Exam 3 Organic Chemistry Reactions- alkene, alkyne, alcohol and oxirane, ethers
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
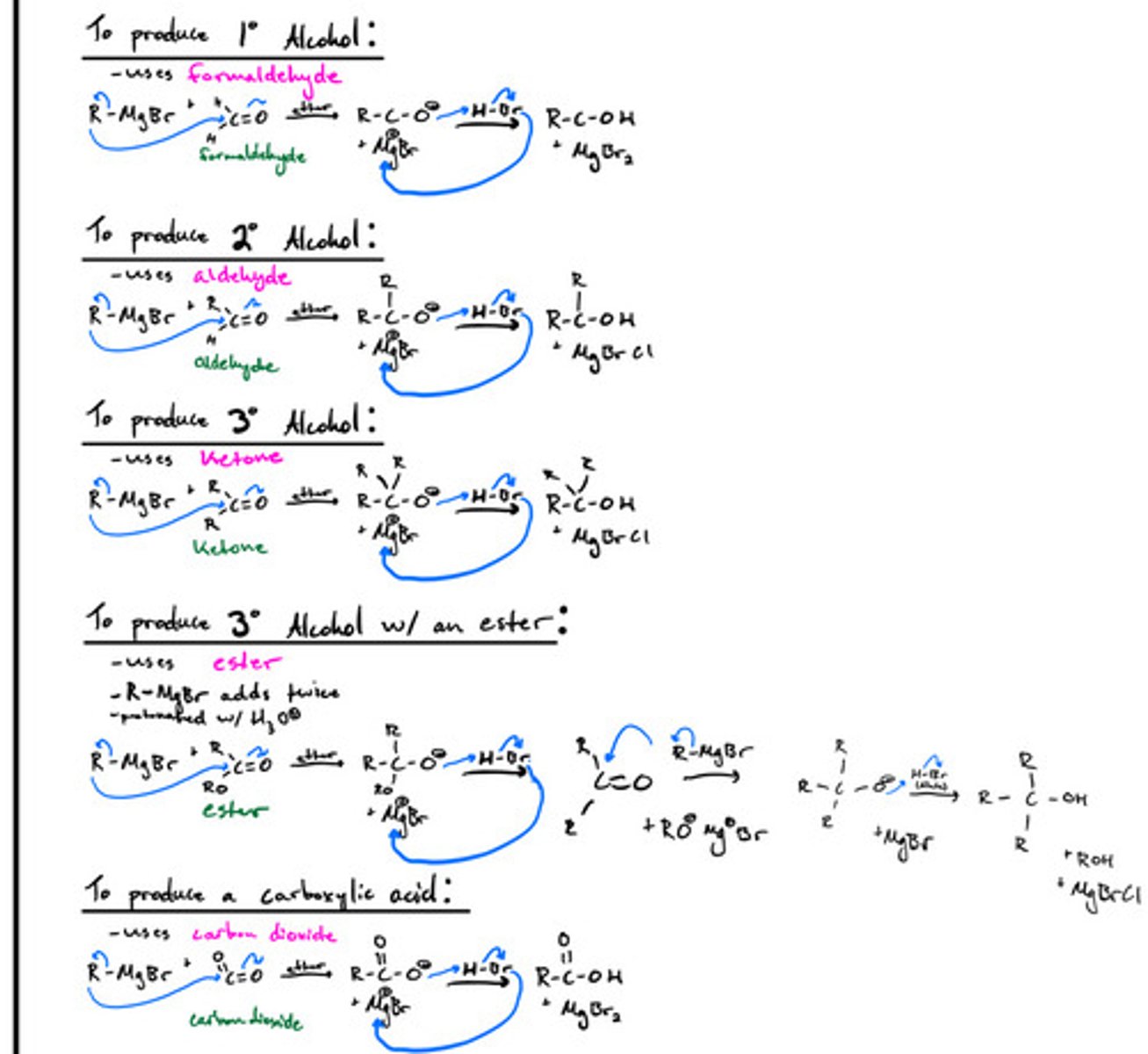
Alcohol formation from grignard reagents: mechanisms for producing primary, secondary, tertiatry (2) alcohols and carboxylic acid.
Producing deuterated alkanes with Mg: mechanism
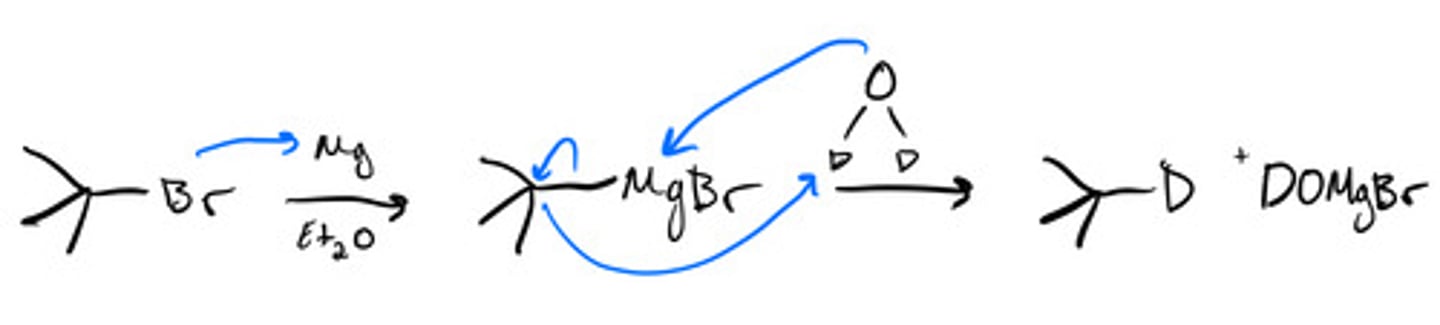
Producing deuterated alkanes with Mg: steps

Reduction of carbonyl compounds to form alcohols w/ LiAlH4 and NaBH4: mechanisms

Reduction of carbonyl compounds to form alcohols w/ LiAlH4 and NaBH4: steps

Ring opening of oxiranes to produce alcohols- Halohydrogenation: mechanism
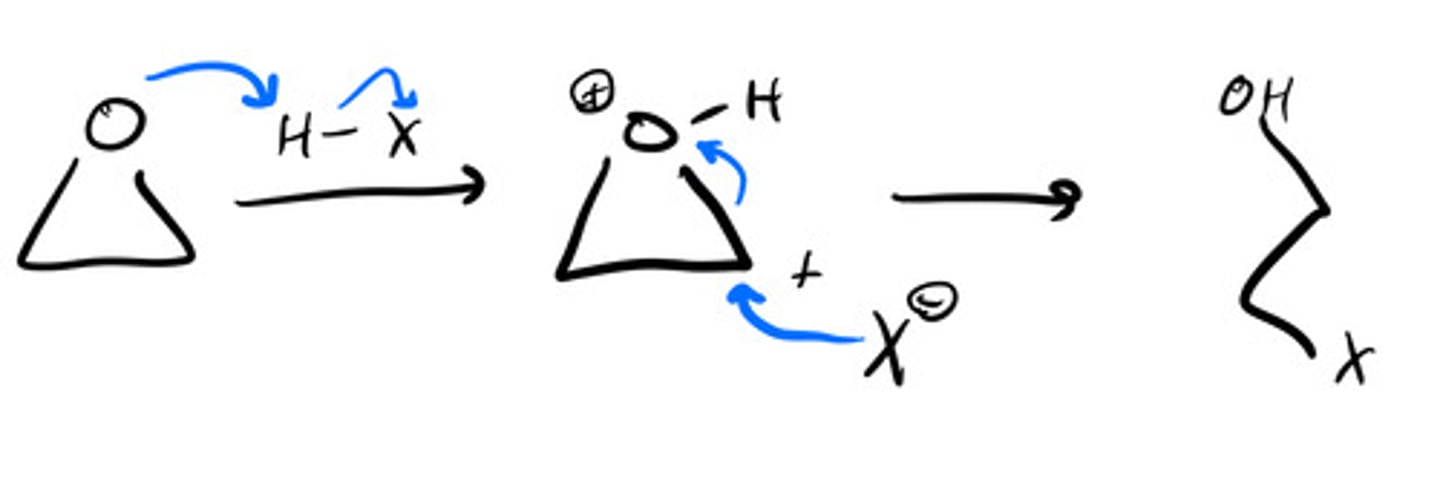
Ring opening of oxiranes to produce alcohols- Halohydrogenation: steps

Ring opening of oxiranes to produce alcohols- acid-catalyzed: mechanism
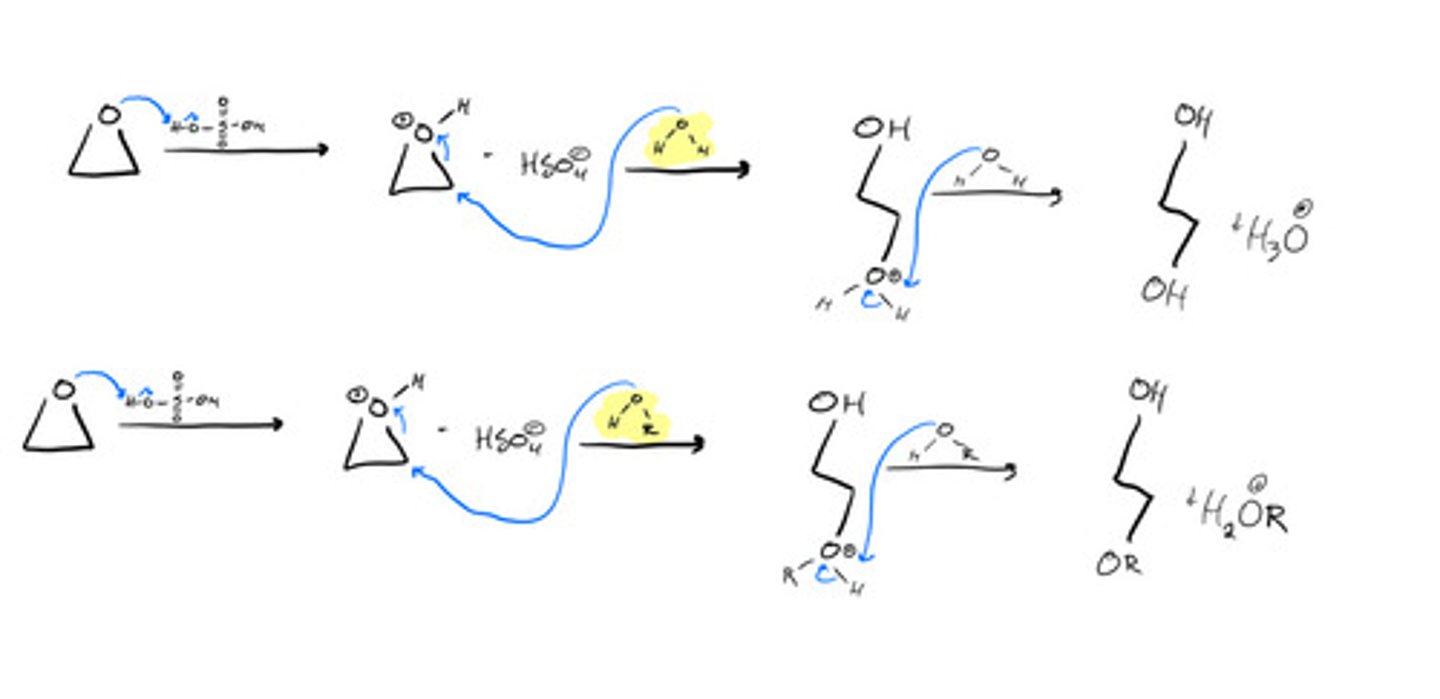
Ring opening of oxiranes to produce alcohols- acid-catalyzed: steps

