UWO Bio 211: Comprehensive Study Guide for Anatomy Exam 4
1/257
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
258 Terms
capillary network
an interconnecting series of capillaries
venule
the smallest kind of vein
vein valves
prevent backflow of blood
superficial veins
located near the body surface
deep veins
located within the tissues and away from the body surface
sinus veins
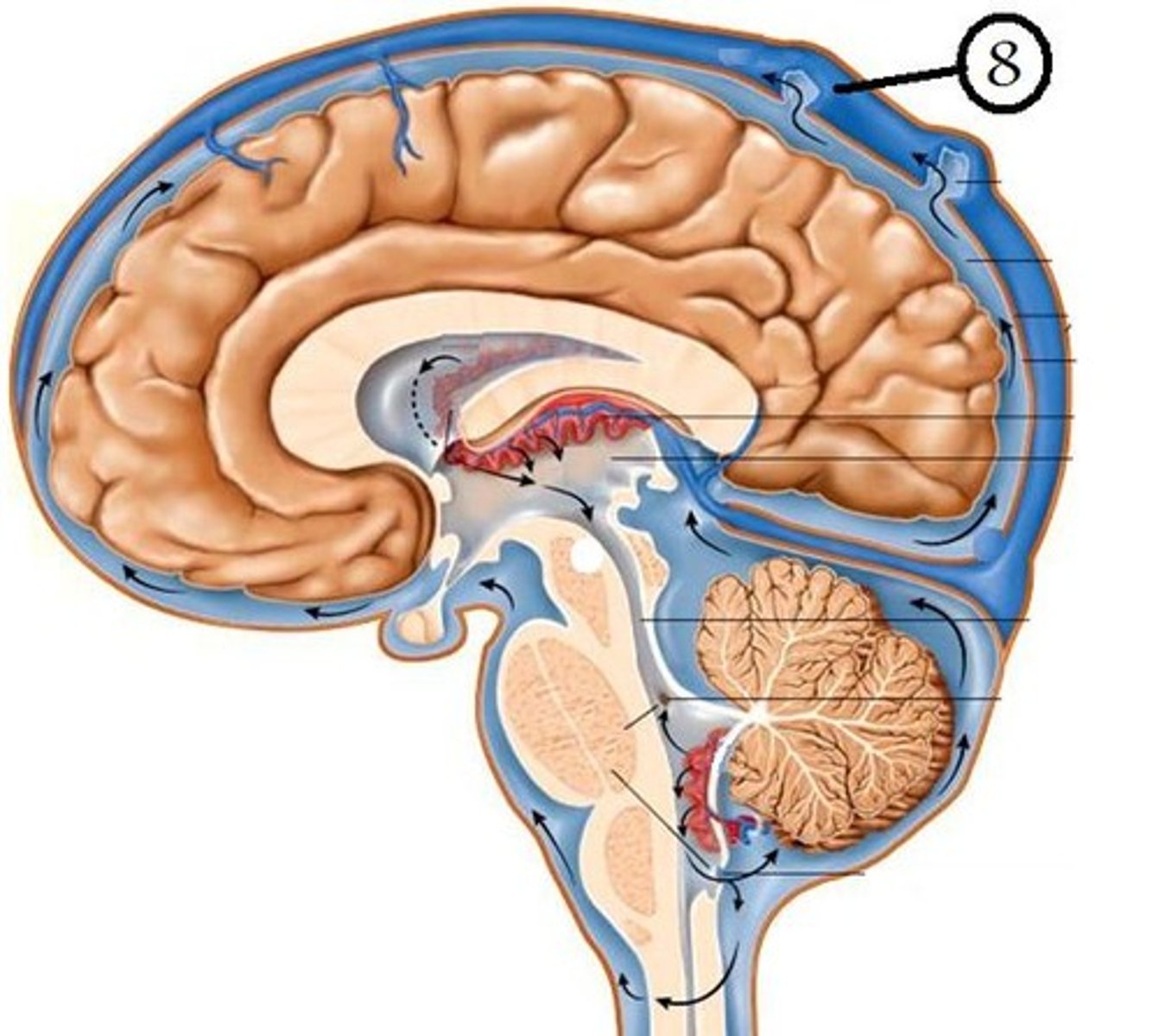
Receive blood from skull
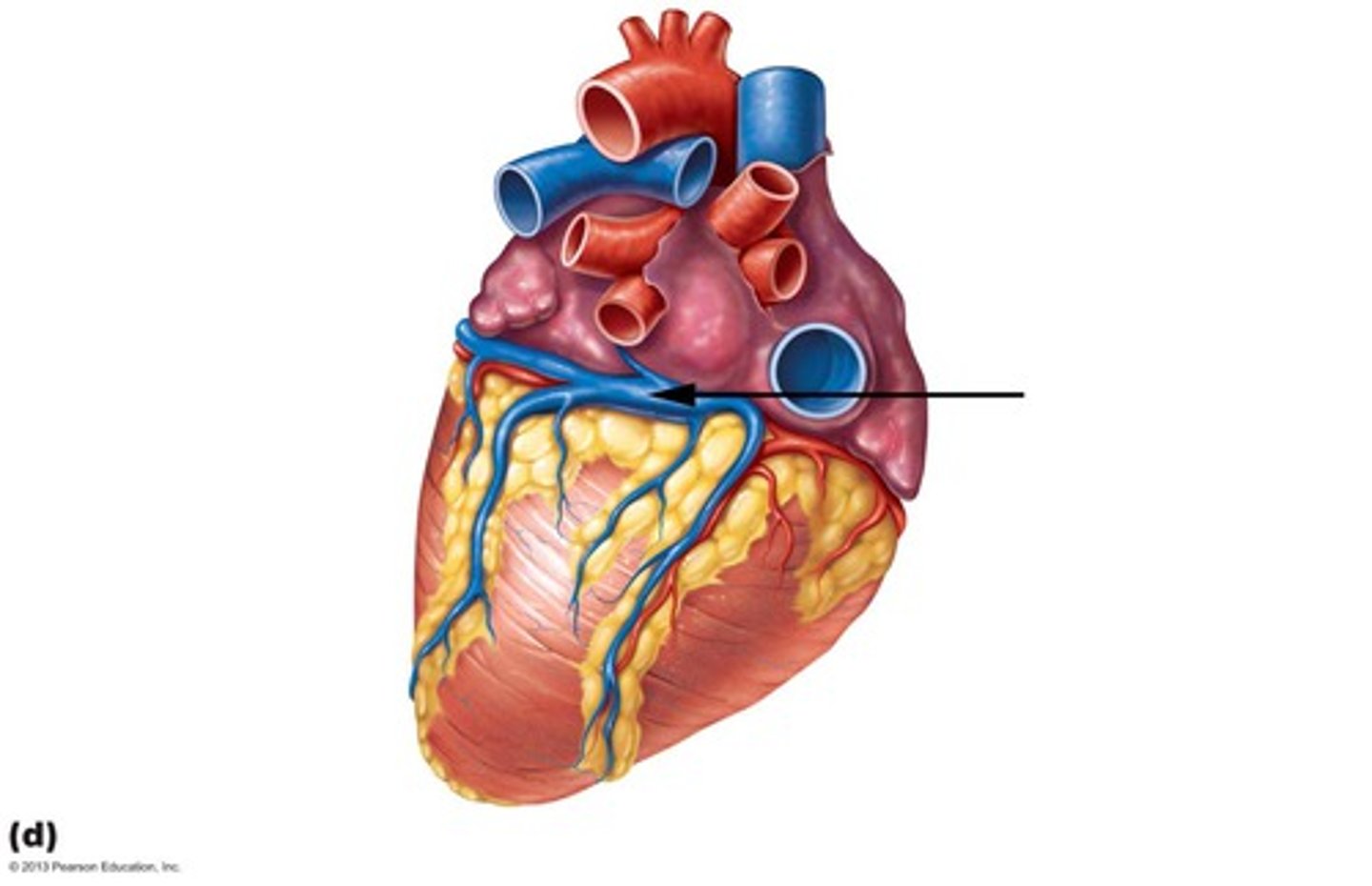
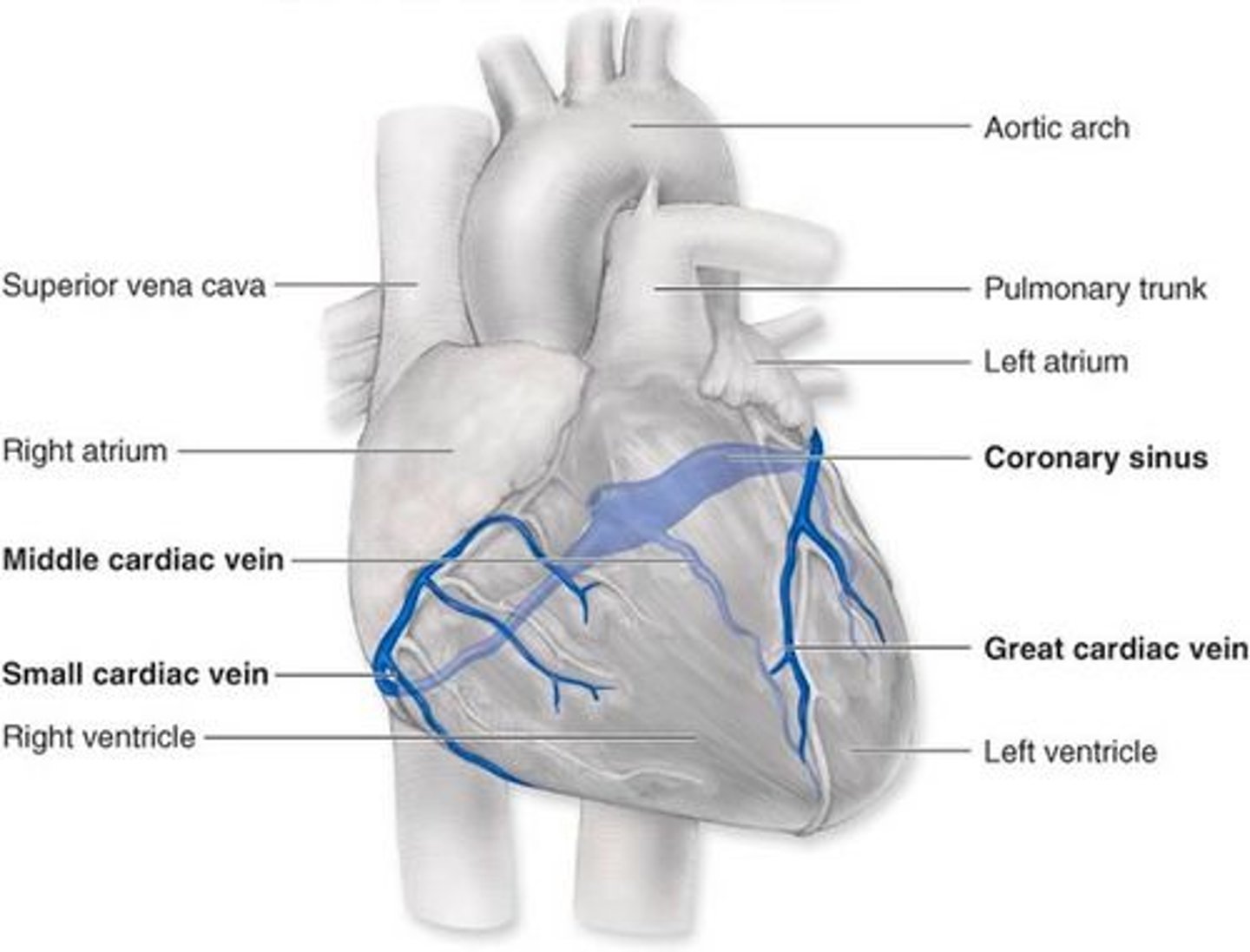
coronary sinus
enlarged vessel on the posterior aspect of the heart that empties blood into the right atrium
