Endocrinology
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What are hormones?
Chemical messengers released from one tissue which produce a specific, receptor-mediated change in another tissue
What do hormones do?
Involved in:
Development - Proliferation, growth, and differentiation
Metabolism - Energy storage, metabolic rate and temperature
Reproduction - Sexual maturation & behaviour, pregnancy & lactation
Fluid homeostasis - Water balance, salt levels, blood volume, pressure
What are the endocrine glands?
Brain
Pituitary
Thyroid
Thymus
Adrenal
Pancreas
Kidney
Testes
Uterus
What tissues have an endocrine function?
Kidney - erythropoietin (EP)
Heart - atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
Gut - gastrin, secretin
Adipocytes - leptin, adiponectin (fat cells)
Pancreas - insulin
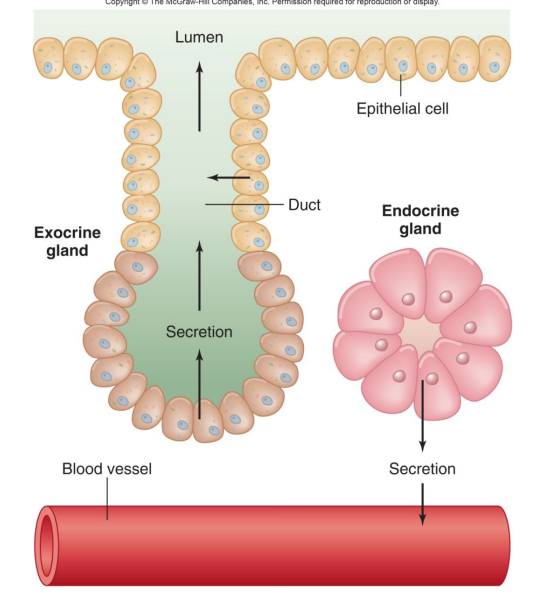
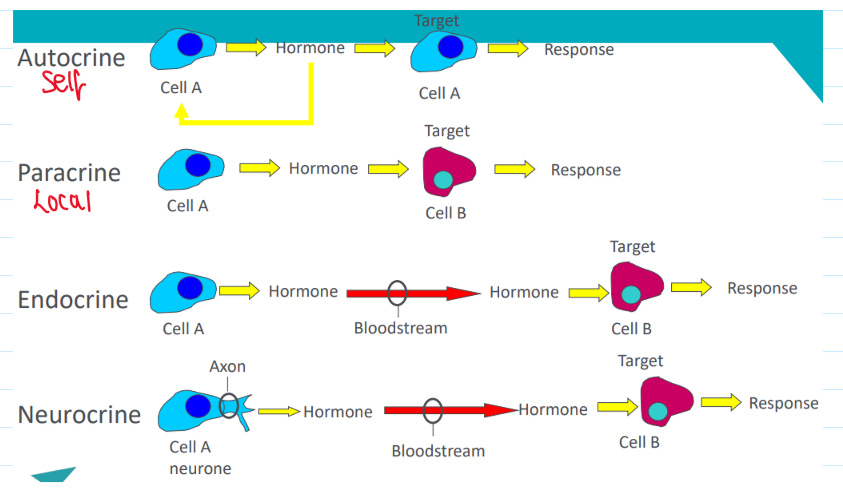
What are the 4 different functions tissues can have?
What are the 3 major chemical classes of hormones?
Amines
Tyrosine, l-dopa, dopamine, noraepinephrine, epinephrine
Peptides and proteins
Steroids
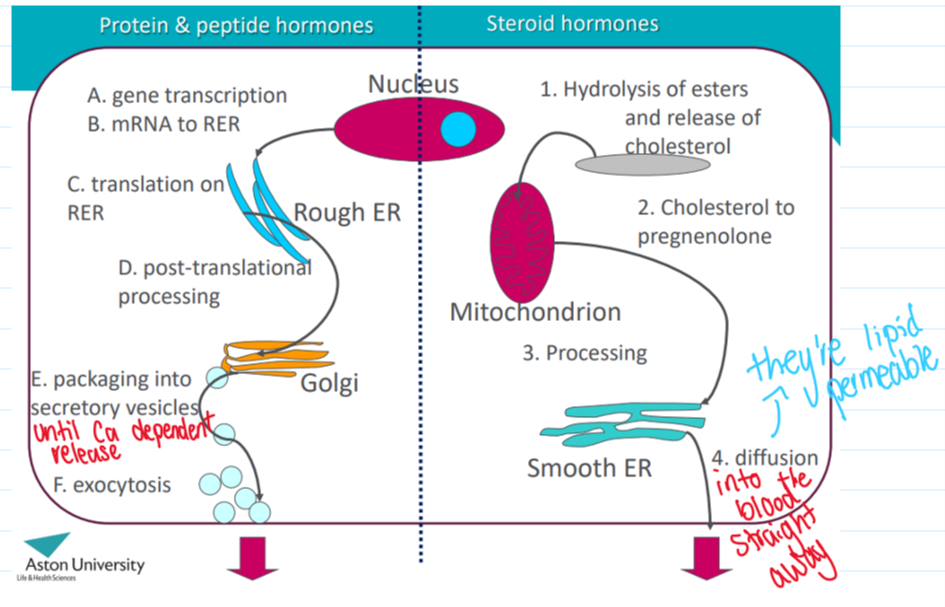
Describe peptide hormones
Synthesised from AAs
Processed in several stages
N-terminal signal sequence cleavage in ER
Glycosylation in ER
Cleavage of pro-hormone by endopeptidases in cell
Prolactin
ACTH
Vasopressin
Oxytocin
Describe steroid hormones
Grouped by the receptor that they bind to
Glucocorticoids - cortisol (metabolism)
Mineralocorticoids - aldosterone (salt balance)
Androgens - testosterone (sex determination)
Oestrogens - oestradiol (sex determination)
Progestogens – progesterone (pregnancy)
What is the synthesis pathwa for hormones?
