Lab 8: Locomotion, Cranial Kinesis, Joints
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Aquatic locomtion
specialized to live in water
Terrestrial locomotion
locomotion on land
Cursorial locomotion
specialized for rapid running
Arboreal locomotion
locomotion through trees
Brachiation
locomotion by arm swings under branches of trees; a form of arboreal locomotion
Fossorial
specialized for digging or burrowing
Saltatorial locomotion
specialized for hopping and jumping
Aerial locomotion
specialized for flying
What adaptations aid in aquatic locomotion?
long and slender body
absence of a functional neck
reduction of projections not needed for propulsion/steering
pectoral girdle attached to skull
pelvic girdle not attached to vertebral column
Stride
full cycle of a limb movement at a particular gait
Speed is the product of ….
stride rate and stride length
What’s an adaptation that increases stride length?
increased limb length; ex. unguligrades have longer functional limbs
repositioning of the scapula
spinal flextion
Plantigrade
the heel is on the ground and strikes first each stride
Digitigrade
the digits bear the weight of the animal
Unguligrade
weight is borne by the tip of the digits
What are two adaptations that increase stride rate?
reduction in number of distal bones
having larger muscles restricted to the proximal limb
What are three adaptations that facilitate brachiation?
prominent clavicle firmly attached to sternum - functions to transfer the weight of the body to the arm
relatively long forelimbs
grasping hands - digits on manus form a hook
What adaptations aid in saltatorial locomotion?
extreme lengthening of the hindlimbs and distal segments
long tails to act as a prop or counterbalance
