Week 8 - Protein Sorting - Lysomes L12
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Where does the assembly of clathrin-coated vesicles occur?
At the trans Golgi compartments.
What do clathrin-coated vesicles carry?
Hydrolytic enzymes and membrane proteins from the trans Golgi to endosomes, lysosomes, and plant vacuoles.
What is the structure of clathrin-coated vesicles?
They have an outer honeycomb-like lattice made of clathrin and an inner shell composed of protein complexes called adaptors.
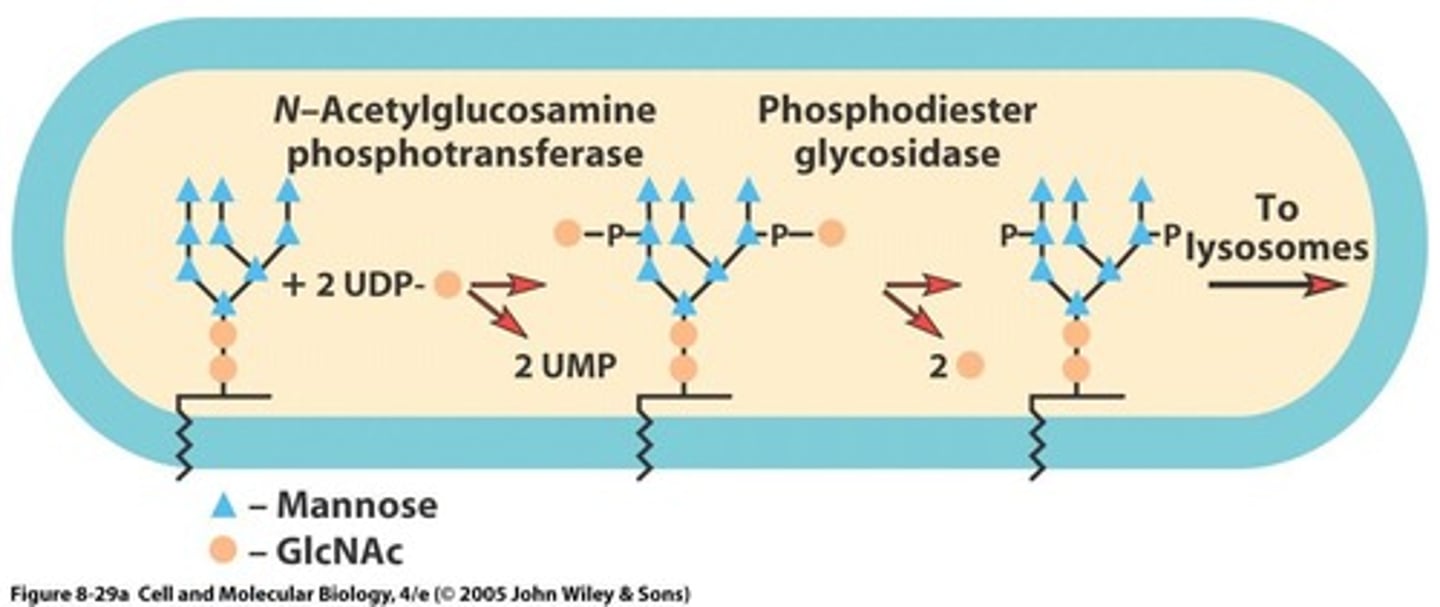
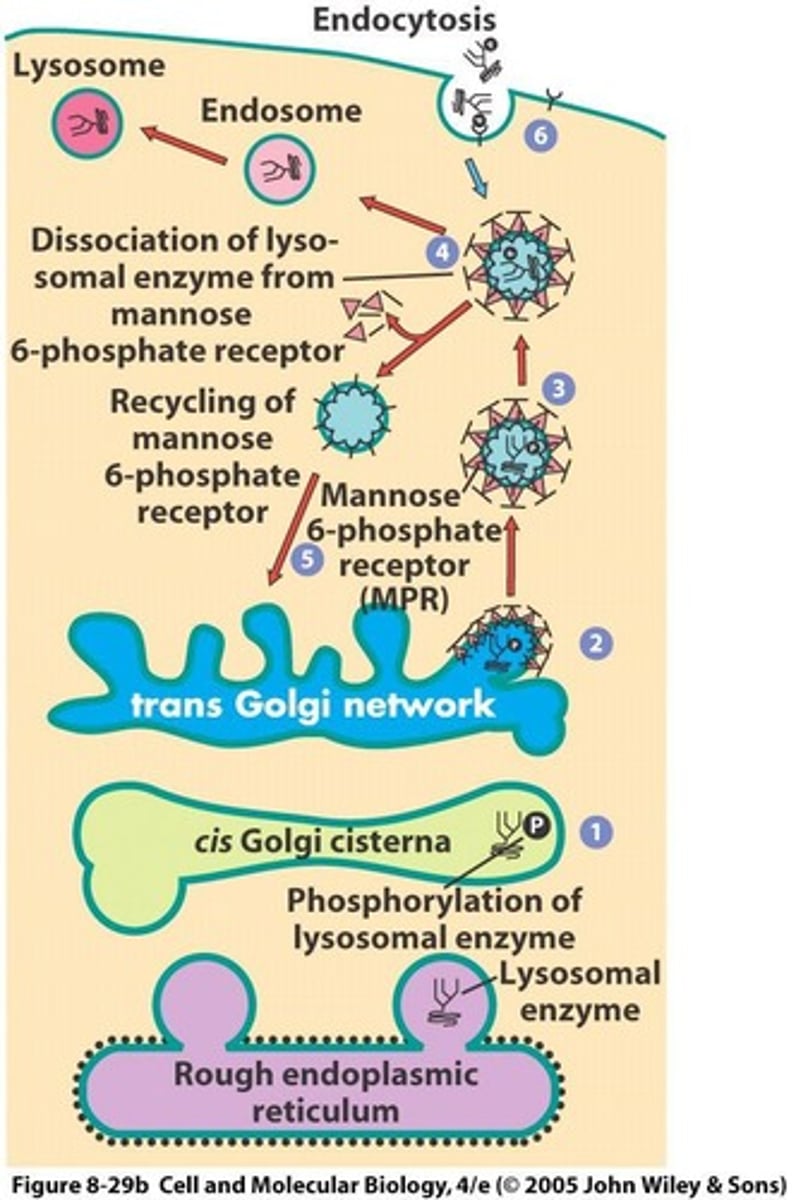
What role do mannose 6-phosphate receptors (MRPs) play in lysosomal enzyme transport?
They capture lysosomal enzymes in clathrin-coated pits of the trans Golgi network.
What is the pH of lysosomes and why is it important?
The pH of lysosomes is approximately 4.6, which is optimal for the activity of acid hydrolases.
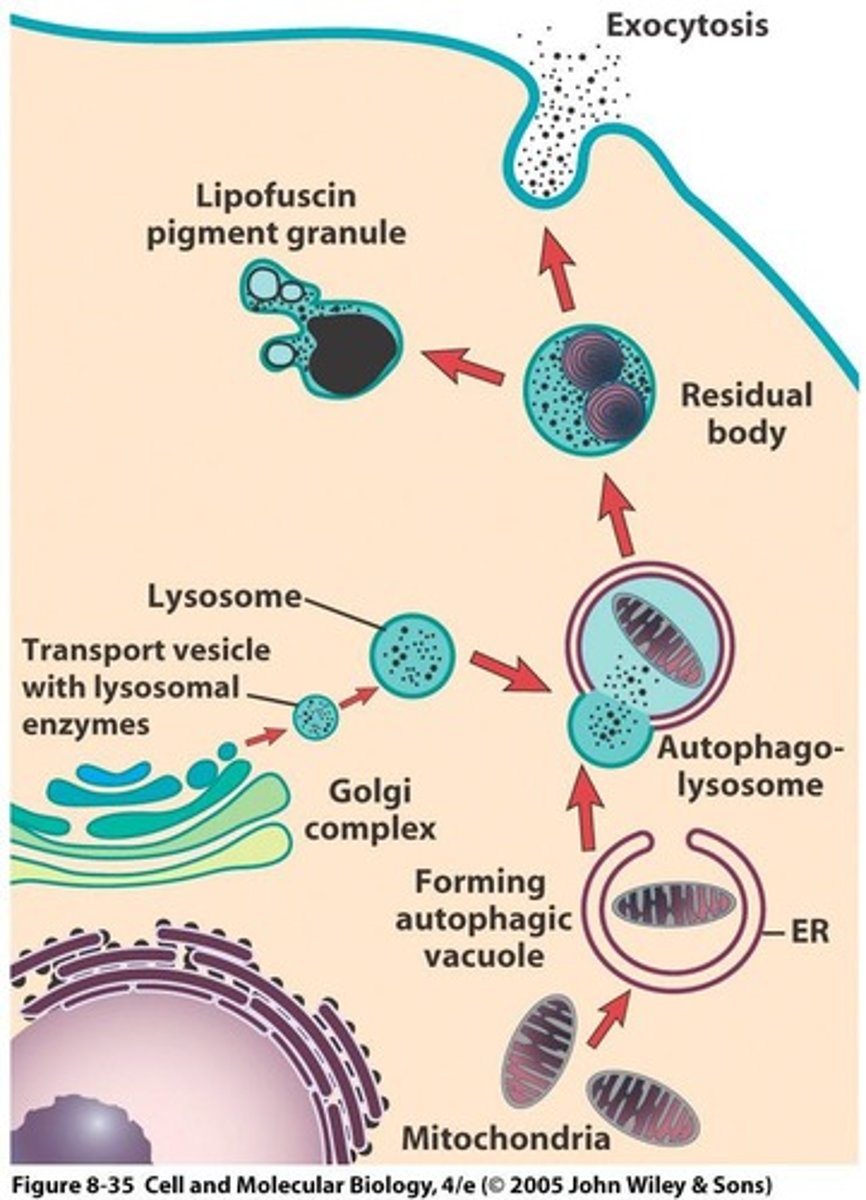
What is autophagy?