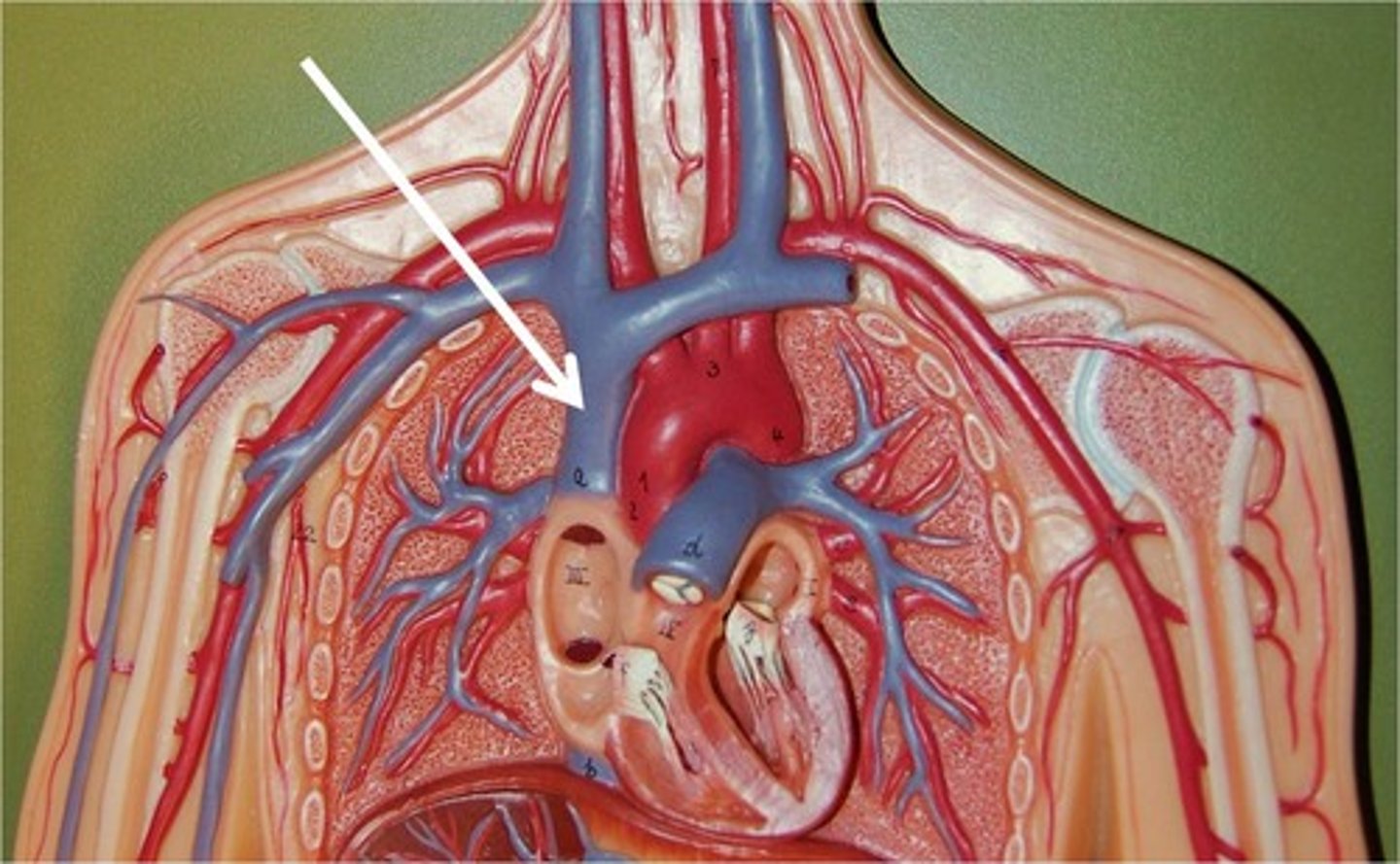
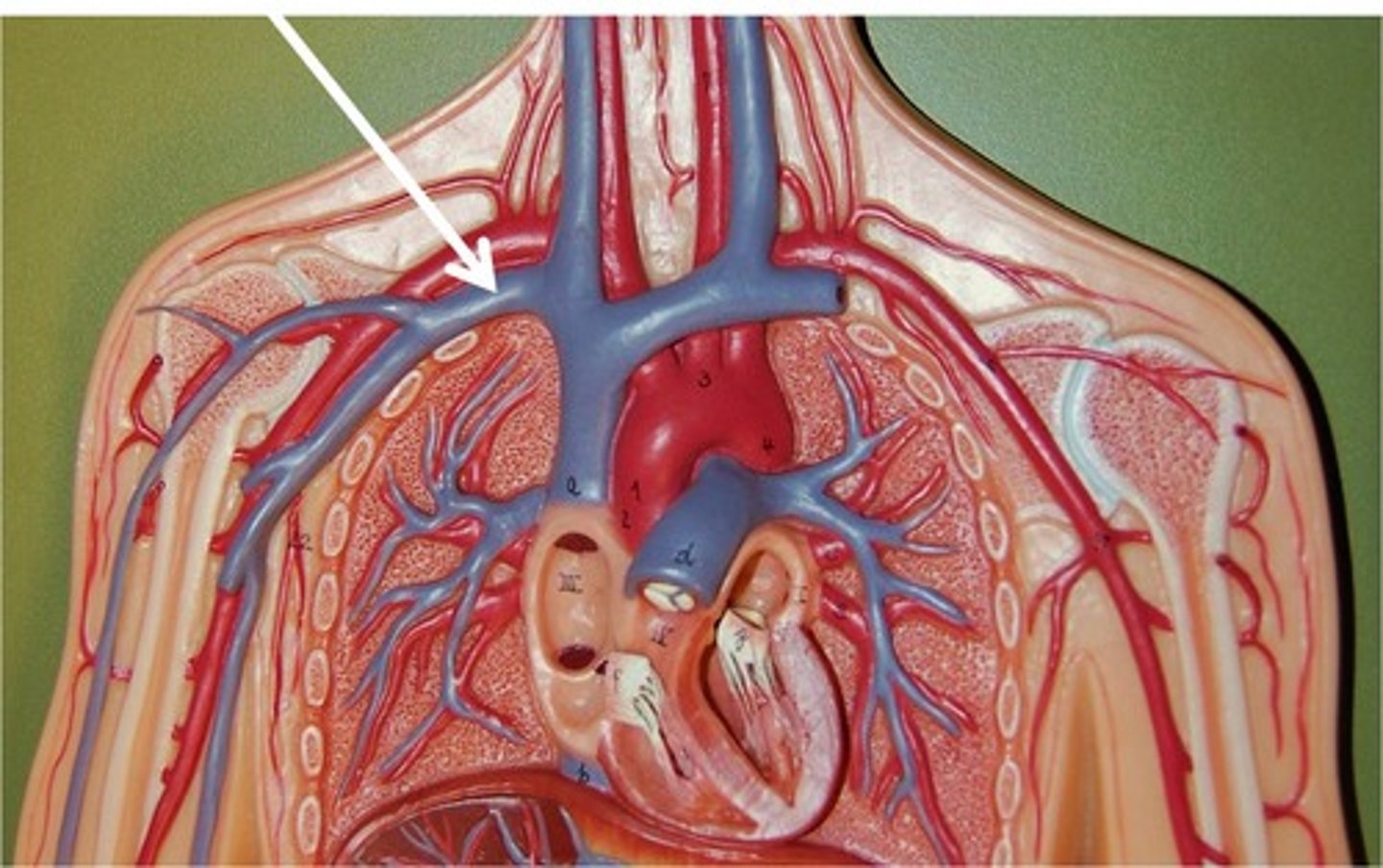
superior vena cava
A vein that is the second largest vein in the human body and returns blood to the right atrium of the heart from the upper half of the body.
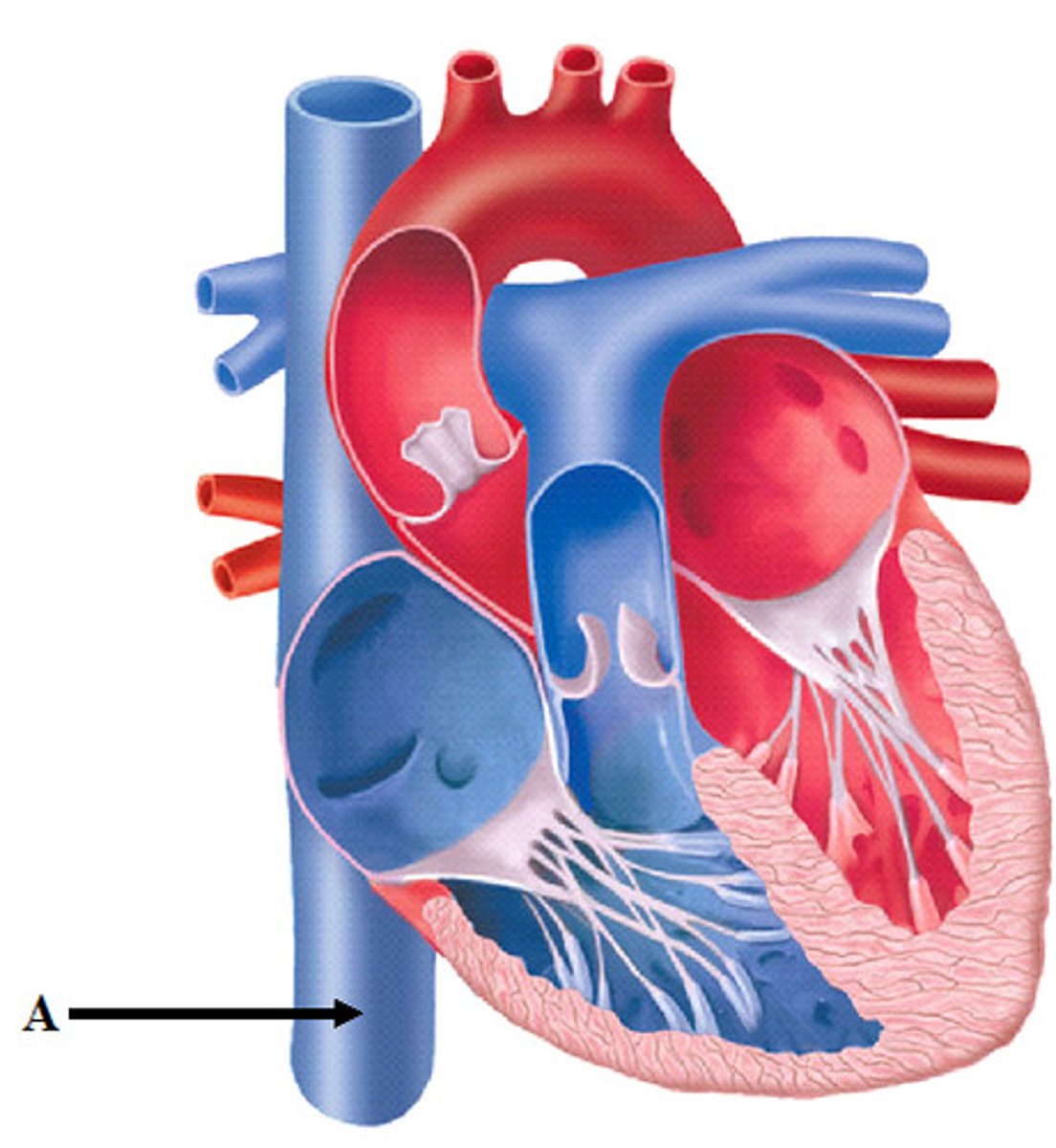
inferior vena cava
A vein that is the largest vein in the human body and returns blood to the right atrium of the heart from bodily parts below the diaphragm.
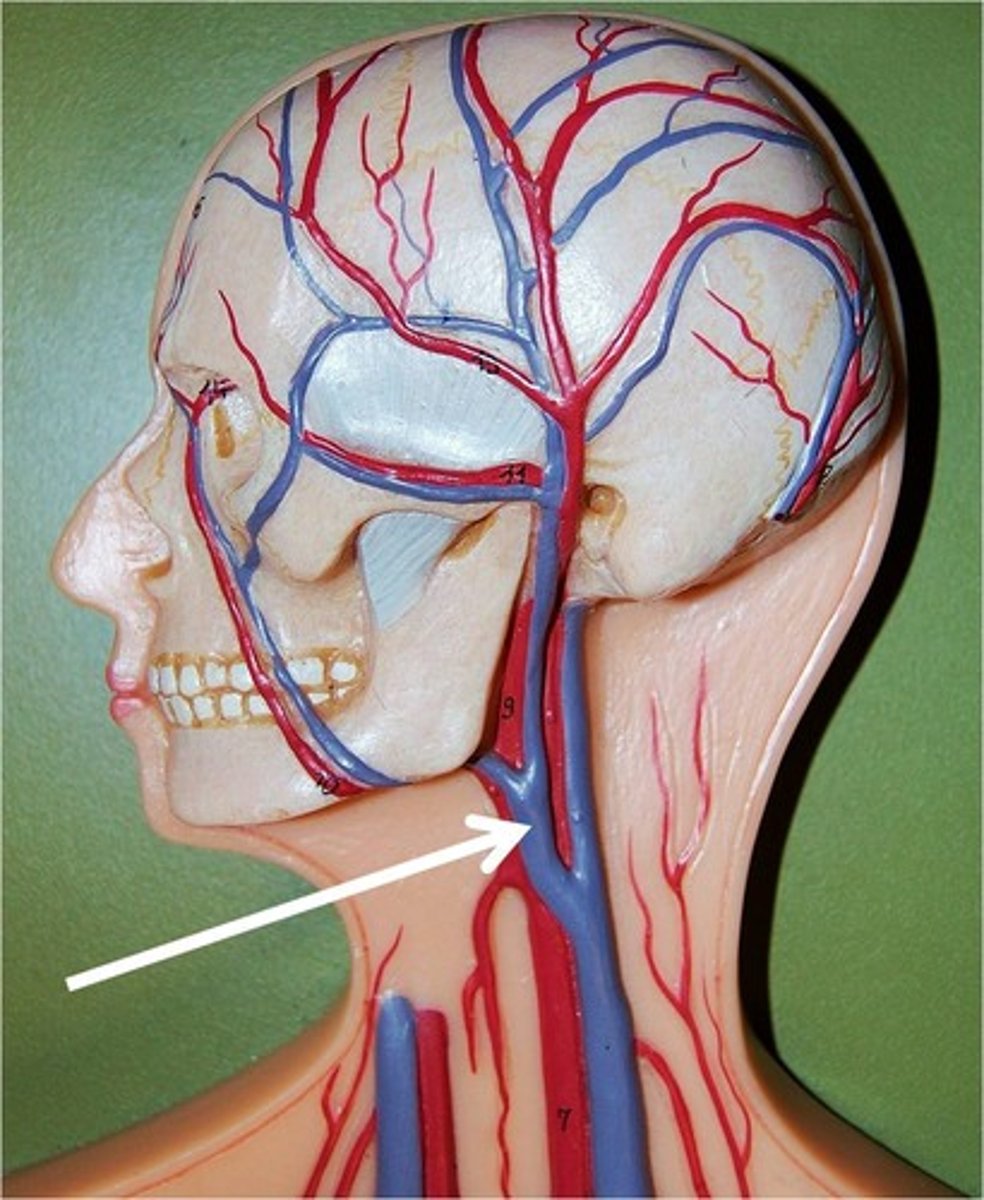
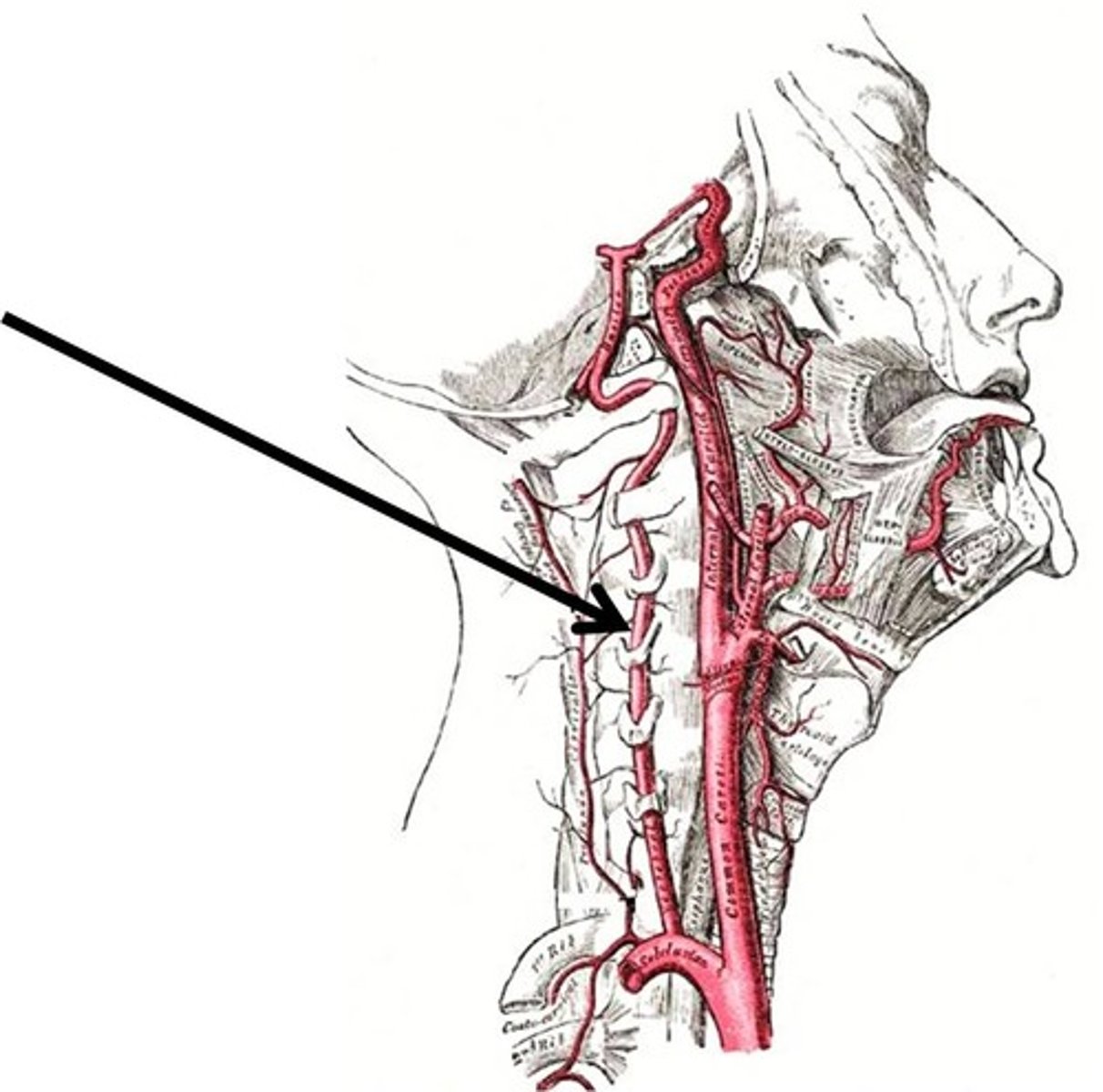
internal jugular vein
Vein located at the side of the neck to collect blood from the brain and parts of the face and neck.
