Midterm 2 ARTHC 201 Flashcards (Winter 2024)
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
ID this image
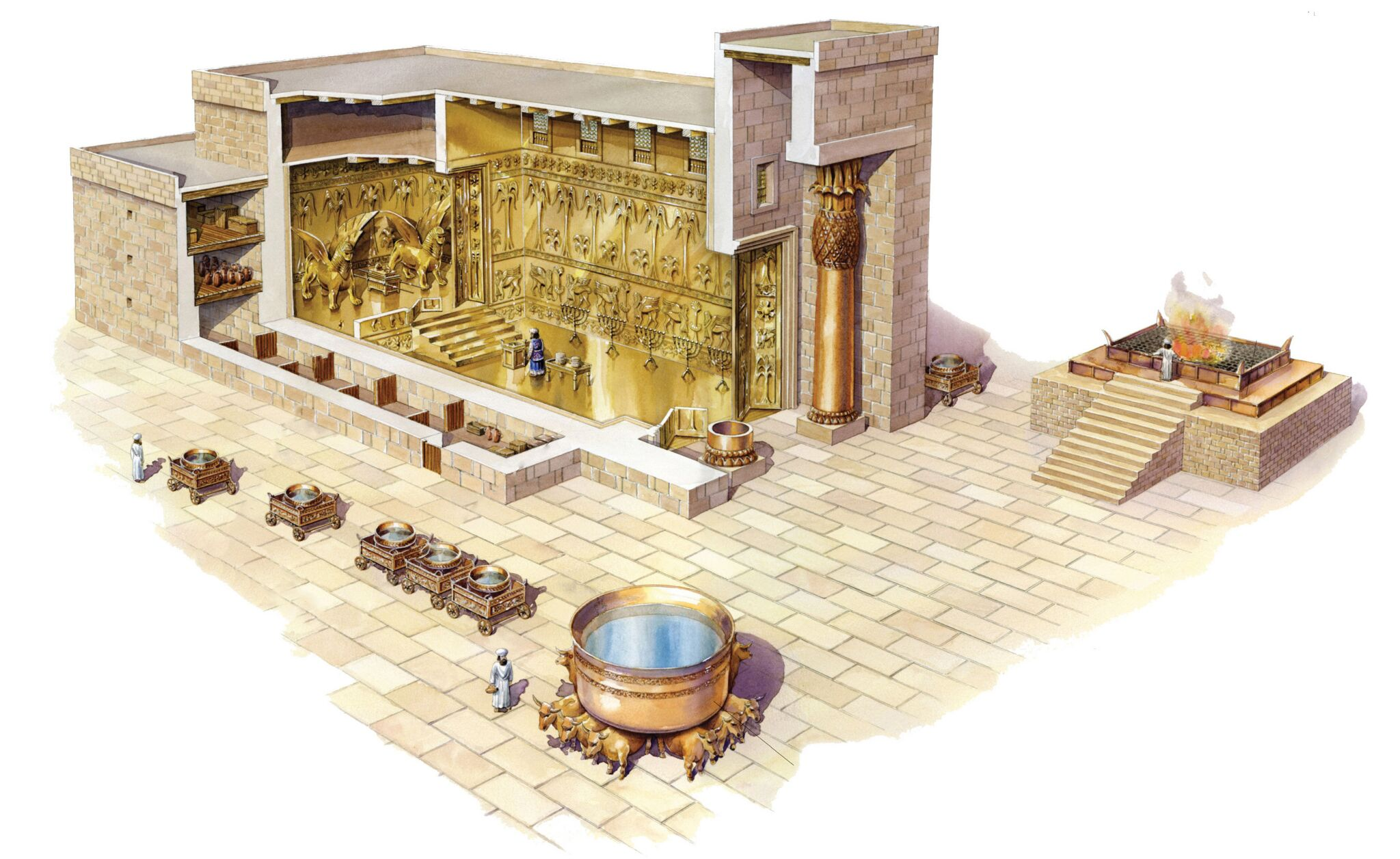
Title: Solomon’s Temple
City: 10th century BCE
Date: Jerusalem
Discuss “Solomon’s Temple”
Oriented to the east - the rising sun
Courtyard contained themes related to the Garden of Eden and Creation - decor of trees and flowers
Destroyed by Babylonians
Location was believed to have been where Abraham attempted to sacrifice Isaac
Included auxilary courts and storehouses
Two large cherubium stood to guard to the Ark of the Covenant in the Holy of Holies
Temple was meant to be a dwelling place for (the name of) God
Likely once elevated → represented getting closer to heaven and God
Located on top of the hill → closer to heaven and God

ID this image
Title: Moses’s tablernacle
City: Sinai wilderness and the Levant
Date: 1200 BCE
Discuss “Moses’s Tabernacle”
A moveable tent shrine intended to be used by migrating Israelites
Courtyard was separated by a fence and gate of white linen
Three zones of sanctity:
Holy of Holies
Perfect cube shape
Only the high priest could enter
Finely woven blue, scarlet, and purple linen separated this space → symbolic of
Housed the Ark of the Covenant
Represented the presence of God (not a graven image)
Holy Place
Insense altar
Table of the bread
Lampstand (Menorah)
Outer Court
Open to the sky
Laver → purification
Great Altar → sacrifice
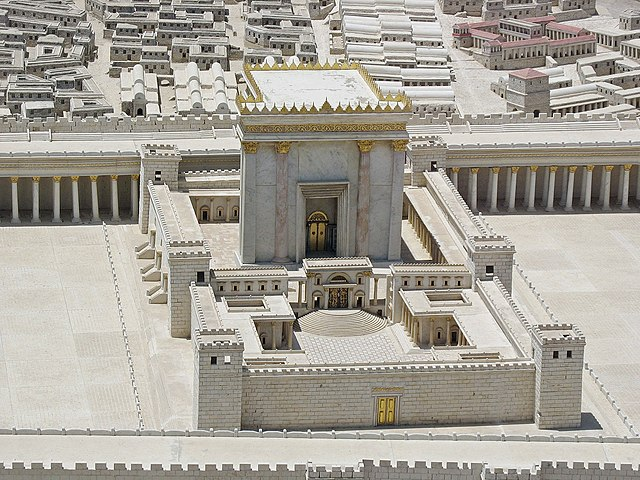

