Purification of proteins (6)
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Basis of protein purification
Modify bacteria for its genome to overexpress a protein : extracted from cell and removing big cellular debris afterwards
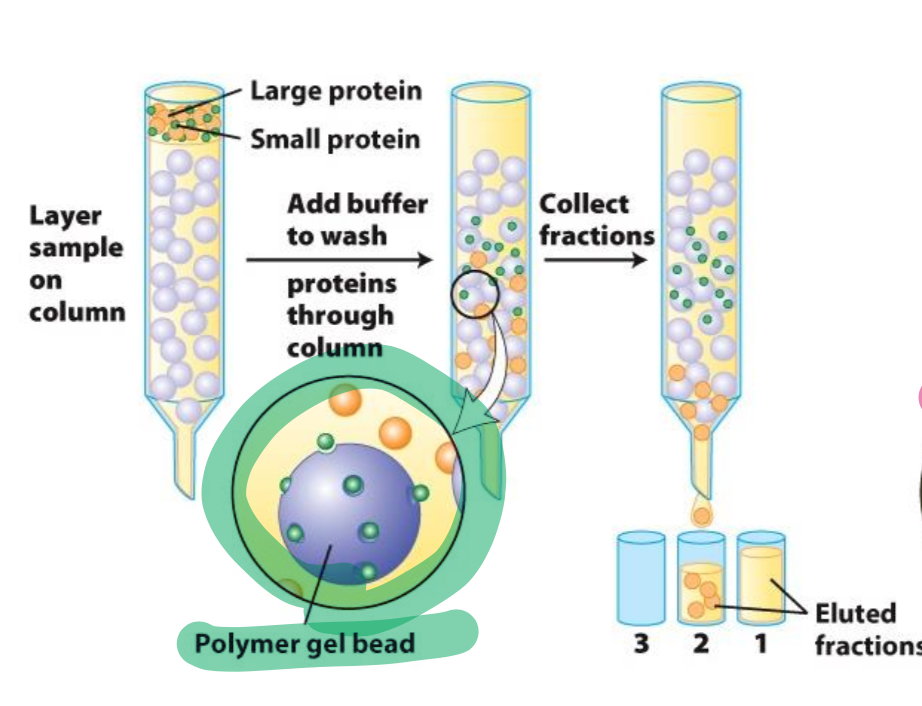
Name of this method (size and shape)
Gel filtration chromatography (GFC)
Solid phase of GFC
Gel beads with pores of molecular dimensions where small proteins can enter and exit freely
Large proteins in GFC
Cannot enter solid phase so they migrate faster and are eluted earlier
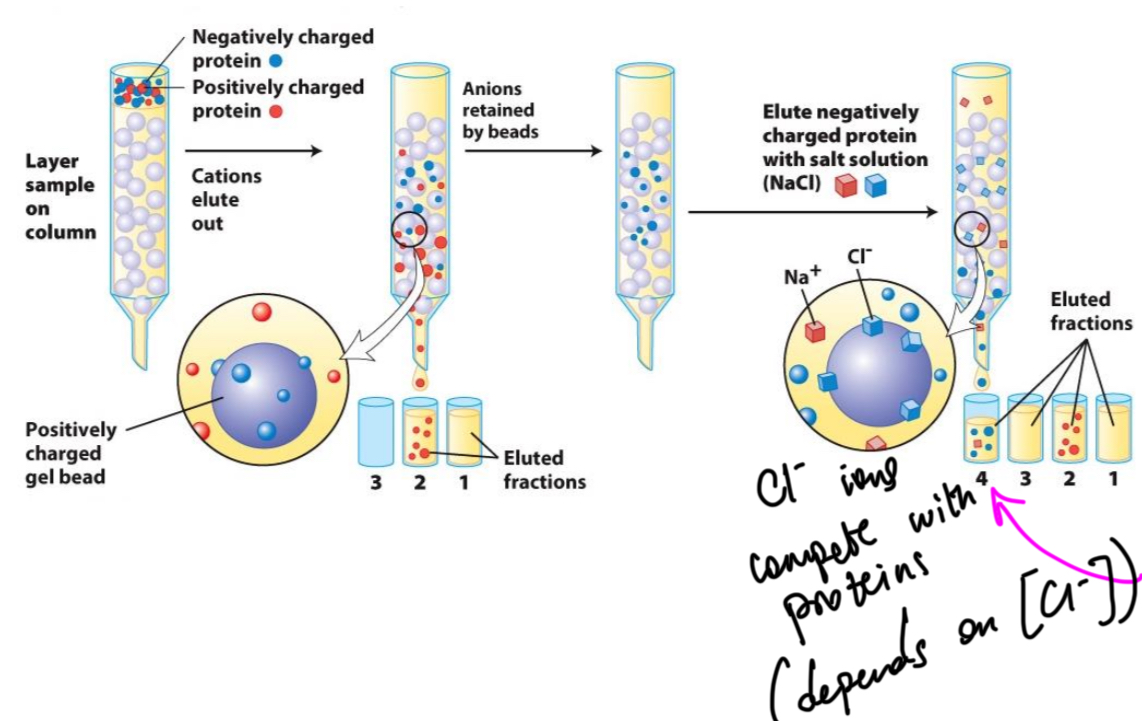
Name of this method (electric charge)
Ion-exchange chromatography (IEC)
Solid phase of IEC
Positively charged bead
Behaviour of mobile phase (IEC)
Protein will bind to the solid phase having the opposite charge and are displaced (ion exchange) with a NaCl solution