The process of destroying and replacing the cell's own organelles, such as mitochondria.
What happens during the process of autophagy?
An organelle becomes surrounded by an ER membrane, fuses with a lysosome to form an autophagolysosome, and is then digested.
What is the role of lysosomes in phagocytosis?
Lysosomes digest materials brought into the cell by phagocytic cells like macrophages and neutrophils.
What is I-cell disease?
A rare inherited condition characterized by bloated lysosomes with undegraded material due to the absence of hydrolytic enzymes.
What is Tay-Sachs disease?
A deficiency of β-N-hexosaminidase A that leads to the accumulation of ganglioside GM2 in the brain, causing progressive dysfunction.
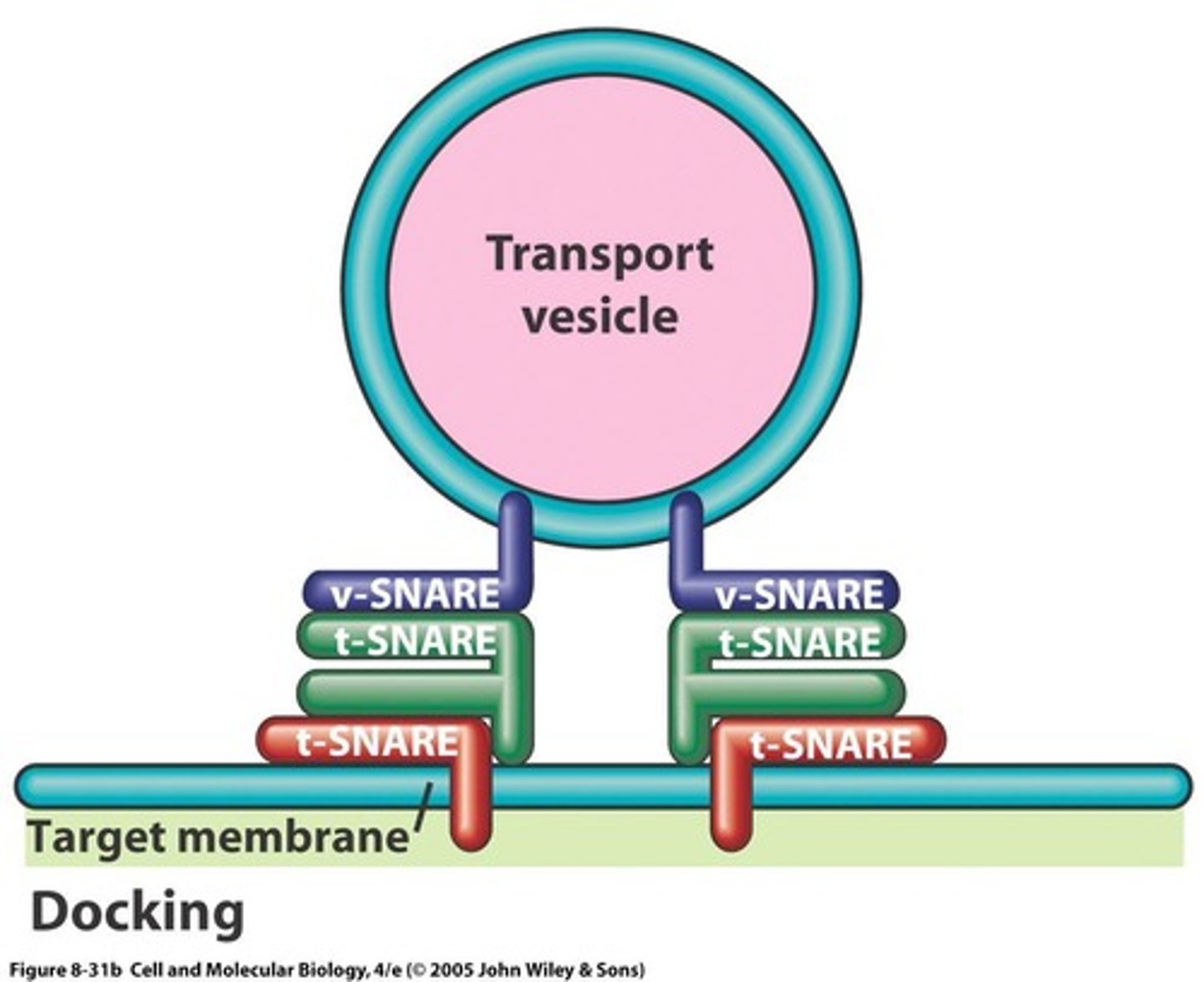
What are SNARE proteins and their role in vesicle fusion?
