Histology Quiz 3
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/123
Earn XP
Last updated 5:42 PM on 2/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
1
New cards
Collagen Type 1 or 2
What fiber is seen here in H&E?

2
New cards
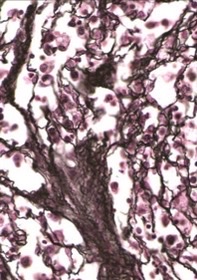
Collagen type 3
What fiber is seen here in silver stain?
3
New cards
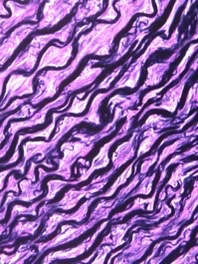
Elastic
What fiber is seen here in Verhoeff’s stain?
4
New cards
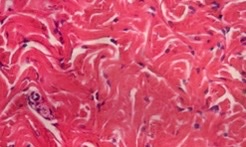
Dense irregular, dermis of skin or digestive system walls
What type of CT proper? Where could it be found?
5
New cards
dense regular, tendons and ligaments
What type of CT proper? Where could it be found?

6
New cards
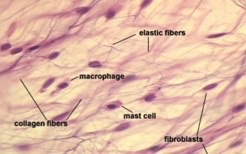
loose, under epithelia and in glands
What type of CT proper? Where could it be found?
7
New cards
dermis of skin, lining of organs, tendons and ligaments
Which tissues do you think might be most affected by mutations in the Collagen I gene?
8
New cards
support and protect other tissues and organs
What is the function of connective tissue?
9
New cards
extracellular matrix
mix of proteins secreted by cells into extracellular environment that can form meshes, gels or hard crystals
10
New cards
ECM, cells
In many connective tissues, the ____ becomes more abundant than the _____ themselves
11
New cards
protein ground substance and fibers
what is ecm composed of?
12
New cards
ground substance
* More heavily glycosylated
* Variety of carbs and glycosylated proteins
* Structure with more flexibility
* Hydrated and gel like-> important for nutrient/waste exchange
* Mediates movement of molecules and cells as well as cellular adhesion
* Variety of carbs and glycosylated proteins
* Structure with more flexibility
* Hydrated and gel like-> important for nutrient/waste exchange
* Mediates movement of molecules and cells as well as cellular adhesion
13
New cards
collagens and elastins
what are the 2 types of fibers
14
New cards
fibers
Component of ecm that provides strength, structure, support, and sometimes flexibility
15
New cards
collagen
\-most abundant protein in body at 30% of dry weight
* Very strong-> resistant to tearing
* Self assemble outside of cell to form bundles of fibers or mesh like sheets
* Very strong-> resistant to tearing
* Self assemble outside of cell to form bundles of fibers or mesh like sheets
16
New cards
types I and II
large collagen fibers, very acidophilic in H&E
17
New cards
type III
very delicate collagen fibers (supports highly cellular environments), not visible w/ H&E use silver stain
18
New cards
elastic
* Flexible, found in tissues that need to stretch
* Musculature, arteries ect
* Don’t stain well w/ H&E (Verhoeff’s often used)
* Usually squiggly bc tissue is relaxed
* Musculature, arteries ect
* Don’t stain well w/ H&E (Verhoeff’s often used)
* Usually squiggly bc tissue is relaxed
19
New cards
connective tissue proper
* Primarily composed of cells called fibroblasts
* Embedded in surrounding ECM
* Produce and secrete the extensive ECM
* Embedded in surrounding ECM
* Produce and secrete the extensive ECM
20
New cards
Embryonic Fibroblasts
actively producing ECM and have enlarges nuclei w/ well developed RER and golgi
21
New cards
inactive, nuclei, cytoplasm
\n Fibroblasts of mature CT are typically _____ and thus have condensed ___ and minimal ________
22
New cards
loose CT
highly cellular; abundant ground substance in ECM; ECM fibers less abundant and scattered (no bundles, may include both collagen and elastin)
23
New cards
dense irregular CT
less cellular; abundant fibers in ECM (mostly collagen I/II), often bundled but not well organized
24
New cards
dense regular CT
ECM is abundant and packed densely with parallel arrays of protein fibers (collagen I/II); cells are sparse and squeezed in between fibers of the ECM
25
New cards
1 and 3
What types of collagen are found in loose CT?
