Muscular System Pt. 2 Flashcards
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/123
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
1
New cards
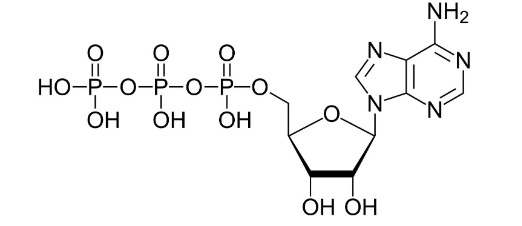
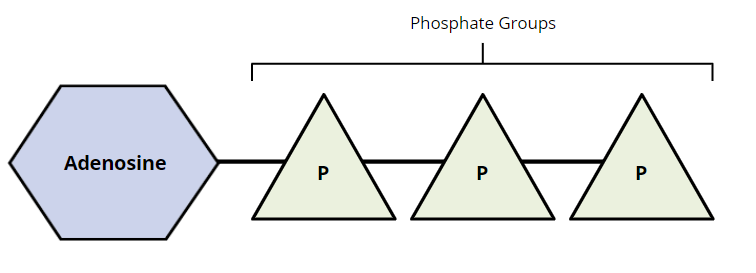
What is ATP?
Adenosine triphosphate is an energy source the body uses to power muscles
2
New cards
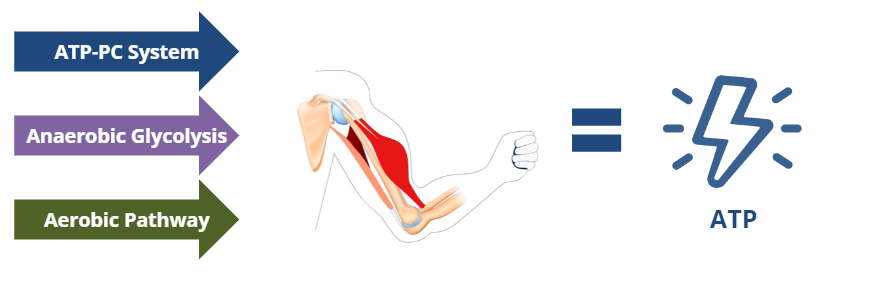
What are the 3 main methods of ATP production?
ATP-PC System, Anaerobic Glycolysis, and Aerobic Pathway
3
New cards
What does PC stand for?
Phosphocreatine
4
New cards
Why does the body need more ATP to complete muscle movements?
Stored ATP in the muscles starts a contraction, is depleted, and now needs more ATP to continue
5
New cards
Glyco means ______ and lysis means ______
sugar ; breakdown
6
New cards
Anaerobic glycolysis
The breakdown of sugar without oxygen
7
New cards
What determines which ATP method is used?
Intensity and duration of physical activity
8
New cards
What starts the muscle contraction?
Stored ATP
9
New cards
What is ATP-PC short for?
adenosine triphosphate-phosphocreatine
10
New cards
What type of energy supplies powerful short-term energy?
