AP Calculus BC Formulas | Quizlet
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
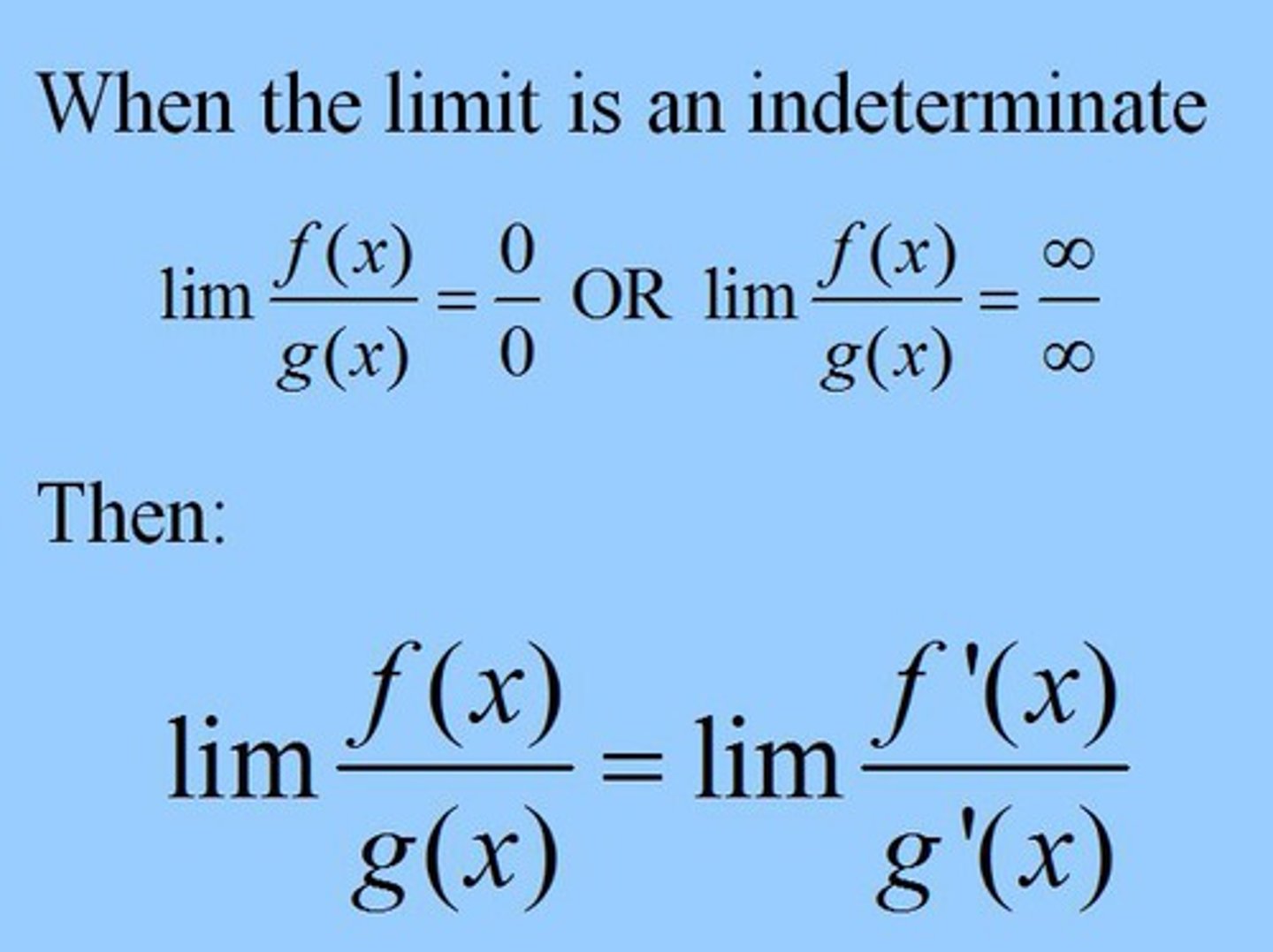
L'Hopital's Rule
When is a function continuous?

Limit Definition of a Derivative
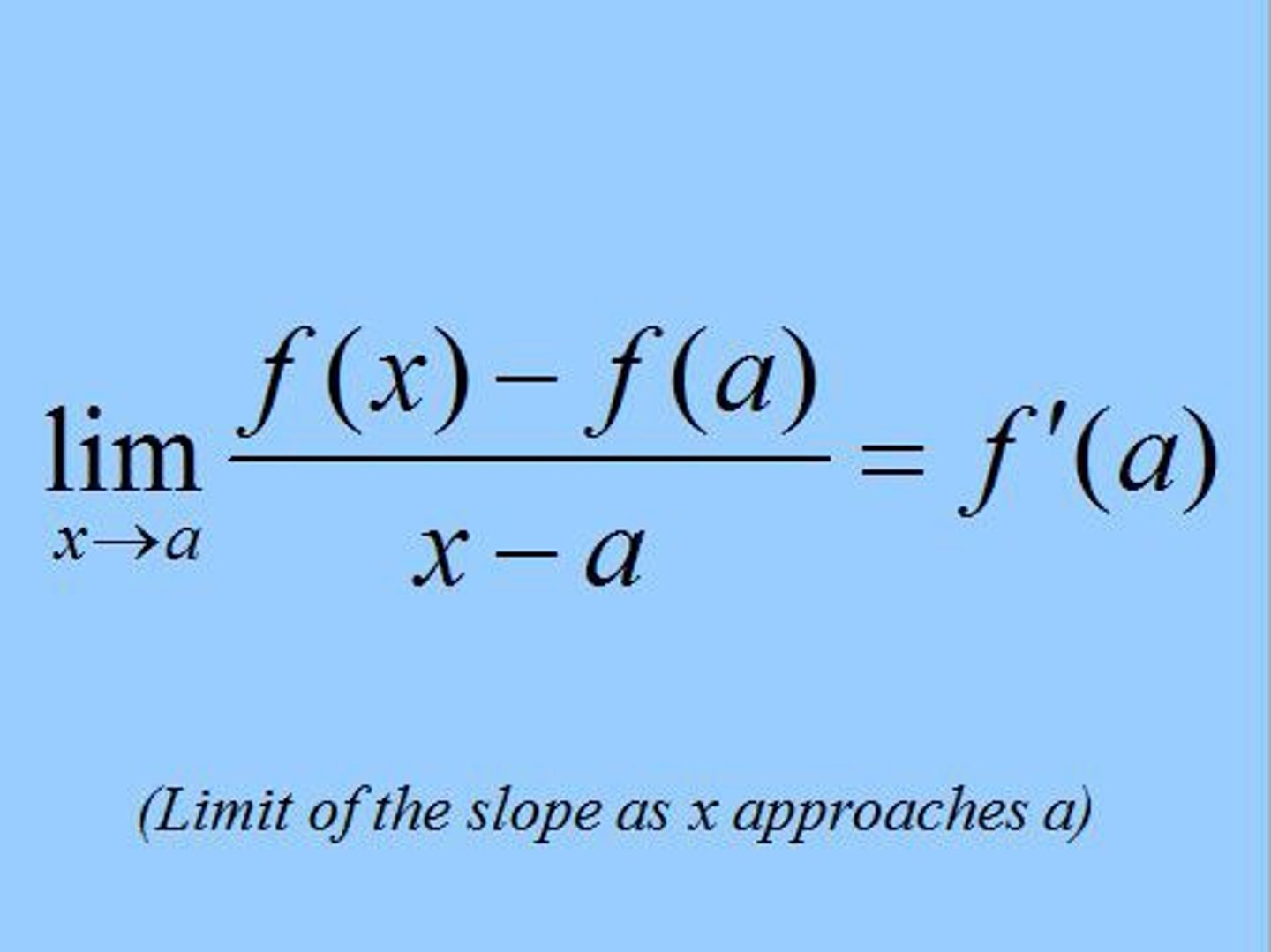
Intermediate Value Theorem (IVT)
If f(x) is continuous on [a, b], then all y-values between f(a) & f(b) exist at some point of c
Mean Value Theorem (MVT)
If f(x) is differentiable, a slope of the ARC exists at some point of c
Extreme Value Theorem (EVT)
If f(x) is continuous on a closed interval of [a, b], f(x) must have a maximum and minimum
