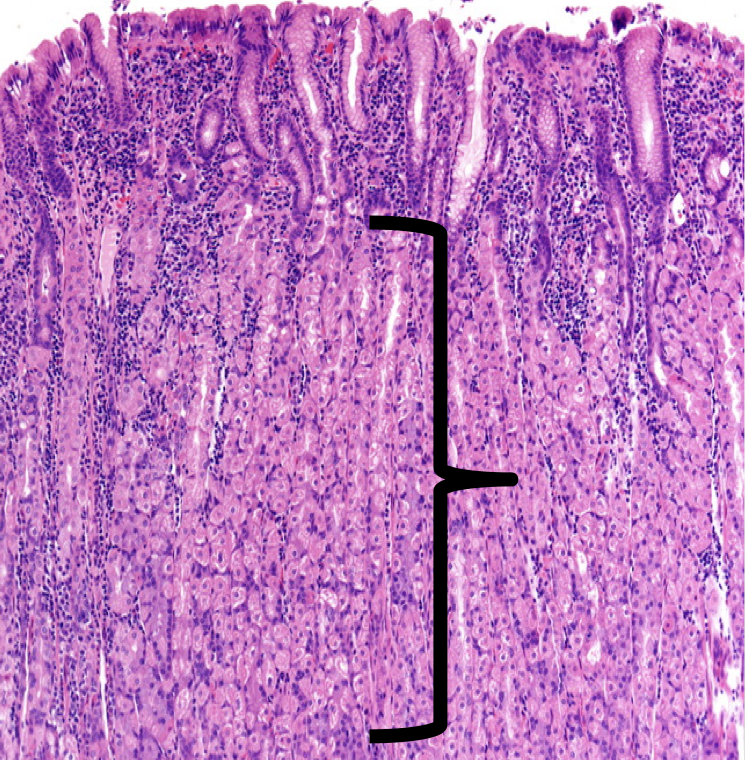
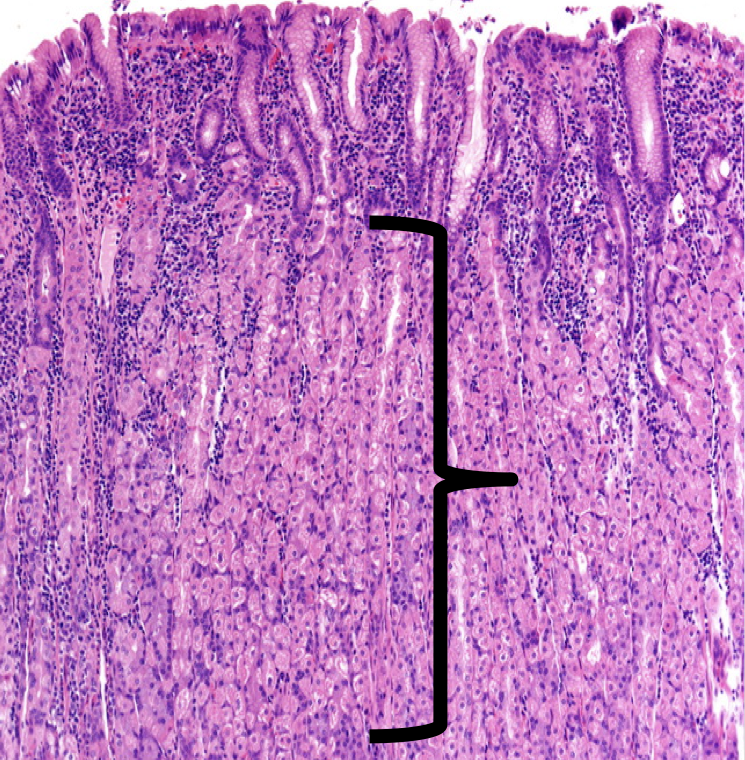
Glands that are responsible for the synthesis and secretion of gastric juice
Gastric glands
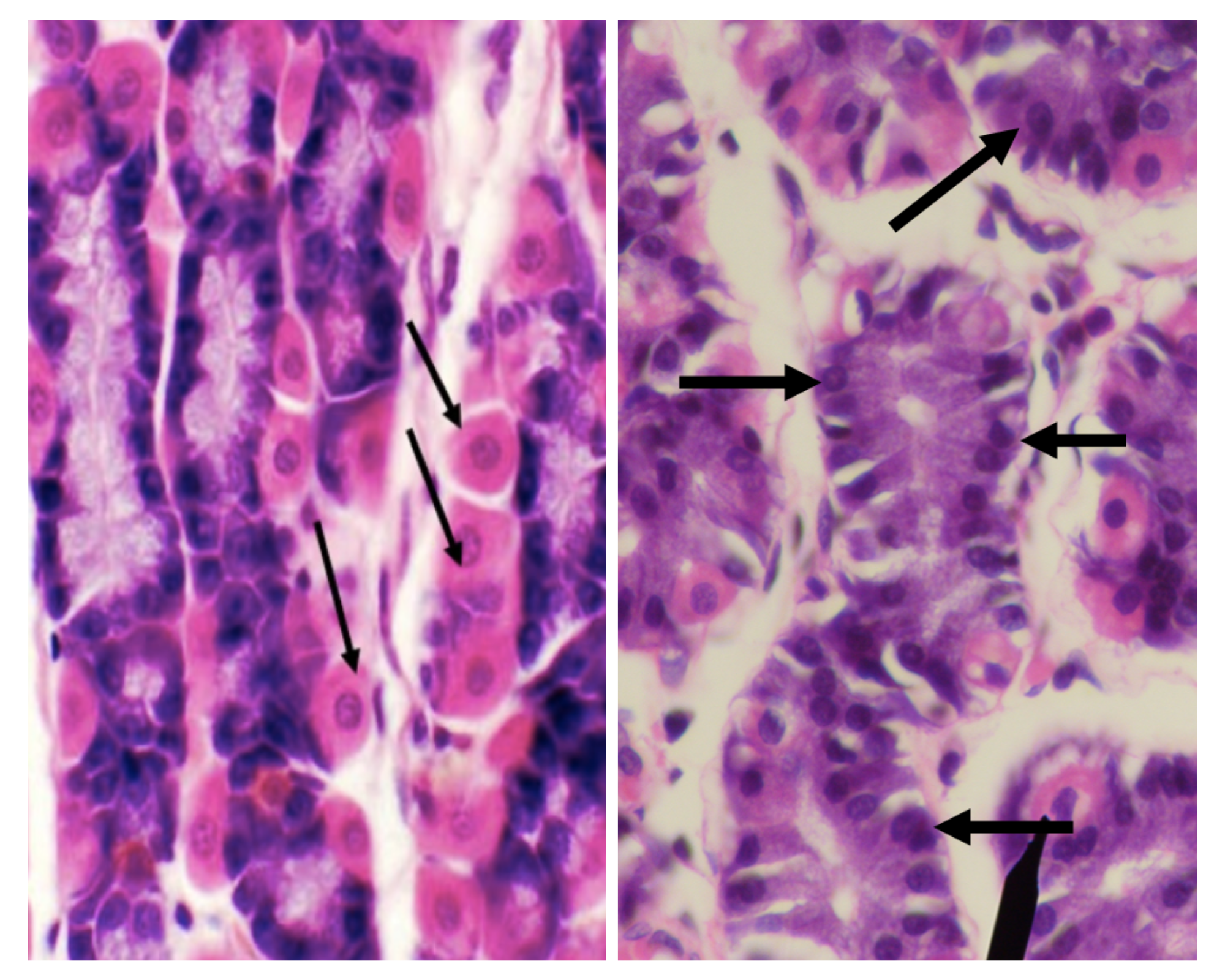
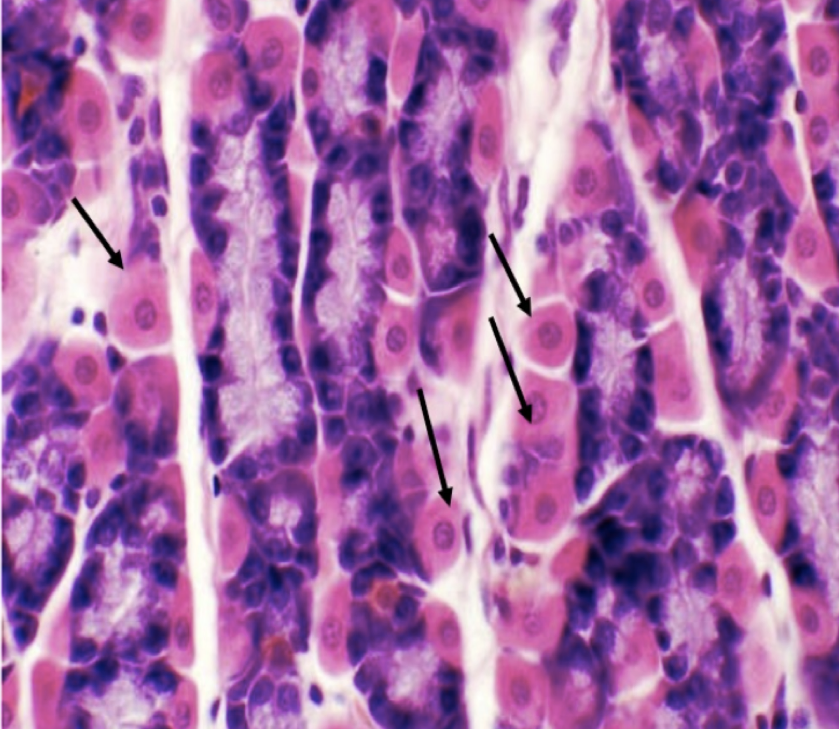
What are the two major cell types in the stomach?
LEFT: Parietal/ Oxyntic Cell
RIGHT: CHIEF/ PEPTIC/ ZYMOGENIC CELL
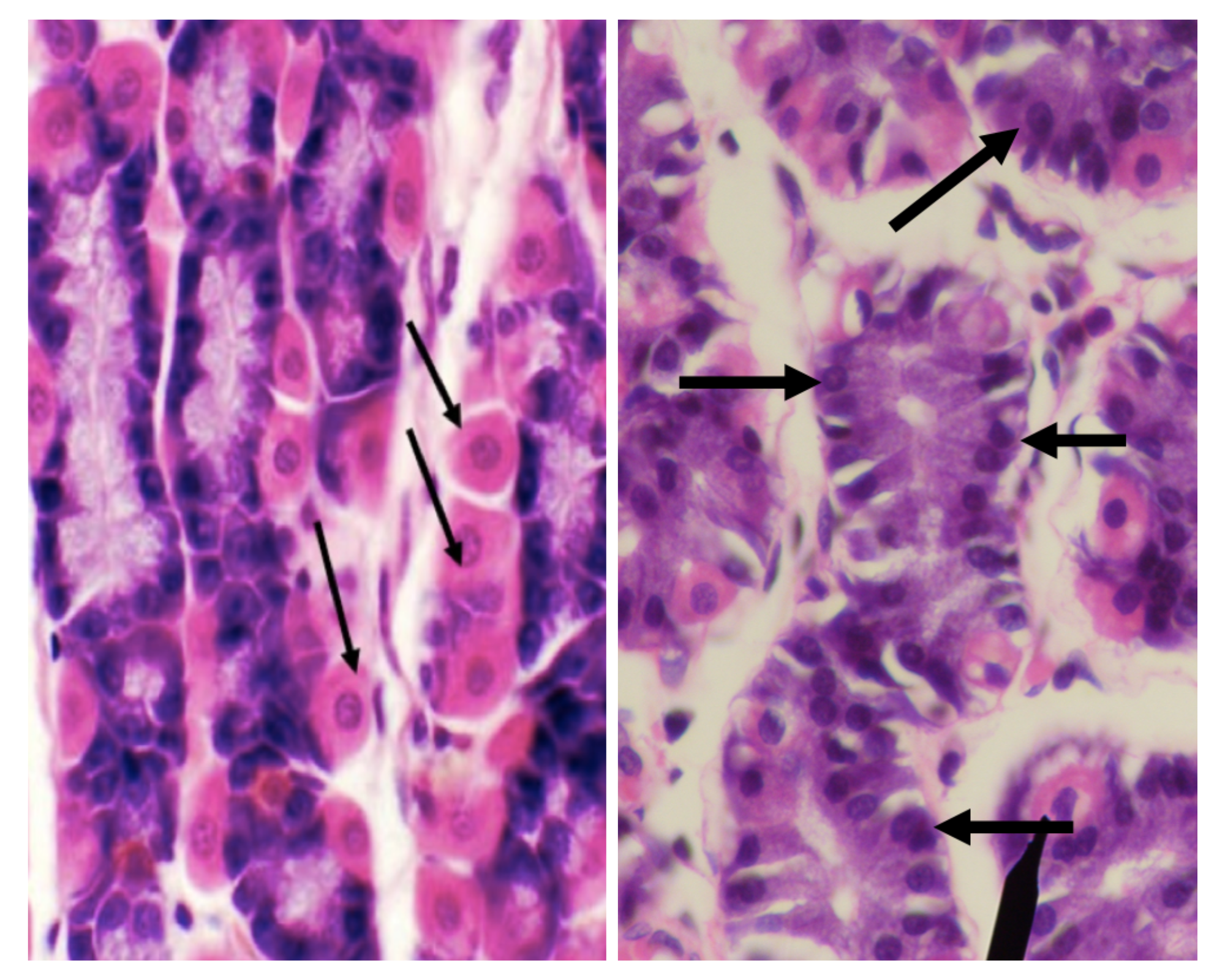
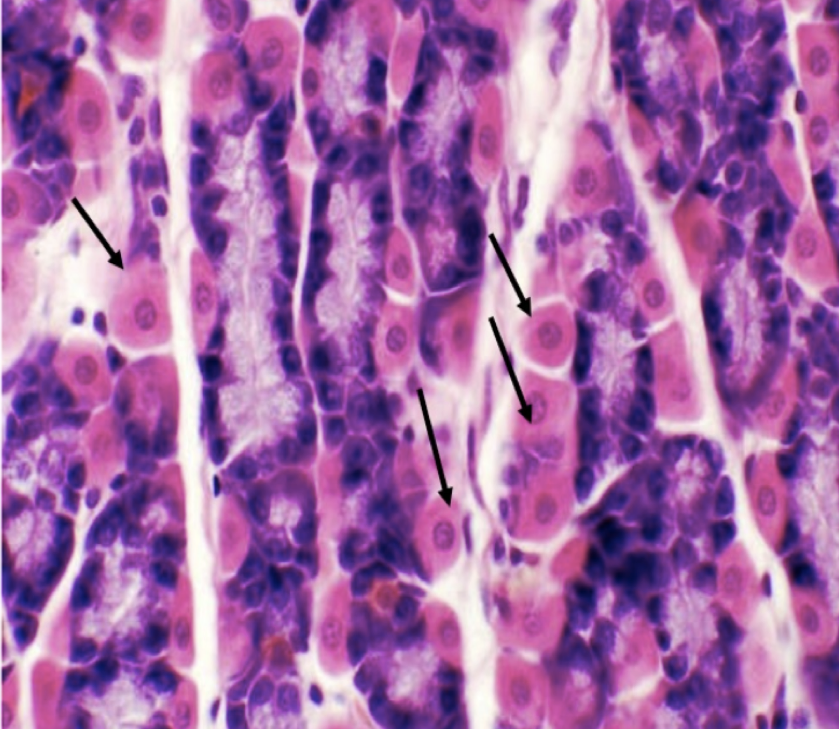
Identify the structure
Parietal/ Oxyntic Cell
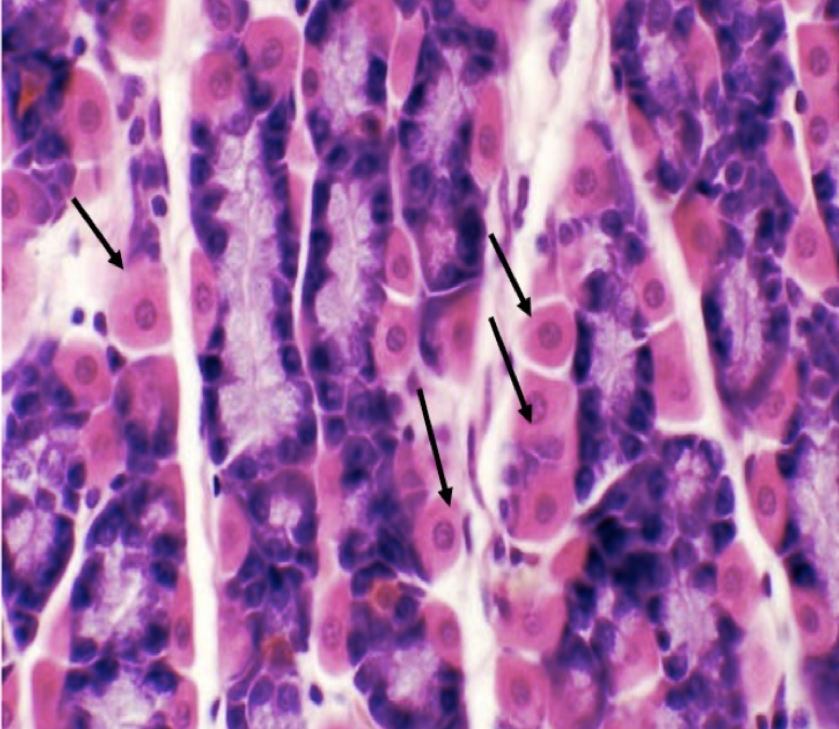
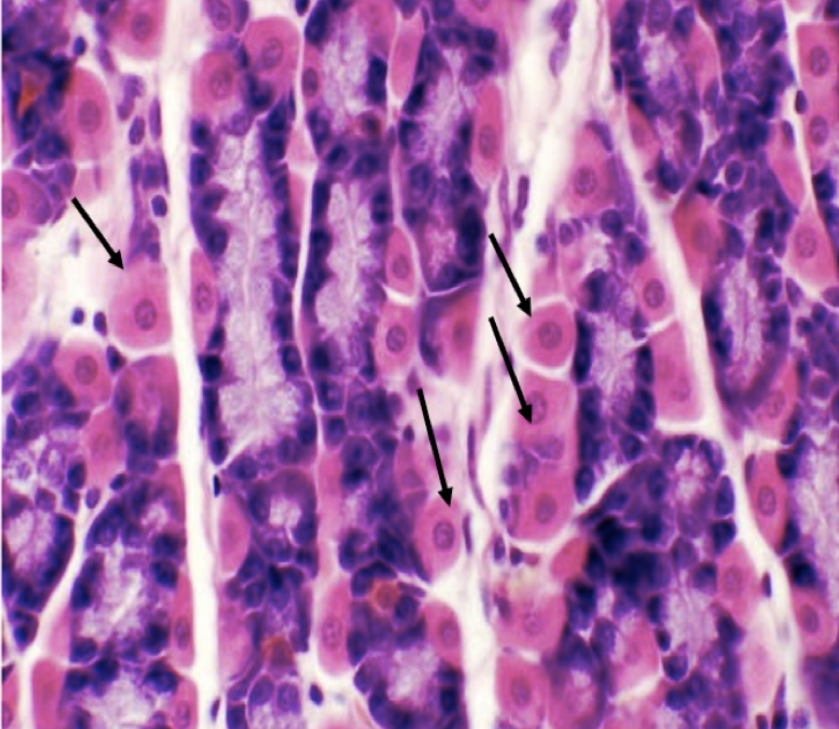
What does this structure secrete?
1. Hydrochloric acid
2. Intrinsic factor
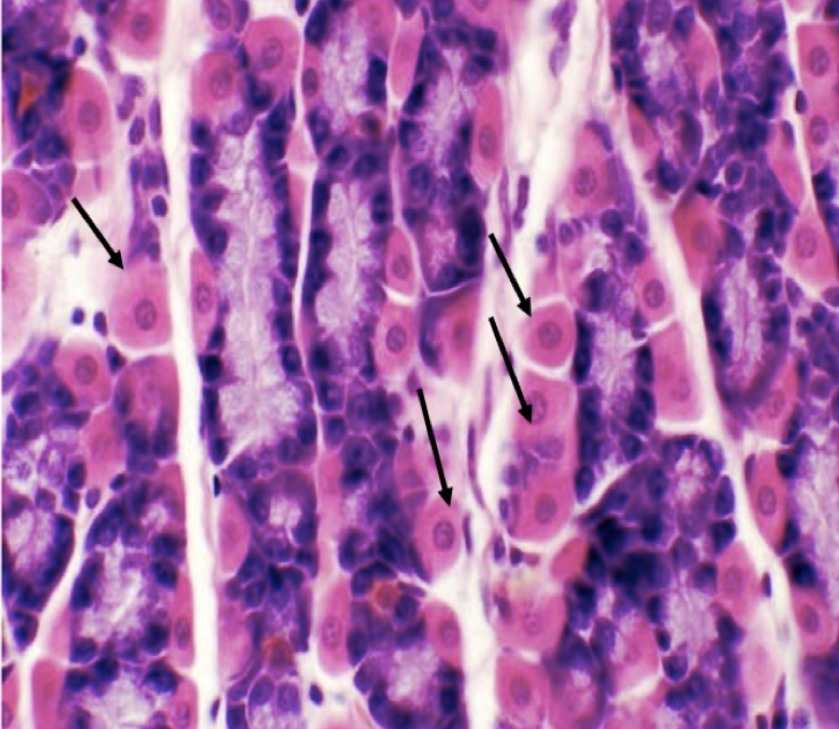
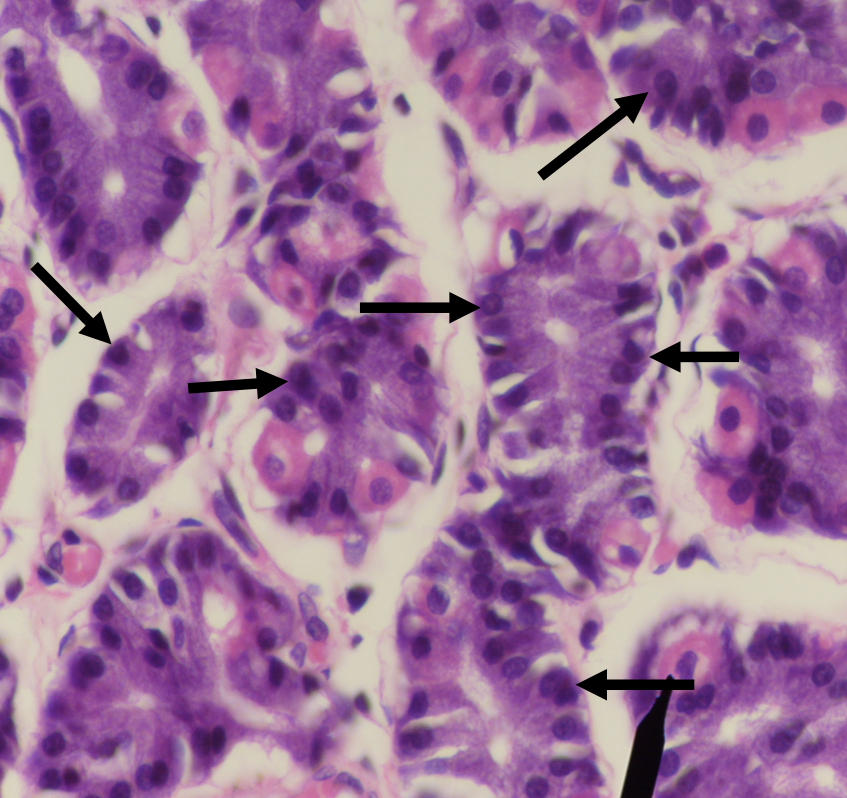
Identify the structure
Chief/ Peptic/ Zymogenic Cell
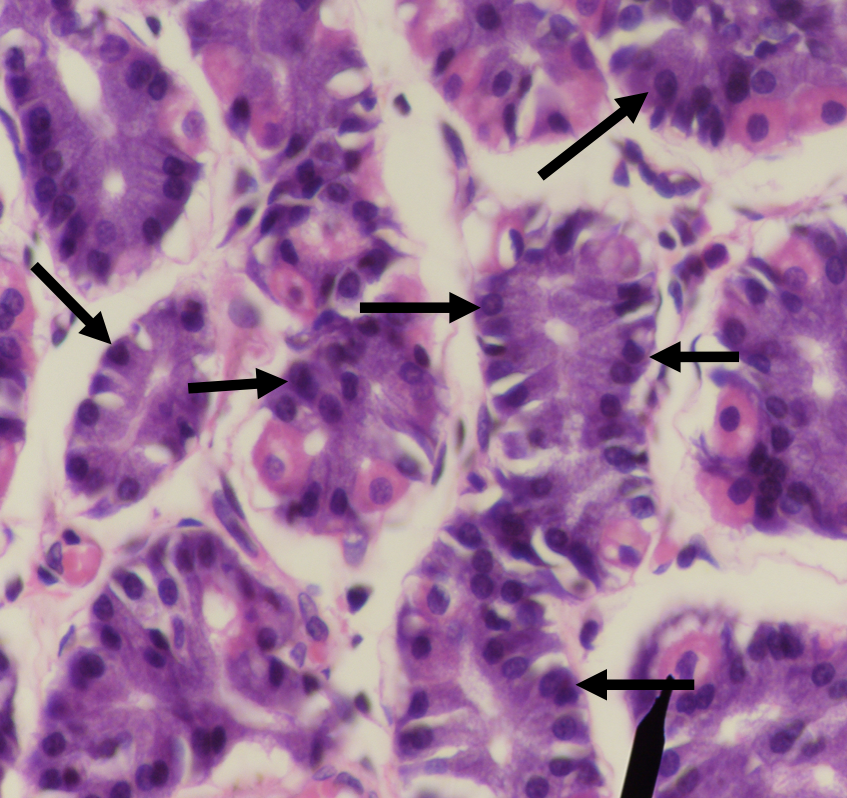
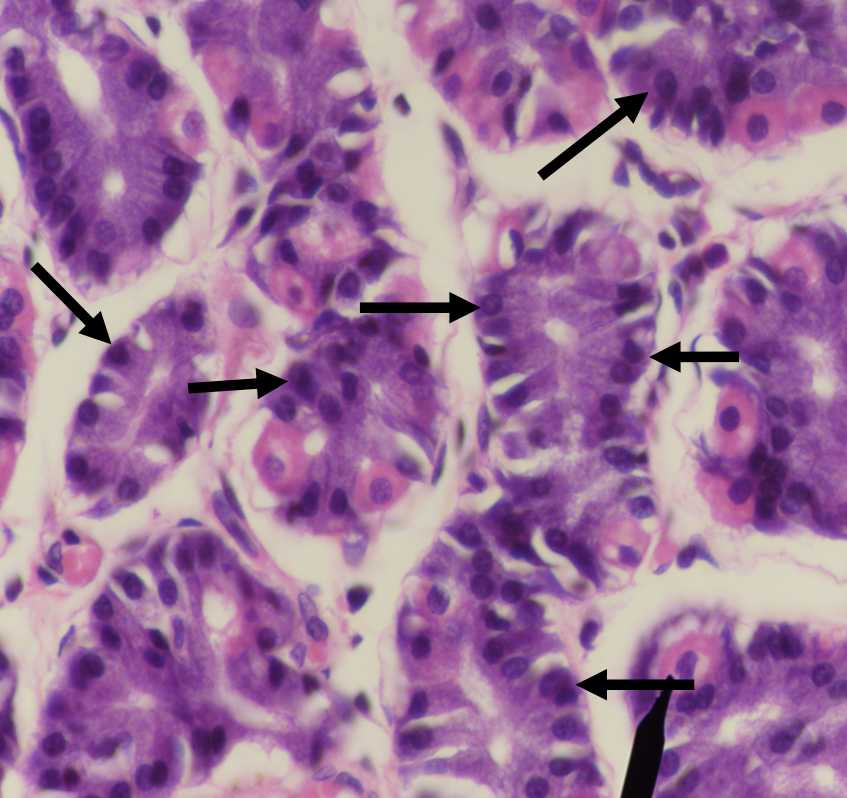
What does this structure secrete?