spinal modifications that concentrate weight in line with the hind legs
What adaptations aid in fossorial locomotion?
Large, robust limb bones with large muscles attached
Elbow lengthened (large olecranon process)
Broad shovel-like manus (see mole skeleton in lab).
What adaptations aid in aerial locomotion?
wings that provide upward force
light weight
compact body
mechanisms to minimize muscle effort
high metabolism
What are skull fenestrae?
Large openings in the temporal region of the deramtocranium in amniotes that increase attachment area for muscles associated with the jaws.
What is cranial kinesis?
Movement between the upper jaw and braincase about a joint between them.
What are some examples of animals that display cranial kinesis?
fish
reptiles
birds
What are two names for the joint between the femur and the tibia?
stifle joint
knee joint
tendon
connects tissue to bone
ligament
connects bone to bone
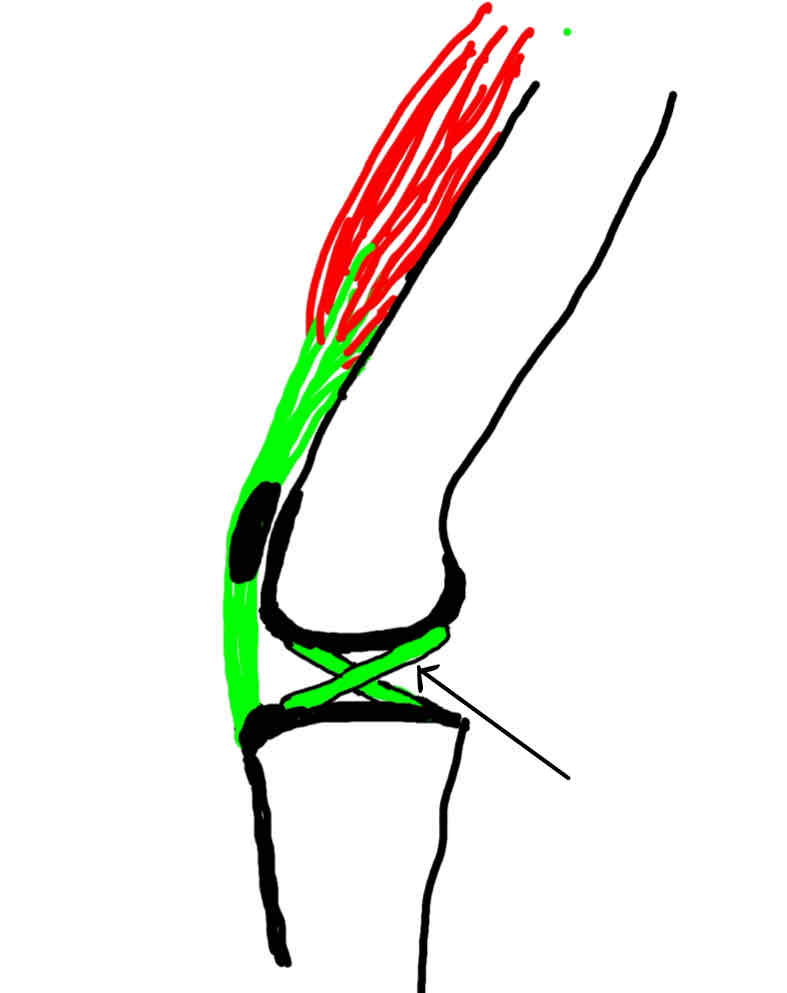
cranial cruciate ligament
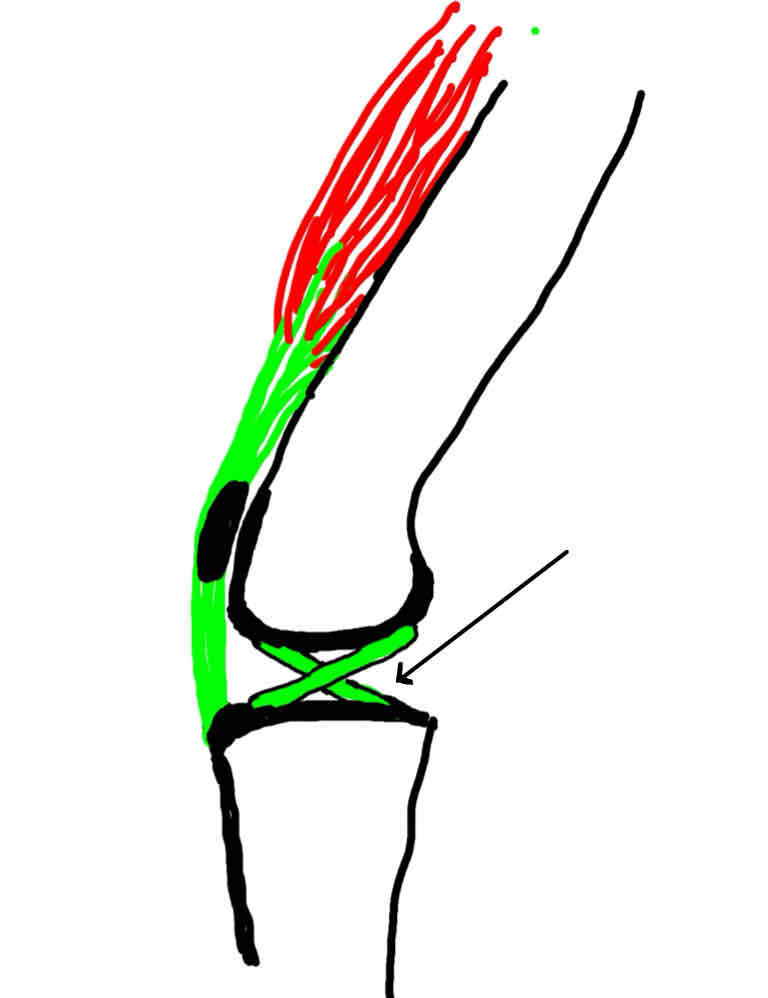
caudal cruciate ligament
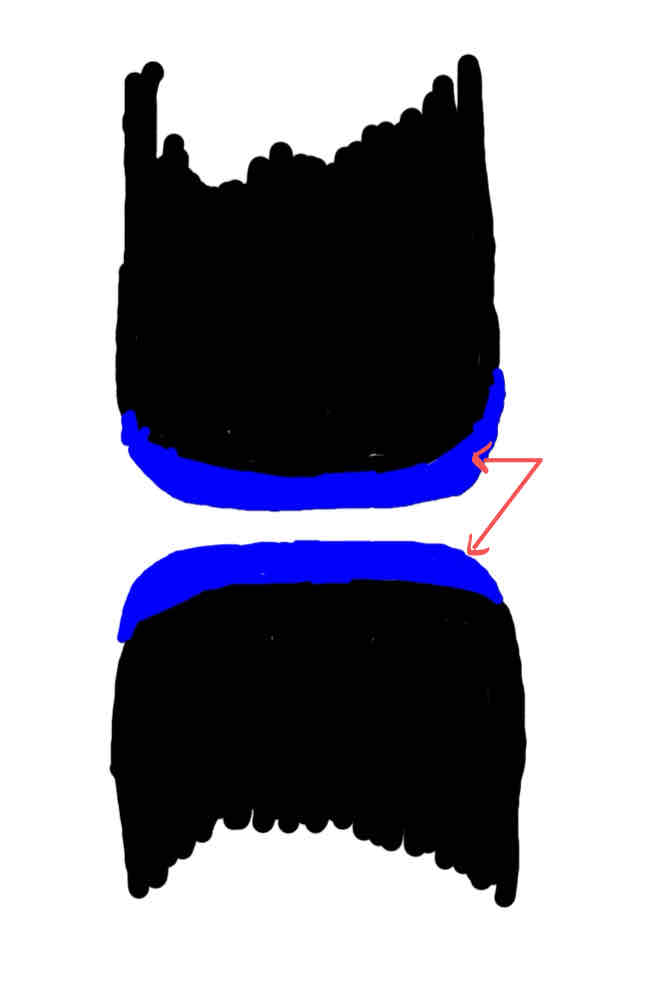
articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage)
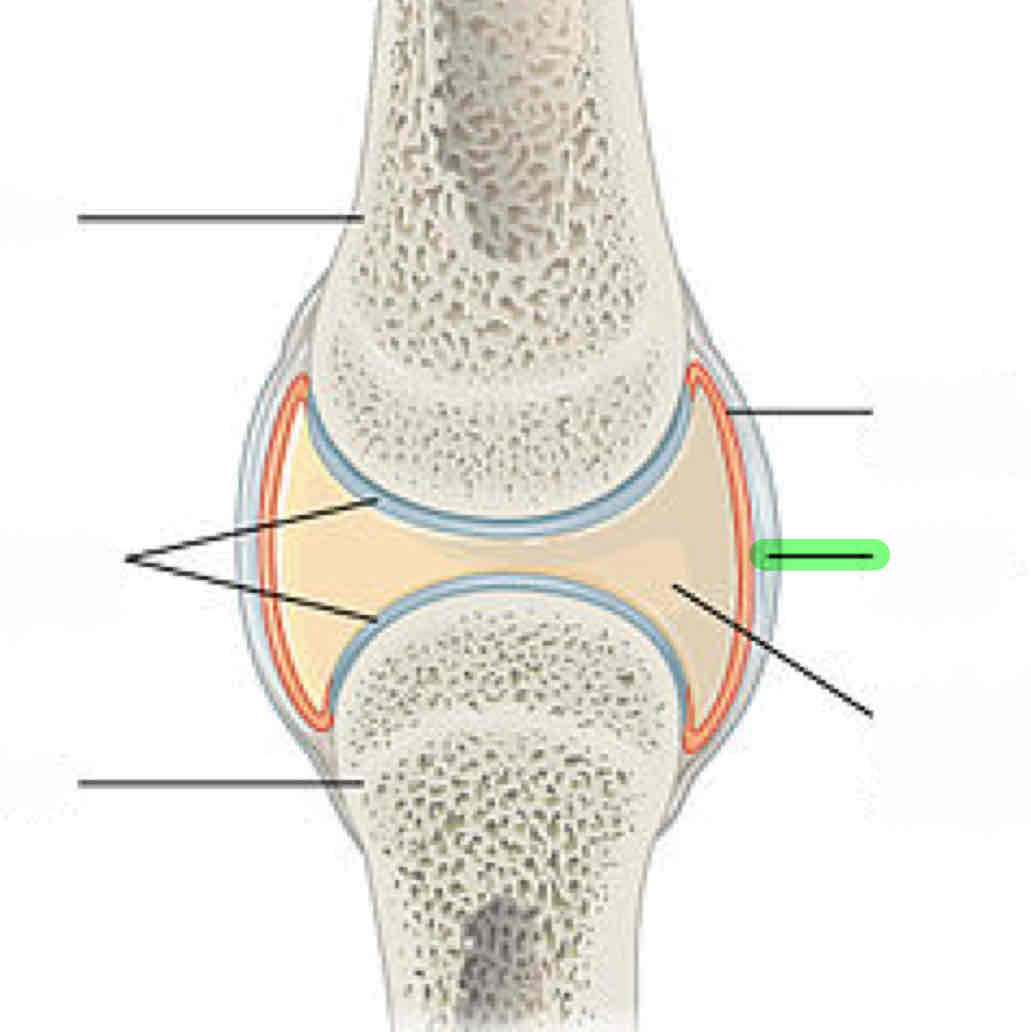
articular/joint capsule: incorporates the collateral ligaments, quadriceps tendon, and the patellar tendon
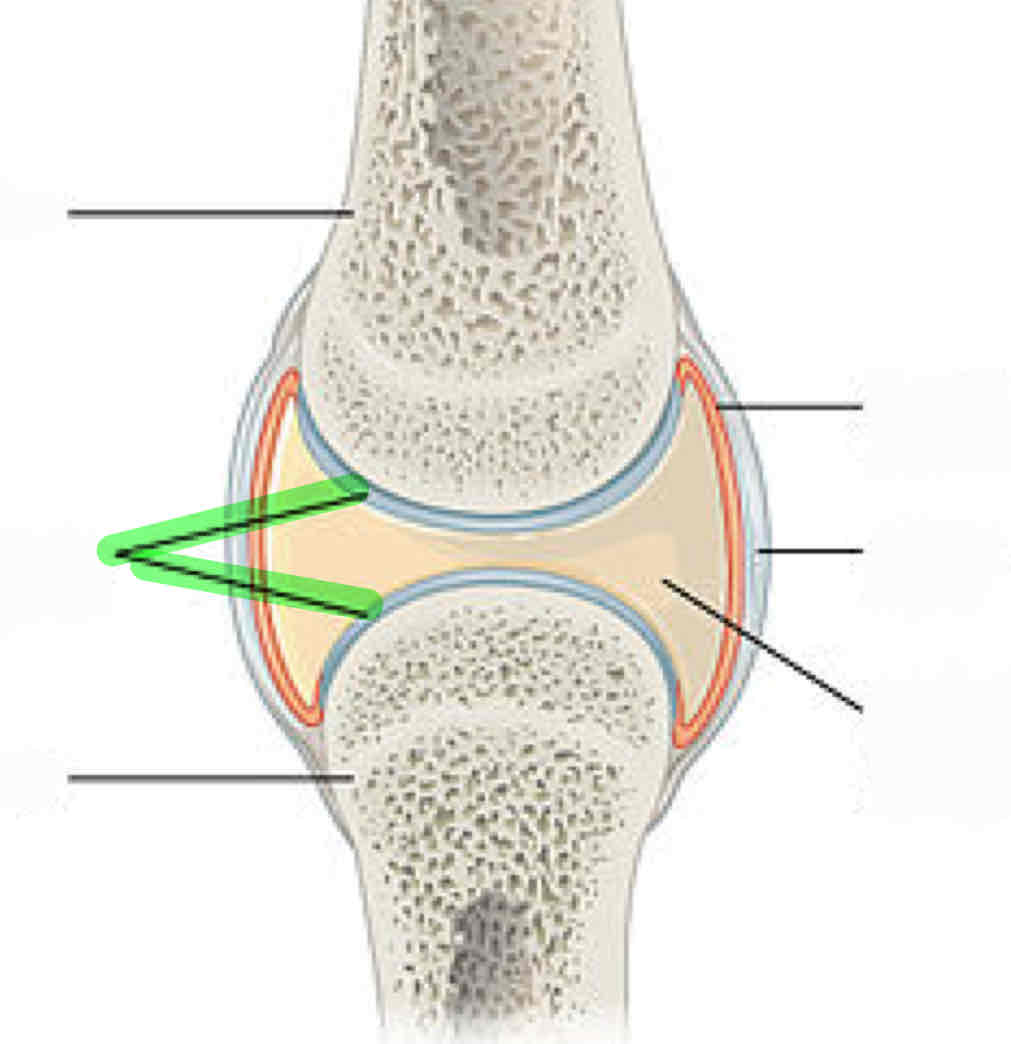
