6.1 LAW OF SINES 6.2 LAW OF COSINES and area of oblique triangle and herons Area formula
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
VERY IMPORTANT FOR CALCULUS
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
6.1 FLASHCARDS go FROM 1-
6.1 = This color
6.2=This color
VERY IMPORTANT=THIS
Overview= normal color
Derivation=THIS
Formula=This
Example=This
INTRODUCTION
In Chapter 4 and in math before we have studied techniques for solving right triangles.
In this section and the next, you will solve oblique triangles—triangles that have no right angles.
Standard notation of Oblique triangles
Upper and lower case
The angles are labeled A,B,C upper case!!!!!!! and their opposote sides are labeled a, b,c lower case!!!!!!
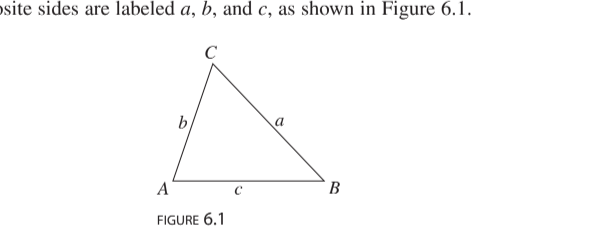
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW TO SOLVE OBLIQUE TRIANGLES!!!
you need to know the measure of at least one side and any two other parts of the triangle—either two sides, two angles, or one angle and one side. This breaks down into the following four cases.
AAS/ASA
SSA
SSS
SAS
WHICH CASES LAW OF SINES AND ONES LAW OF COSINES
SUPER IMPORTANT
LAW of SINES
AAS/ASA
SSA
LAW of COSINES
SSS
SAS
AAS/ASA Case for solving
need to know two angles and any side
SSA case for solving
Two sides and an angle opposite one of them
SSS case for solving
Three sides
SAS case for solving
Two sides and their included angle
LAW OF SINES FORMULA
if ABC is a triangle with sides a,b,c, then
a/sinA = b/sinB = c/sinC
and the recipricol is sinA/a= SinB/b= SinC/c
Picture that shows law of Sines Proof Kind of
Reoriented acute and obtuse
Works for both ACUTE AND OBTUSE
ACUTE
Drop altitude -h (height)
Sin A= h/b so h=bsinA
Sin B = h/a so h=asinB
so they both equal h so
bsinA=asinB
so then divide both sides by SinAsinB and then get
a/sinA = b/sinB
Obtuse
Drop altitude -h (height)
Sin A= h/b so h=bsinA
Sin B = h/a so h=asinB
so they both equal h so
bsinA=asinB
so then divide both sides by SinAsinB and then get
a/sinA = b/sinB
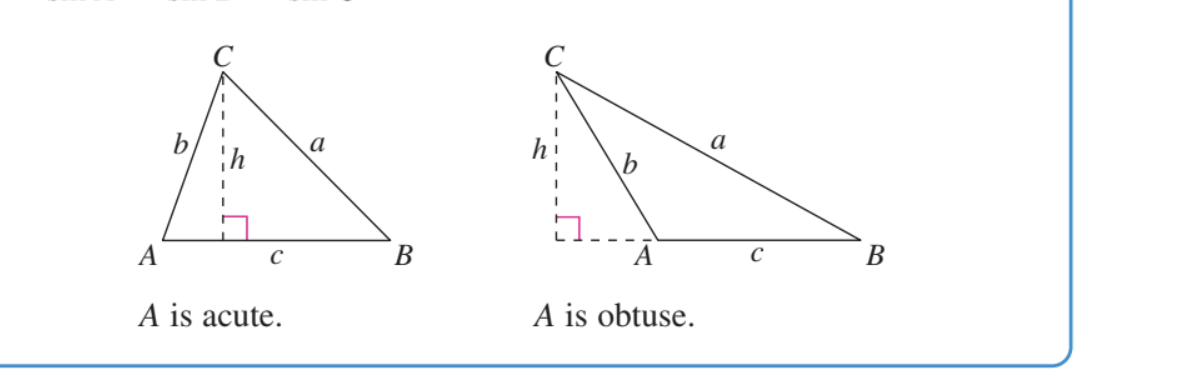
DERIVATION/PROOF OF LAW OF SINES
Make oblique triangles. The angles are labeled A,B,C upper case!!!!!!! and their opposote sides are labeled a, b,c lower case!!!!!!
can reorient triangle in tons of ways
A can be acute or obtuse
PROOF
Let h be the altitude of either triangle in the figure.
for A is acute
Then use sin identity to get
sinA=h/b or h=bsinA
sinB=h/a or h=asinB
then you can set equal because both equal to h and so bsinA=asinB
so then divide both sides by SinAsinB and then get
a/sinA = b/sinB
for A is obtuse
construct an altitude (h) from vertex B to side AC (extended in the obtuse triangle),
Then use sin identity to get
sinA=h/c or h=csinA
sinC=h/a or h=asinC
then you can set equal because both equal to h and so csinA=asinC
so then divide both sides by sinAsinC and then get
a/sinA = c/sinC
THEN BY Transitive Property of Equality you know that
a/sinA=b/sinB = c/sinC
LAW OF SINES

Example 1 Given Two Angles and One Side—AAS
How to do:
To solve 3rd angle A just know 180 degrees in a triangle and then subtract and get the missing angle.