1. Pepsinogen
2. Gastric lipase
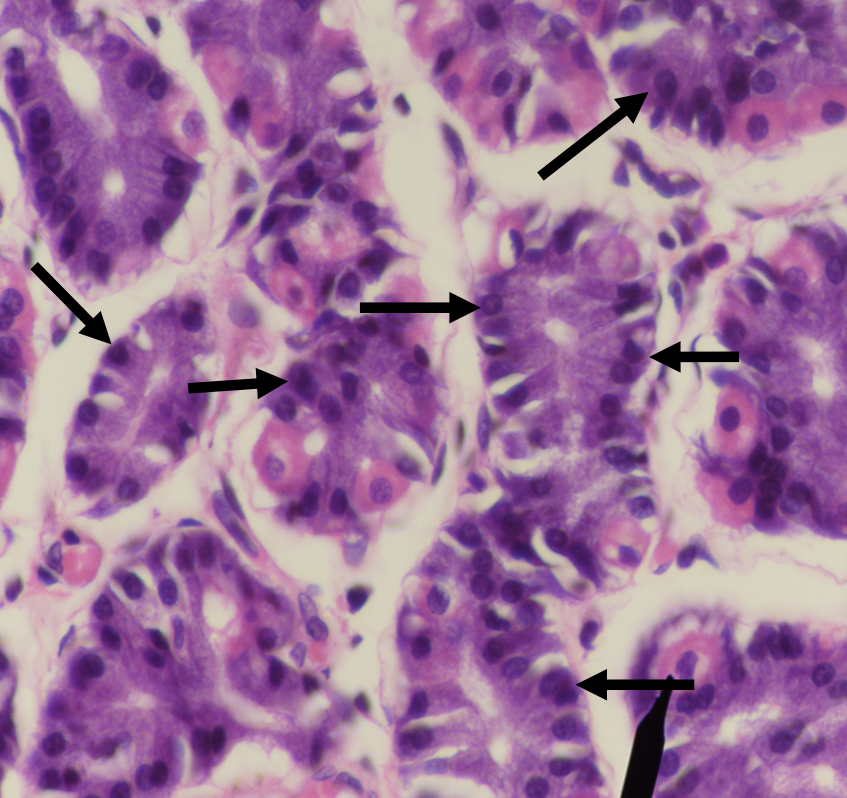
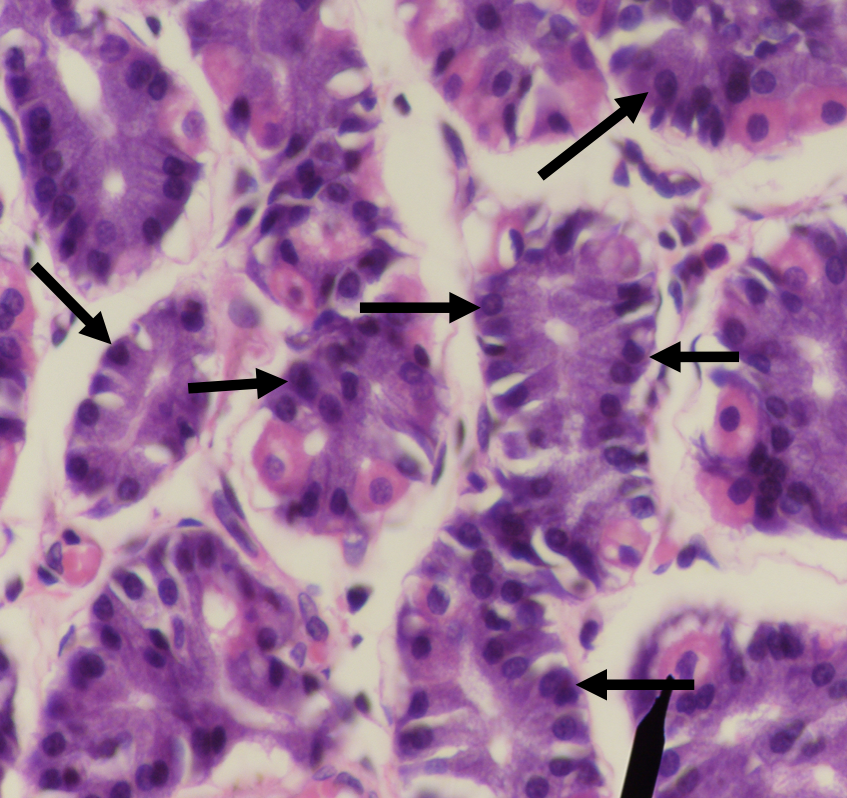
A secretion of this structure that is activated into pepsin when it comes in contact with gastric acid
Pepsinogen
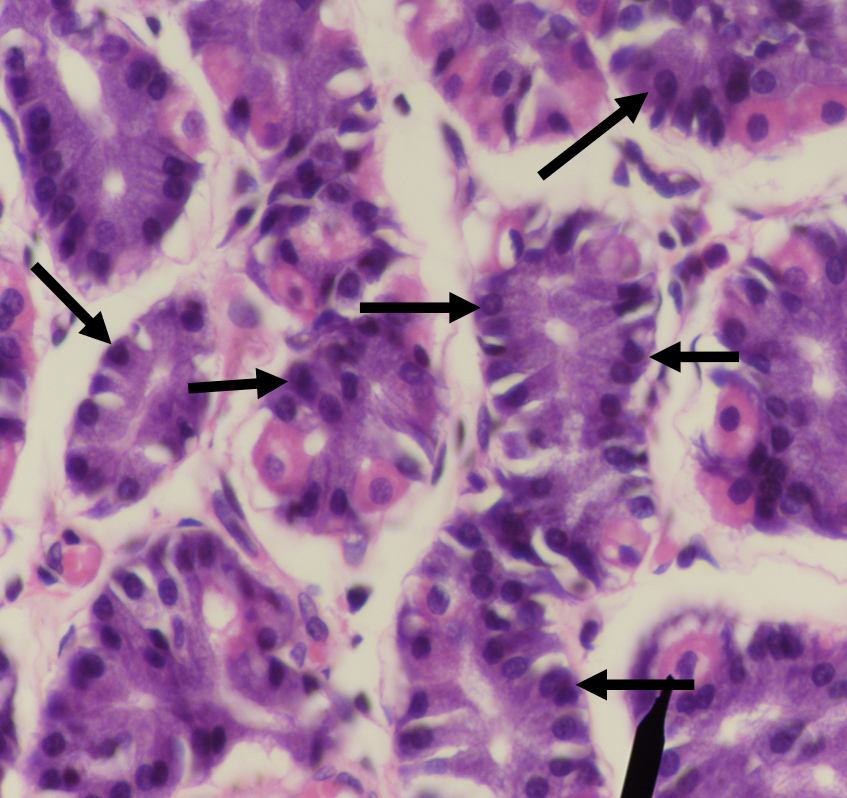
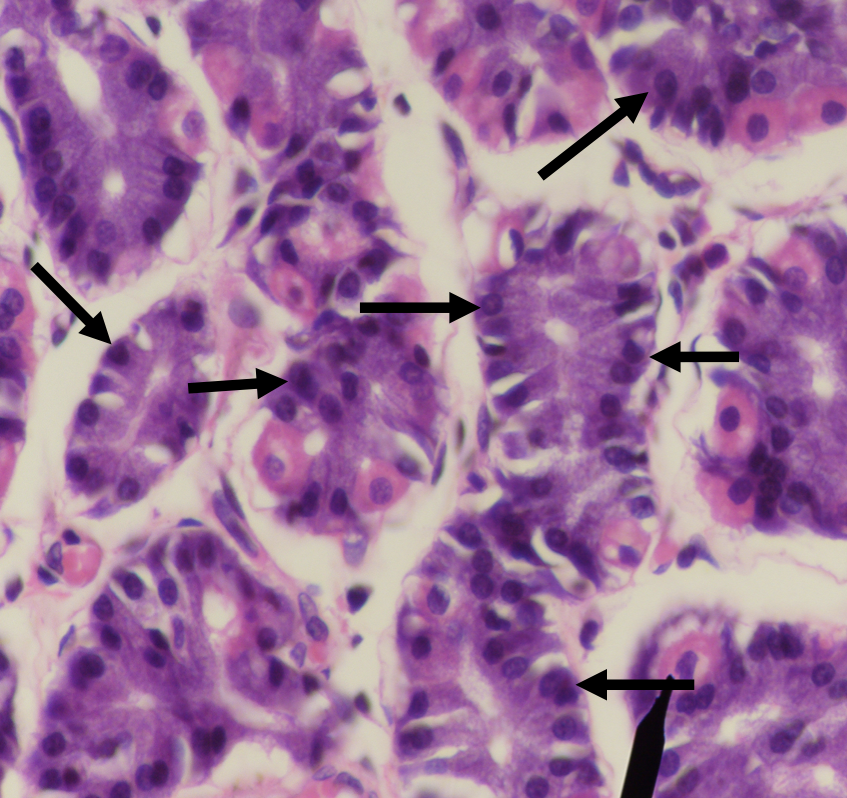
Lipase found in the stomach which also aids in the digestion of lipids
Gastric lipase
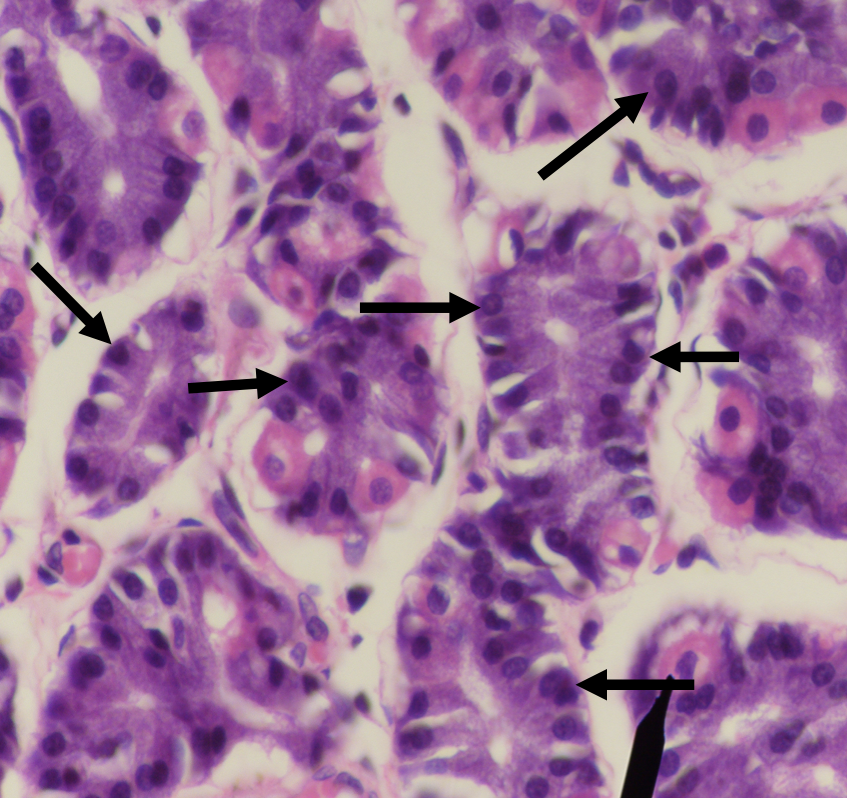
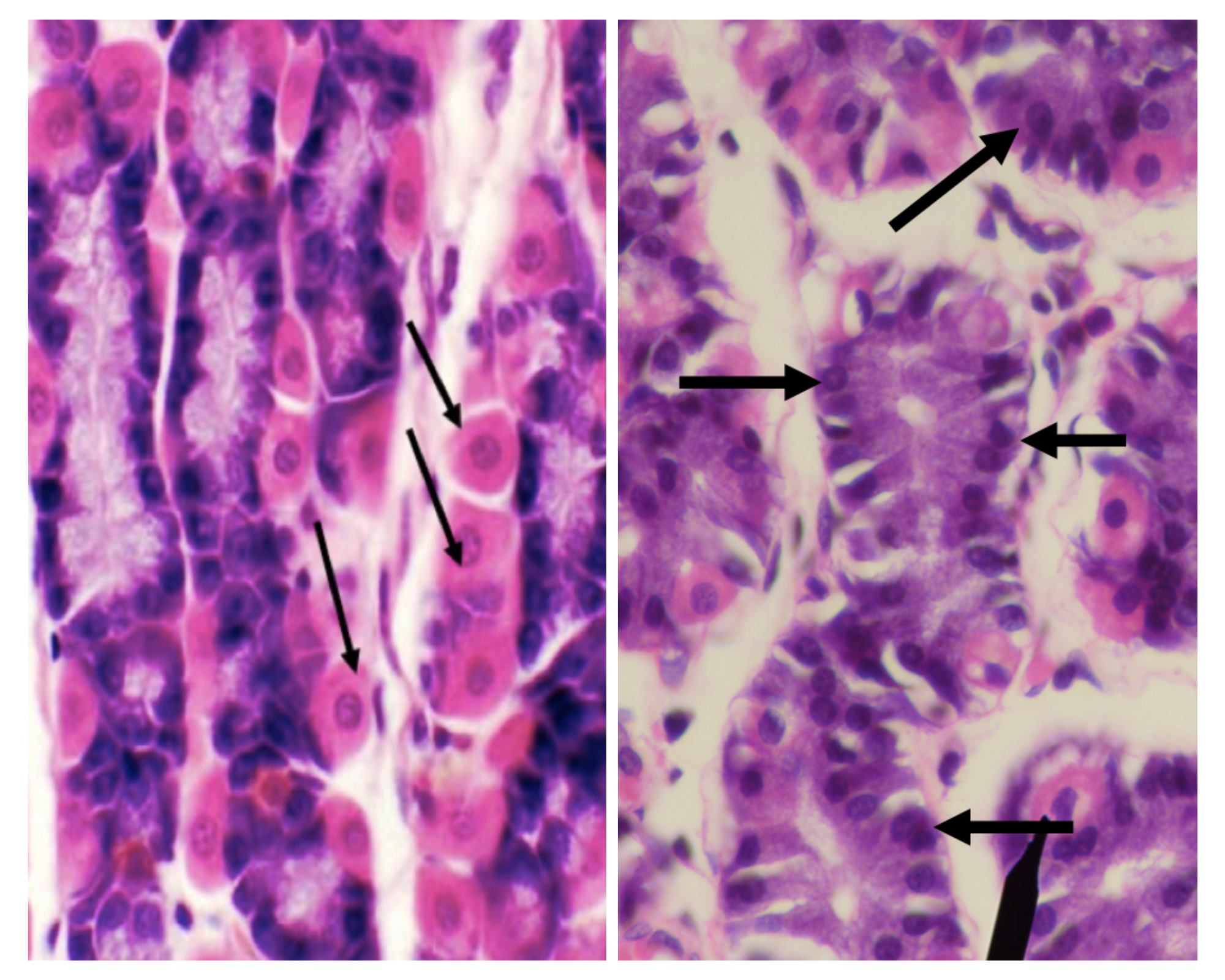
Which among the two cells is the parenchyma of the stomach?
Parietal/ Oxyntic Cell
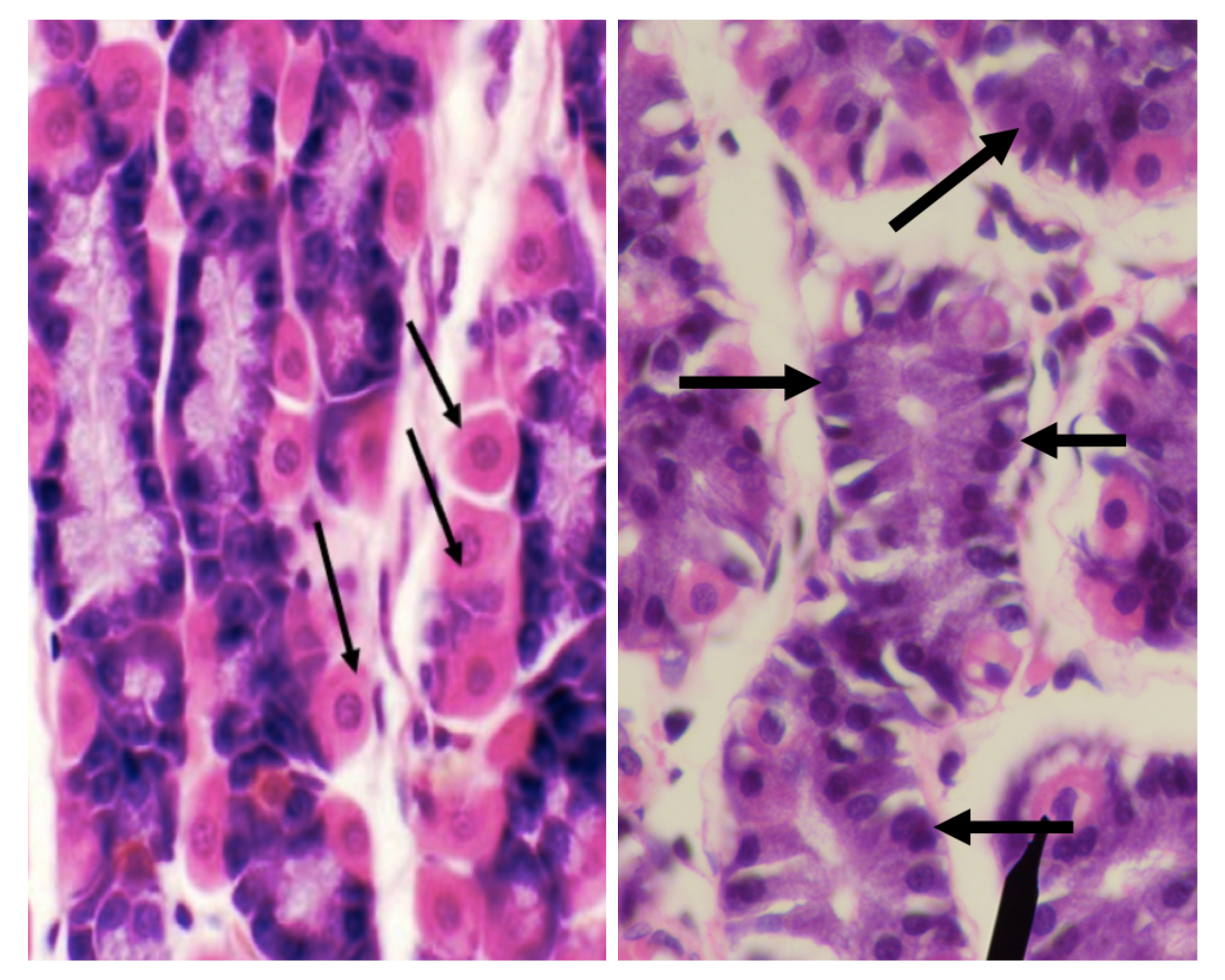
Which among the two cells is more numerous in the stomach?
Chief/ Peptic/ Zymogenic Cell
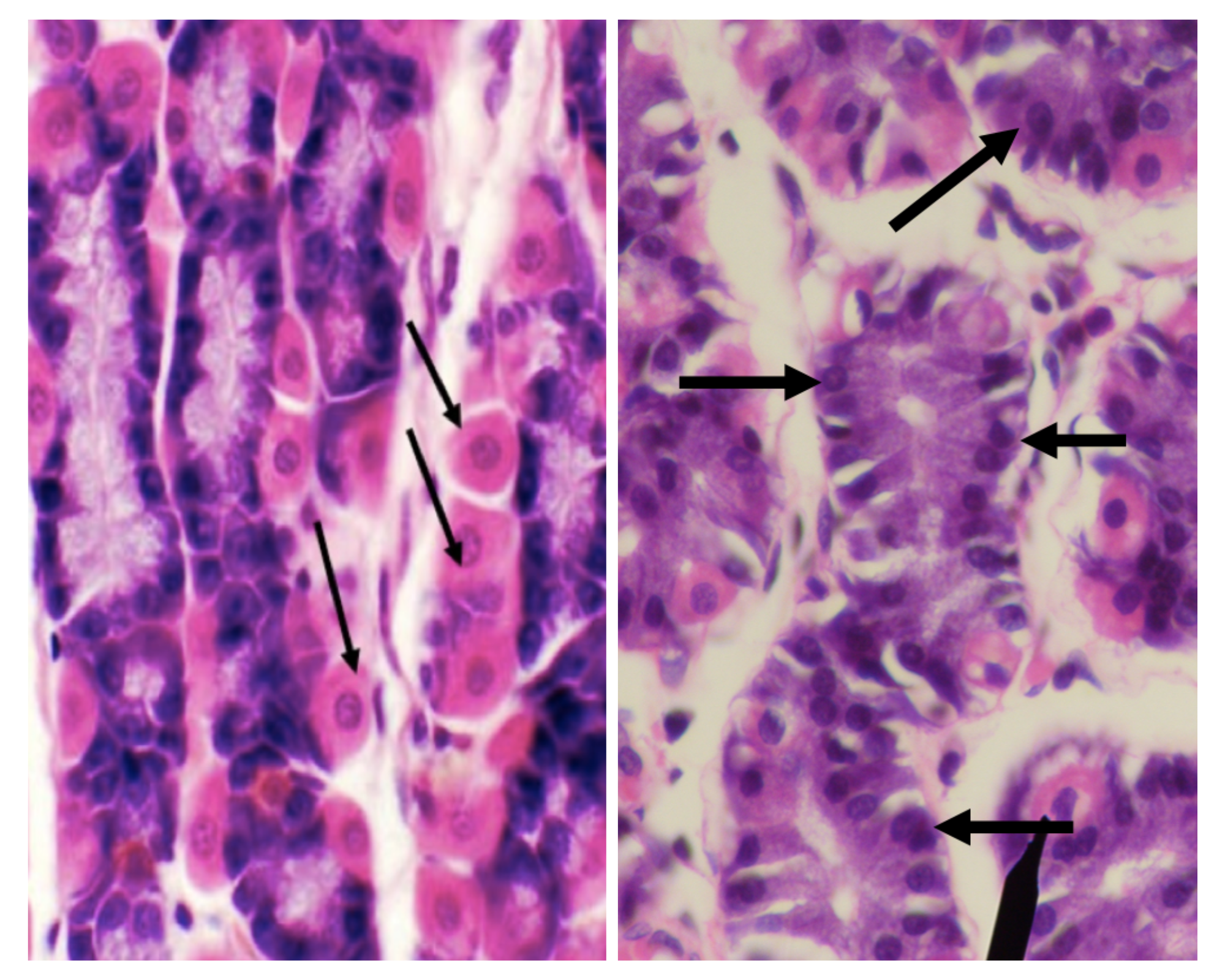
Which among the two cells is basophilic in staining?
Chief/ Peptic/ Zymogenic Cell
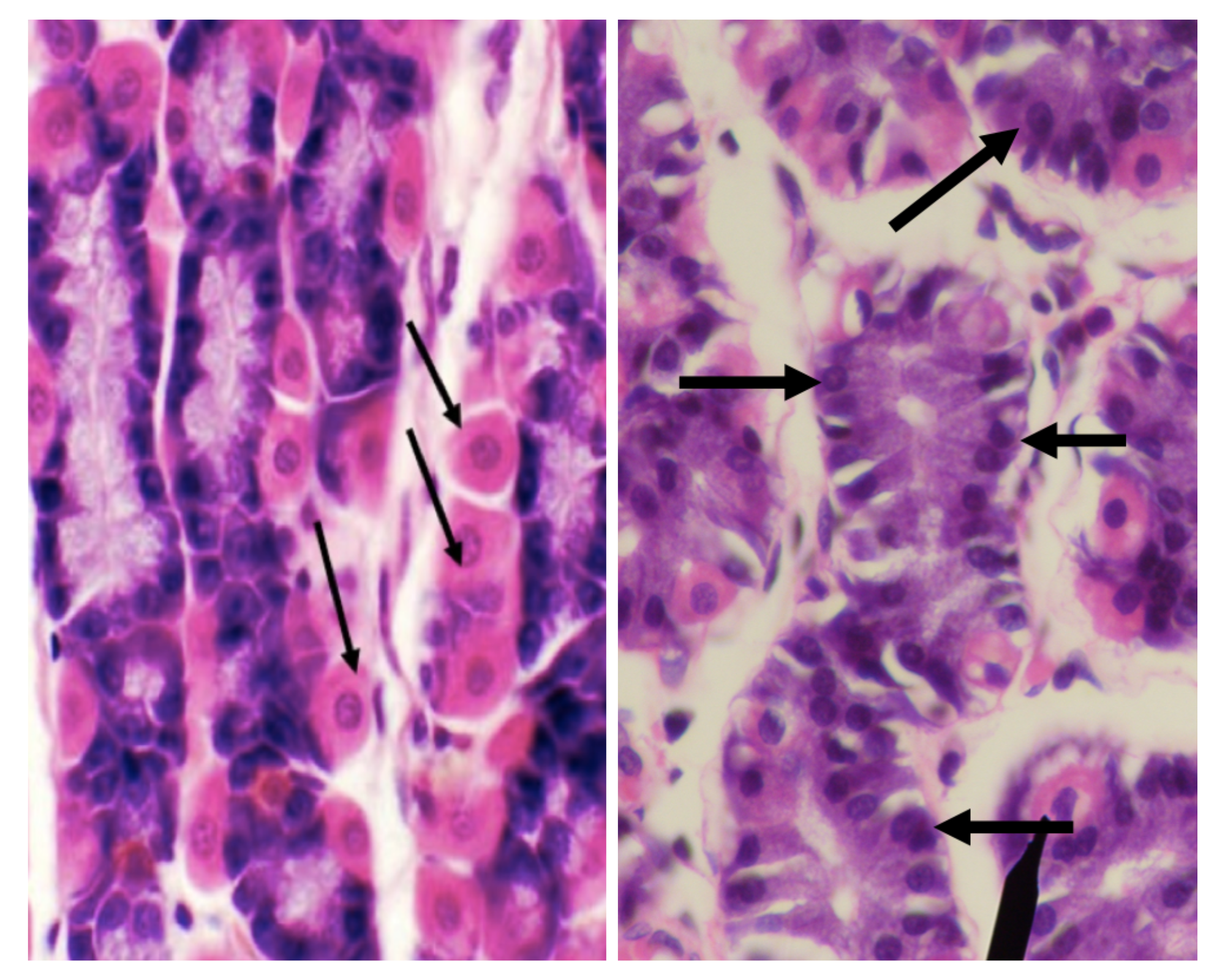
Which among the two cells has a large round nucleus with eosinophilic cytoplasm
Parietal/ Oxyntic Cell
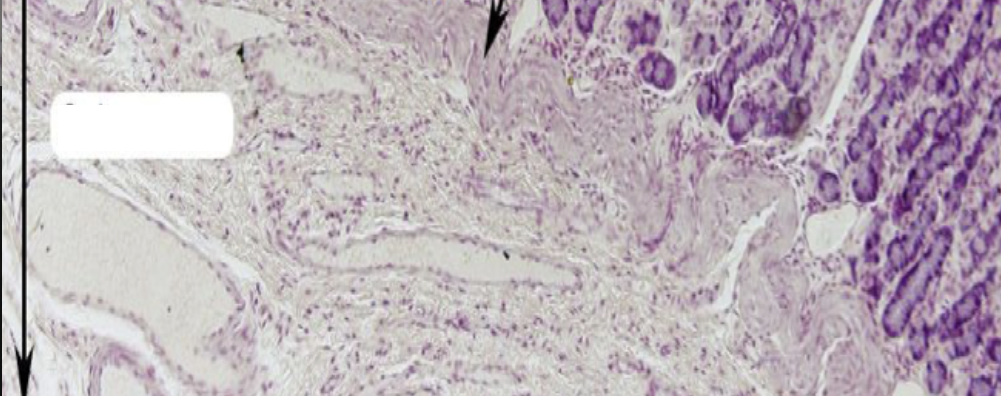
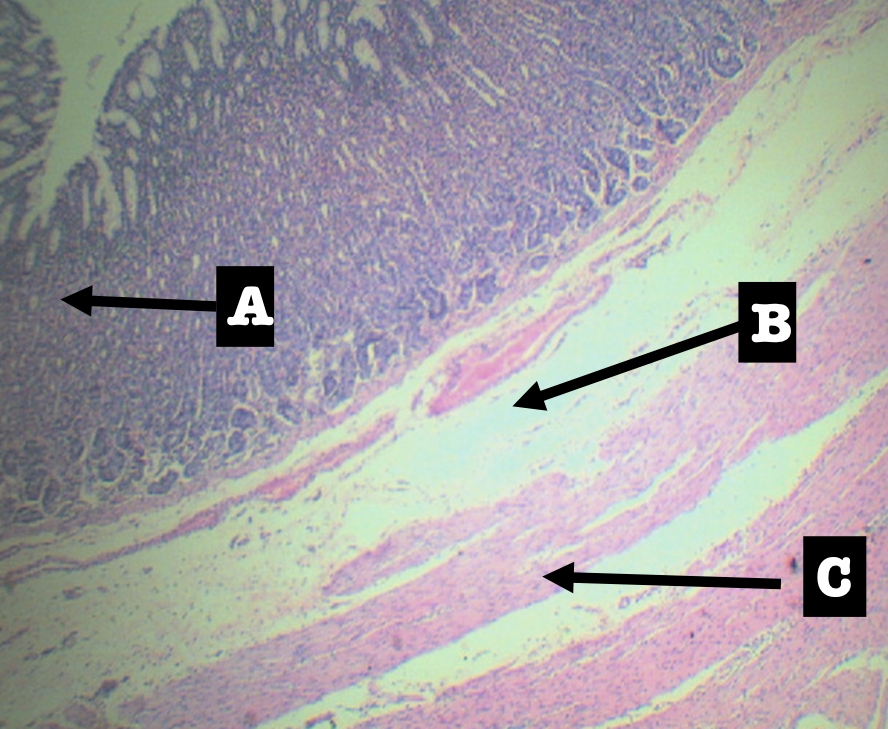
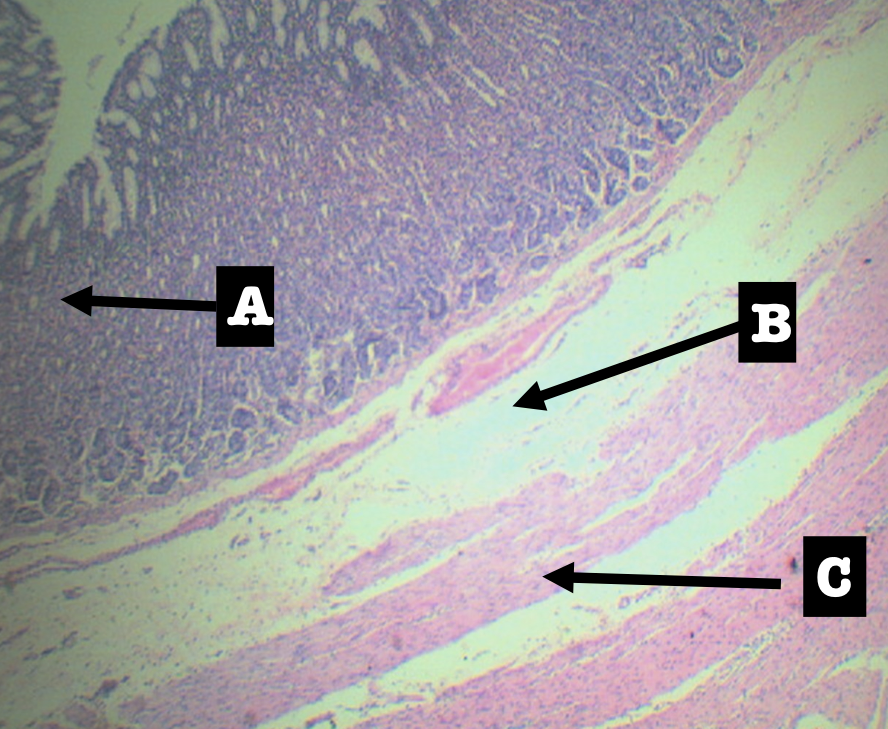
Identify the layer
Submucosa (B)
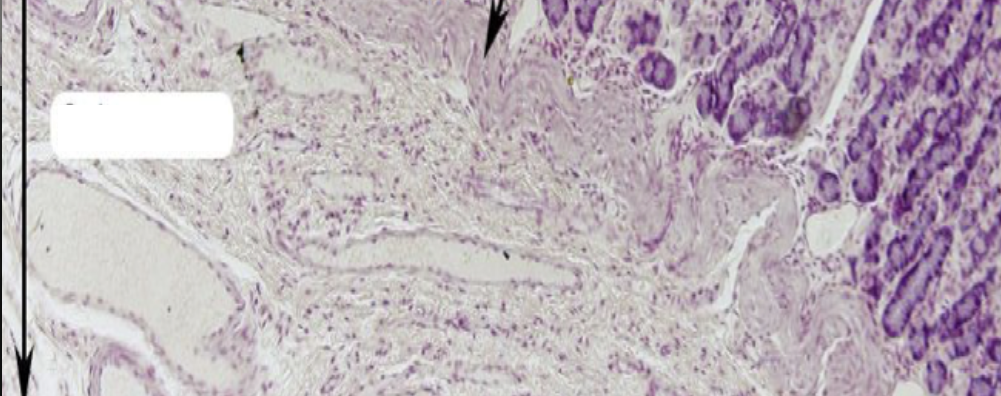
This layer is composed of?
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
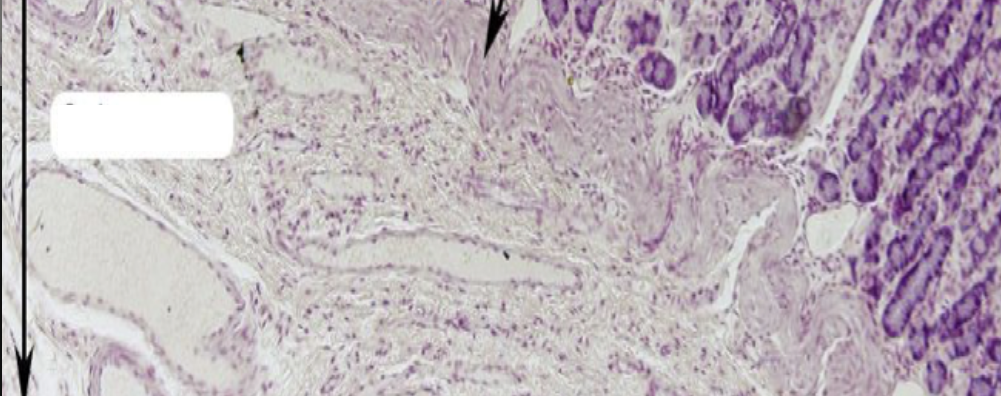
T OR F:
The layer has:
Meissner’s plexus
blood and lymphatic vessels
gastric glands
FALSE
There are no gastric glands present in this layer.
