adolescence 2
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
what are the research traditions in identity in adolescence?
self-esteem
self-concept
identity formation
what is self-efficacy?
a person’s judgement of their capabilities to organise and execute courses of action required to attain designated types of performances
what is self-esteem?
an individual’s confidence in their worth or abilities
what is self-concept?
a view constructed of one’s self, which is developed through experiences and evaluations adopted from others
what is self-evaluation?
the perceptions and beliefs that a person holds about themselves, specifically the emotionally-valanced qualities, characteristics and traits and the person’s judgement of the value of these attributes
what did James (1892) say about self-esteem?
results from good performance in domains/’subsets of the self’ deemed important
what did Cooley (1902) say about self-esteem?
came up with the looking glass self - opinions of others are a large determinant of self-esteem
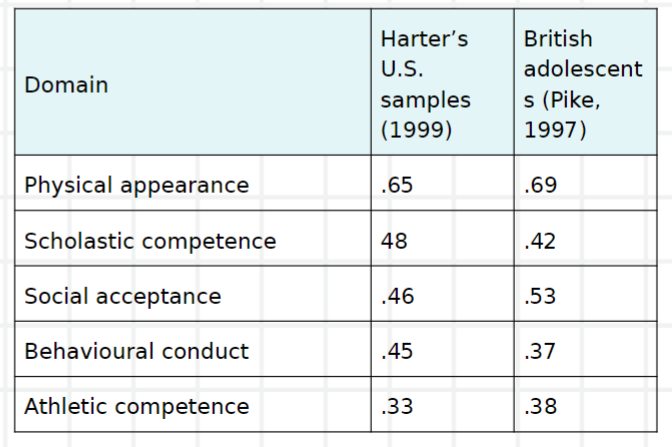
what does Harter (1999) say about development of self-concept?
shift from concrete to abstract self-portraits
shift from social comparisons and normative standards to internalised standards
shift towards differentiation of self into multiple domains
integration of multiple selves into unified self-concept
how does adolescence affect imagined selves?
able to distinguish between real and ideal selves (Rogers)
greatest discrepancy between selves in middle adolescence (Strachen & Jones)
presentation is dependent on the audience (Harter & Lee)
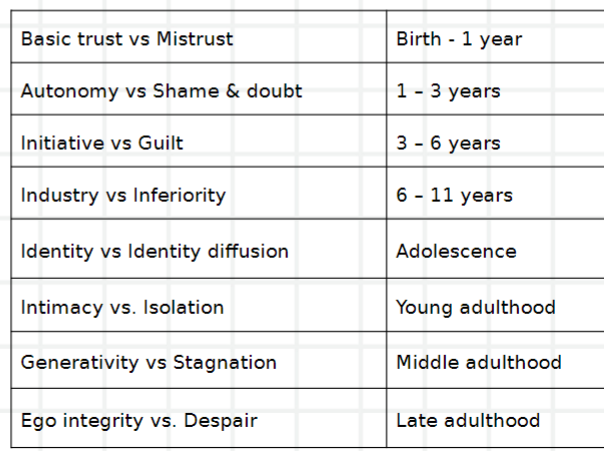
what does Erikson’s psychosocial stages say about adolescence?
the most important thing that develops in this stage in identity
the crisis is identity, defined as “confidence in one’s inner continuity amid change”
men must achieve a stable identity prior to intimacy
women’s identity is defined through her intimate roles of wife and mother
describe Marcia’s 4 identity statuses
identity depends on whether or not we are in crisis and whether we are committed to that identity
achievement, foreclosure, moratorium, diffusion
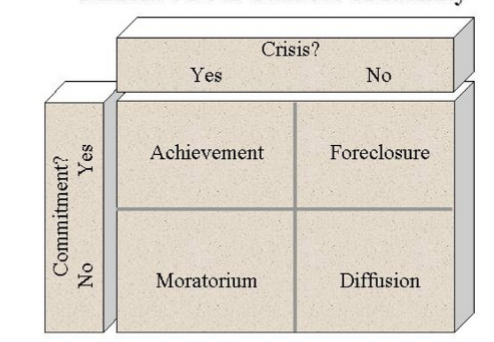
How does Marcia describe achievement?