ID this image
Title: Herod’s Temple
City: 50 CE
Date: Jerusalem
Discuss “Herod’s Temple”
Built with gleaming/blinding white marble
Believed to have been the center of beauty, both economic and spiritual
A statement of the political power of Herod
Placed in the middle of where lots of exchange would happen
Lectures, teaching, etc. would happen here → exchange of ideas and intellect
Marketplace → exchange of goods
Temple → exchange of religious ideas
Contained multiple different courts, but also still had the three main sections
Zones of holiness get increasing more narrow → cuts or sacrifices to become more righteous/holy
Didn’t have the Ark of the Covenant → lost and destroyed after pilaging
Instead had the main rock, where the Dome of the Rock now resides

ID this image
Title: Interior of the Duro Europos Synagogue
City: Dura Europos, Syria
Date: 250 CE
Discuss “Interior of the Duro Europos Synagogue”
Heiratic scale → prophets are depicted larger and the hand of God is much larger
Imagery is very Roman inspired → Roman togas, Roman facial features, etc.
Ethereal and flat → floating in the air
We want to depict the point of the story, not give an illusion or trick of the eye
Lots of Biblical scenes depicted all over the wall
Earliest preserved Christian/Jewish imagery
Included the orant gesture → raising of hands up to God in prayer
Torah was stored under the niche/arch in the main synagogue room
Contained a shell → Greek motif that represented Aphrodite, goddess of love
Symbolized this is a building of love and worship to God → no animal sacrifices here
ID this image
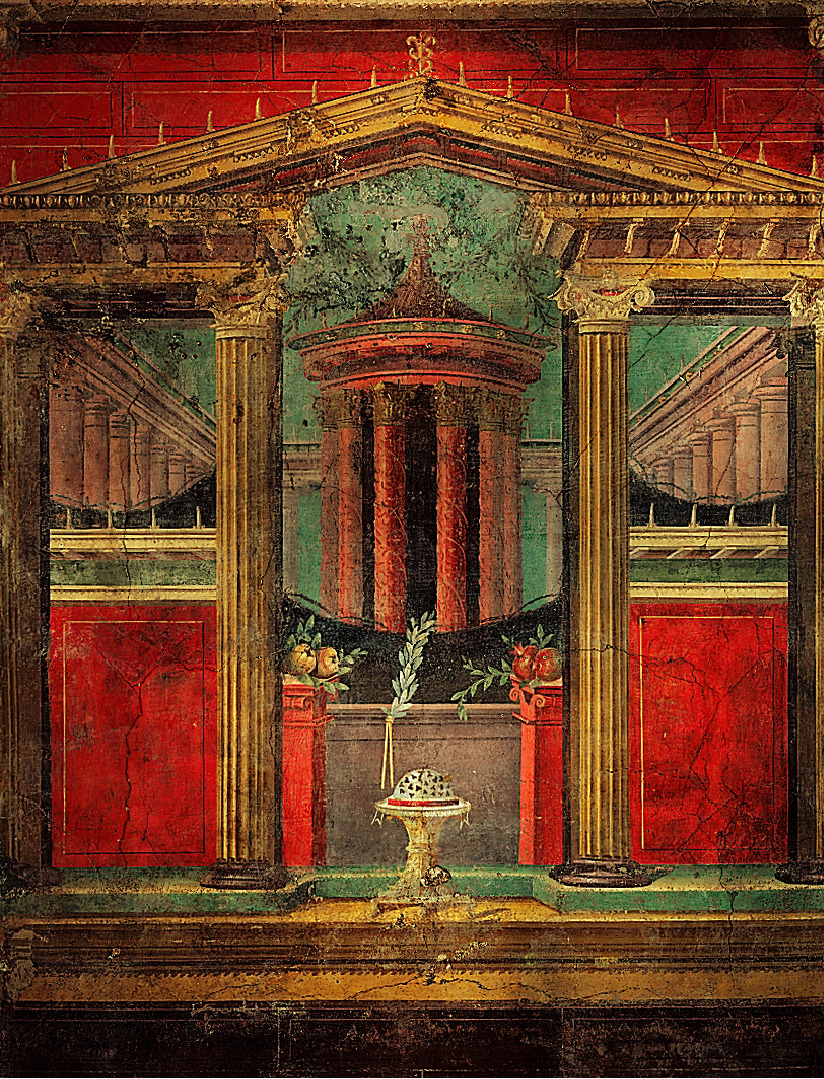
Title: Second style wall paintings from cubiculum M of the Villa of Publius Fannius Synistor
City: Boscoreale, Italy
Date: 50-40 BCE
Discuss “Second style wall paintings from cubiculum M of the Villa of Publius Fannius Synistor”
Second style → focus/emphasis was on disolving the walls to create an illusion of a 3D world
Created towns, temples, colonaded courtyards, etc.
Used linear perspective → it went deep into the wall (depth)