![<p>If f(x) is continuous on a closed interval of [a, b], f(x) must have a maximum and minimum</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ff741943-0db1-4263-ae7f-758bbecf3169.jpg)
1st Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
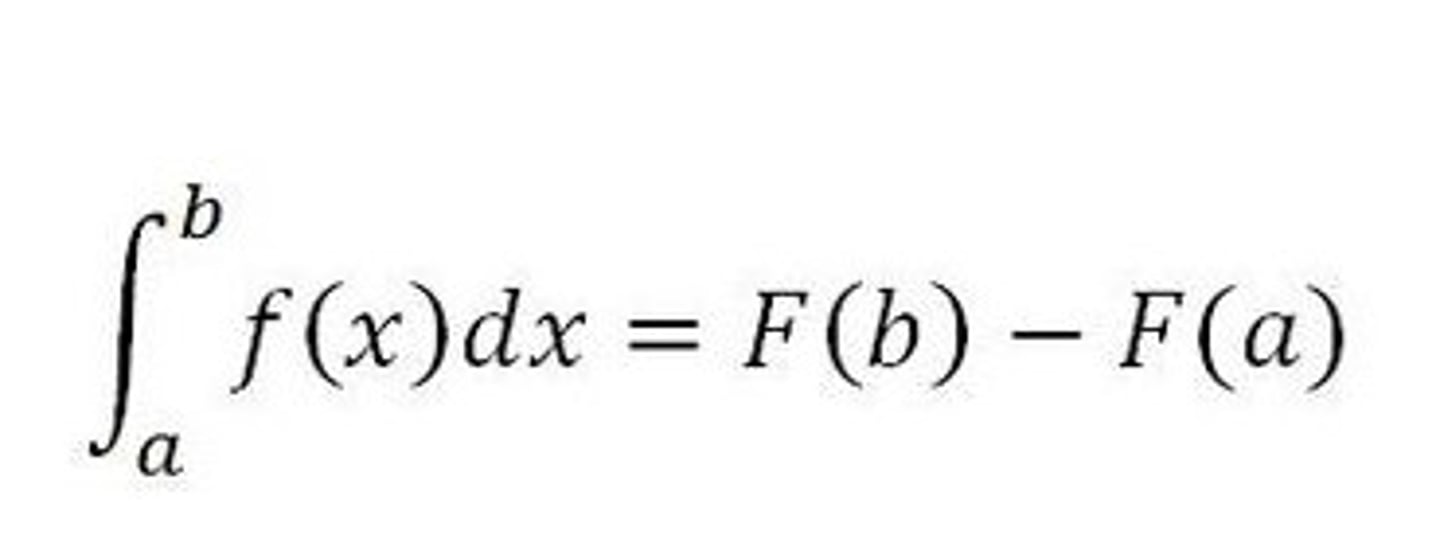
2nd Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
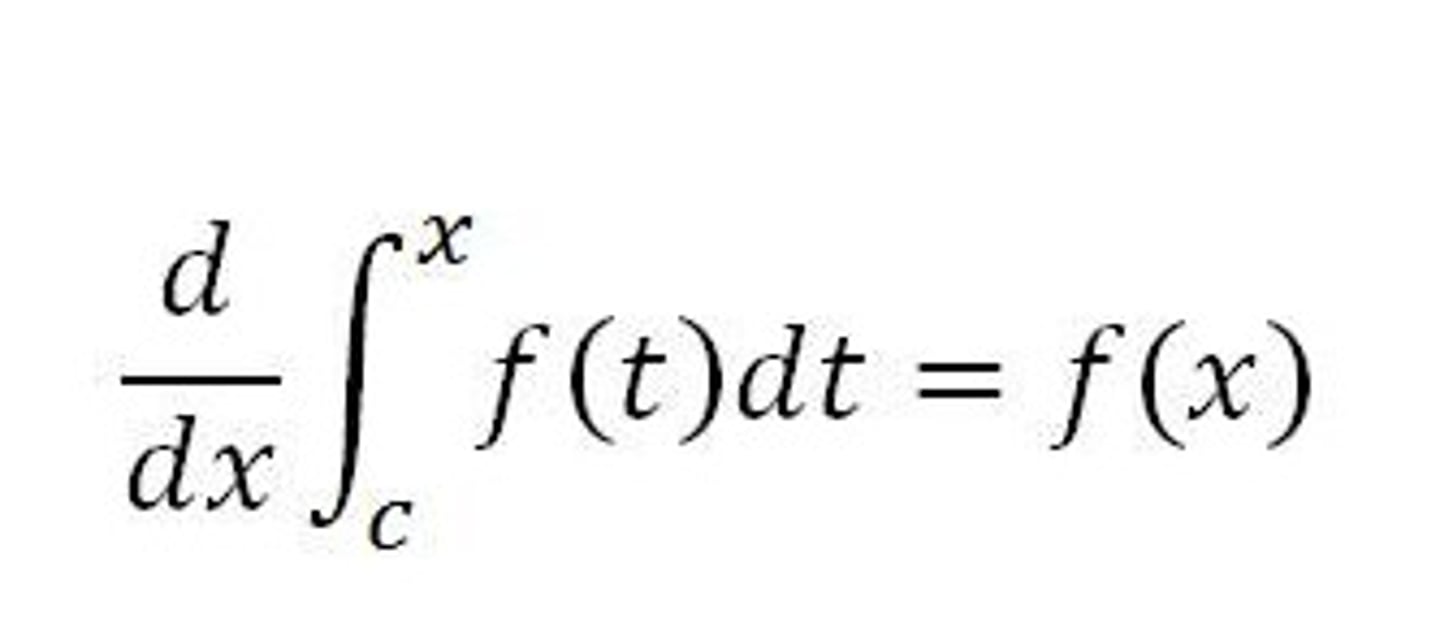
Product Rule
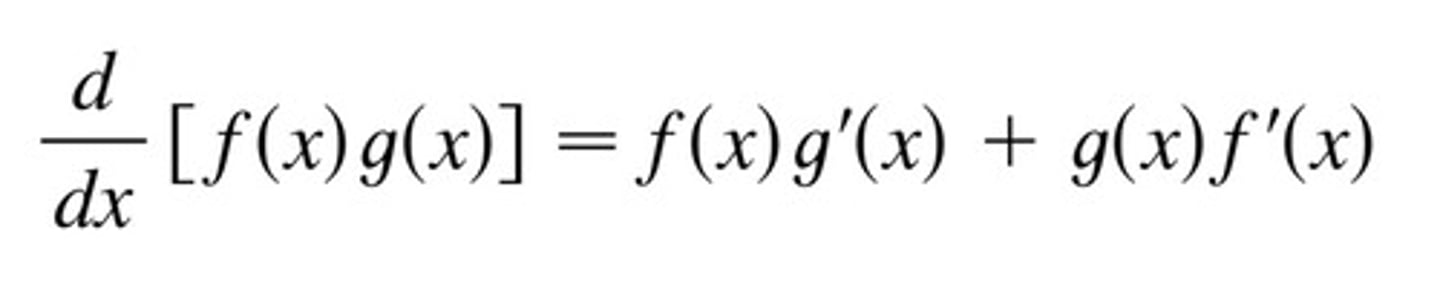
Quotient Rule
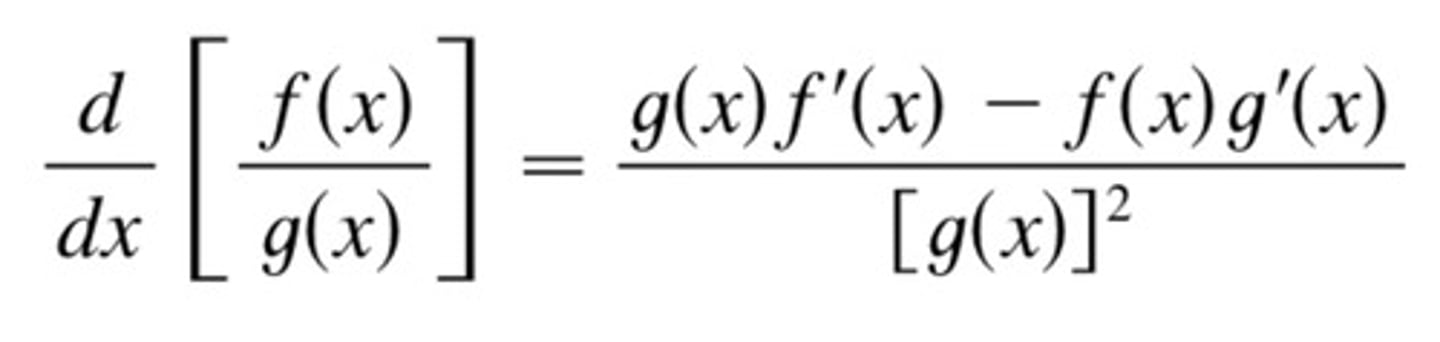
Chain Rule
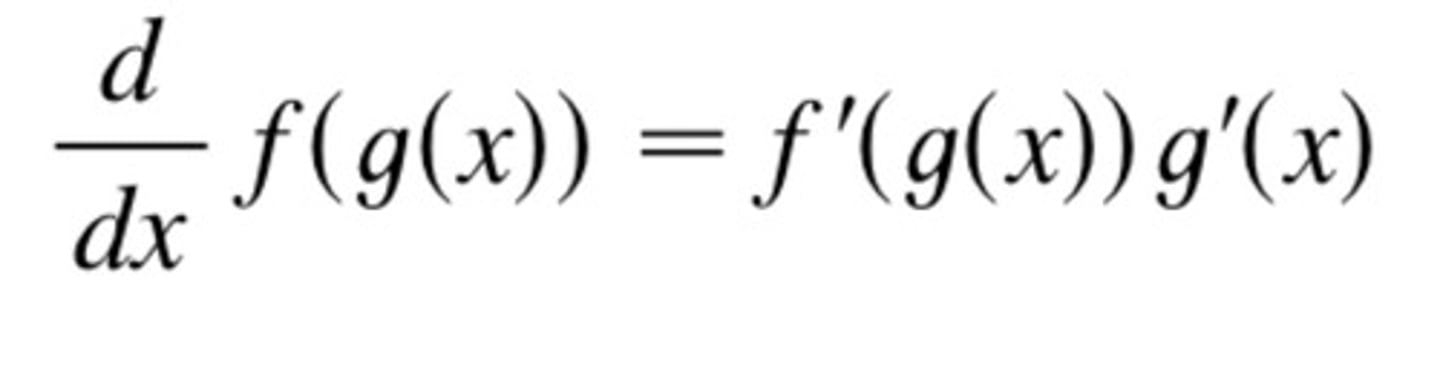
Power Rule
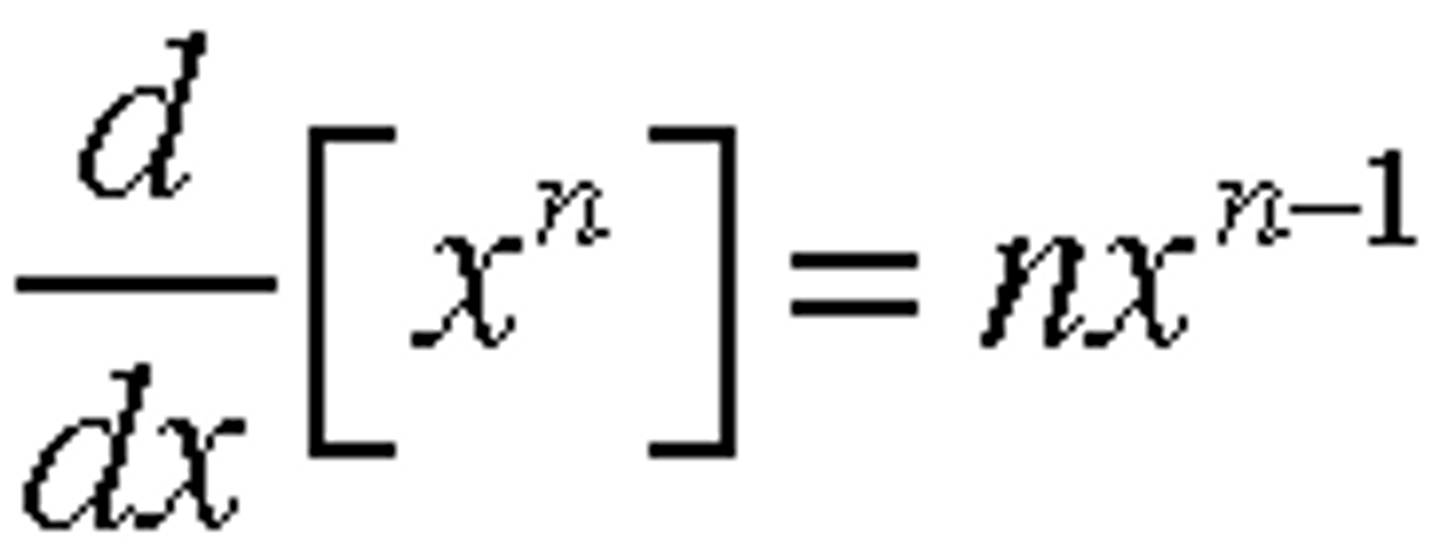
