Nuclear Model and Stability
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Atom
the basic building block of all matter
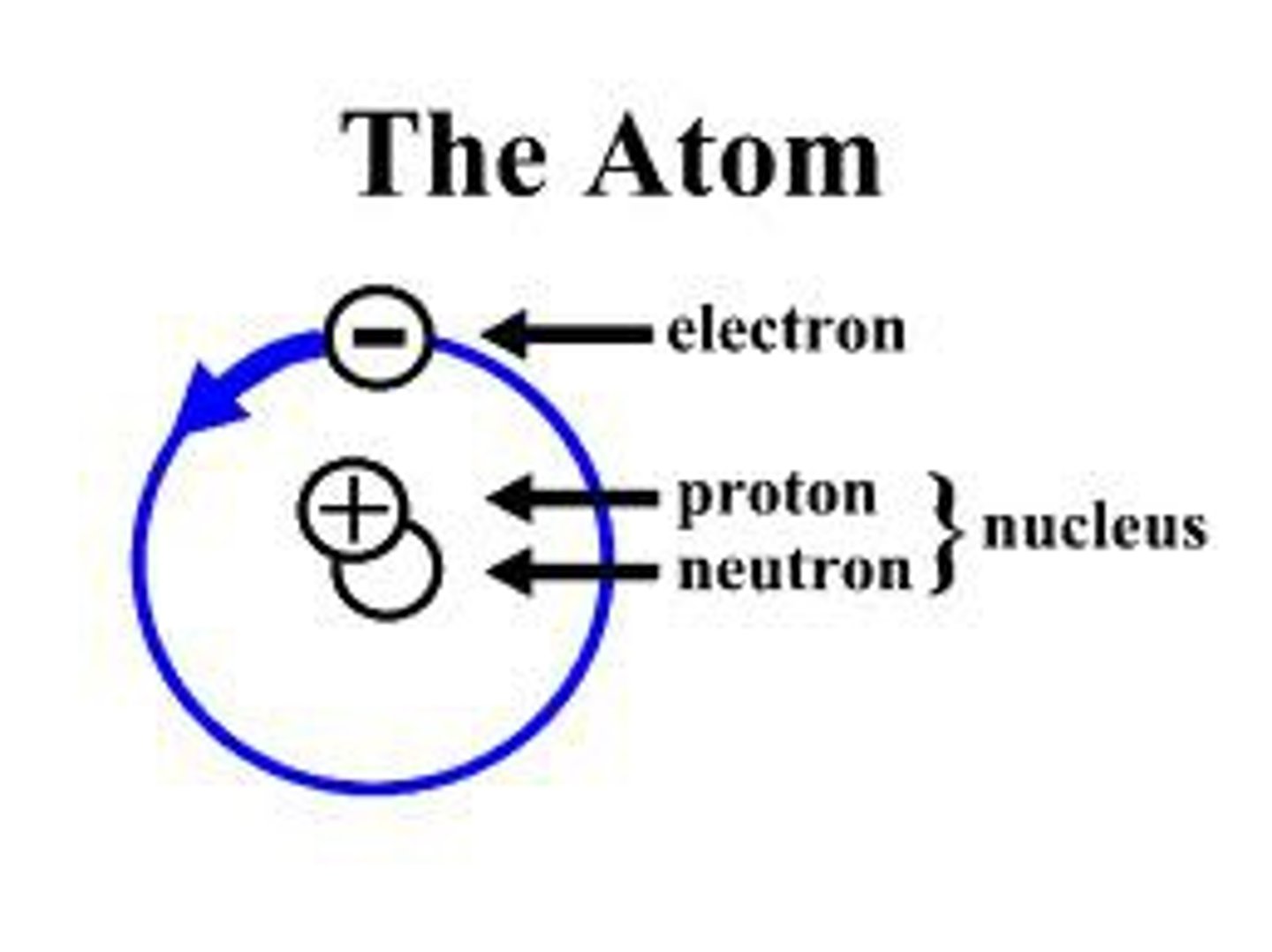
Nucleus of an atom
consists of positively charged protons and neutral neutrons, surrounded by much lighter negatively charged electrons.