ID this image
Title: Christ blessing
City: Mount Sinai
Date: 6th century CE
Discuss “Christ blessing”
Blessing gesture
Represents the idea of the polymorphic Jesus → people see Jesus differently than someone else might

ID this image
Title: Mummy portrait of a priest of Serapis
City: Faiyum, Egypt
Date: 150 CE
Discuss “Mummy portrait of a priest of Serapis”
Perhaps painted while the inidivudal was alive, then cut down to fit in mummy cases
Colors mixed with hot wax → encaustic
Curls of the hair → artist’s expertise in creating texture with the materials they have
Very Roman, but the corkscrew curls identify him as a follower of Serapis
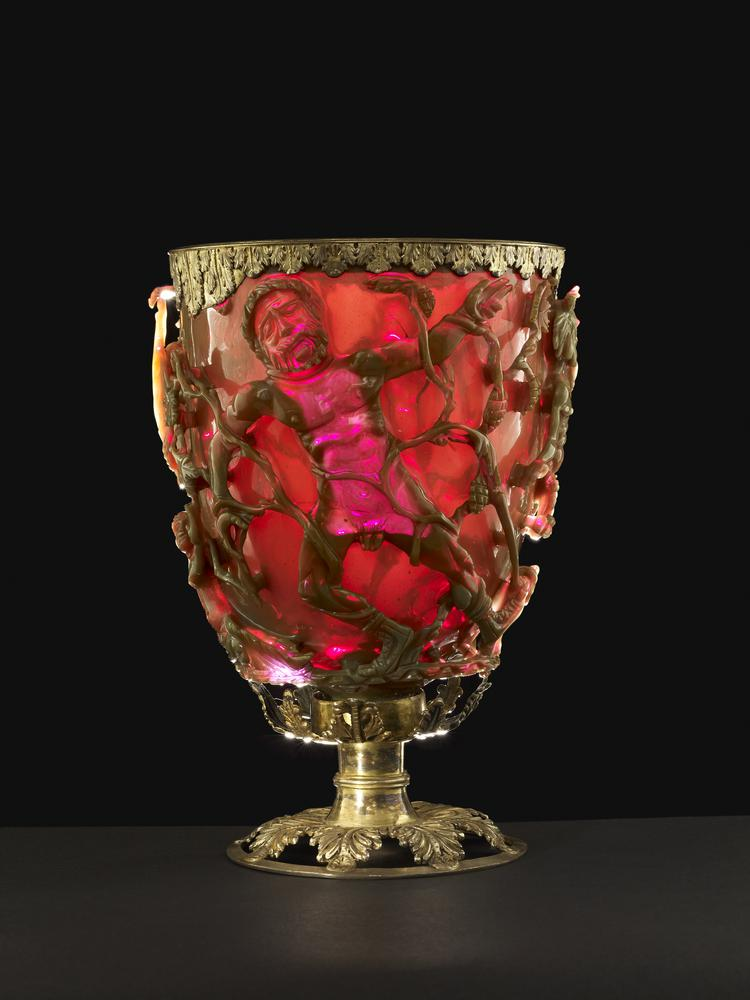

ID this image
Title: The Lycurgus Cup
City: The British Museum, London (findspot unknown)
Date: 4th century CE
Discuss “The Lycurgus Cup”
Made with glass → Roman glassworkers put stuff in the glass so that it would turn to the red color
Story is that King Lycurgus was cursed by Bacchus and hallucinates, attacking a nymph, who turns into a vine and shackles the king, who sees serpents and in an attempt to fight them off, he cuts off his own foot → he becomes a shade in the underword
Shade in the underworld = some definitions, shade is the inside of a cup
The work of the cup makes us “hallucinate” or imagine the rest of the story