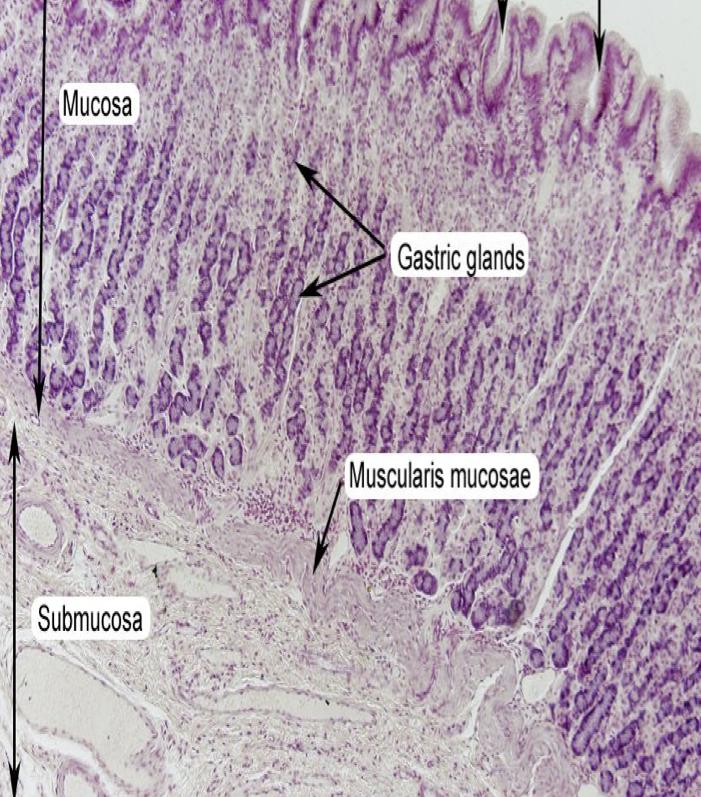
Identify the layer
Tunica Muscularis (C)
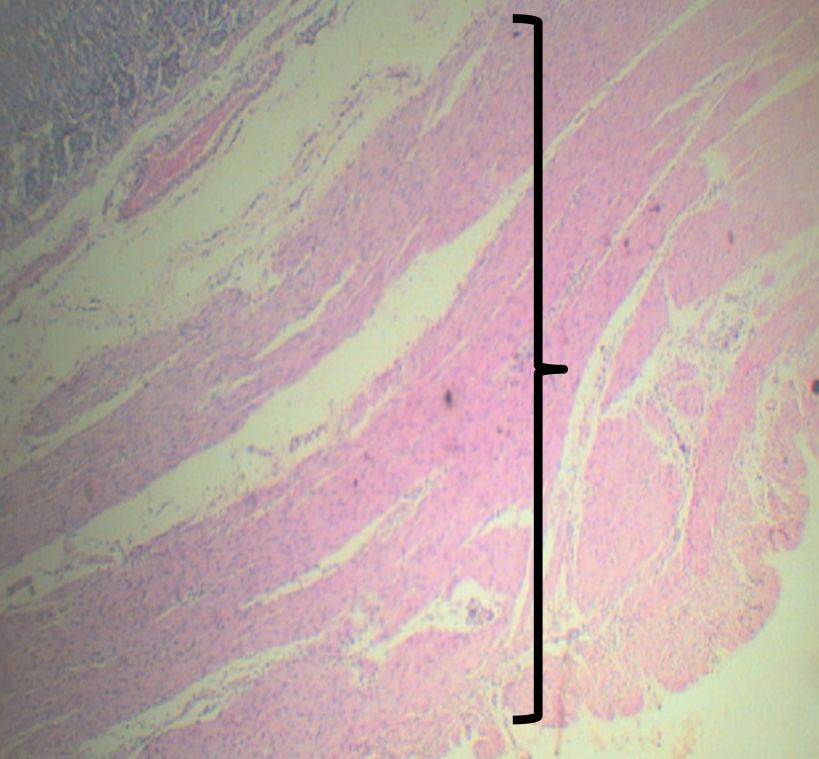
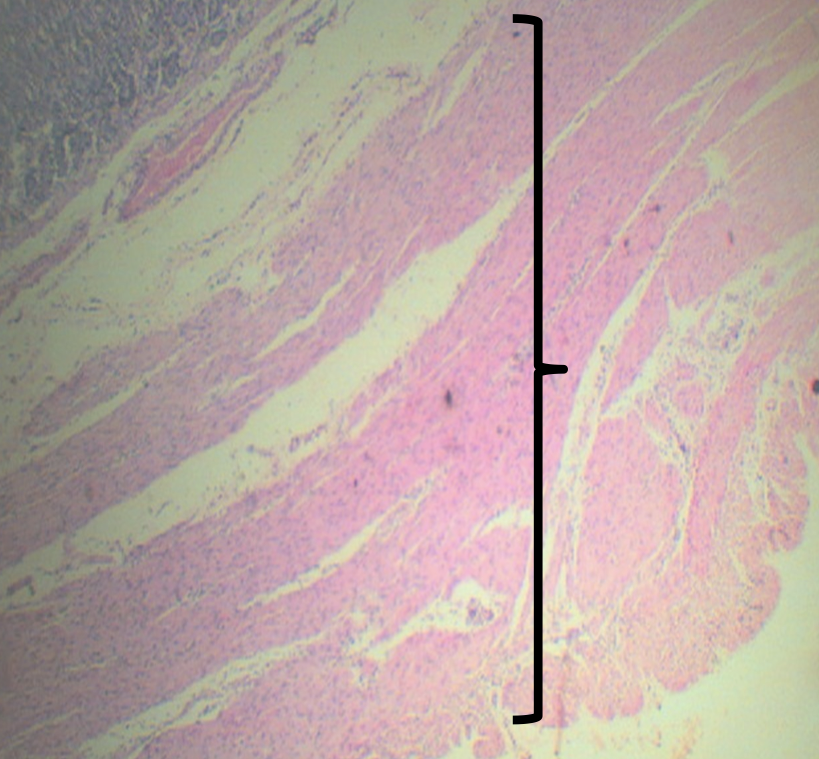
Arrangements of the layer
Smooth muscle arranged in 3 LAYERS:
1. Outer Longitudinal
2. Middle Circular
3. Inner Oblique
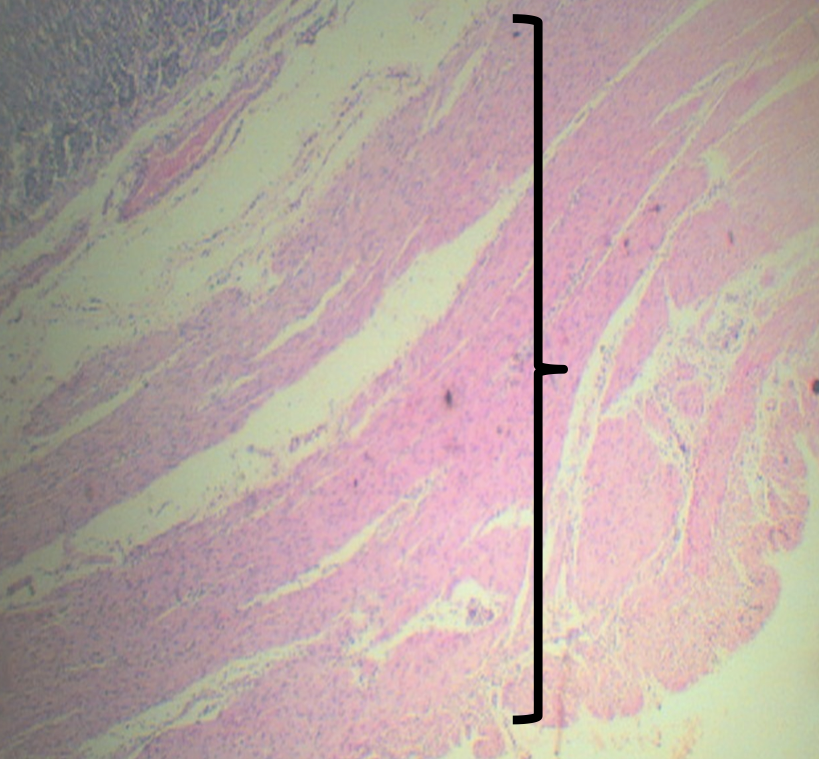
T OR F:
From the esophagus down to large intestine, except the stomach, the arrangement of tunica muscularis is ICOL
TRUE
The arrangement for the stomach is:
1. Outer Longitudinal
2. Middle Circular
3. Inner Oblique
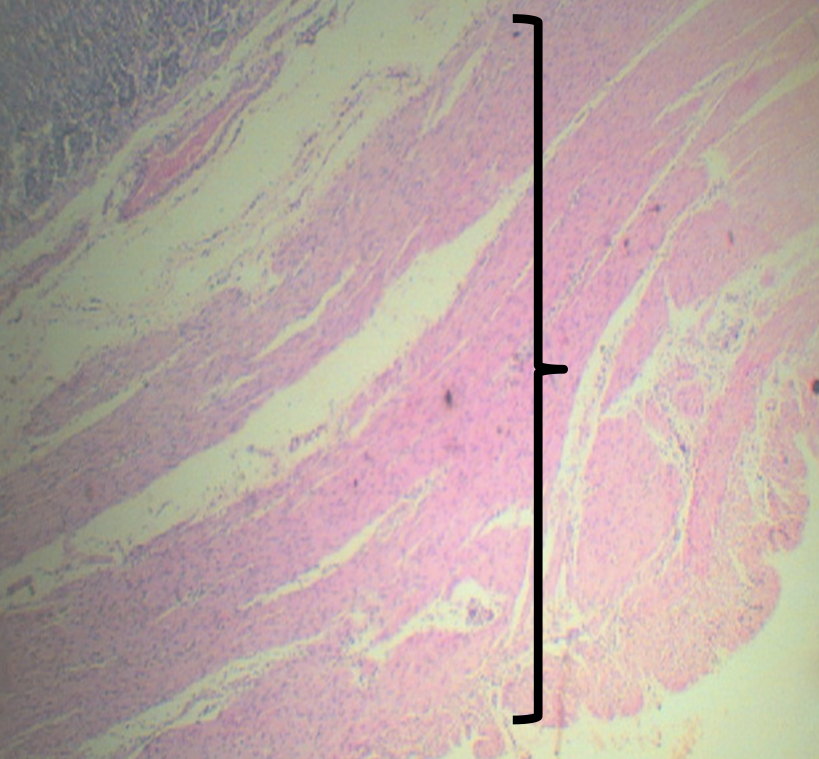
What plexus is present
Myenteric/ Auerbach’s plexus
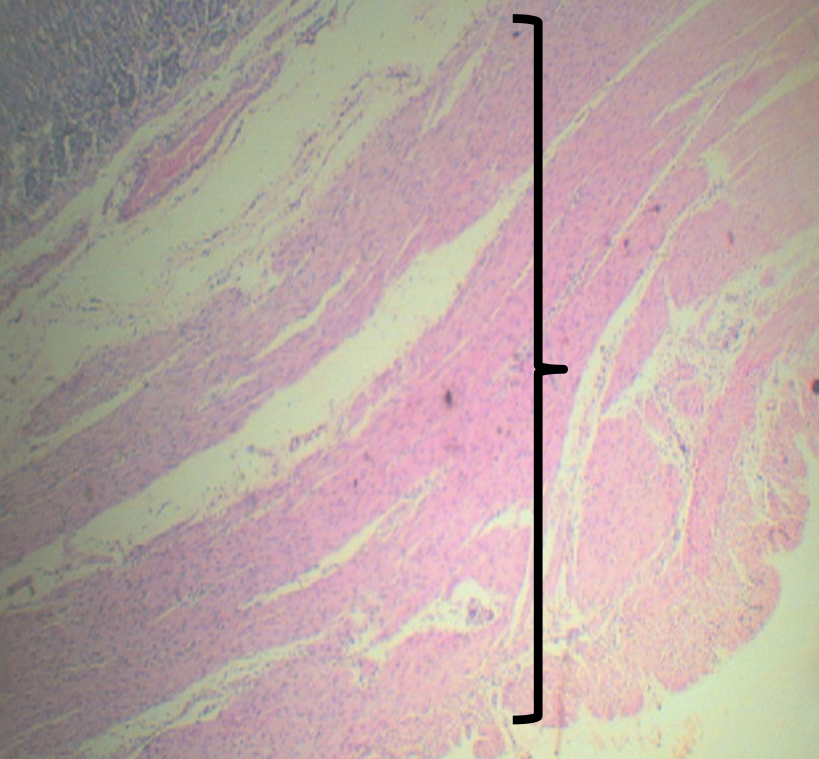
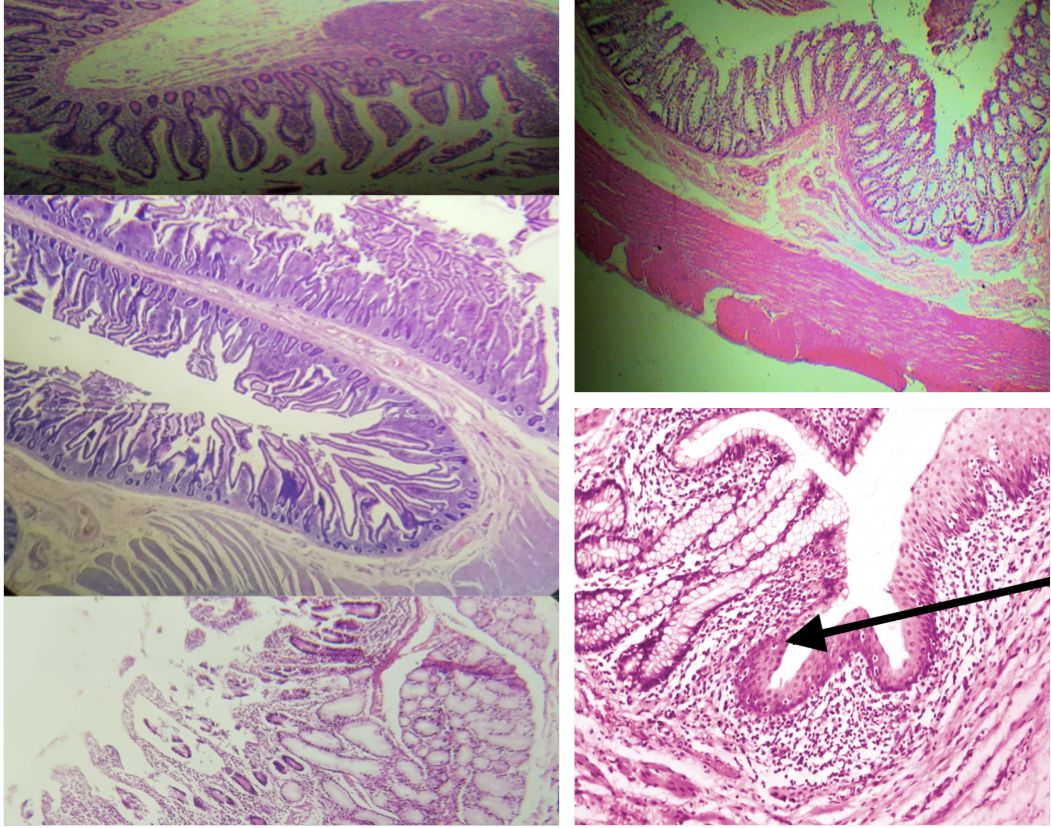
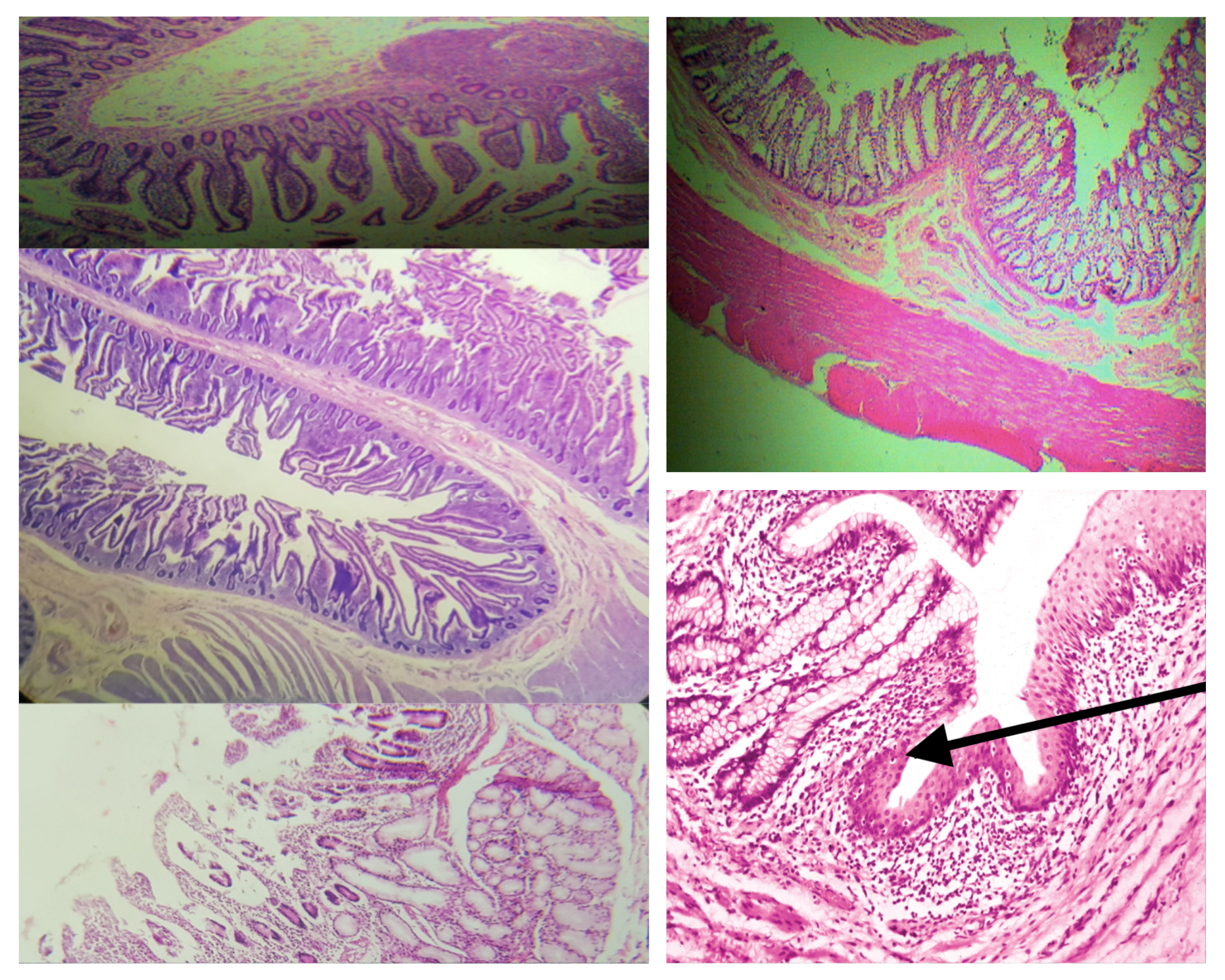
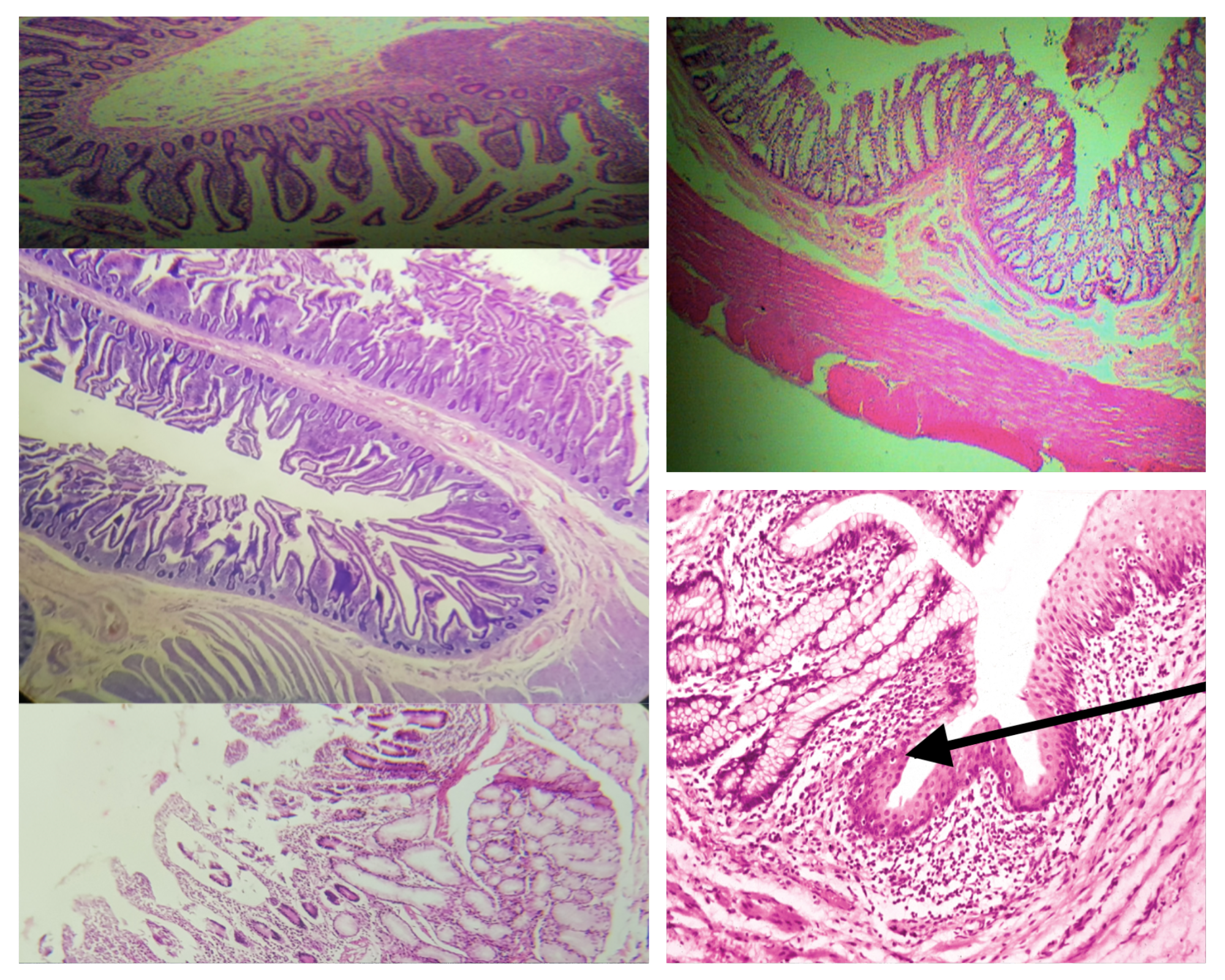
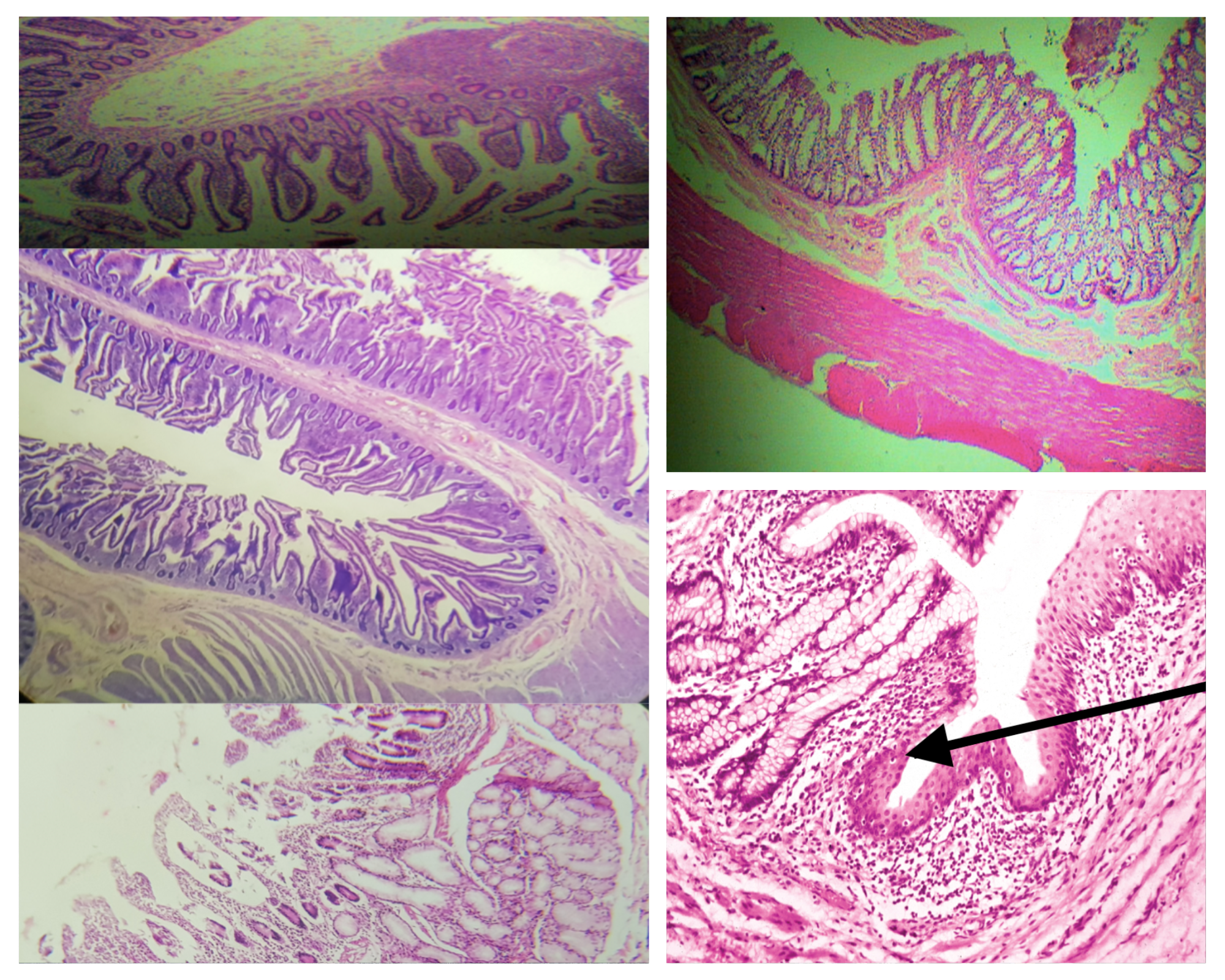
Identify the Main Organ
Small Intestine
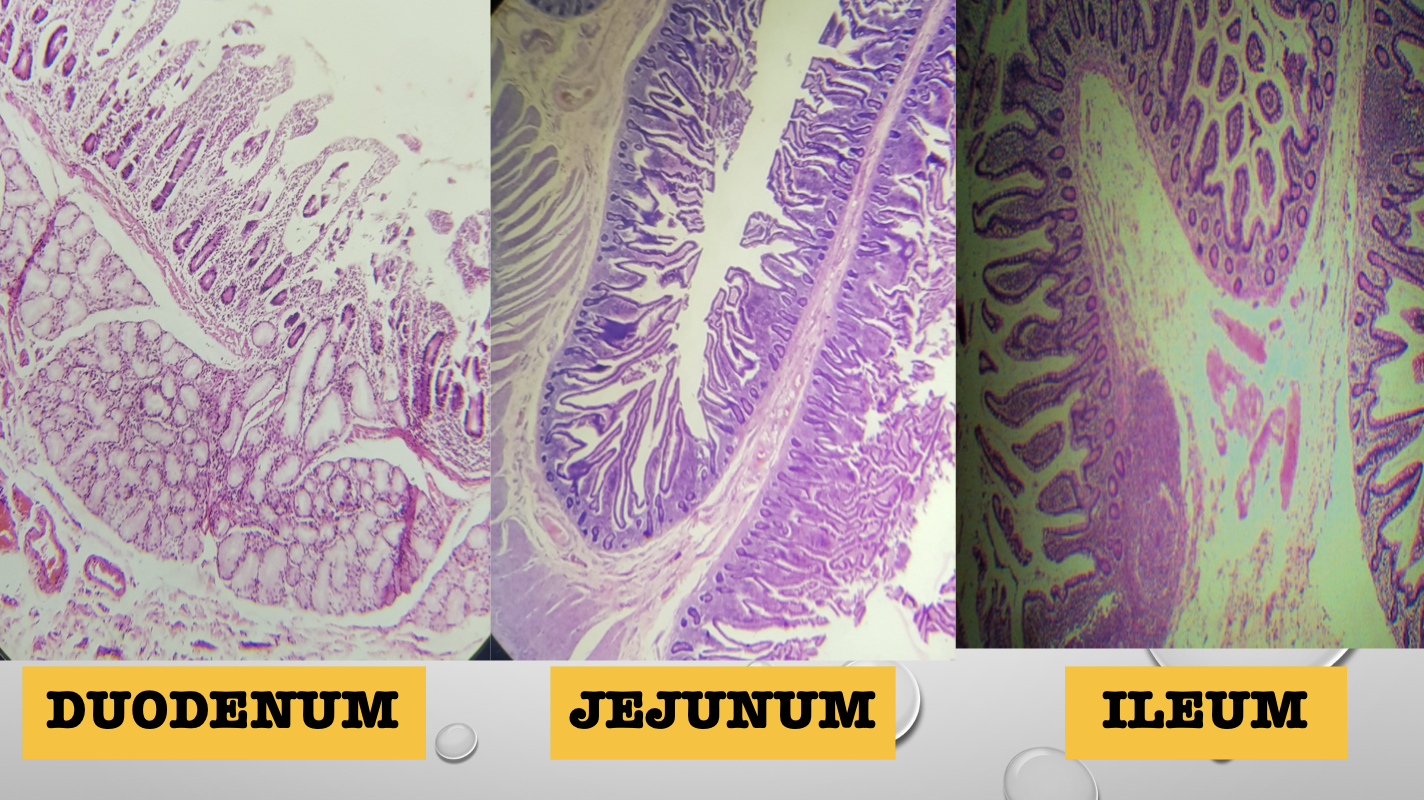
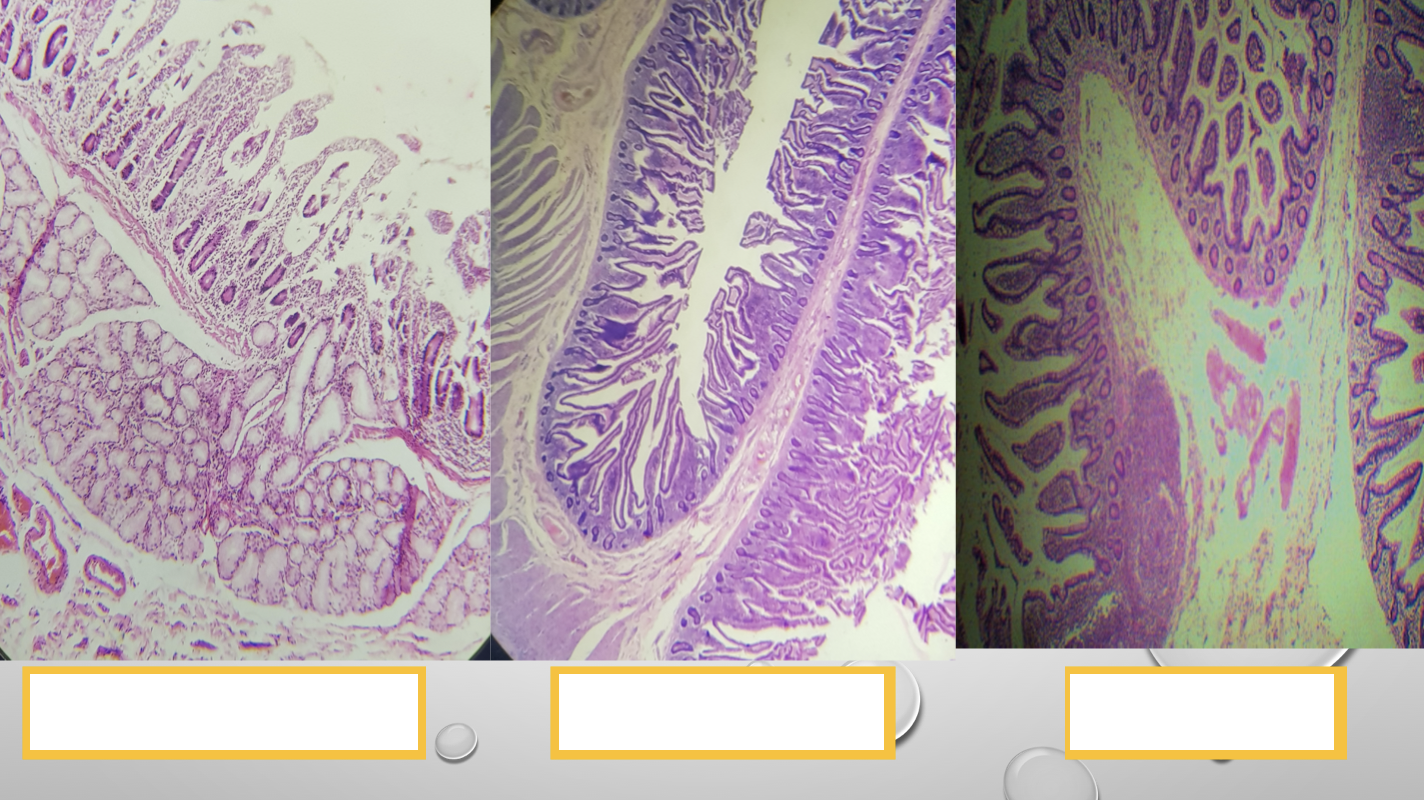
