T1 L1 Introduction to anatomy
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
what is anatomy
study of the structure of our bodies which involves:
osteology
gross anatomy
imaging
surface anatomy
embryology
anatomical position
Standing/ lying supine
Face forward
Feet together facing forward
Arms by side with palms up
(supinated)Penis erect
anatomical planes
sagittal= split right to left (down nose)
coronal= split front to back (down ears)
transverse= split top superficto bottom
superficial vs deep
superficial- close to surface of body
deep- further from surface of body
medial vs lateral
medial- towards middle of body
lateral- towards side of body
posterior vs anterior
posterior- towards the back of the body
anterior- towards the front of the body
dorsal and ventral
dorsal = posterior
ventral = anterior
inferior vs superior
inferior- below
superior- above
caudal vs cranial
caudal- towards the tail
cranial- towards the brain
proximal vs distal
proximal- nearer to the point of attachment
distal- further from the point of attachment
flexion vs extension
movement:
flexion- smaller angle
extension- larger angle
abduction vs adduction
movement:
abduction- towards midline
adduction- away from midline
pronation vs supination
movement:
pronation- palm downwards
supination- palm upwards
protraction vs retraction
movement:
protraction- anterior movement away from midline
retraction- posterior movement towards midline
elevation vs depression
movement:
elevation- superior movement
depression- inferior movement
circumduction
movement:
circumduction- movement in a circle
rotation
movement:
rotation- turn along a long axis
components of thoracic cage
thoracic vertebrae and intervertebral discs

sternum
ribs and costal cartilages
function of thoracic cage
protection of viscera (soft internal organs)
muscle attachment
relations of thoracic cage
pectoral girdle (clavicle/scapula)
parts of sternum
manubrium (green)
body (blue)
xiphoid process (purple)
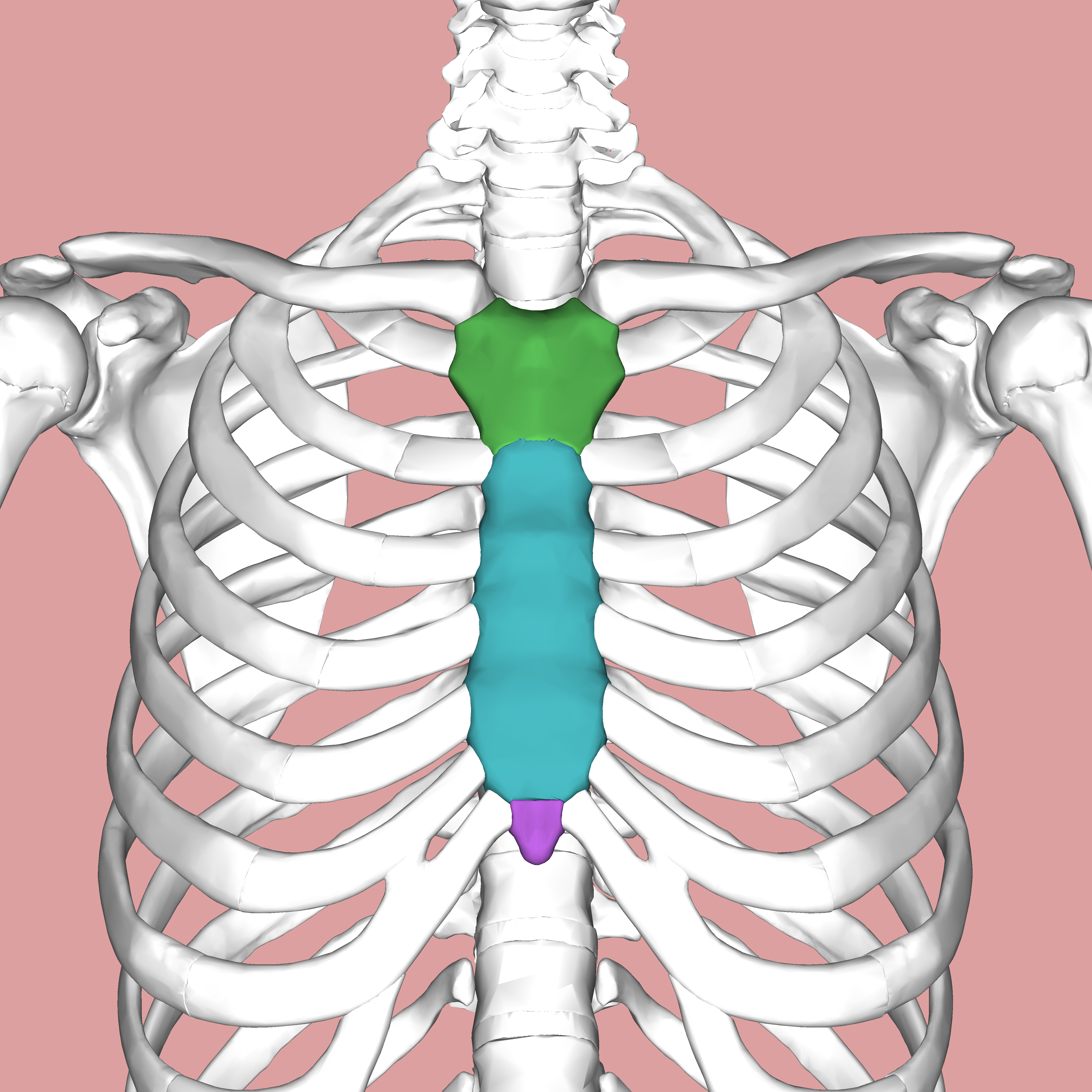