ATP-PC
11
New cards
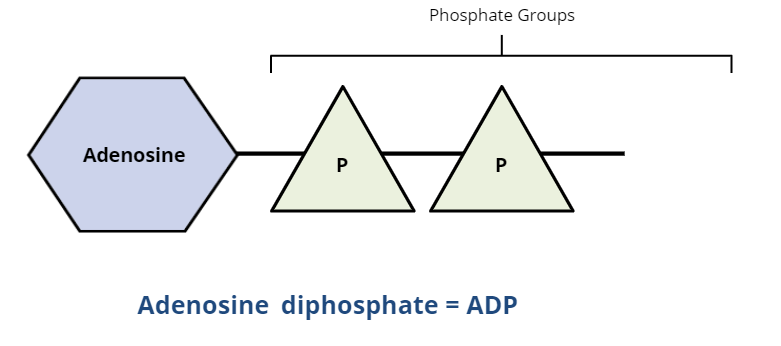
ADP is ____
Not energy
12
New cards
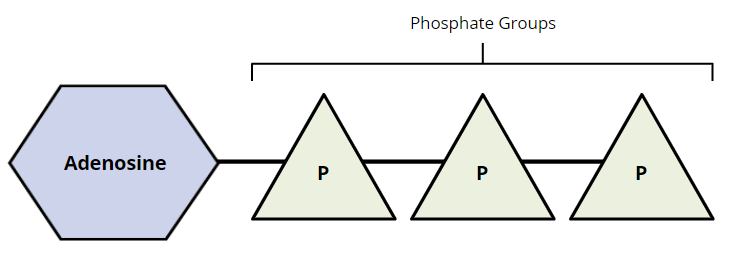
ATP is ____
Energy
13
New cards
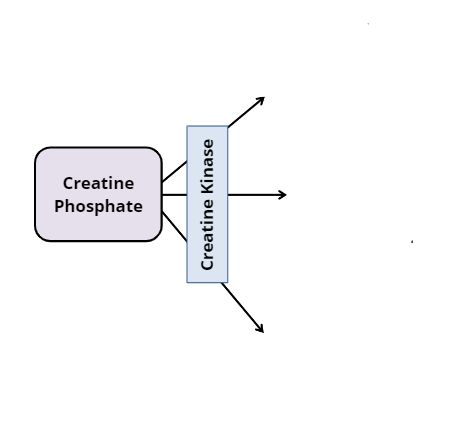
What does creatine phosphate break down into?
Creatine, a phosphate group, and energy
14
New cards
Where is glycogen found?
Muscle cells
15
New cards
Creatine Phosphate (definition)
a high-energy molecule stored only in muscle cells that can add another phosphate group to ADP
16
New cards
Where is creatine phosphate found?
Muscle cells
17
New cards
How does the ATP-PC System add another phosphate group to the ADP?
With creatine phosphate
18
New cards
What breaks down creatine phosphate?
19
New cards
What does ADP combine with to make ATP?
a Phosphate group
20
New cards
What is ATPase?
an enzyme used to combine the extra phosphate from the creatine phosphate with the ADP
21
New cards
What does the ATP creation pathway not require?
Oxygen
22
New cards
The extra phosphate from the creatine phosphate breakdown….
combines with ADP to create a new ATP molecule
23
New cards
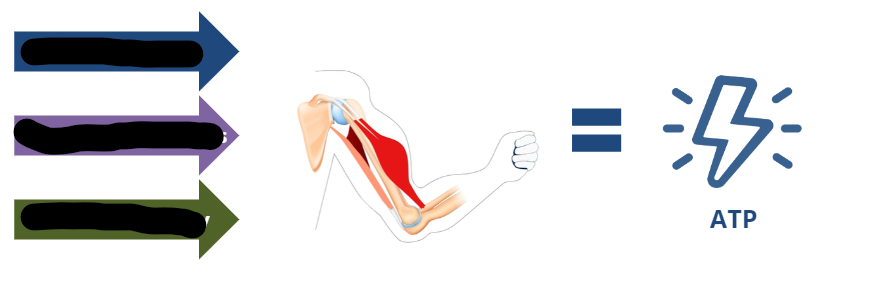
What is the next source of energy after the ATP-PC System is depleted?
Anaerobic glycolysis
24
New cards
How long does anaerobic glycolysis last?
\~2 min
25
New cards
When does anaerobic glycolysis experience a dip in power?
45 sec
26
New cards
Anaerobic
no oxygen is involved
27
New cards
Glycolysis
the breakdown of glucose into ATP
28
New cards
Glucose
a simple sugar
29
New cards
Motor unit
A group of a single motor neuron and the muscle fibers it stimulates
30
New cards
Where do motor neurons live?
