SHS: Labs 6-8
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Spectrogram
“A spectrogram is a representation of how the frequency content of a signal changes with time. Time is displayed along the x-axis, frequency along the y-axis, and the amount of energy in the signal at any given time and frequency is displayed as a level of grey.”
Has formants
What is this?
Glottal Source Signal
“A glottal source signal refers to the sound wave generated by the vibration of the vocal folds (glottis) before it is shaped by the vocal tract. It is the raw, unfiltered sound that serves as the basis for voiced speech sounds.”
What is this?
Vocal Tract Filter Wave
“A vocal tract filter wave refers to the sound wave that results after the glottal source signal has been shaped by the resonances of the vocal tract (the throat, mouth, and nasal cavity). This filtering process is what allows humans to produce different speech sounds, such as vowels and consonants.”
What is this?
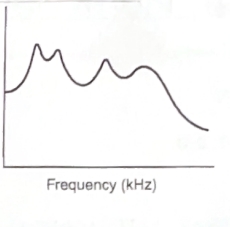
Speech Signal
“A speech signal is an acoustic waveform that represents spoken language. It is a time-varying signal that carries information about the speaker’s voice, linguistic content, and emotion.”
What is this?
Lungs
Power source is in the…?
Produces
The source _______ the sound?
Shapes
The filter _____ the sound?
Periodic
The source produces a ______ sound
Vocal Folds
The source is also known as the…?
The vocal tract; everything above the glottis: Nasopharynx, oropharynx, sinuses, etc.
The filter includes…?
Formants
Resonant frequencies applied to the voice are called…?
Peaks of harmonics shown on the output spectrum
What are formants…?
Periodicy and pitch
Intensity
Duration
Phonation quality (Breath, modal, and creaky)
Functions of source:
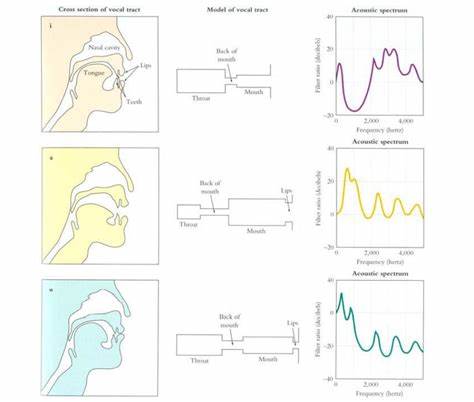
Vowel/tongue height
Vowel/tongue advancement
Rounding (oo)
Functions of Filter:
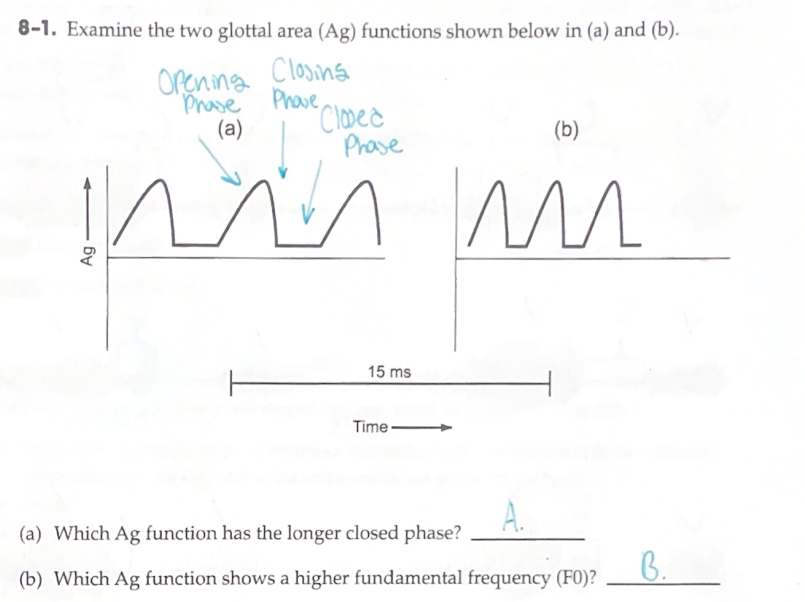
The lungs represent the closed part of the system, while the nose and mouth form the open part. This is because the lungs connect to the trachea, which leads to the nose and mouth—serving as the open end of the vocal tract.
Why is the tube closed at one end of the correct acoustic (resonator) model of the vocal tract?
Nasal and Oral Cavities
The spectrogram of a nasalized vowel includes resonances from the…?
Resonance and Antiresonance because of the vibrations within both cavities
The nasal cavity has both...?
Fundamental frequency; which is periodic
F0 is also called…?
The Vocal Folds
Frequency of voiced speech signals originating from…?
Friction Interval
What is the acoustic event that represents aeromechanical event of turbulent flow at expanding constriction?