dy/dx sin(x)
= cosx
dy/dx cos(x)
= -sin(x)
dy/dx tan(x)
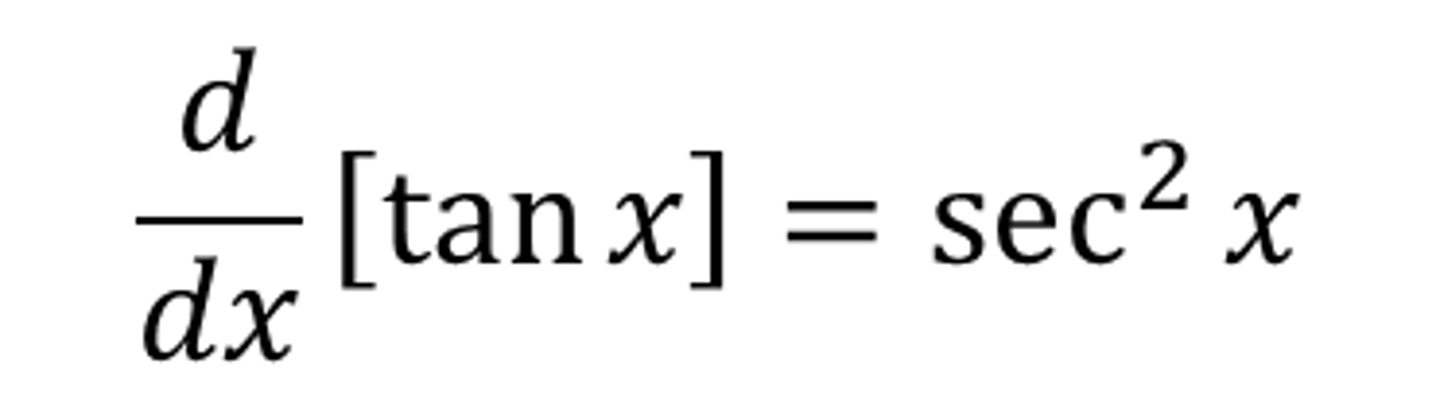
dy/dx cot(x)
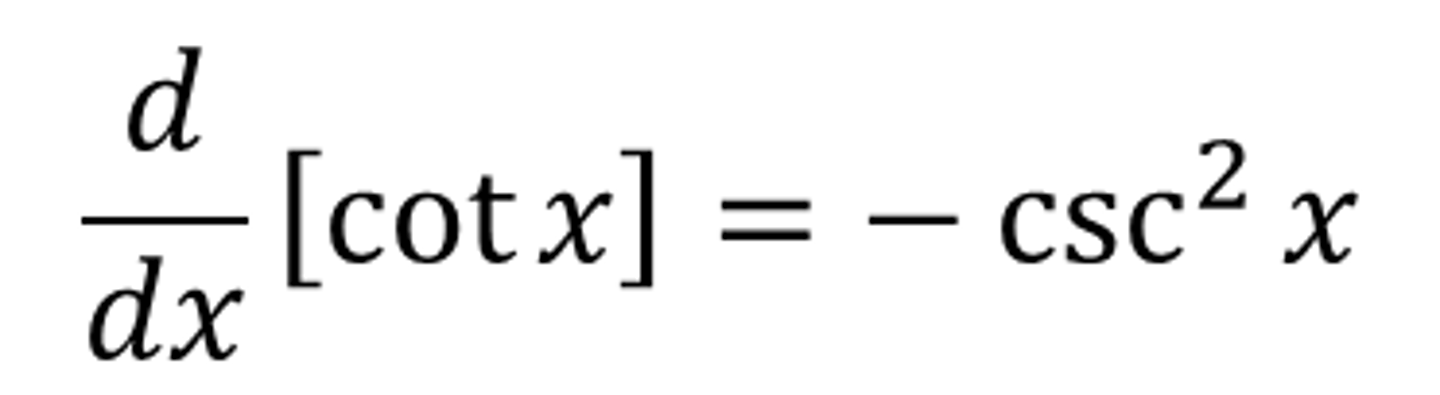
dy/dx sec(x)
= sec(x)tan(x)
dy/dx csc(x)
= csc(x)cot(x)
dy/dx arcsin(x)
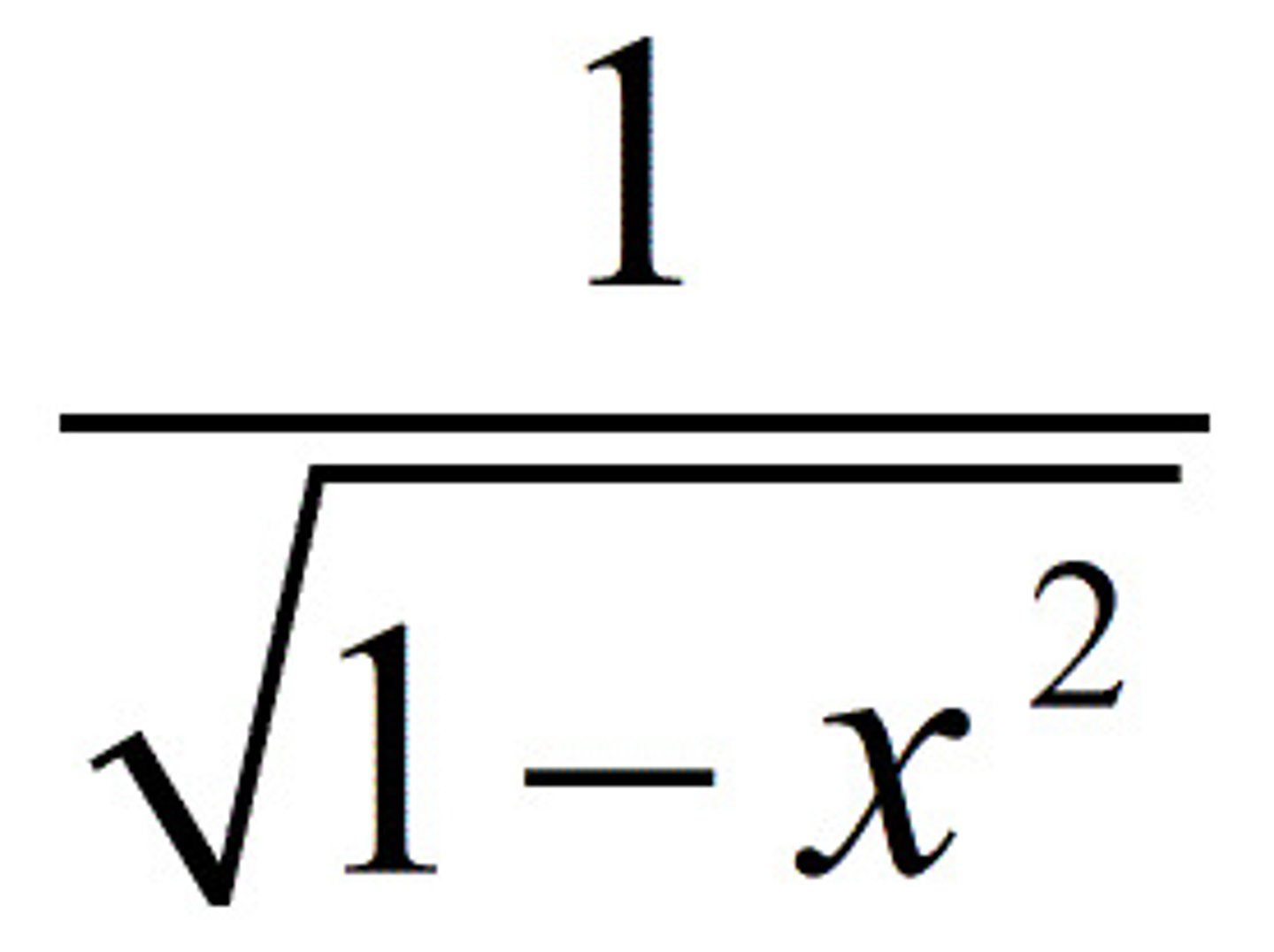
dy/dx arctan(x)
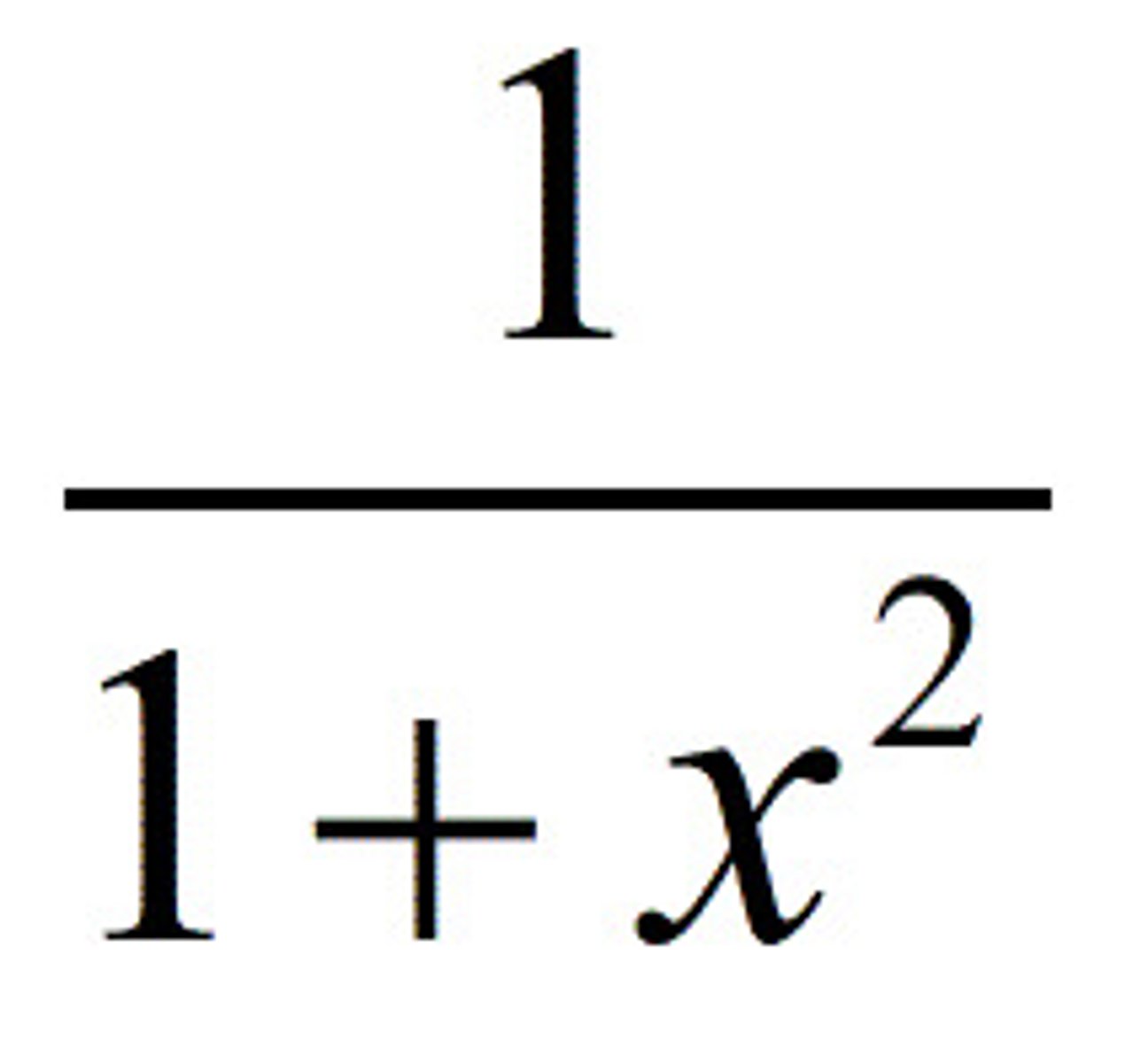
Critical Value
If f'(a)=0 or is undefined, a is a critical value

First Derivative Test
When the value x=a is a critical value:
1) If f'(x) switches from (+)→(-), f(c) is a relative maximum
2) If f'(x) switches from (-)→(+), f(c) is a relative minimum