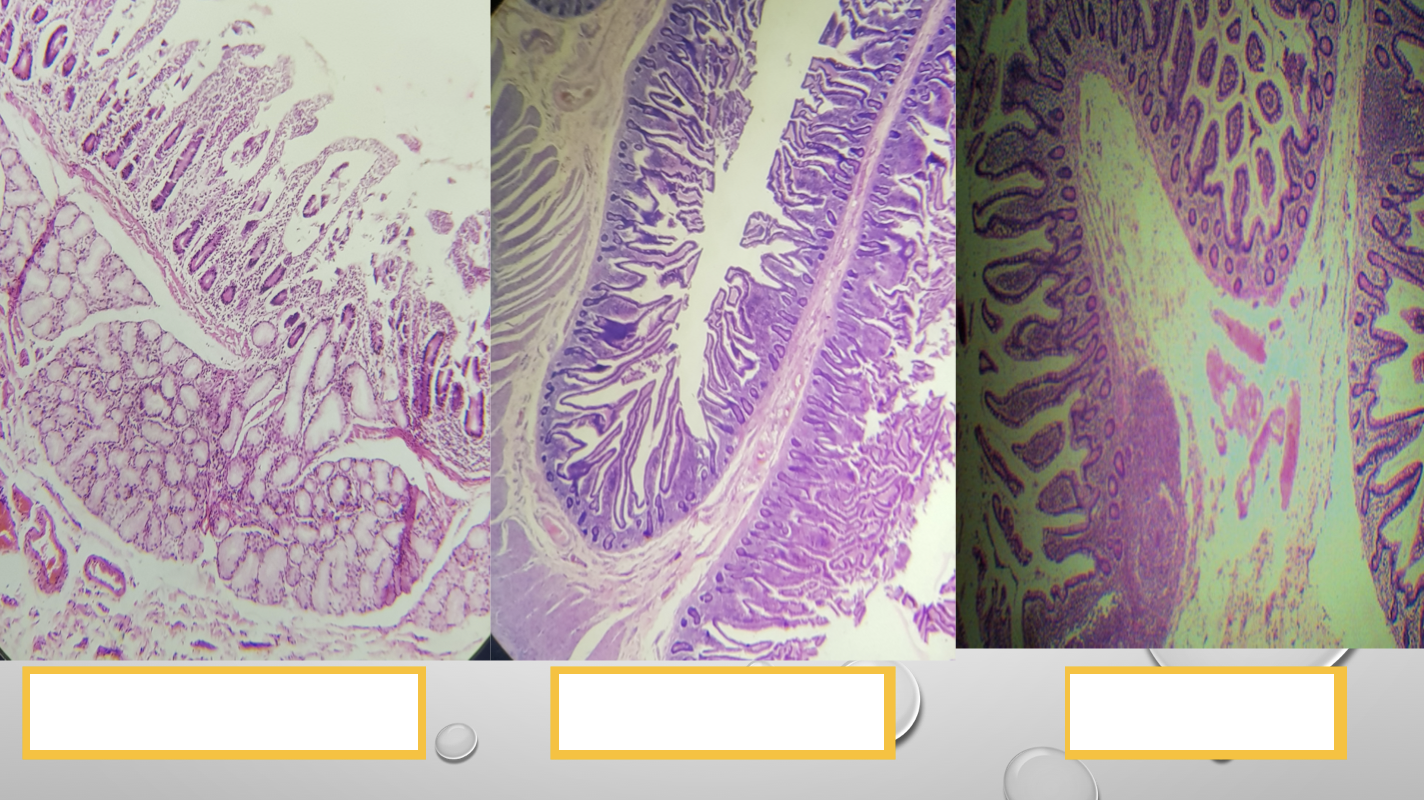
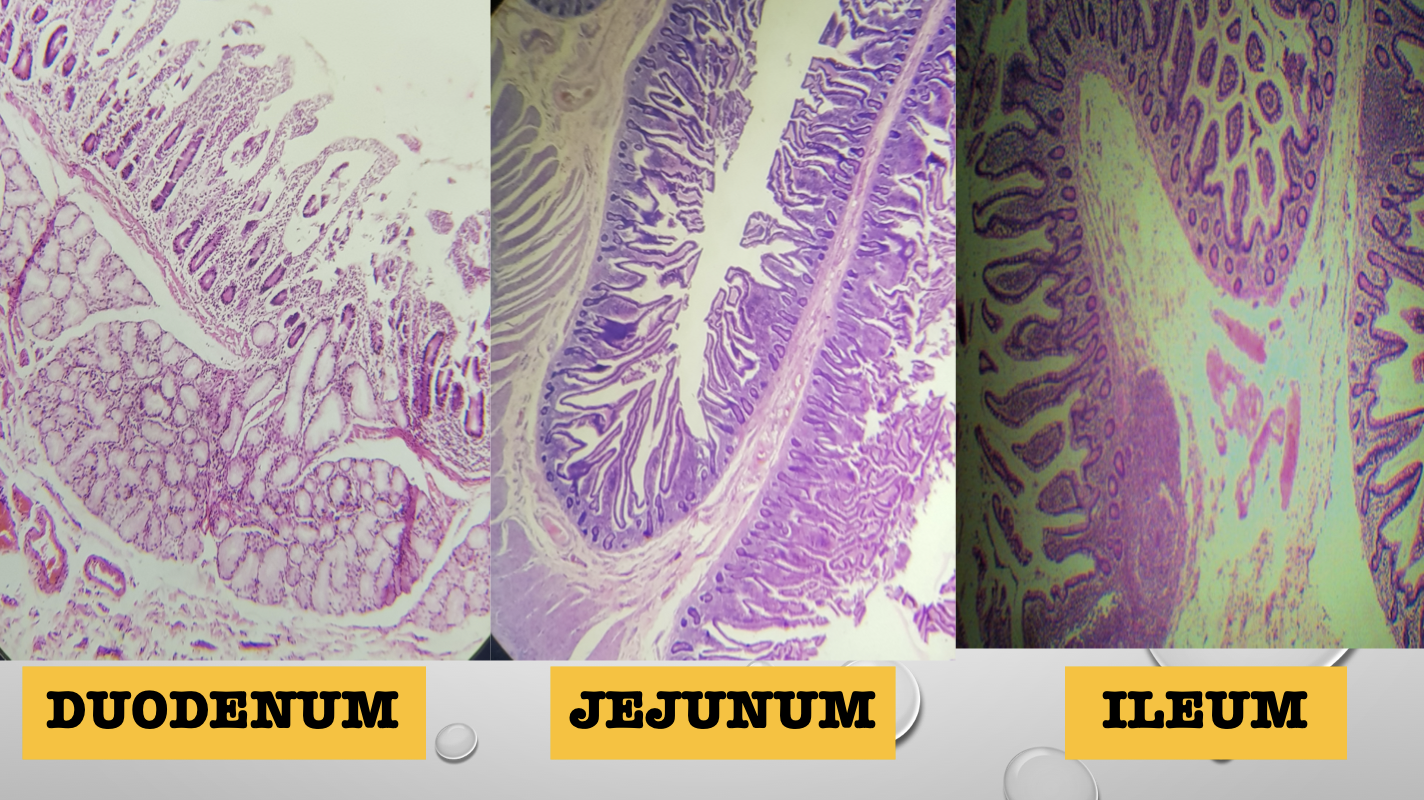
Identify the three segments of the small intestine
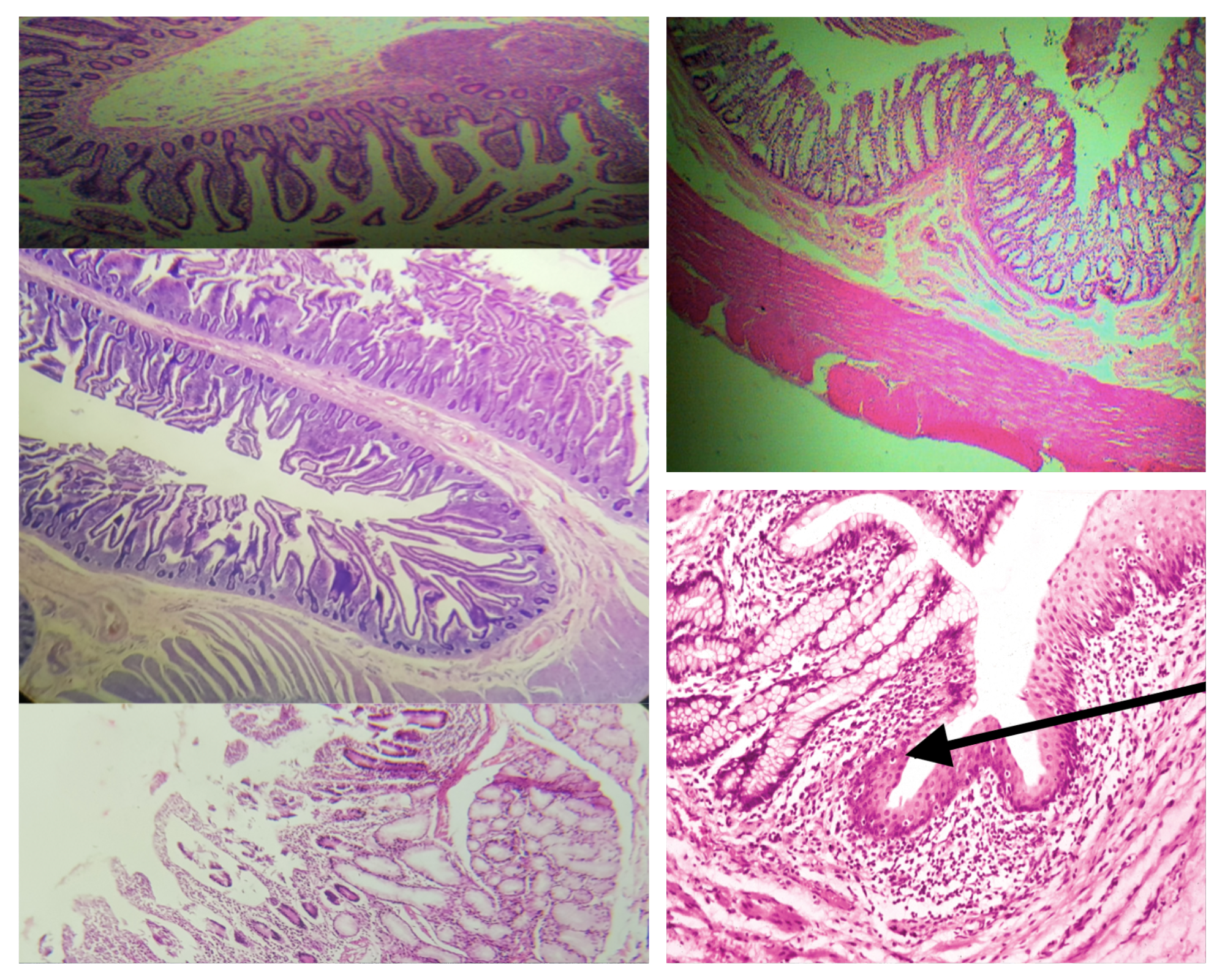
Layers of the Wall of the Intestines (same for small and large)
Mucosa
Submucosa
Tunica Muscularis
Tunica Adventitia
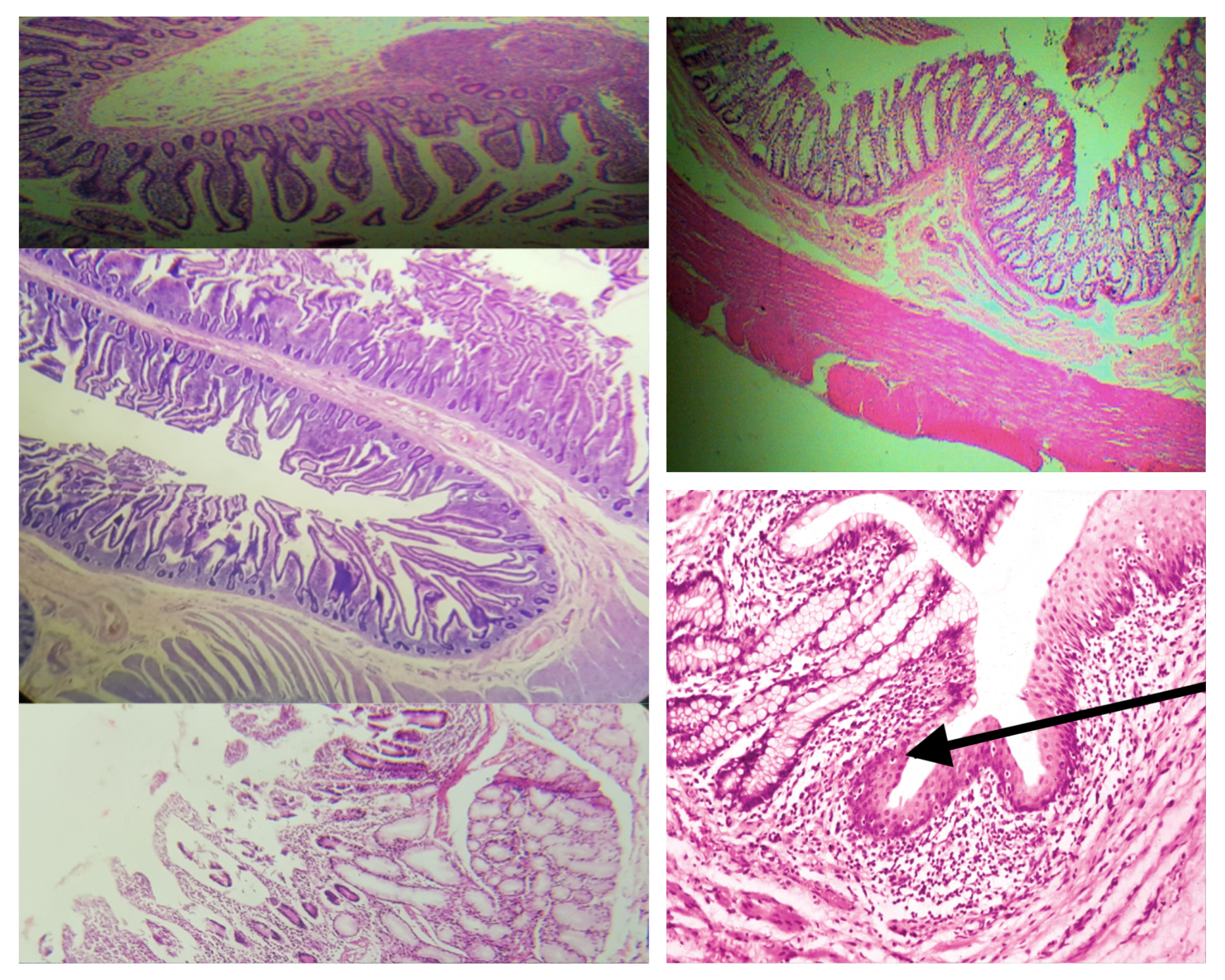
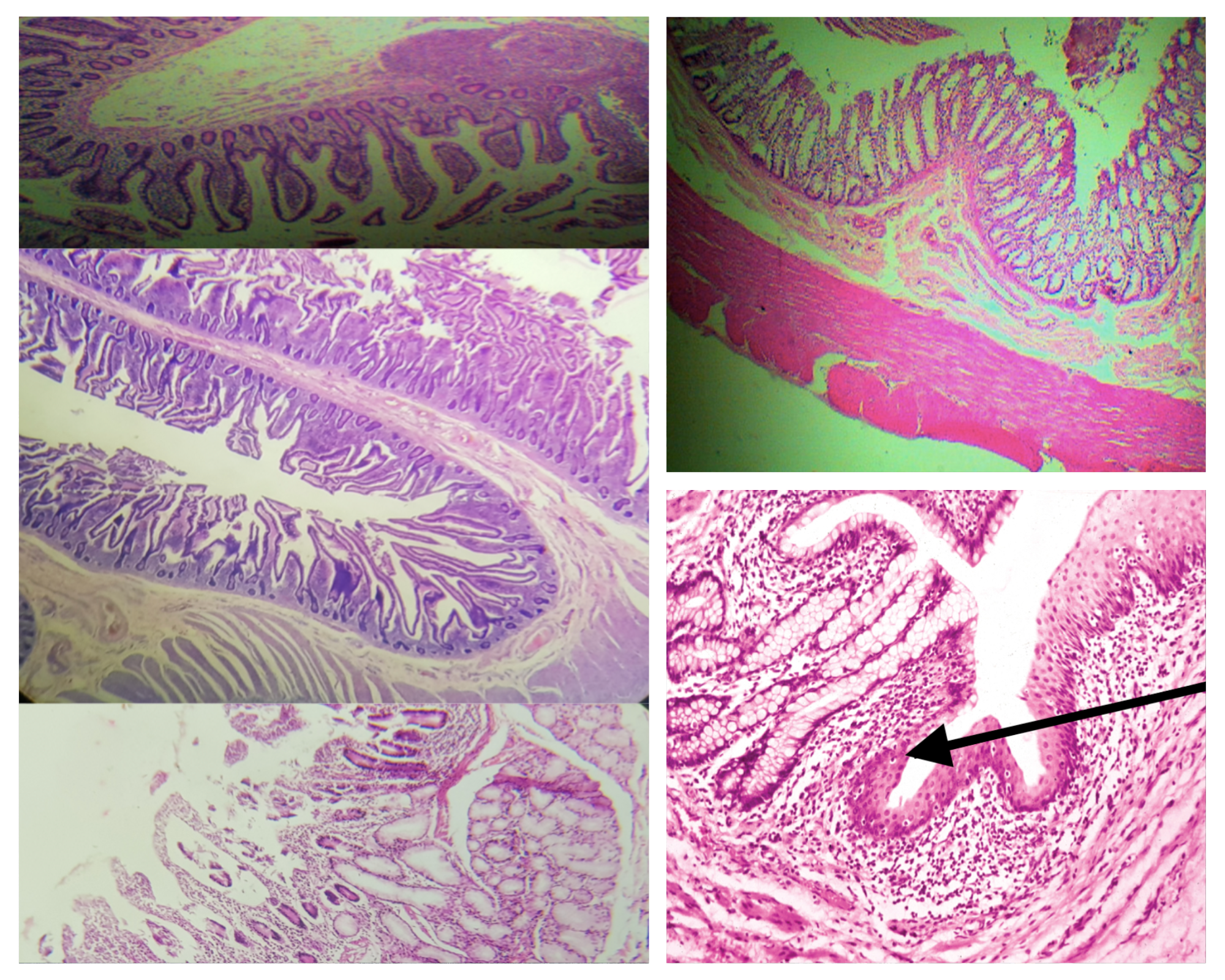
Sublayers of the Mucosa (same for small and large)
Lining epithelium
Lamina propria
Muscularis mucosa
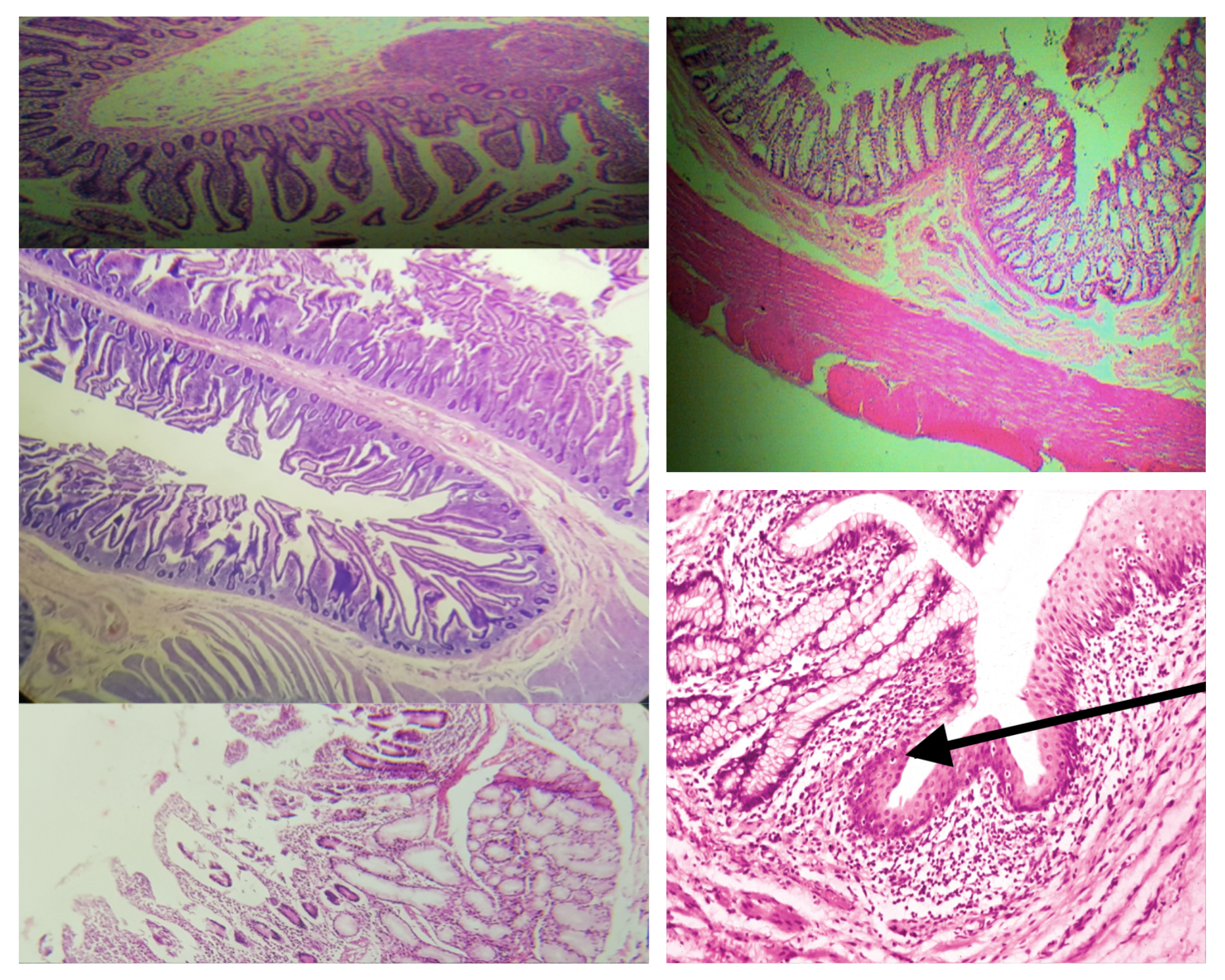
Lining Epithelium (same for small and large)
Simple columnar with goblet cells
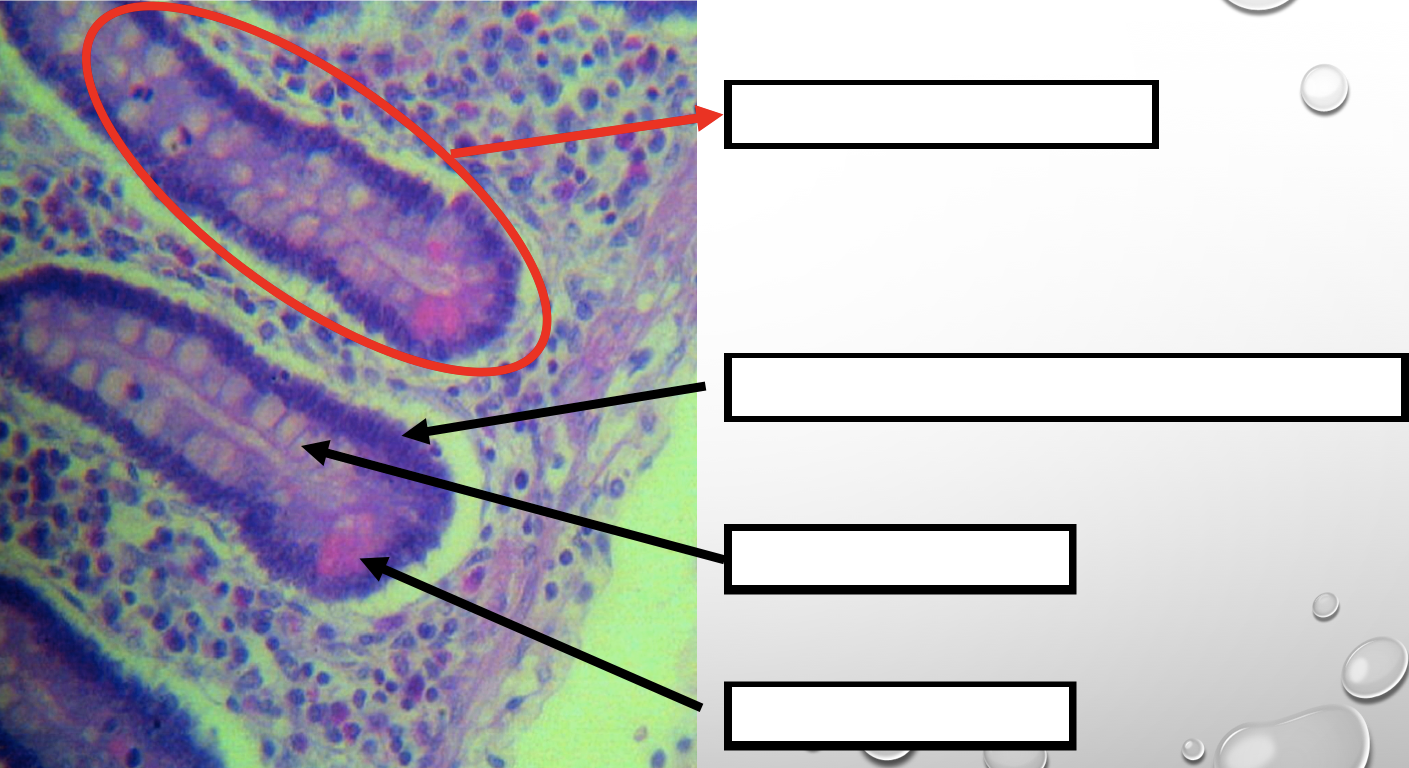
Lamina propia (same for small and large)
Loose connective tissue
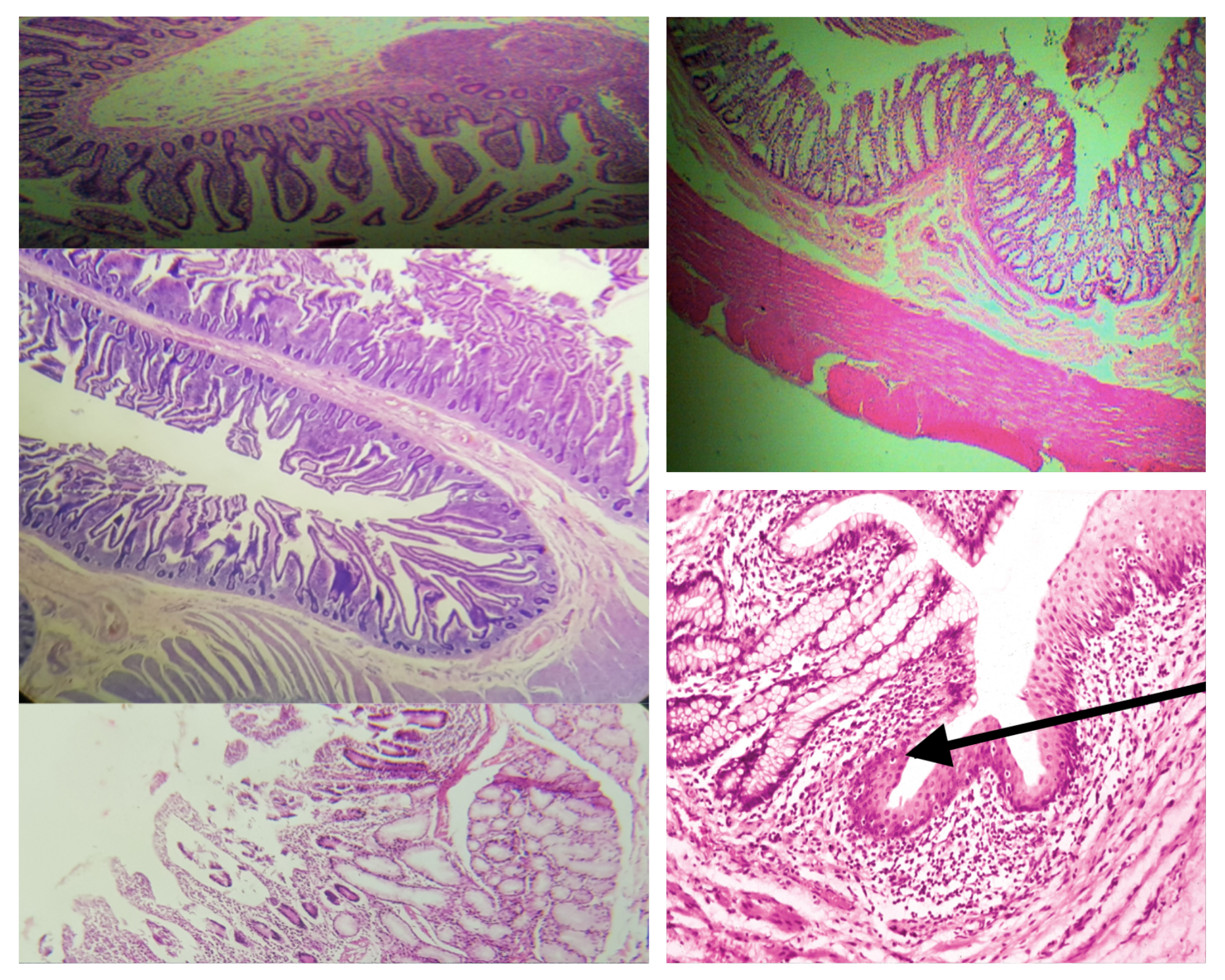
Muscularis mucosa (same for small and large)
2 thin layers of smooth muscle
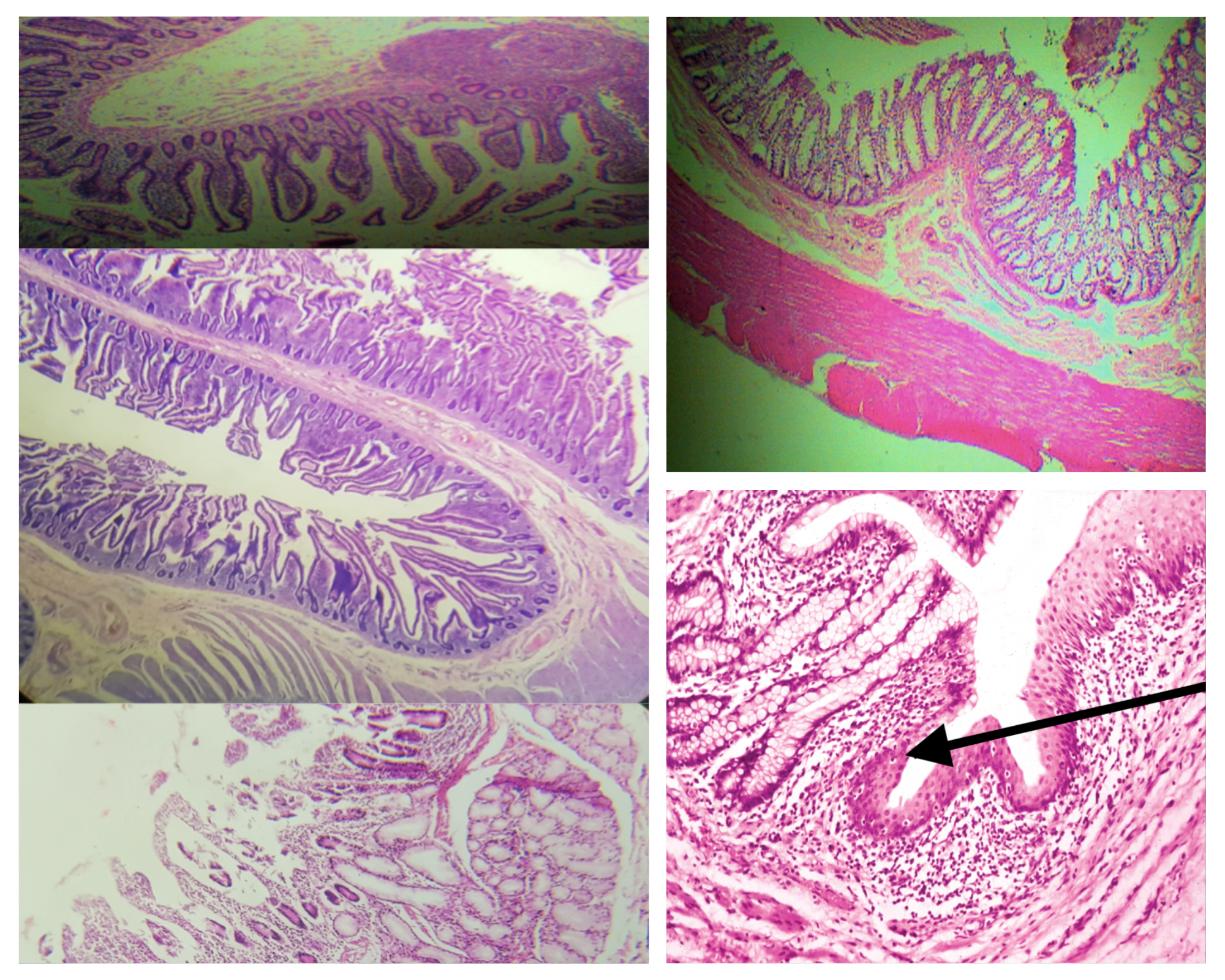
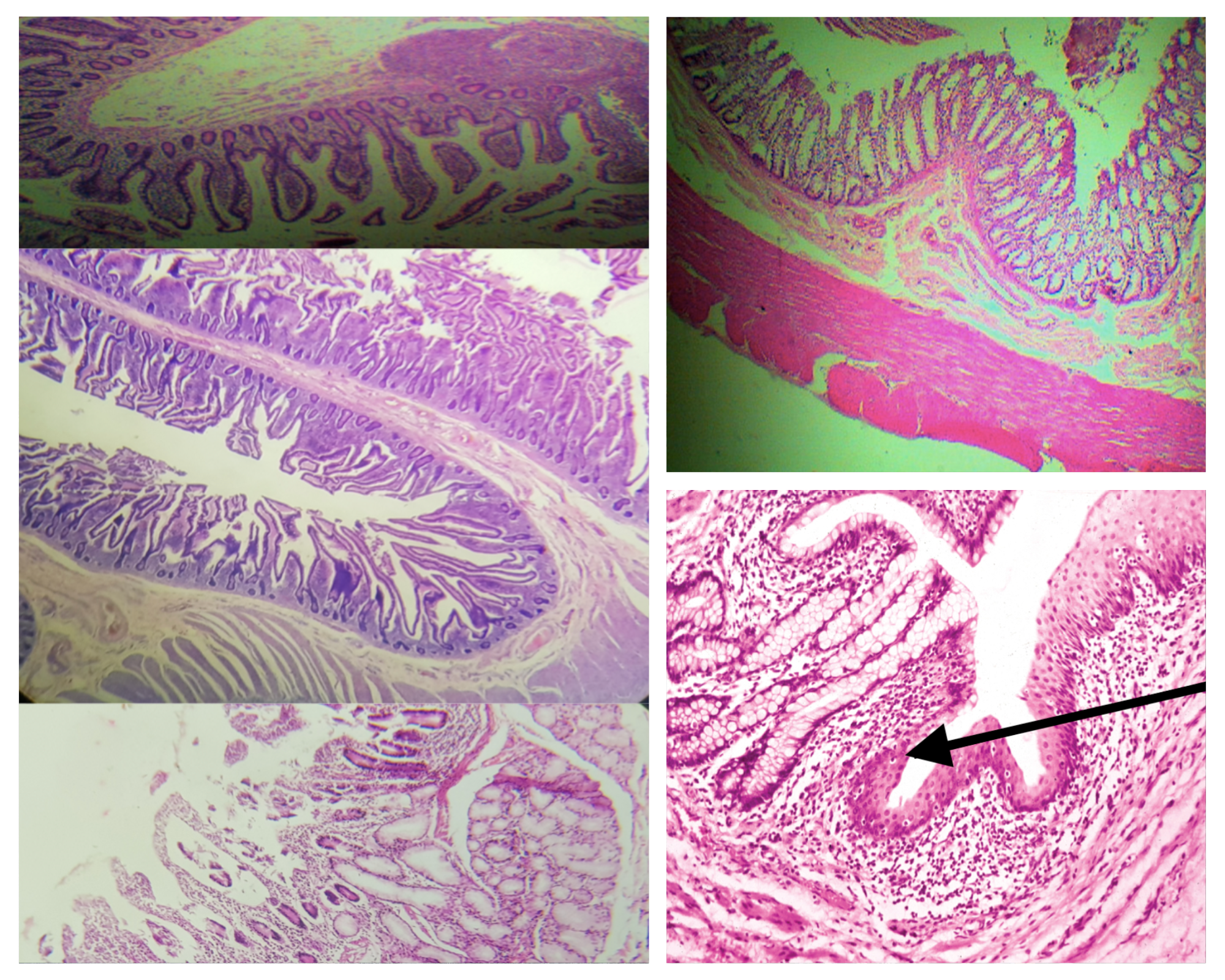
Composition of the submucosa (same for small and large)