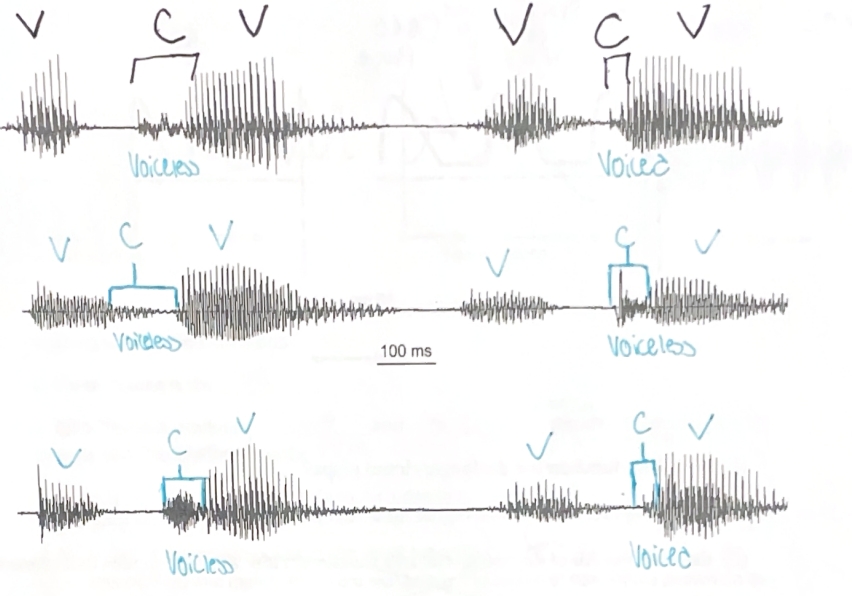
Vowels: Peaks of periodicity
Consonants: Aperiodic bursts of sound
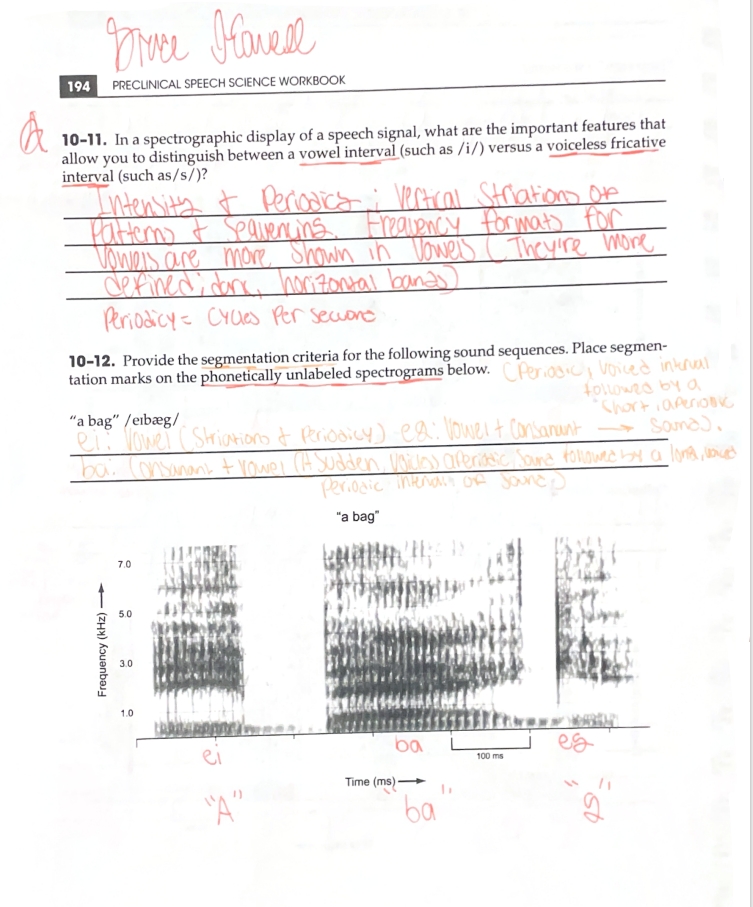
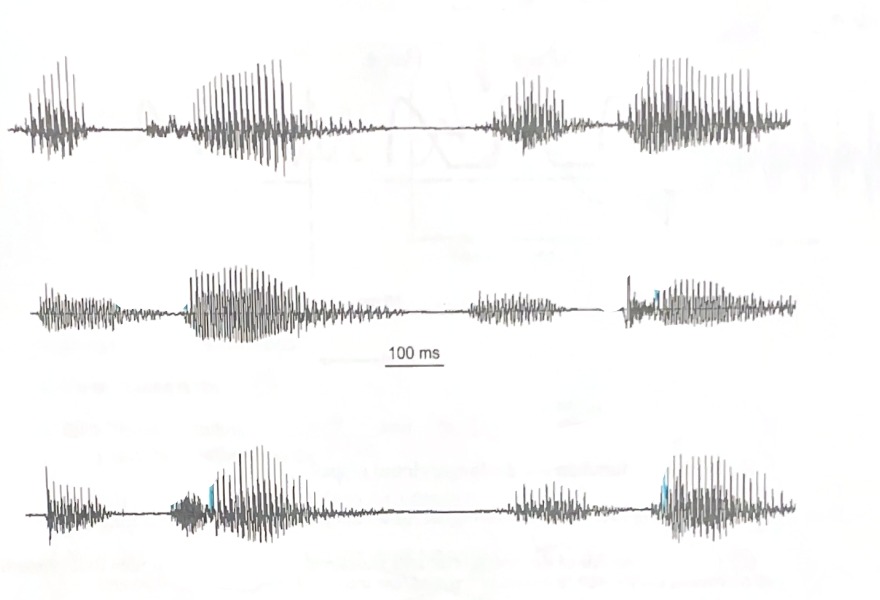
Identify which are voiced and nonvoiced and which are vowels and consonants.