Spinal cord
31
New cards
Axon terminals are…
scattered to the muscle fibers
32
New cards
Axons extend to…
Muscle
33
New cards
Neuron (definition)
nerve cell
34
New cards

Elasticity
muscle”s ability to return to its original length
35
New cards
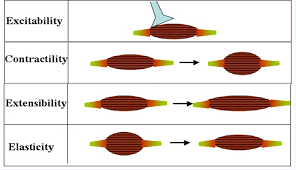
Extensibility
muscles ability to stretch or extend
36
New cards
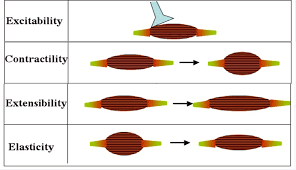
Contractility
muscles ability to contract forcefully
37
New cards
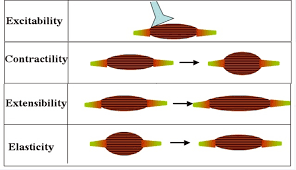
Excitability
a muscles ability to respond to stimuli
38
New cards
What triggers muscle movement?
Nerve impulse
39
New cards
Describe the Aerobic Pathways Power and Fuel source
It doesn’t produce as much power as the other two systems, but its fuel source is large and takes a long time to run out
40
New cards
Function of the aerobic pathway system
Allows a person to perform activities that require more endurance
41
New cards
Why dont muscles become acidic after the Electron Transport Chain?
Hydrogen ions are removed in the water by-product
42
New cards
Resultants of the Electron Transport Chain
* 34 ATP molecules and water as a by-product
43
New cards
In the Krebs cycle, acetyl coenzyme A is broken down into…..?
carbon dioxide which is expelled through breathing and hydrogen ions which are used in the next step
44
New cards
Acetyl coenzyme A (function)
Allows the energy system to continue breaking down glucose into energy
45
New cards
What substance is produced in aerobic glycolysis?
acetyl coenzyme A
46
New cards
The _______ pathway uses _____ which can fix the ______ problem caused by the hydrogen ions
aerobic; oxygen; acidity
47
New cards
Lactate temporarily ______ and ______
reduces acid buildup; stops ATP production
48
New cards
The body creates _____ to correct the acidic environment
lactate
49
New cards
______ cause muscles to become more acidic
Hydrogen ions
50
New cards
By-product of anaerobic glycolysis
hydrogen ions
51
New cards
ATP molecules used to fuel the glycolysis process go through several transformations and produce _________ and _________
pyruvate and hydrogen ions
52
New cards
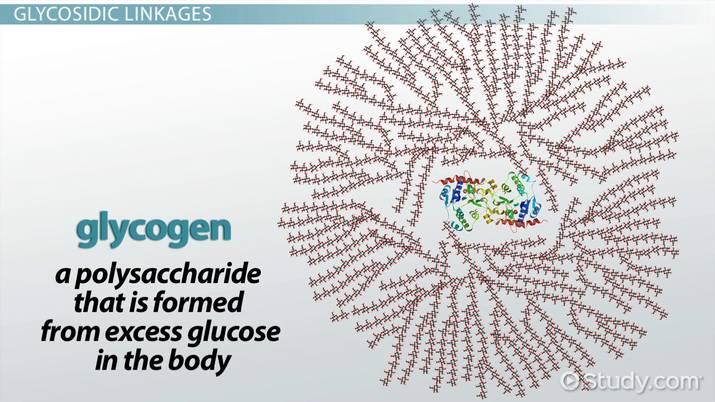
What does the body do with extra glucose?
Form glycogen to later be stored in the muscles
53
New cards
Pyruvate
a protein the body produces
54
New cards
Steps of the aerobic pathway
Aerobic glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, Electron Transport Chain
55
New cards
Anaerobic Glycolysis System Steps
Glycogen is converted into glucose, The two ATP in the glucose break down into two ADP and two phosphates, Four ATP molecules are created, Two ATP are used for glycolysis fuel and two are for muscle contraction
56
New cards
Anaerobic glycolysis (formal)
a complex conversion of glucose to lactate when oxygen is NOT available
57
New cards
How many molecules of ATP is in 2 glucose molecules
4 molecules
58
New cards
When glycogen is broke down, what do we get?
2 glucose molecules
59
New cards
What is the TOTAL amount of energy the ATP-PC System lasts?