Dense connective tissue with BV, LV, and Meissner’s plexus
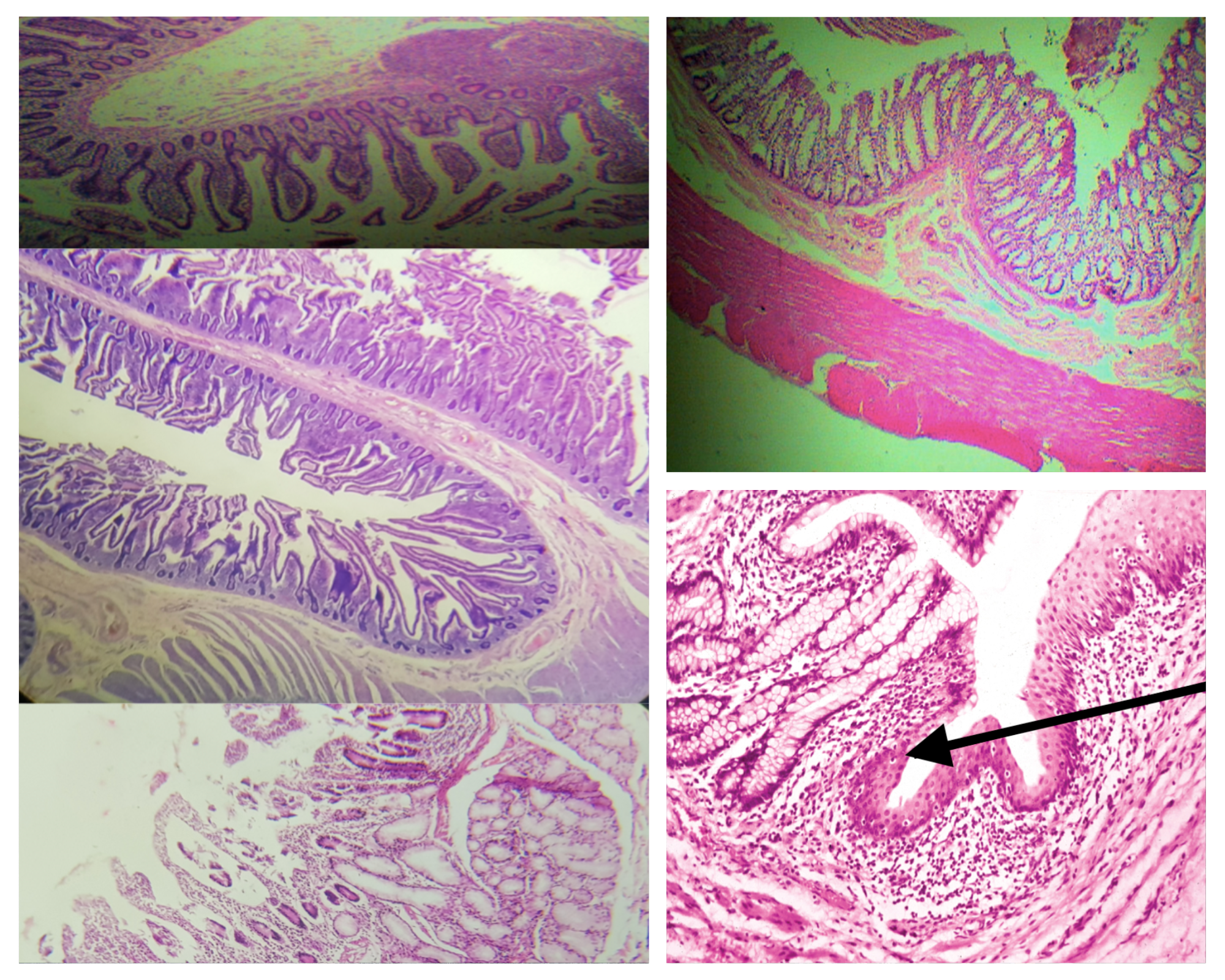
Nerve Plexus present in submucosa (same for small and large)
Meissner’s plexus
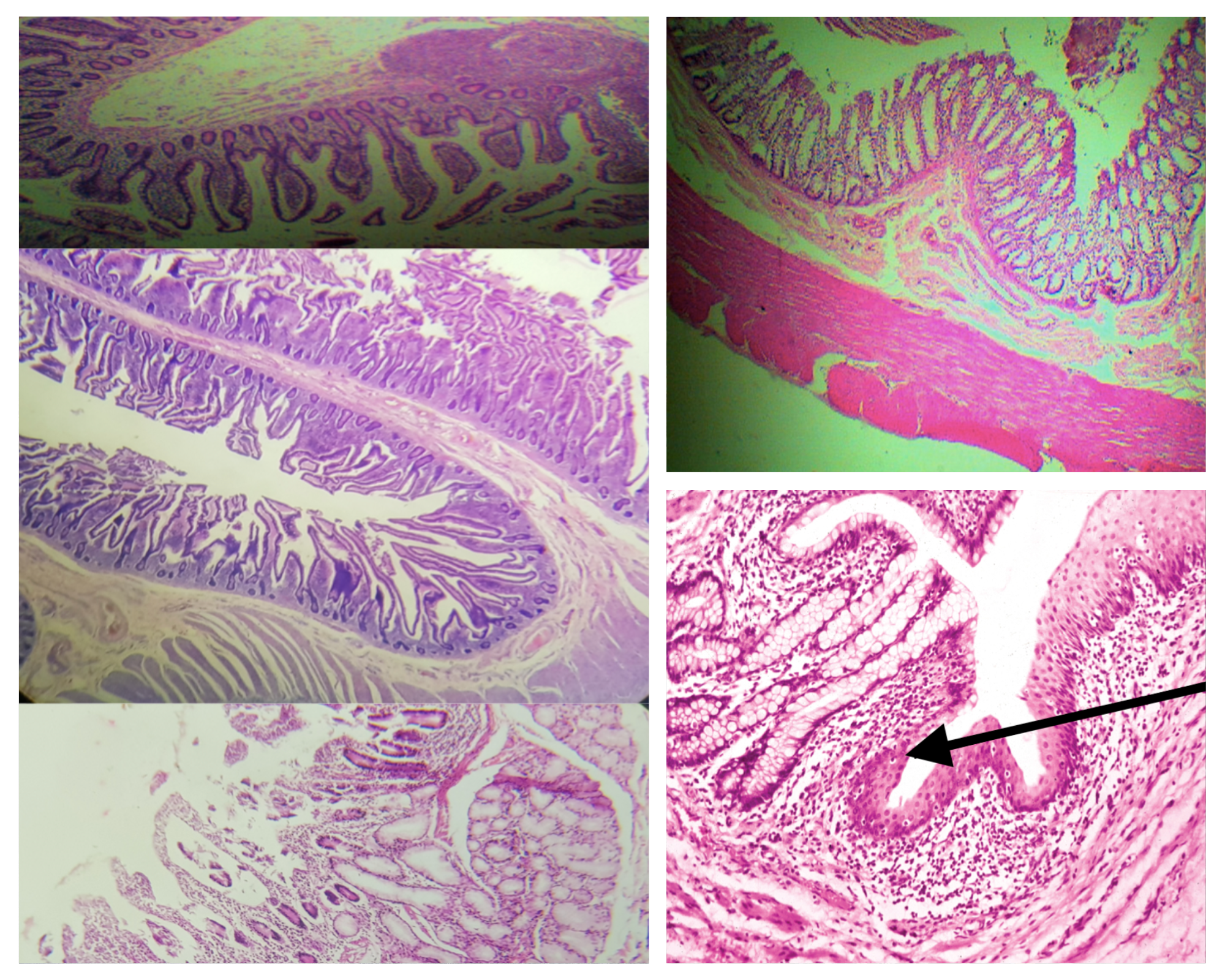
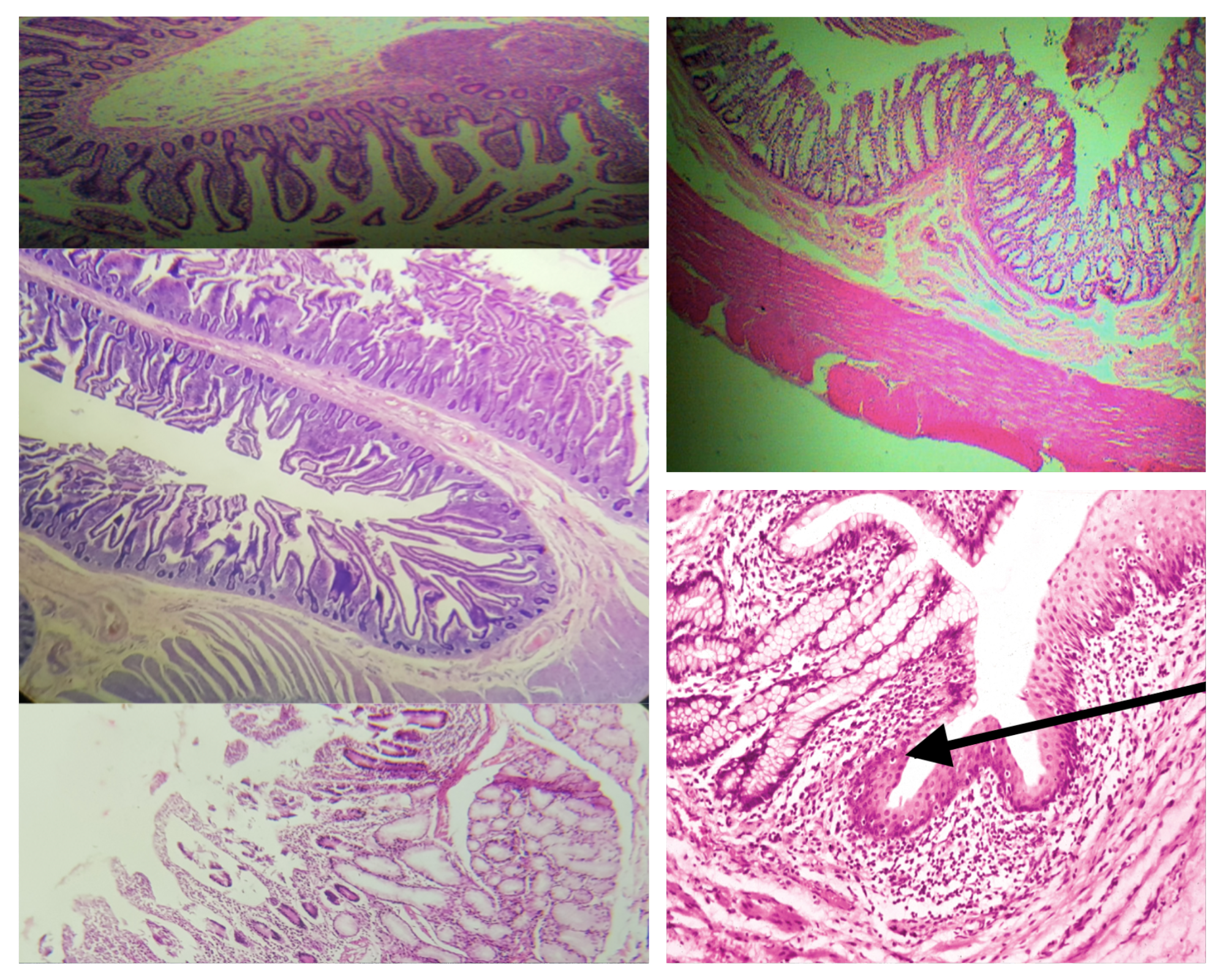
Arrangement of Tunica Muscularis (same for small and large)
Inner Circular Outer Longitudinal (ICOL)
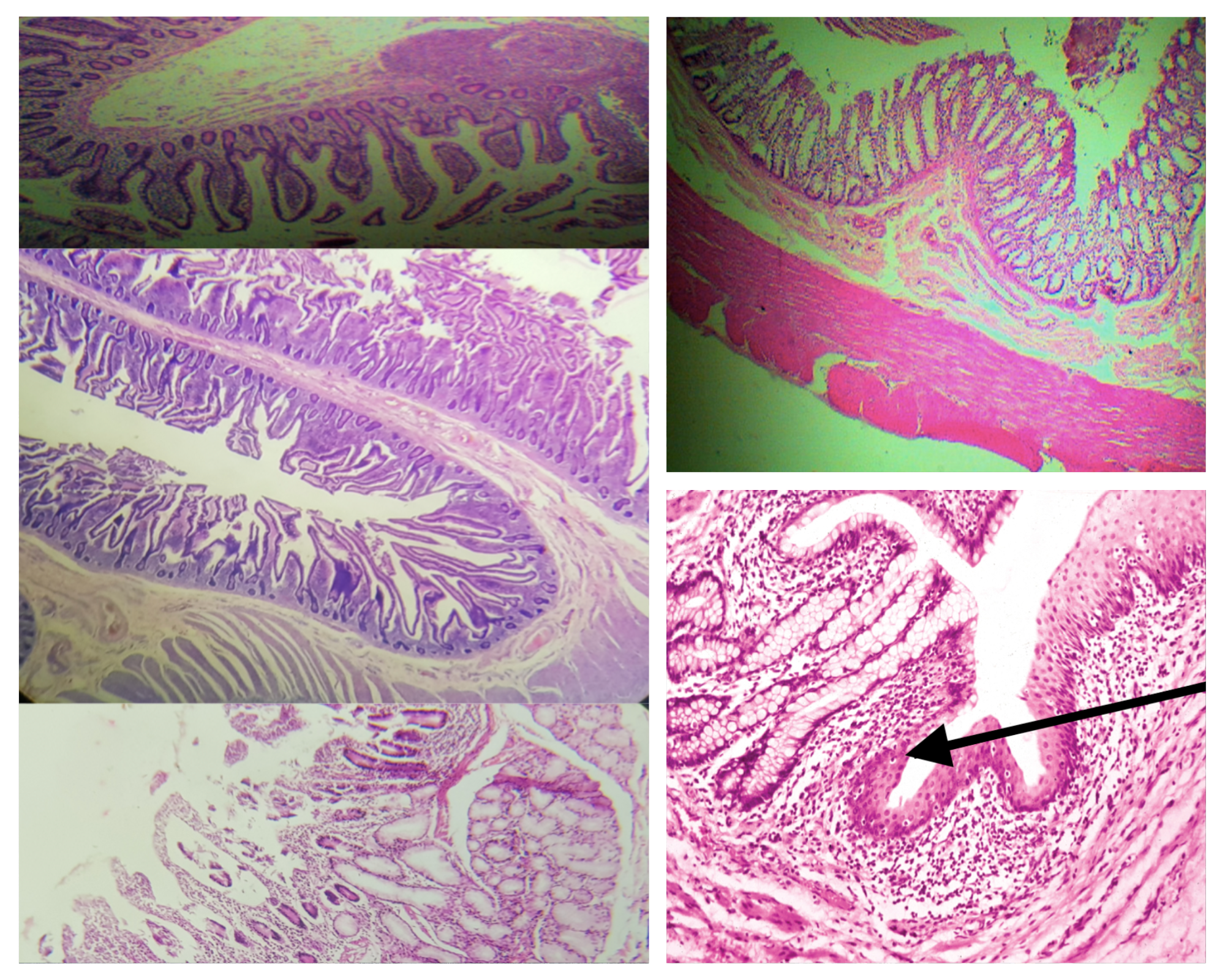
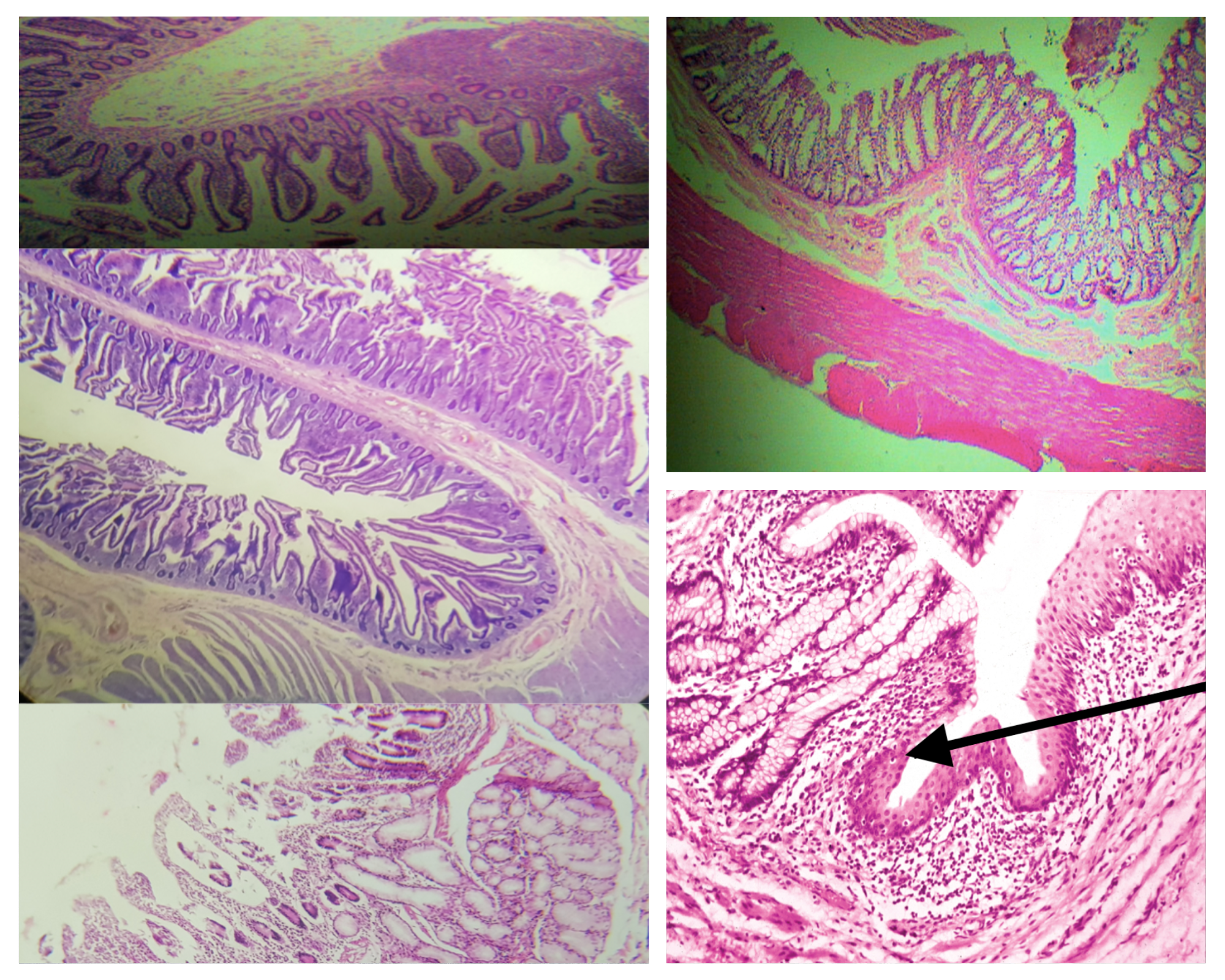
Nerve Plexus present in Tunica Muscularis (same for small and large)
Auerbach’s plexus
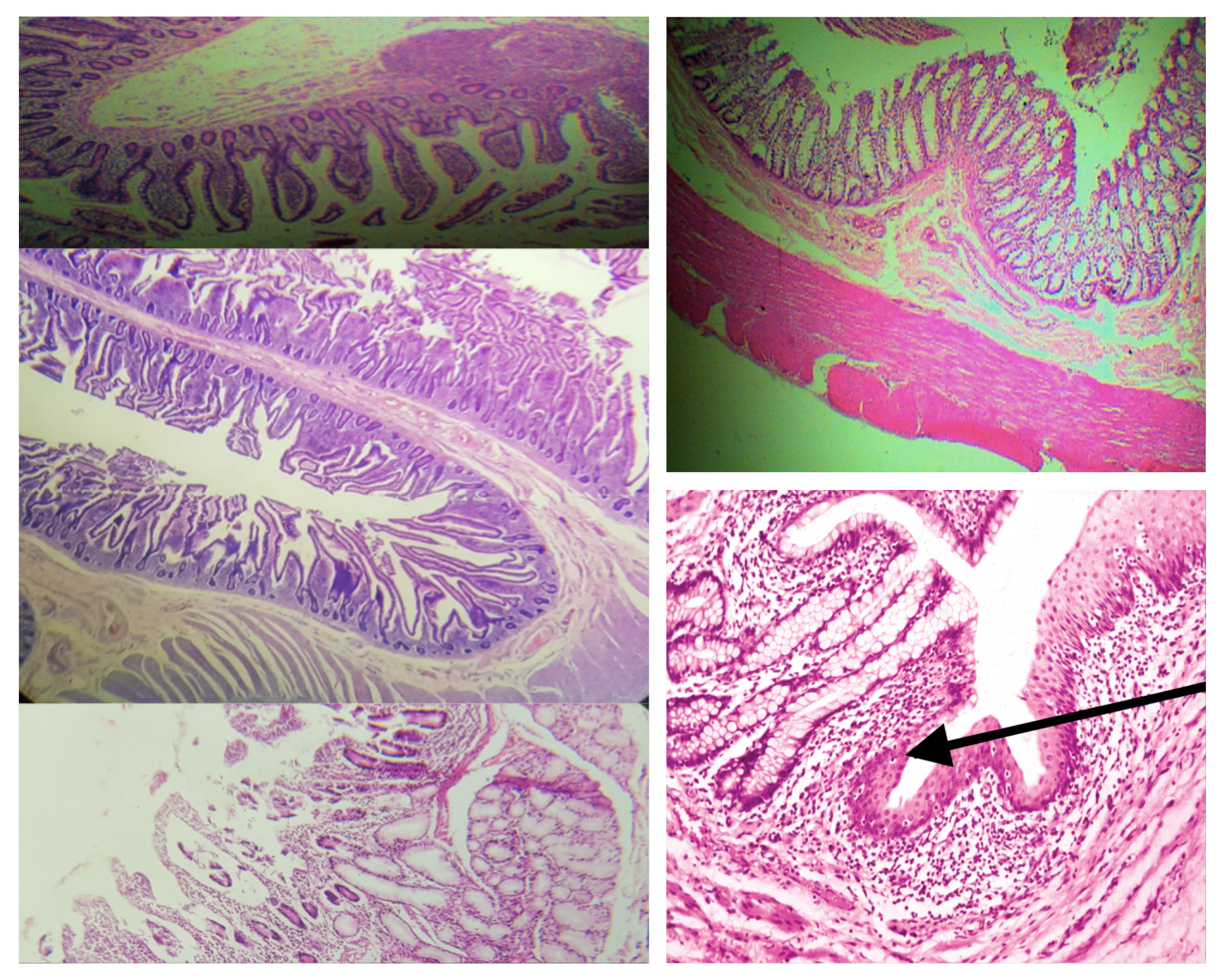
Composition of Tunica Adventitia (same for small and large)
Loose connective with BV, LV, and nerve
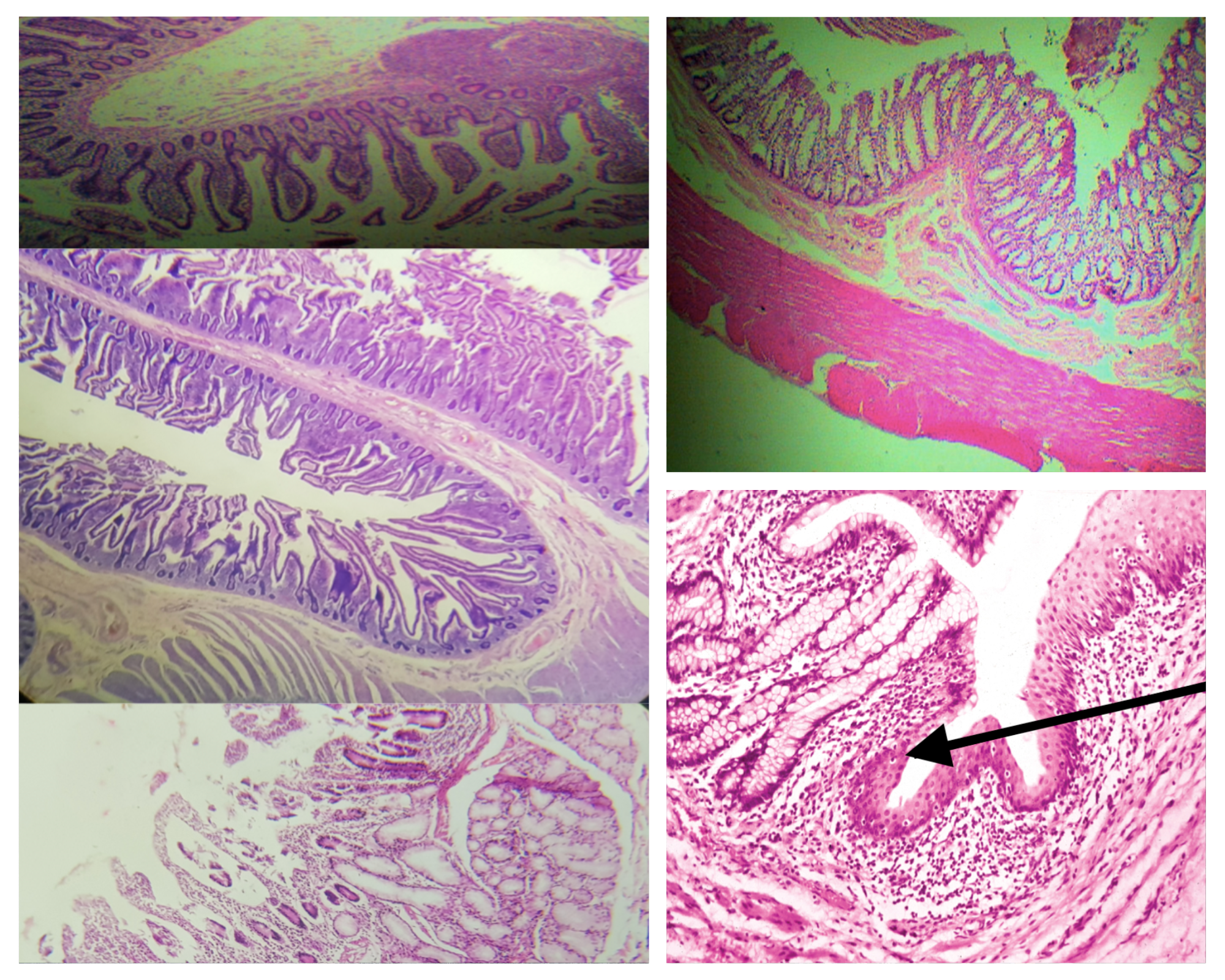
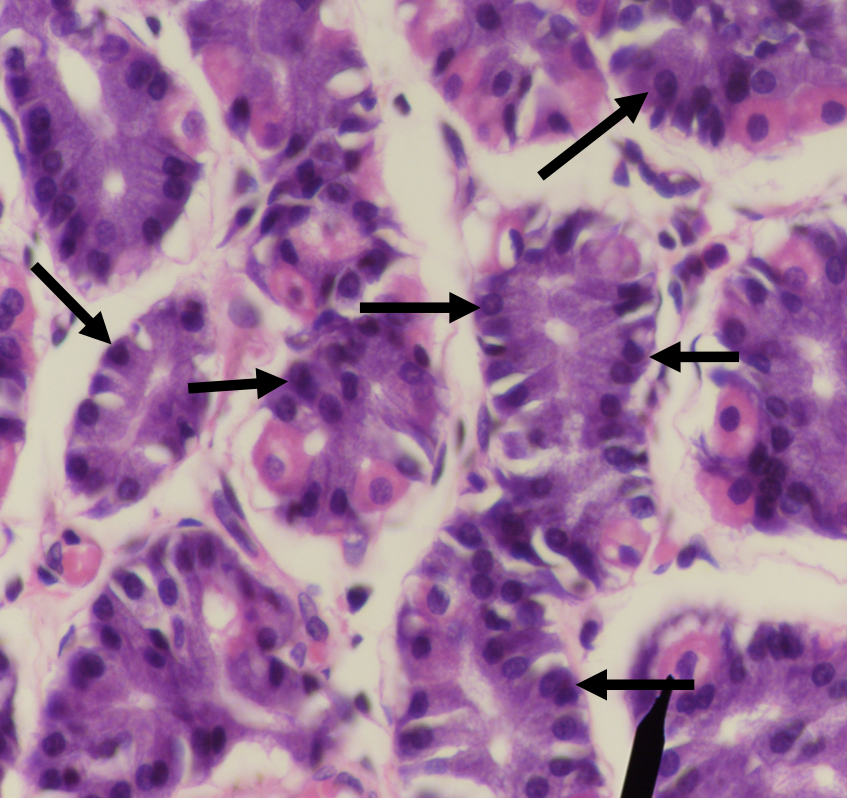
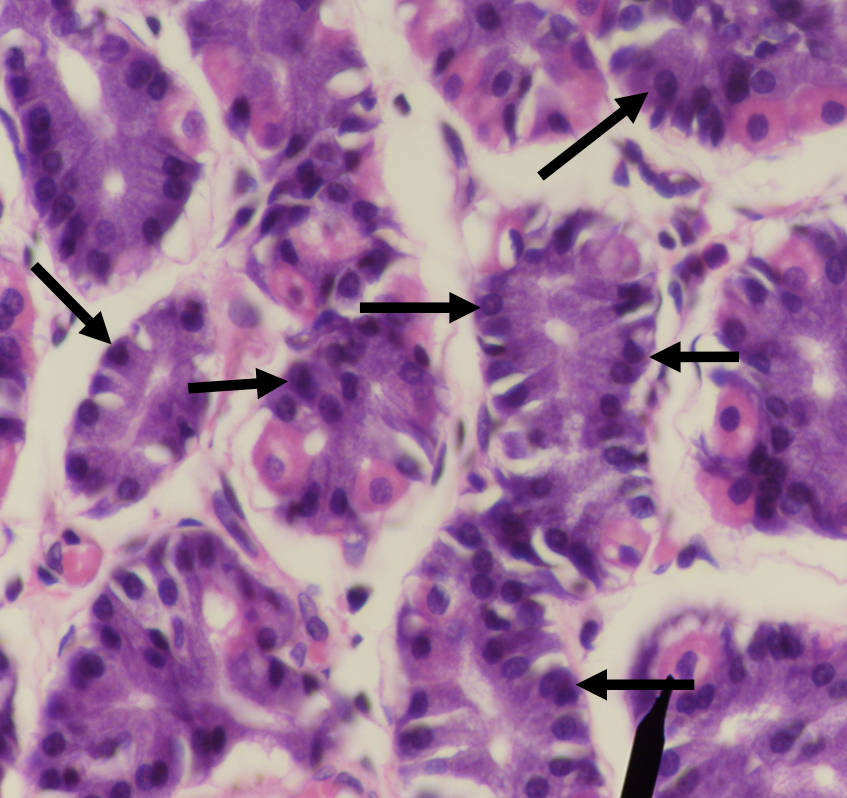
Identify the encircled structure
NOTE: present in both small and large intestine
Intestinal Gland(s)
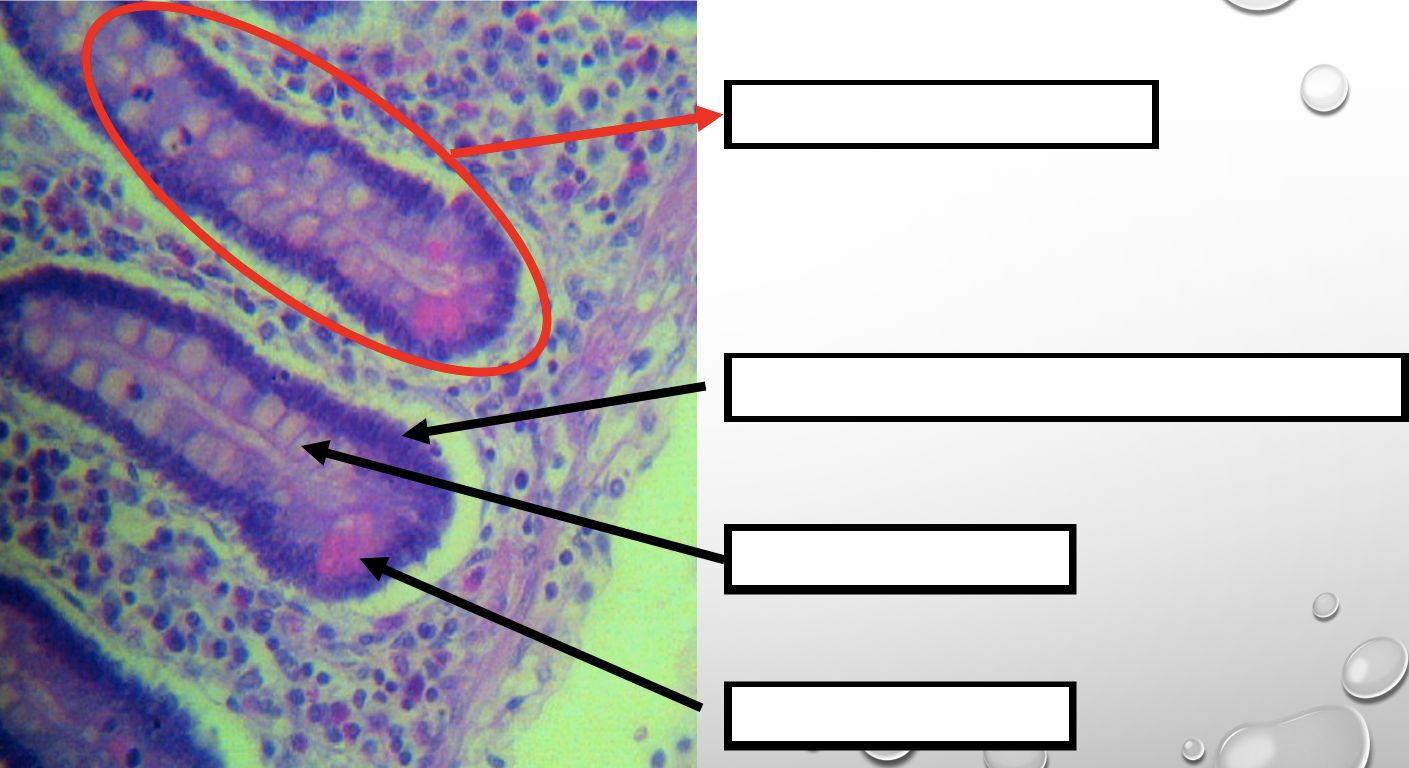