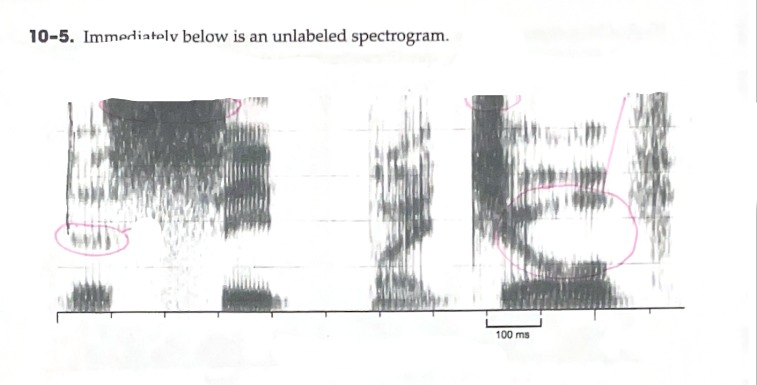
Horizontal (X-Axis): Milliseconds/Time
Vertical (Y-Axis): Hertz/Hz
Z-Axis: Intensity
Label the axis of a spectrogram
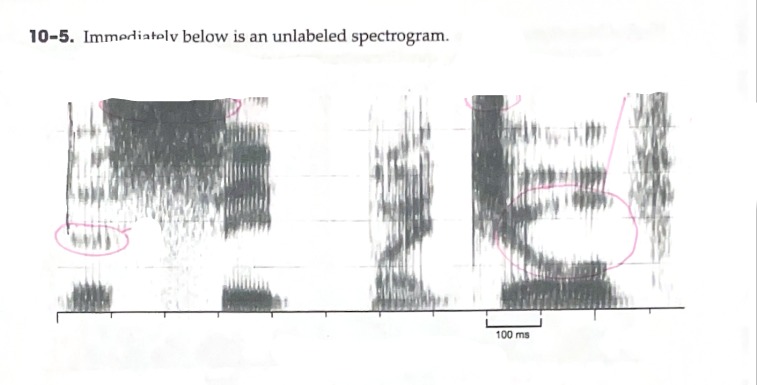
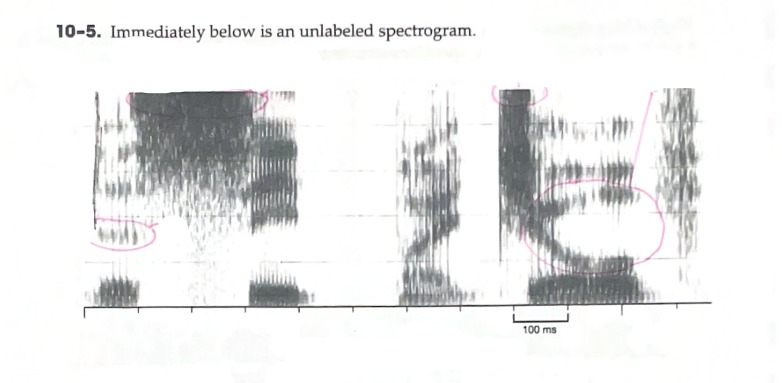
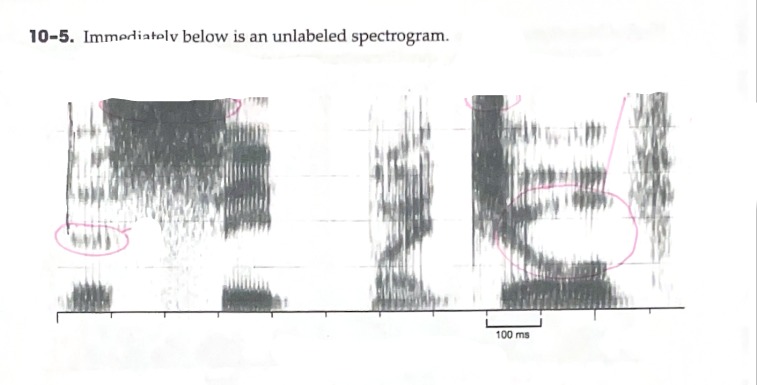
B: Identify (any) region of energy that is clearly greater than one other region of energy.