ID this image
Title: Rosanno Gospels
City: Diocesan Museum, Rosanno Cathedral
Date: 6th century CE
Discuss “Rosanno Gospels”
Dyed parchment or dyed lamb skin
Represents the blood of the Lamb of God → it made the book physically holy
Pages were gilded with gold and silver
Contained the earliest representation of Jesus in Gesthemane, but it took a long time to get this representation
There was this stigma against depicting a god or holy being as suffering because it was thought to be “weak”, so many descriptions of Jesus suffering in Gesthemane were erased and lost
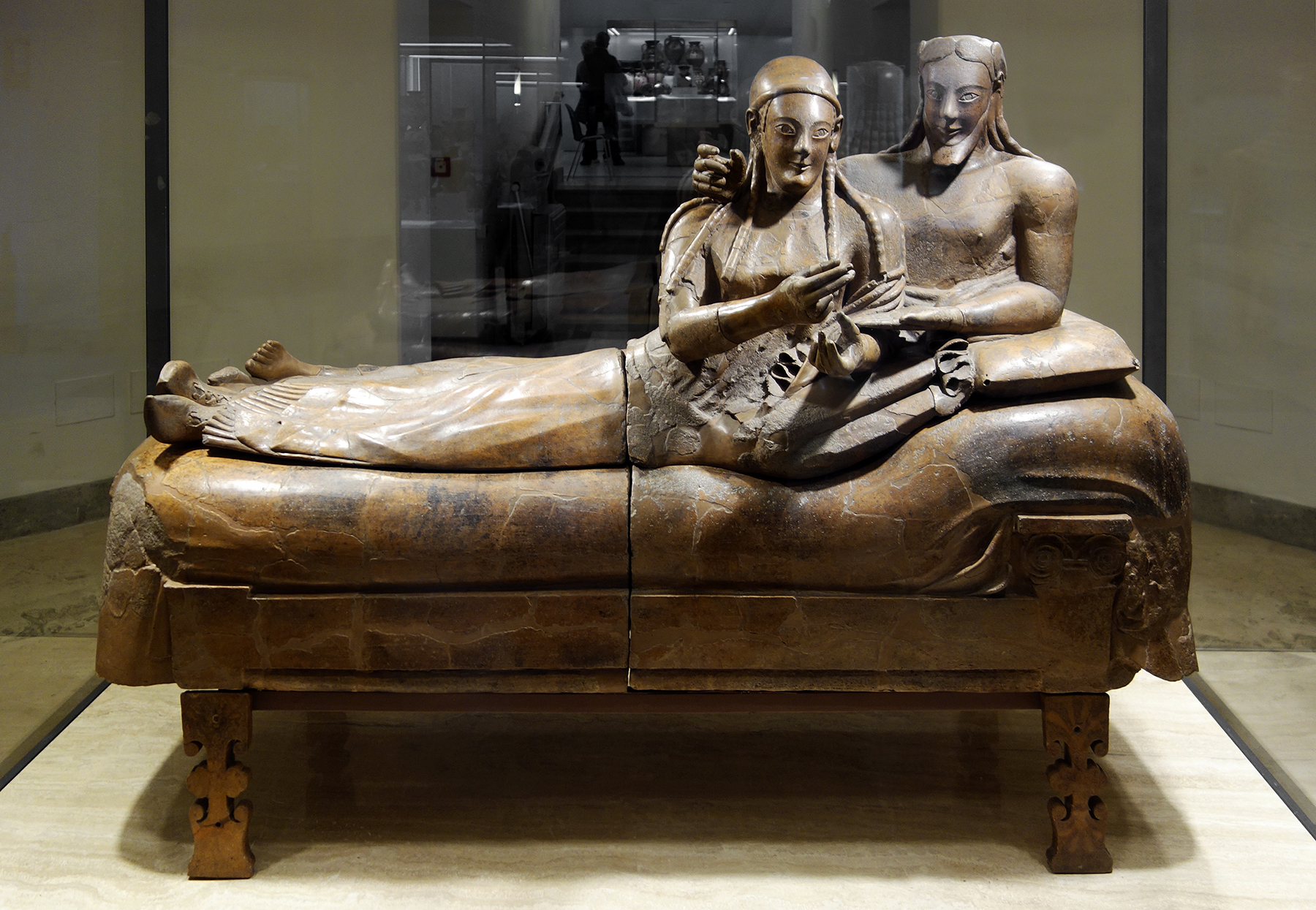

ID this image
Title: Sarcophagus with reclining couple
City: Cerveteri, Italy
Date: 520 BCE
Discuss “Sarcophagus with reclining couple”
Husband and wife recline on a banqueting couch
Once brightly painted
The man embraces his wife while she speaks, listening to her
Uniquely Etruscan → Etruscan women had more rights than other cultures at that time
More of a focus on the upper half of the body → more detail, more realistic

ID this image
Title: Apulu, from the roof of the Portonaccio temple
City: Veii, Italy
Date: 500 BCE
Discuss “Apulu, from the roof of the Portonaccio”
Painted in gold and yellow → sun would cause the statue to glitter
Abstract → we understand what is depicted, but it also beyond comprehension and not from the mortal realm
Not nude! → Etruscan
There is a slight movement of one leg forward, more weight on the frontal leg
Would have been displayed fighting Hercules
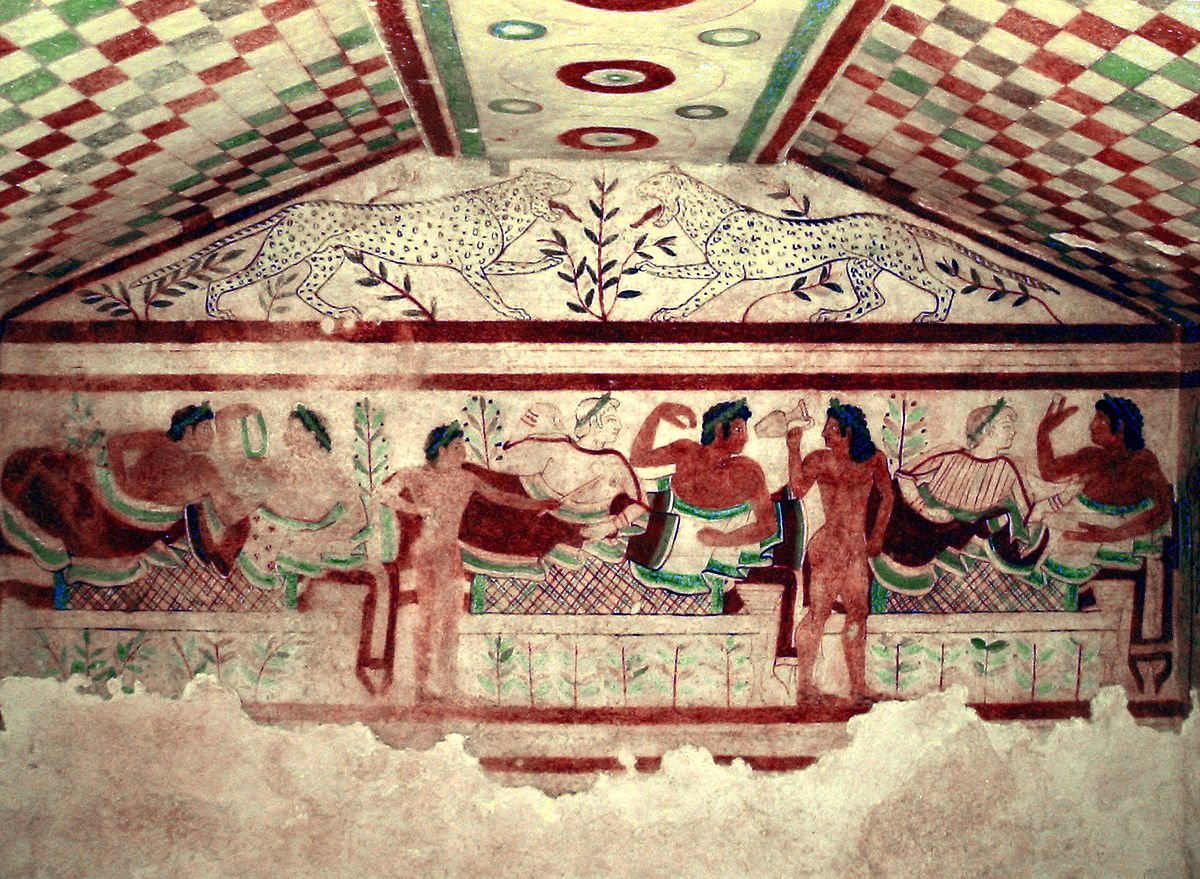

