Macroeconomics Unit 1 Vocabulary
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The total income earned domestically, including the income earned by foreign-owned factors of production; the total expenditure on domestically produced goods and services
Inflation rate
The rate at which prices are rising
Unemployment rate
The percentage of those in the labor force who do not have jobs
Recession
A sustained period of falling real income
Depression
A very severe recession
Deflation
A decrease in the overall level of prices
Model
A simplified representation of reality, often using diagrams or equations, that shows how variables interact
Endogenous variable
A variable that is explained by a particular model; a variable whose value is determined by the model’s solution
Exogenous variable
A variable that a particular model takes as given; a variable whose value is independent of the model’s solution
Supply and Demand equation
Q^d = D(P,Y)
Where Q^d is demand, P is price, Y income, and D() expresses how the variables in parentheses determine the quantity of pizza demanded
Market-Clearing model
A model that assumes that prices freely adjust to equilibrate supply and demand
Microeconomics
Study of how households and firms make decisions and how these decisionmakers interact in the marketplace
Utility
Level of satisfaction
What makes up GDP?
Administrative data (tax collection, education, defense, etc.)
Statistical data (Surveys of retail, manufacturing, farms, etc.)
What is the purpose of GDP?
To summarize all the data into a single number to represent economic activity in a given period of time
National income accounting
The accounting system that measures GDP and many other related statistics
Stock
A variable measured as a quantity at a point in time
Flow
A variable measured as a quantity per unit of time
Value added
The value of a firm’s output minus the value of the intermediate goods the firm purchased
Imputed value
An estimate of the value of a good or service that is not sold in the marketplace and therefore does not have a market price
Housing in GDP
Renting is buying house services and providing income for the landlord, making the rent part of GDP
For owning homes, GDP includes the “rent” these homeowners “pay” to themselves for enjoying housing services
Nominal GDP
Value of goods and services measured at current prices
Real GDP
Value of goods and services using a constant set of prices
GDP Deflator
A measure of the overall level of prices that shows the cost of the currently produced basket of goods relative to the cost of the basket in a base year
National income accounts identity
The equation showing that GDP is the sum of consumption, investment, government purchases, and net exports
Consumption
Household expenditures on goods and services
Investment
Items bought for future use
3 Types of investment
Business fixed
Residential fixed
Inventory
Government pruchases
Goods and services bought by federal, state, and local governments
Net exports
Exports - Imports
Consumer price index (CPI)
A measure of the overall level of prices that shows the cost of a fixed basket of consumer goods relative to the cost of the same basket in a base year
GDP Deflator vs CPI (3 differences)
Deflator measures the prices of all goods and services produced, whereas the CPI measures the prices of only the goods and services bought by consumers
Deflator only includes goods produced domestically
CPI assigns fixed weights while deflator is flexible
PCE deflator
Ratio of nominal personal consumption expenditure to real personal consumption expenditure; a measure of the overall level of prices that shows the cost of the currently consumer basked of goods relative to the cost of that basket in a base year
Issues with CPI
Because price is fixed, it does not reflect the ability of consumers to substitute goods (substitution bias)
Increase in purchasing power from the introduction of a new good is not reflected
Changes in quality are unmeasured
Labor force
Number of people employed and unemployed
Unemployment rate
Percentage of the labor force that is unemployed
Labor-force participation rate
Percentage of the adult population that is in the labor force
Factors of production
Inputs used to produce goods and services
Capital
Set of tools that workers use (ex. calculators or a construction crane)
Labor
Time people spend working
How do we differentiate between fixed and not fixed capital and labor?
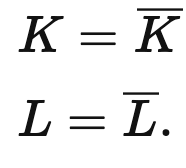
Production function
Mathematical relationship showing how the quantities of the factors of production determine the quantity of goods and services produced
Constant returns to scale
A property of a production function whereby a proportionate increase in all factors of production leads to an increase in output of the same proportion
Factor price
The amount paid for one unit of a factor of production
Competition
A situation in which there are many individuals or firms, and the actions of any one of them do not influence market prices
Marginal product of labor (MPL)
Extra amount of output the firm gets from one extra unit of labor, holding the amount of capital fixed
Diminishing marginal product
The marginal product increases at a decreasing rate
Real wage
The payment of labor measured in units of output
Marginal product of capital (MPK)
Amount of extra output the firm gets from an extra unit of capital, holding the amount of labor constant
Real rental price of capital
Rental price measured in units of goods rather than in dollars
Economic profit
The amount of revenue remaining for the owners of a firm after all the factors of production have been compensated
Accounting profit
The amount of revenue remaining for the owners of a firm after all the factors of production except capital have been compensated
Cobb-Douglas Production Functrion
A production function of the form F(K,L)=AK^α(L^1−α) where K is capital, L is labor, and A and α are parameters
Disposable income
Income remaining after the payment of taxes
Consumption function
Relationship between consumption and disposable income
Marginal propensity to consume
Amount by which consumption changes when disposable income increase by one dollar
Interest rate
The market price at which resources are transferred between the present and the future
Nominal interest rate
Rate of interest that investors pay to borrow money
Real interest rate
Nominal interest rate corrected for the effects of inflation
National Savings
A nation’s income minus consumption and government purchases; the sum of private savings and public savings
Private savings
Disposable income - consumption
Public saving
Government receipts minus government spending (Budget surplus)