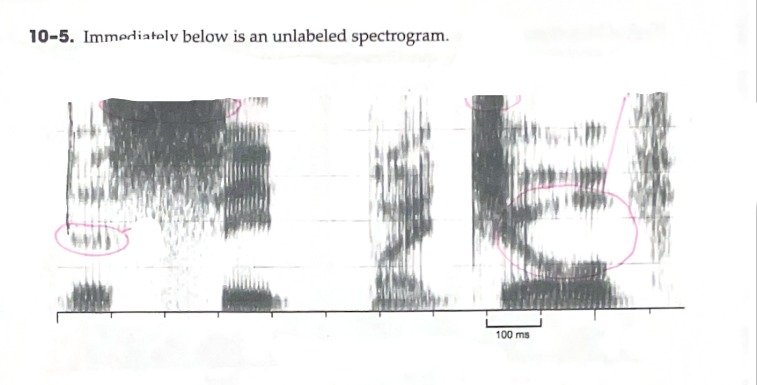
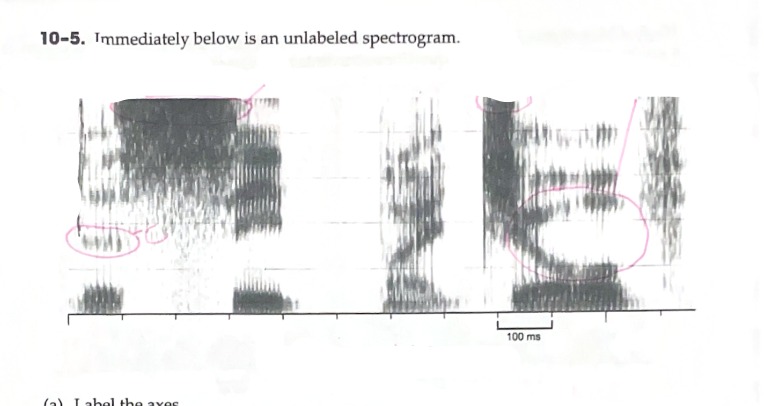
C: Identify a vowel that has an F2 around 2000 Hz
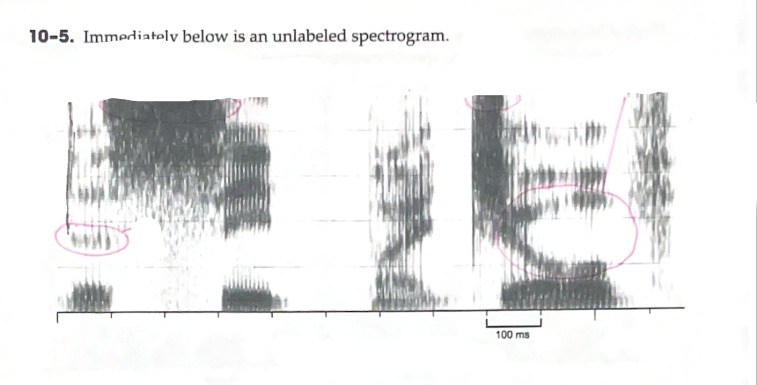
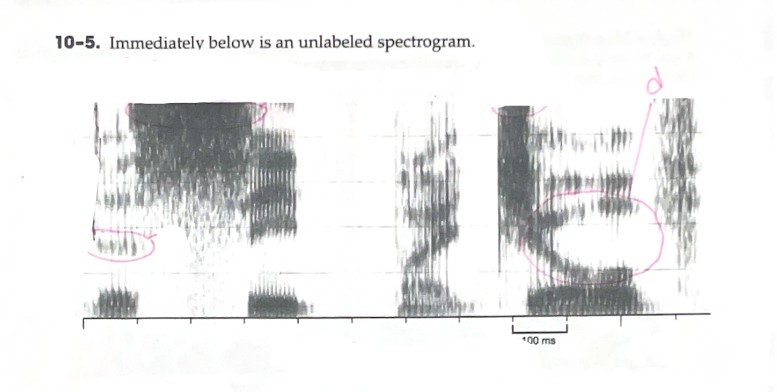
D: Identify a vowel with a large formant transition
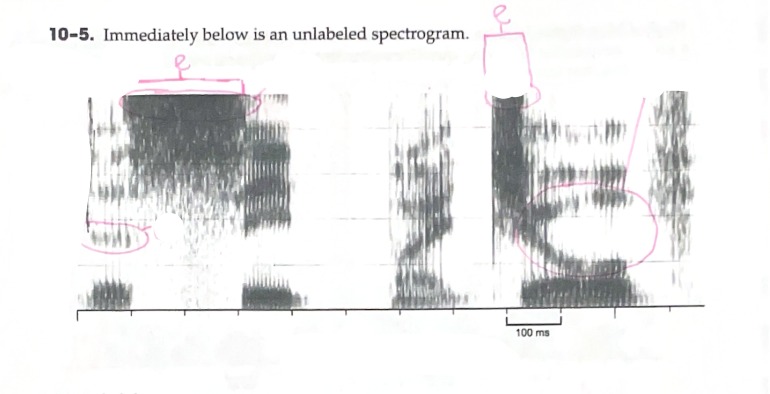
E: Identify a fricative with very intense energy in the higher frequencies
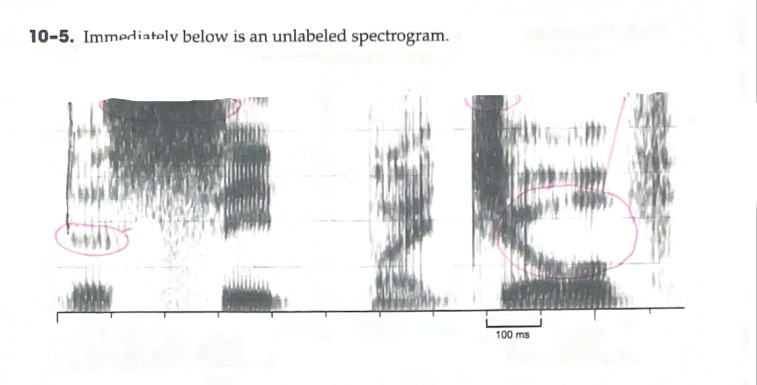
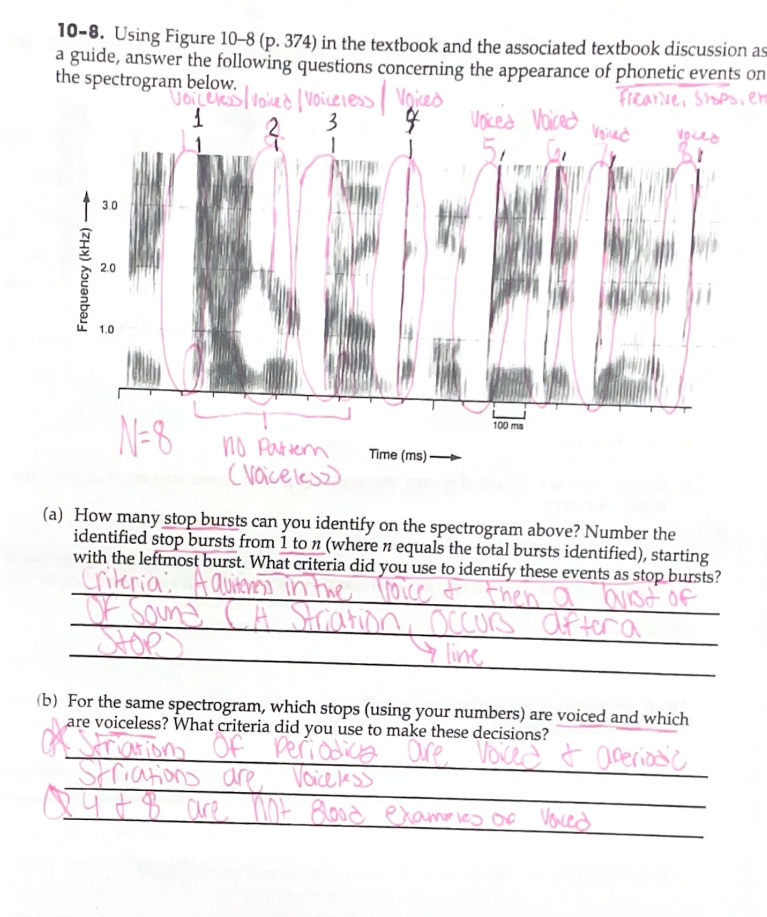
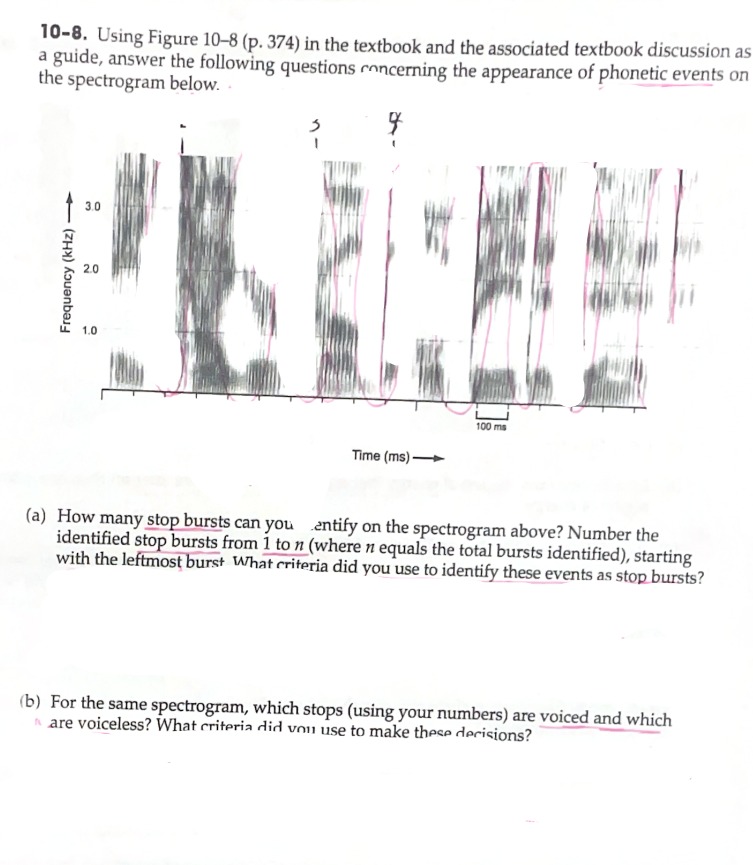

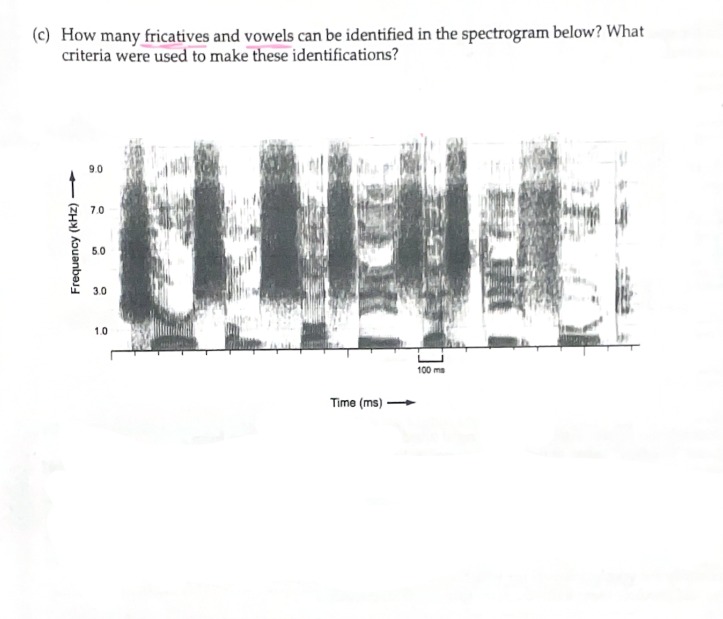