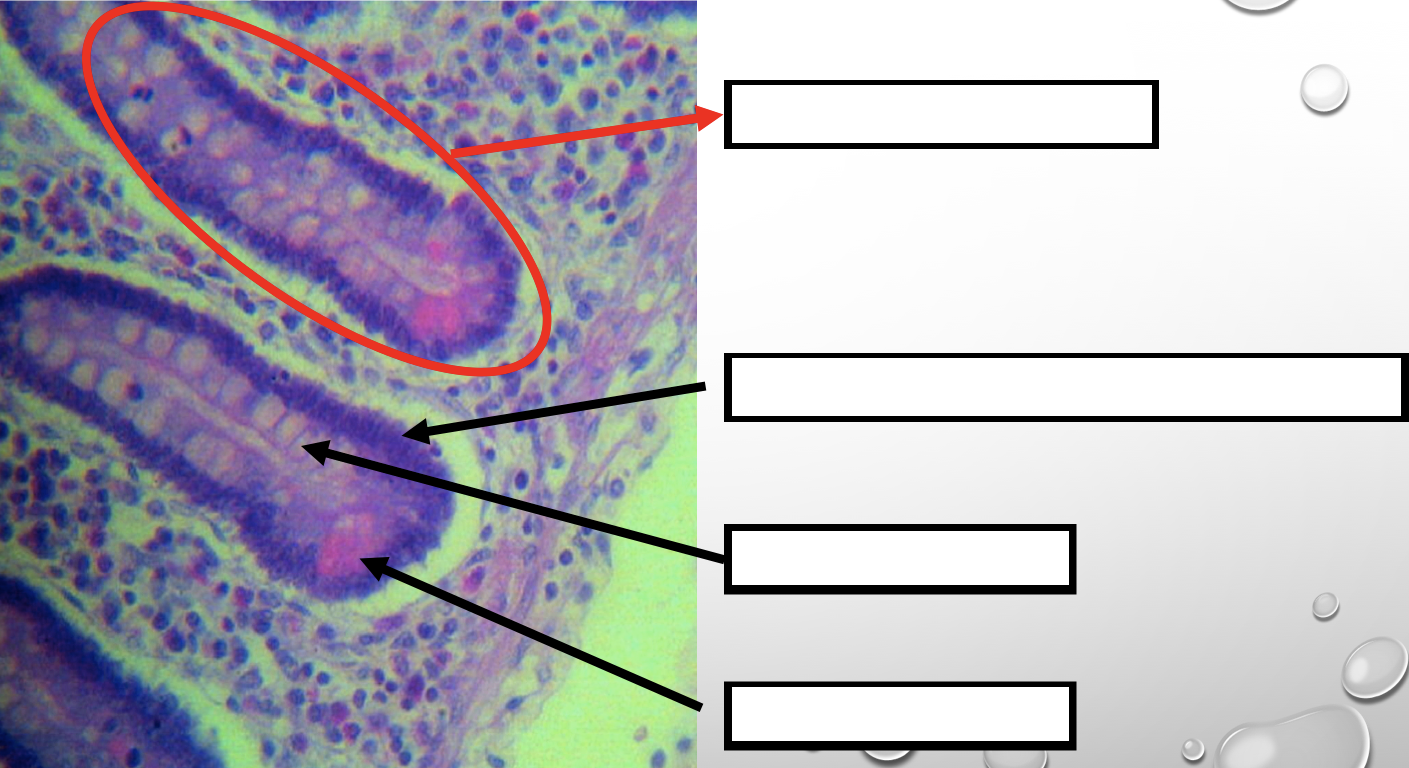
Label
NOTE: present in both small and large intestine
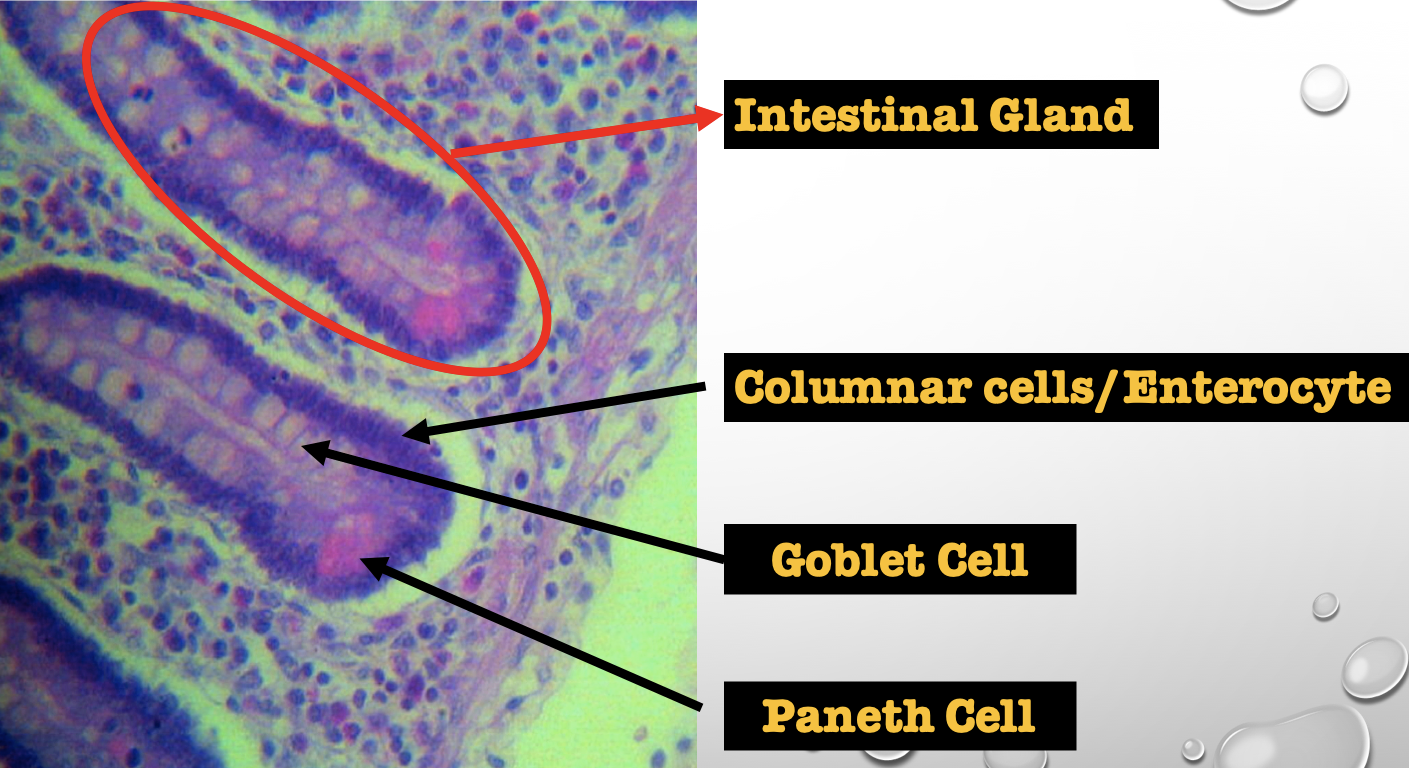
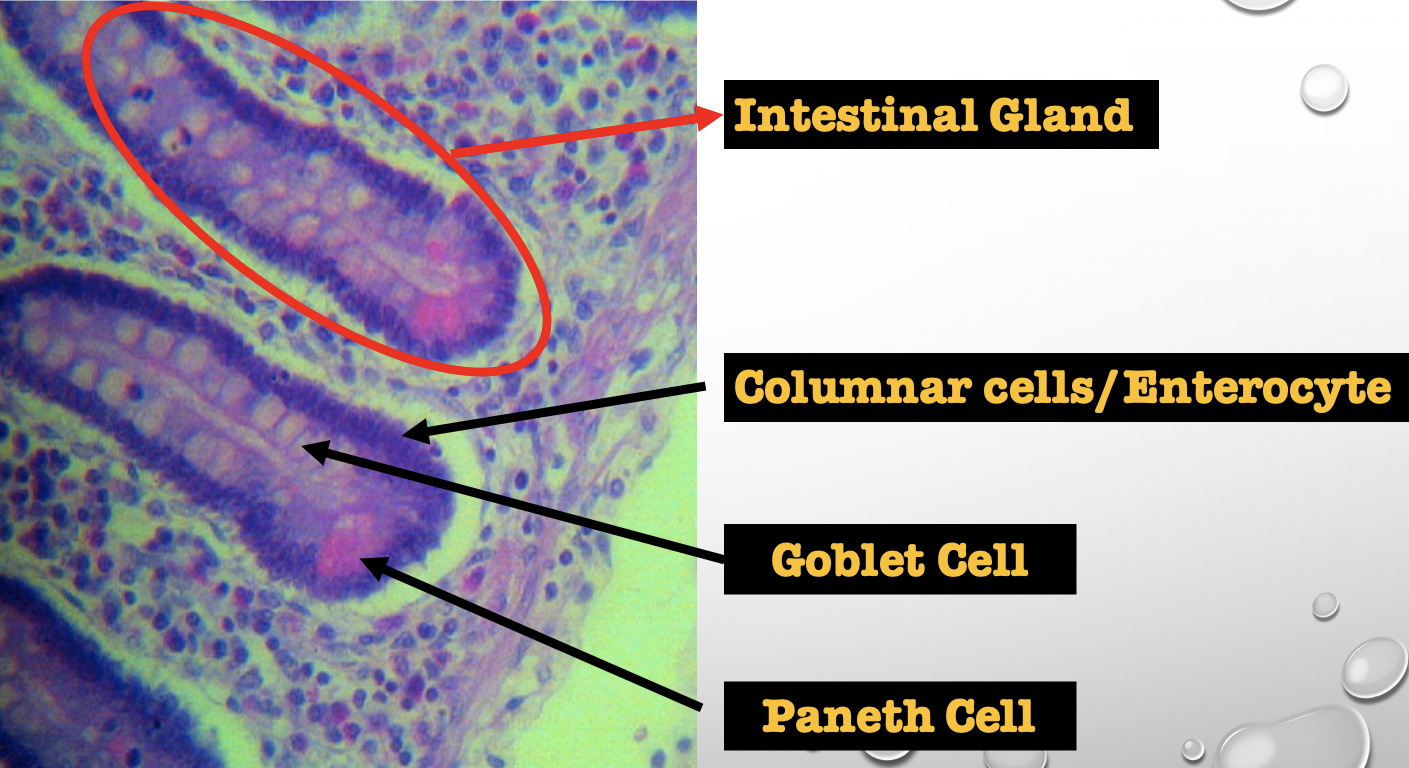
Another term for the encircled structure
Crypts of Lieberkuhn
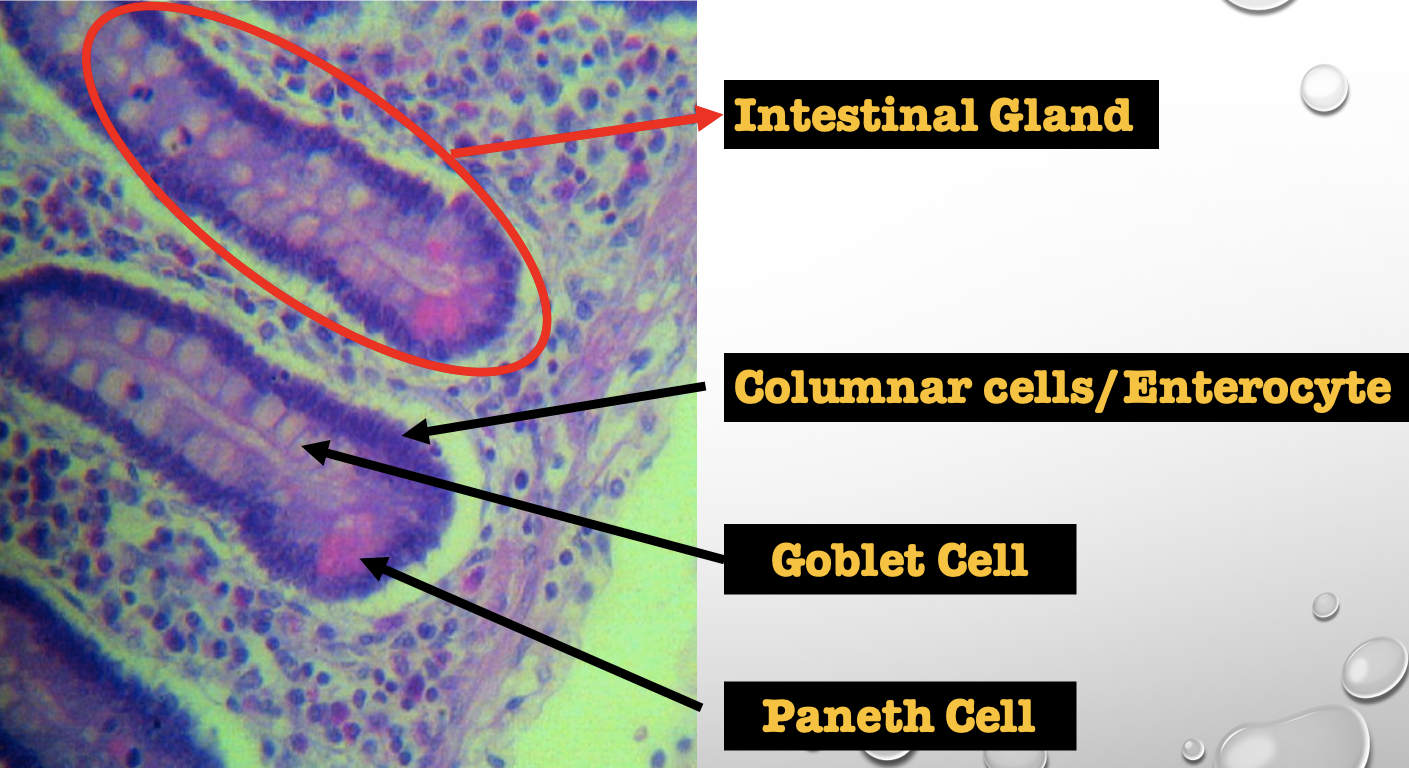
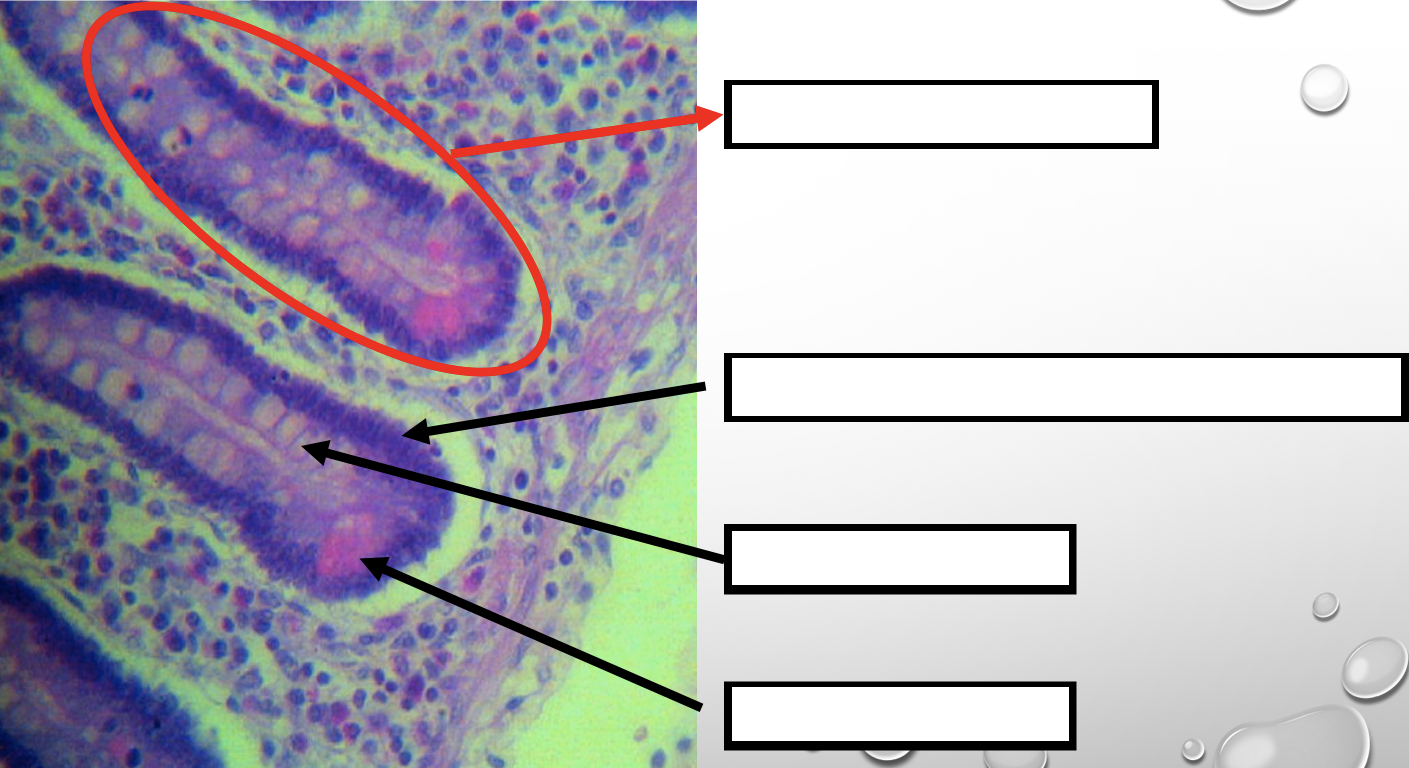
What specific layer are these structures found
Lamina Propia
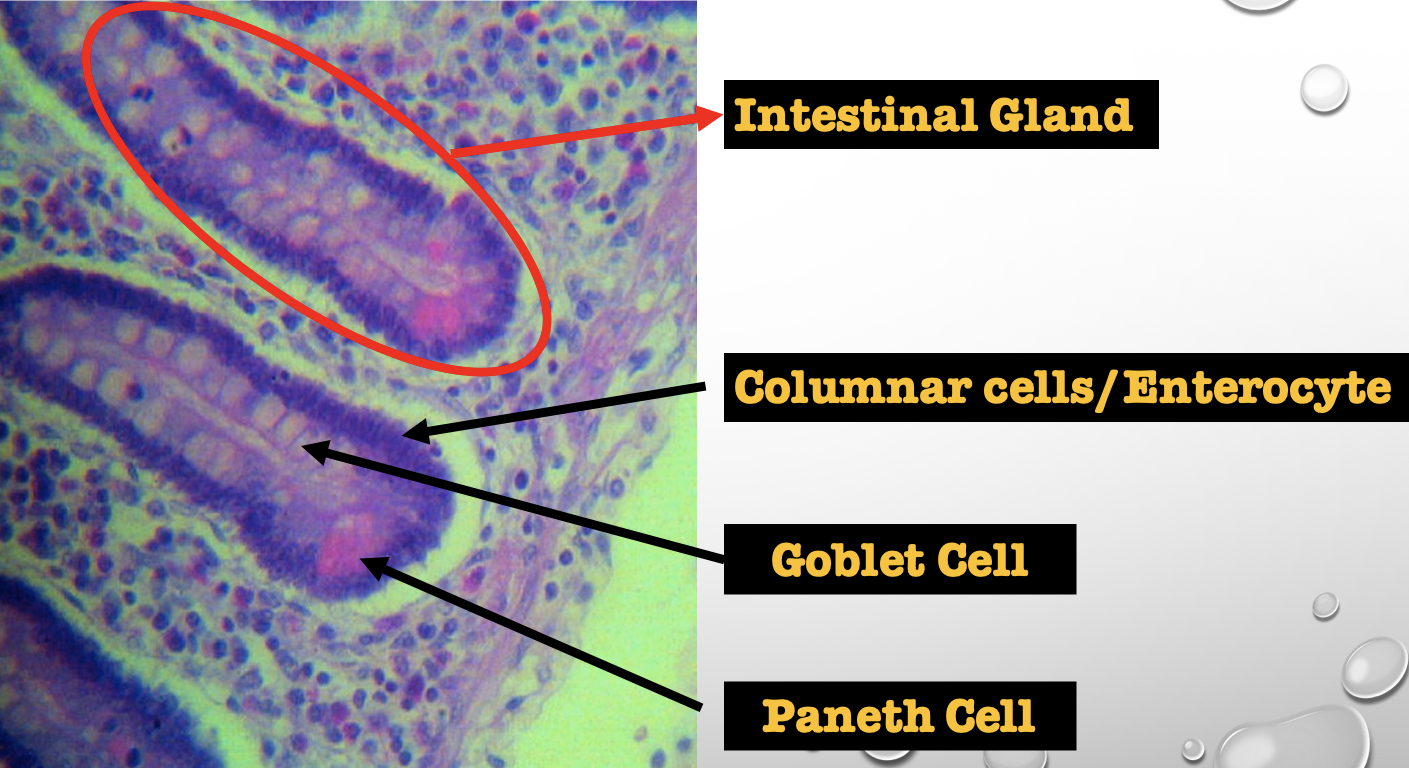
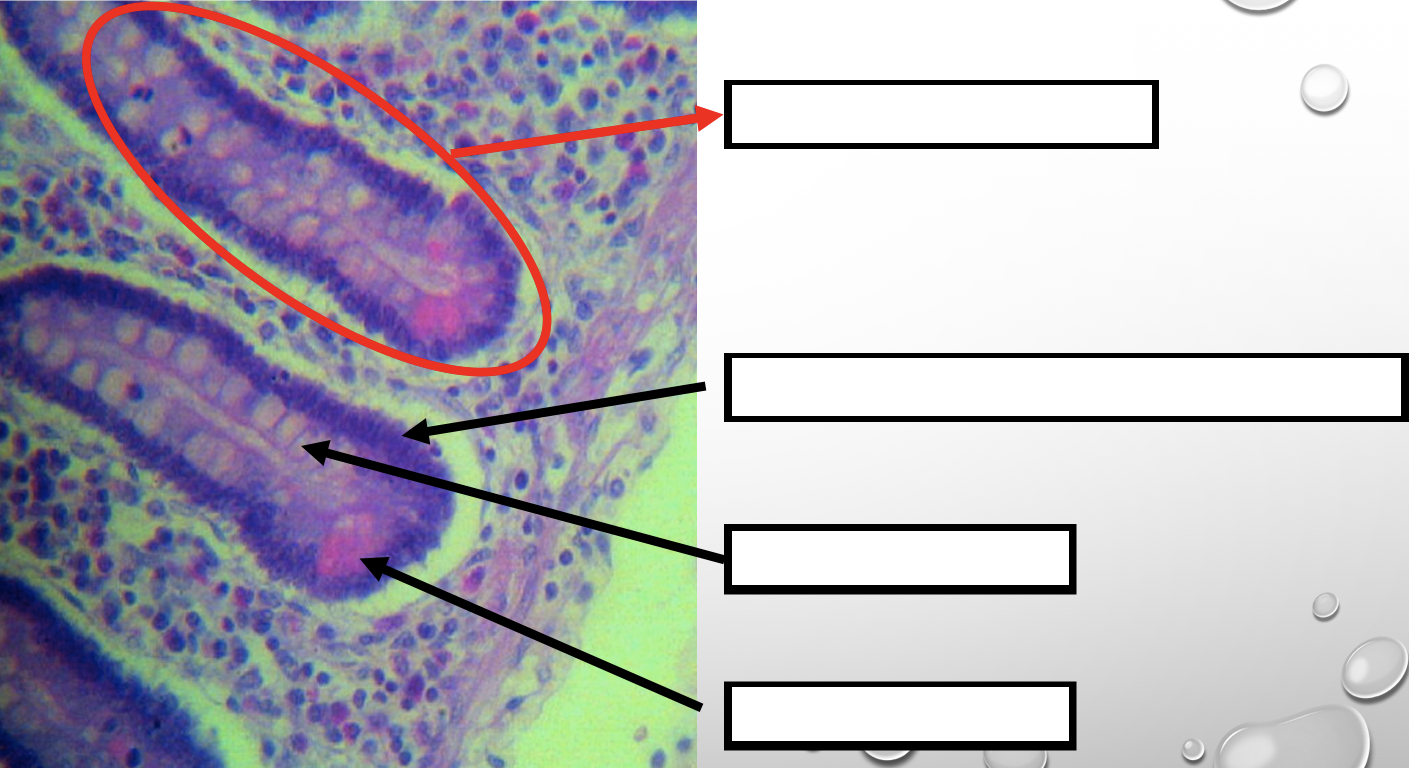
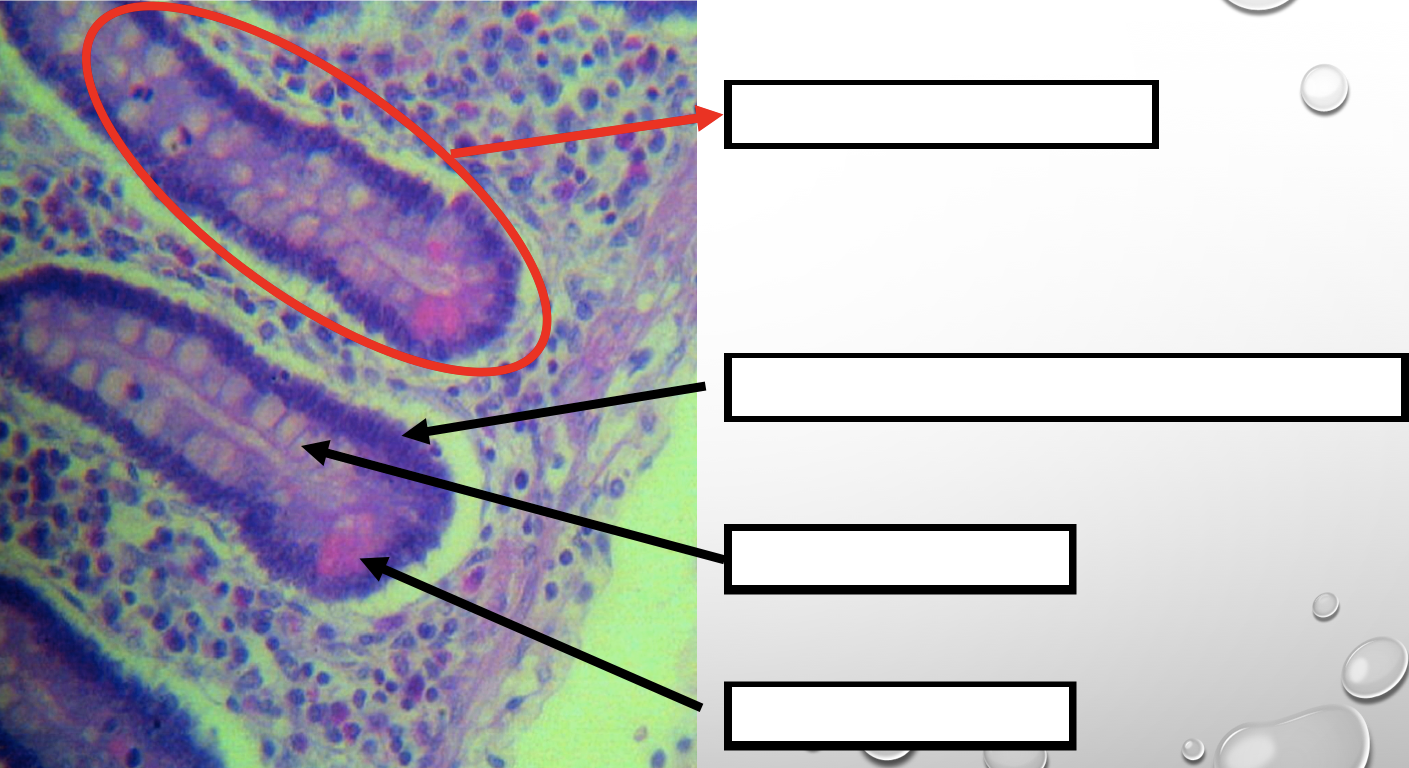
Four Cells of Intestines/ Intestinal Gland
1. Columnar cells (enterocytes)
2. Goblet cell
3. Paneth cell
4. Argentaffin cell/ Enteroendocrine cell (not seen in staining)
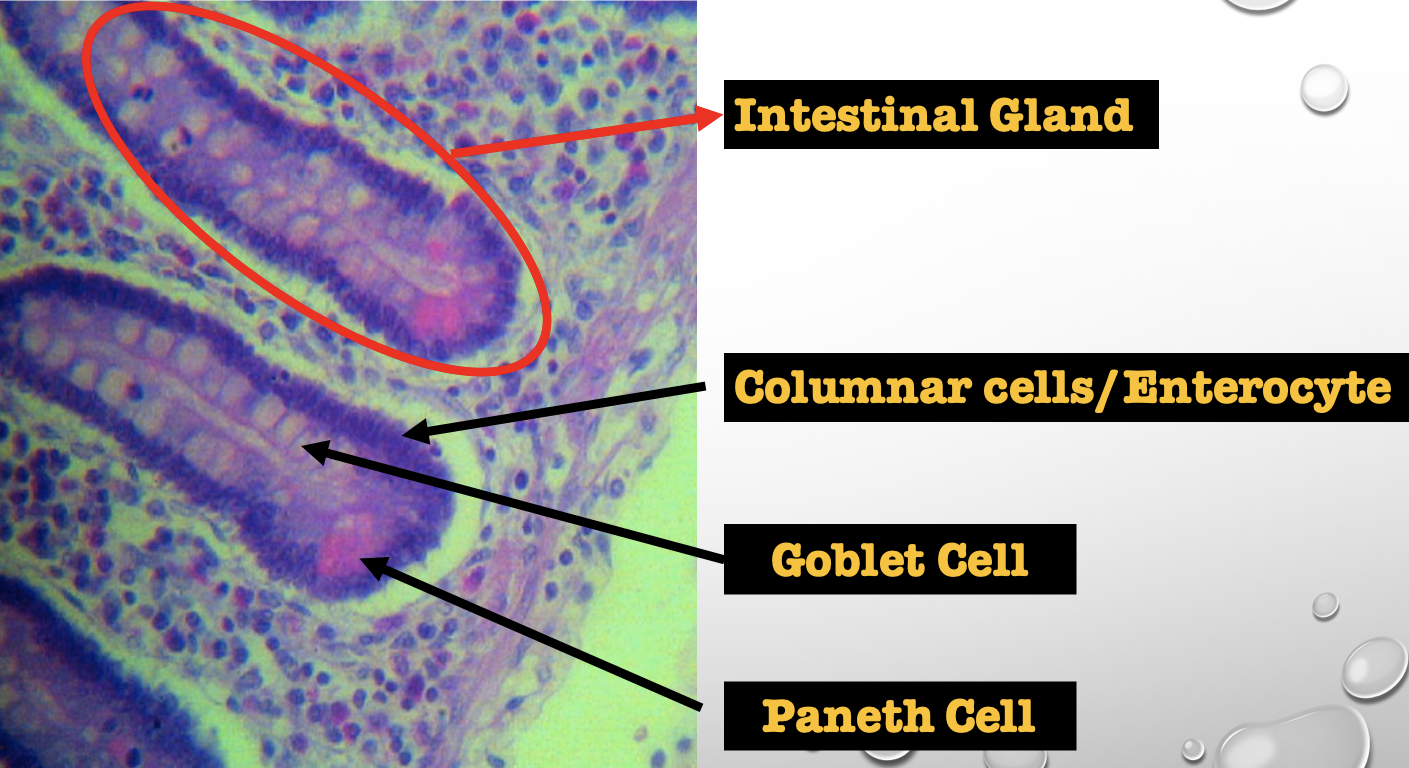
Which cell is the parenchyma
Columnar cells (enterocytes)
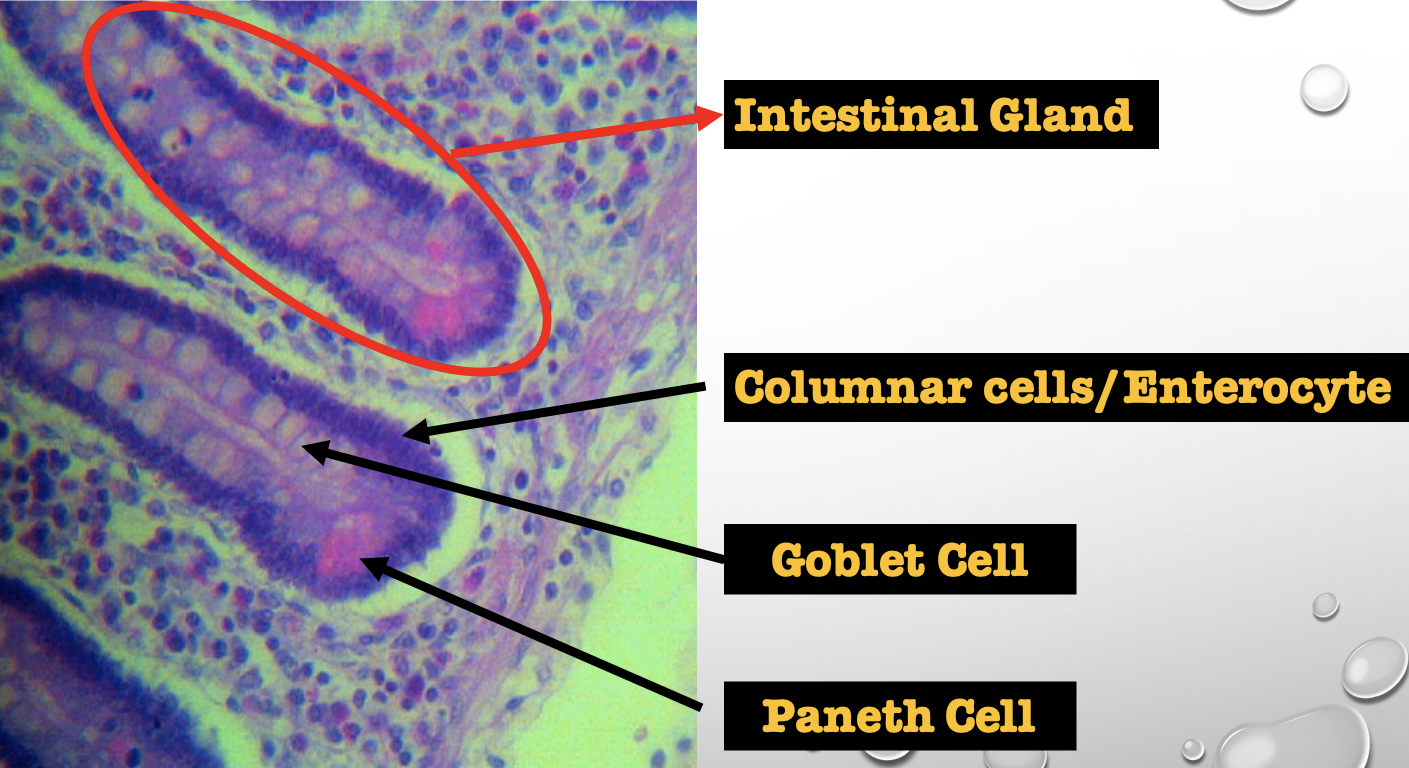
Which cell is the most numerous
Columnar cells (enterocytes)
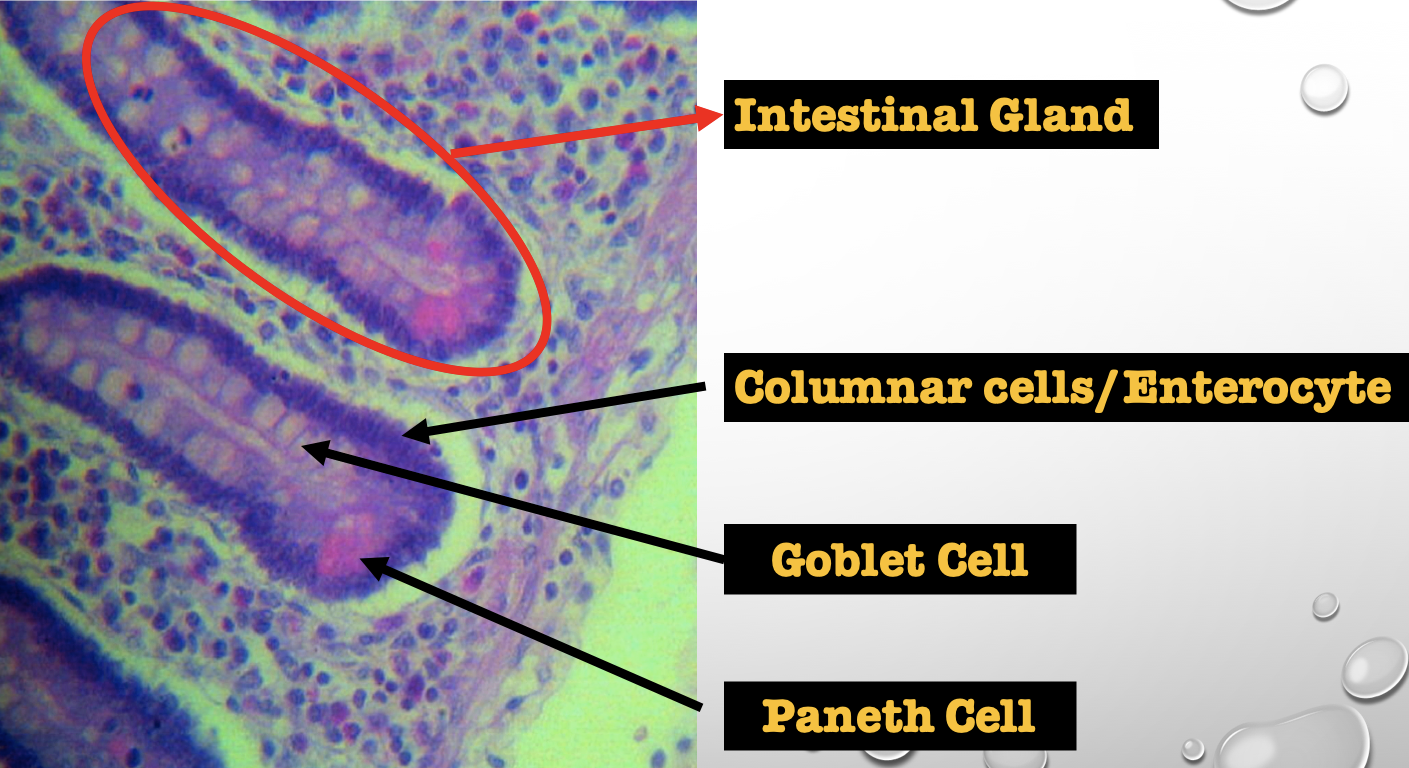
Mucin producing epithelial cells
Goblet Cell