26
New cards
1
What types of collagen are found in dense irregular CT?
27
New cards
adhesion beneath epithelia and in glands, permeable for diffusion
function of loose ct
28
New cards
directly under epithelia and in glands
Where is loose CT found in the body?
29
New cards
not very active or permeable, tough and supportive with some flexibility
function of dense irregular CT
30
New cards
dermis of skin, walls of organs
Where is dense irregular CT found in the body?
31
New cards
extremely tough but lacks activity for repair
function of dense regular CT
32
New cards
tendons and ligaments
Where is dense regular CT found in the body?
33
New cards
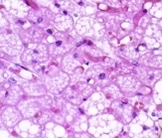
brown
What type of adipose tissue?
34
New cards
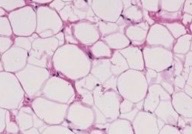
white
What type of adipose tissue?
35
New cards
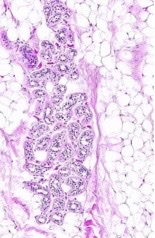
white (embedded in other tissue)
What type of adipose tissue?
36
New cards
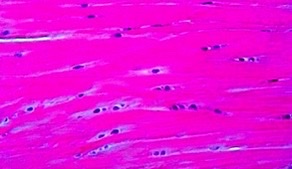
fibrocartilage
What type of cartilage?
37
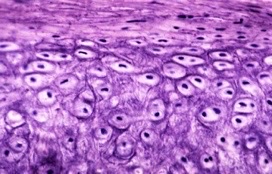
New cards
elastic
What type of cartilage?
38
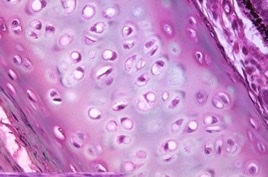
New cards
hyaline
What type of cartilage?
39
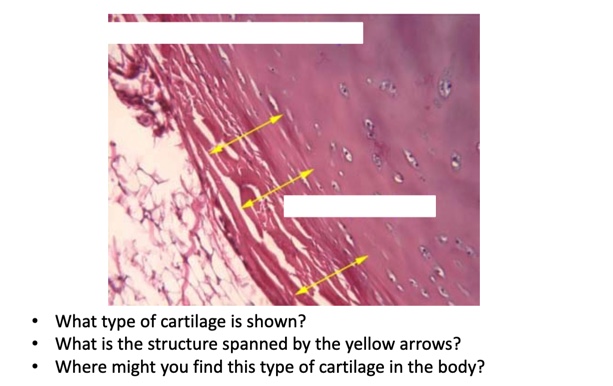
New cards
Hyaline, perichondrium, nose or respiratory system
40
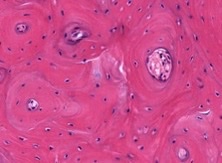
New cards
demineralization
how was this bone prepared?
41
New cards
ground bone
how was this bone prepared?

42
New cards
demineralized, osteocytes, osteoblasts osteoclasts osteoprogenitor
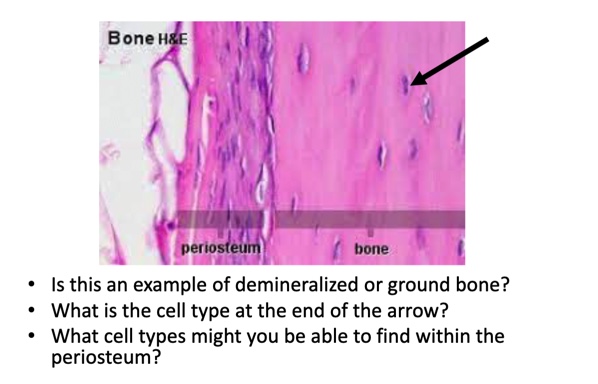
43
New cards
adipose tissue
•“Fat” \n •Distributed throughout body, both in specific deposits and embedded within other tissues
44
New cards
energy storage, cushioning and protection, temp regulation, metabolic signaling
functions of adipose tissue
45
New cards
adipocytes
name of adipose tissue cells
46
New cards
lipid
Adipocytes are dominated by internal ______ deposits
47
New cards
no
does adipose tissue have a lot of ecm?