dural venous sinuses
large veins in the dura mater that drain the cranium
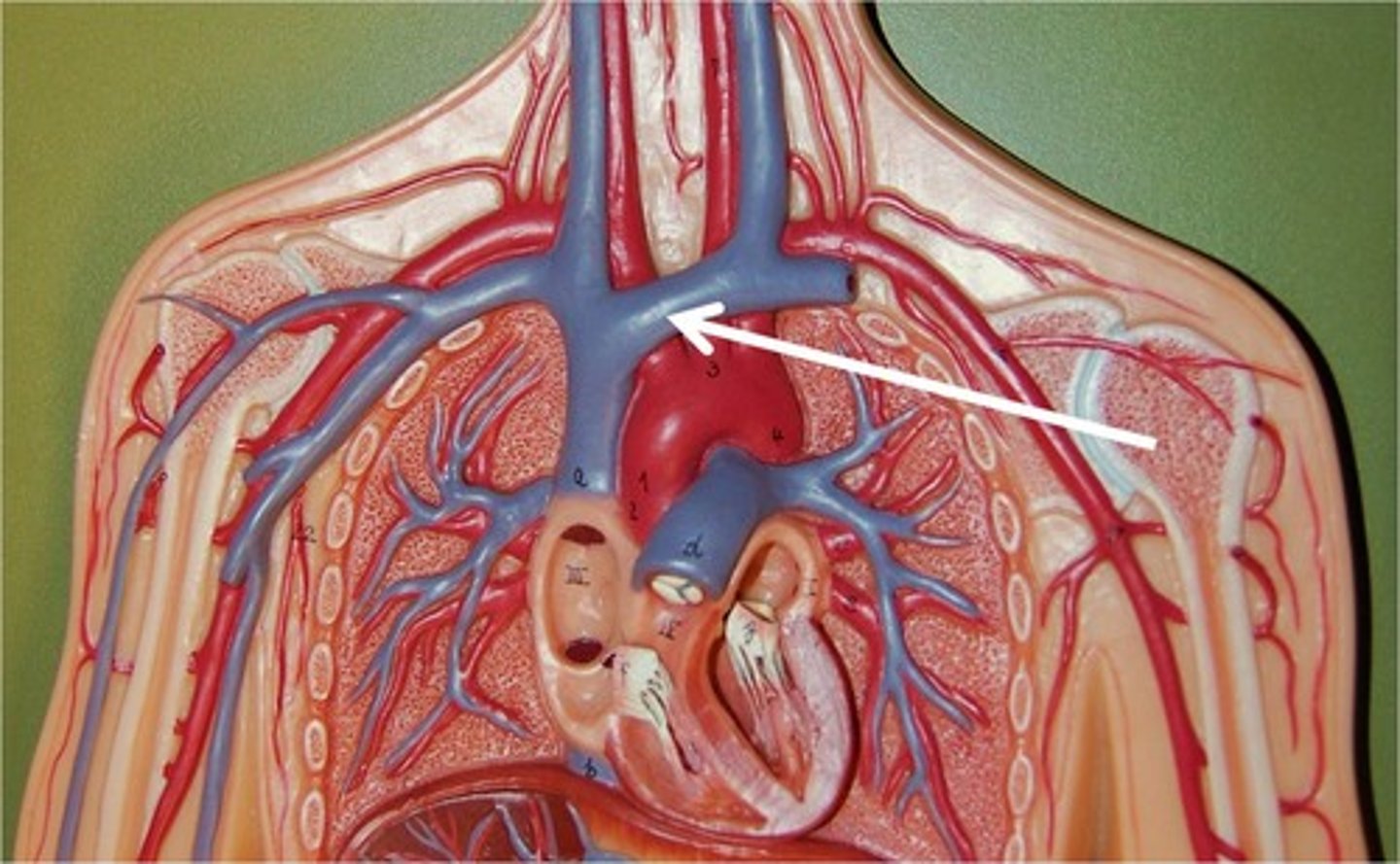
right brachiocephalic vein
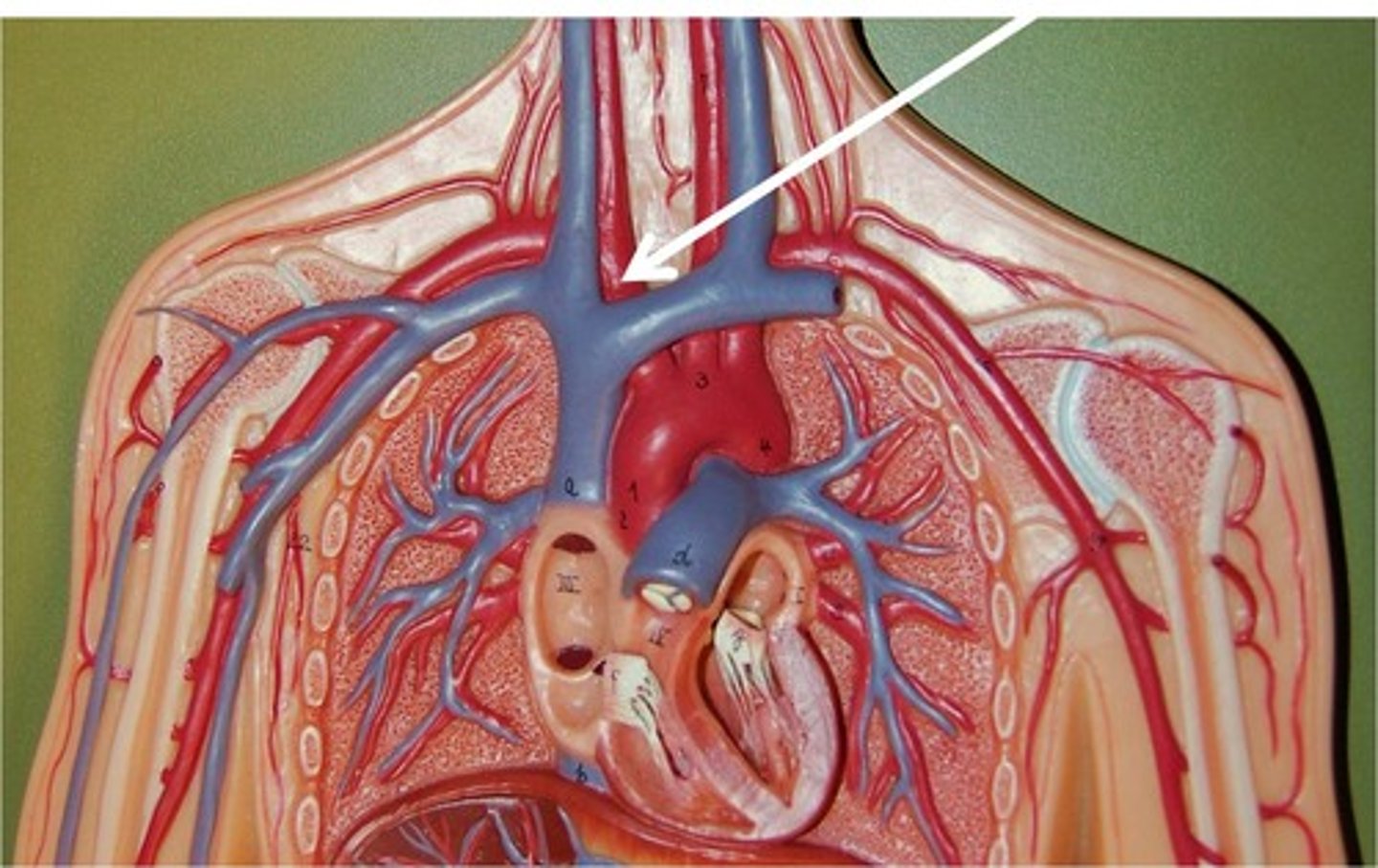
left brachiocephalic vein
external jugular vein
Vein located at the side of the neck that carries blood returning to the heart from the head, face, and neck.