Ring opening of oxiranes to produce alcohols- Sn2: mechanism
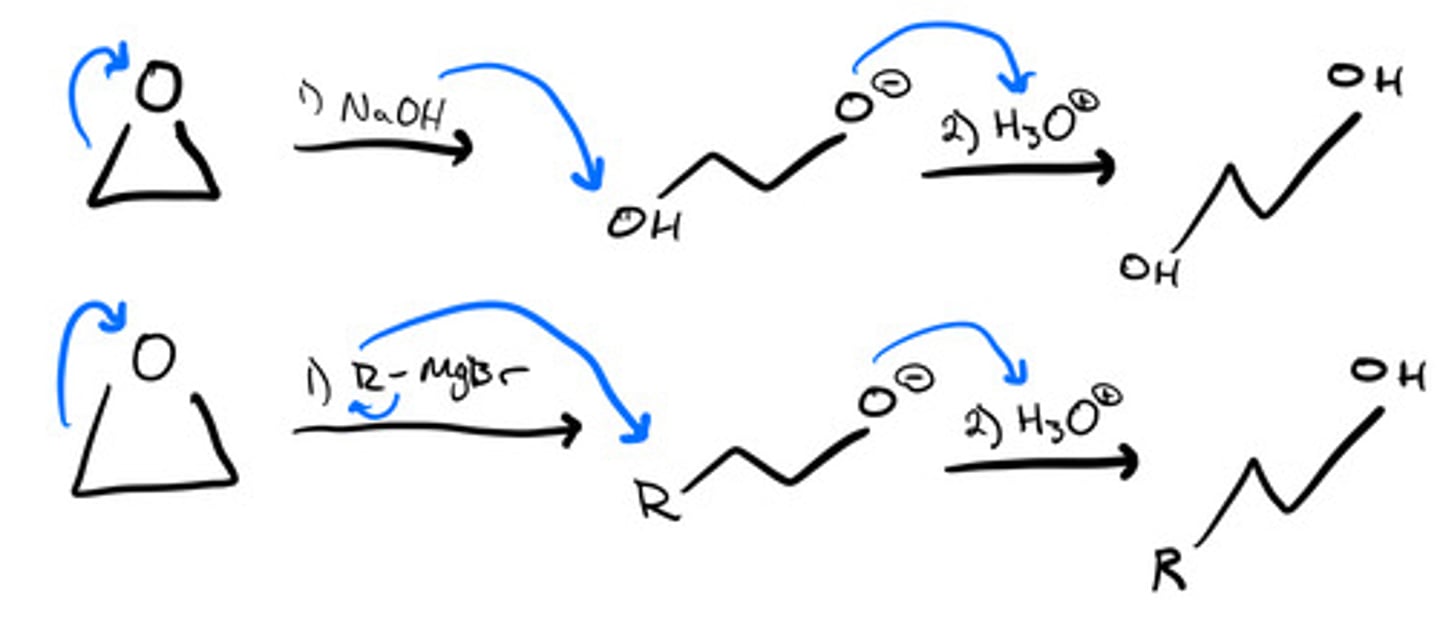
Ring opening of oxiranes to produce alcohols- Sn2: steps

Chromate ester from primary alcohol to form carboxylic acid: mechanism

Chromate ester from primary alcohol to form carboxylic acid: steps

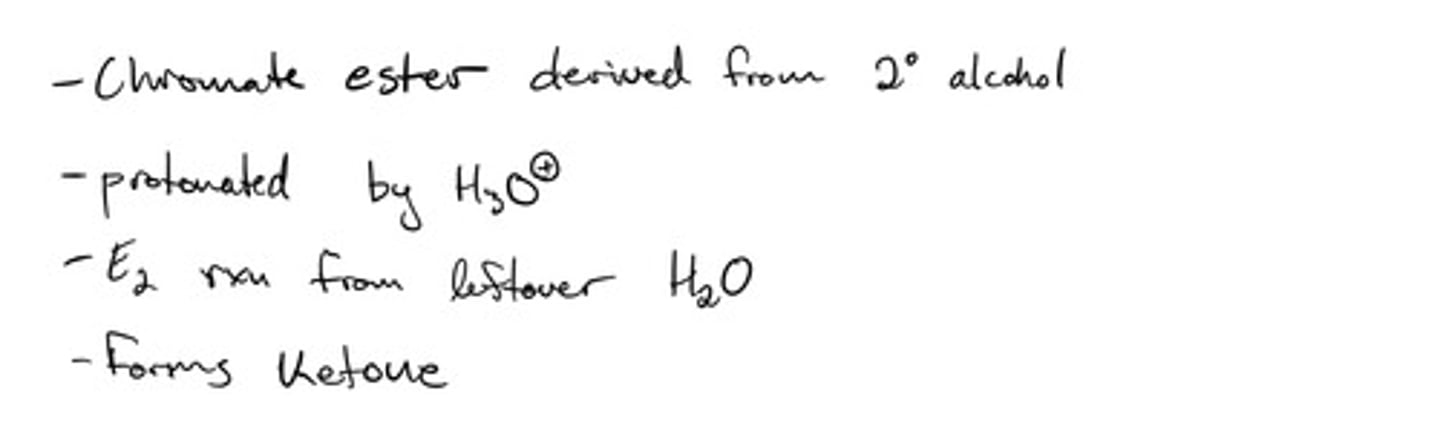
Chromate ester from secondary alcohol to form ketone: mechanism
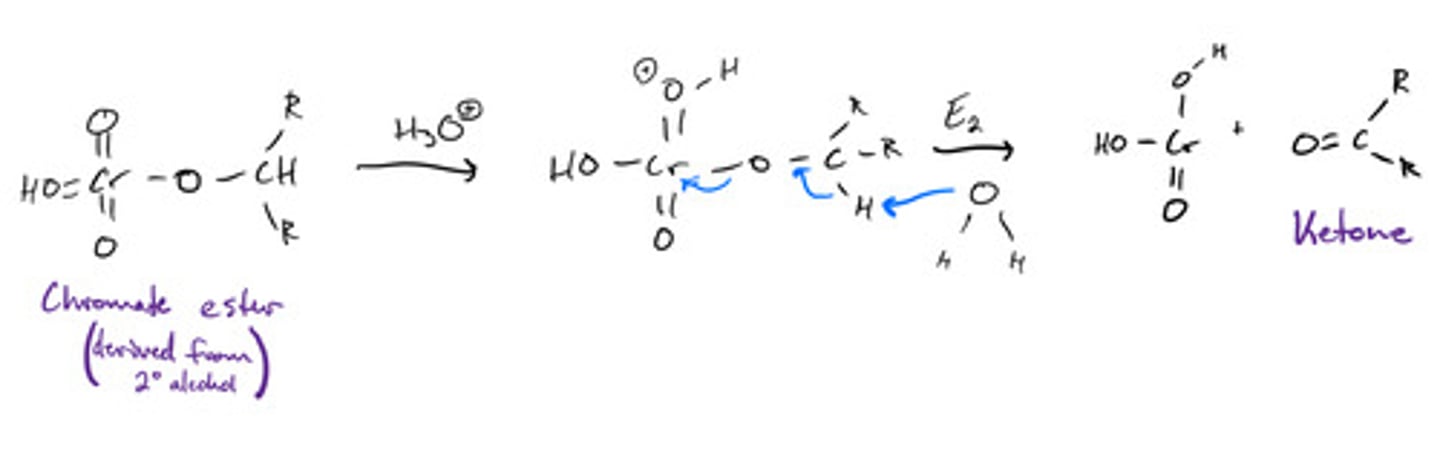
Chromate ester from secondary alcohol to form ketone: steps
Oxidation of alcohols using DMP: steps

Converting primary and secondary alcohols using phosphorous halides: mechanism
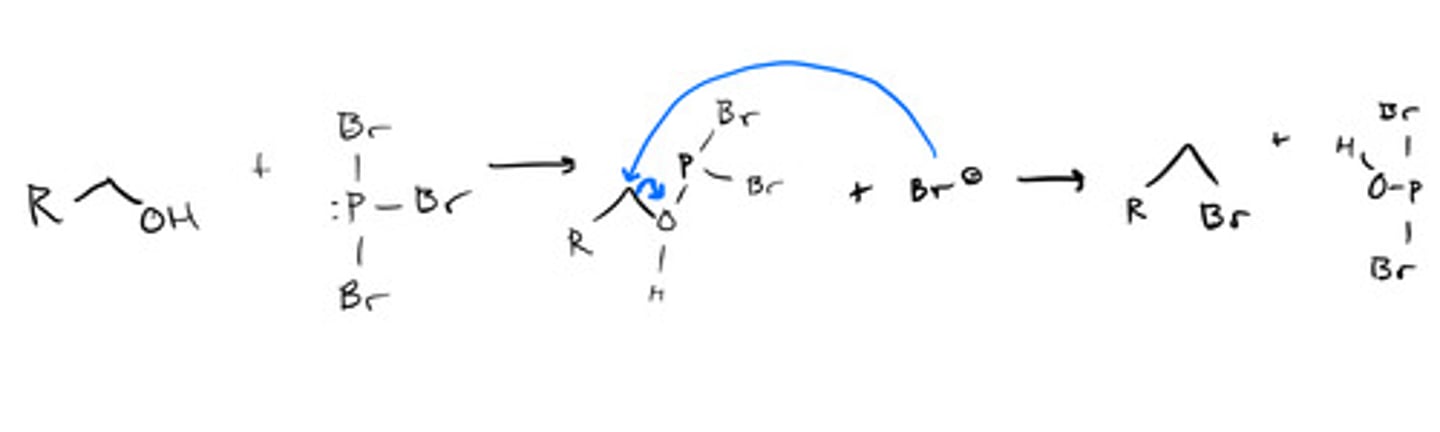
Converting primary and secondary alcohols using phosphorous halides: steps
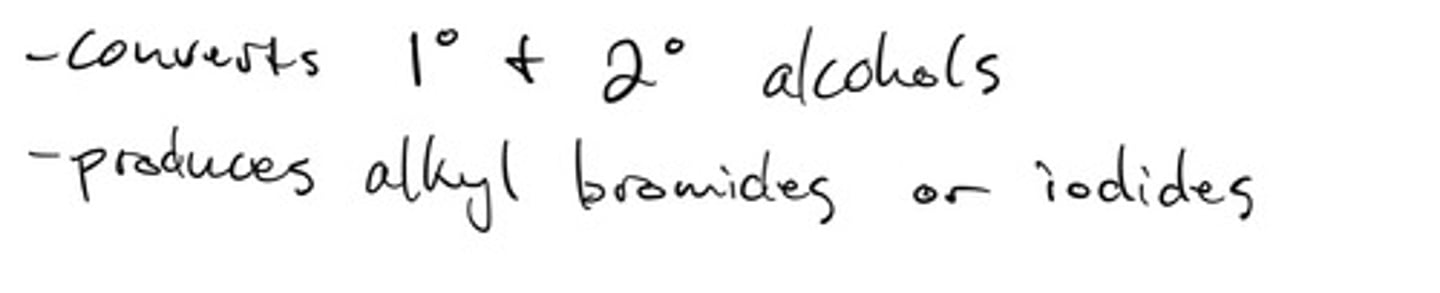
Converting primary alcohol to an alkyl halide using lucas reagent: mechanism