When does the Second Derivative Test indicate f(x) is a relative minimum?
f'(x)=0 and f''(x)>0
When does the Second Derivative Test indicate f(x) is a relative maximum?
f'(x)=0 and f''(x)<0
What indicates that f(x) is concave up?
f'(x) is decreasing or f''(x) > 0
What indicates that f(x) is concave down?
f'(x) is increasing or f''(x) < 0
Points of Inflection
occur when:
1) if f''(a)=0/dne AND switches signs
2) if f''(a)=0/dne AND f'(a) changes from increasing to decreasing or decreasing to increasing
Reimann Sums
for a
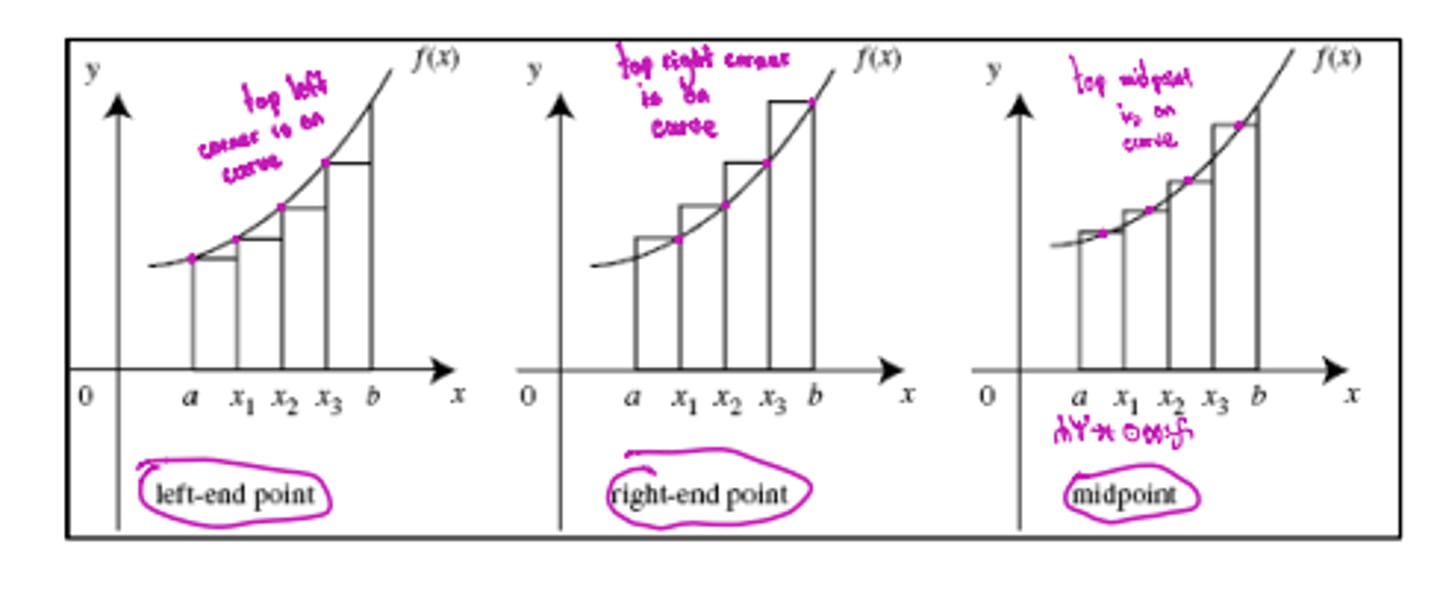
Trapazoidal rule
for a
Average Value
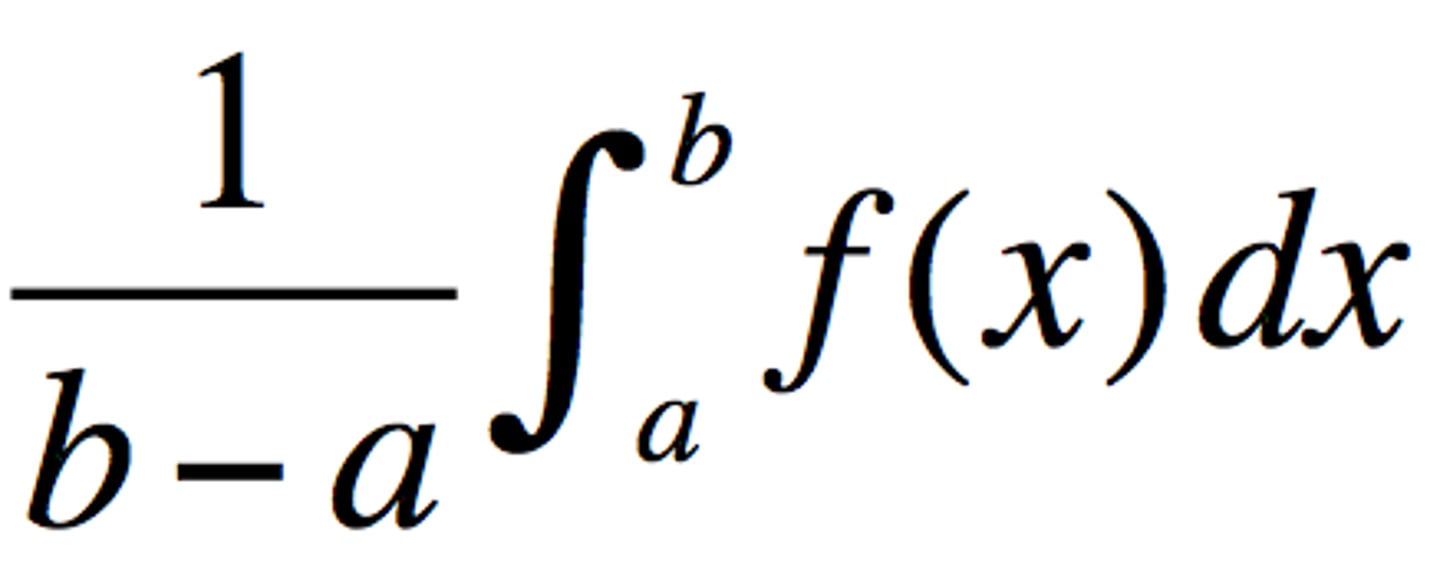