Individuals who after a period of exploration emerge with firm identity commitments
How does Marcia describe moratorium?
The active period of exploration when individuals examine alternatives in an attempt to arrive at a choice
How does Marcia describe foreclosure?
Individuals have adopted identities, prescribed by parents or other authority figures without ever exploring options or experiencing an identity crisis
How does Marcia describe diffusion?
Individuals who have little sense of commitment and are not actively seeking to make decisions
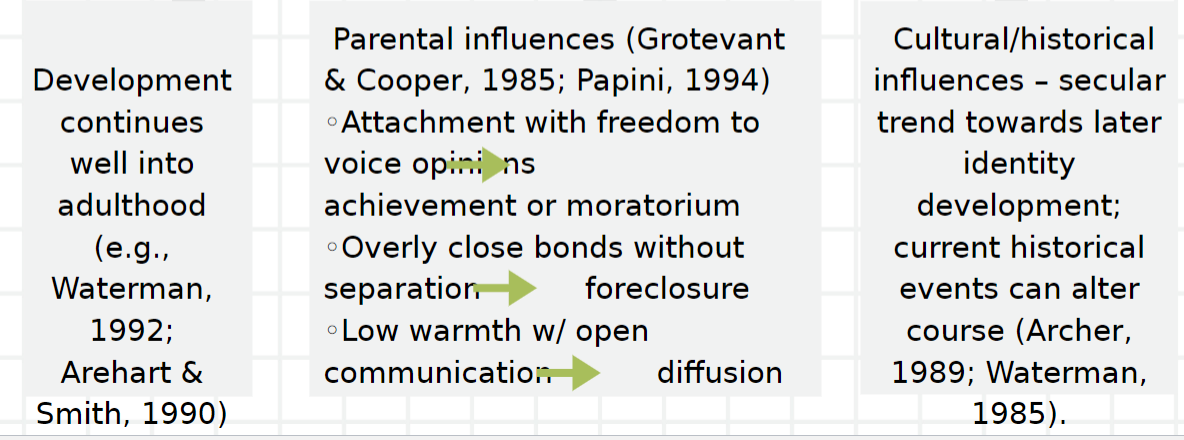
What are the key areas in the development of identity formation and identity statement?
The way in which development continues into adulthood
Parental influences
Cultural/historical influences
How does positive self-concept affect life outcomes?
better general well-being
better quality of life
Greater confidence in actions and abilities
How does negative self-concept affect life outcomes?
increase likelihood of:
Adjustment problems
Externalising problems
Internalising problems
How do emotional disorders relate to self-concept?
There is a strong relationship between emotional disorders and negative self-concept
Problems with self perceptions are reflected in diagnostic criteria for anxiety and depression
Positive self-concepts function as protective factors in development of emotional disorders
Results of Delgado et al. (2013)
Adolescence with social anxiety are more likely to perceive relationship with peers as more negative
They consider themselves to be less attractive, less athletic, and more emotionally unstable
How does self-concept link to depression?
evidence that adolescence view themselves more negatively and less positively when they are depressed compared to when they are not depressed
Orchard and Reynolds (2018), found the ratings of self perceptions were as good at identifying presence of depression diagnosis as a depression symptom questionnaire
How does self-concept relate to early onset psychosis?
Negative beliefs about self consistently linked with chronic psychosis (Fowler et al., 2006)
Theorised that development of dysfunctional self-concept could play a role in development of psychosis symptoms
Studies have found that adolescence at high risk of psychosis, indoor negative self beliefs more than healthy controls
How does self-concept relate to gender?
Females have significantly more negative self-concepts than males
Gender differences have been suggested as a possible explanation for mental health problems being significantly more prevalent in women