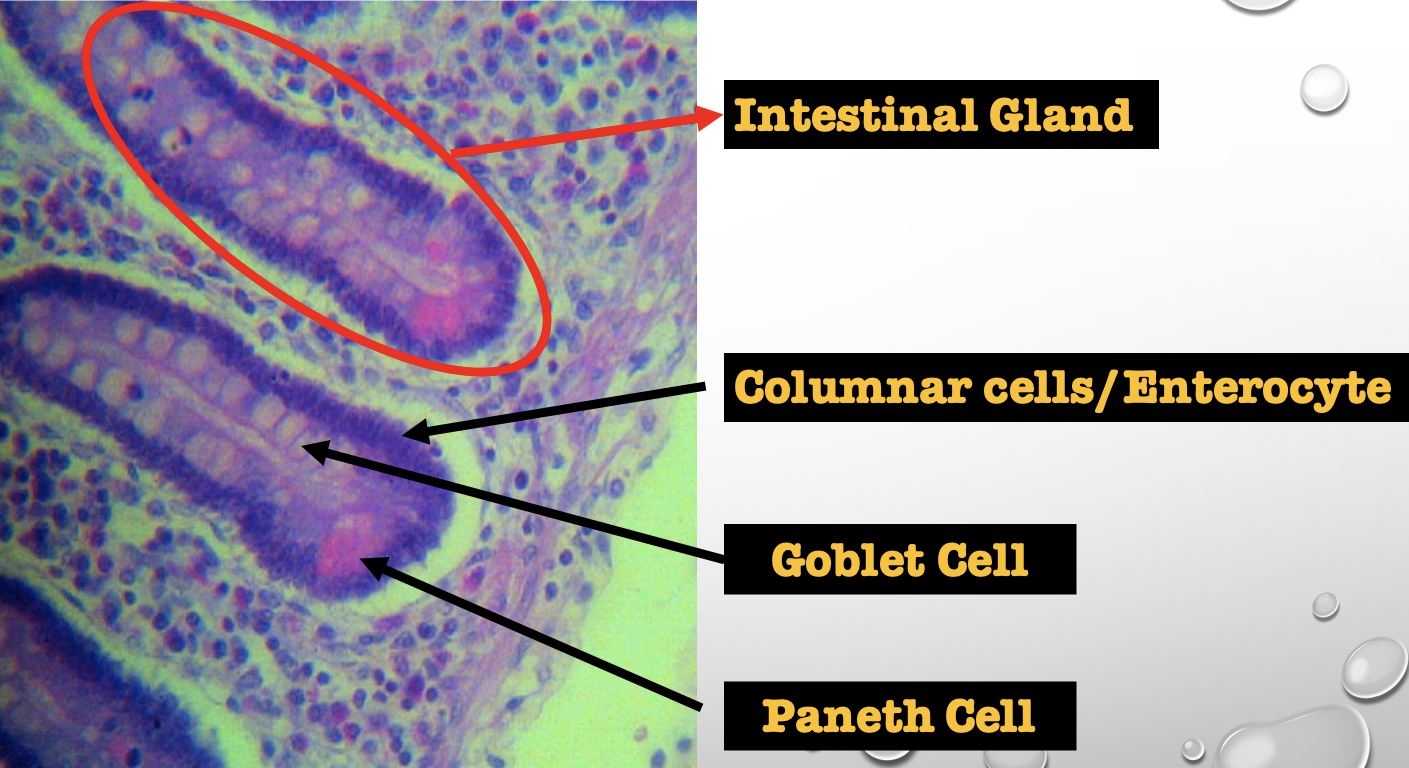
Which cell is pyramidal in shape
Paneth Cell
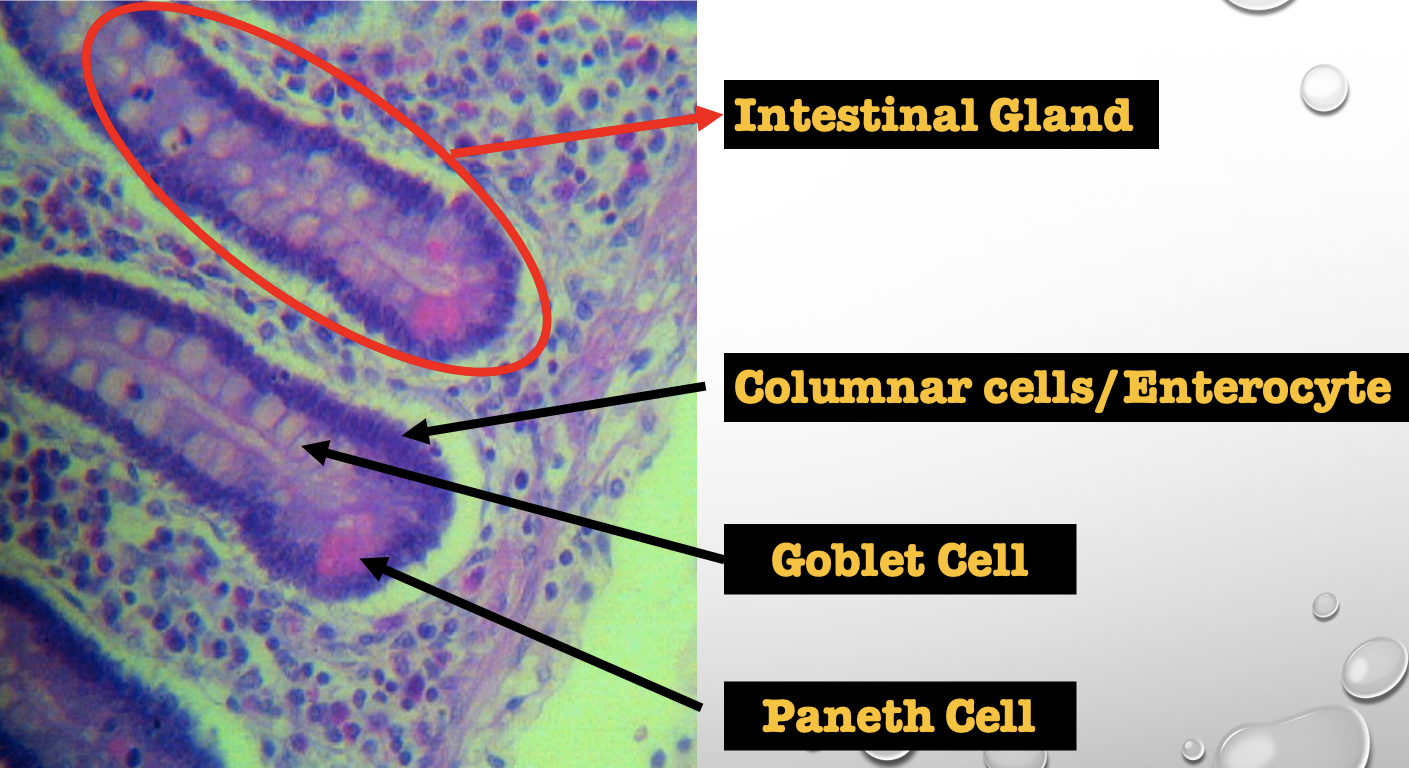
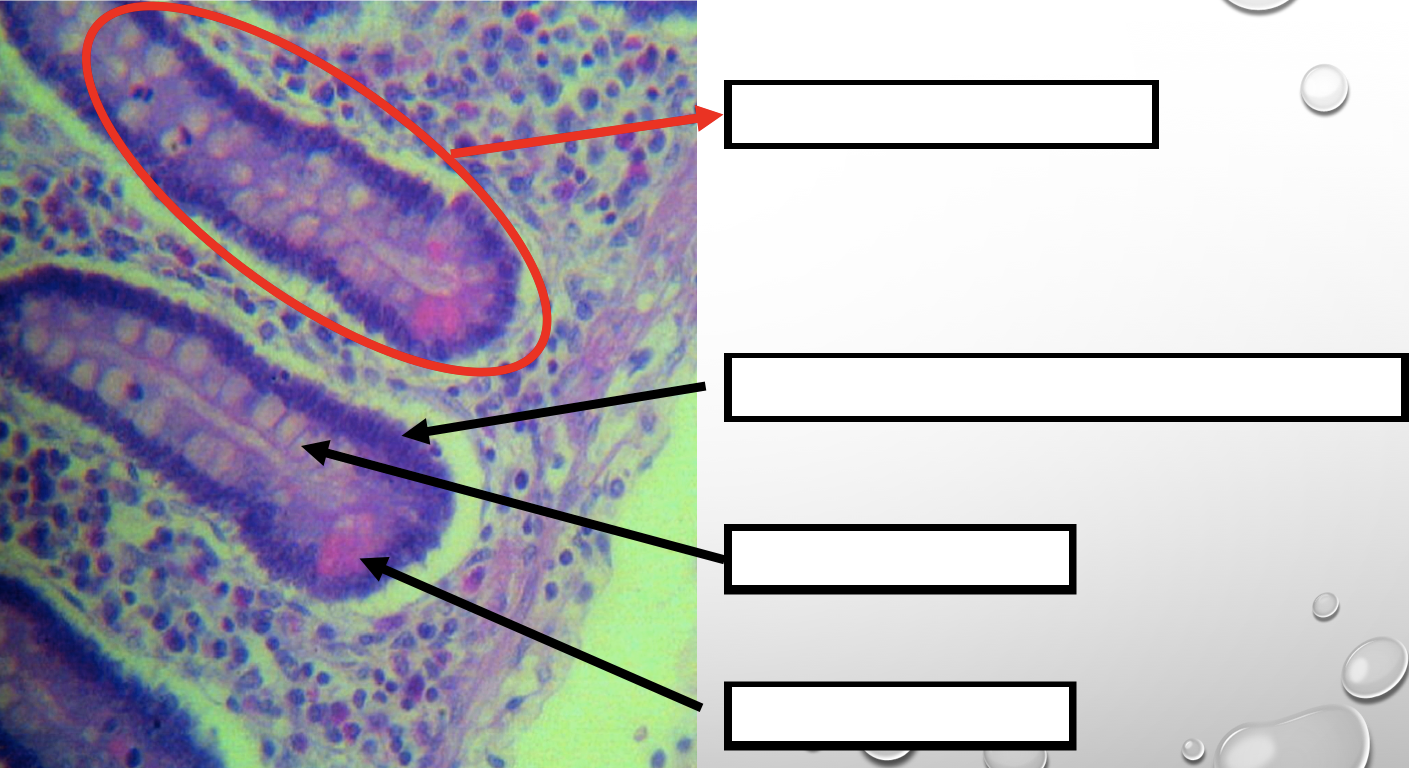
Which cell is found at the base of the glands
Paneth Cell
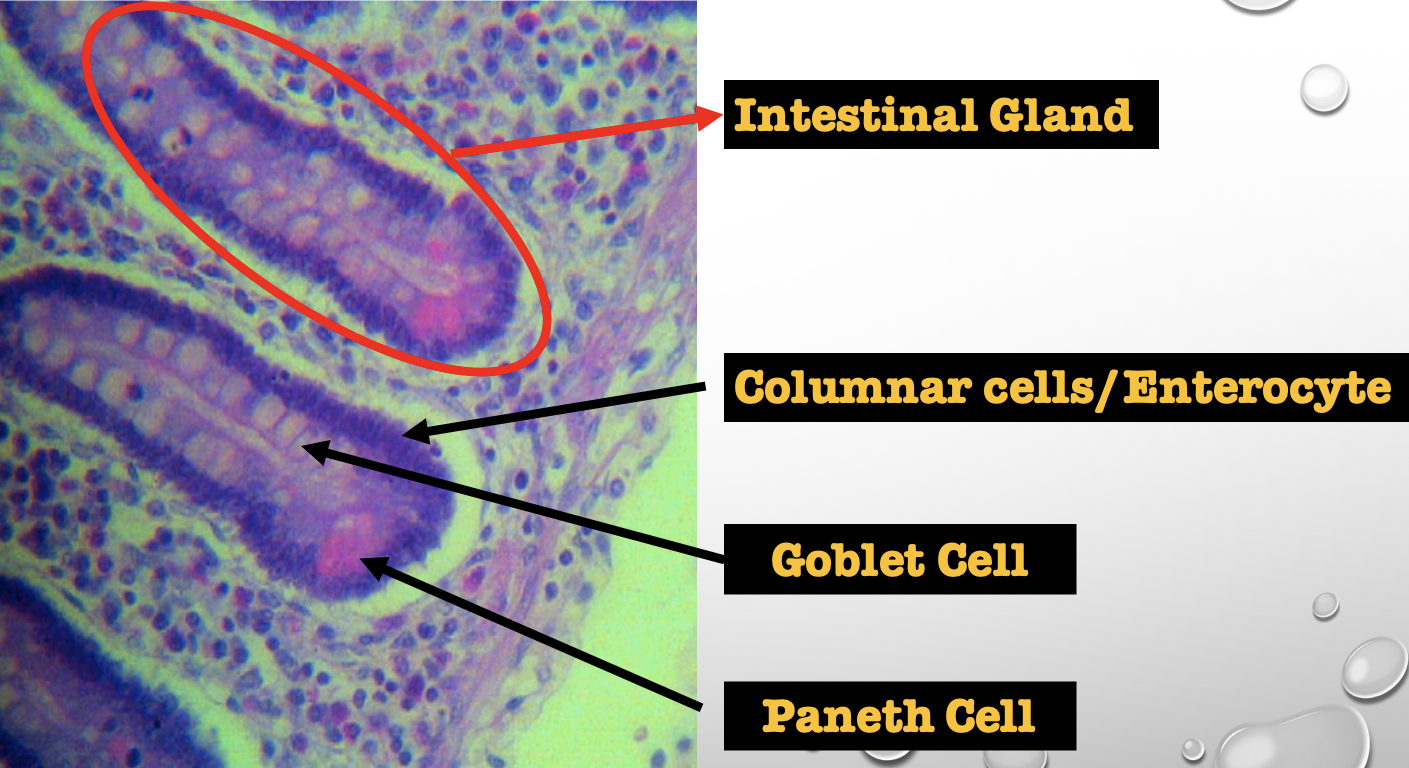
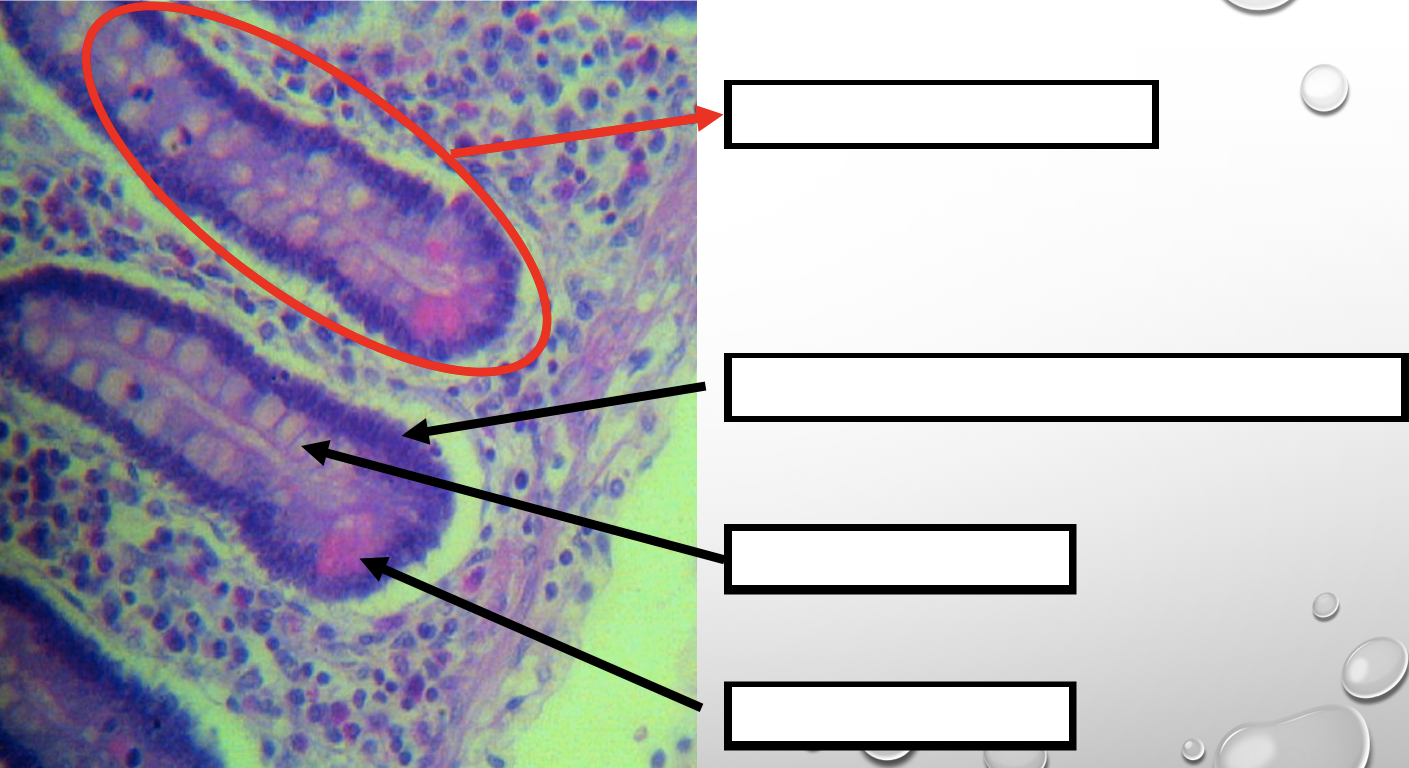
Which cell is highly acidophilic
Paneth Cell
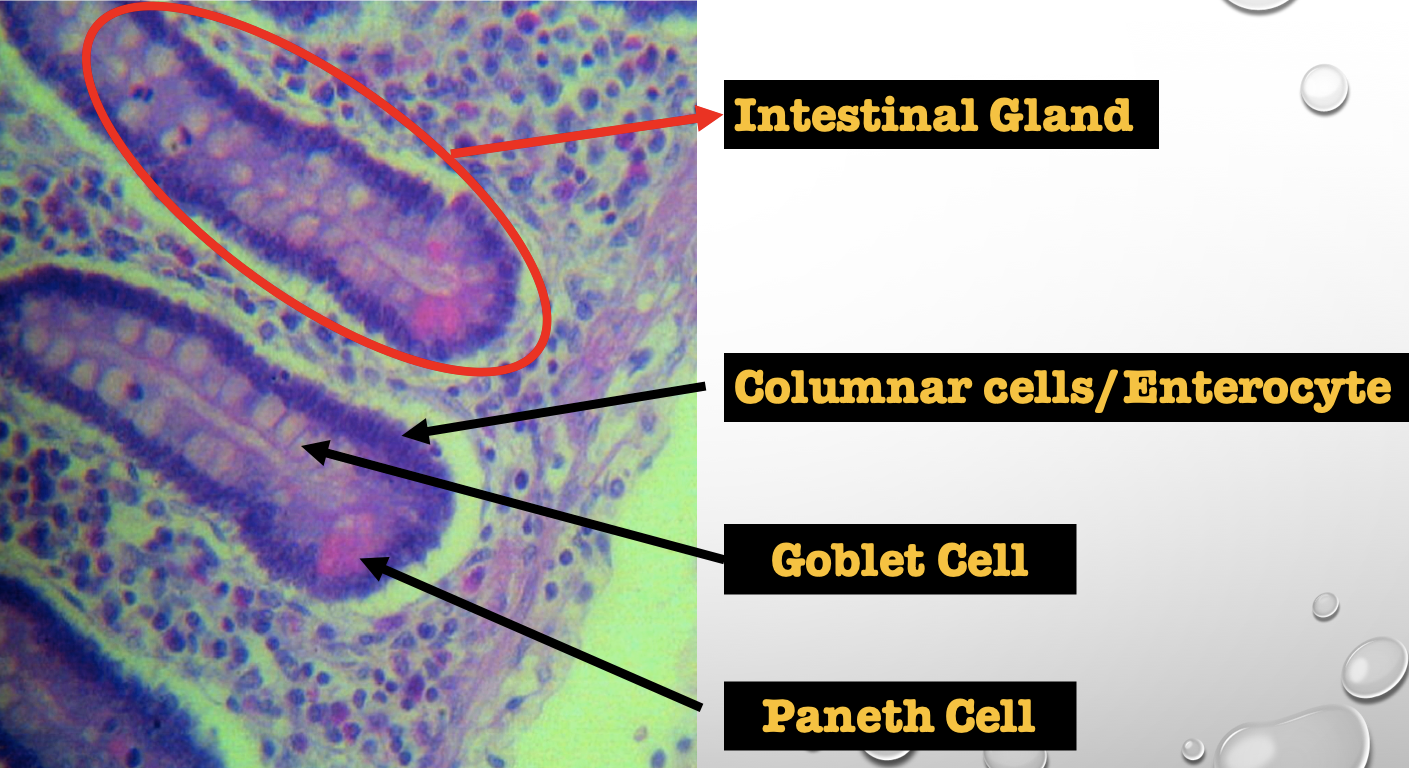
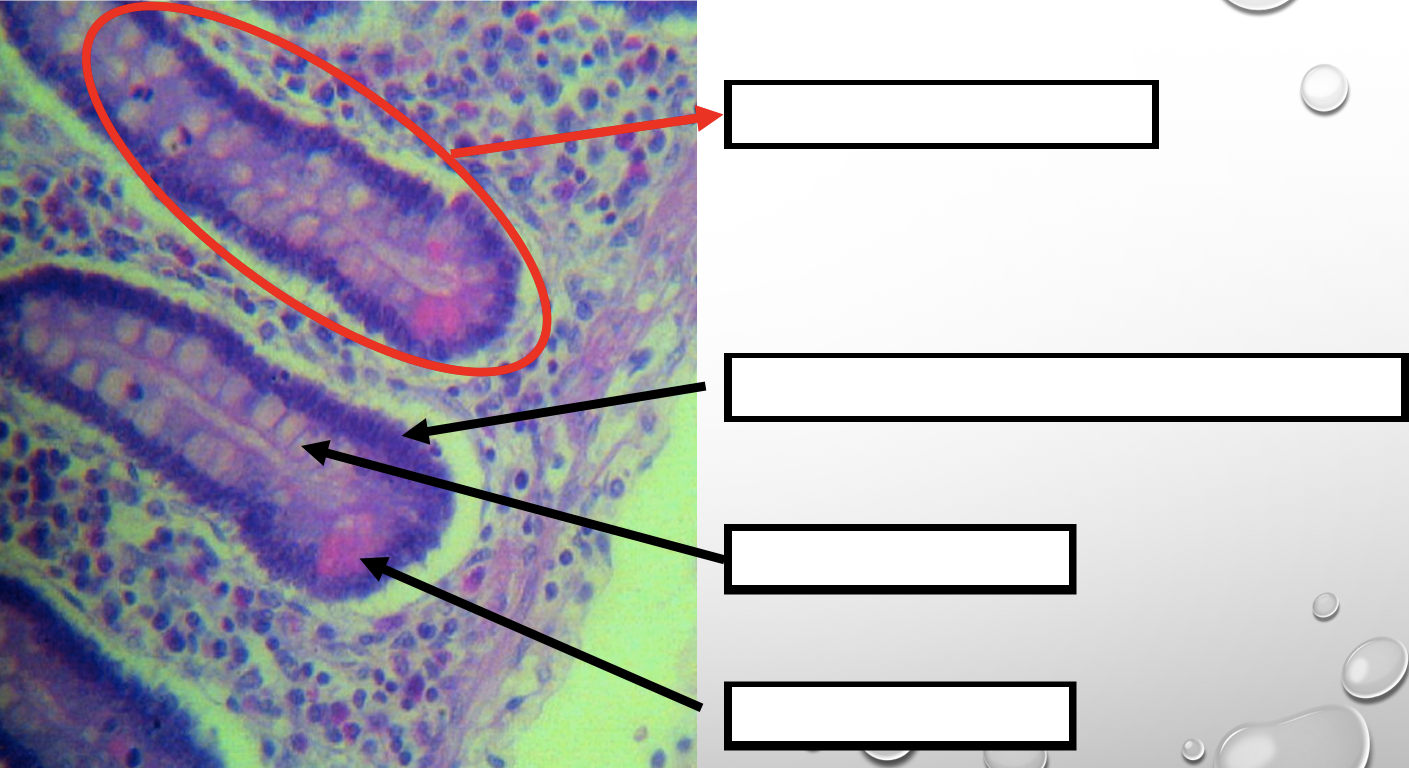
Which cell precipitate silver salts
Argentaffin cell/ Enteroendocrine cell
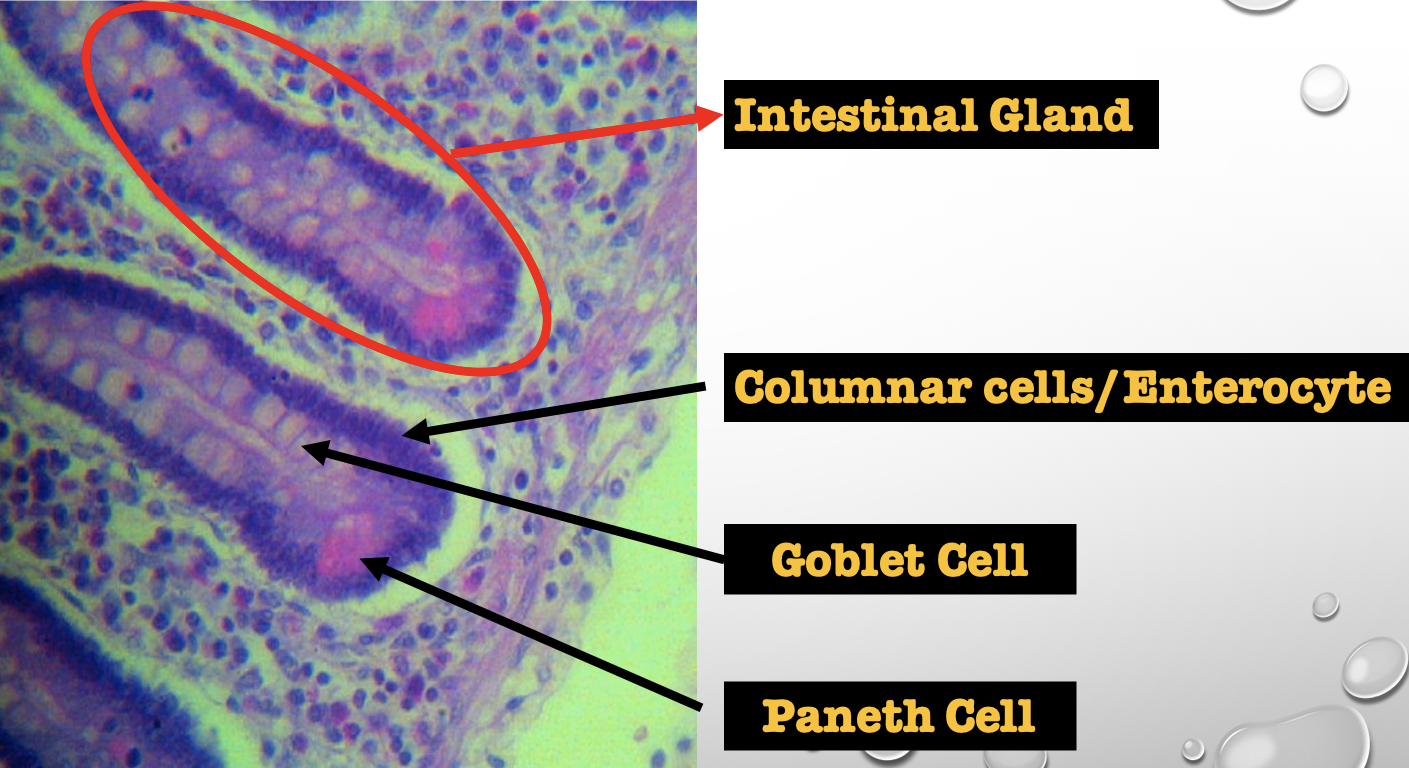
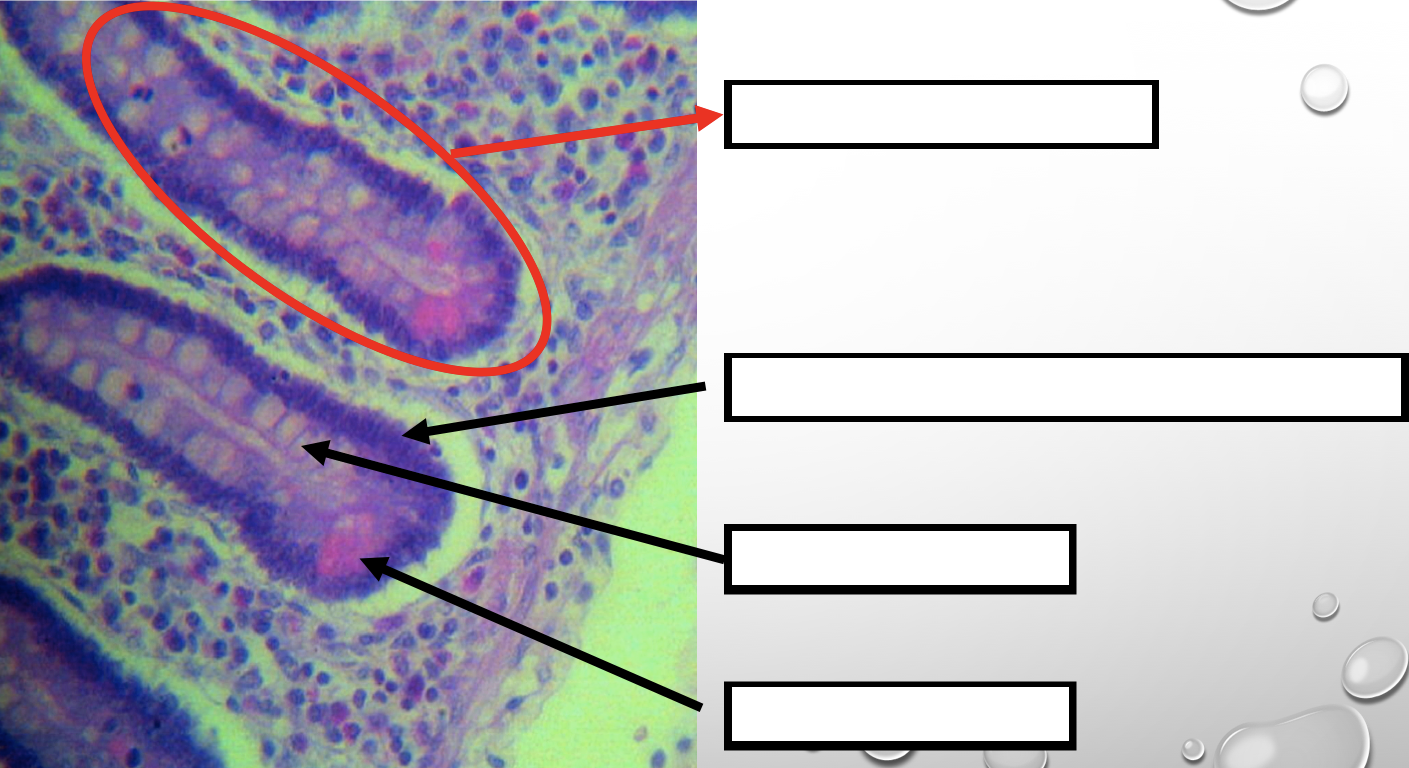
Which layer are these cells found
Mucosa; specifically Lamina Propia
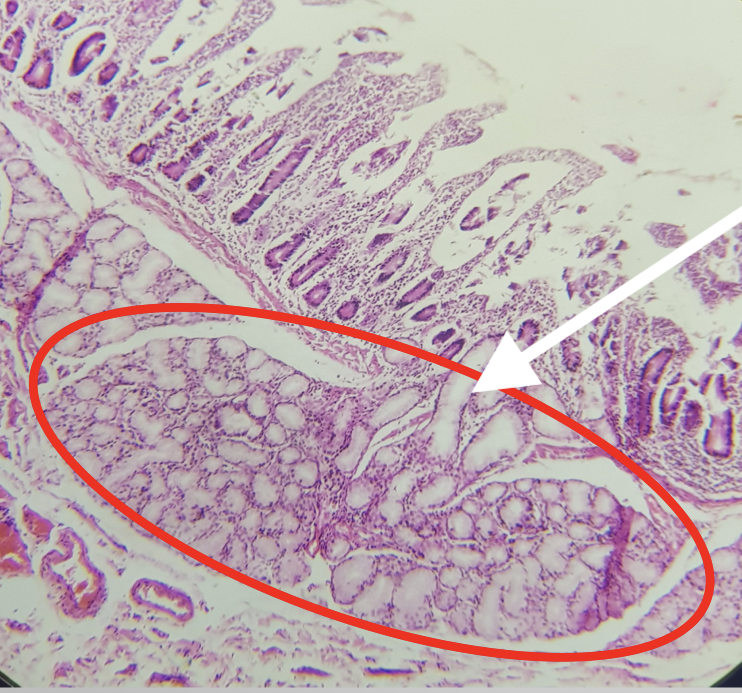
Identify the Segment
Duodenum
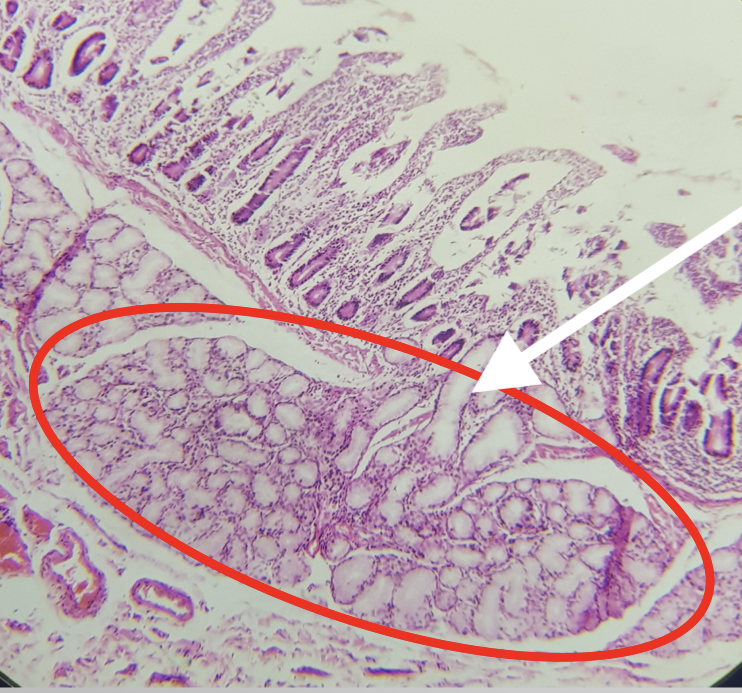
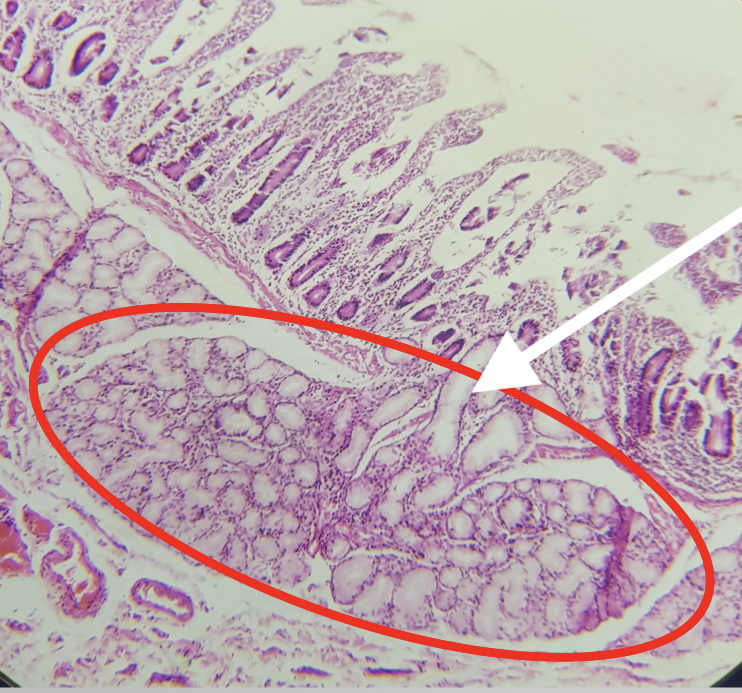
Identify the encircled structure
Brunner’s/ Duodenal Gland
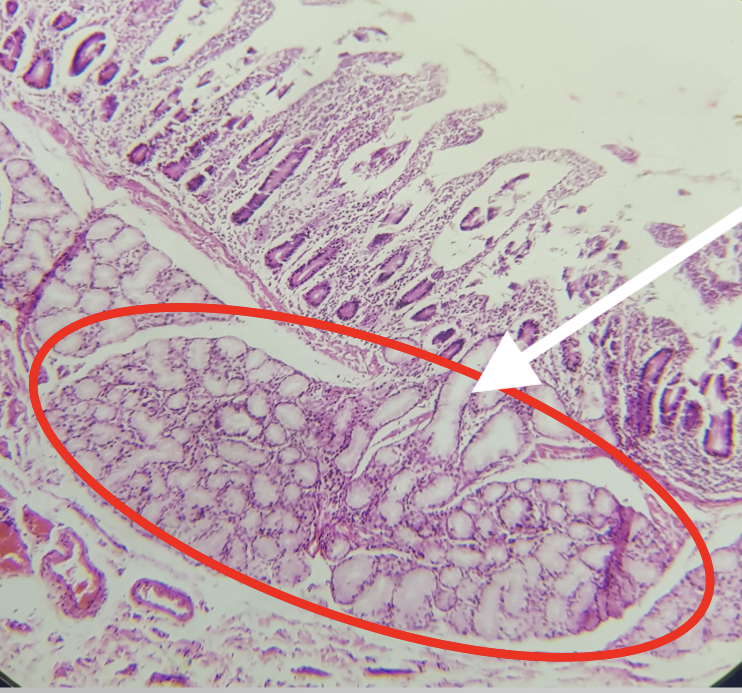
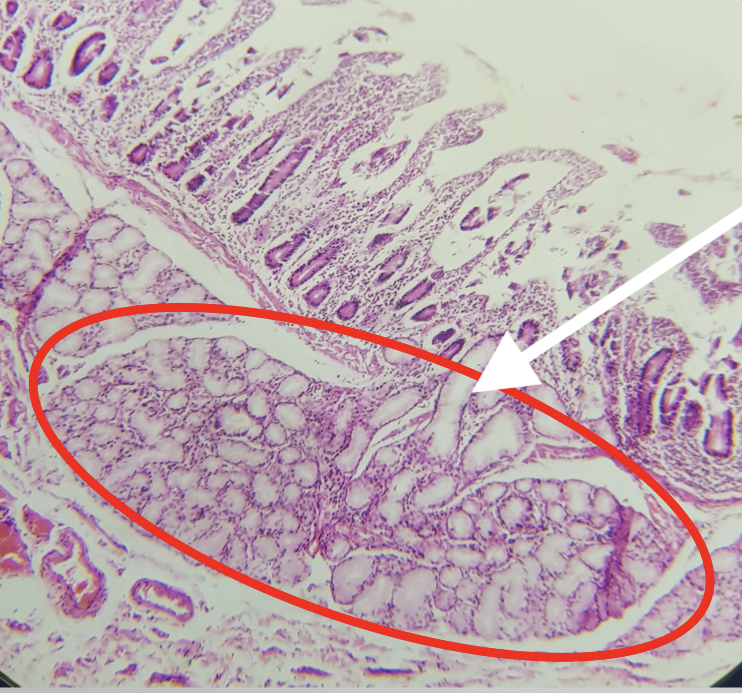