where is the sternal angle
junction between manubrium and body- palpable bony landmark
2nd rib joins to sternum at sternal angle
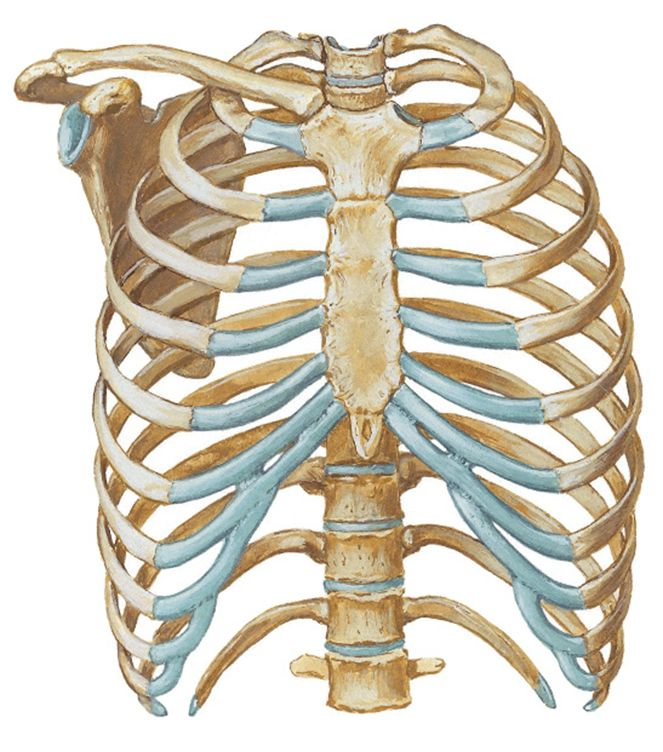
costal cartilage


(in blue)
12 pairs of ribs
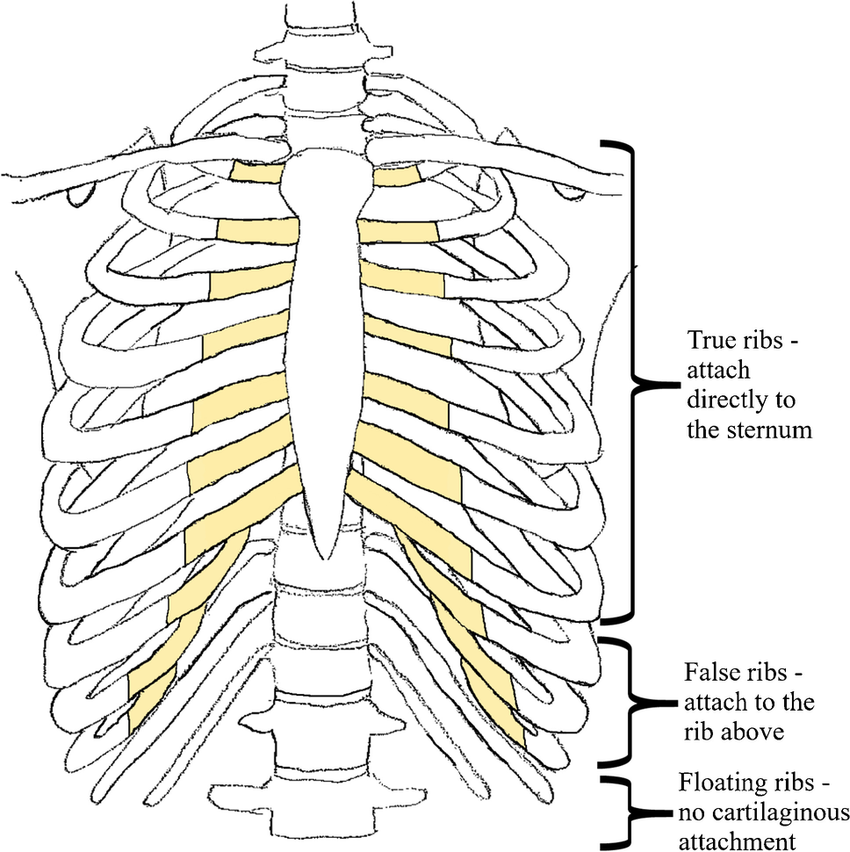
classification of ribs
true- cartilage directly to the sternum (pairs 1-7)
flase- cartilage looping up to rib above (pairs 8-10)
floating- no cartilage + at back (pairs 11 + 12)
what is the costal margin
margin formed by lower costal cartilages as they join rib above (7th pair)
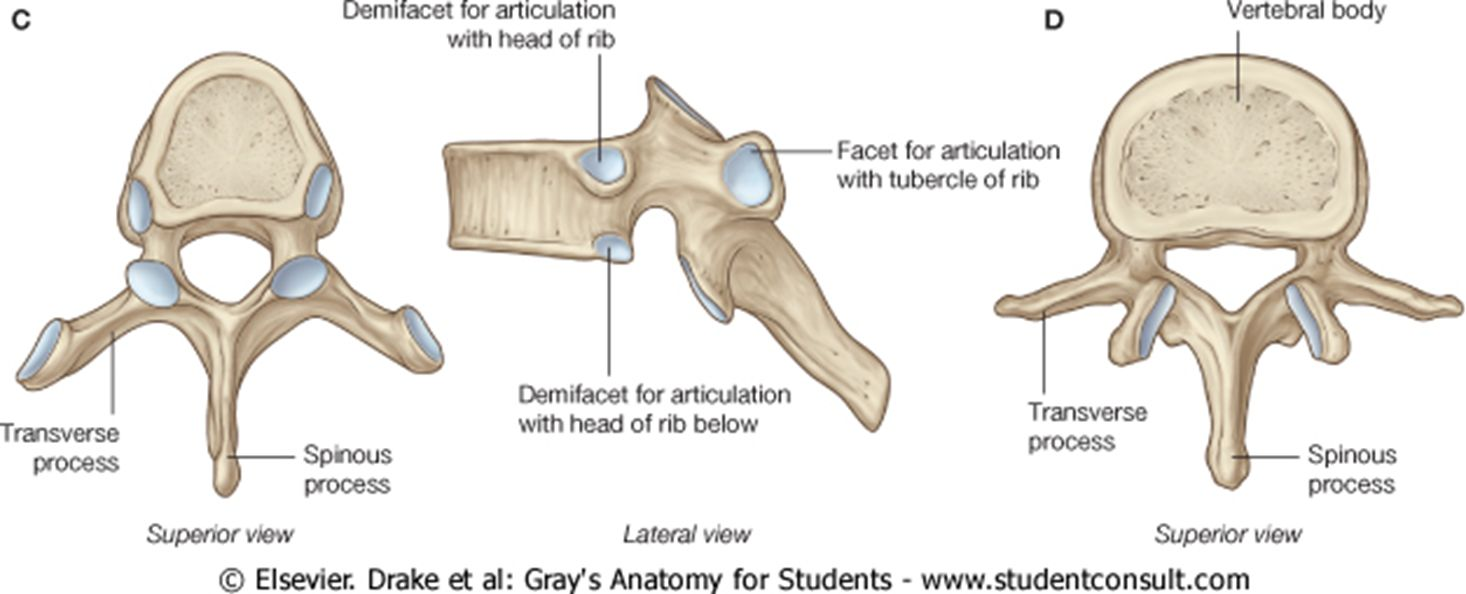
typical vs atypical ribs
typical: has head with 2 facets, angle, tubercle, body with costal groove and joins to cartilage
- 3rd to 9th pair
atypical: 1st, 2nd, 10th, 11th and 12th pair
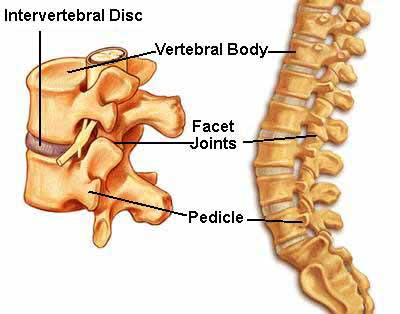
thoracic vertebrae parts
heart shaped body with demi facets
costal facets of transverse process
inferior pointing spinous processes
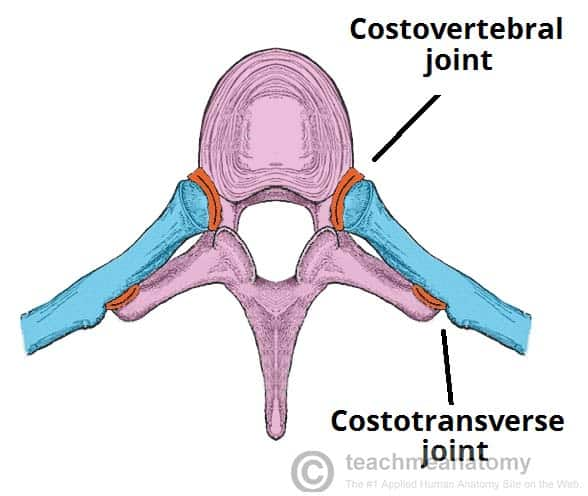