Cholesterol → Pregnenolone → Progesterone → all other hormones
Where are hormone receptors?
Levels are normally low
They can be inside the cell or on the cell membrane
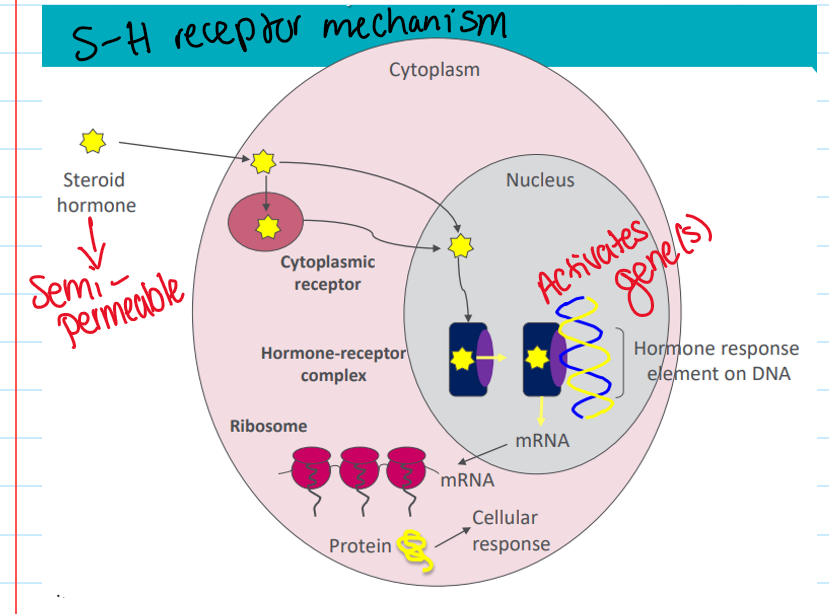
Thyroid and steroid hormone receptors
Polypeptide and protein receptors
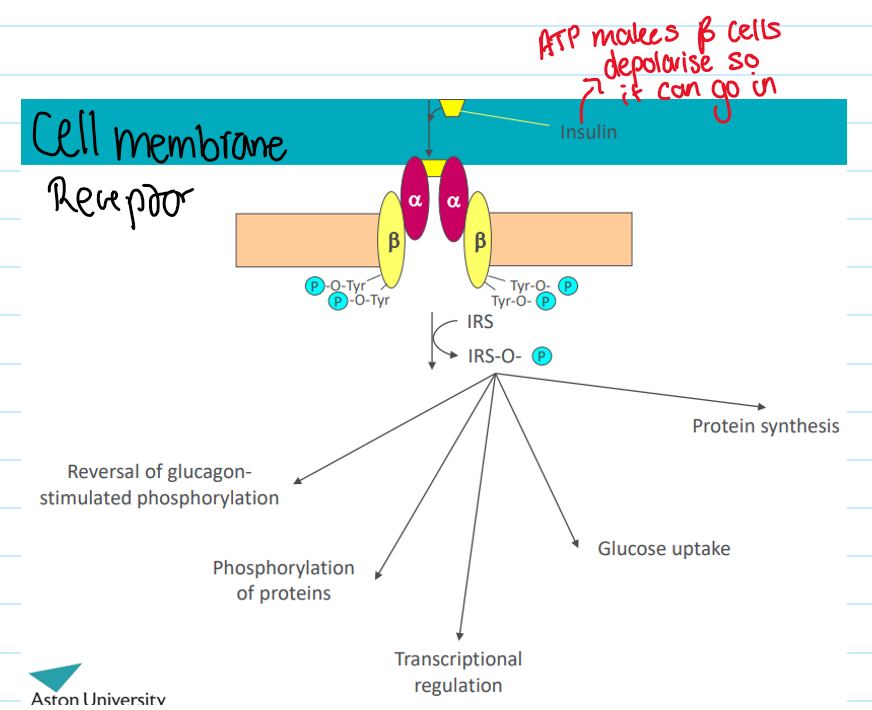
Cell membrane receptor
Steroid-hormones receptor mechanism (estrogen/thyroid)
What is up and down regulation?
Up regulation - increase in the number of receptors for a hormone
Down regulation - decrease in the number of receptors for a hormone
What factors alter the rate of hormone secretion?