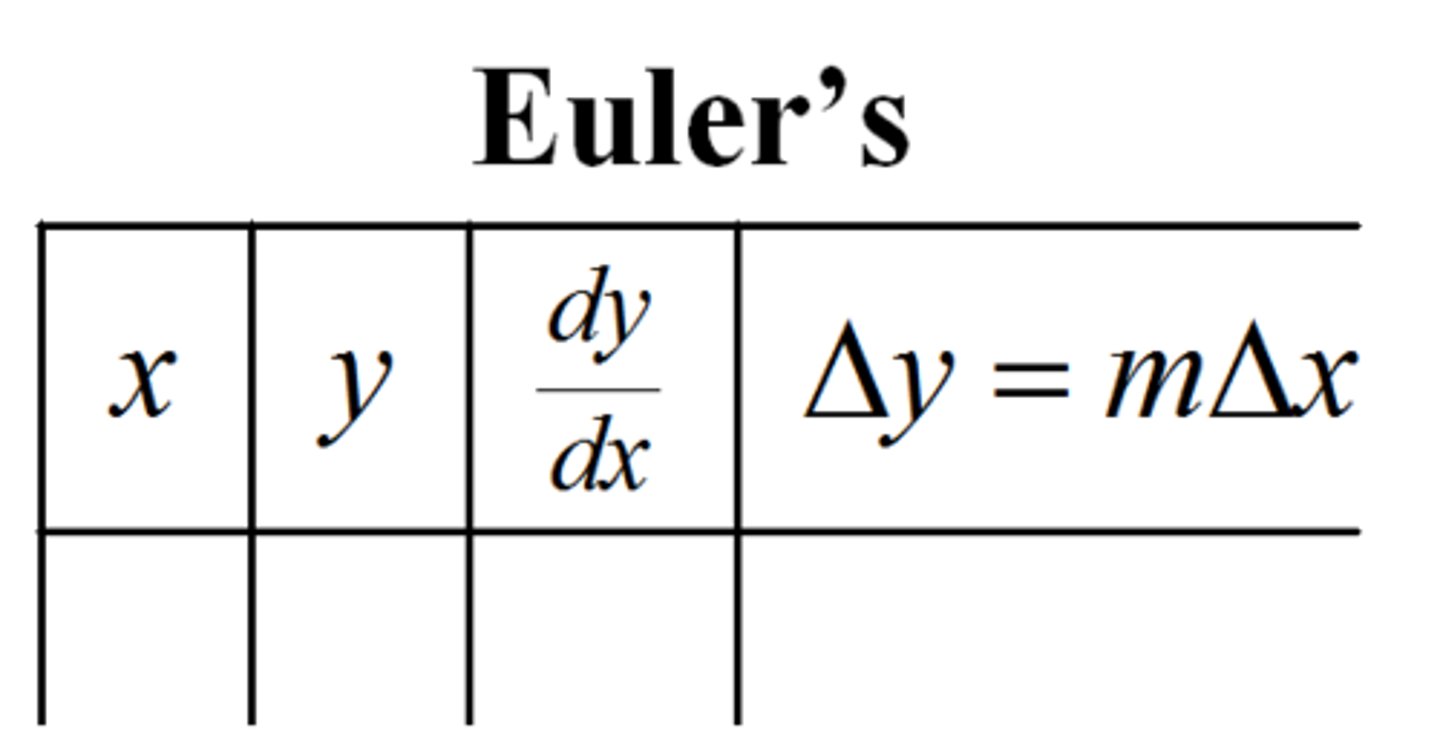
Euler's Method
new-y = old-y + (dy/dx)(new-x - old-x)
Integration by Parts
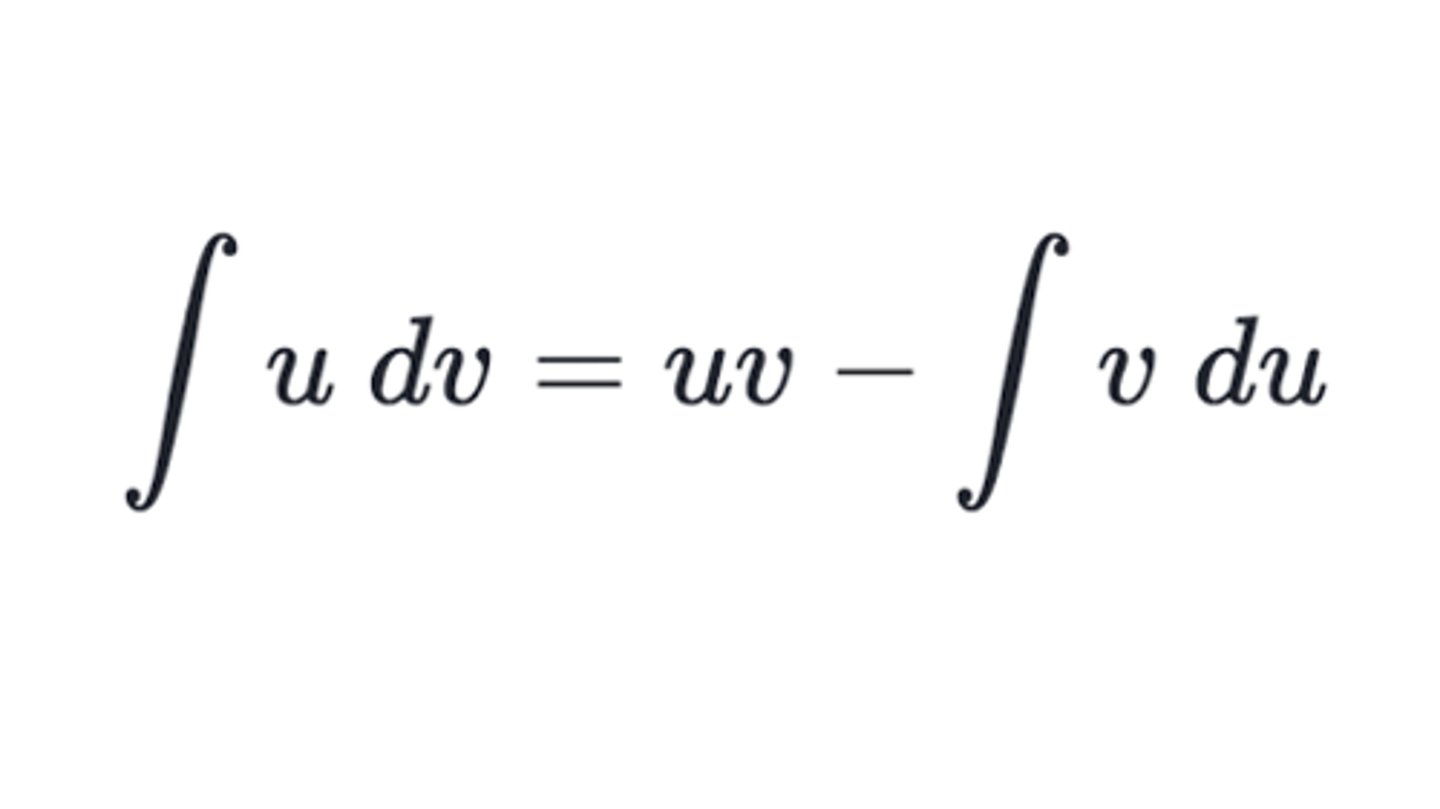
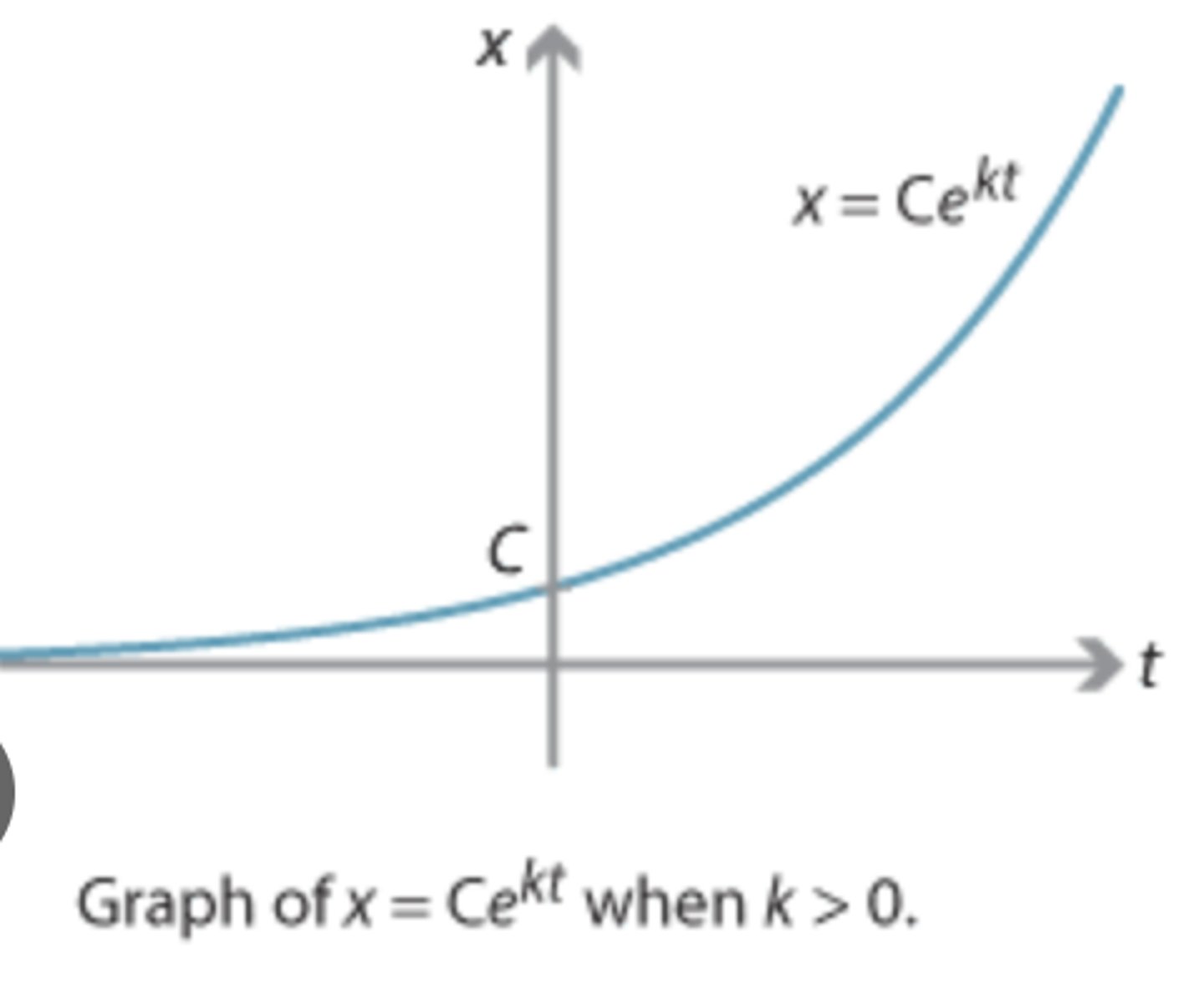
Exponential Growth & Decay
y=Ce^kt
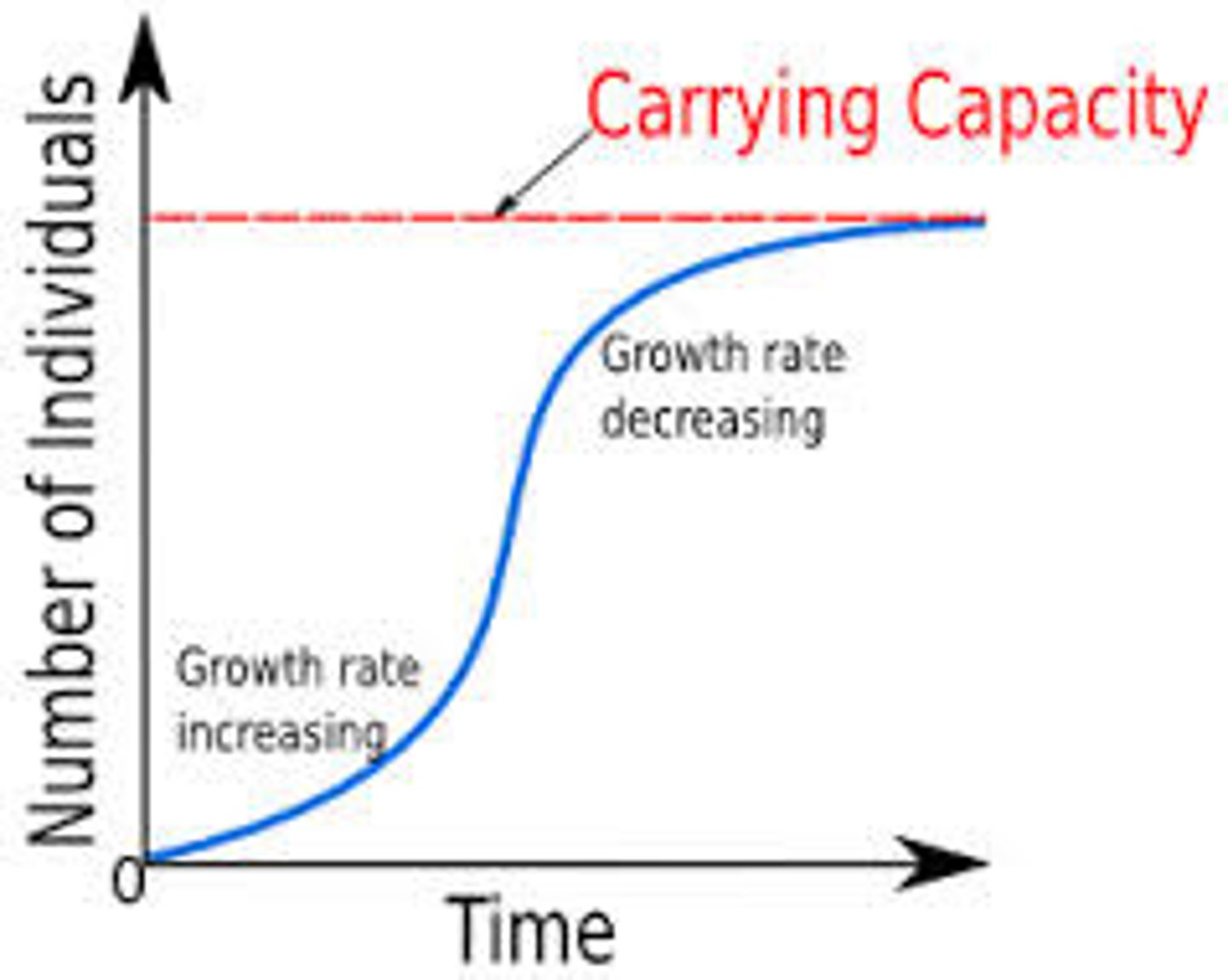
Logistic Differential Equations
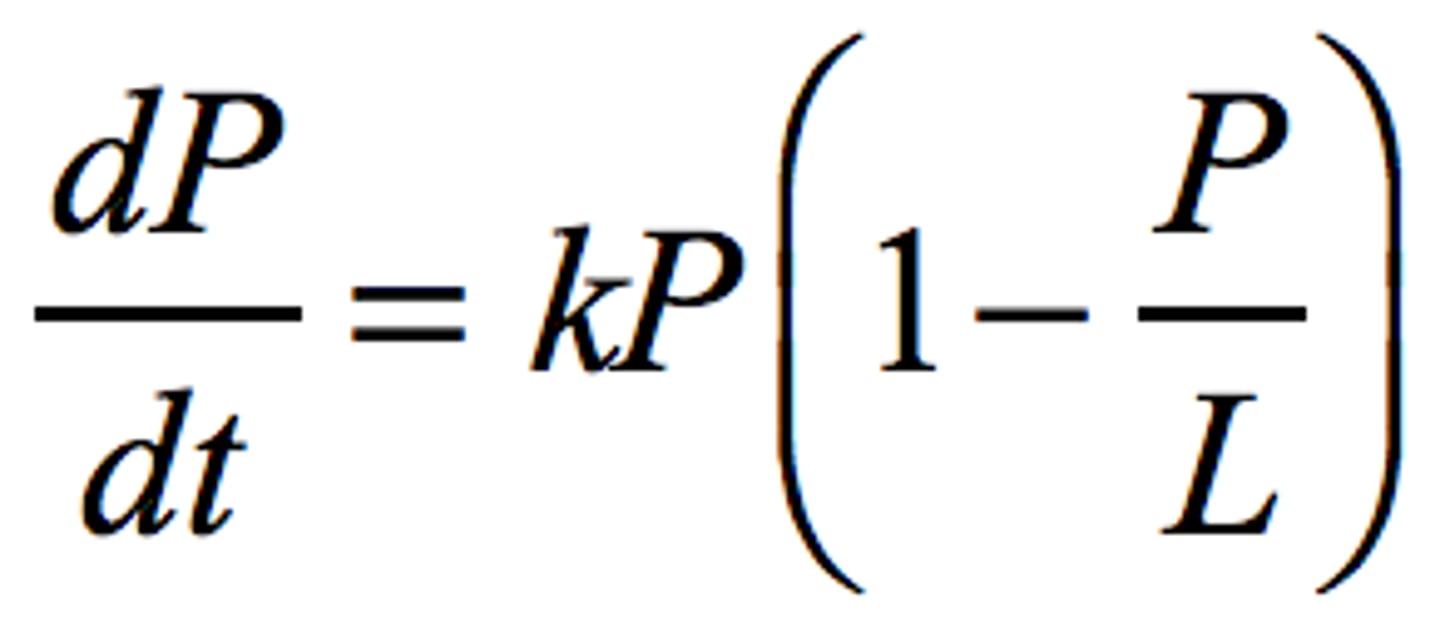
Logistic Growth Fomula
P = M/(1+Ae^-kt)
What is the formula for the area under a curve in terms of x?
A = ∫[a, b] (upper - lower)^2 dx
What is the formula for the area under a curve in terms of y?
A = ∫[a, b] (right - left)^2 dy