ID this image
Title: Interior of the Tomb of the Leopards
City: Tarquina, Italy
Date: 480 BCE
Discuss “Interior of the Tomb of the Leopards”
Once very brightly colored → meant to be eye catching
Painted in fresco → last for a long, long time
The multicolored patterned ceiling reflects the Etruscan belief that heaven was made up multicolored gems
Depicts banqueting couples, musicians, etc.
A celebration of life, not a somber grief in the loss of someone
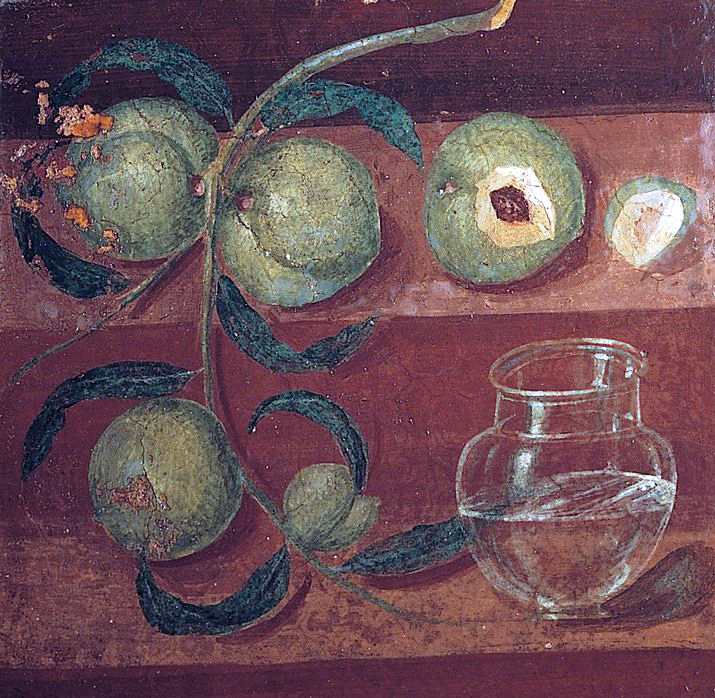

ID this image
Title: Still life with peaches, detail of a Fourth Style wall painting, from the House of the Stags
City: Herculaneum, Italy
Date: 70 CE
Discuss “Still life with peaches, detail of a Fourth Style wall painting, from the House of the Stags”
Fourth style
Brings together all the styles from beforehand → figures in illusionistic architecture
Painter showed off mastery of realism with shadows and light on the fruit
Emphasis on realism → wanted it to look like you could pluck it right off the wall