Converting primary alcohol to an alkyl halide using lucas reagent: steps
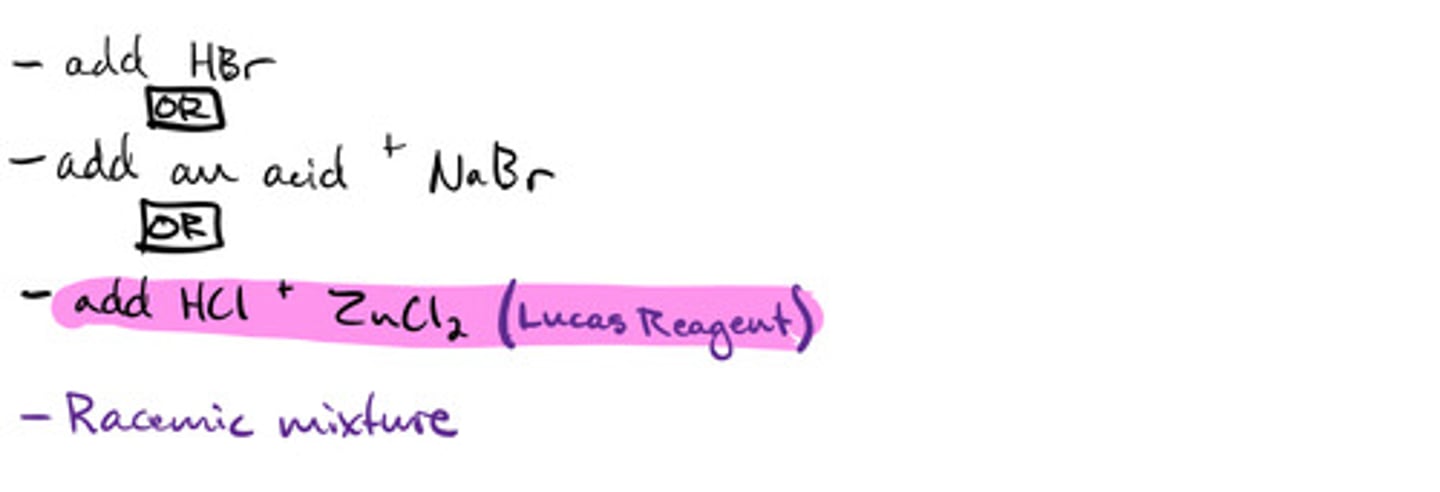
Oxidation of alcohols to aldehyde- TEMPO catalyst: mechanism

Oxidation of alcohols to aldehyde- TEMPO catalyst: steps
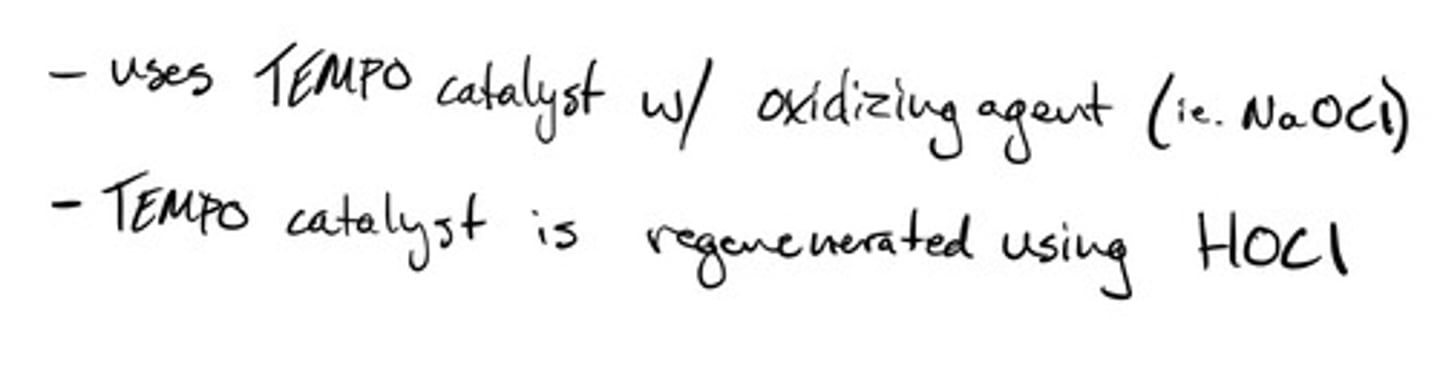
Alcohols are converted to sulfonates using....?
Tosylate (OTs), Mesylate (OMs), Triflate (OTf)
Acetylide ion to form C-C bonds: mechanism
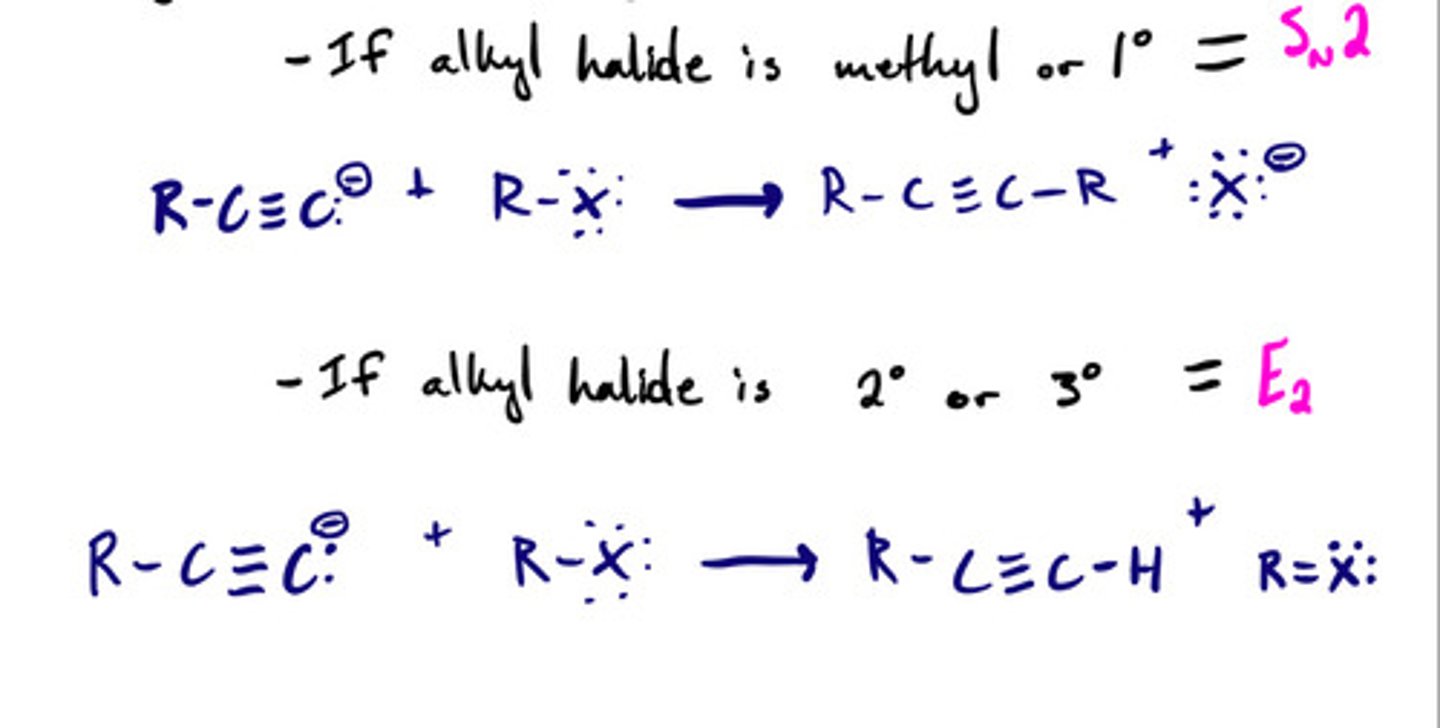
Acetylide ion to form C-C bonds: steps
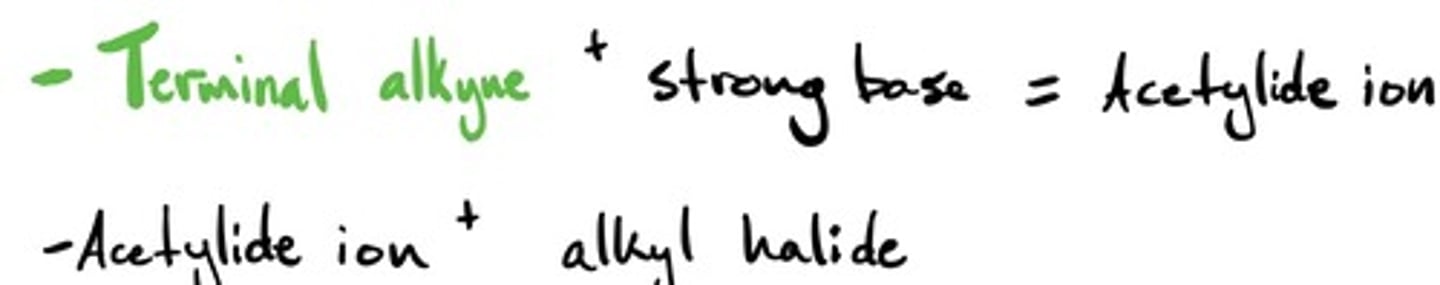
Acetylide ion to form alcohol: mechanism
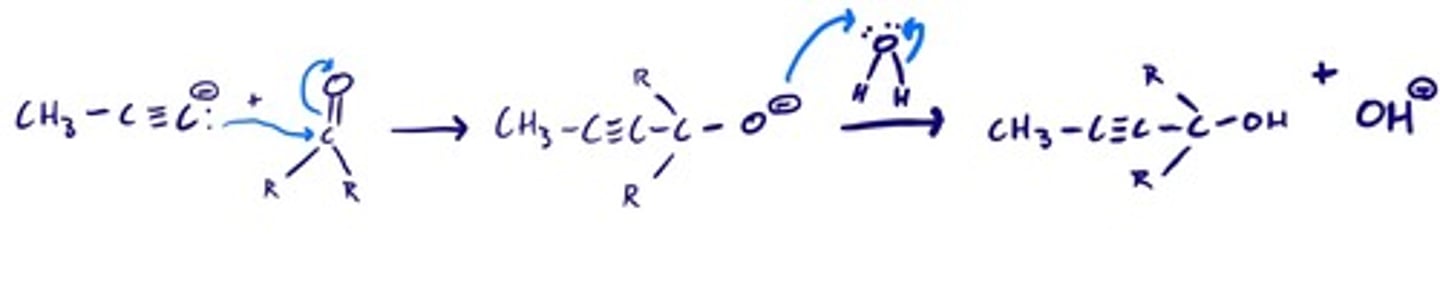
Acetylide ion to form alcohol: steps