Ions/nutrients
NTs
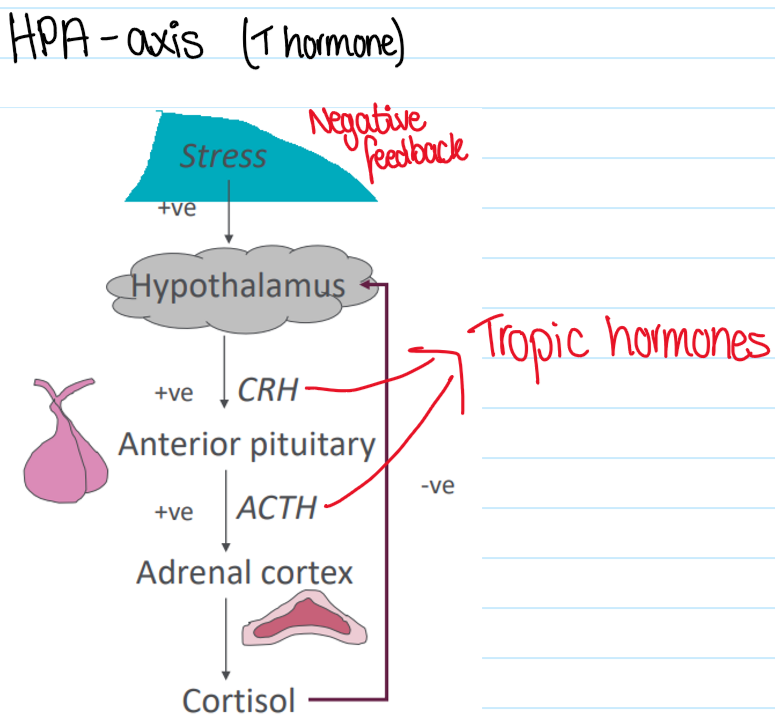
Tropic hormones
Hormones that stimulate endocrine glands to secrete
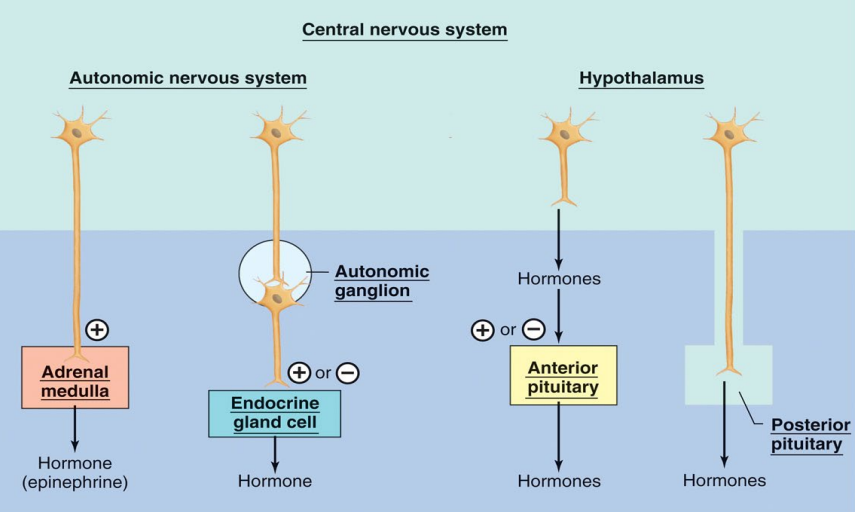
Neural control of hormones
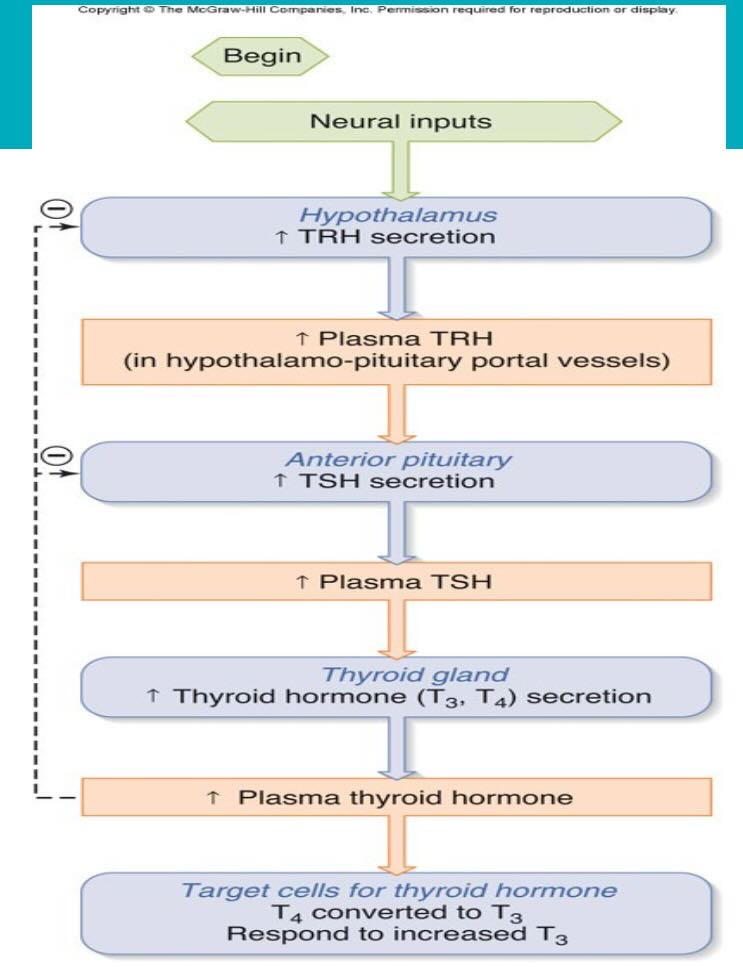
HPA-axis (T hormone) feedback mechanism
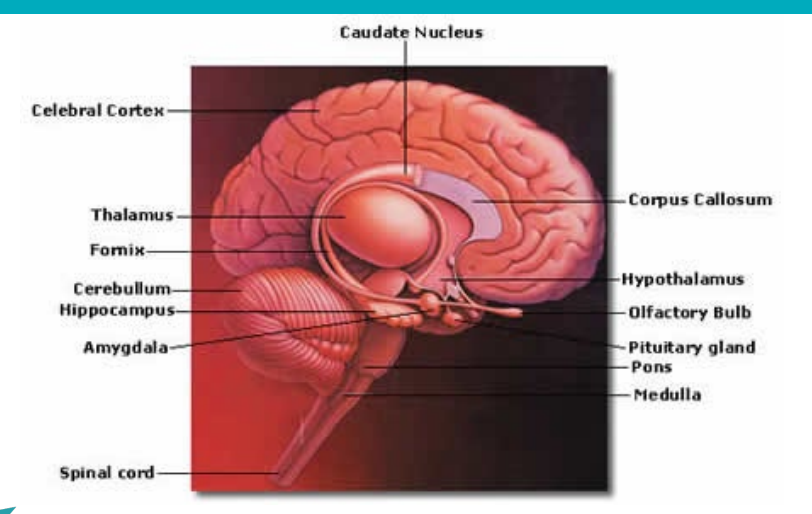
What is the hypothalamus and its role in the endocrine system?