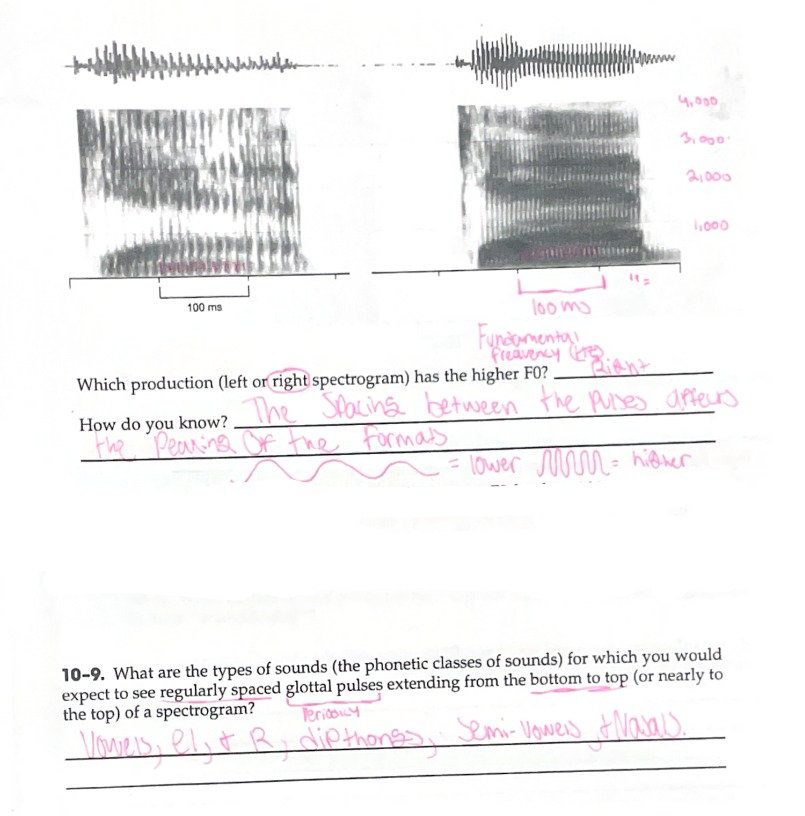

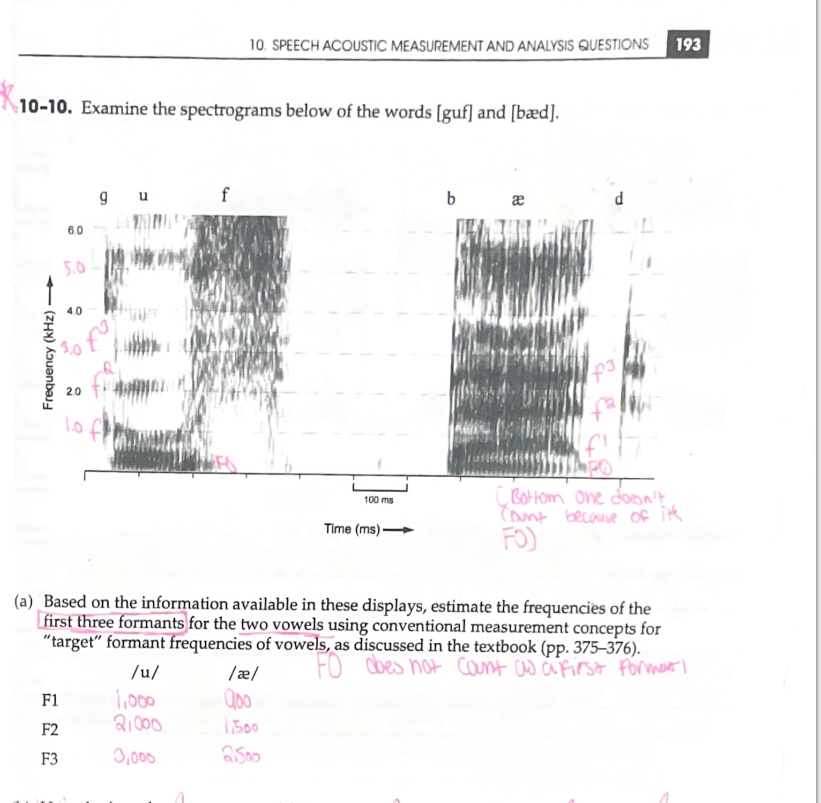
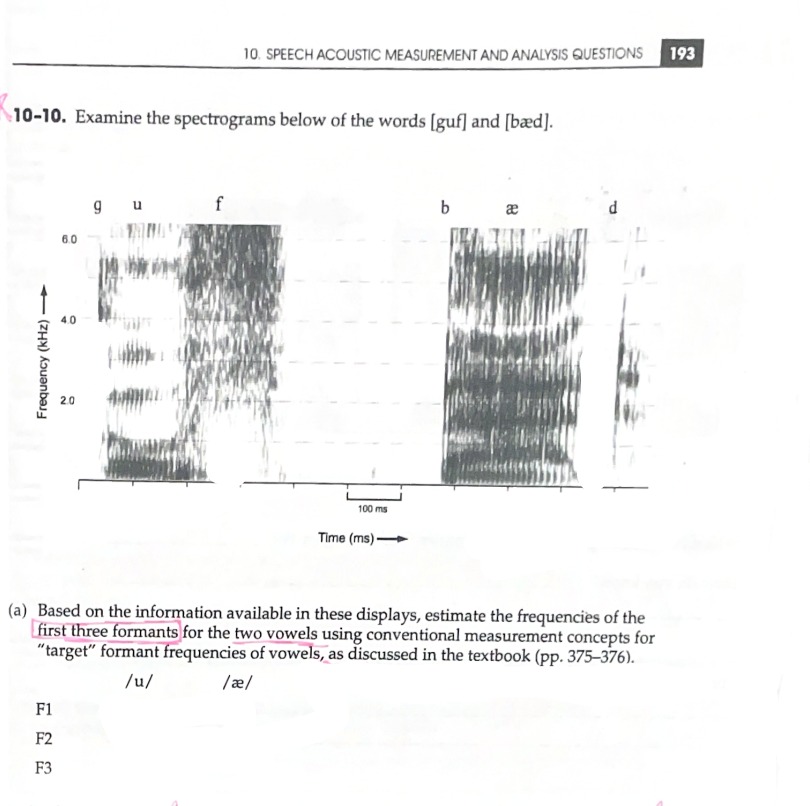
A Visual Representation of Sound
What is spectrogram?
Shows Variation of Air Pressure Over Time
What is a speech waveform?
They cannot be quantified from these displays because formants require resonance, which alters the waveform's appearance and is necessary to observe resonance.
Can formants be quantified from a speech waveform?
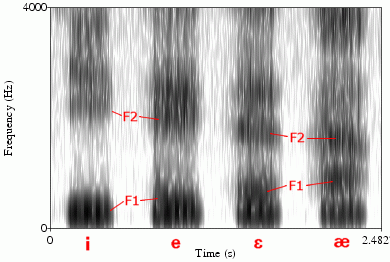
Formants are Shown as Dark Bands
How are formants determined on a spectrogram?