Dialkylation: steps
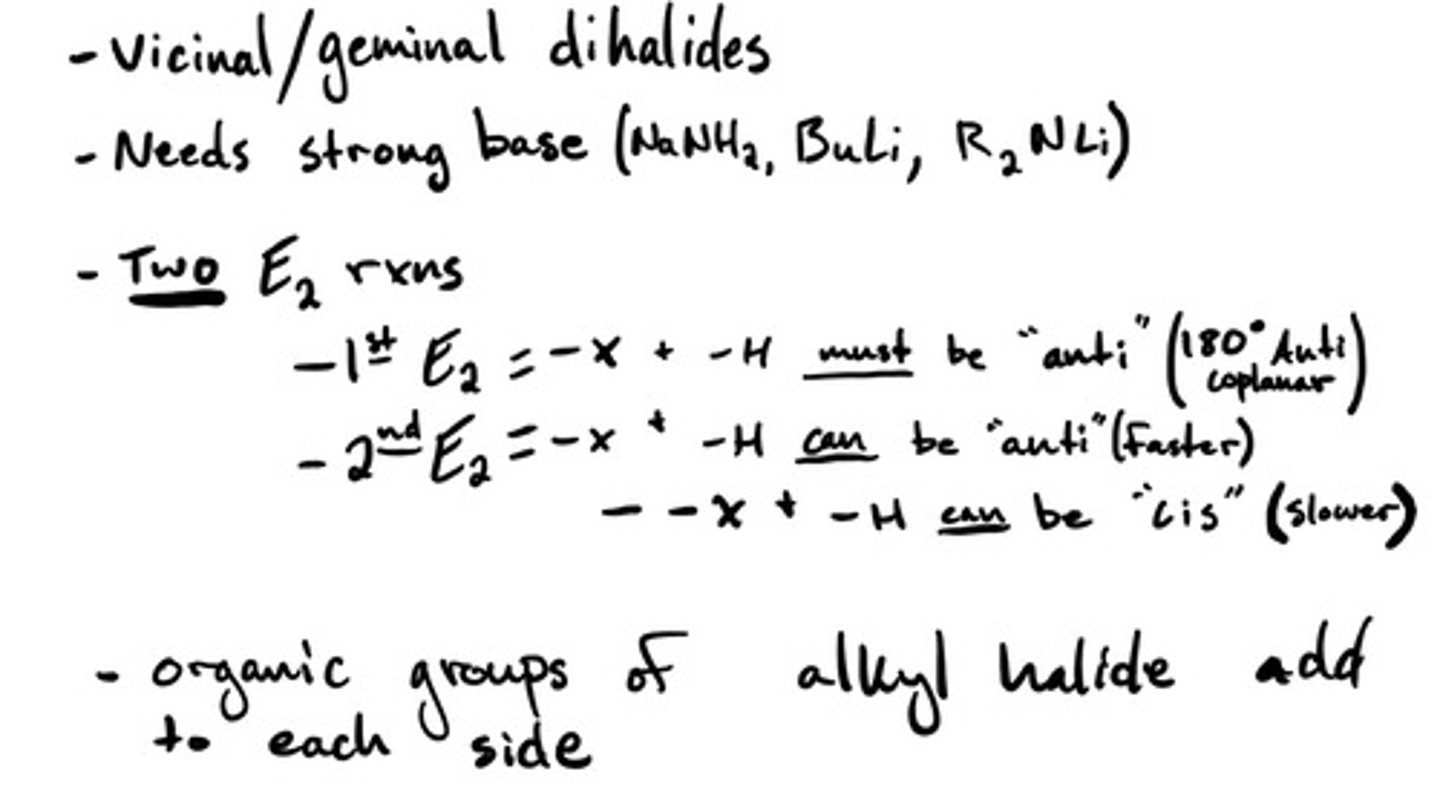
Dialkylation: mechanism
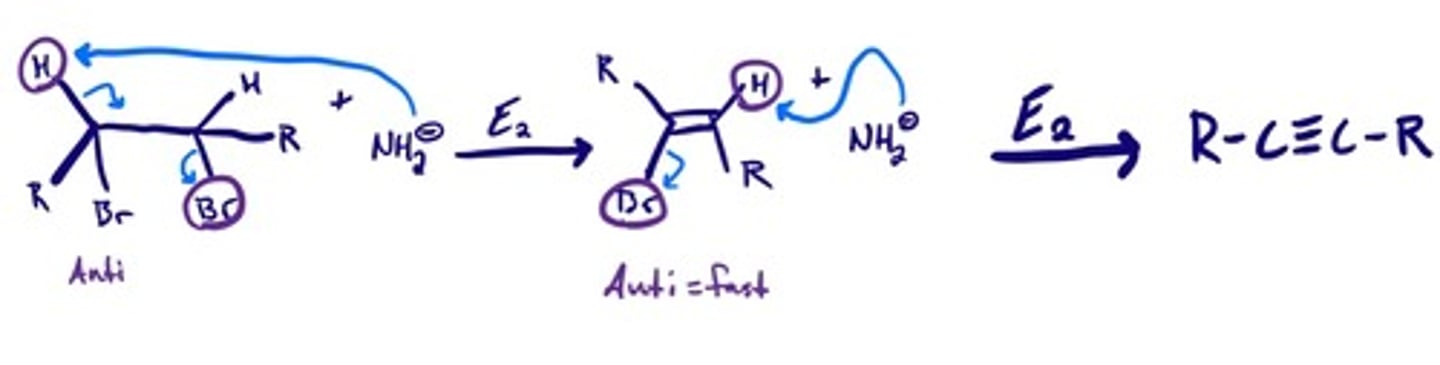
Reduction of alkynes- dissolving metals: mechanism
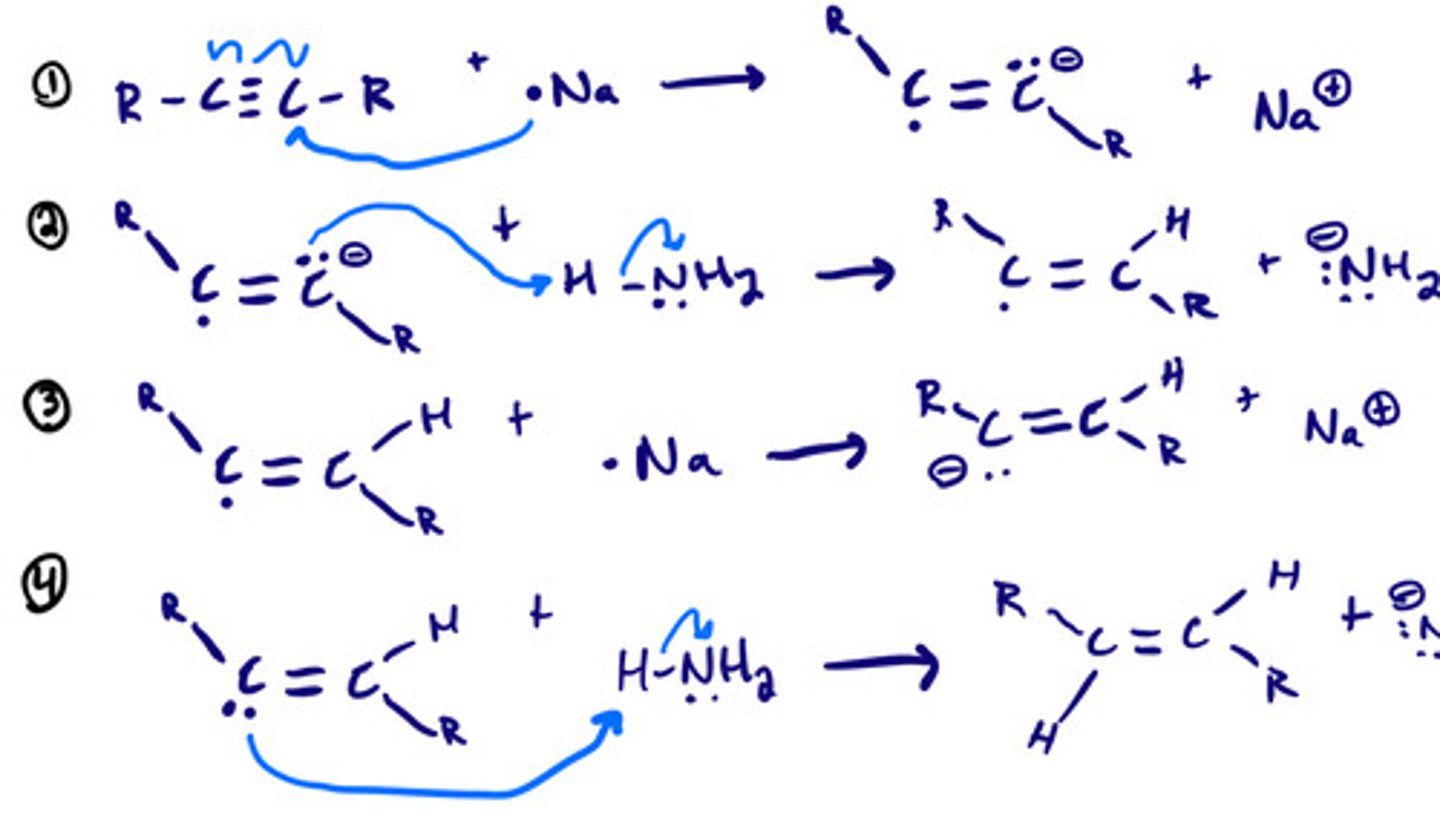
Reduction of alkynes- dissolving metals: steps
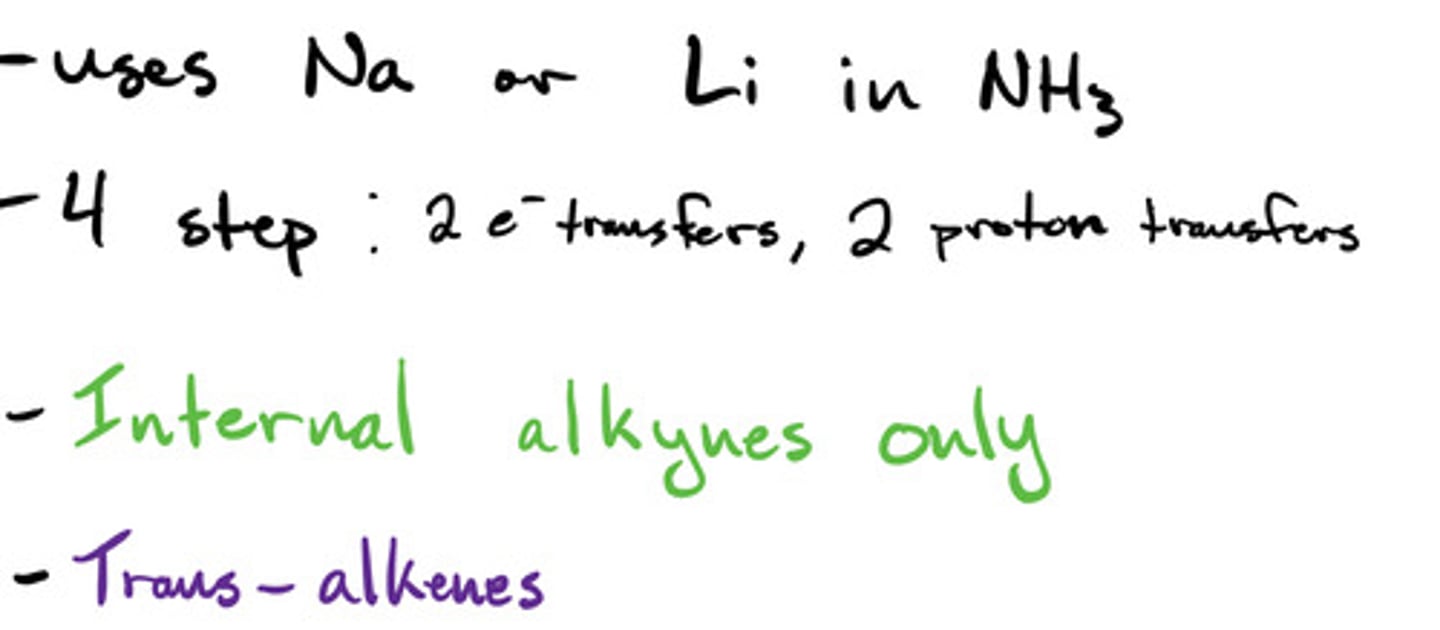
Reduction of alkynes- hydrogenation: mechanism
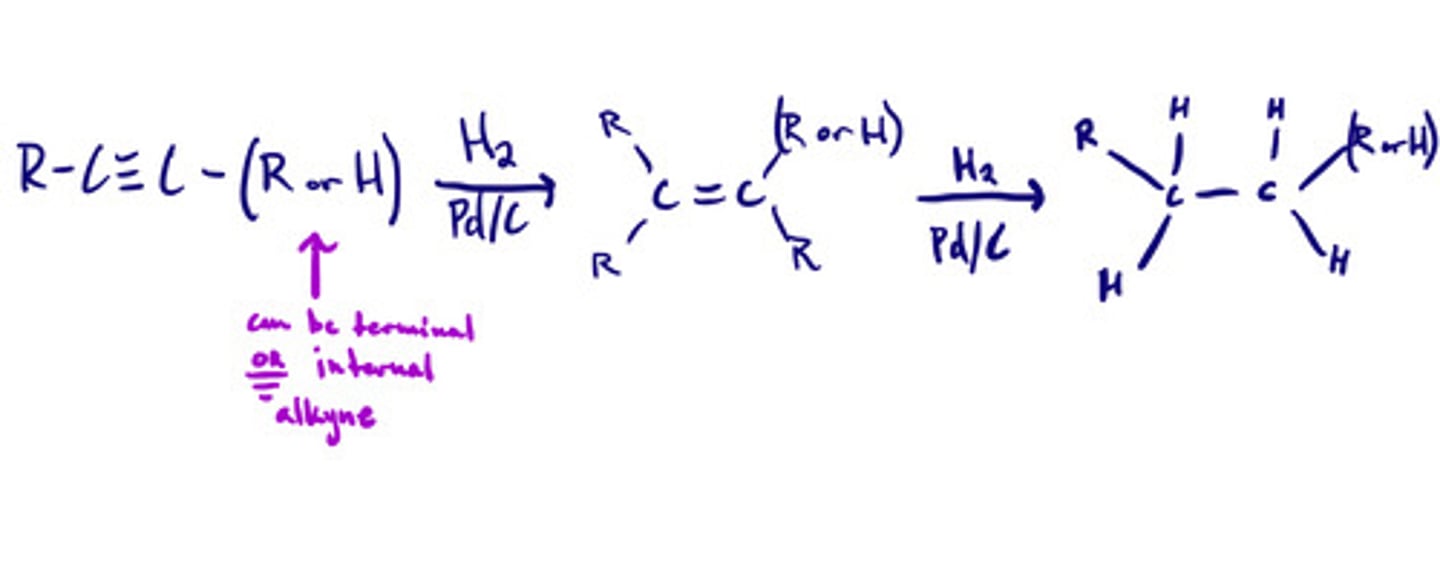
Reduction of alkynes- hydrogenation: steps