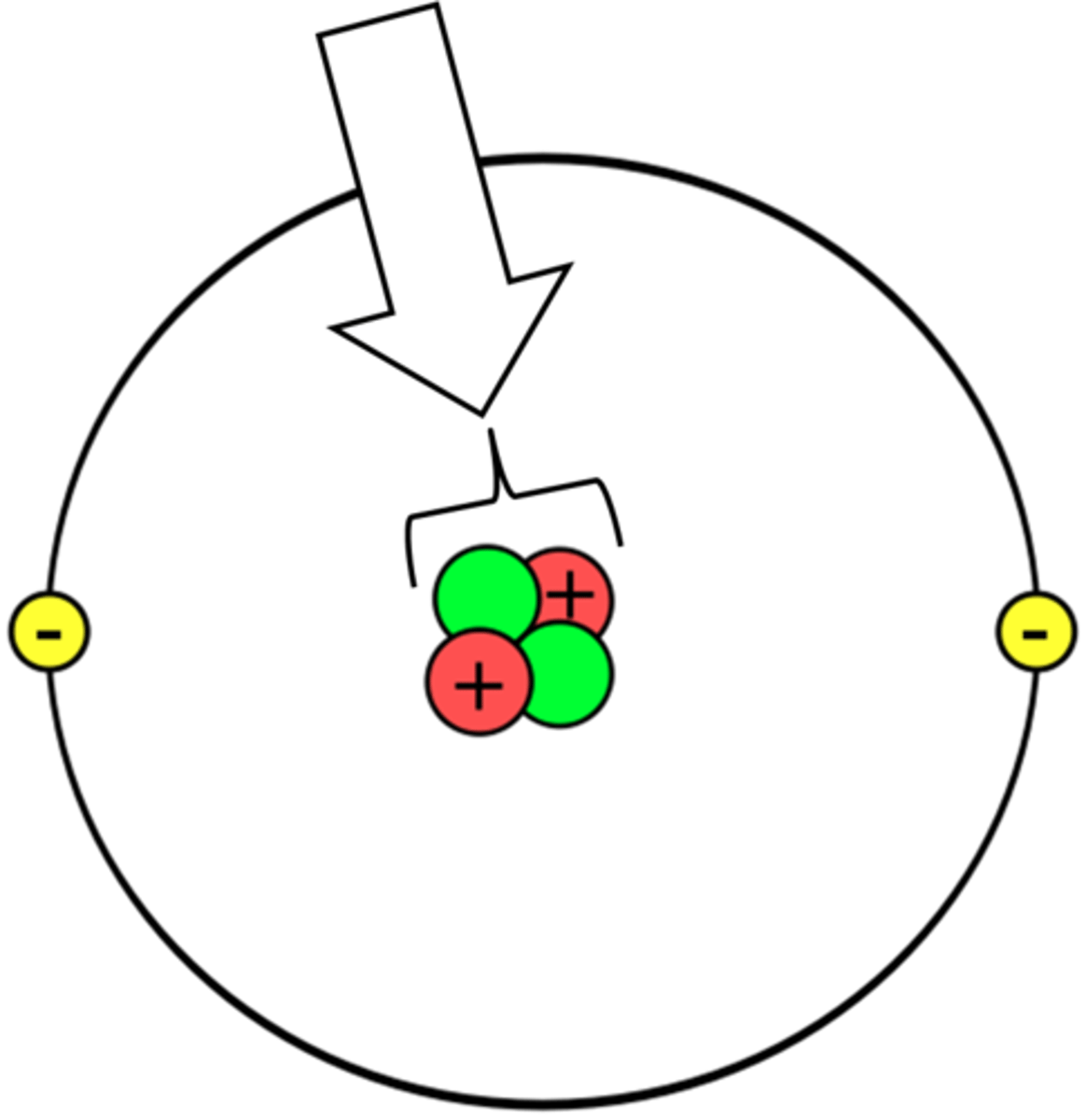
Protons
have a positive charge and a mass almost 2000 times the mass of an electron. The number of protons in the nucleus of the atom determines the element. eg. Hydrogen has one proton, Helium has 2 protons.
Neutrons
have no charge hence they are neutral.