SNARE proteins mediate the docking of vesicles with target membranes, facilitating fusion.
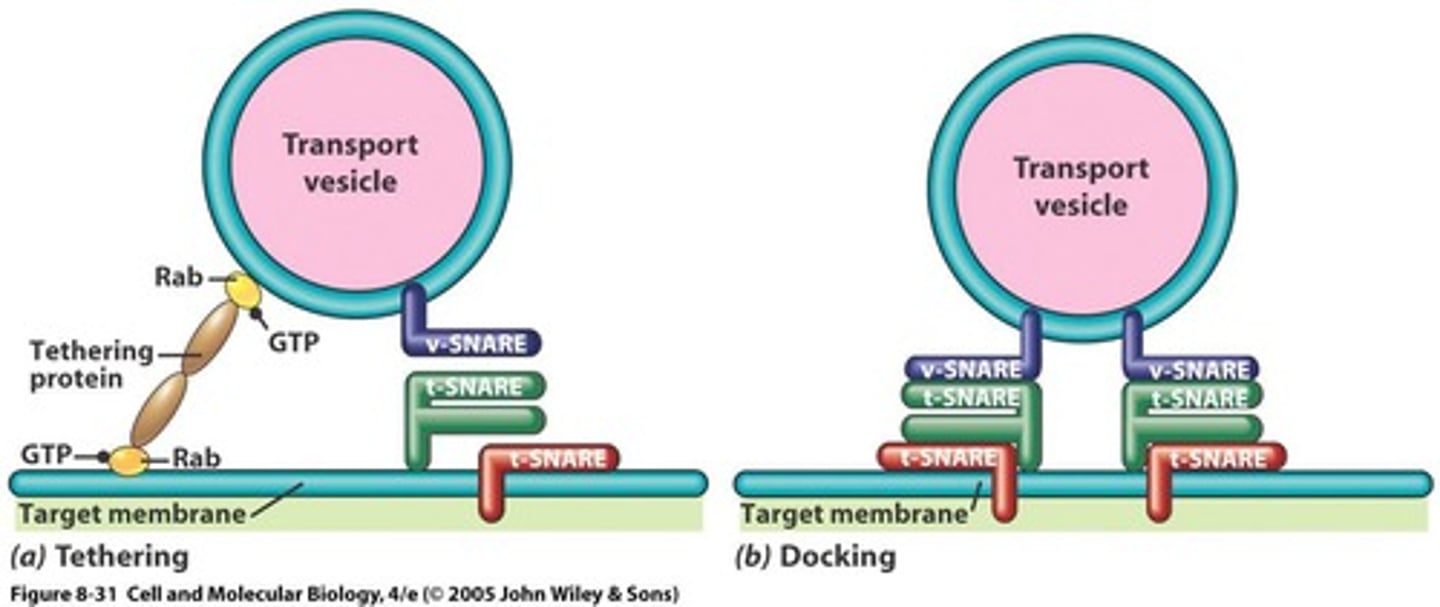
What is the four-step process for targeting vesicles to a specific component?
1. Movement towards the target
2. Tethering by Rabs
3. Docking with SNAREs
4. Fusion of membranes.
What triggers the exocytosis of vesicles?
A local increase in calcium ion concentration.
What is the function of synaptotagmin in vesicle fusion?
It is a calcium-binding protein that mediates the fusion of synaptic vesicles with the presynaptic membrane.
How do lysosomes contribute to fertilization?
Lysosomal enzymes in the acrosome of sperm digest the outer covering of the egg, allowing sperm to reach the egg surface.
What is the role of glycosylated integral membrane proteins in lysosomal membranes?
They form a protective lining that shields the membrane from attack by enclosed enzymes.
What is Pompe disease?
A lysosomal storage disease caused by the absence of α-glucosidase, leading to the accumulation of undigested glycogen.
What happens to lysosomal enzymes after they are captured by mannose-6-phosphate receptors?
They separate from the receptors, which return to the Golgi complex or the plasma membrane.
What is the function of Kupffer cells?
They are phagocytic cells in the liver that engulf aging red blood cells.
What is the significance of the protective carbohydrate chains on lysosomal membranes?
They shield the membrane from damage by the hydrolytic enzymes contained within lysosomes.
What is the role of the proton pump (H+-ATPase) in lysosomes?
It maintains a high internal concentration of hydrogen ions, contributing to the acidic pH of lysosomes.
How can lysosomal storage diseases be diagnosed?
They can be diagnosed prenatally by amniocentesis.