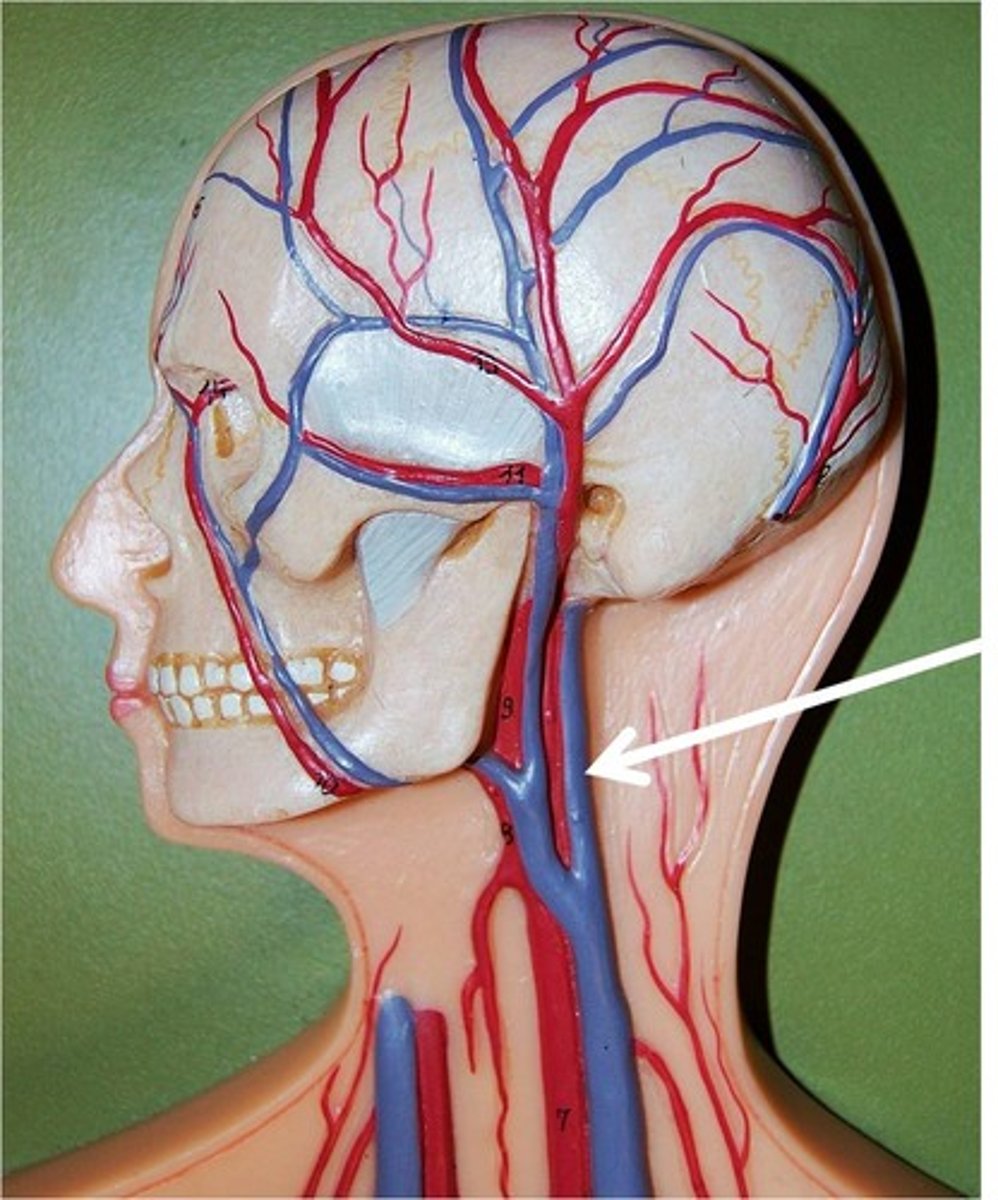
vertebral veins
serves posterior head, cervical vertebrae, spinal cord
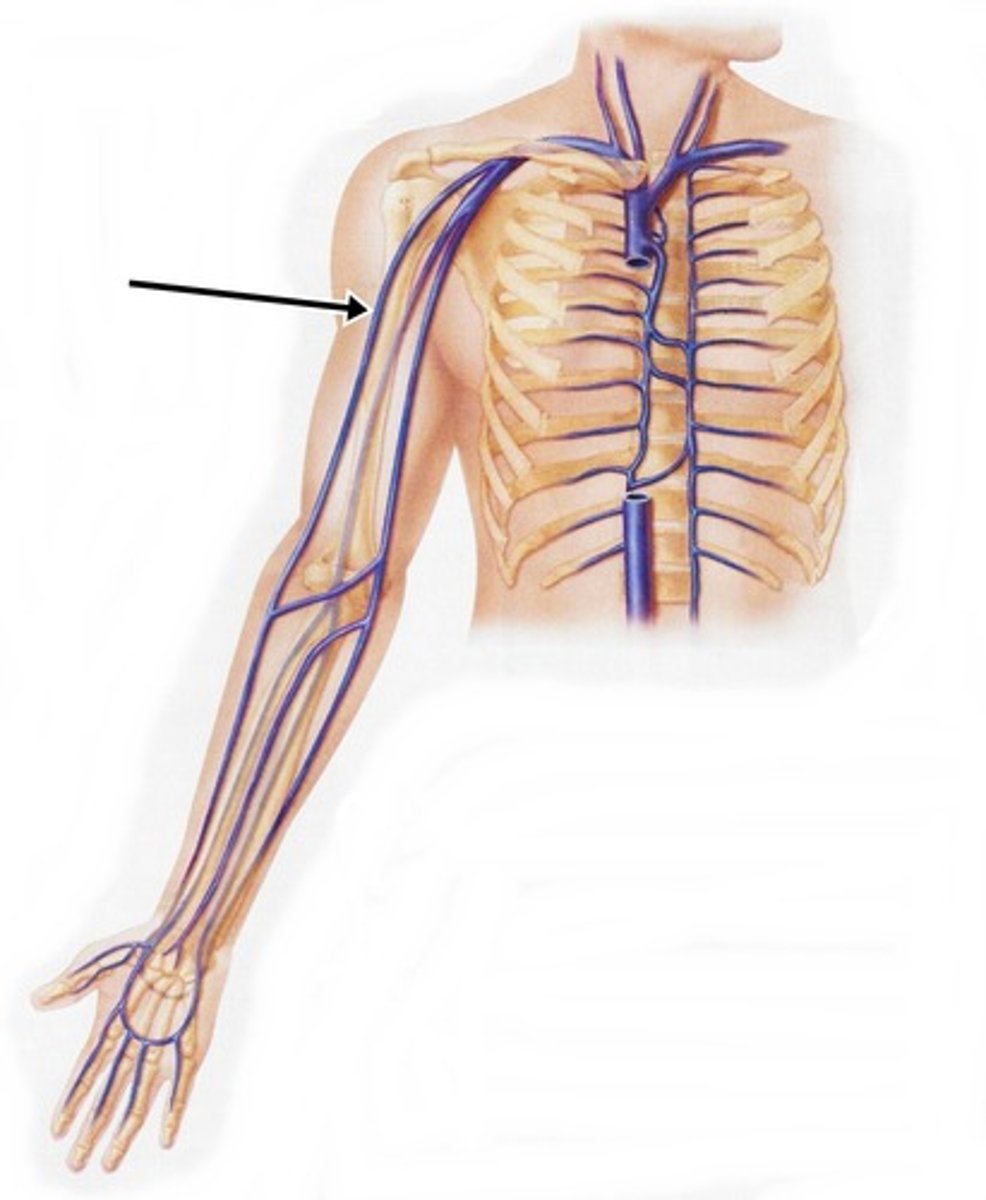
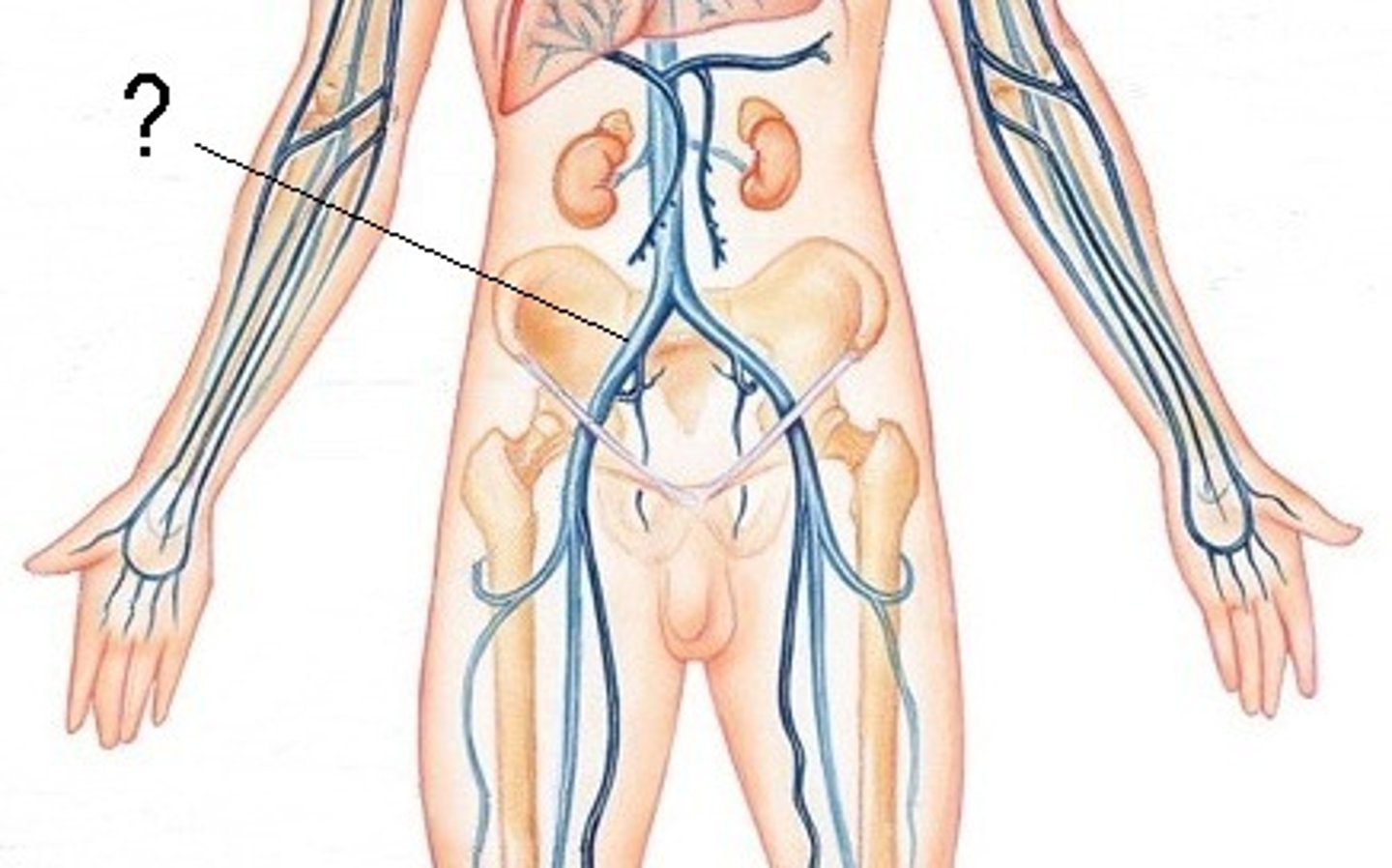
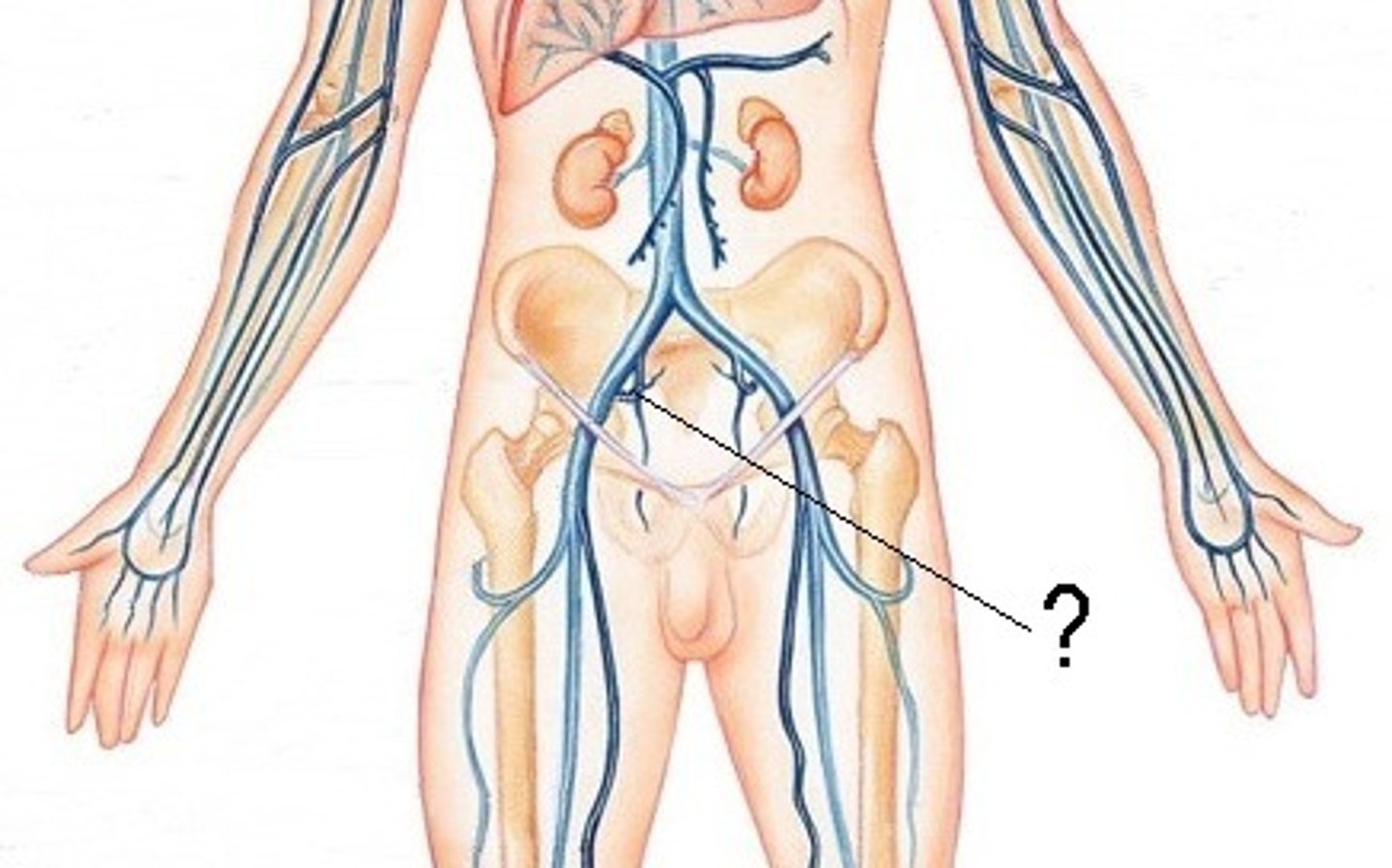
subclavian vein
axillary vein
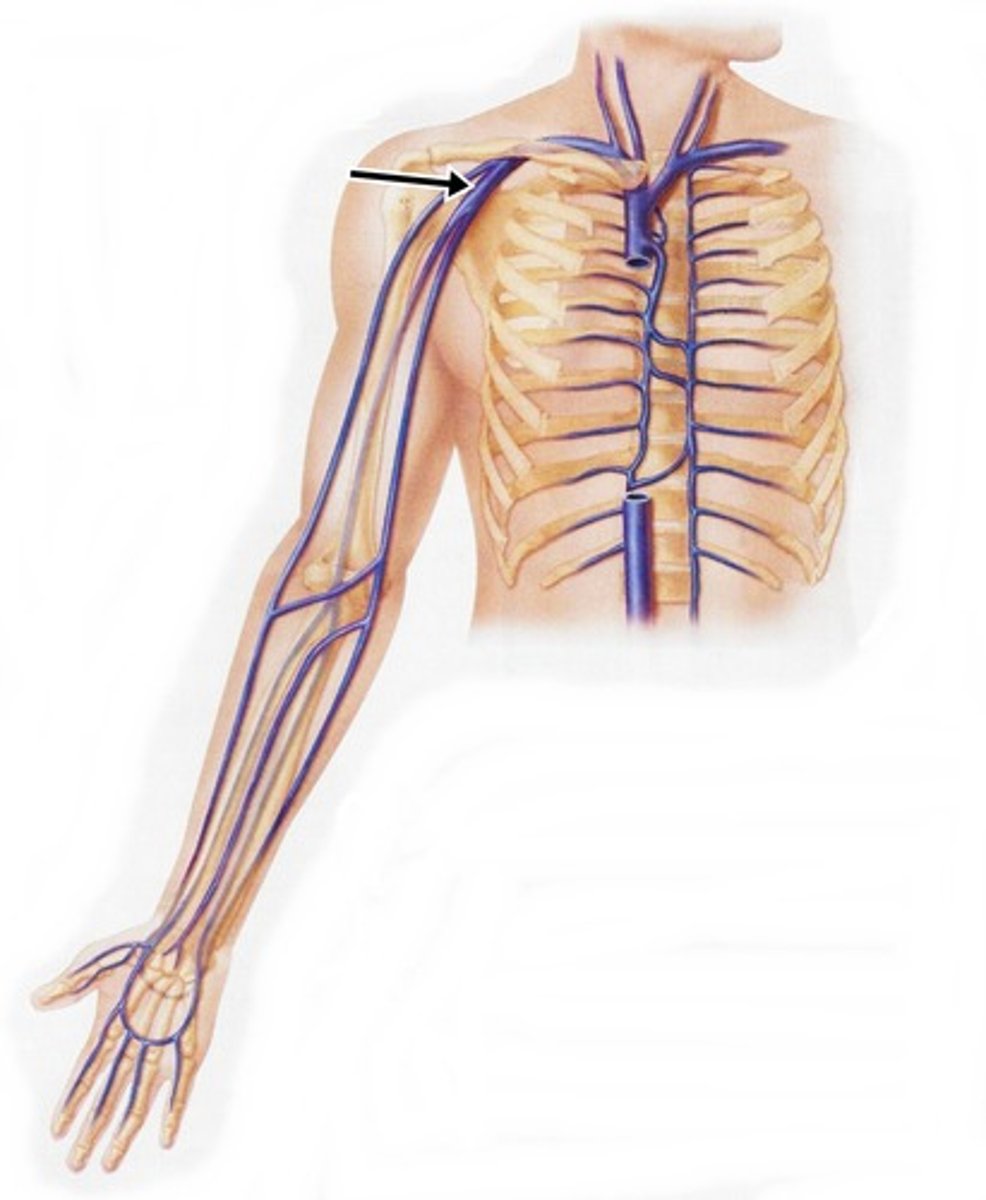