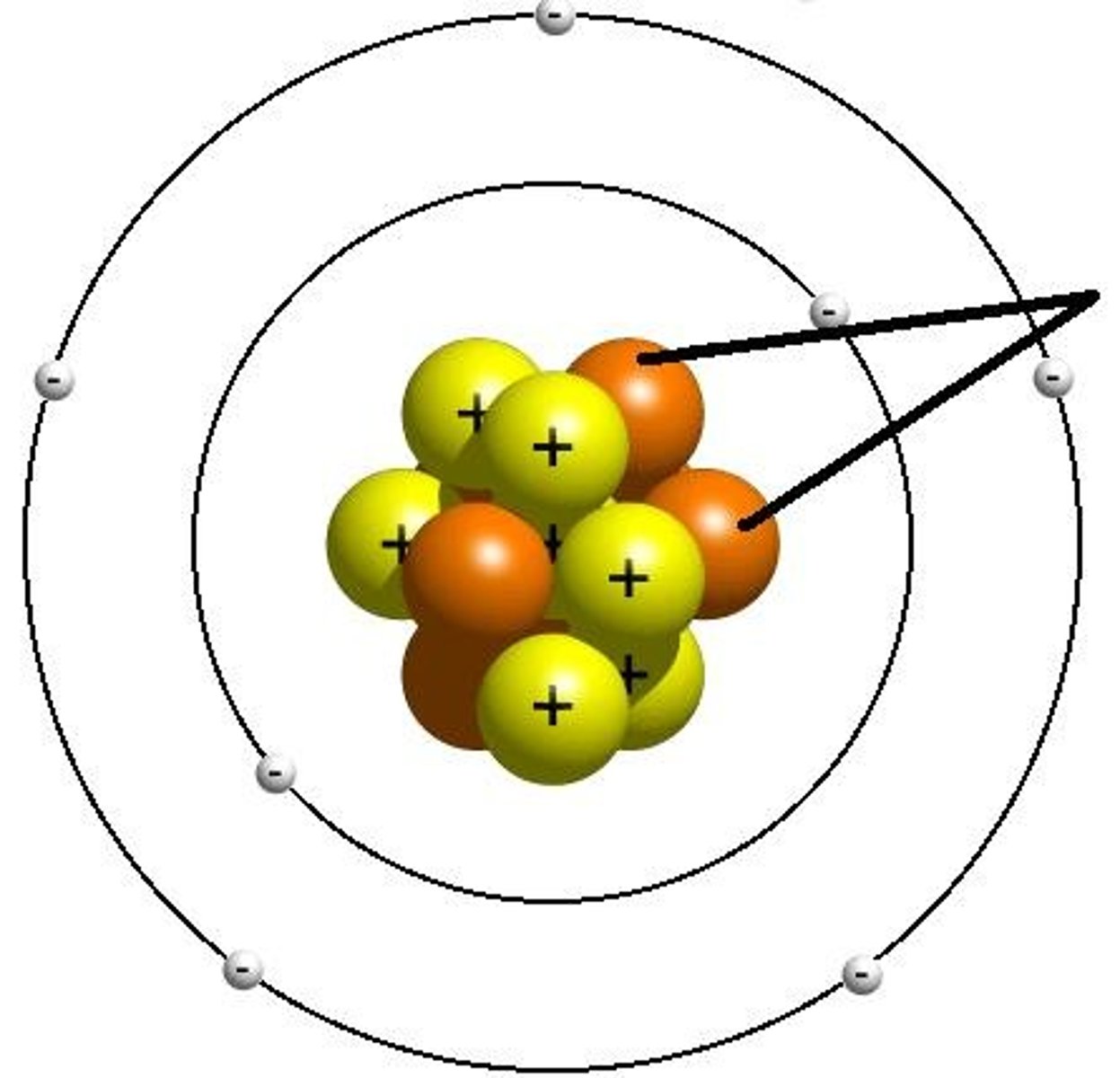
Electrons
have a negative charge and are significantly smaller than protons and neutrons.
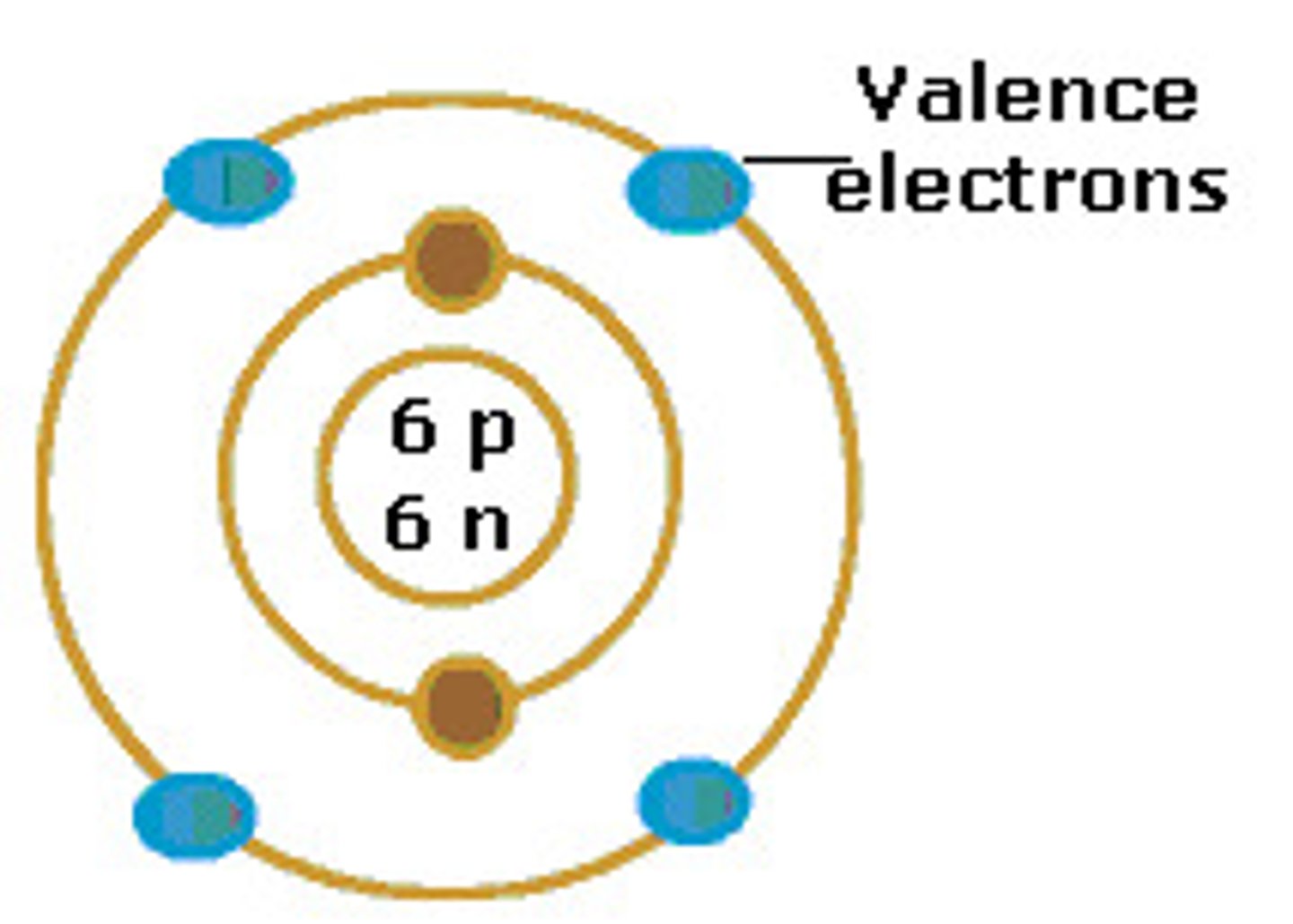
Nucleons
protons and neutrons comprise the nucleus
Nuclide
the nucleus protons and neutrons make up
atomic number, Z
the number of protons in a nucleus tells us