What is the formula for the volume using the Disk Method with a horizontal axis of rotation?
V = π ∫[a, b] (upper - lower)^2 dx
What is the formula for the volume using the Disk Method with a vertical axis of rotation?
V = π ∫[a, b] (right - left)^2 dy
What is the formula for the Washer Method when using a horizontal axis of rotation?
V = π ∫[a, b] (upper)^2 - (lower)^2 dx
What is the formula for the Washer Method when using a vertical axis of rotation?
V = π ∫[a, b] (right)^2 - (left)^2 dy
Length of a Curve / Arc Length
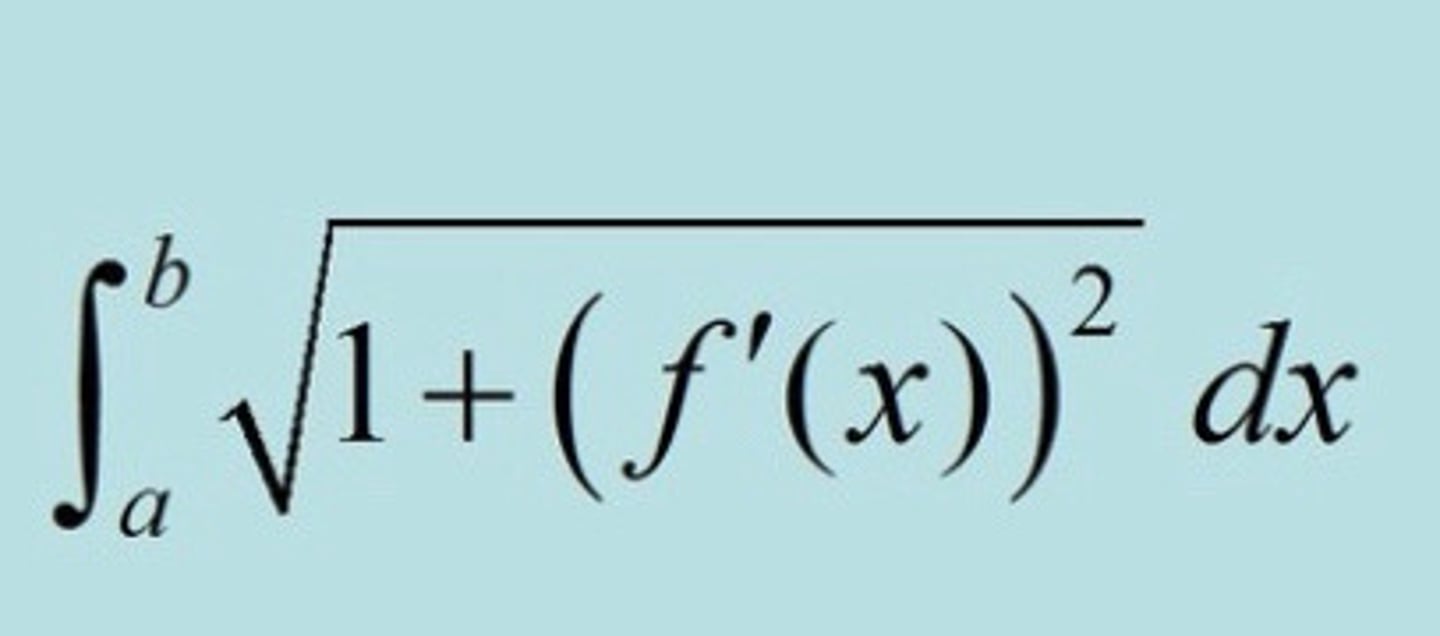
Cross Section Perpendicular to the x-axis Formula