brachial vein
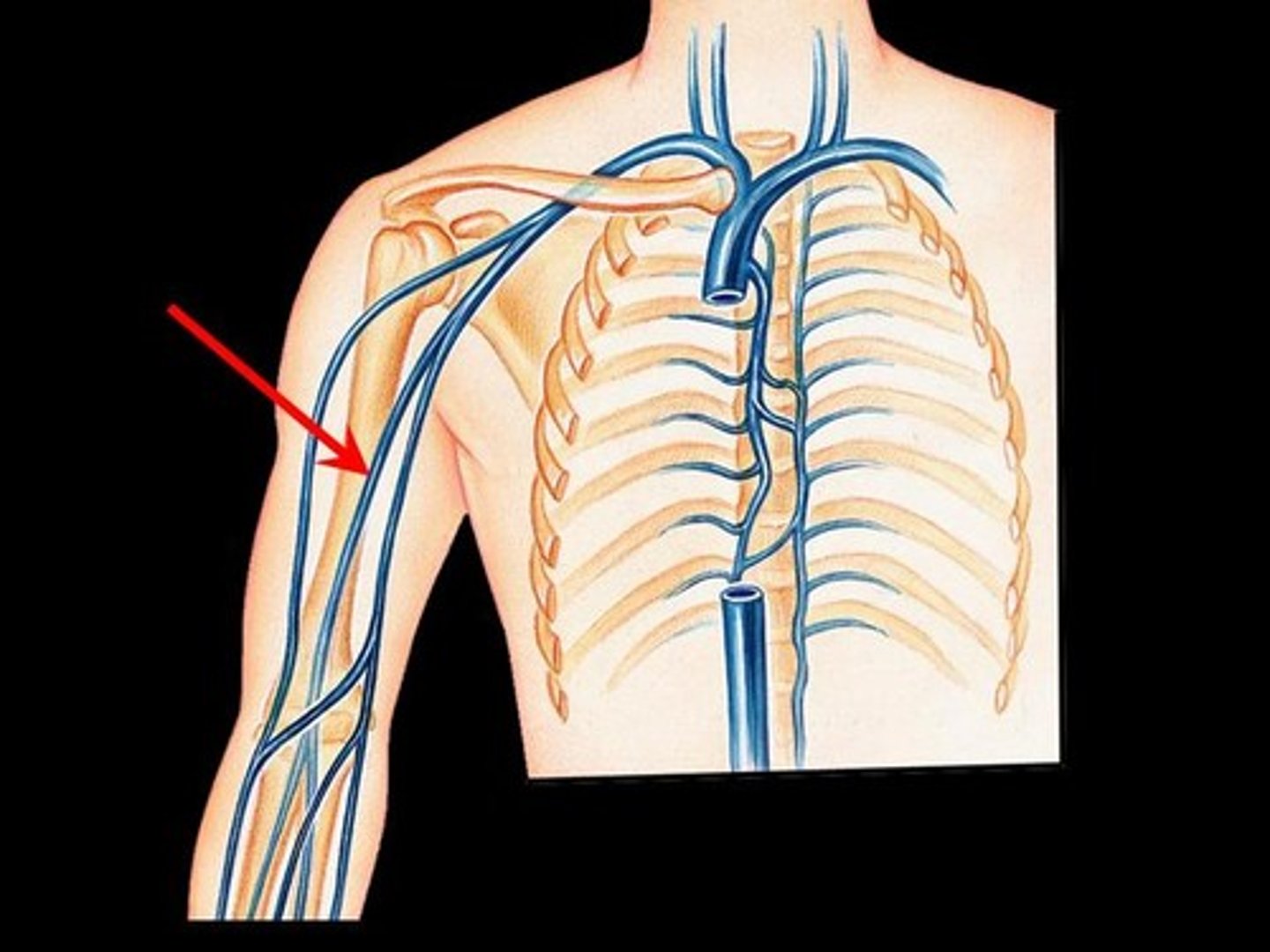
radial vein
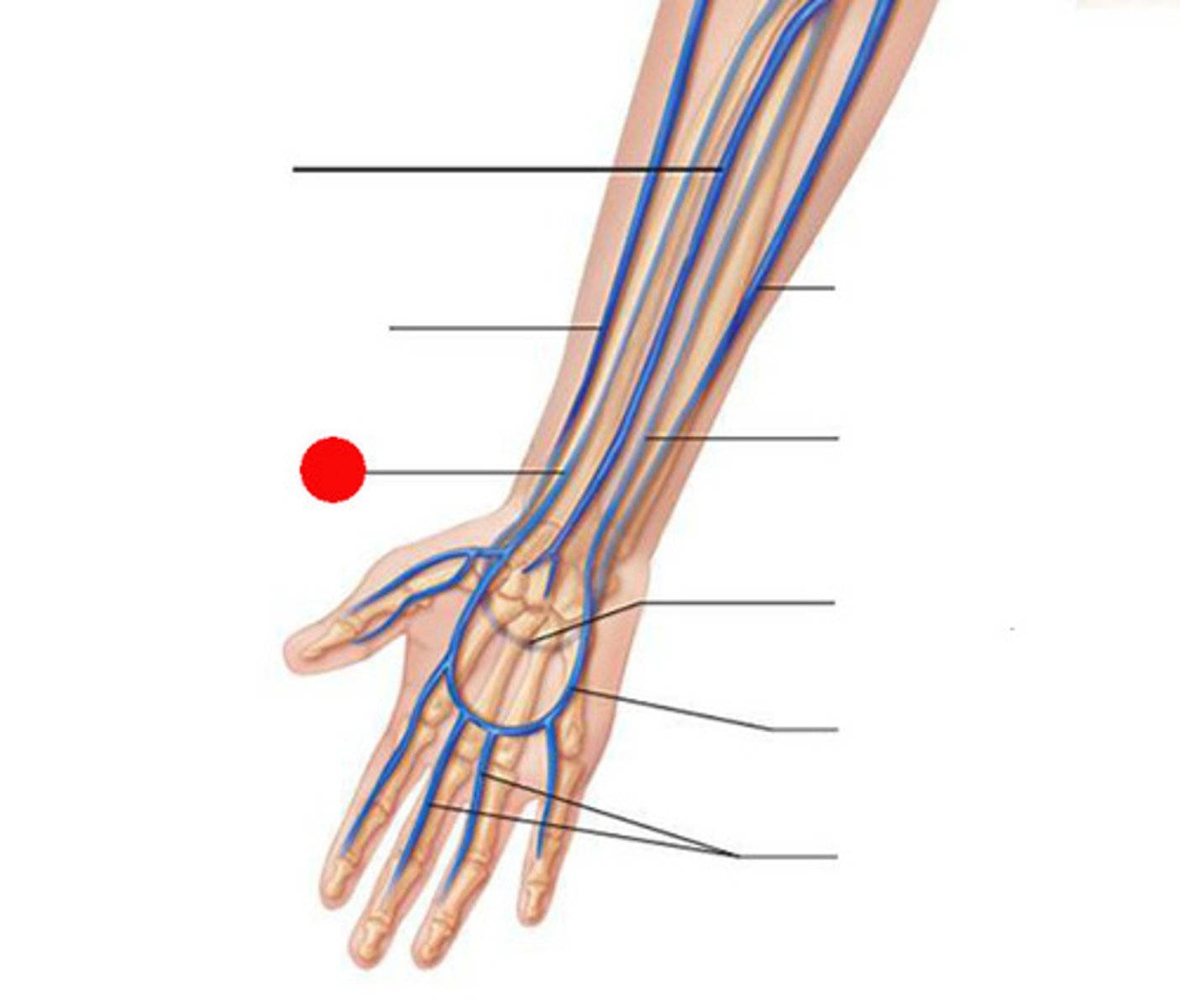
ulnar vein
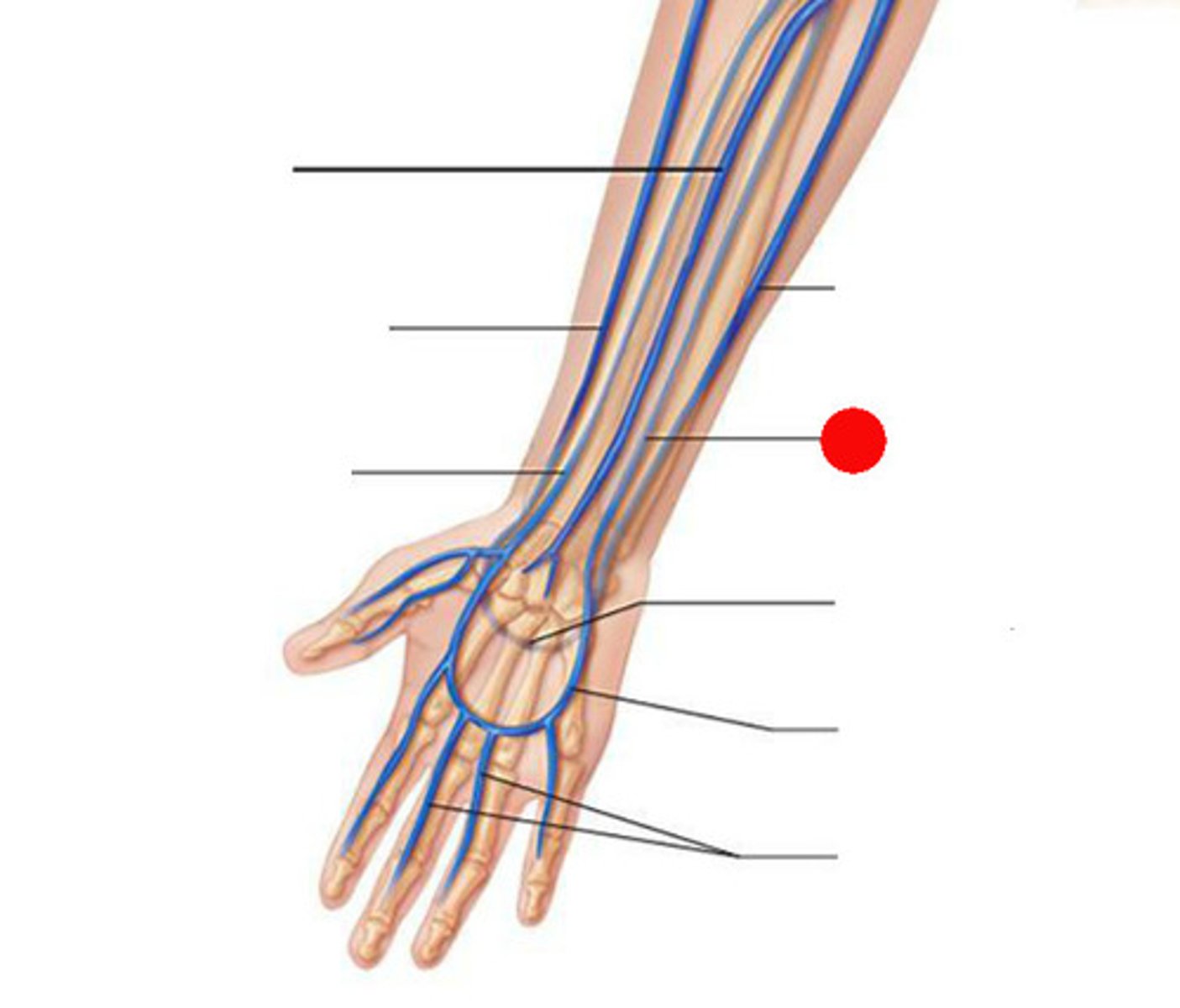
cephalic vein
basilic vein
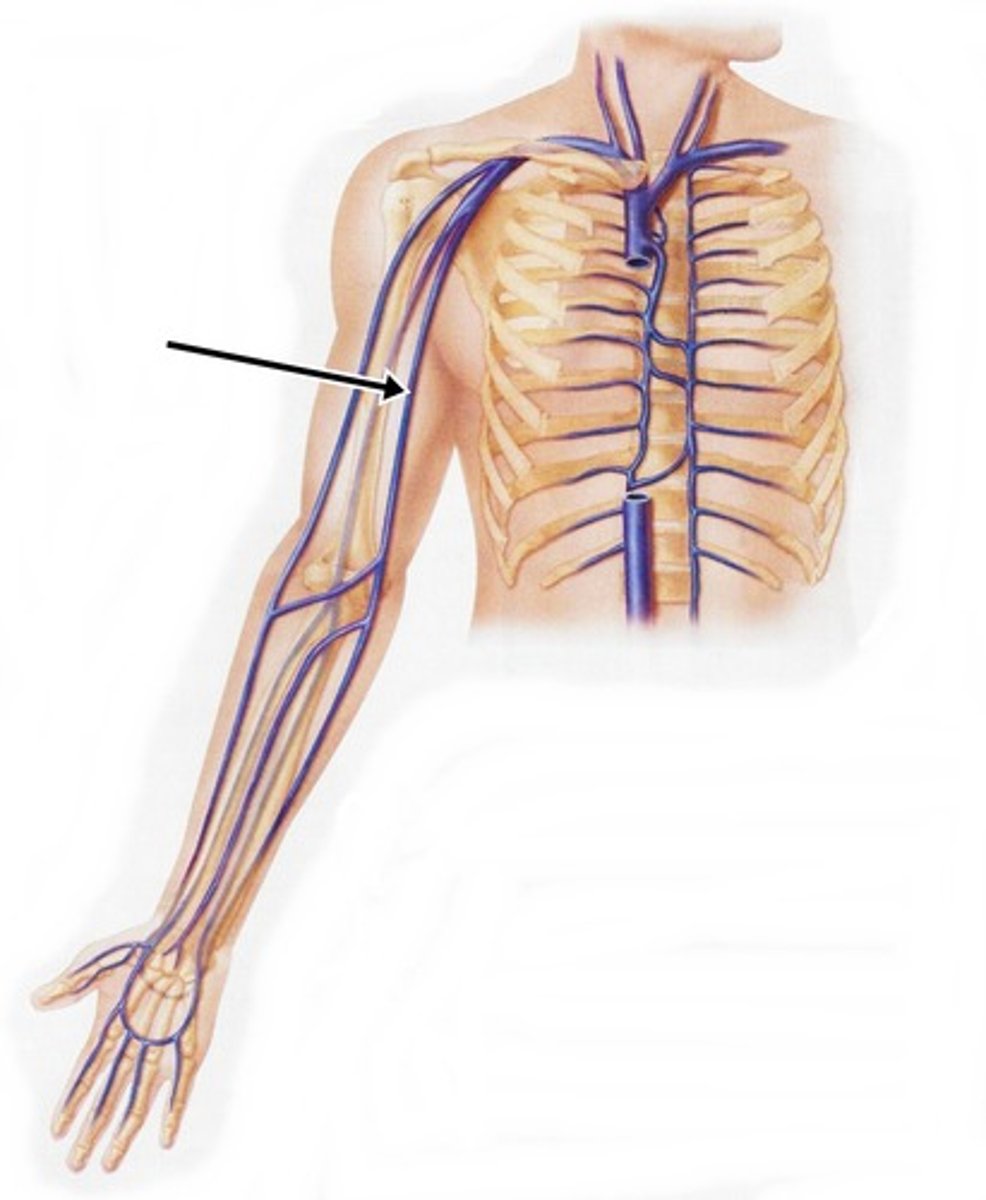
Which veins of the shoulder and upper limb are considered deep?