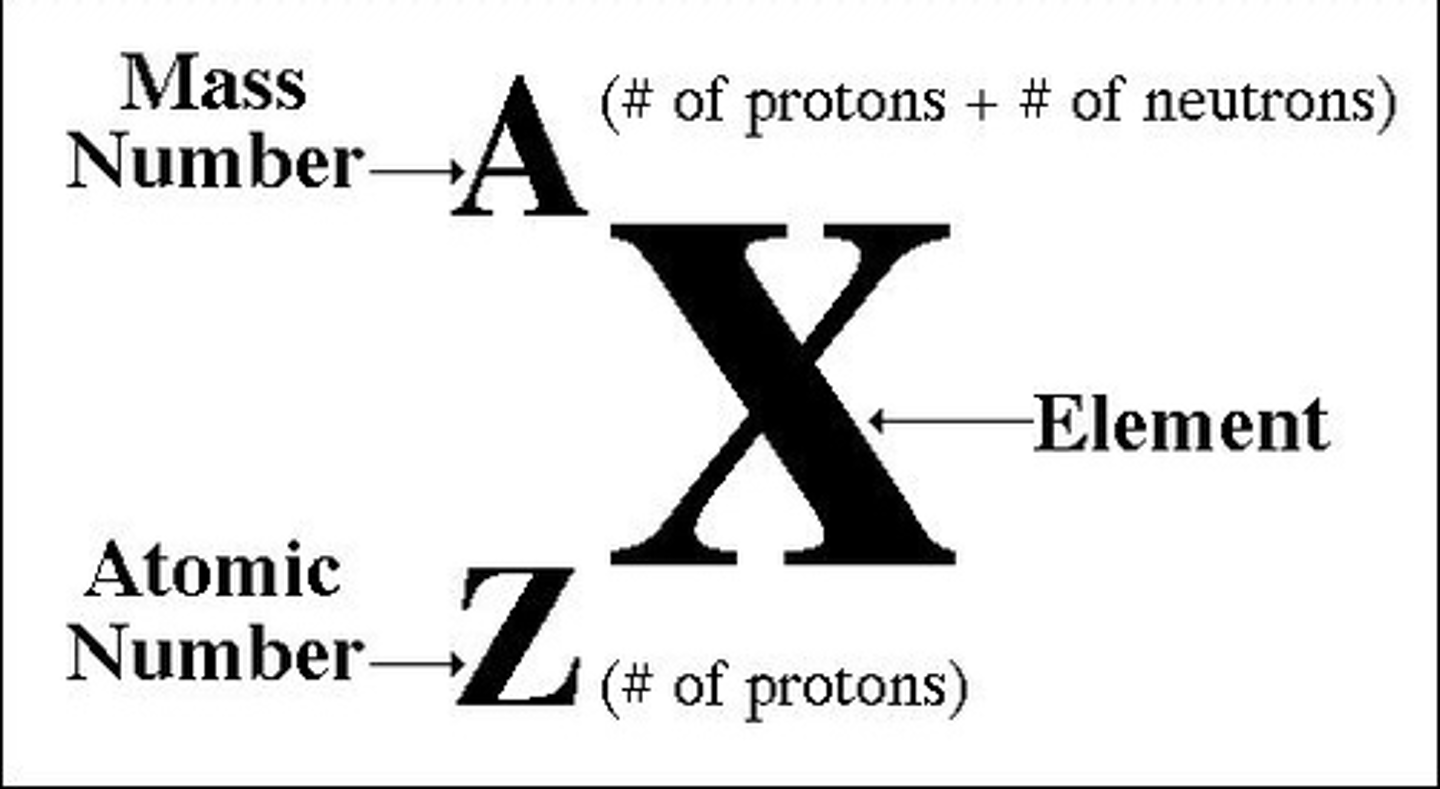
mass number, A
the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in a nucleus tells us
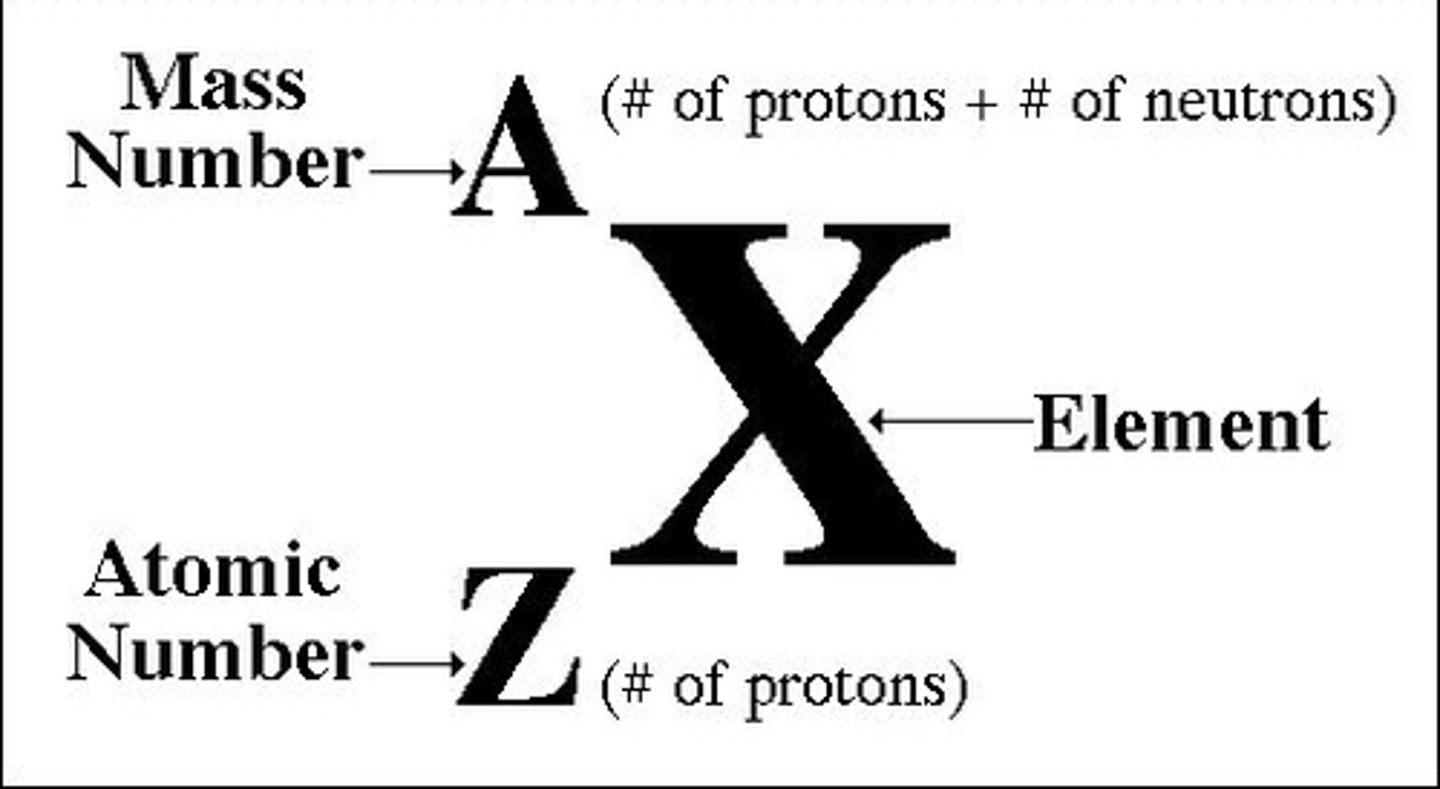
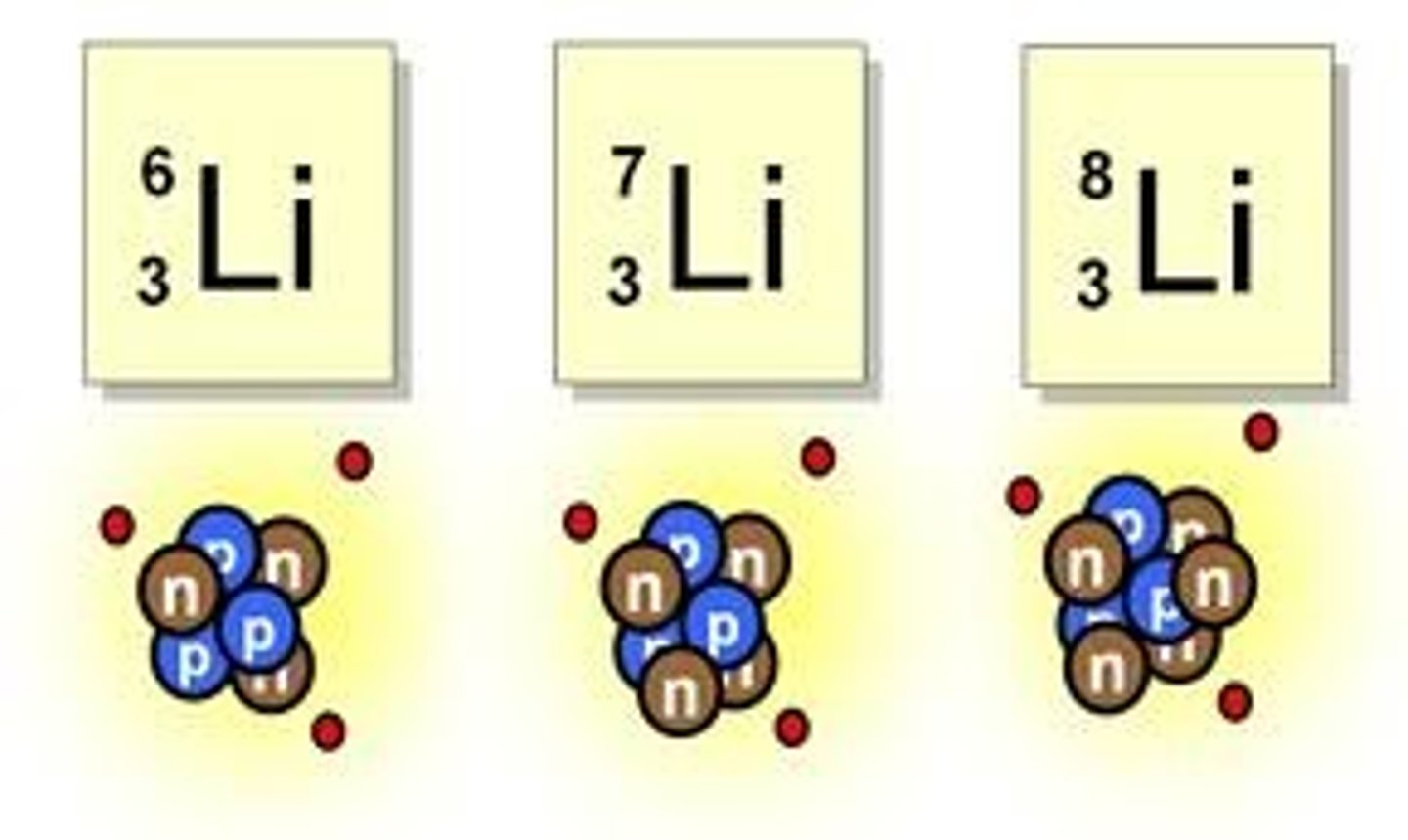
Isotope
an atom that contains the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons.