Then to get the other 2 sides a and c do the law of sines
so you know b=27.4 and know all the angles so you know 3 parts of the equation To find A
a/sinA=b/sinB so then solve for a to get a= b/sinB (sinA) and then plug in numbers to get 43.06 feet for a
you also know 3 parts for C
c=b/sinB (sinC) and then plug in numbers and get 55.75 feet for c

Example 2 Given Two Angles and One Side—ASA
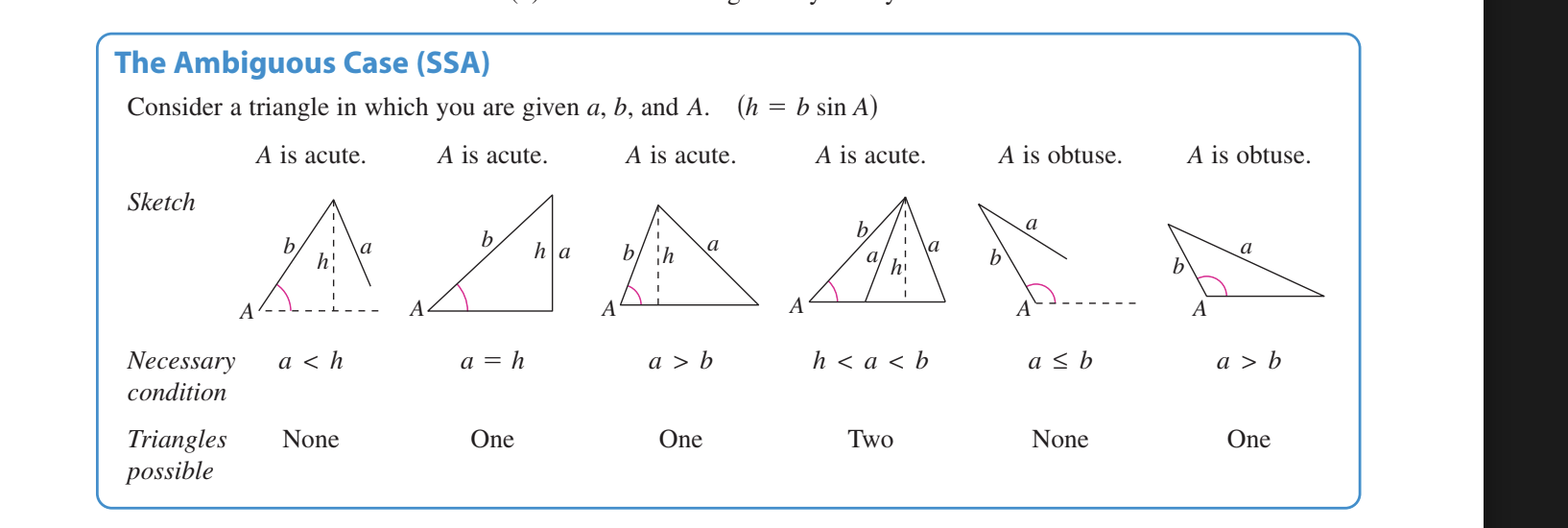
LAW OF SINES Ambiguous Case (SSA)
Two angles and one side determine a unique triangle.
However, if two sides and one opposite angle are given, three possible situations can occur: (1) no such triangle exists, (2) one such triangle exists, or (3) two distinct triangles may satisfy the conditions.