subclavian, axillary, brachial, radial, and ulnar veins
Which veins of the shoulder and upper limb are considered superficisal?
cephalic and basilic vein
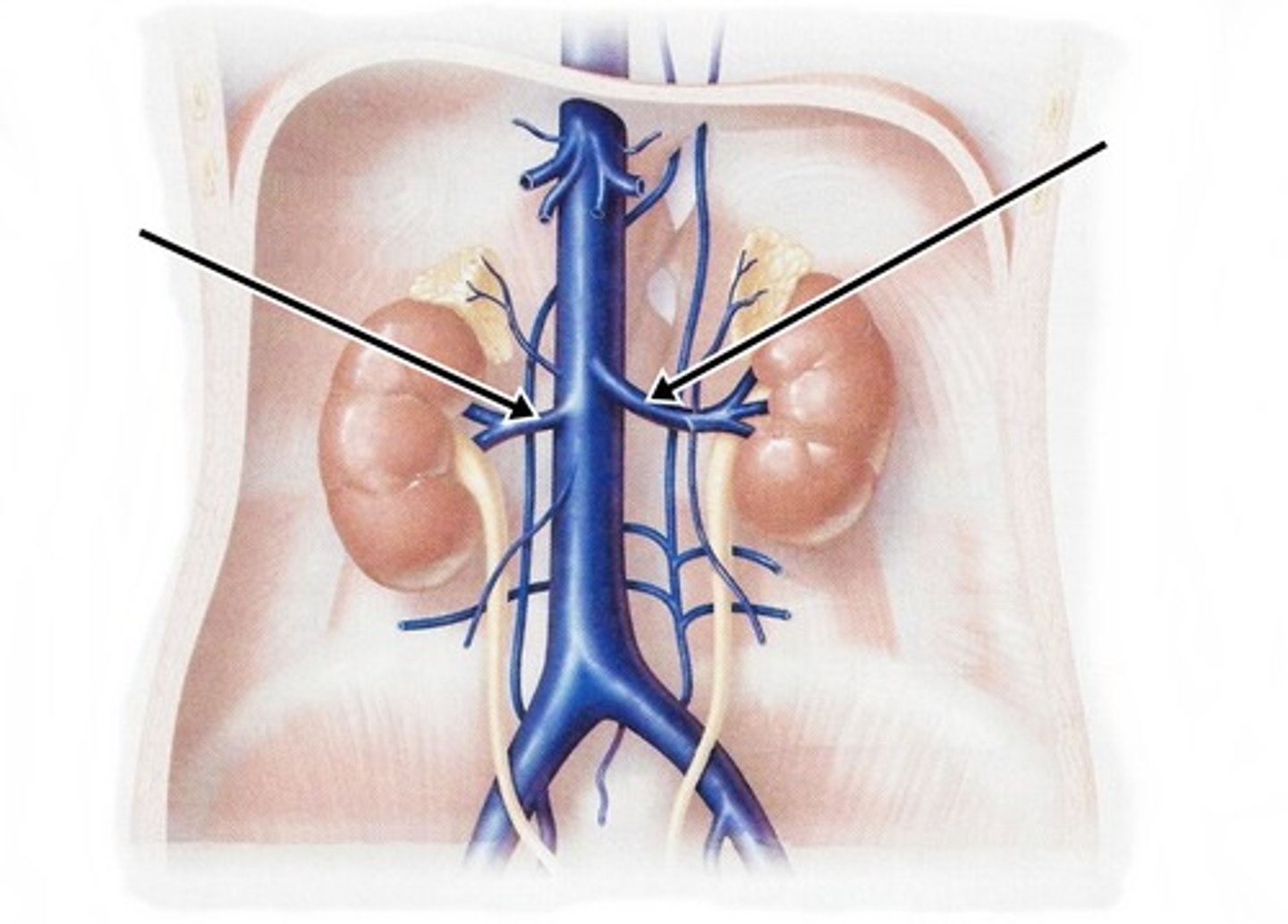
renal veins
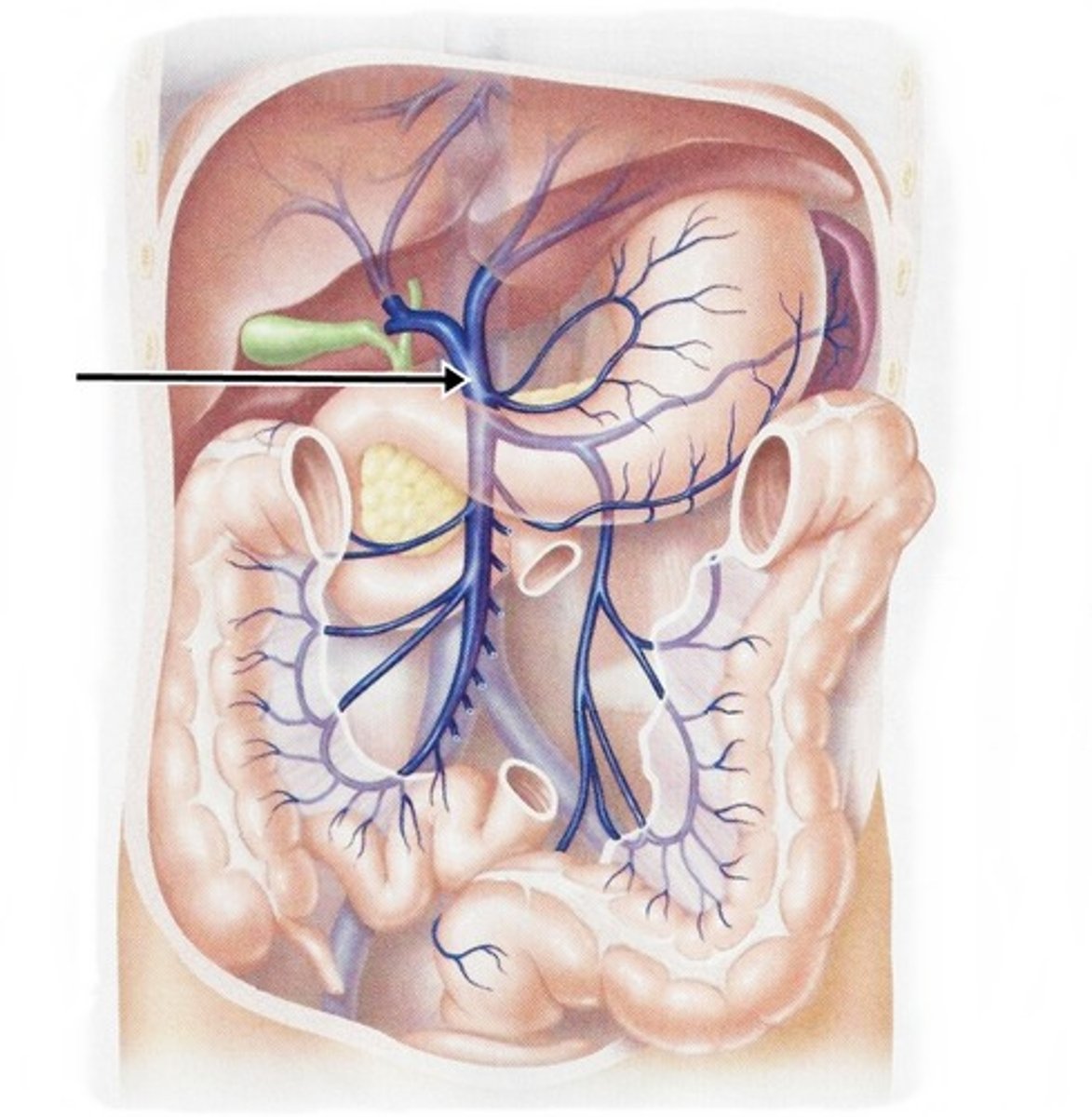
hepatic portal vein
the vein that collects blood from the GI tract and conducts it to the liver
superior mesenteric vein
drains small intestines and ascending colon
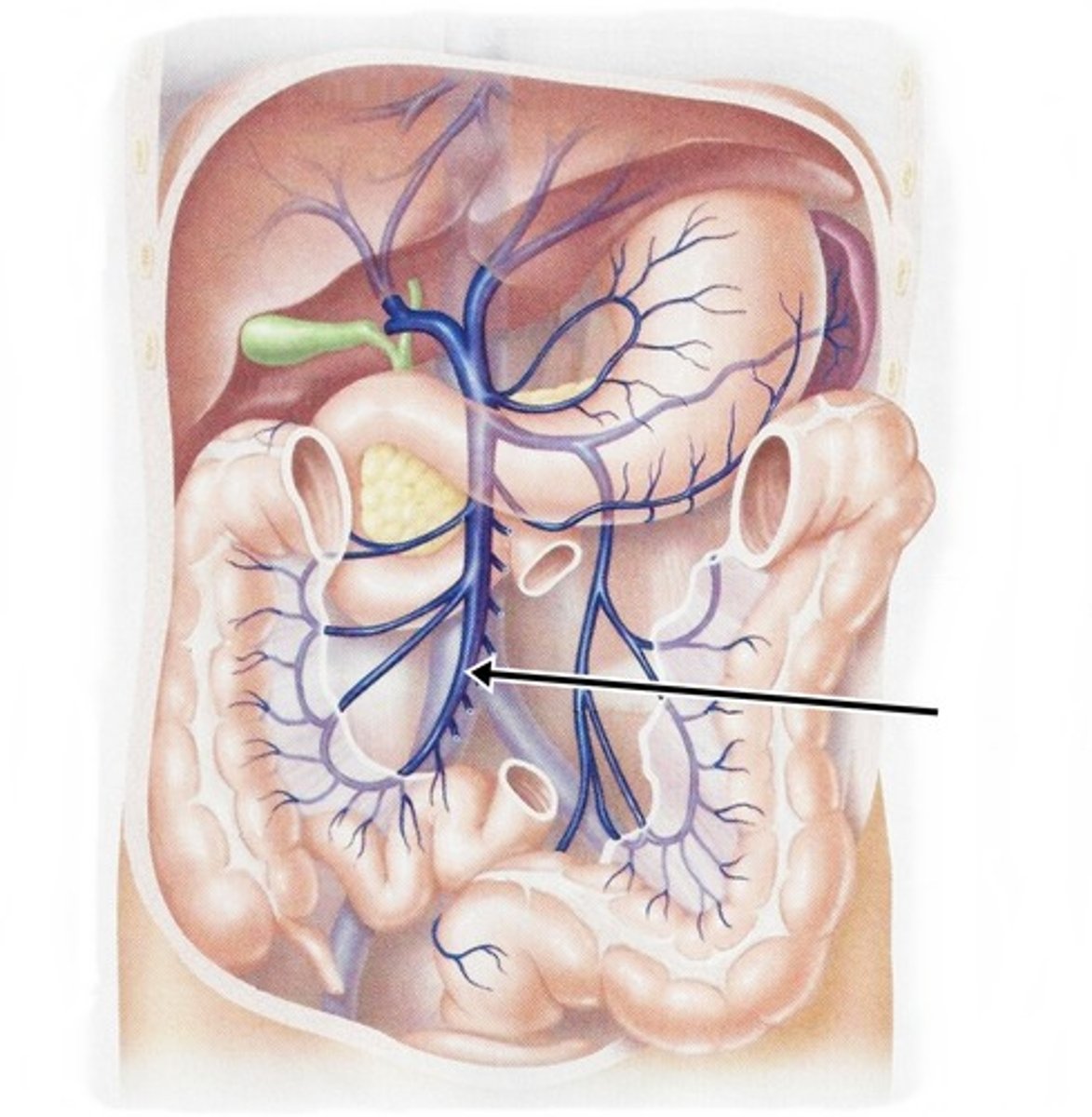
inferior mesenteric vein