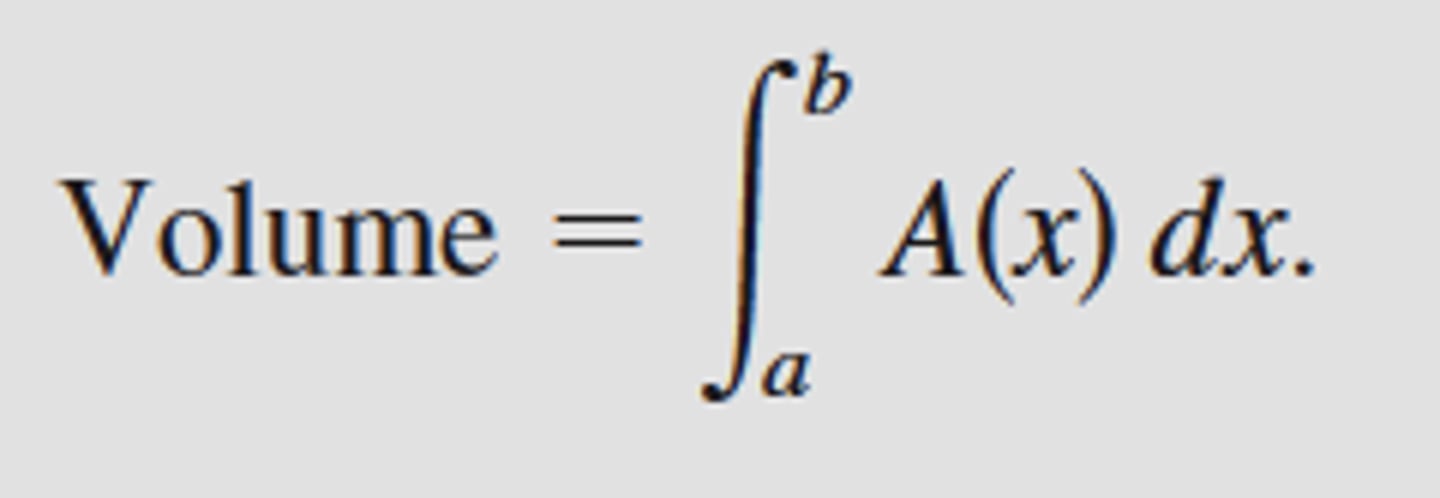
Cross Section Perpendicular to the y-axis Formula

Velocity
x'(t)
Speed
|v(t)| or |x'(t)|
Acceleration
v'(t) or x''(t)
Displacement (Change in Position)
∫[a, b] v(t) dt
Finding position with displacement
Position = Initial Position + Displacement
Total Distance Traveled
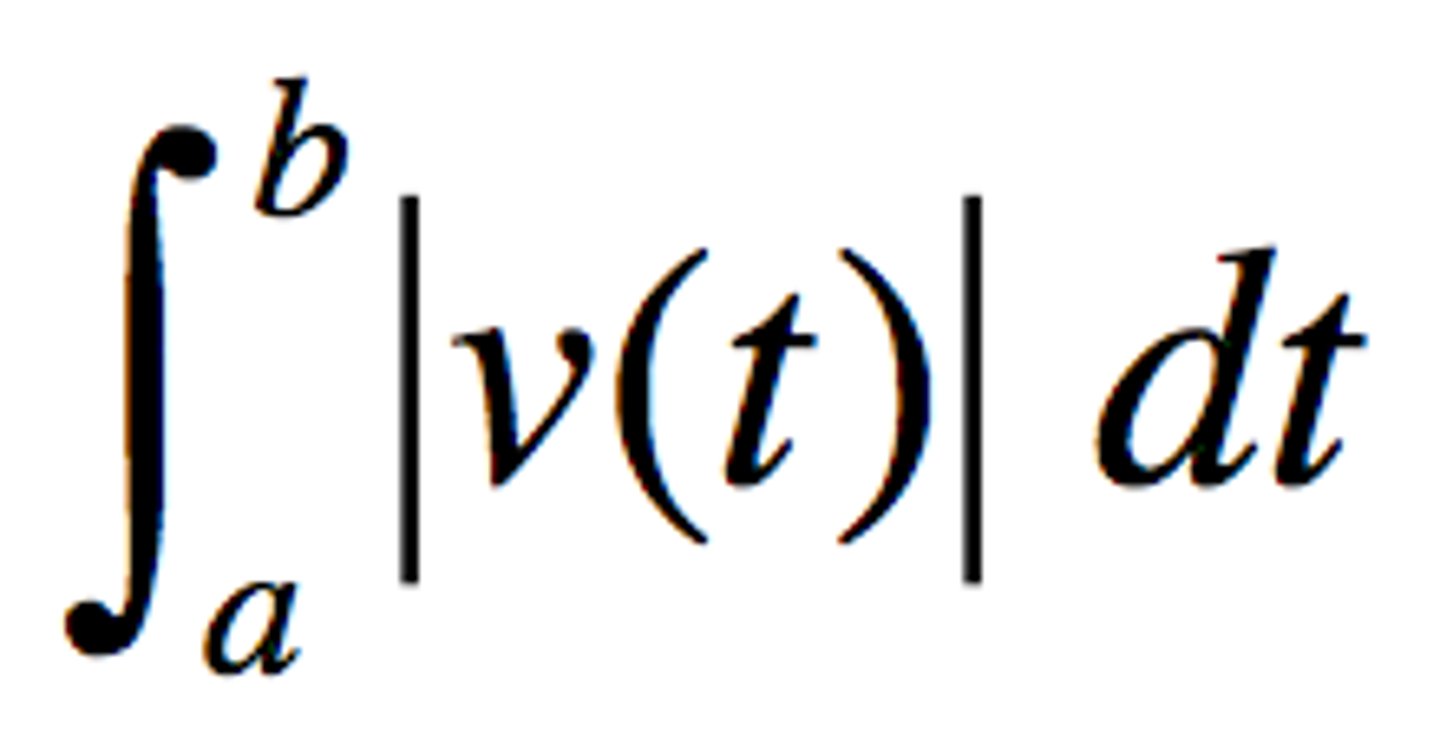
Parametric First Derivative
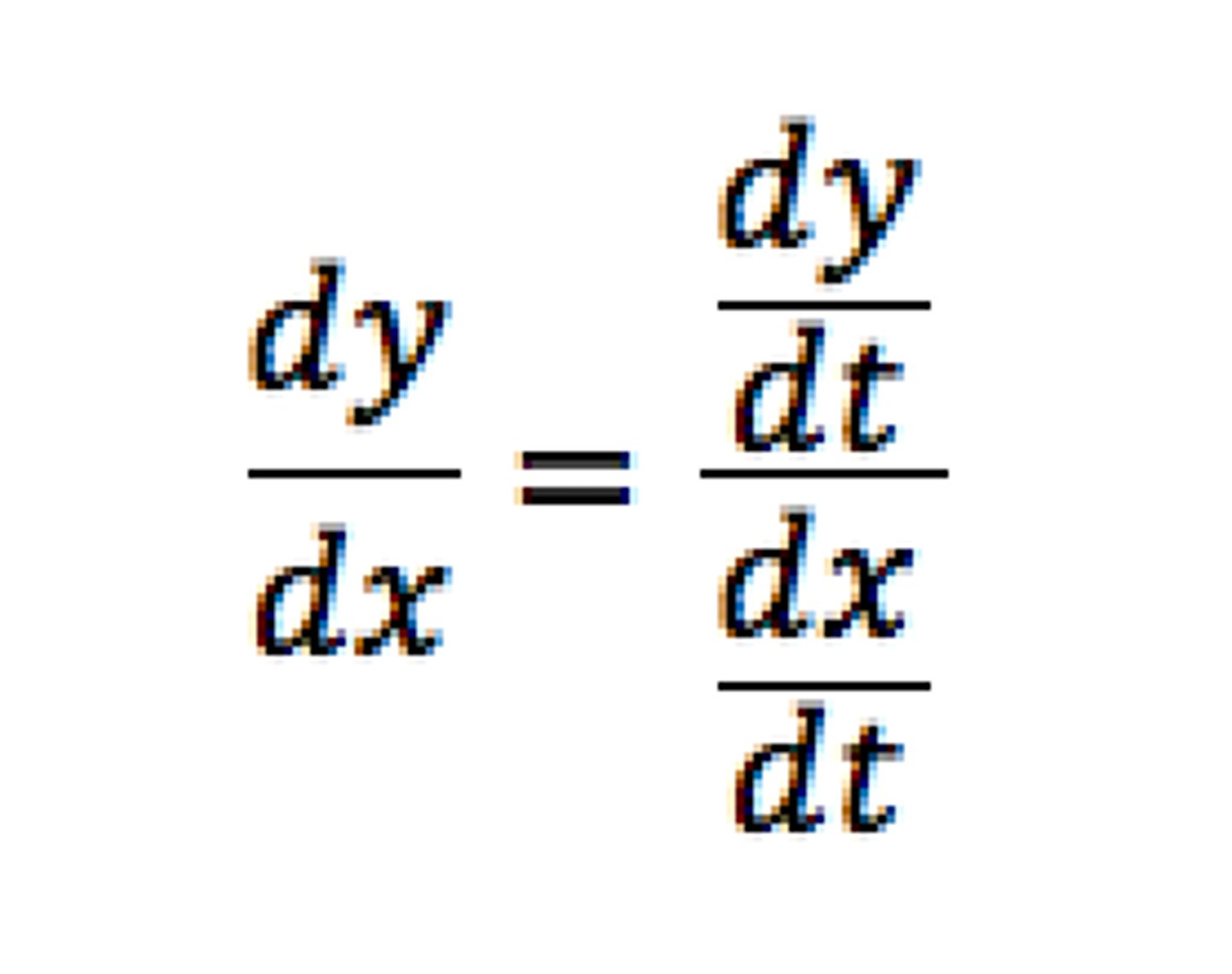
Parametric Second Derivative
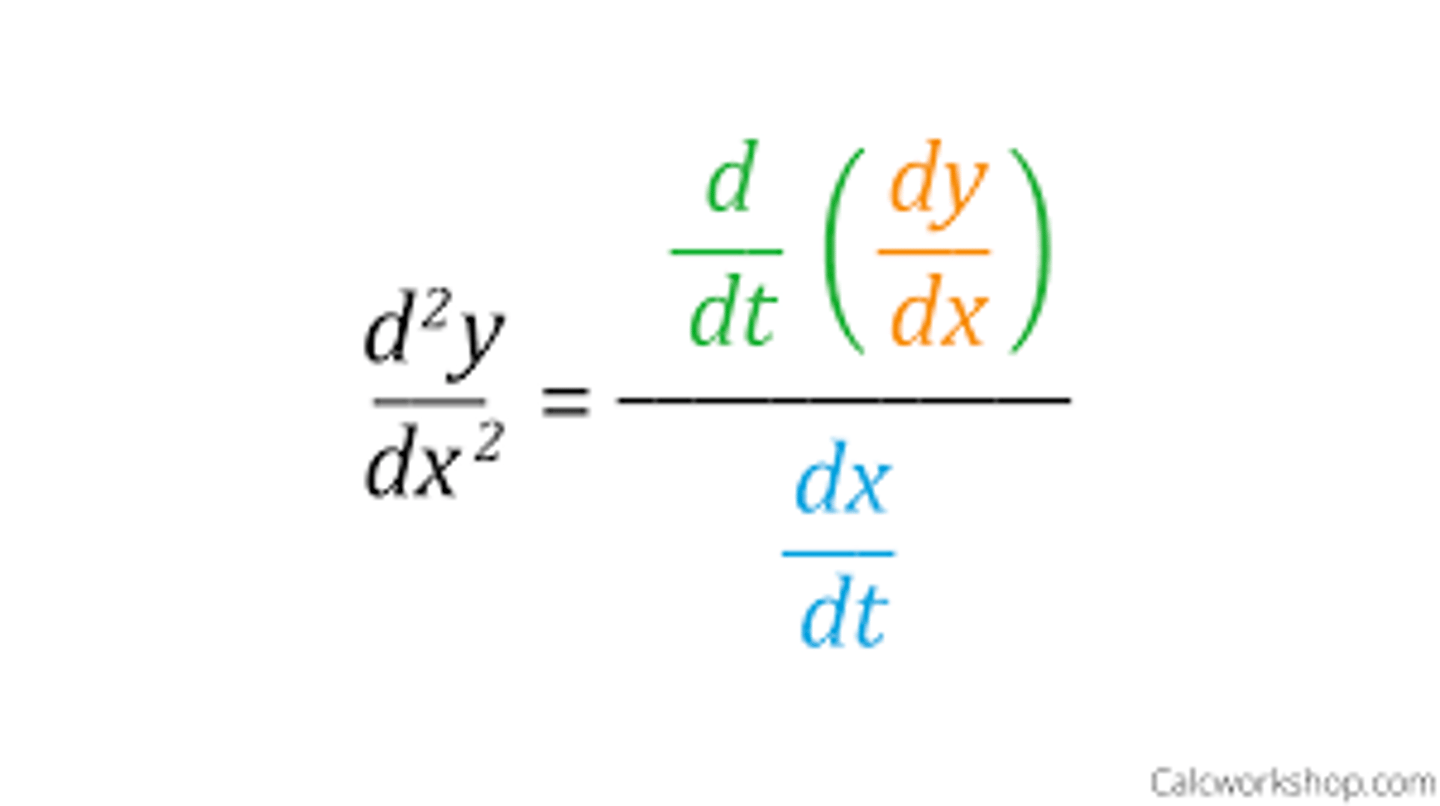
Parametric Arc Length
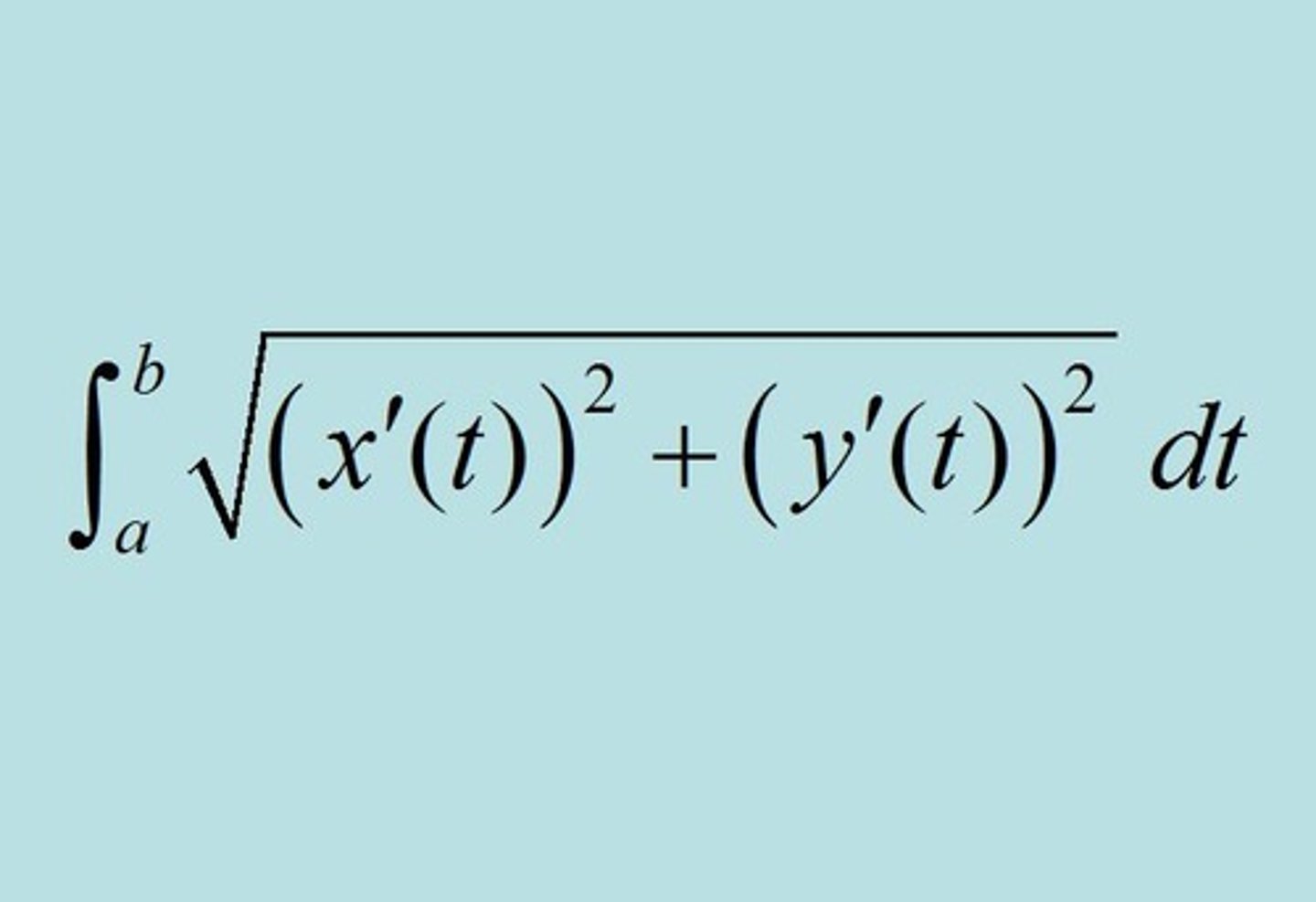
Position Vector
< x(t), y(t) >
Velocity Vector