Changes in Formant Frequency Over Time and/or Articulation Changes
What are formant transitions?
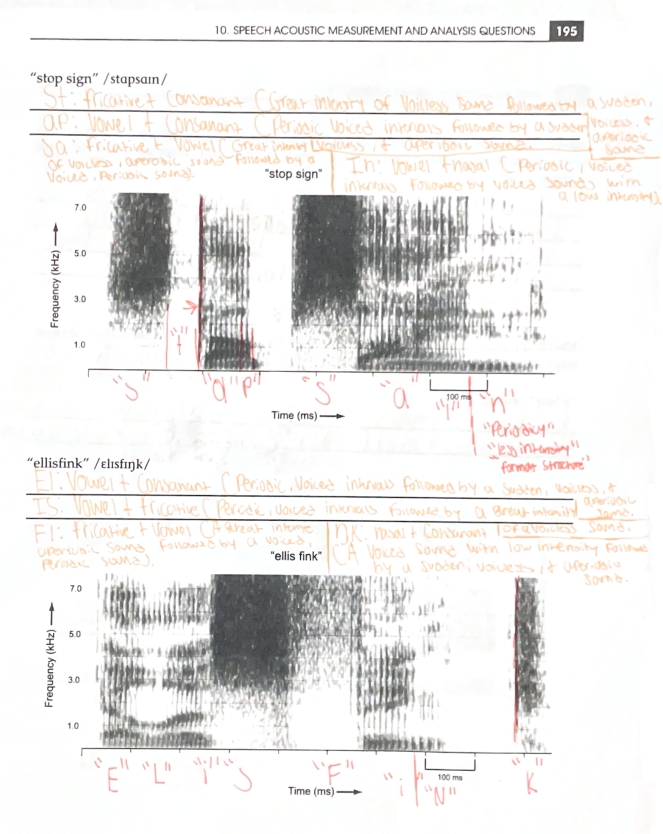
Regularly Spaced Vertical Intervals (Striations) Represented by Glottal Pulses; Periodic
Characteristics of a vowel
Irregular Spaced Vertical Intervals (striations) with Mainly Higher Energy and Frequency Concentration; Aperiodic
Characteristics of a fricative
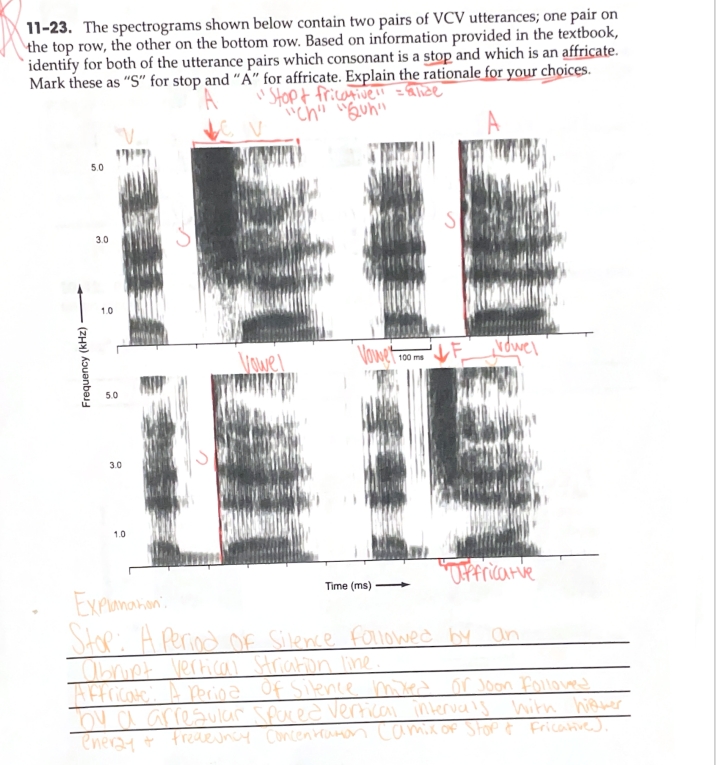
A period of silence followed by an abrupt vertical line
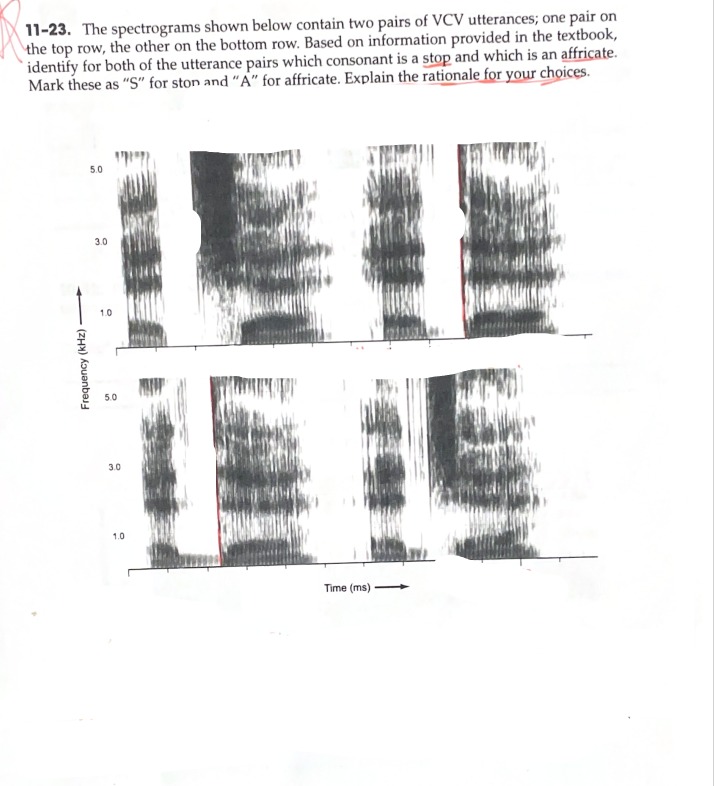
Characteristics of a stop
A Brief Period of Silence or Near-Silence, followed by a Burst of Energy and Irregularly Spaced High-Frequency Concentration, Resembling Both a Stop and a Fricative
Characteristics of an affricate
Less Intensity Than Surrounding Vowels, but still Contain Periodic Striations But typically lack well-defined formant structures due to antiresonances and damping.
Characteristics of a Nasal Murmur
Well-defined formant Structures that are Extensive and Rapid (Extensive = Covering a large range of frequencies and Rapid = Transition has a steep slope)
Characteristics of a Diphthong
Contains Well-Defined Formant Structures, have Complex, Underlying Articulatory Causes, and A Brief Constriction Interval in Each sound
Characteristics of a Semivowel
Darkest
The highest amplitude is represented by the _______ region on a spectrogram?
The Acoustics of Semivowels Have Complex, Underlying Articulatory Causes
Why are semivowels mastered later in child development…?
Articulation
Order:
Bilabial
Lingua-alveolar
Velar
(Babies love voice)
Voice onset time (VOT) varies by the place of __________ with VOT increasing in what order…?