Stable nucleus
if a particular nuclide does not gain or lose any protons, neutrons or energy over time
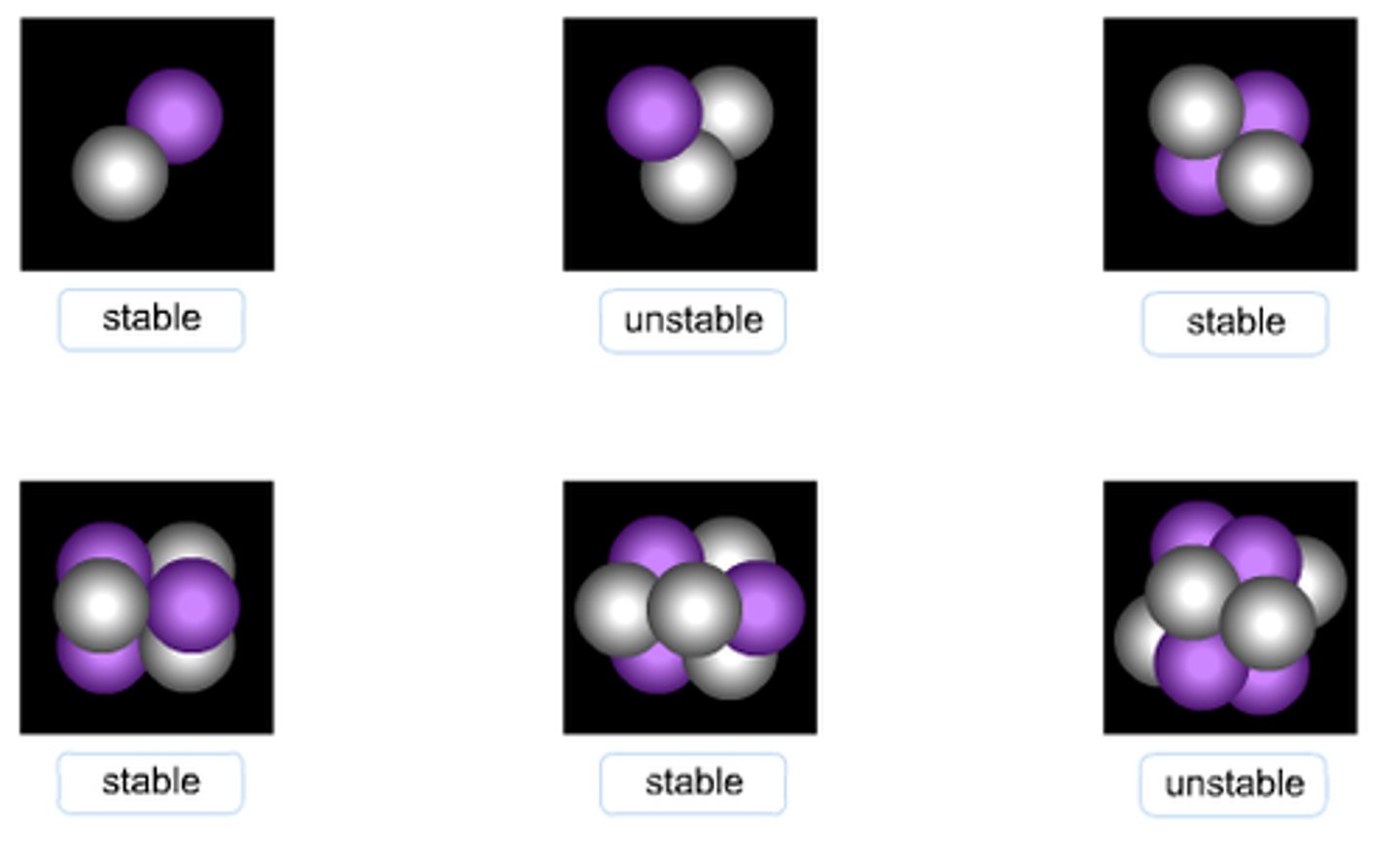
Unstable nucleus
radioactive

Radioactivity
is the natural, spontaneous decay of a nucleus into smaller pieces with the emission of other particles and/or energy in the form