joints of thoracic cage
sterno-costal = cartilaginous- rib to sternum
costo-chondral = cartilaginous- cartilage to rib
costo-vertebral= synovial- head of rib with demi facets to vertebrae and IV disk
exceptions 1st, 11th and 12th which only articulate
with one vertebrae: T1, T11, T12 respectively.
costo-transverse= synovial- tubercle of rib to transverse processes
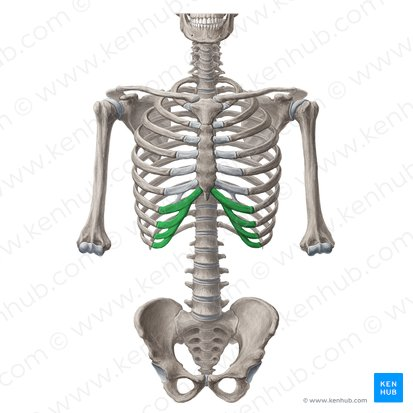
intercostal muscle
11 on right side
11 on left side
Clinical relevance:
5th intercostal space in midclavicular line on
left hand side =
Surface landmark for the Apex of the Heart
layers of intercostal muscles
external intercostals
internal intercostals
innermost intercostals
Supplied by an intercostal artery, vein and nerve
which run in the (sub)costal groove of each
intercostal space
arterial supply of thoracic cage
posterior intercostal arteries- from aorta
anterior intercostal arteries- from internal thoracic artery- branch of subclavian artery
Venous drainage via azygos and hemiazygos