ID this image
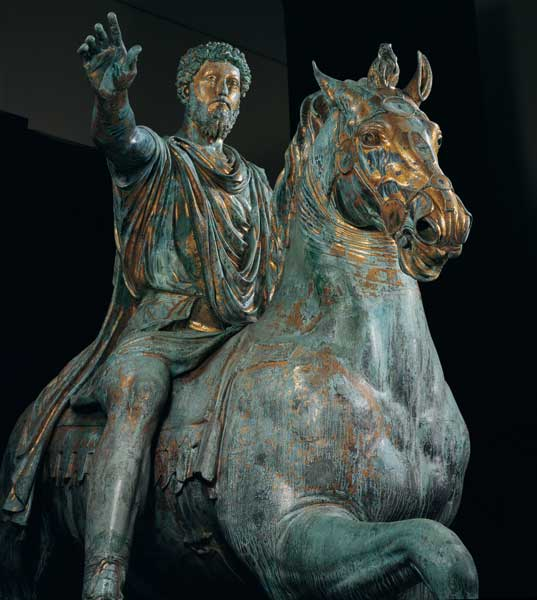
Title: Equestrian Statue of Marcus Aurelius
City: Rome, Italy
Date: 175 CE
Discuss “Equestrian Statue of Marcus Aurelius”
Proportionally larger than his horse (not realistic)
God-like dignity
Heiratic scale
Right arm is stretched out → symbol of greeting and clemency
Originally would have had an enemy beneath the horse, begging for mercy
Survived the period when bronze statues were melted down because it was thought to have been a statue of Constantine
Was one of the first emperors to depict himself like his enemies → curly, long hair, bearded, etc.
Seeing himself through the eyes of his enemies and had compassion on his enemies
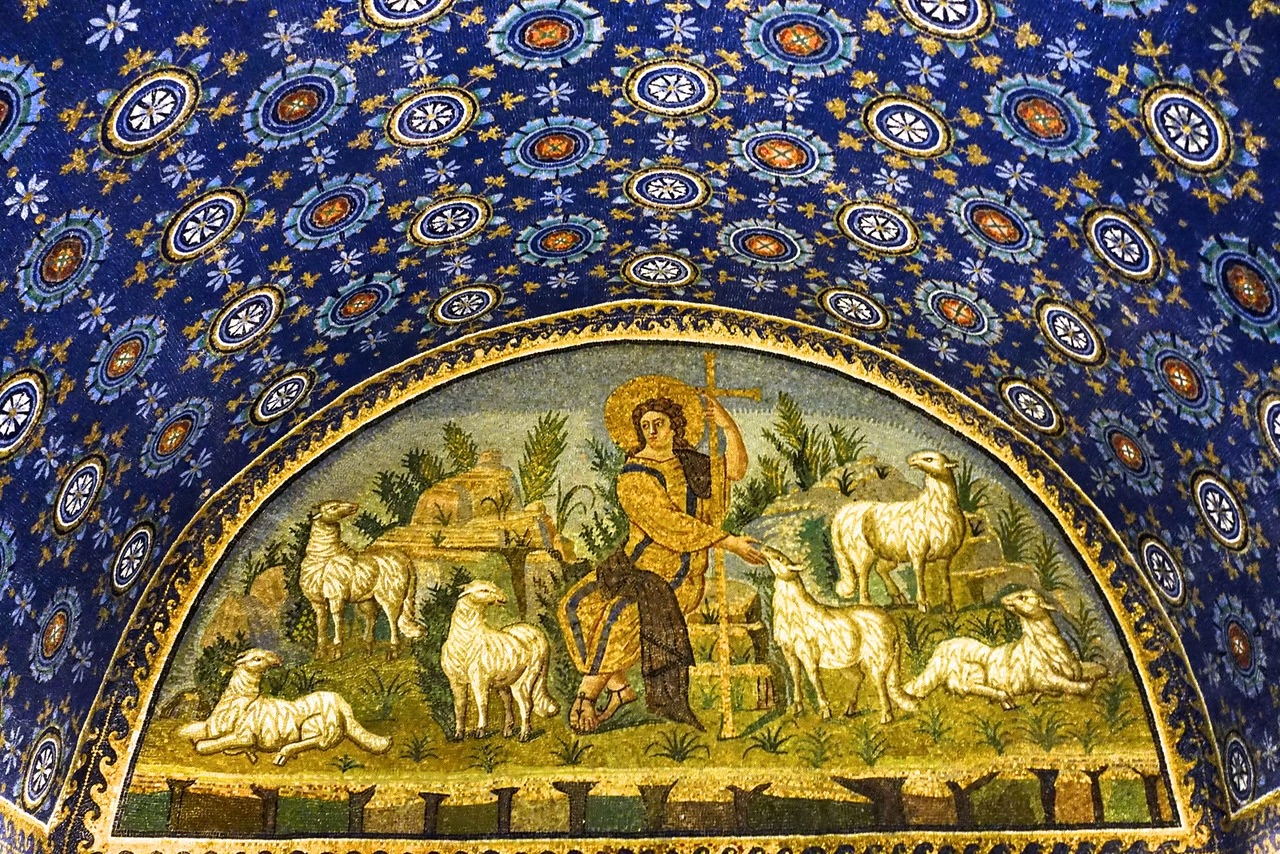

ID this image
Title: Christ as a Good Shepherd, mosaic from the entrance wall of the Mausoleum of Galla Placidia
City: Ravenna, Italy
Date: 425 CE
Discuss “Christ as a Good Shepherd, mosaic from the entrance wall of the Mausoleum of Galla Placidia”
Jesus sits among the flock with a golden halo and purple and gold robes
Represents his power, leadership, and holiness
Lots and lots of detail in the mosaic → characteristic of Late Antique
In a background, not the golden backdrop of heaven
Very dark interior with candlelight would have created a great effect where the gold in the tesserae interact and glitter → idea of transformation

ID this image
Title: Transfiguration, mosaic in the apse of the Church of the Virgin, monastery of St. Catherine
City: Mount Sinai, Egypt
Date: 550 CE
Discuss “Transfiguration, mosaic in the apse of the Church of the Virgin, monastery of St. Catherine”
Christ in the center, hovering in the air
Gold background → represents heaven
No shadows → this is not the natural world
Almost appears like an eye with the band surrounding the mosaic
Above and below are icons that represent Christ → believed that as Christ descended from heaven, He took mutliple different forms
Located by the altar

ID this image
Title: The baker Terentius Neo and his wife, mural painting from house VII
City: Pompeii, Italy
Date: 70 CE
Discuss “The baker Terentius Neo and his wife, mural painting from house VII”
A metapicture - a painting about a painting
The painter purposefully shows the makeup on the woman’s face → ideals for women at the time
Woman touches stylus to her face → shows that she is elegant and beautiful in physical appearance and writing
Wax/stylus is the hasty rough draft and the scroll the man holds is the final product
Two individuals shown as creative, very well-educated individuals