drains distal portion of large intestine
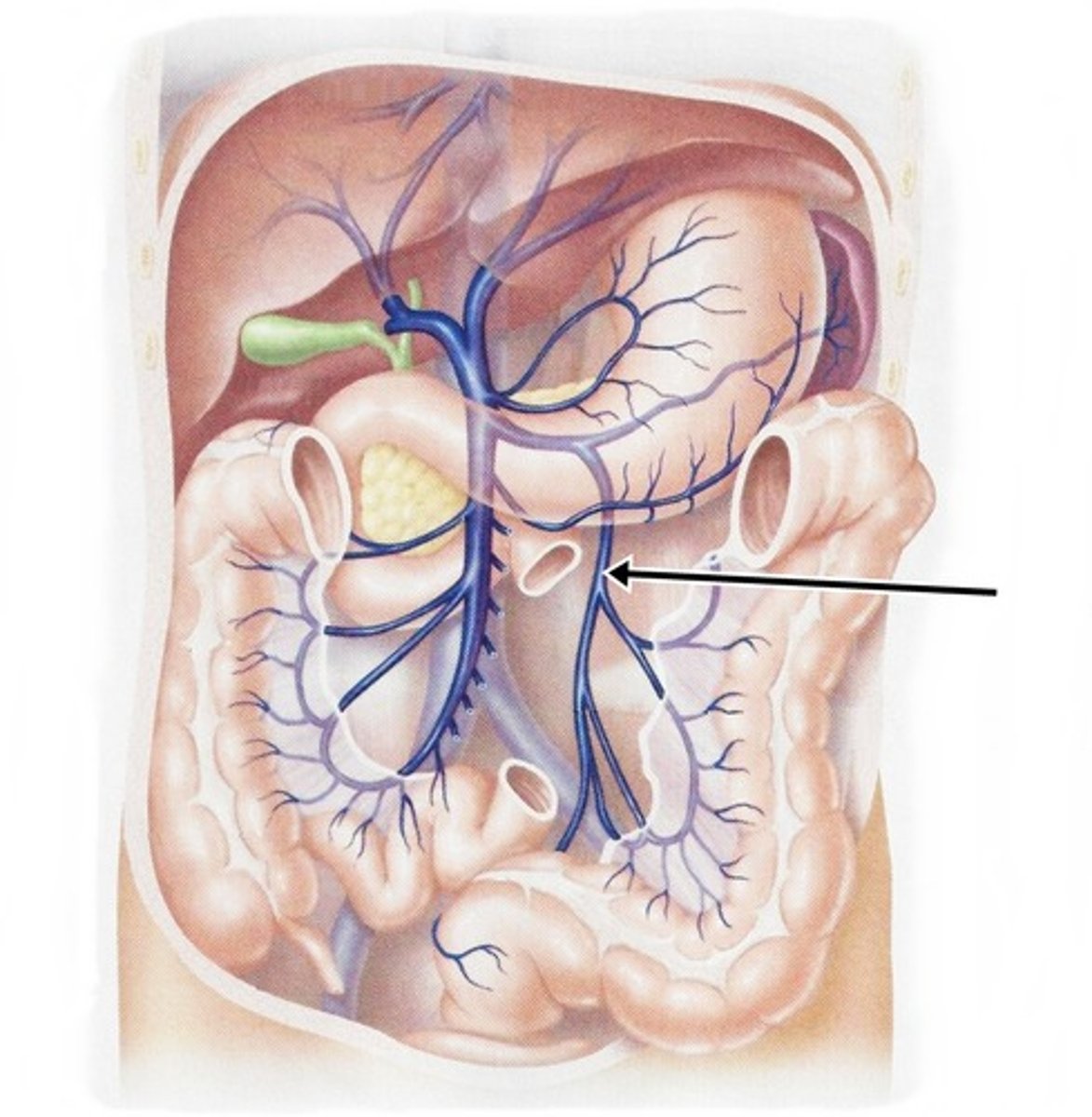
splenic vein
drains spleen
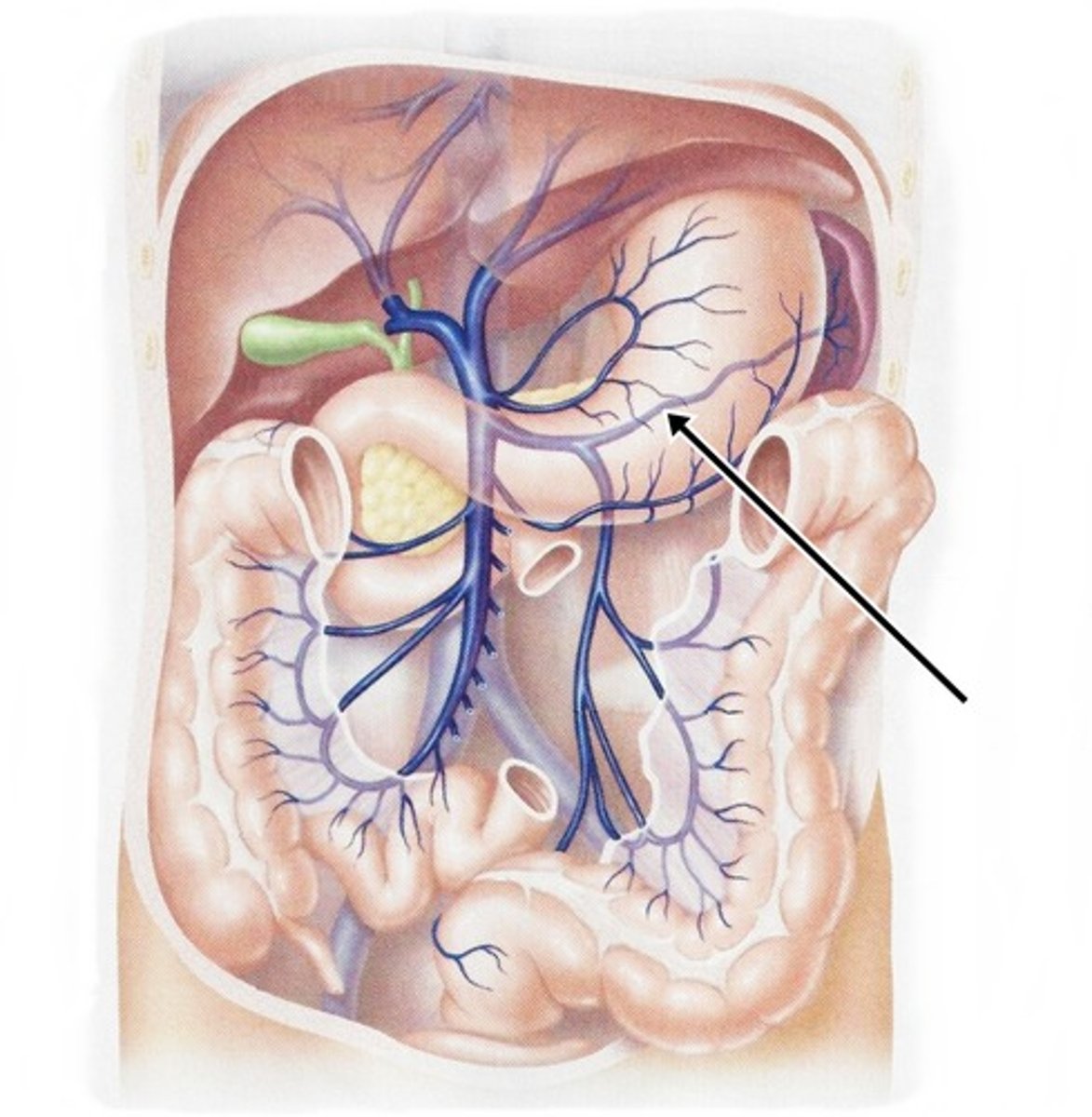
gastric vein
drains stomach
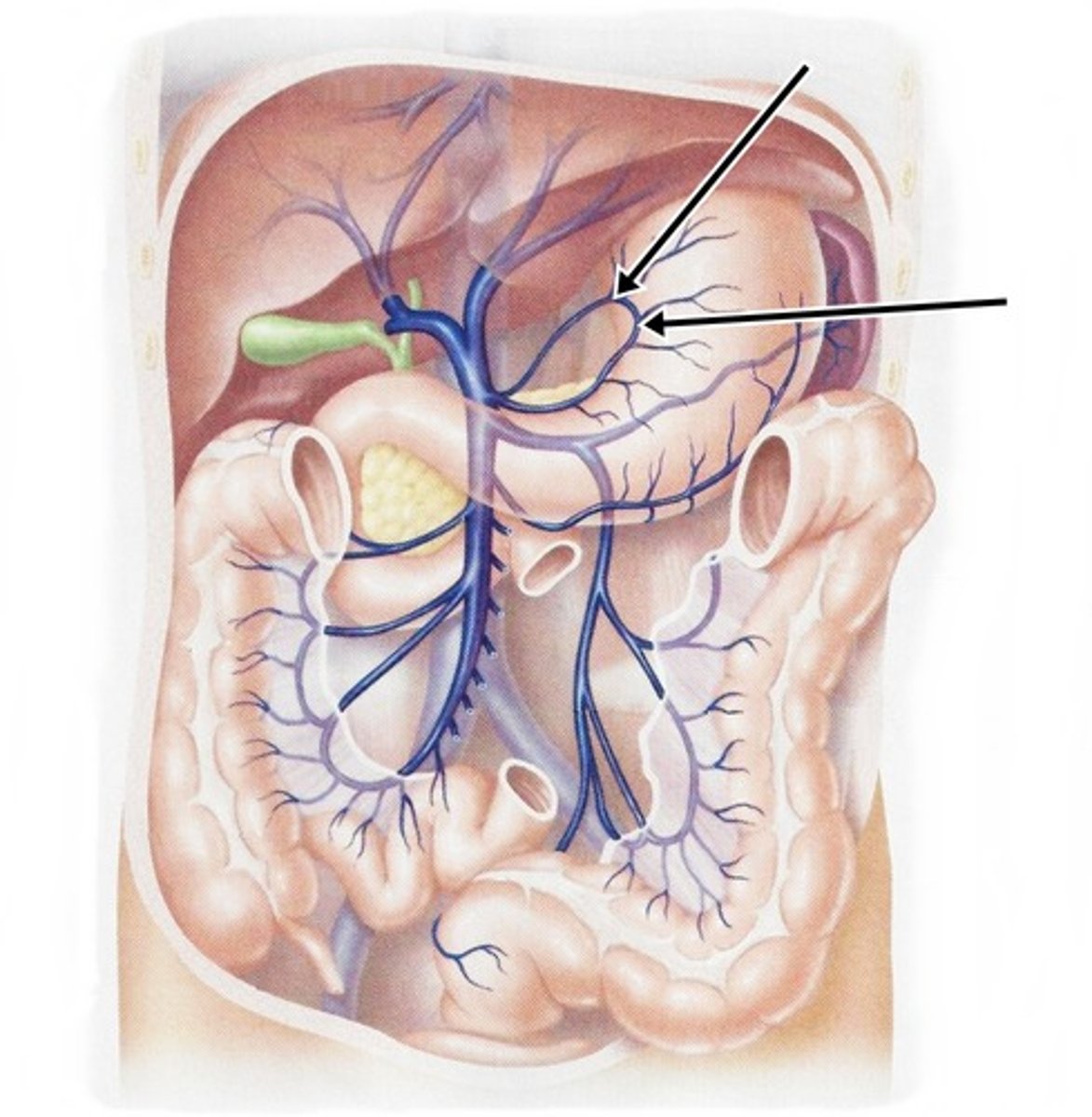
common iliac vein
internal iliac veins
external iliac veins
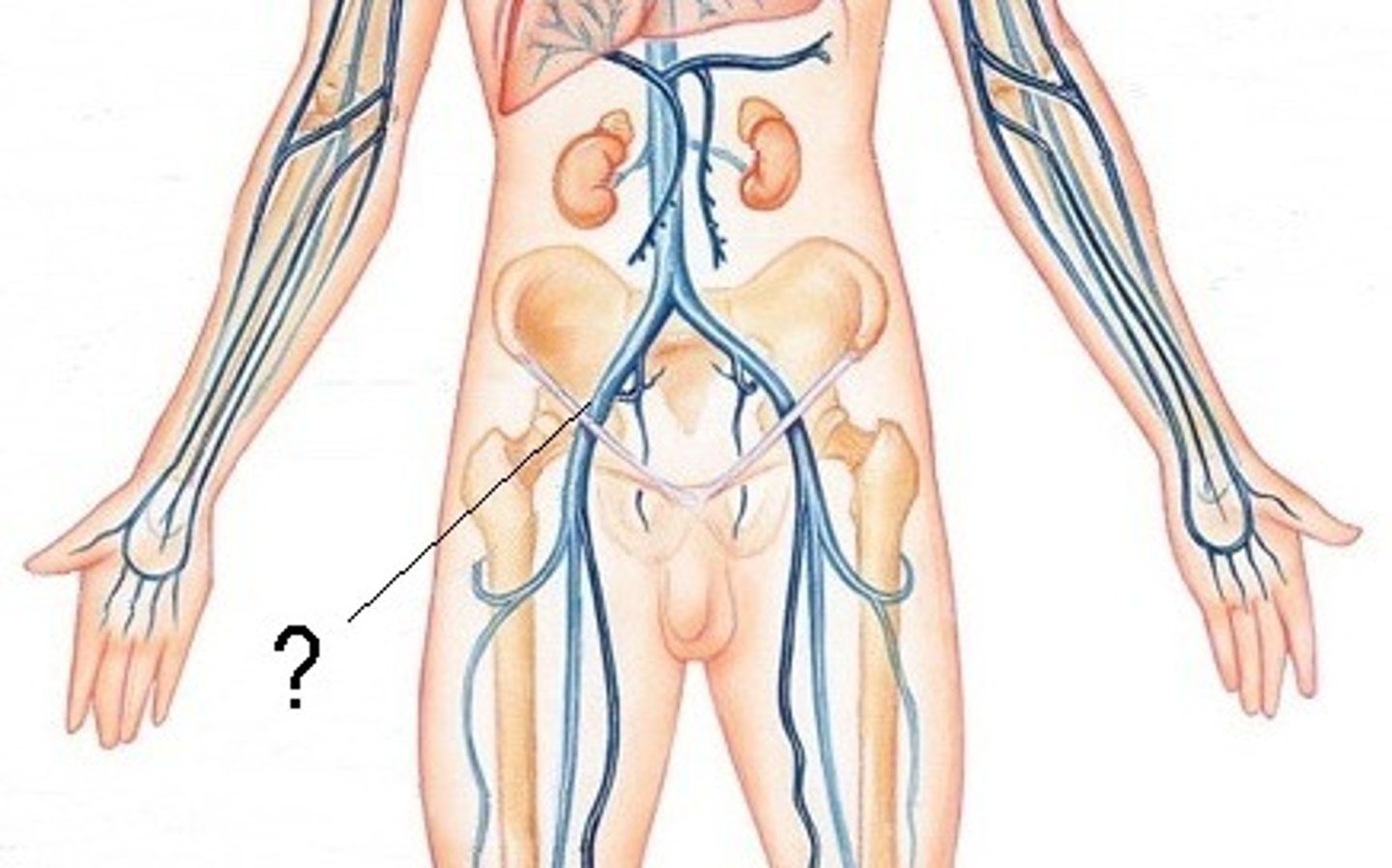
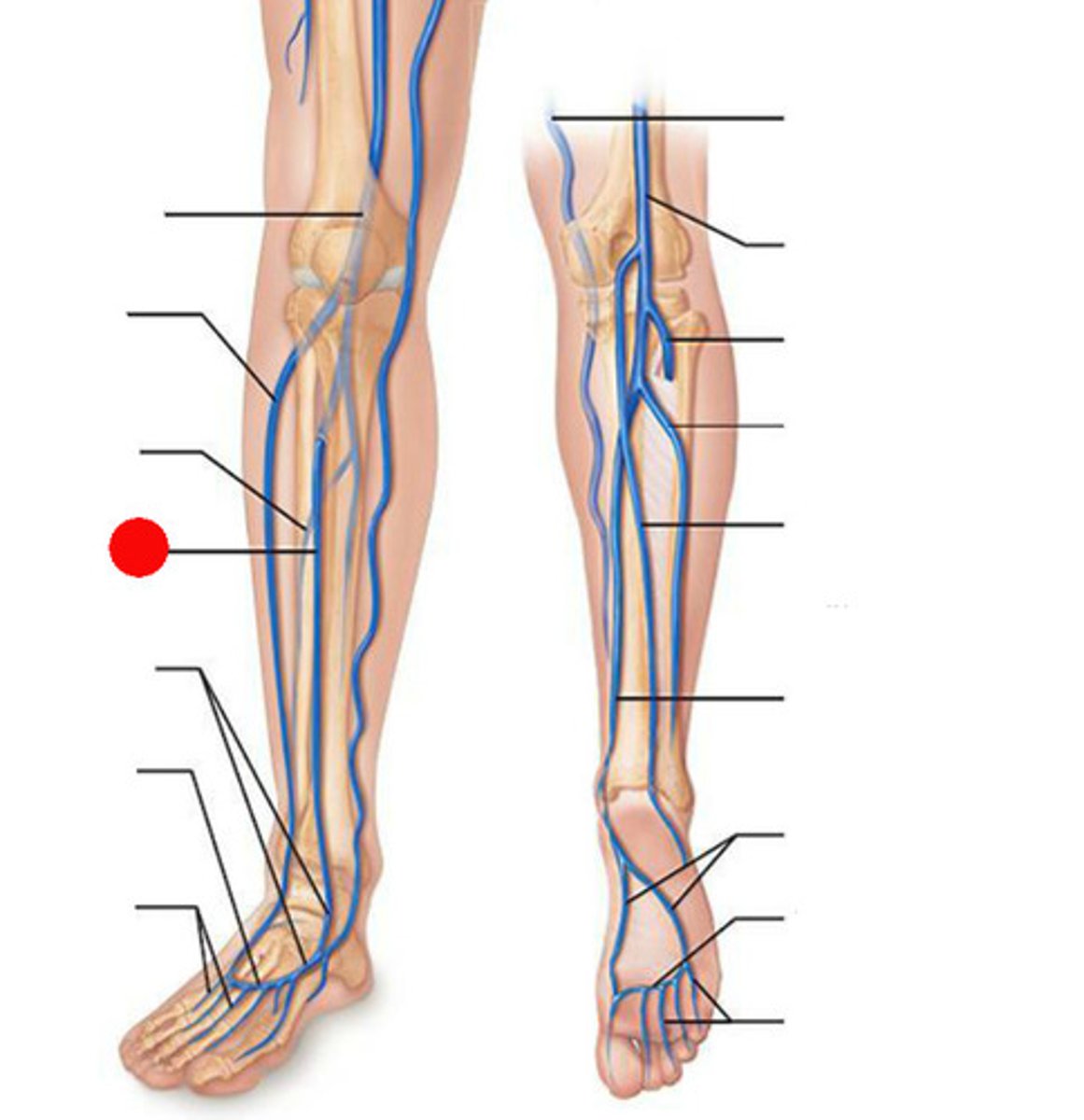
femoral vein
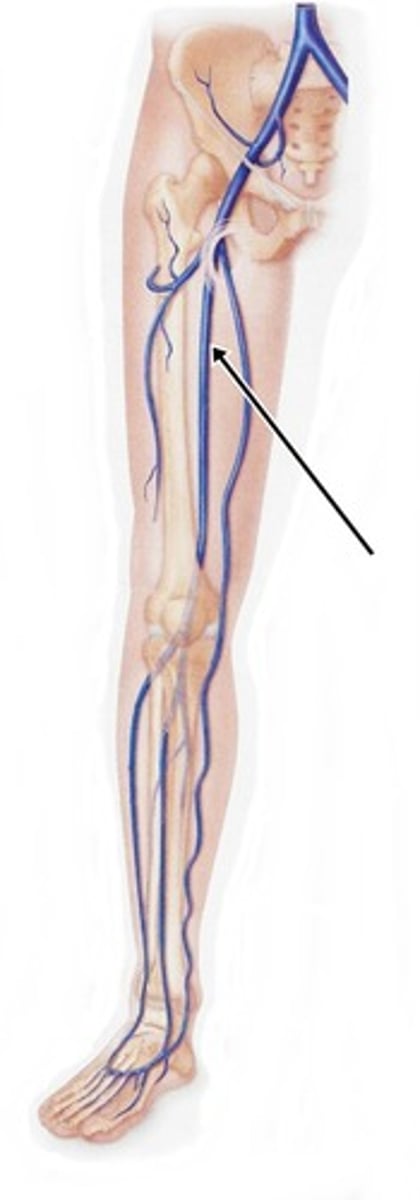
popliteal vein