articular cartilage
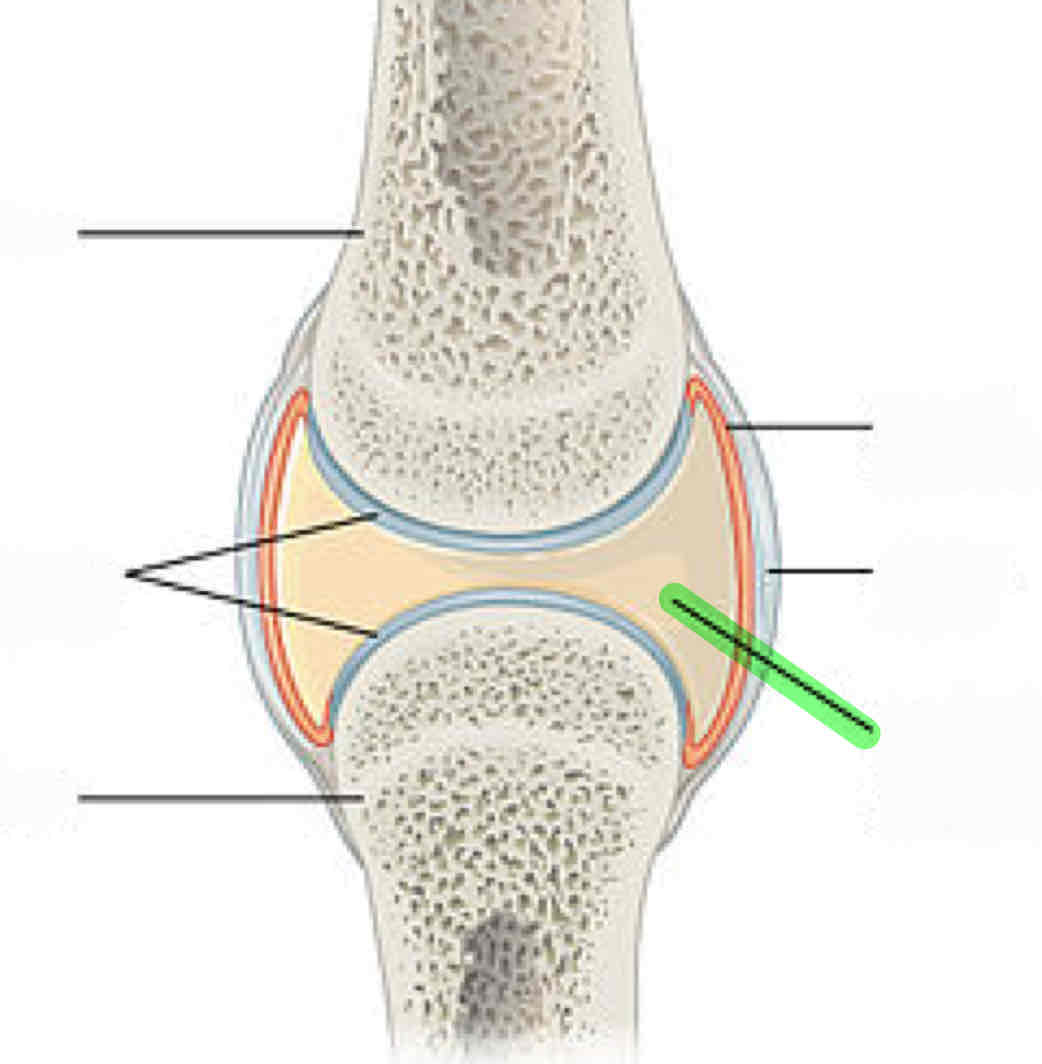
synovial fluid: lubricates the joint to prevent friction
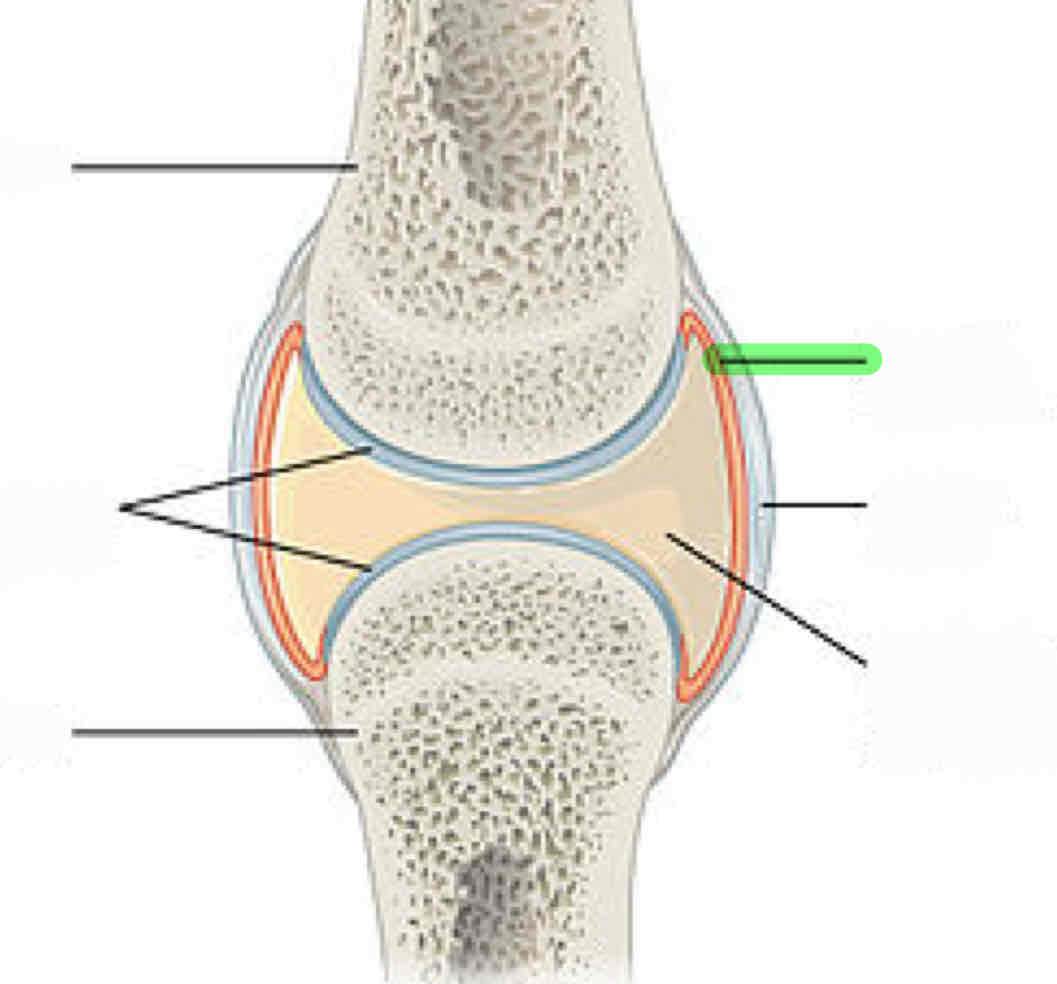
synovial membrane: secretes synovial fluid
meniscus (composed of fibrocartilage)
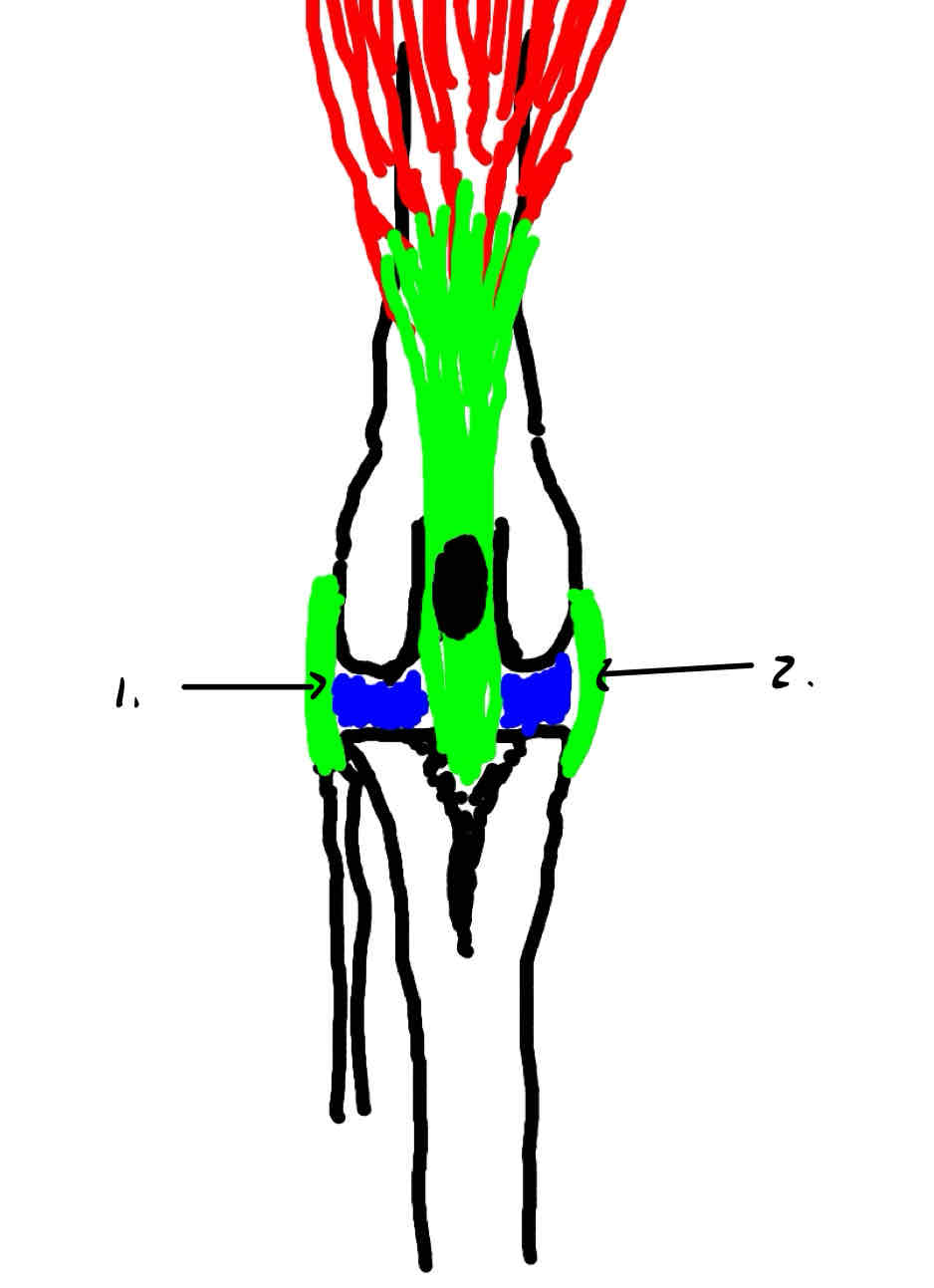
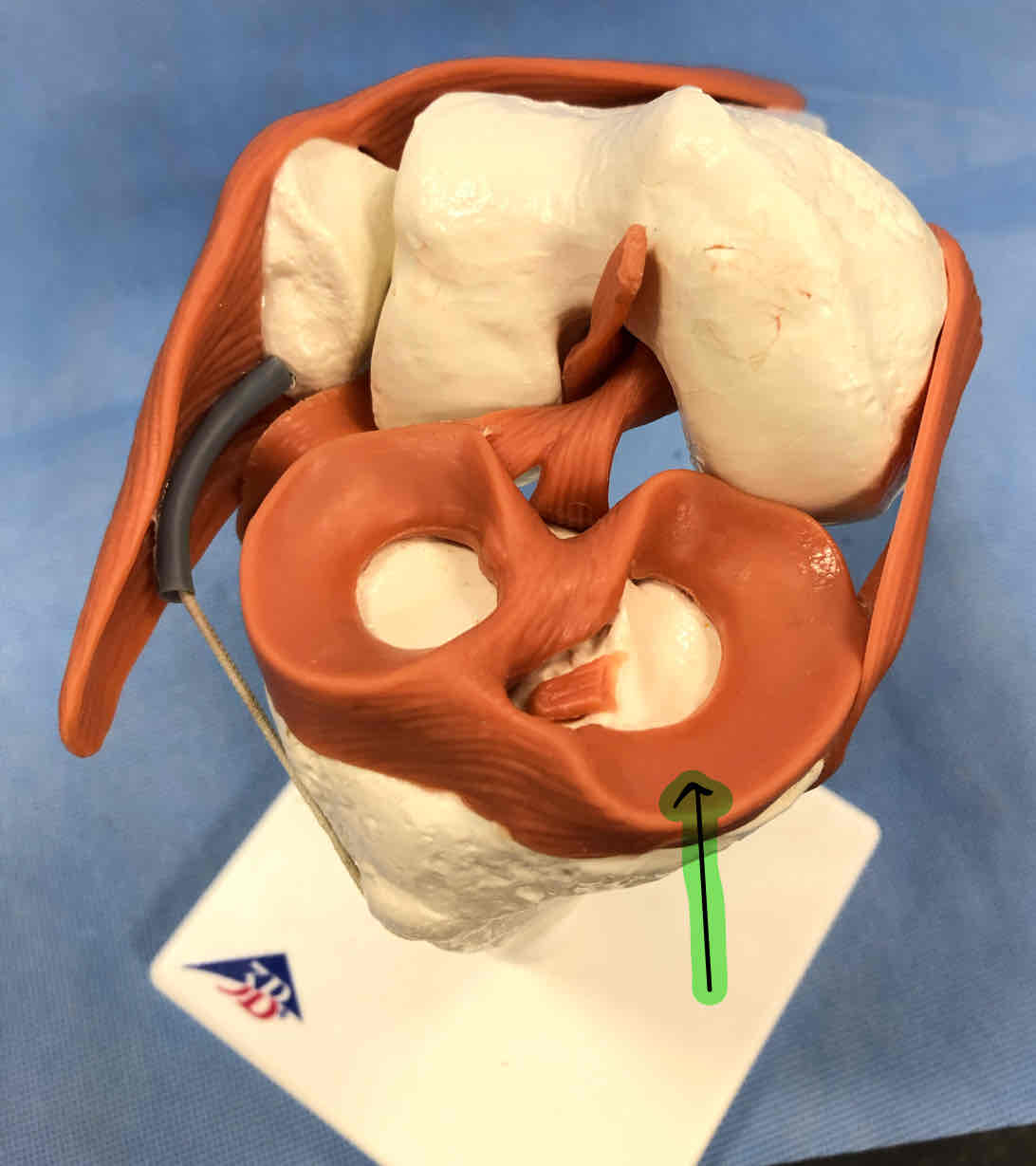
lateral collateral ligament (because the fibula is lateral to the tibia)
medial collateral ligament