consider a triangle that you are given a,b, A
Key idea
Drop a height:
h=bsinA
Compare side a to height h and side b
📐 If A is ACUTE
Condition | # of Triangles |
|---|---|
a<h | 0 (no triangle) |
a=h | 1 (right triangle) |
a>b | 1 |
h<a<bh | 2 (ambiguous case!) |
📐 If A is OBTUSE
Condition | # of Triangles |
|---|---|
a≤b | 0 |
a>b | 1 |
🧠 Memory Tip
Only SSA causes ambiguity
Two triangles only when A is acute and h<a<bh < a < bh<a<b
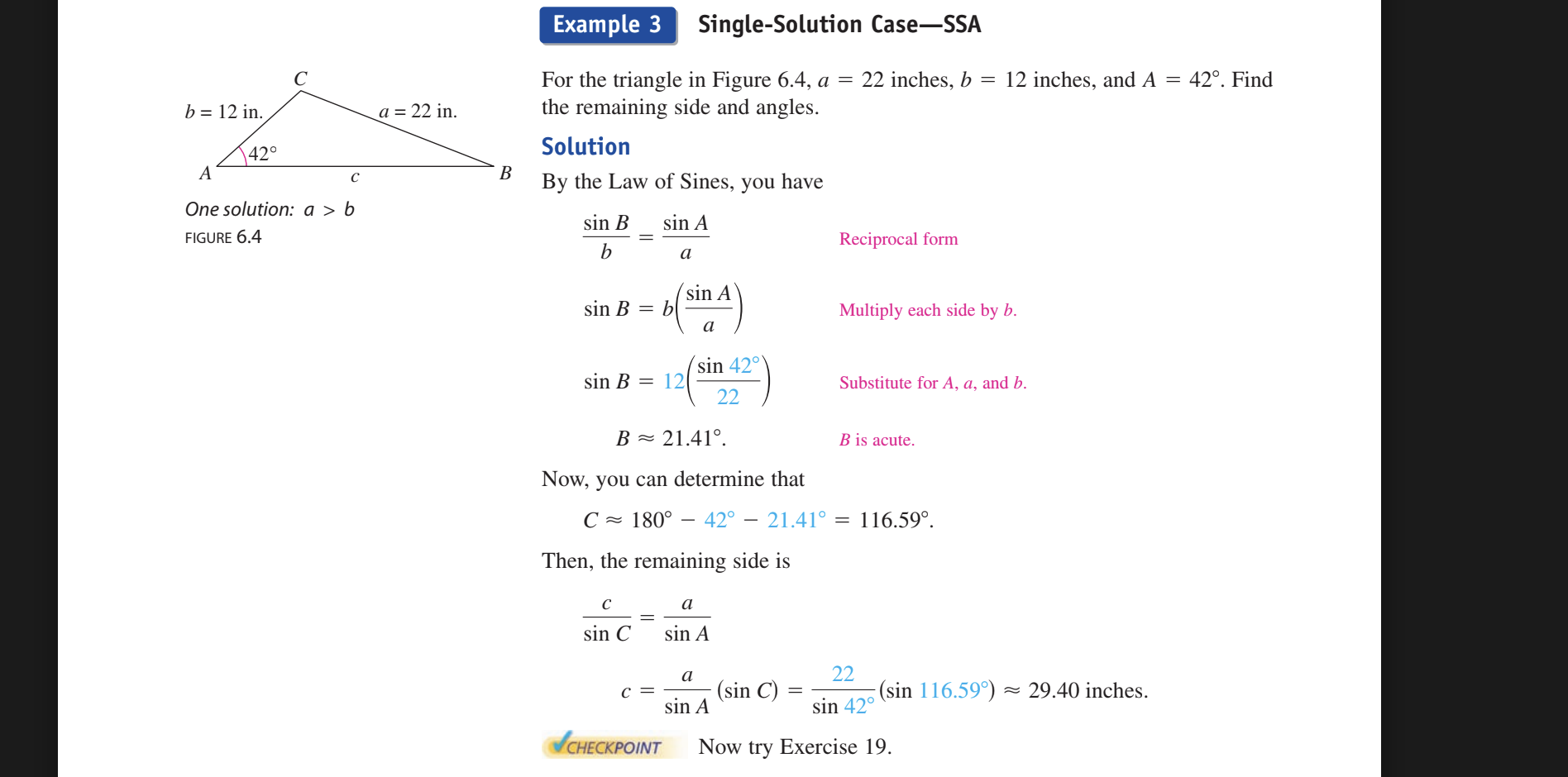
Example 3 Single-Solution Case—SSA
Example 4 No-Solution Case—SSA

Example 5 Two-Solution Case—SSA
HARDEST ONE
Find 2 triangles for which a=12 meters, b=31 meters, A=20.5 degrees
By using law of sines
b/sinB=a/sinA so cross multiply to get aSin B= bsinA and then get sinB=((bsinA)/a) and then plug in the numbers and get sinB=0.9047
However from the unit circle sinB=.9047 has 2 solutions
Refrence angle of 64.8 degrees so B1=64.8 degrees and B2=115.2
SO THEN YOU SOLVE FOR REST OF STUFF USING THE ANGLE. HAVE TO SOLVE FOR ALL OF THE OTHERS FOR ANGLE 1 AND ALL OF THE OTHERS FOR ANGLE 2
B1=64.8 angle solved
Solve for C So to get the angle C you do 180 degrees - 20.5 - 64.8 and get 94.7 degrees for C
Solve for c So to get side c you do the LAW OF SINES
c= a/sinA (sinC) and then plug in and get C=34.15 meters.