Made of neurones called nuclei or areas
As an endocrine organ that controls the anterior pituitary (AP; major function)
Via nerve fibres that innervate the posterior pituitary (PP)
Via autonomic innervations of more distant glands (adrenal medulla, pineal, kidney parathyroid, pancreatic islets)
What does the hypothalamus regulate?
Blood pressure
Temperature
Fluid and electrolyte balance
Body weight
Sleep
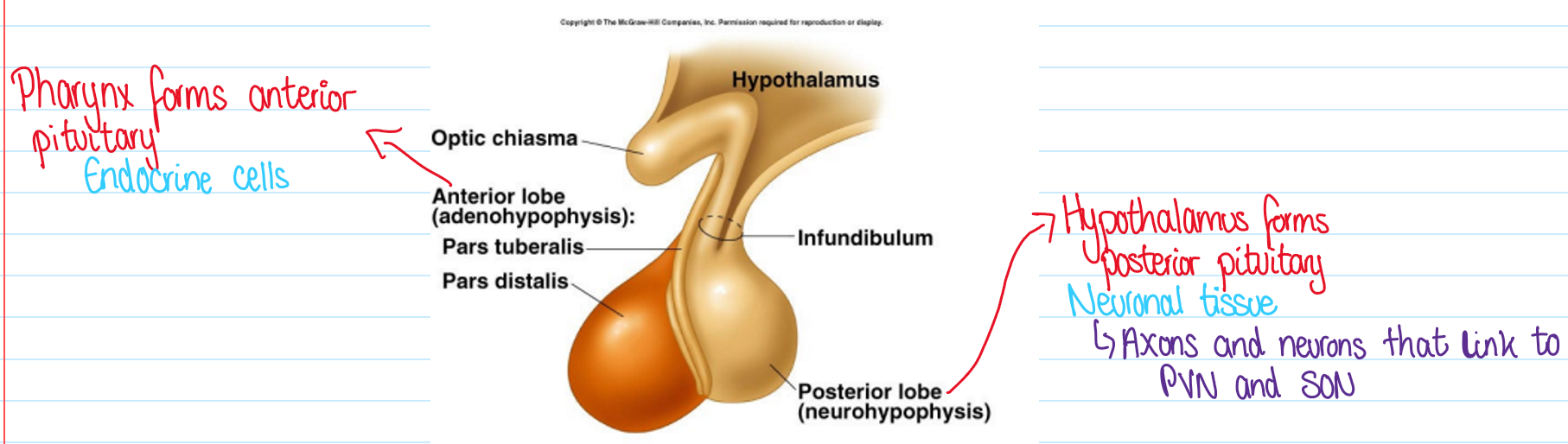
What connections does the pituitar gland (hypophysis) have?
Direct - neuronal connection (posterior)
Indirect - portal blood vessels (anterior)
What can the hormones from the anterior pituitary act on?
Adrenal function
Thyroid function
Gonadal function
Water balance (kidneys)
Lactation
Metabolism
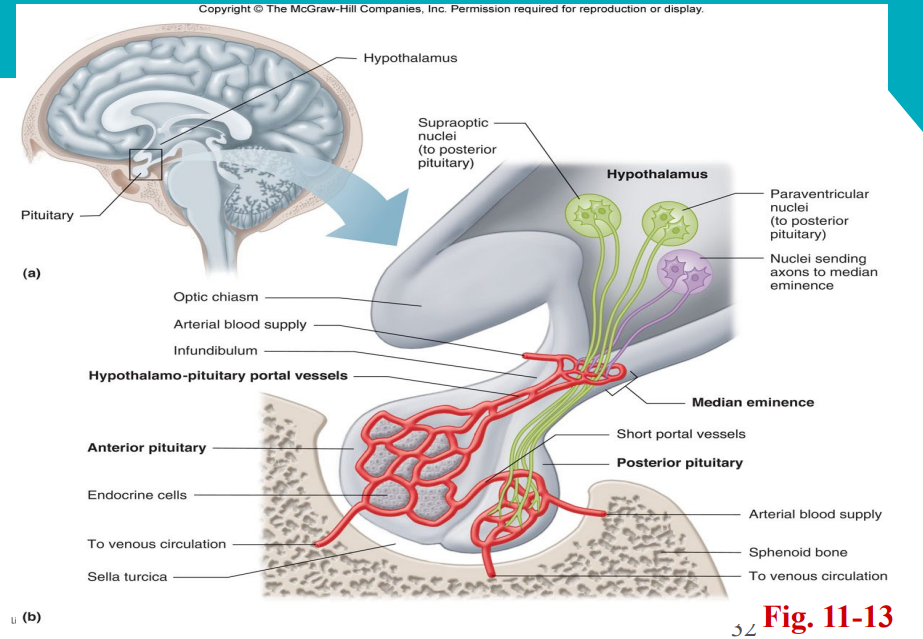
How does the pituitary gland get its blood supply?