48
New cards
yes
is adipose tissue highly vascularized
49
New cards
white and brown
2 types of adipose tissue
50
New cards
thermoregulation
function of brown adipose tissue
51
New cards
energy storage, metabolic and endocrine signaling, insulation, cushioning
functions of white adipose tissue
52
New cards
single large fat droplet
in white adipose tissue, cytoplasm is dominated by ______
53
New cards
hormones, insulin, pancreas, glucagon, norepinephrine, adrenal medula
Fatty acid storage and release is regulated by ________
–____ from ____ stimulates uptake/storage \n __–_______ from pancreas and _____ from ________ stimulate release
–____ from ____ stimulates uptake/storage \n __–_______ from pancreas and _____ from ________ stimulate release
54
New cards
adipokines
White adipose tissue secretes hormones called _____ that help to regulate body weight and energy homeostasis
55
New cards
leptin
best studied adipokine known to act on hypothalamus and regulate satiety and energy expenditure
56
New cards
cytokines
White adipose tissue also releases signals called ______ that stimulate the immune system
57
New cards
multiple small fat droplets
brown adipose tissue structure consists of…
58
New cards
mitochondria, acidophillic
brown adipose tissue has abundant ____ resulting in ______ cytoplasm
59
New cards
thermogenesis
\n process that generates heat in response to norepinephrine from sympathetic nervous system
60
New cards
ATP production
thermogenesis triggers hydrolysis of triglycerides and activation of _______ in mitochondria
61
New cards
heat
BAT mitochondrial enzymes generate ___ during atp production
62
New cards
infants
in who is BAT more abundant
63
New cards
higher
Individuals with higher proportions of BAT have _____ \n metabolic rates
64
New cards
cells called chondrocytes and abundant ecm
what is cartilage made of?
65
New cards
lacunae
Chondrocytes produce and secrete abundant ECM, then become trapped in that ECM in cavities called _______
66
New cards
extensive, vasculature
cartilage ECM is _____ and lacks ______
67
New cards
ground substance
Cartilage ECM has lots of ground substance that forms a gel that is good at absorbing shock
68
New cards
perichondrium
Some types of cartilage are surrounded by a fibrous sheath called the ________ that holds vasculature
69
New cards
hyaline cartilage
\-smooth, faintly staining appearance in H&E staining
\-ECM is strong and supportive, but more flexible than bone \n •EMC also has a gelatinous texture that makes it good for \n absorbing shock, and also good at reducing friction surfaces
\-ECM is strong and supportive, but more flexible than bone \n •EMC also has a gelatinous texture that makes it good for \n absorbing shock, and also good at reducing friction surfaces
70
New cards
respiratory system, nose, ribcage
where can hyaline cartilage be found?
71
New cards
elastic cartilage
\-chondrocytes are located in lacunae, and separated from one another by extensive ECM
\-in that it contains more fibers than hyaline– specifically, more elastic fibers \n •“streakier” in H&E; elastic fibers are even more prominent \n when using specialized stains such as Verhoeff’s
\-in that it contains more fibers than hyaline– specifically, more elastic fibers \n •“streakier” in H&E; elastic fibers are even more prominent \n when using specialized stains such as Verhoeff’s
72
New cards
hyaline and elastic
which cartilage types can have perichondrium?