B2=115.2 angle solved
Solve for C So to get the angle C you do 180 degrees - 20.5 - 115.2 and get 44.3 degrees for C
Solve for c So to get side c you do the LAW OF SINES
c= a/sinA (sinC) and then plug in and get C= 23.93 meters

LAW OF SINES Area of an Oblique Triangle How to get it
The procedure used to prove the Law of sines leads to a simple formaula for area of an oblique triangle
using the law of sines, the height of the triangle is
h=bsinA
the area of all triangles is
A=1/2 bh
This equals
A=1/2 (c ) (bsinA)
which equals
A= 1/2bcsinA
C is the base because on the normal orientation c is the base. bsinA is the hight of the triangle and you just put them together

LAW OF SINES Area of an Oblique Triangle Formulas
By different orientations you can get:
So the area of any triangle is one-half the product of the lengths of two sides times the sine of their included angle. That is,
Area= 1/2 bcsinA If you change orientation
Area=1/2 absinC if you change orientation
Area=1/2 acsinB
LAW OF SINES Area of an Oblique Triangle IF RIGHT ANGLE
Note that if angle A is 90 degrees then the formula gives the area for a right triangle:
Area=1/2bc (sin90) which sin90=1 so
A= 1/2 bc which is ½ base times height
The same results are also for B and C to equal 90
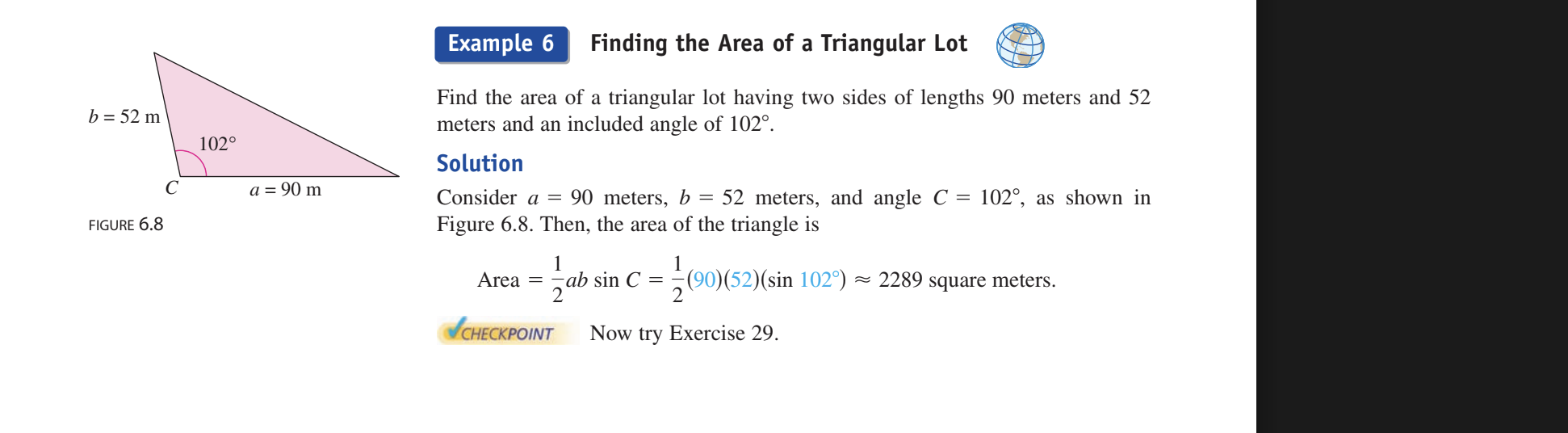
Example 6 Finding the area of a triangular lot
Plug into formula
6.2 LAW OF COSINES
LAW OF COSINES Introduction
Two cases remain in the list of conditions needed to solve an oblique triangle—SSS and SAS. If you are given three sides (SSS), or two sides and their included angle (SAS), none of the ratios in the Law of Sines would be complete. In such cases, you can use the Law of Cosines.
6.2 Proof of law of Cosines
set up a normal triangle with the standard notation of oblique triangles.
Then you drop an altitude and solve for the inside right triangle with B as the angle
Then for the height of the triangle h you get asinB because when you do sinB you get sinB=h/a and then h=asinB
Then for the base of the triangle which is c for the right side of the base right of the altitude you get acosB because you do cosB you get cosB=x/a and then x, which is the side of the small triangle to be x= acosB
You know the base is c so the 2 parts that are cut off by the altitude equal c so then the other side left of altitude is c-acosB because the 2 peices of the base have to add up to c and c-acosB + acosB =c
Then you do the pythagorean theorem for the left inside triangle which has side lengths c-acosB (left side of c), asinB (height), and b as the hypotenuse
you get
(c-acosB)² + (asinB
you do