Acceleration Vector
Speed of a Parametric
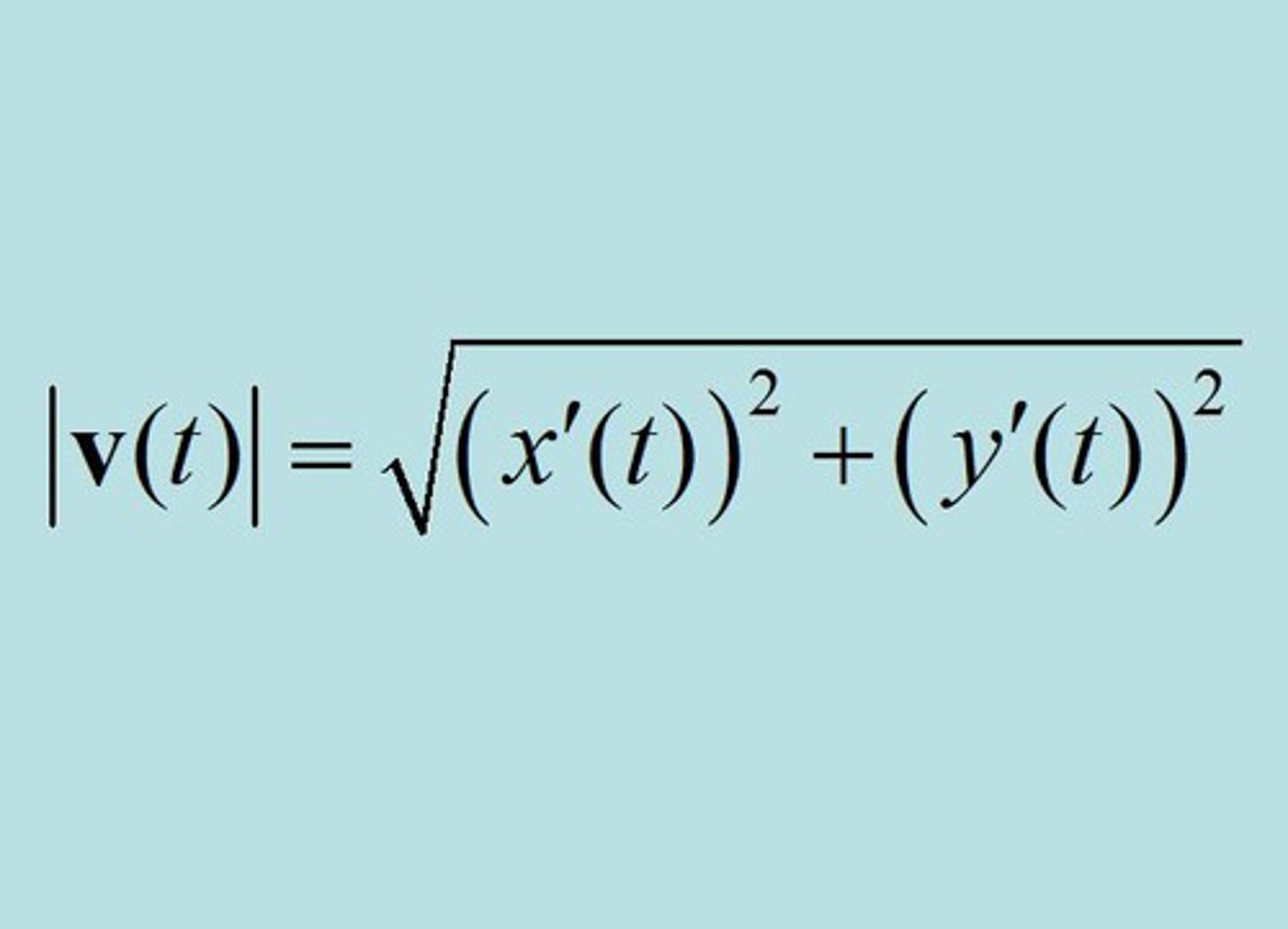
Displacement of a Parametric
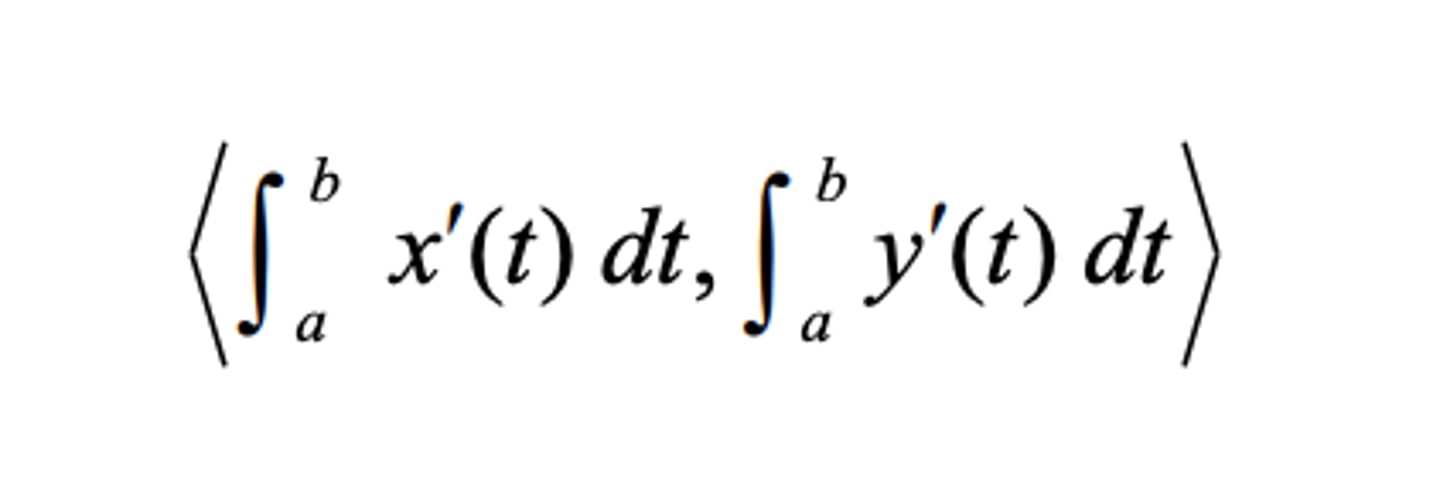
Distance Traveled (Arc Length) for a Parametric
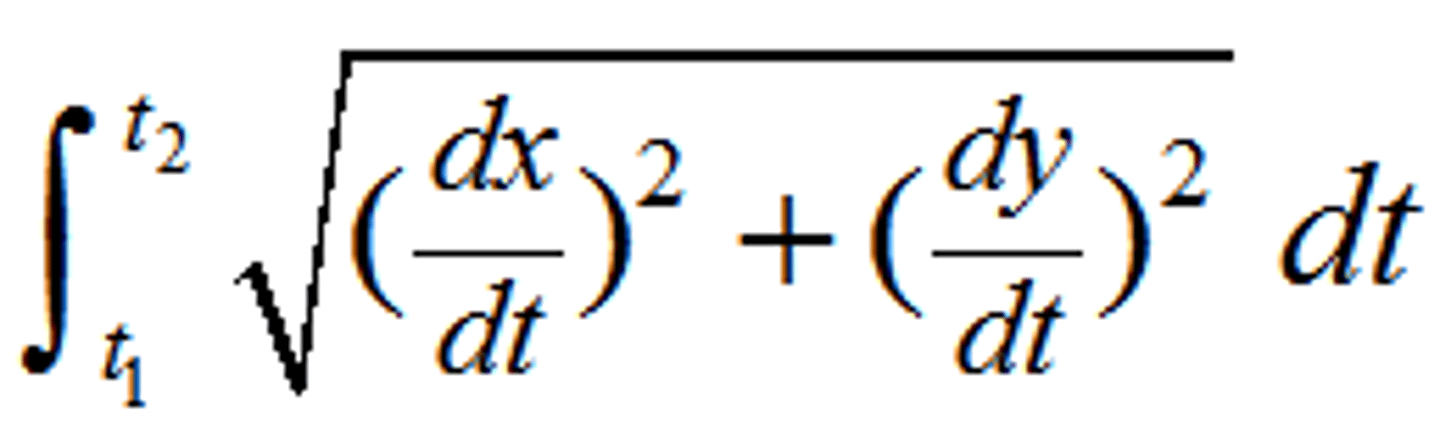
x in polar terms
x = rcosθ
y in polar terms
y = rsinθ
Area inside a polar curve
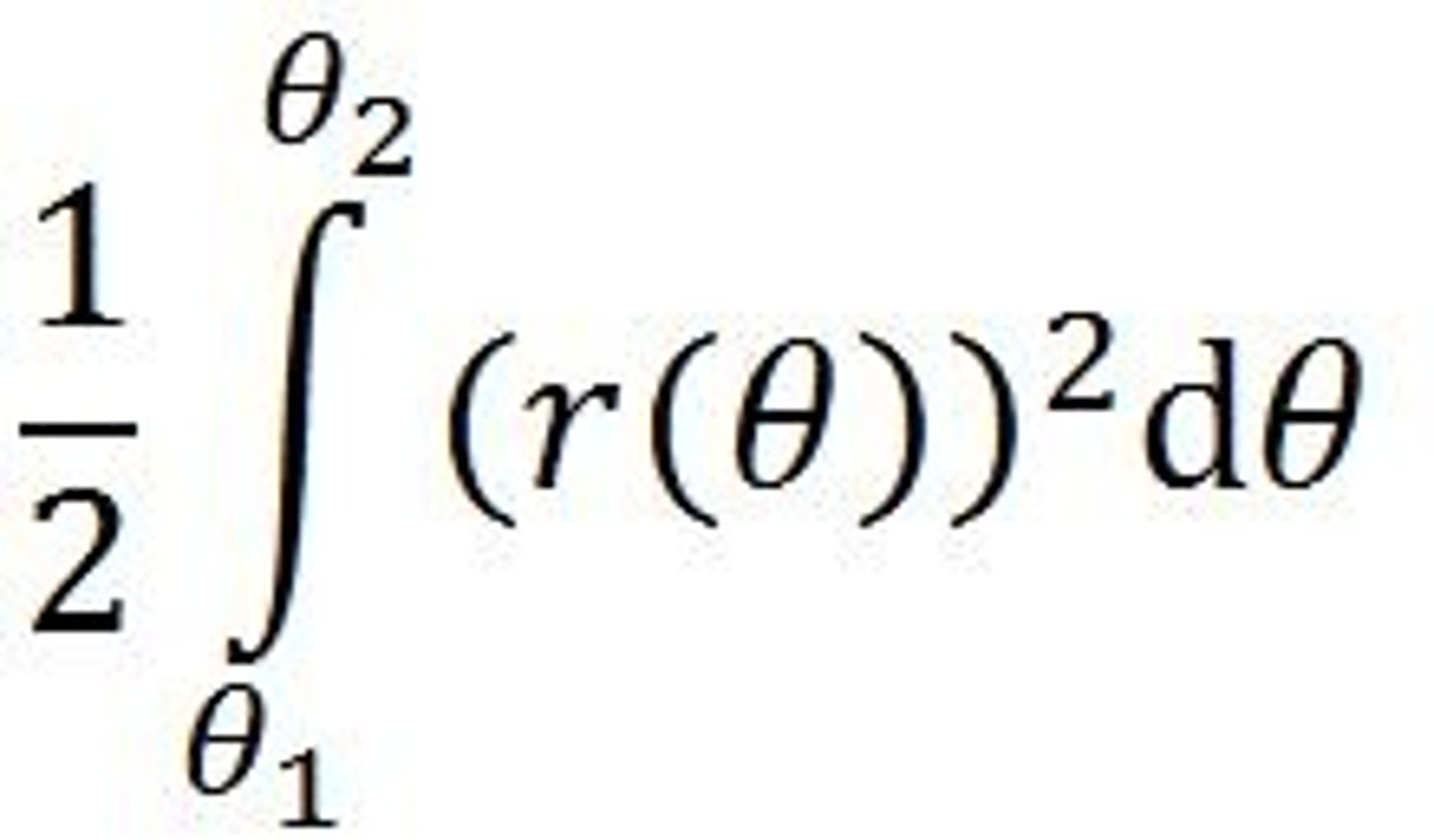
Area between 2 polar curves
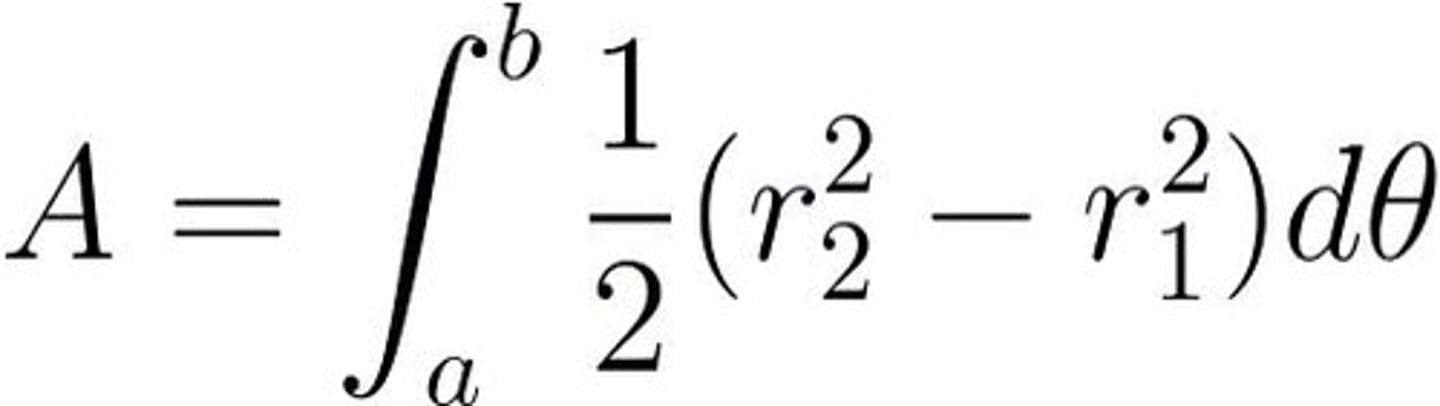
Taylor Polynomial Formula
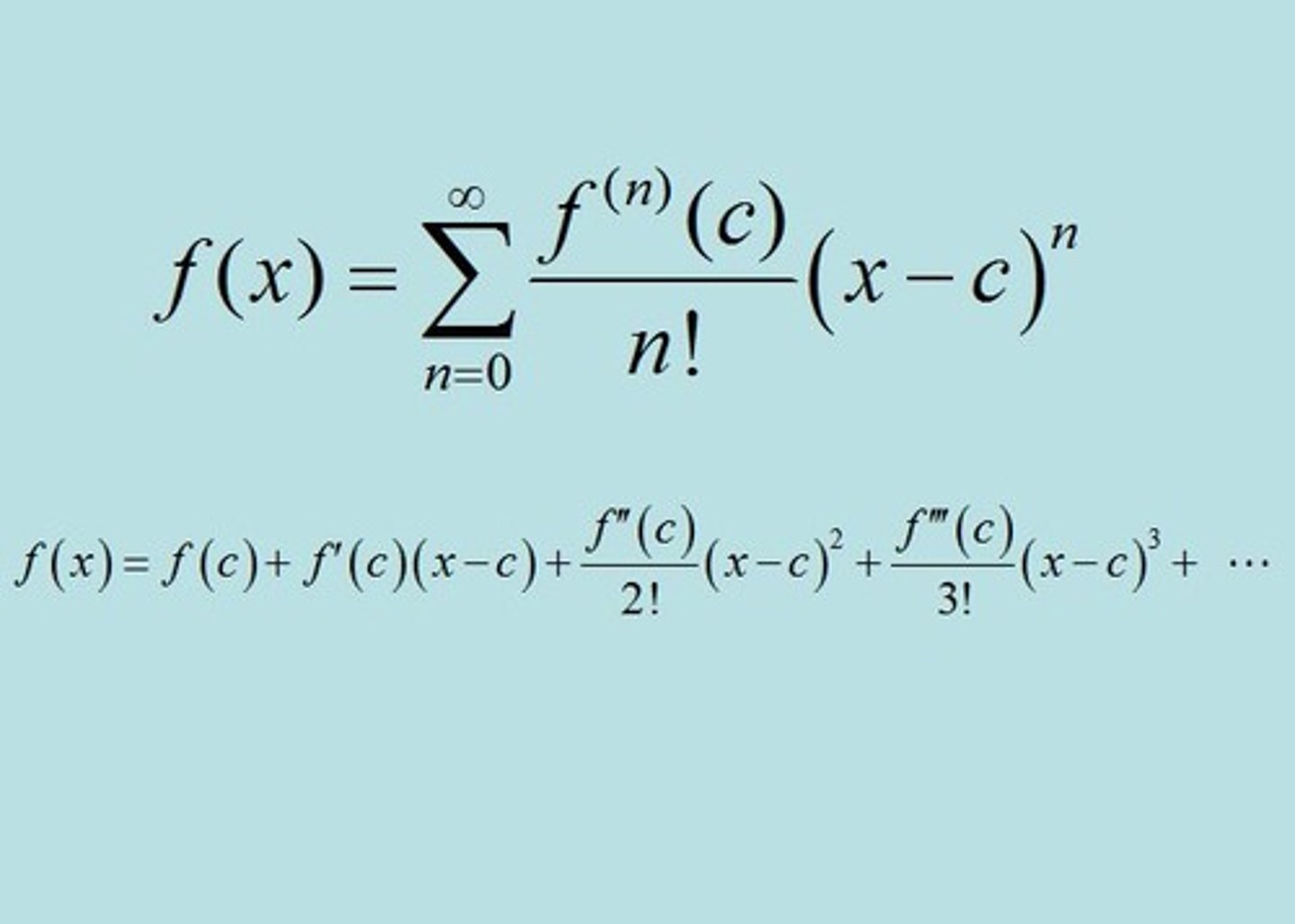
Lagrange Error Bound Formula
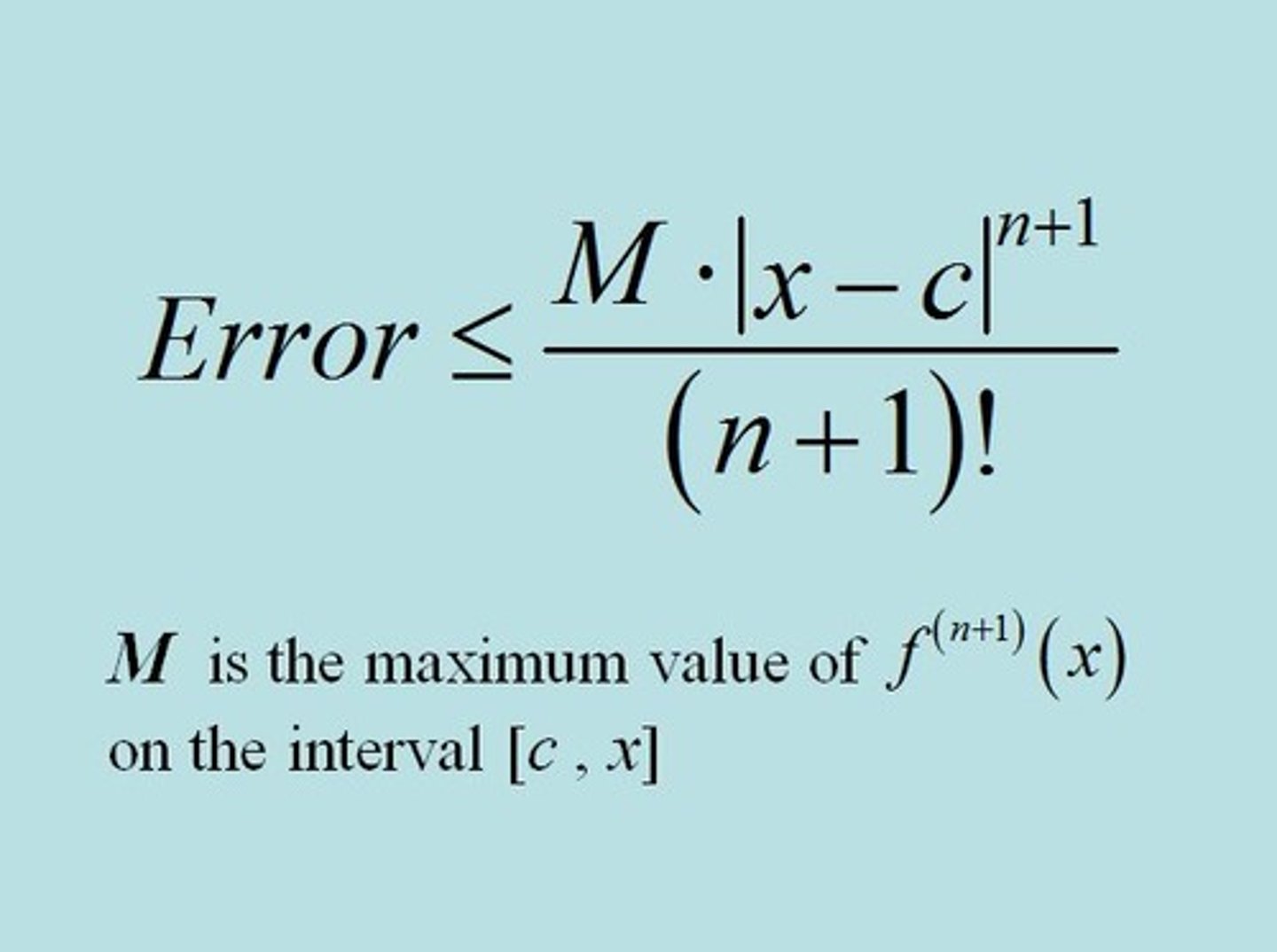
Alternating Series Remainder Formula