\~10-20 sec
60
New cards
How long does the breakdown of creatine phosphate last?
\~5-8 sec
61
New cards
How long does the INITIAL ATP-PC energy last?
\~6-15 sec
62
New cards
What are the 3 things you need for a muscle to contract?
Energy System, Nerve Impulse, Action Potential
63
New cards
Sarcolemma
a plasma membrane beneath the endomysium
64
New cards
Primary Function of the Sarcolemma
to help with the absorption of calcium that is required for muscle contraction
65
New cards
Neuromuscular junctions
junctions formed by the axon terminals of the motor unit with the sarcolemma in various muscles
66
New cards
Interstitial fluid
allows the neurotransmitter involved in the impulse to work and is found in the synaptic cleft
67
New cards
Acetylcholine (Ach)
a neurotransmitter located in vesicles of the axon terminal at the neuromuscular junction
68
New cards
Another word for impulse is…
Action Potential
69
New cards
What are the three that start a muscle contraction?
Energy Systems, Nervous System, Action Potential
70
New cards
Step 1 of Action Potential Sequence
A nerve impulse travels to the axon terminals of the muscle
71
New cards
Step 2 of Action Potential Sequence
Calcium channels open, allowing calcium to enter the axon terminal
72
New cards
Step 3 of Action Potential Sequence
The presence of calcium causes the release of the enzyme
73
New cards
Step 4 of Action Potential Sequence
ACh (acetylcholine) spreads across the synaptic cleft and attaches to receptors on the sarcolemma
74
New cards
Step 5 of Action Potential Sequence
The ACh (acetylcholine) opens channels in the sarcolemma, allowing sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+) ions to build up in muscle fibers, changing the electrical charge
75
New cards
In Step 5 of the Action Potential Sequence, the change in electrical charge __ and __
triggers myosin and actin to use ATP which is later broken down into ADP ; produces an electrical current or the Action Potential
76
New cards
Step 6 of Action Potential Sequence
AChE (acetylcholinesterase) breaks down the ACh (acetylcholine) in the synaptic cleft, causing the sarcolemma channels to close, stopping muscle fiber contraction
77
New cards
One nerve impulse produces…
one contraction
78
New cards
Muscle cells (myocytes) are also called
muscle fibers
79
New cards
Myocyte Shapes
long and cylindrical
80
New cards
Fascicle
several bundles of individual muscle fibers
81
New cards
What is each fascicle wrapped?
Connective Tissue
82
New cards
Epimysium
a tough outer coat that extends past the muscles tapered end and blends into the tendon, wrapping the skeletal muscle
83
New cards
Perimysium
wraps the muscle fascicles
84
New cards
Endomysium
wraps individual muscle fibers
85
New cards
Mitochondria
part of the cell that produces energy
86
New cards
Skeletal muscle characteristics
striated, multinucleated, 2-3x more mitochondria organelles
87
New cards
Organelle
a subunit within a cell that has a specific function
88
New cards
Sarco-
flesh
89
New cards
Sarcolemma
a plasma membrane that wraps the muscle fibers
90
New cards
Sarco- Lemma-
flesh sheath
91
New cards
Organelles of Muscle Cells/Myocytes
Sarcoplasm, Sarcoplasmic reticulum, Myofibrils
92
New cards
Sarcoplasm
liquid that fills the muscle fiber and is made mostly of water, salts, and proteins
93
New cards
3 Functions of Sarcoplasm
hold inner contents of muscle fibers together, protecting it from damage, allows for chemical reactions to occur, allows for organelle operation
94
New cards
Myofibril
a bundle or group of smaller thread-like fibers called myofilaments
95
New cards
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
a net-like structure that surrounds each myofibril
96
New cards
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Function
storing and releasing calcium from the muscle fiber
97
New cards
Myofilaments
thread-like fibers found bundled in the myofibril
98
New cards
Two Types of Myofilament
Thick and thin
99
New cards
Myosin
thick myofilament protein
100
New cards
Actin
thin myofilament protein