Addition of hydrogen halides to alkynes: mechanism
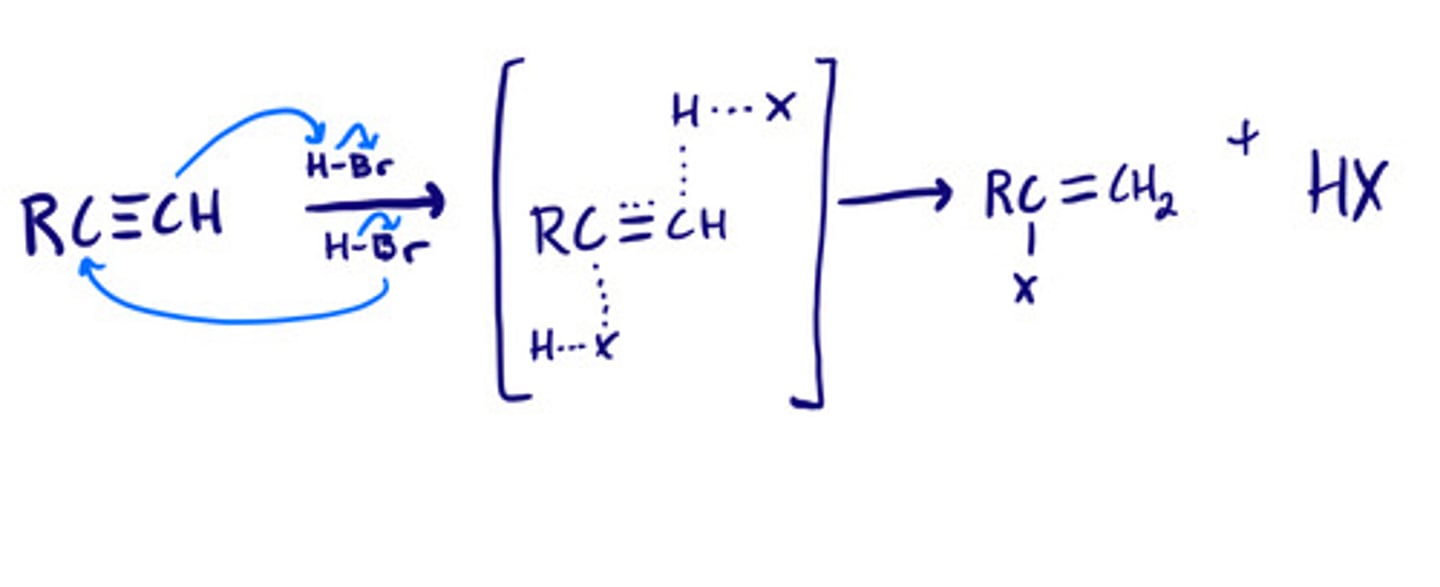
Addition of hydrogen halides to alkynes: steps

Hydration of alkynes: mechanism
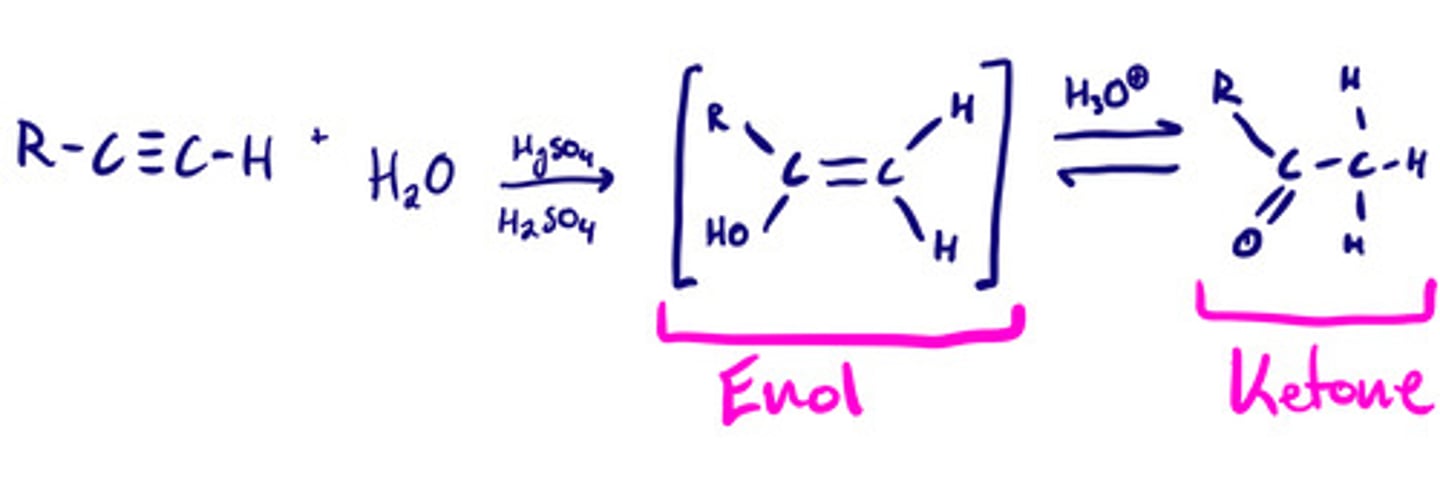
Hydration of alkynes: steps

Oxidative cleavage- ozonolysis of alkynes: mechanism
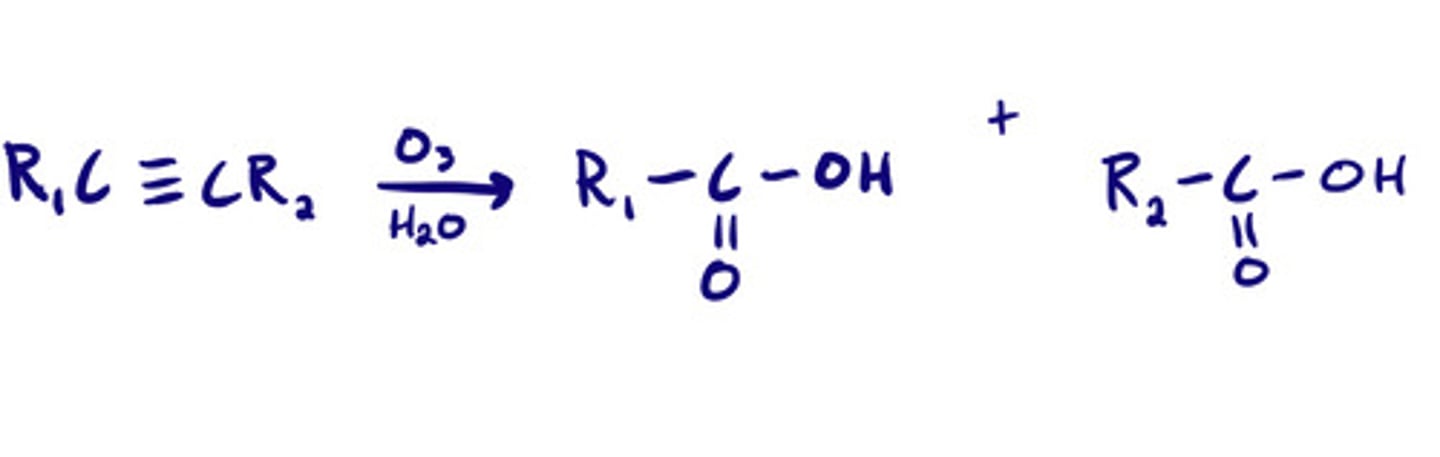
Oxidative cleavage- ozonolysis of alkynes: steps