The AP receives blood after it has been through the hypothalamus
The blood drains into the hypothalamic-hypophysial portal system and runs down the infundibulum and releases into the AP
Hormones from hypophysis can enter anterior pituitary
Hormones secreted by the pituitary are then taken away into the venous return
The posterior lobe has a separate blood supply and drainage
Small # that go: pp → ap → h
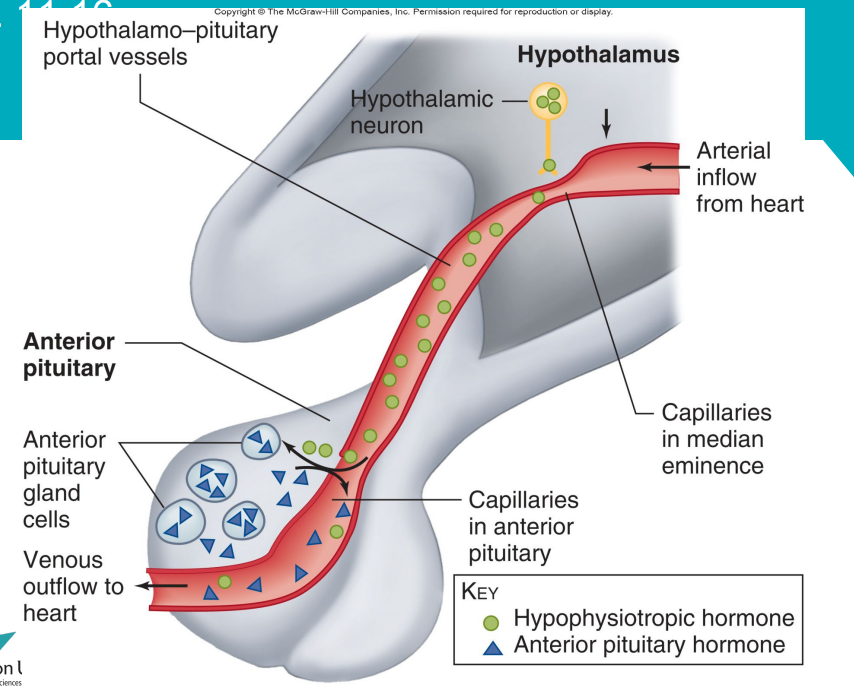

What are the main hypophysiotropic hormones?
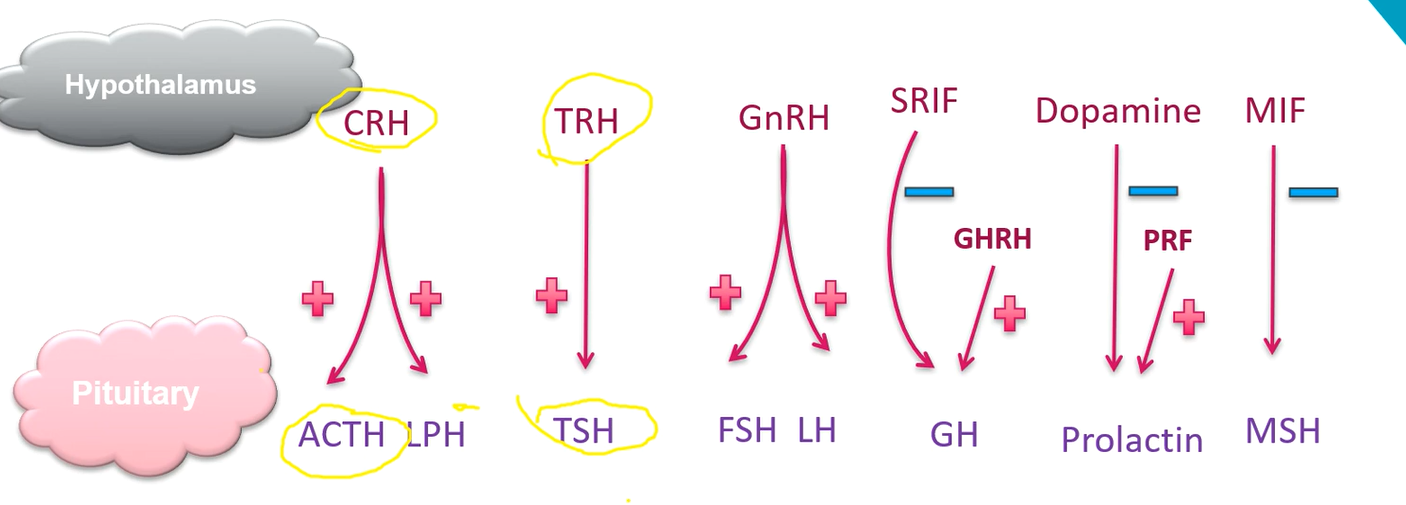
What is corticotropin releasing hormone?
Highly conserved, 41 amino acid peptide
Stimulates secretion of ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) and LPH (lipotropin)
The pre-curser molecule for these (any many others) is Proopiomelanocortin (POMC)
CRH secreting neurons have bodies in PVN
CRH is secreted in pulsatile bursts, especially in early morning
Physical, emotional or chemical stress (stimulation from higher brain centres)
What is thyrotropin releasing hormone?
Highly conserved, 3 amino acid peptide
TRH secreted from neurons in the dorsomedial region of hypothalamus
Stimulates secretion of TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) from cells in the anterior pituitary known as thyotropes.