Where is the encircled structure found
Submucosa
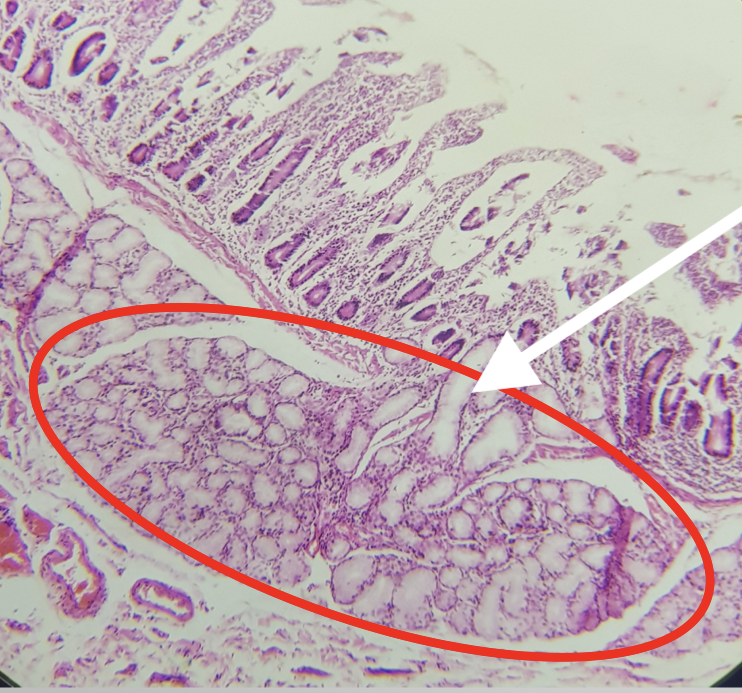
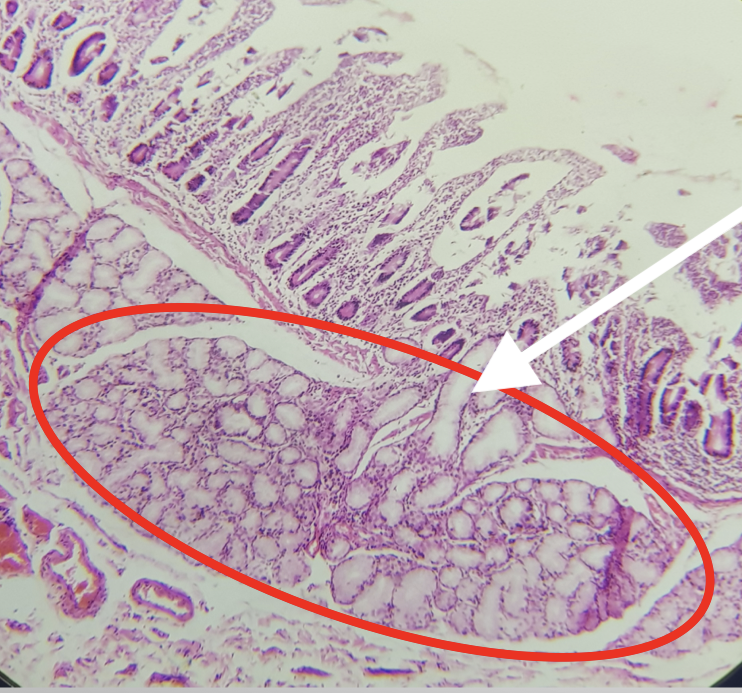
Function of the encircled structure
produces an alkaline fluid composed of mucin, protecting it from the acidic chyme of the stomach
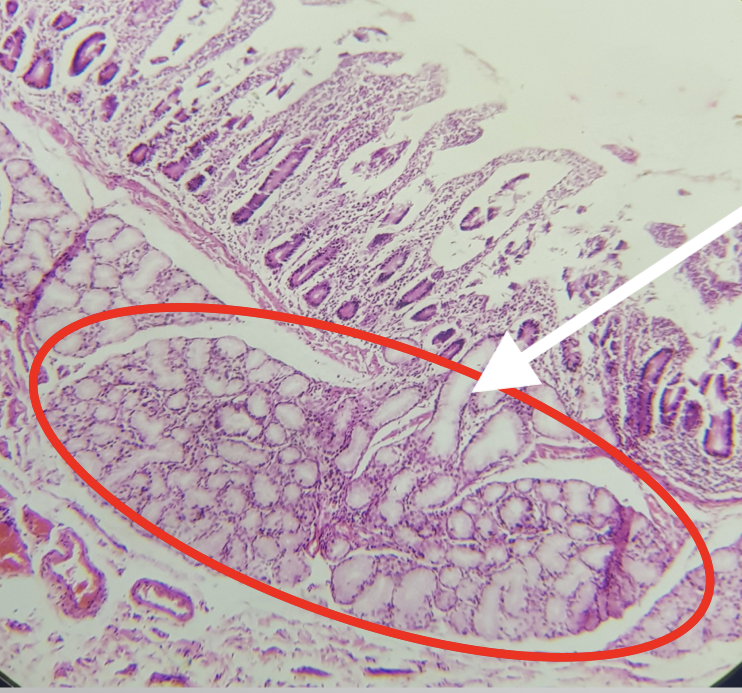
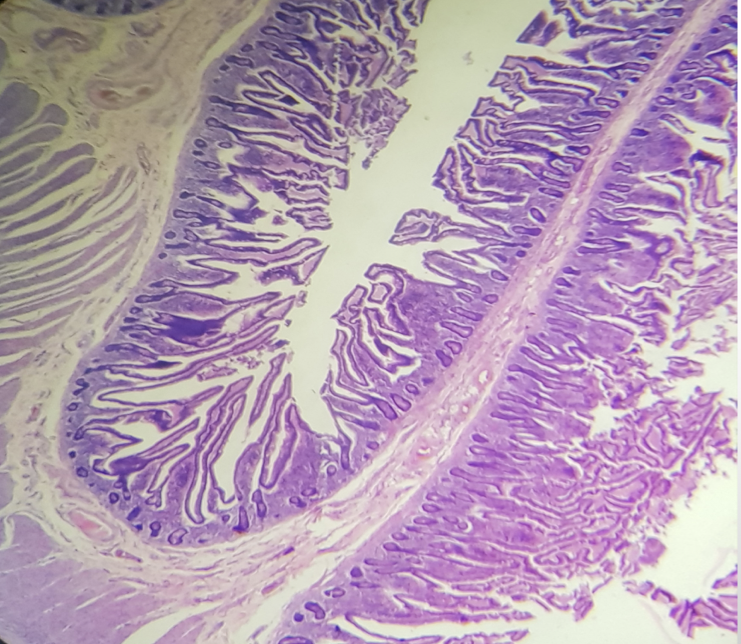
Identify the segment
Jejunum
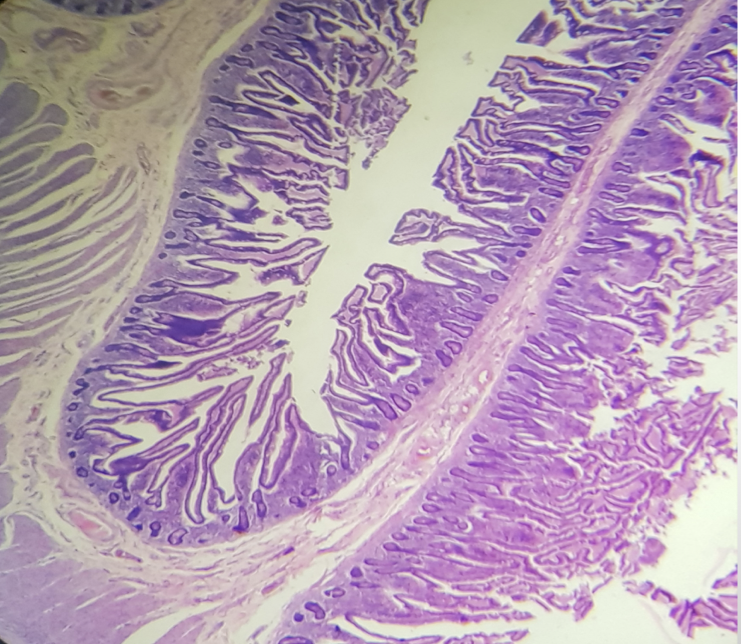
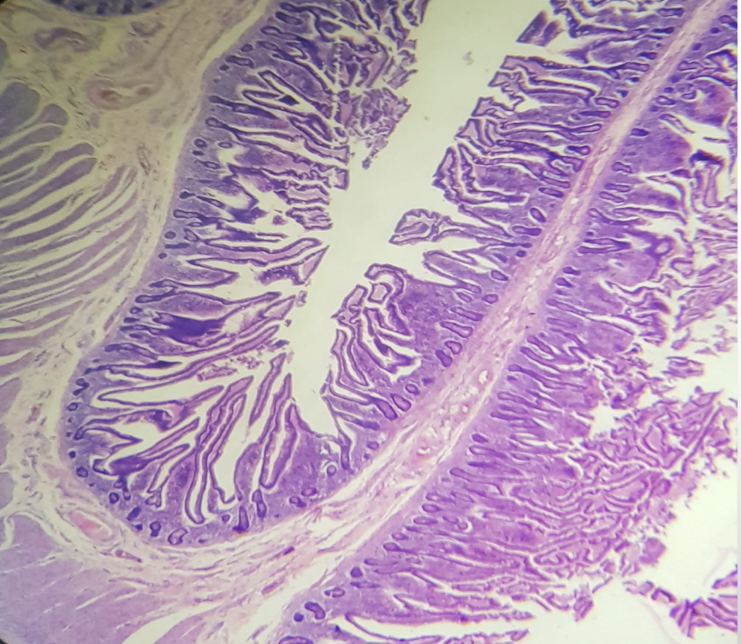
Characteristic feature of the segment
prominent and numerous plicae circularis
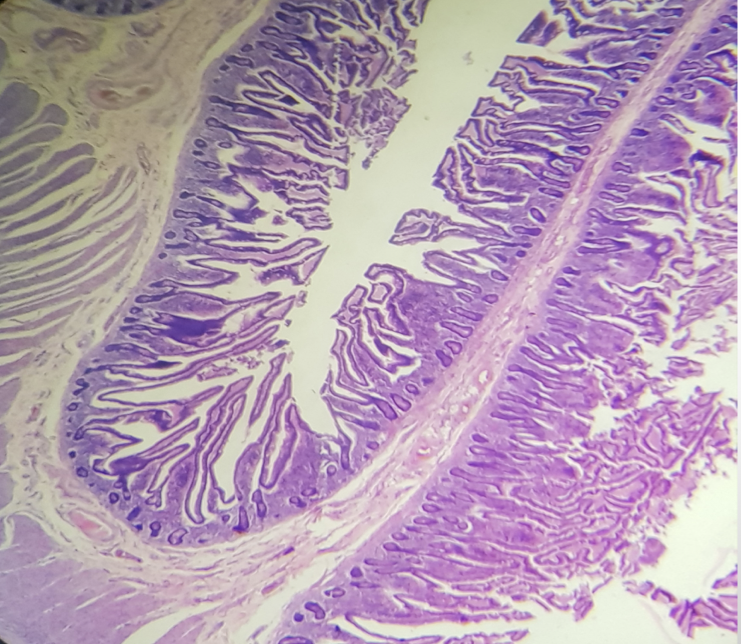
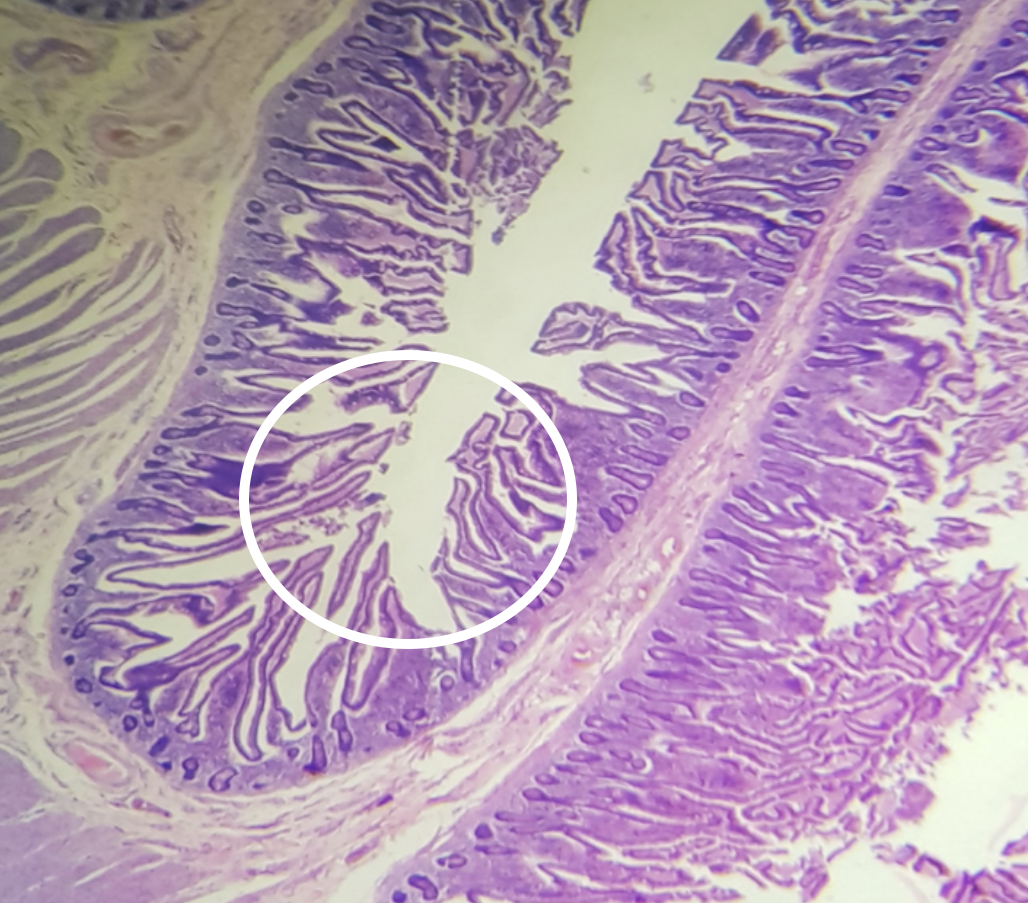
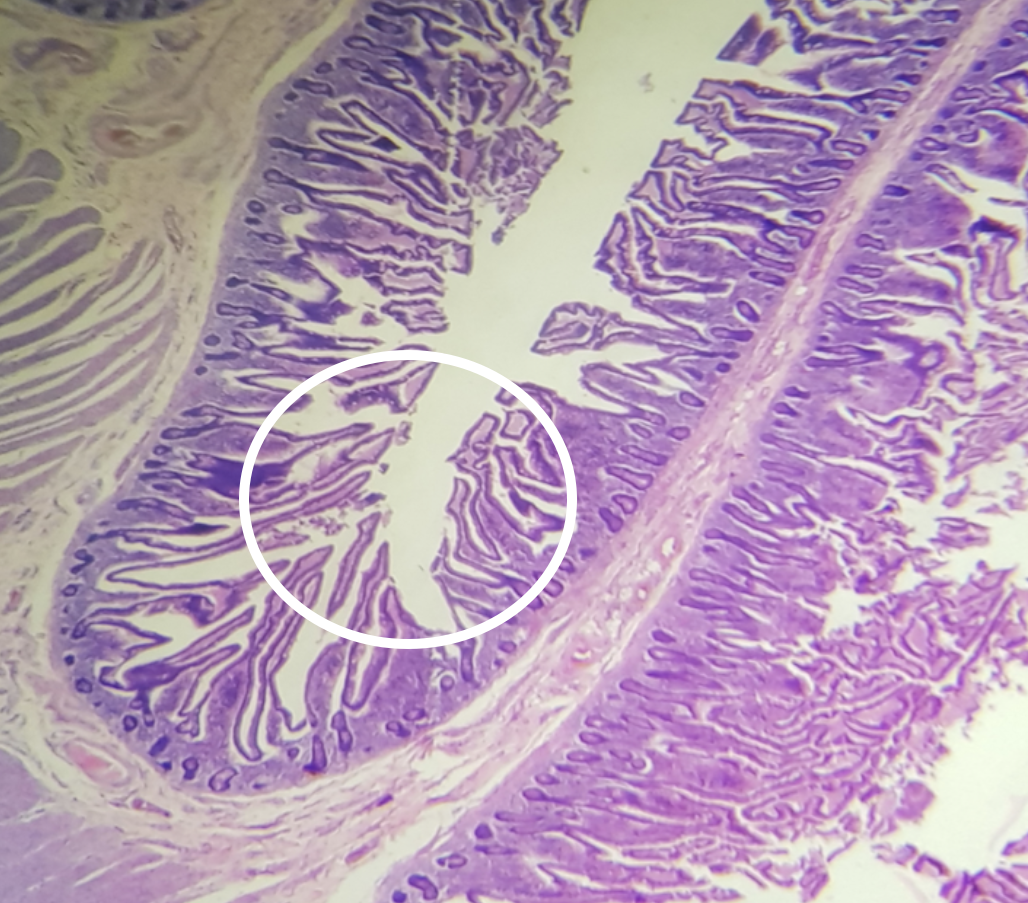
Identify the encircled structure
plicae circularis
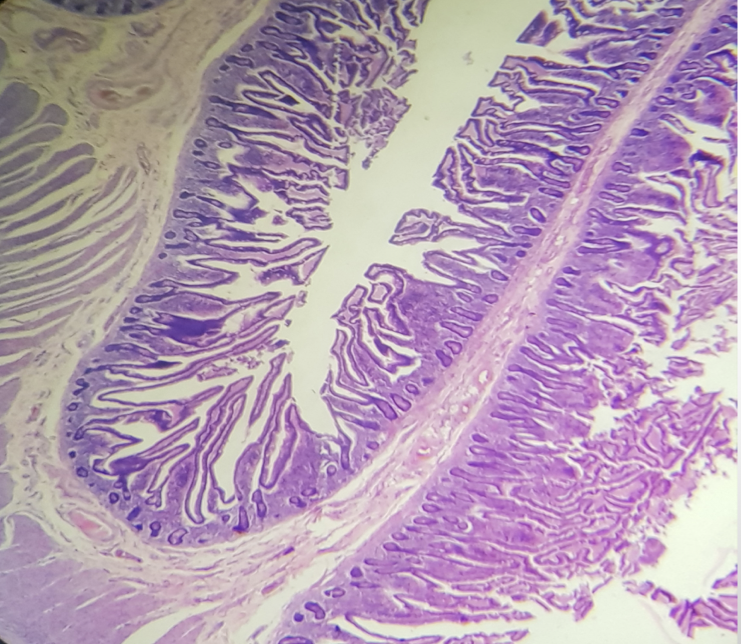
Function of the encircled structure
To increase the amount of surface area available for nutrient absorption
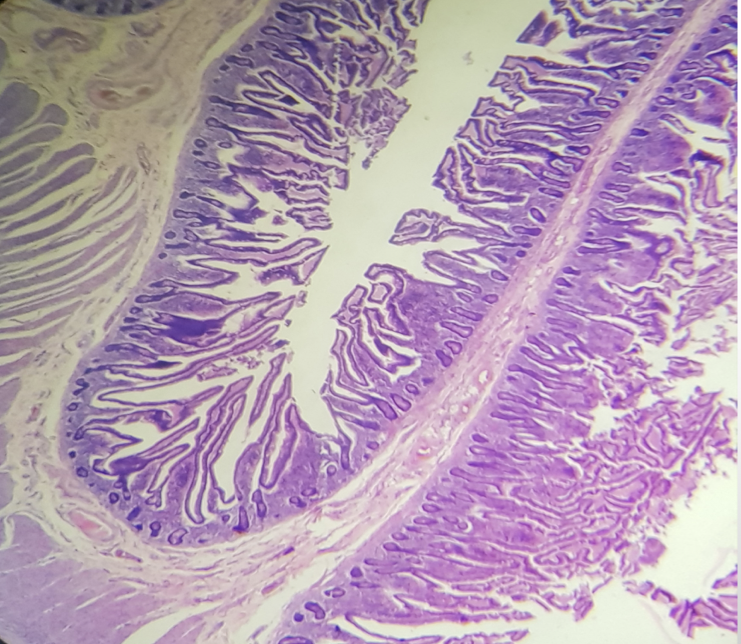
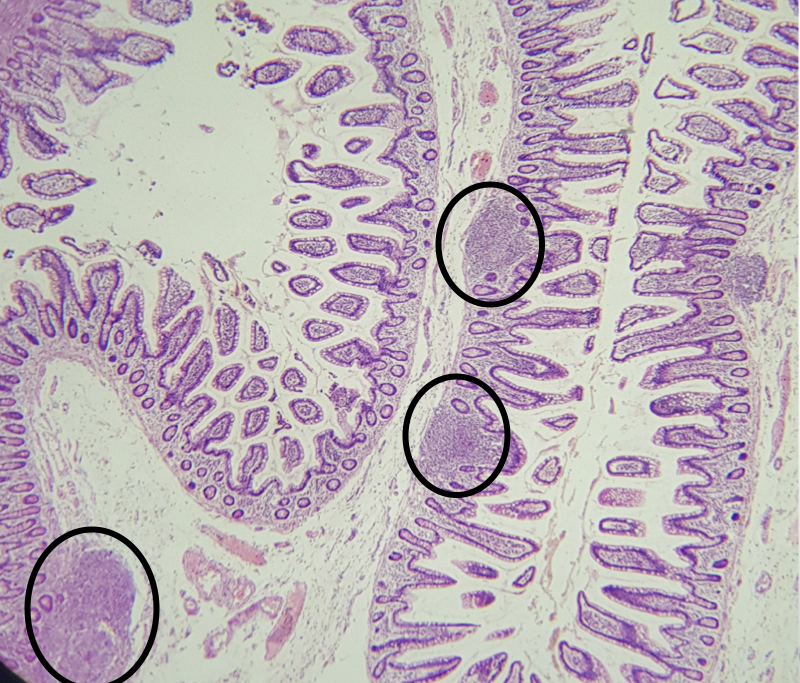
Identify the segment
Ileum