Hydrohalogenation of alkenes: steps

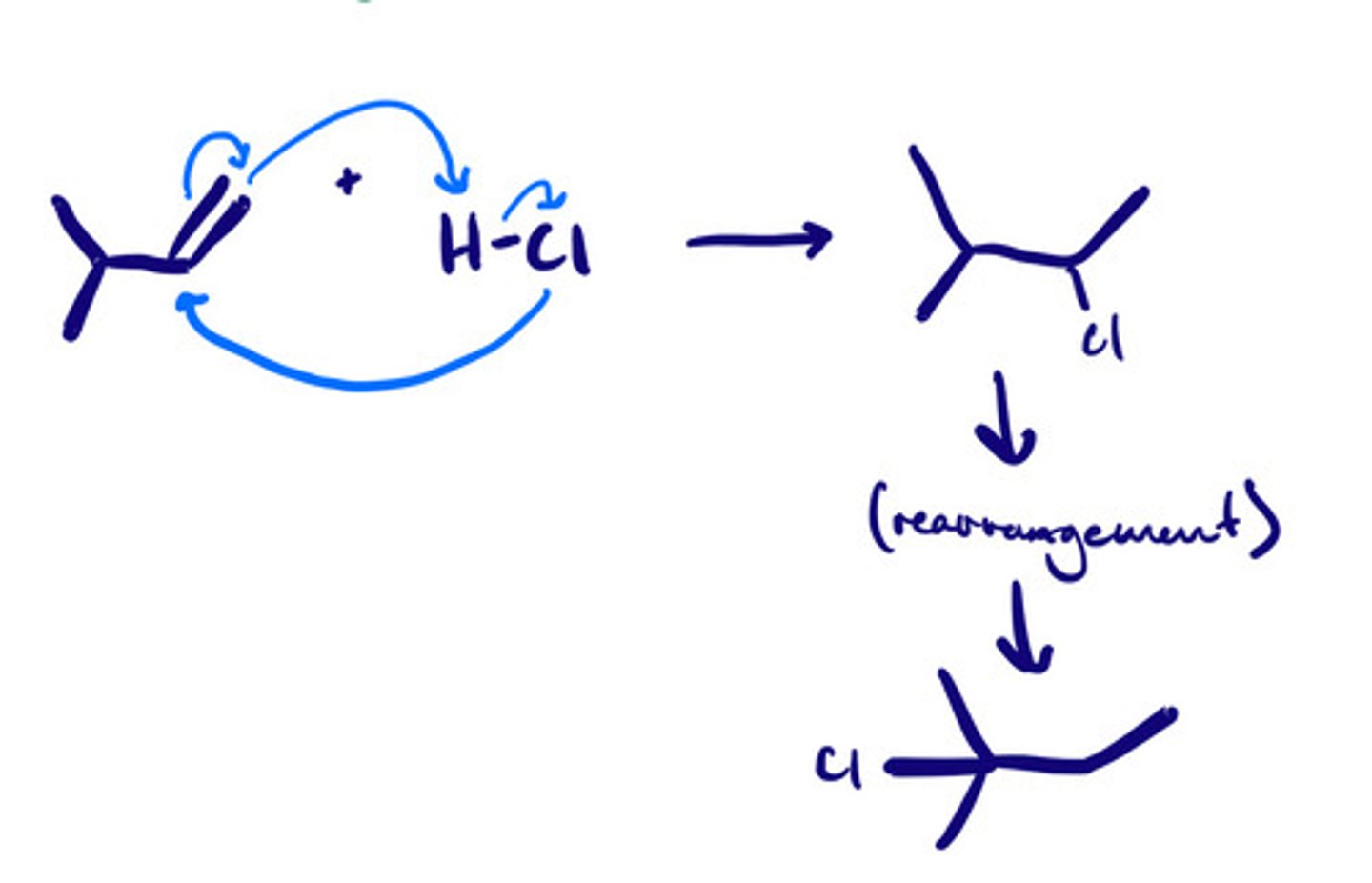
Hydrohalogenation of alkenes: mechanism
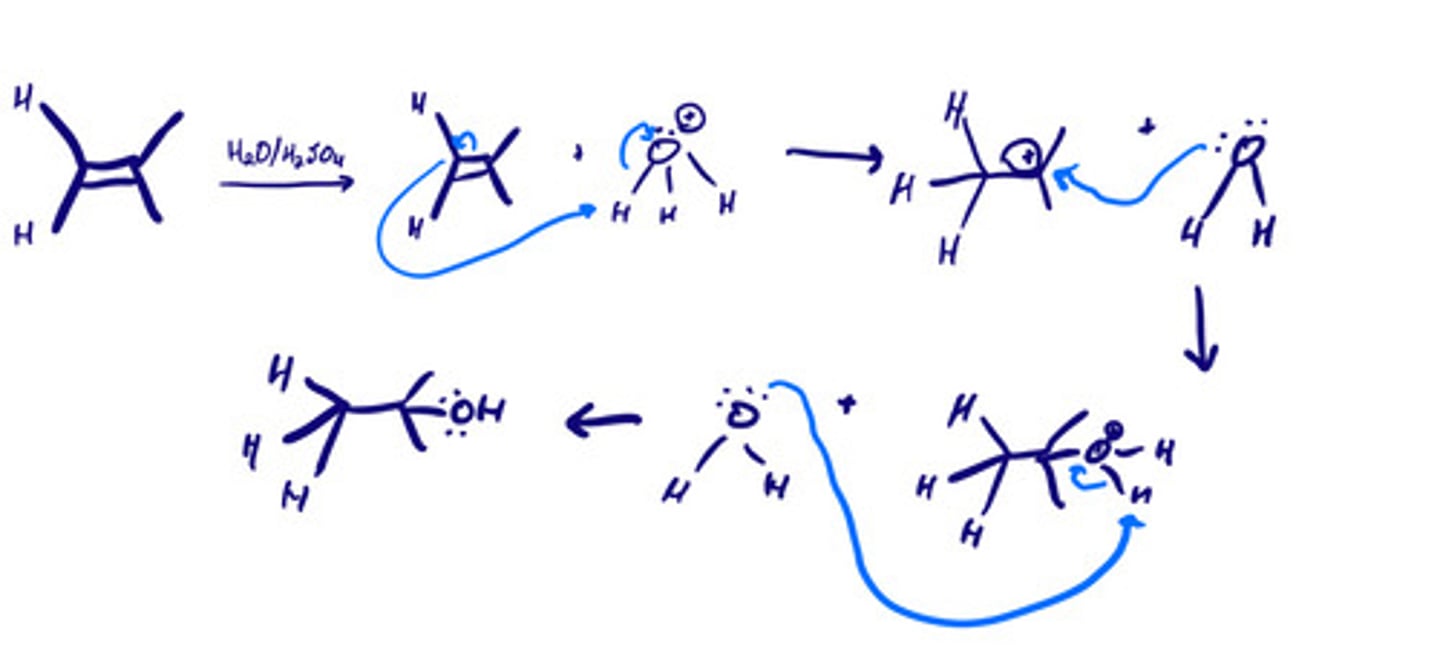
Acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes: mechanism
Acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes: steps
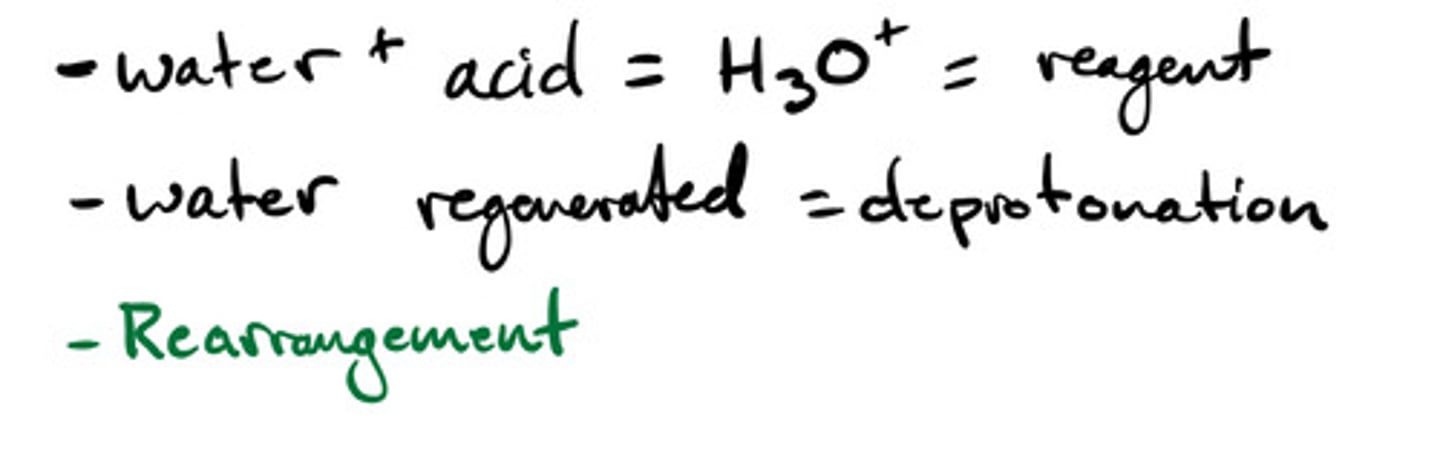
Hydroboration-oxidation to form alcohols: mechanism
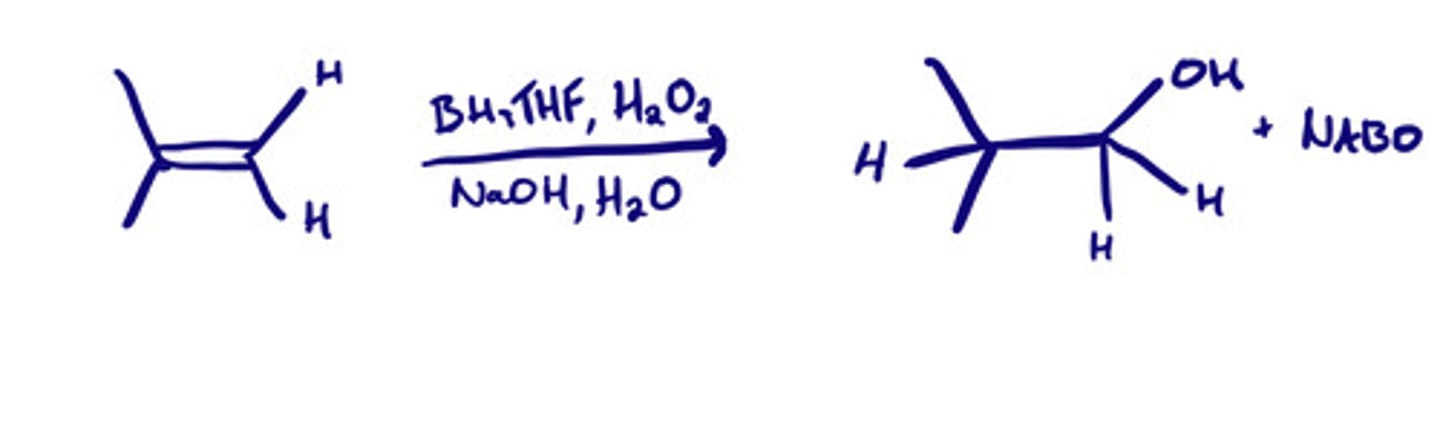
Hydroboration-oxidation to form alcohols: steps
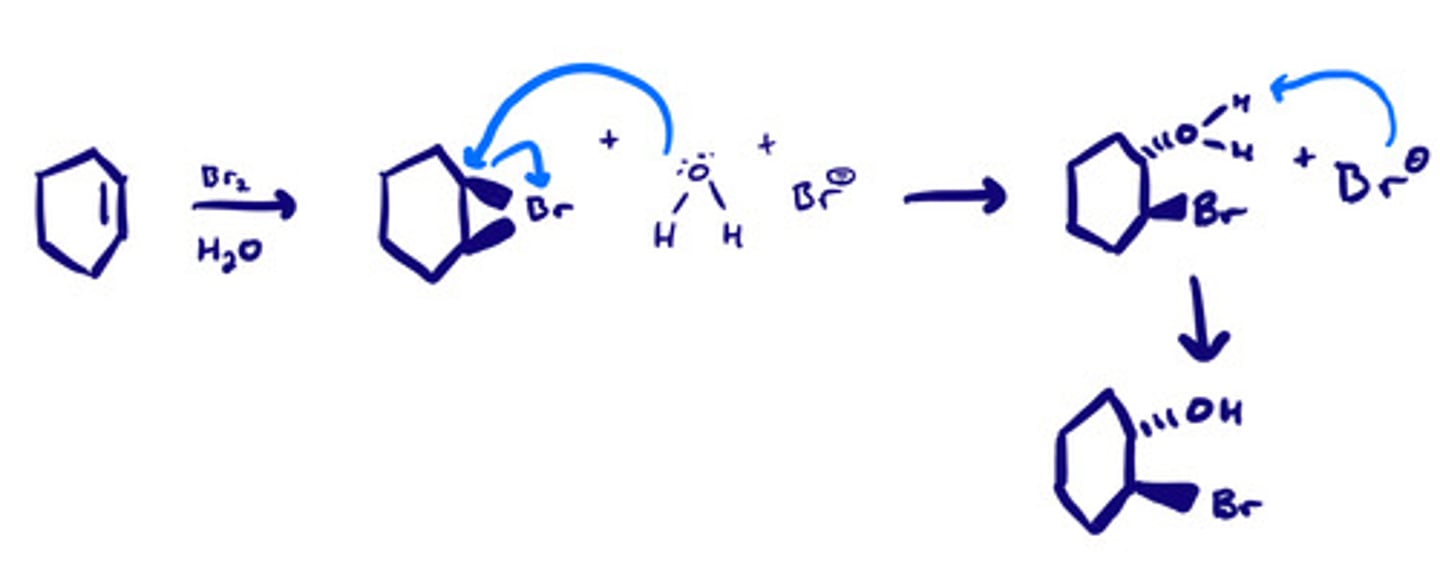
Bromination and chlorination (F2 & I2) w/ a nucleophilic solvent: mechanism
Bromination and chlorination (F2 & I2) w/ a nucleophilic solvent: steps
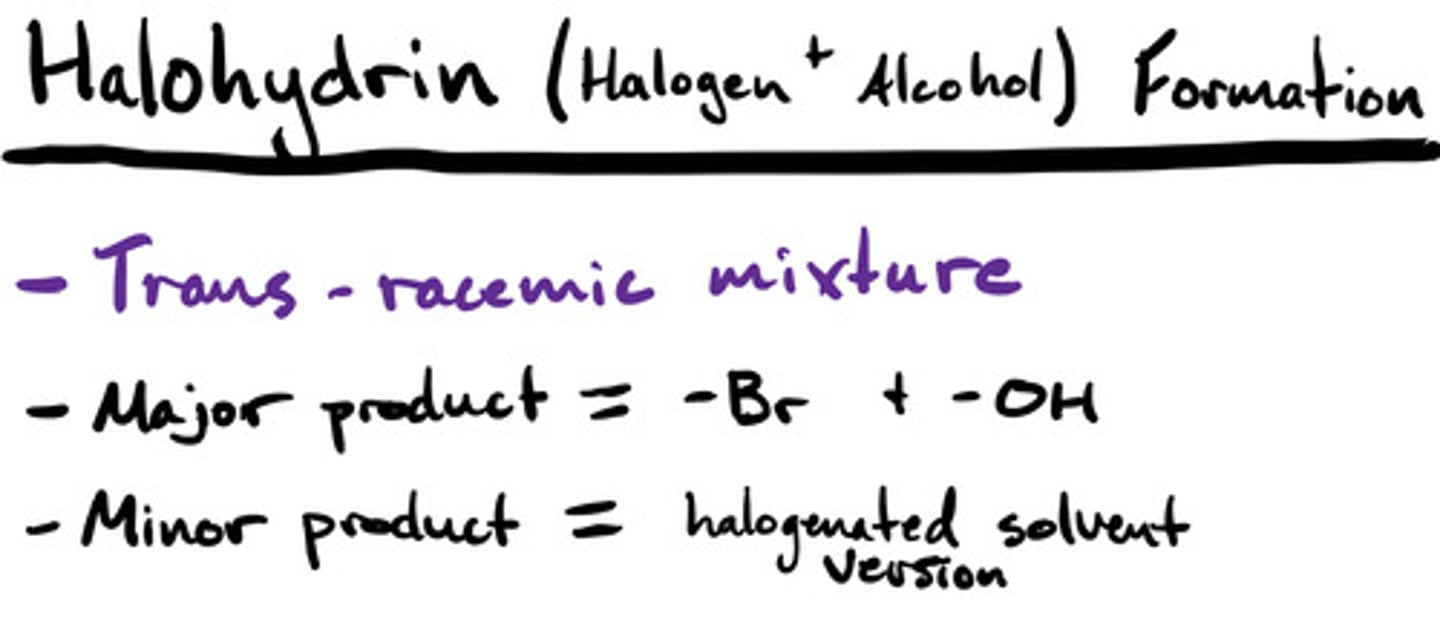
Bromination and chlorination (F2 & I2) w/ a halogenated solvent: mechanism
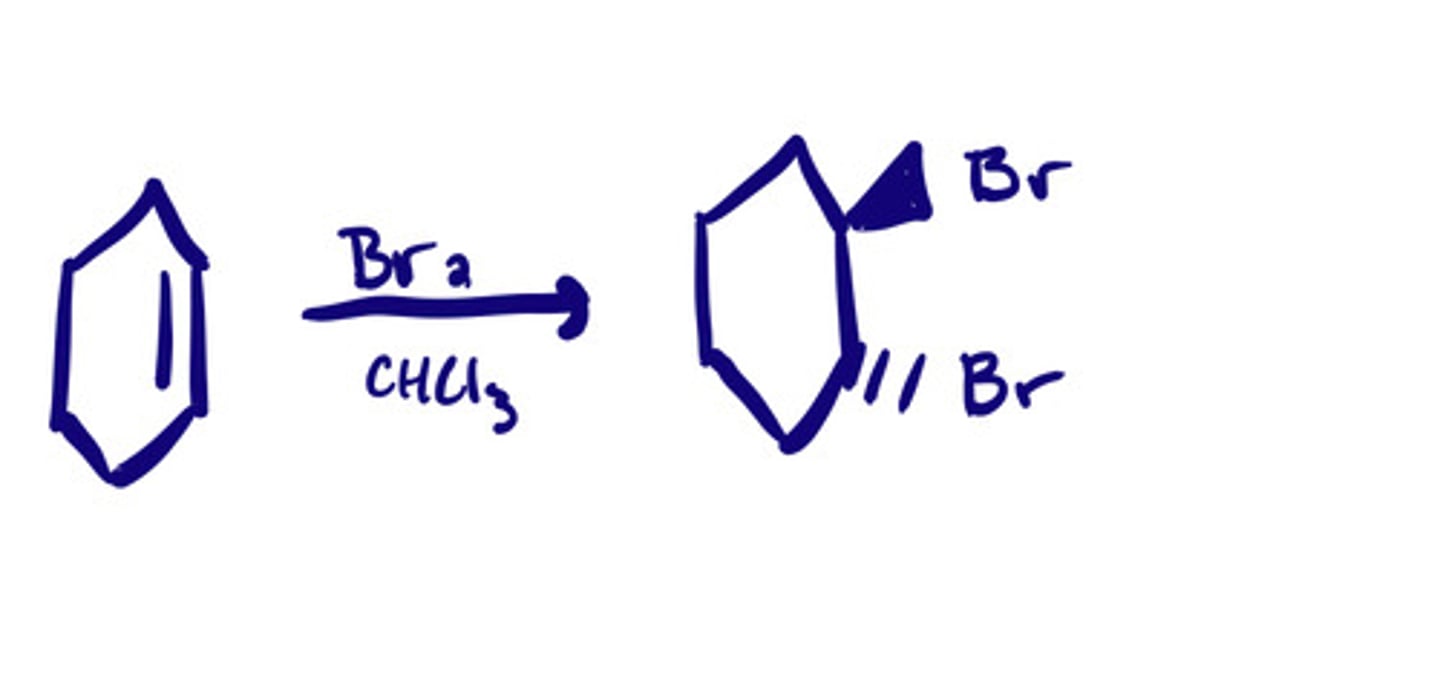
Bromination and chlorination (F2 & I2) w/ a halogenated solvent: steps