Also stimulates Prolactin
Secretion is regulated by higher brain centres via noradrenergic neurons.
Pharmaceutical form is used to test pituitary response (secondary hypothyroidism)
What are the pituitary hormones?
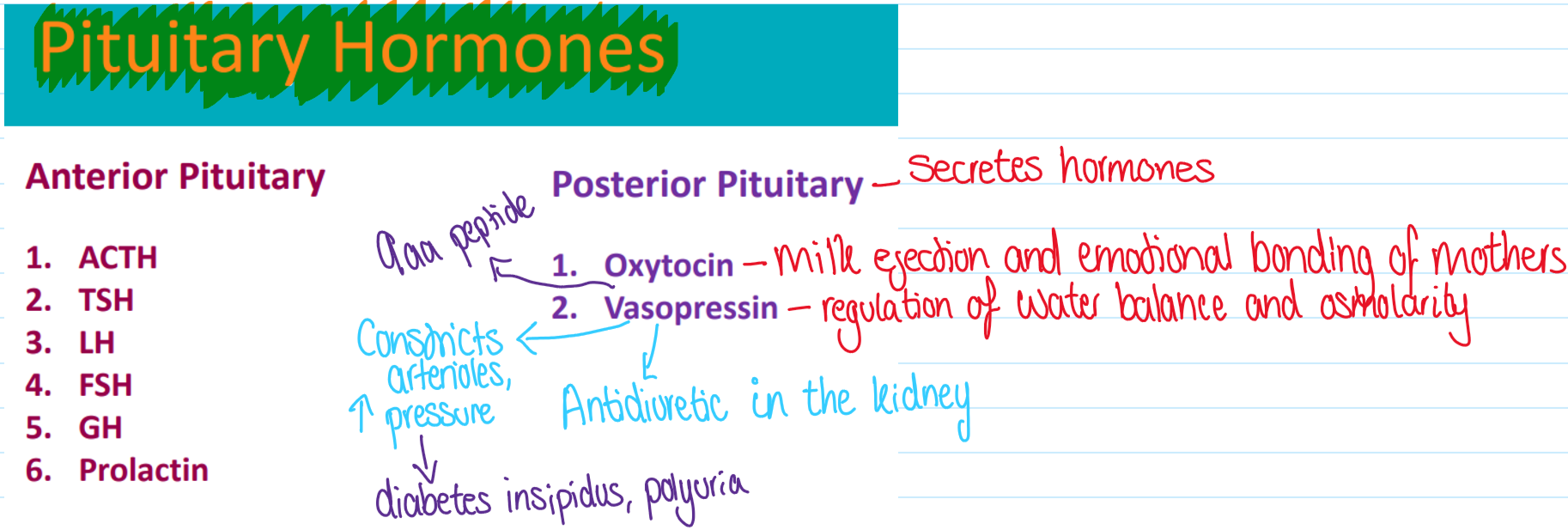
What does vasopressin do in the kidney?
Vasopressin binds to receptors on cells in the collecting ducts of the kidney
Promotes reabsorption of water back into the circulation
Without vasopressin, the collecting ducts are impermeable to water, and it flows out as urine
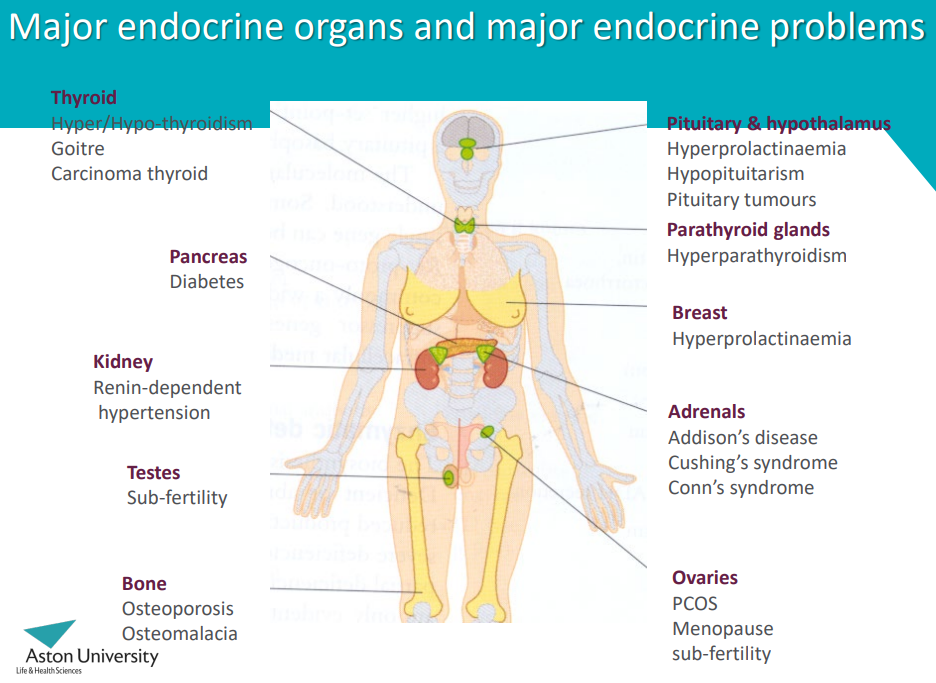
What are different endocrine disorders and diseases?