of electromagnetic waves (typically Xrays or gamma rays).

The unstable nucleus is called
a radionuclide
A radioactive isotope
radioisotope
Coulomb Force or Electrostatic Force.
a fundamental law of physics states that charged particles have a force acting on them that causes them to move
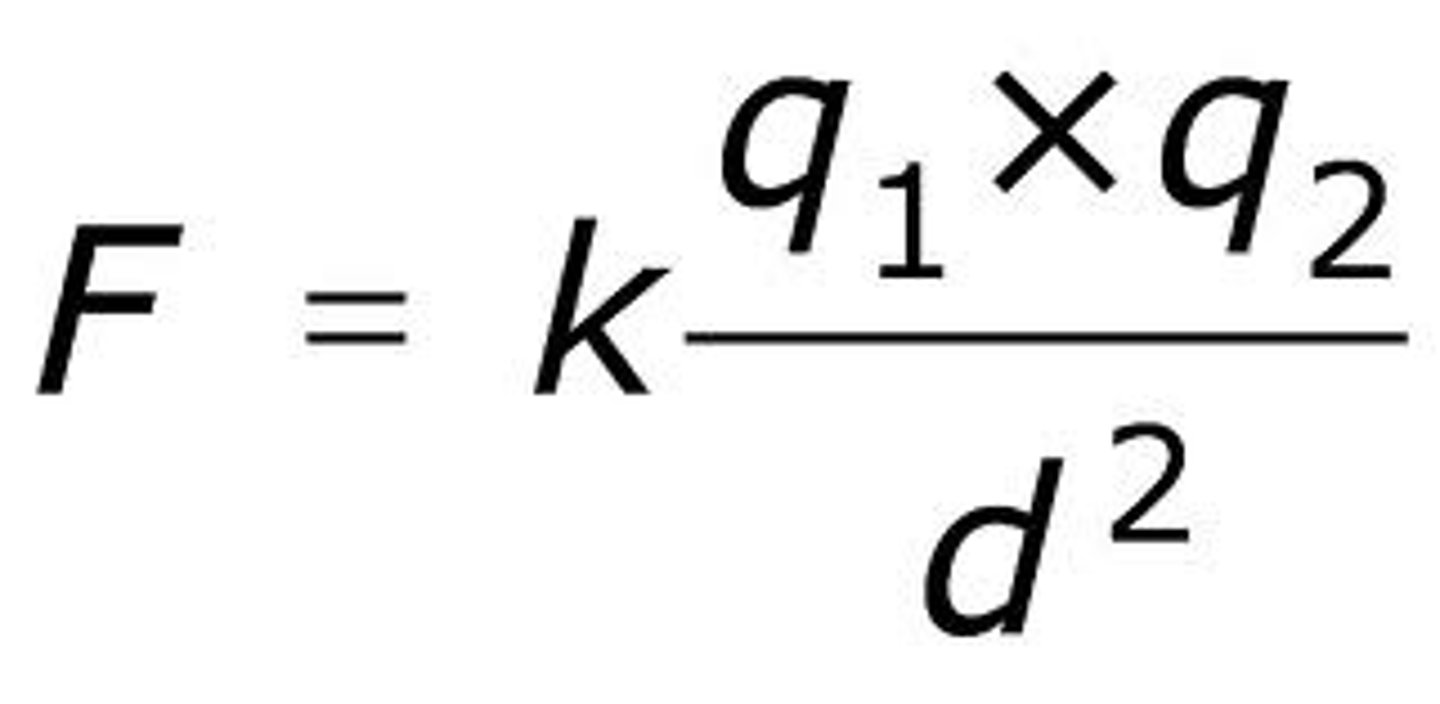
Strong Nuclear Force (SNF)
one of the four fundamental forces that exist in the universe. The others are electromagnetic (Coulomb force), gravity and weak nuclear force
* the SNF is mainly attractive, it acts only in the nucleus on protons and neutrons, and it acts at only very short distances.