Name of this method
Antibody affinity chromatography (AAC)
Solid phase of AAC
Covalently coupled to an antibody specific to a protein
Separation of antibody from the protein
Lowering the pH with a buffer solution

Principle of how electrophoresis works
Speed of migration is determined by charge/mass ratio + shape
Advantage of SDS-PAGE
Proteins only migrate depending of their size because charge (SDS coat) proportionate to their length and unfolded
Immunoblot
Proteins in SDS-PAGE gel transferred to membrane
Primary + Secondary = fluorescence
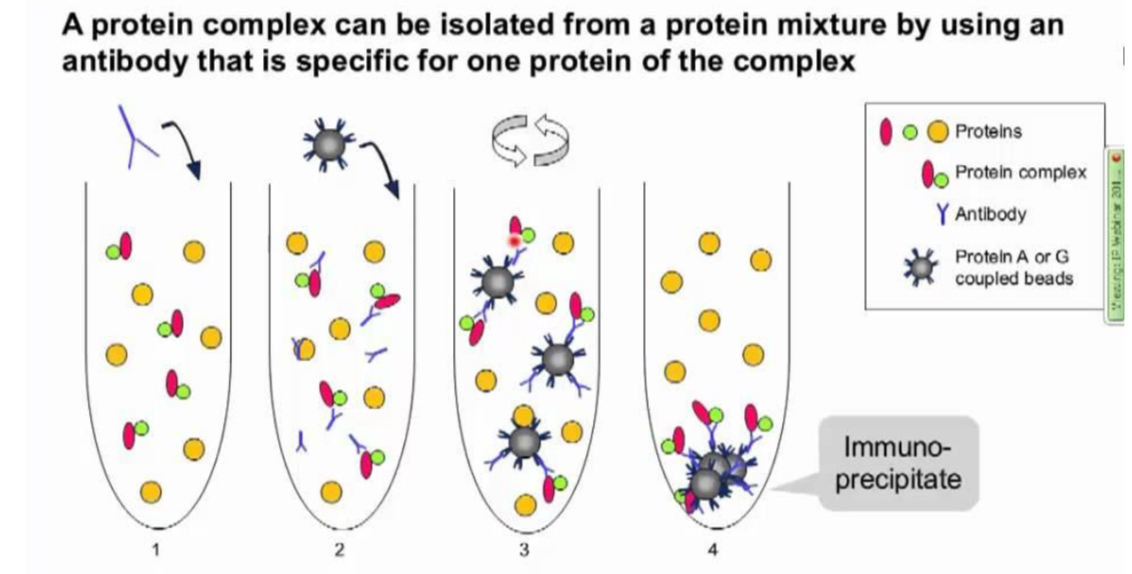
Co-immunoprecipitation
To co-purify other proteins that interact with it : allows to identify a protein in a protein complex
Ex of co-immunoprecipitation
Testing the interaction between GR and PPARa