ID this image
Title: First style mural painting Samnite House
City: Herculaneum, Italy
Date: late second century BCE
Discuss “First style mural painting Samnite House”
First style
Goal was to imitate costly marble panels through painted stucco
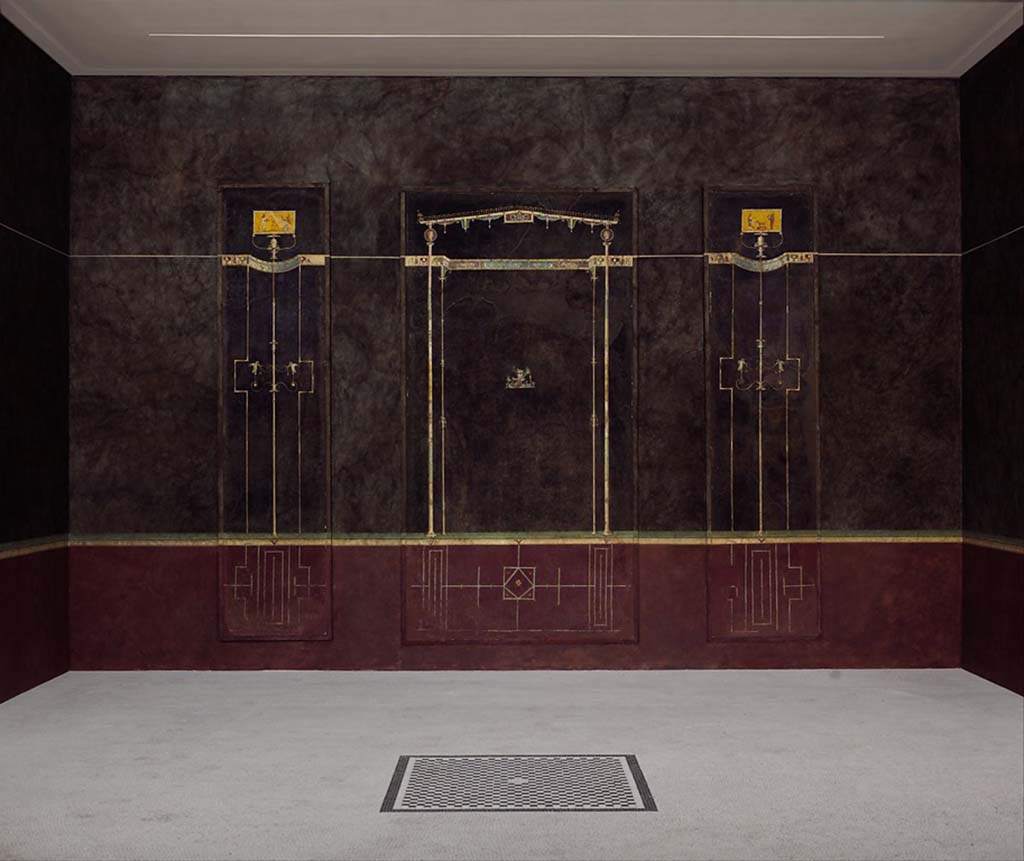