Endocrine disorders:
Excess secretion of a hormone
Deficient secretion of a hormone
Failure to respond to a hormone
Usually due to absence or malfunction of a receptor
Endocrine diseases:
Diabetes mellitus - insulin deficiency or insensitivity
Thyroid disease (too little or too much)
Infertility (hypothalamic, pituitary, gonadal)
Obesity (leptin)
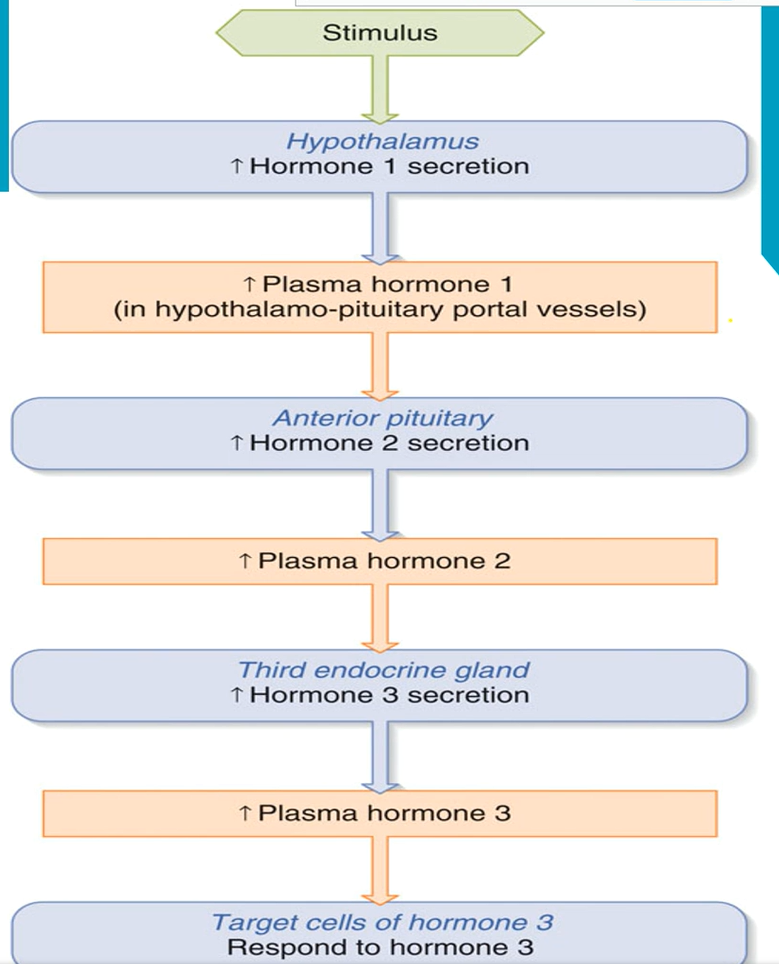
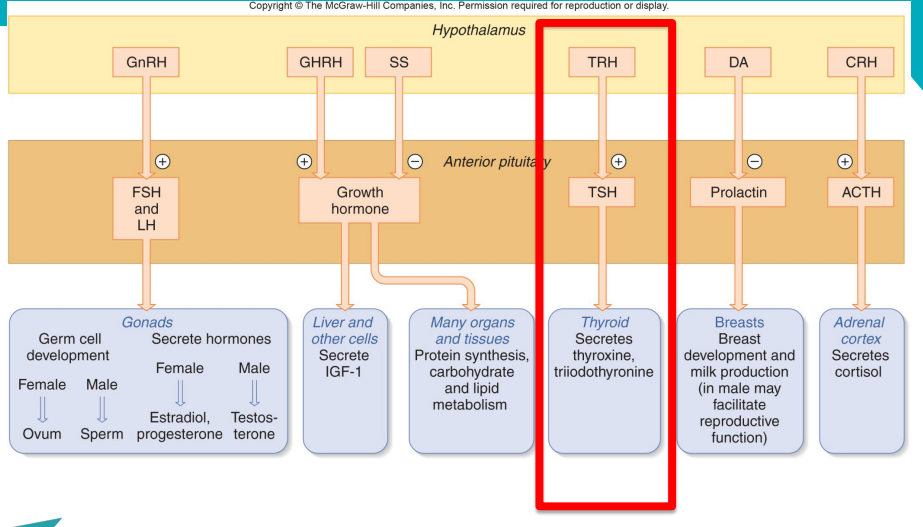
Control systems involving the hypothalamus and pituitary
Endocrine axes
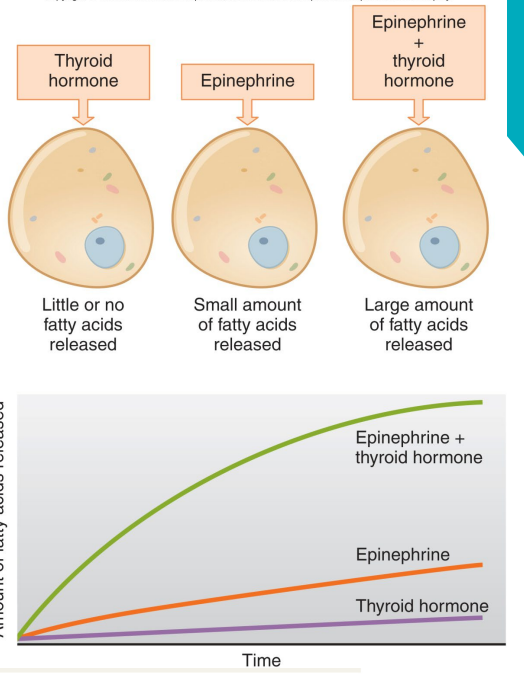
How much fatty acids get released in the thyroid?
