ORGANIC FUNCTIONAL GROUPS lect 1 (copy)
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What fraction of drugs are organic molecules?
The vast majority
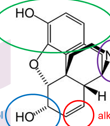
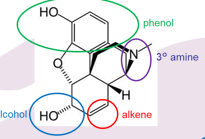
Name all functional groups
phenol alcohol alkene and 3 amine
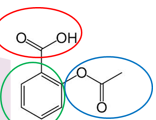
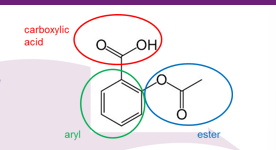
Name all functional Groups
carboxylic acid - aryl - ester
What happens to the electron pair in a polar bond?
It moves towards the more electronegative atom, creating a dipole.
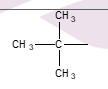
What type of alkyl group is formed when one hydrogen is replaced?
Primary (1°) alkyl group.
Why are alkanes considered stable and inert?
They have only non-polar C-C and C-H bonds.
What defines the solubility of alkanes?
Alkanes are insoluble in water due to the lack of polarity.
What is the difference between alkenes and alkanes in terms of bonds?
Alkenes contain at least one double bond, while alkanes do not.
What is formed during the addition reaction of alkenes?
An alkane is produced when a hydrogen molecule (H2) is added.
What type of reaction adds water to alkenes in the presence of an acid catalyst?
Hydration reaction.
How does a carbocation relate to the stability of different alkyl groups?
3° carbocations are the most stable and easiest to form.
What are epoxides?
Highly reactive compounds formed via oxidation.
What is the significance of double bonds in chemical reactivity?
They enhance reactivity and can participate in addition reactions.
What structural feature differentiates alkyl halides?
They have a polar bond between the carbon alkyl group and a halogen.
What type of substitution reaction do alkyl halides commonly undergo?
Nucleophilic substitution reactions.
What type of reaction occurs when heating alkyl halides with bases?
Elimination reactions to form alkenes.
What is unique about conjugated double bonds compared to isolated ones?
Conjugated double bonds have overlapping adjacent p orbitals.
What is the significance of UV light in relation to conjugated systems?
They absorb UV light to determine structure.
Why do colored compounds have extended systems of conjugation?
Their UV absorptions extend into the visible region
What type of molecular structure is b-Carotene?
A conjugated system.
How does the stability of conjugated π bonds compare to isolated π bonds?
Conjugated π bonds are generally more stable and less reactive.
What happens during the addition of 1,3-butadiene with a molecule A-B?
A mixture of products is obtained due to the presence of conjugation.
What characteristic of alkyl groups helps identify their type?
The number of hydrogen atoms replaced by other alkyl groups.
What happens in a tertiary alkyl group
all 3H atoms are replaced by alkyl groups