Oxymercuration-demercuration to produce alcohols: mechanism
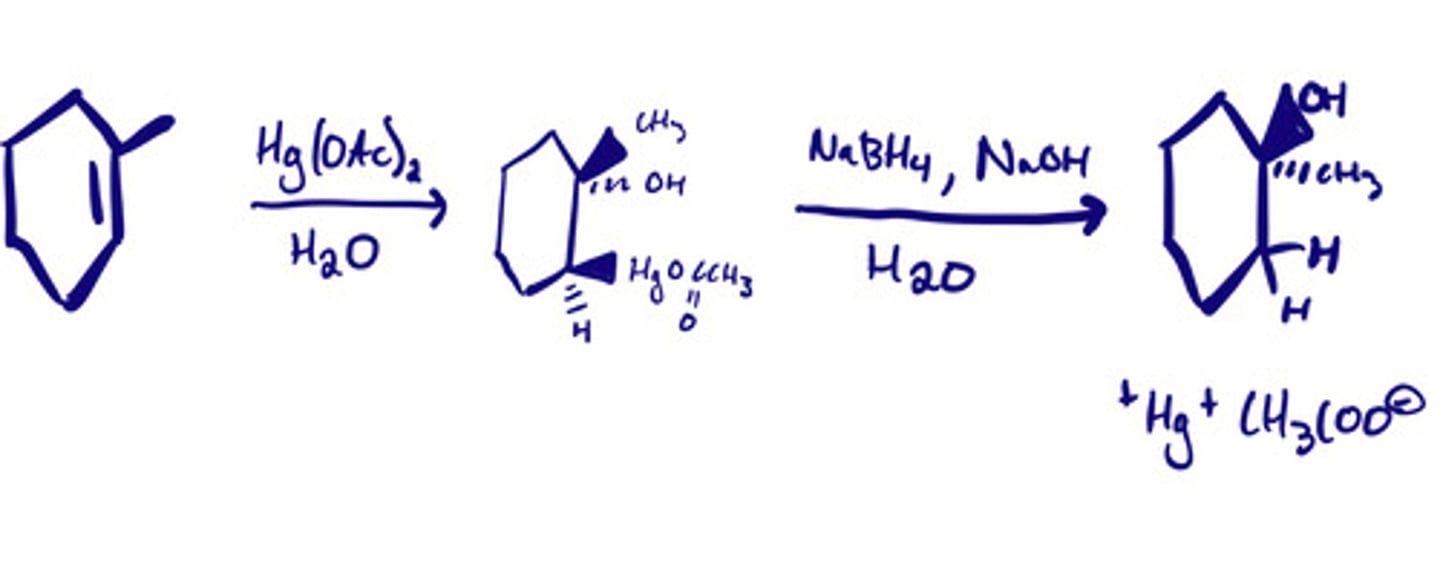
Oxymercuration-demercuration to produce alcohols: steps
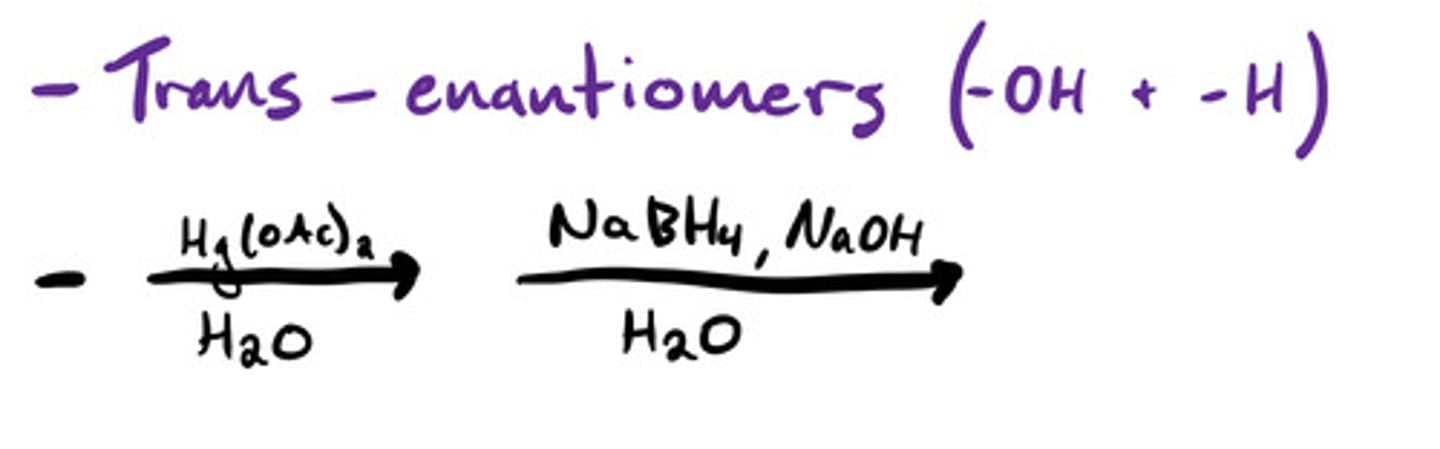
Oxaycyclopropane (epoxide/oxirane) formation: mechanism