ID this image
Title: Third Style mural painting, from the Black room, Villa of Agrippa Postumos
City: Boscaetrucase, Italy
Date: 10 BCE
Discuss “Third Style mural painting, from the Black room, Villa of Agrippa Postumos”
Third Style
Monochromatic backgrounds with delicate, architectural fantasies (would be impossible to actually make)
Tiny, impossibly thin columns hold pediment-like roofs → architecturally impossible
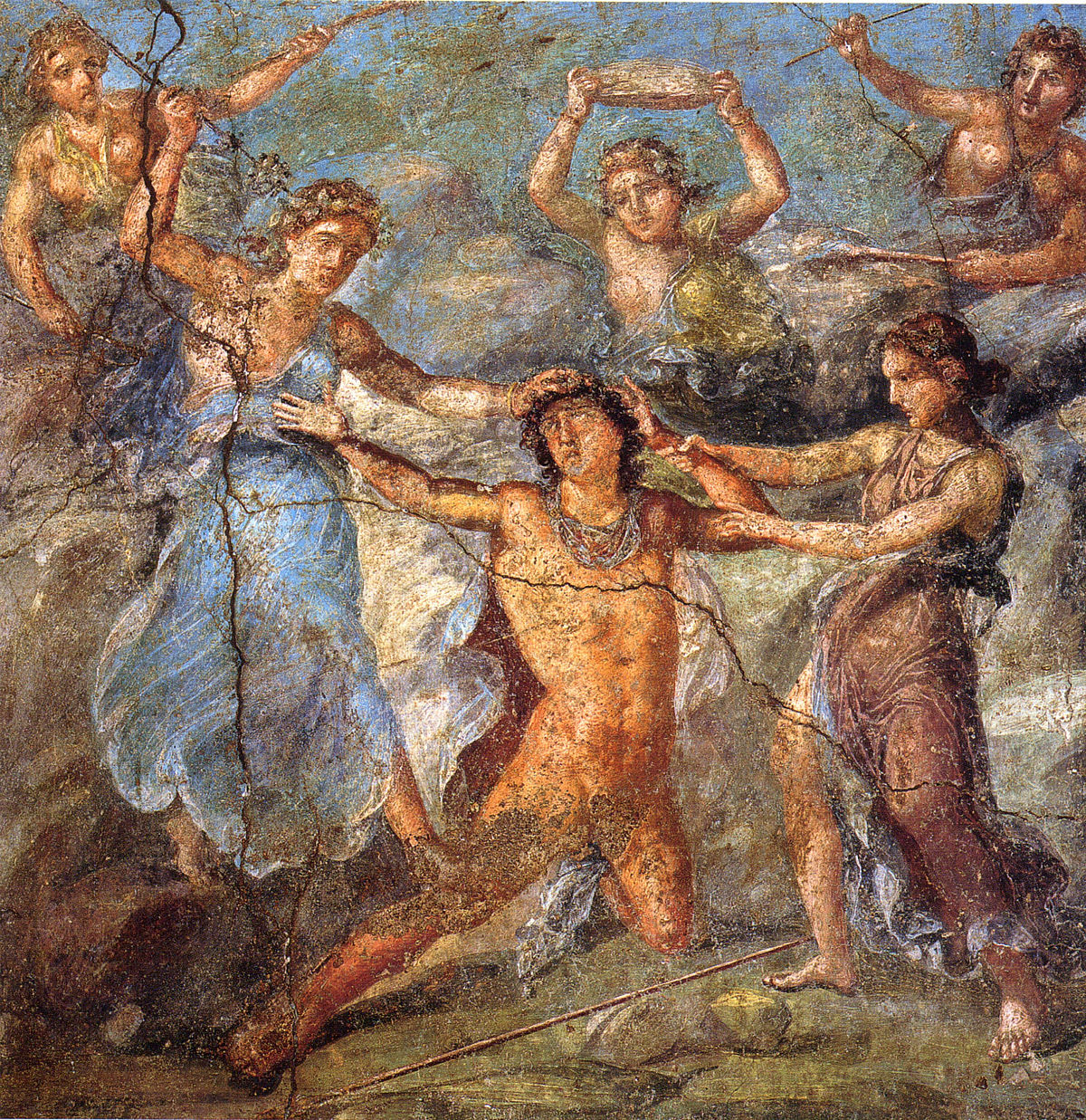

ID this image
Title: Fourth style mural paintings, Myth of Pentheus, Hercules, and Dirce, House of the Vettii
City: Pompeii, Italy
Date: 70 CE
Discuss “Fourth style mural paintings, Myth of Pentheus, Hercules, and Dirce, House of the Vettii”
Fourth Style
Combination of all previous styles → very colorful, crowded, and illusionistic
Fragmented architecture → mythological scenes interupt the architecture of the room
Art depicted hints at the myth, not depicting all of it → imagination/hallucination
On either side of the myth of Pentheus, Hercules is attached by snakes and Dirce is attacked by a bull
Creates a connection and illusion that Pentheus, is being torn apart by the female followers of Bacchus, is attacked by wild animals
What is a still life?
A picture depicting an arrangement of innanimate objects
What is a visual analogy?
A painting that symbolizes the artist’s intended subject
What is idealism?
A refined, “perfect” realism
What is verism?
A kind of rugged realism that shows who you are, sometimes exagerated
How is the soul represented in various forms of art? How do you use the body to represent the soul? What about animals?
Soul is shown by displaying the character of the individual, giving clues and details to that person
What is physiognomy?
Discerning the soul from the individuals’ physical appearance
What are the characteristic features of the 1st style in Roman art?
Immitating marbles and masonry
What are the characteristic features of the 2nd style in Roman art?
Illusionism → emphasis on depth and perspective to disolve the walls
What are the characteristic features of the 3rd style in Roman art?
Fantastical architecture with exotic motifs on monochromatic backgrounds
What are the characteristic features of the 4th style in Roman art?
A combination of all the previous styles, including living individuals in the illusionistic worlds
What does the imagery of Marcus Aurelius teach us about clemency? What is clemency?
A kind of mercy
Marcus Aurelius was someone who saw himself in the eyes of his enemies → didn’t see him as higher or better than them
What are the various ways that Roman artworks could animate beliefs? What role did materials play in these animations? What role does sensory experience play?
Art would transform or change
Discuss the similarities and differences between Etruscan, Greek, and Jewish temples
Why was the Arch of Titus constructed?
Commemorated the parade that celebrated Roman victory over the Jews
What rights did women have or not have in Etruscan culture?
Women could read and write, hold property, and couples were depicted together as a unit
What features and elements were characteristic of Etruscan art and sculpture?
Etruscans worked with terracotta and clothed their statues
Architecture had flatter, longer roofs and sculptures were on top of the roofs
What are the Greek, Roman, and Etruscan beliefs about marriage and life after death?
Etruscan
Believed that if you depicted objects in tombs, they would carry over into the afterlife
Held funerary games in celebration of life
What kind of portraits were popular during the Roman empire?
When does the commandment to “not make graven images” apply in ancient Judaism, particularly in the context of the temple?
What were the different approaches to art in the Jewish temples?
“Cult Images”
Figural Art
Abstract Images
Performative Images
Phenomenology
Discuss the evolution of the Jewish temple (features, symbolism, etc.)
How is the synagogue similar or different from temples?
What cultures use naturalism?
What cultures use abstraction?
What cultures use embodiment?
What cultures use animation?
What is the relationship between Byzantine art and naturalism and optical perspective?
In Greco-Roman and Byzantine culture, how do static images represent transformations? What are the artistic techniques?