73
New cards
ear and epiglottis
where is elastic cartilage found
74
New cards
fibrocartilage
\-mixture of cartilage and dense CT
\-ECM is enriched with collagen fibers, often in parallel arrays
\-identifiable by the presence of collagen rich ECM, \n chondrocytes AND fibroblasts, and distinctive rows of chondrocyte isogenous groups packed in between collagen fibers
\-ECM is enriched with collagen fibers, often in parallel arrays
\-identifiable by the presence of collagen rich ECM, \n chondrocytes AND fibroblasts, and distinctive rows of chondrocyte isogenous groups packed in between collagen fibers
75
New cards
intervertebral discs and pubic symphysis
where is fibrocartilage found?
76
New cards
less
Types of cartilage w/ no perichondrium _____ capable of regeneration
77
New cards
rare and slow growing
Cancers within cartilage are ______ because cells are not effective at growth or division
78
New cards
bone
Provides structure and support, Protection for vital organs, site of hematophatosis
79
New cards
osteocytes
bone cells within lacunae
80
New cards
bone matrix
what is bone ecm called?
81
New cards
osteoblasts
Cells called _______ secrete type 1 collagen and ground substance in bone
82
New cards
periosteum
Fibrous sheaths lining external surfaces of bone matrix
83
New cards
endosteum
Fibrous sheaths lining internal surfaces of bone matrix
84
New cards
osteoblasts
* Cells that can produce new bone matrix
* Tend to have basophilic cytoplasm
* Lots of rough ER for collagen synthesis
* Tend to have basophilic cytoplasm
* Lots of rough ER for collagen synthesis
85
New cards
osteoclasts
* Can break down existing bone matrix
* Large, multinucletate cells
* Often slightly acidophillic cytoplsm
* Large, multinucletate cells
* Often slightly acidophillic cytoplsm
86
New cards
demineralization
* place in solution to dissolve minerals, soften tissue, and re-expose original collagen foundation of bone ecm
* Then stain/section
* Keeps living cells alive
* Then stain/section
* Keeps living cells alive
87
New cards
ground sectioning
* grind down bone, typically unstained or treated w/ black ink that settles into cracks
* No living cells
* No living cells
88
New cards
long bones
humerus, femur, etc
89
New cards
flat bones
\n scapula, bones of the skull, ect
90
New cards
compact and spongy
bones can contain what 2 regions?
91
New cards
lamellar
layered bone
92
New cards
alternate direction perpendicularly
Within each layer of bone collagen fibers are organized in parallel bundles
\-Bundles ________ to increase strength
\-Bundles ________ to increase strength
93
New cards
ostens
\n In compact bone, cylindrical structures called ______ are apparent
94
New cards
concentric layers, central canal
Within osteons, lamellae are organized into _____ surrounding a central open space called the ________ holding blood vessels and nerves
95
New cards
volkmann canals
Blood vessels also found in perforating canals which are called…
96
New cards
canaliculi
Osteocytes access volkmann canals via cytoplasmic projections which they extend through tiny tunnels in the matrix called ______
97
New cards
resting zone, proliferation zone, hypertrophic zone, calcification zone, ossification zone
name each zone in an epiphyseal growth plate
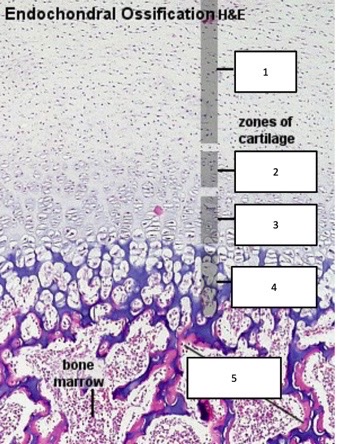
98
New cards
body will take calcium out of bones, osteoclasts will be activated
If your diet is low in calcium, you may experience a decrease in bone density – why? Which cell type will be activated in response to low blood calcium concentration?
99
New cards
embryonic development
when does most bone development occur?
100
New cards
\n Intramembranous and endochondral ossification
2 mechanisms to produce new bone