Oxaycyclopropane (epoxide/oxirane) formation: steps

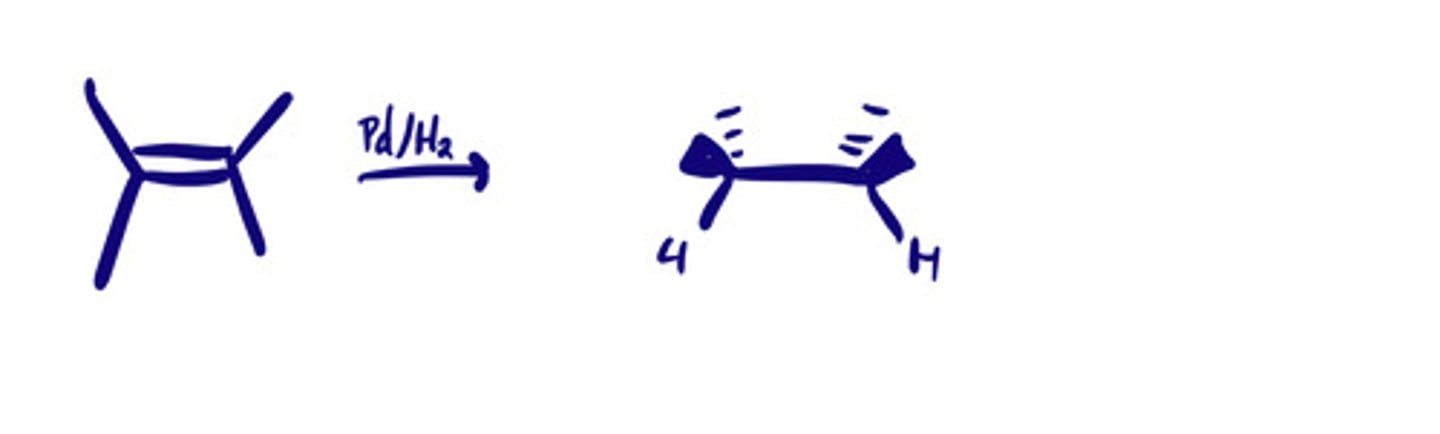
Hydrogenation: steps

Hydrogenation: mechanism
Addition of HBr w/ peroxide: mechanism
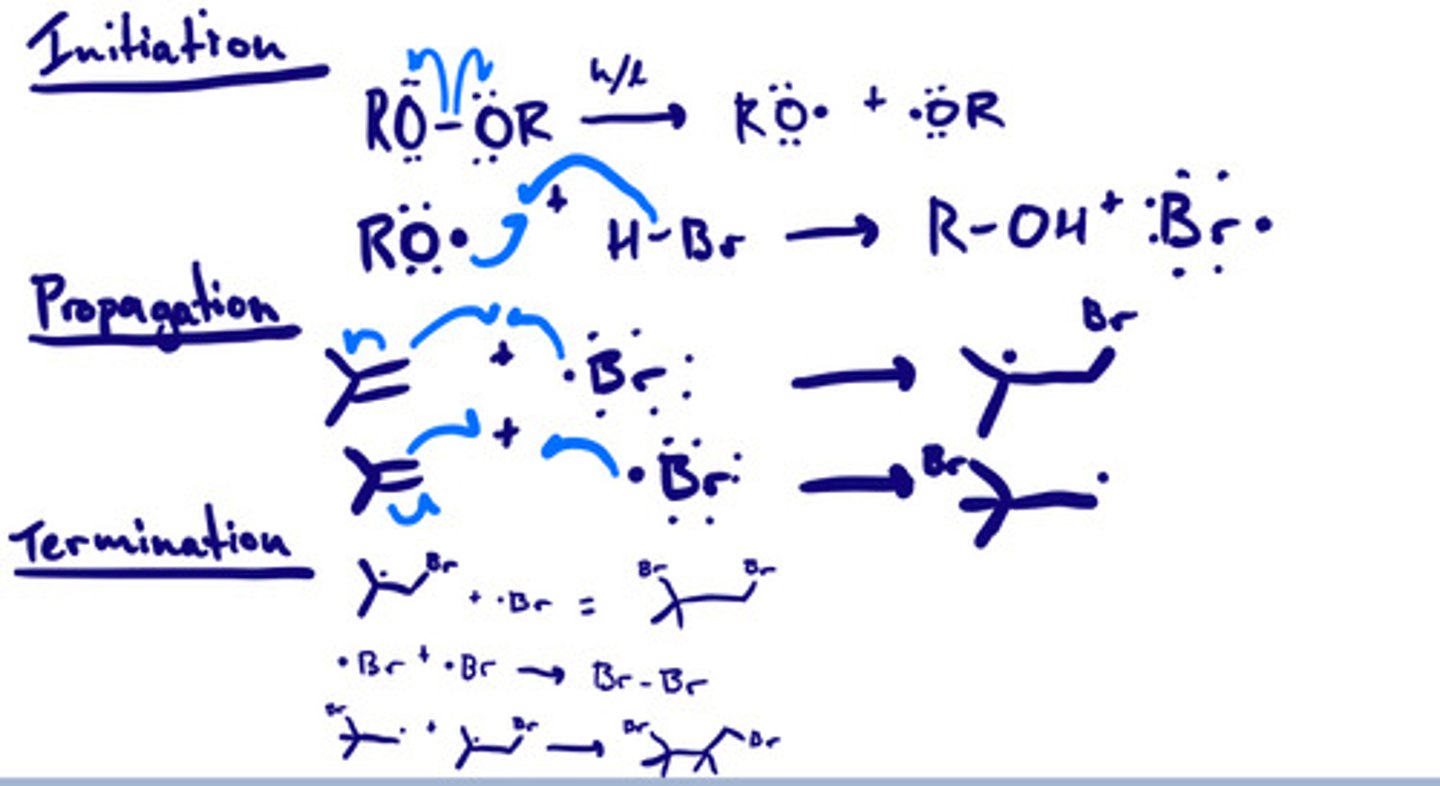
Addition of HBr w/ peroxide: steps

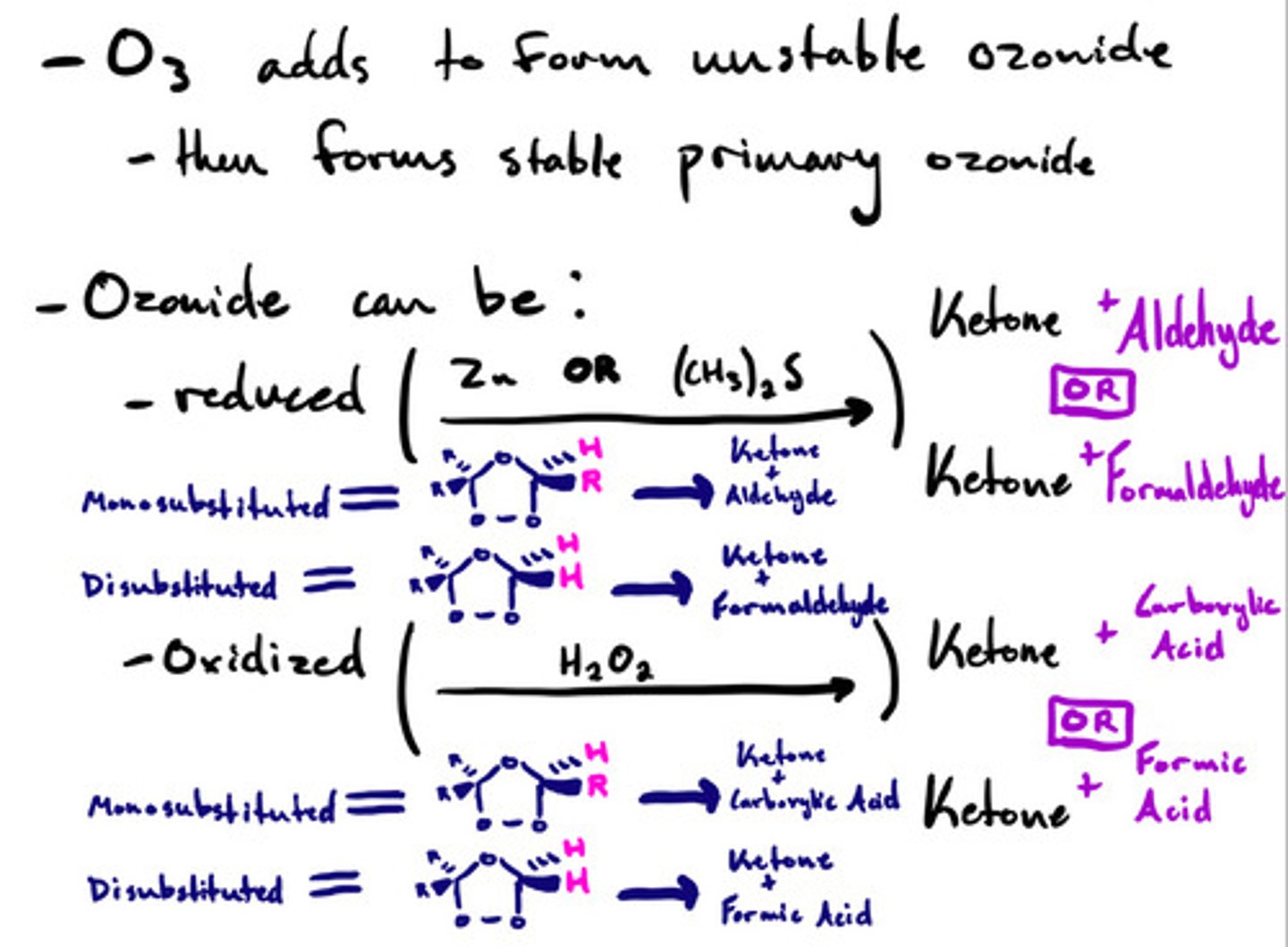
Oxidative cleavage- ozonolysis: mechanism

Oxidative cleavage- ozonolysis: steps
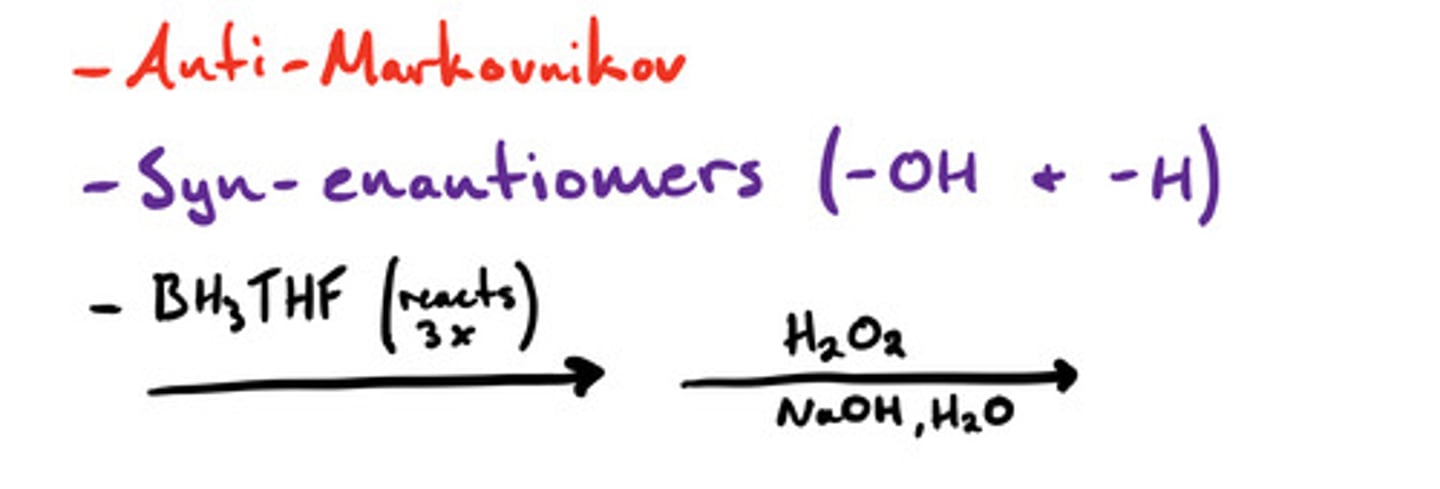
What reactions are anti-markovnikov?
-Hydroboration-oxidation to form alcohols
-Addition of HBr w/ Peroxide
-Ring opening of oxiranes to produce alcohols- Sn2
What reactions form syn/cis-enantiomers?
-Hydroboration-oxidation to form alcohols
-Dihydroxylation
-Hydrogenation of alkenes
-Hydrogenation of alkynes
Which reactions allow for rearrangement?
-Hydrohalogenation
-Acid-catalyzed hydration