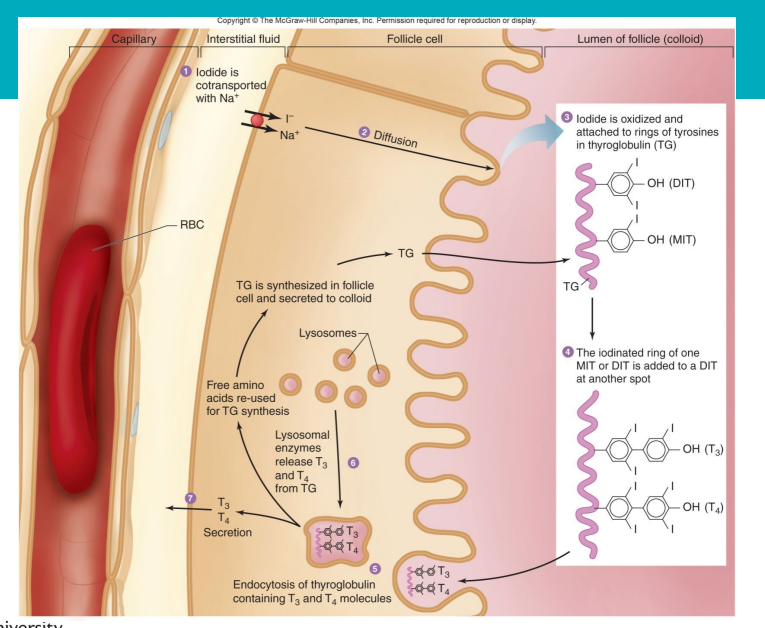
Synthesis of thyroid hormones
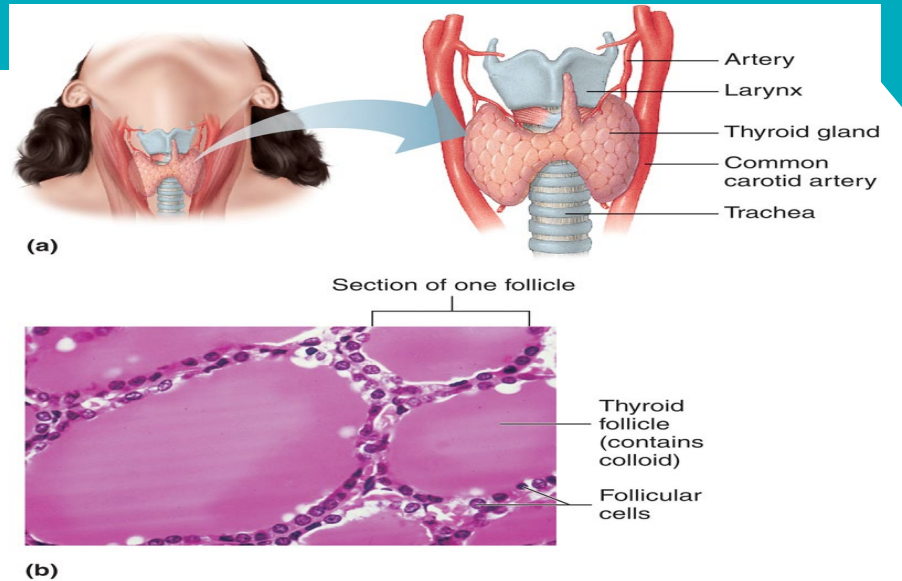
What are the different structures of the thyroid gland?
What is hypothyroidism?
Primary defect of the gland
Causes by iodine deficiency
Symptoms: feeling cold, wait gain, lethargy, cardiac effects
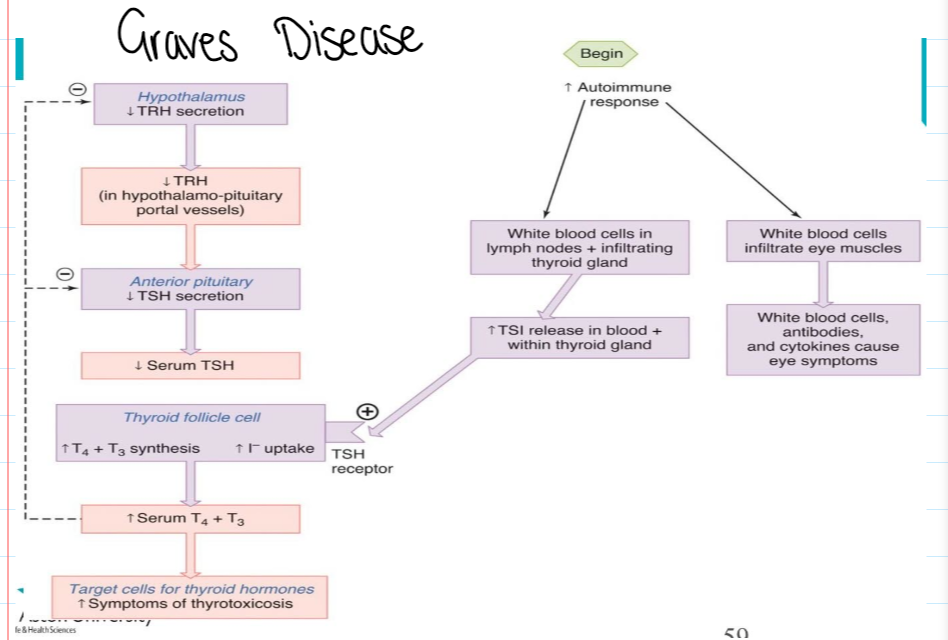
Autoimmune- Hashimoto’s disease, Graves’ disease
How is hypothyroidism treated?
Drugs that block T3/T4 production
Radioactive iodine
Thyroidectomy