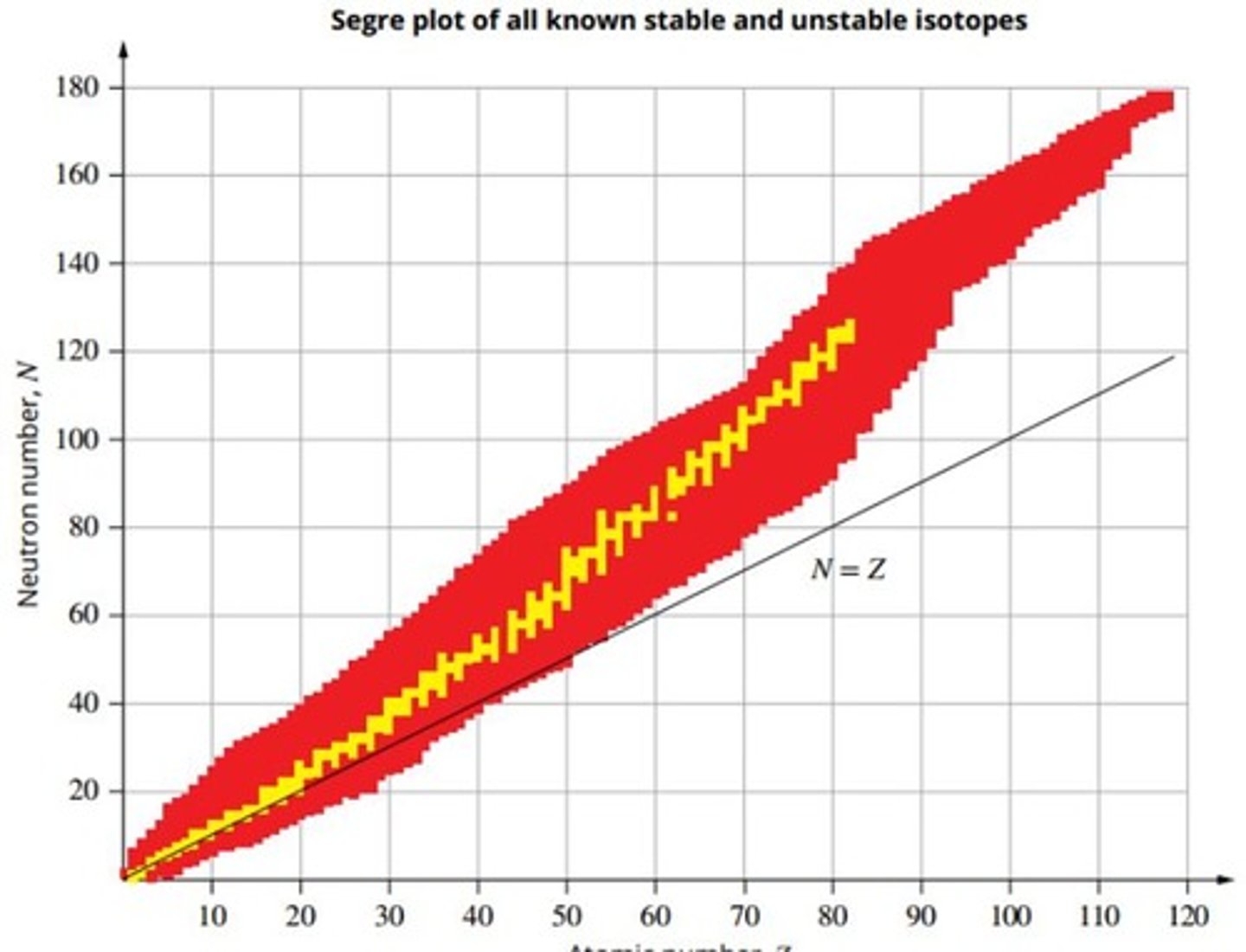
Segre plot
A plot of neutron number (N) against atomic number (Z) for all stable nuclides