The vein that forms when the anterior and posterior tibial veins unite at the knee.
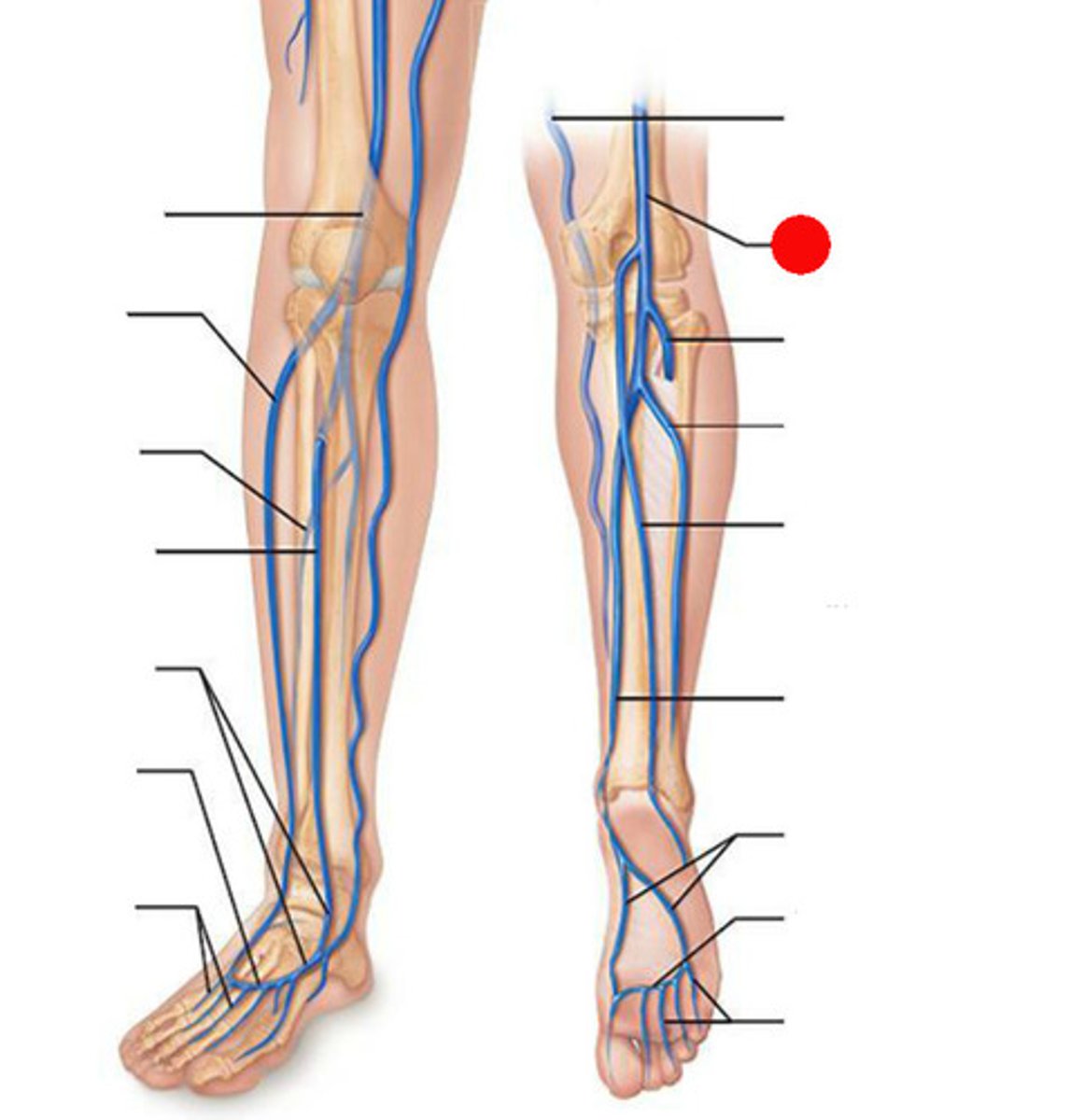
anterior tibial veins
Drain blood from the dorsum of the foot and the anterior compartment of the calf
posterior tibial veins
run with the posterior tibial artery, drain blood from the foot and posterior compartment of the leg
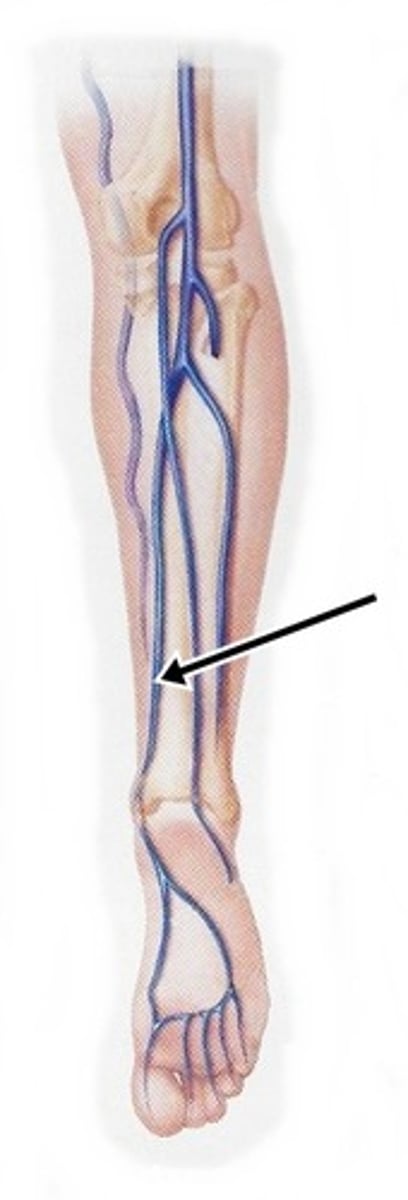
great saphenous vein
longest vein in body;
drains blood from foot, leg, and thigh;
joins with femoral vein
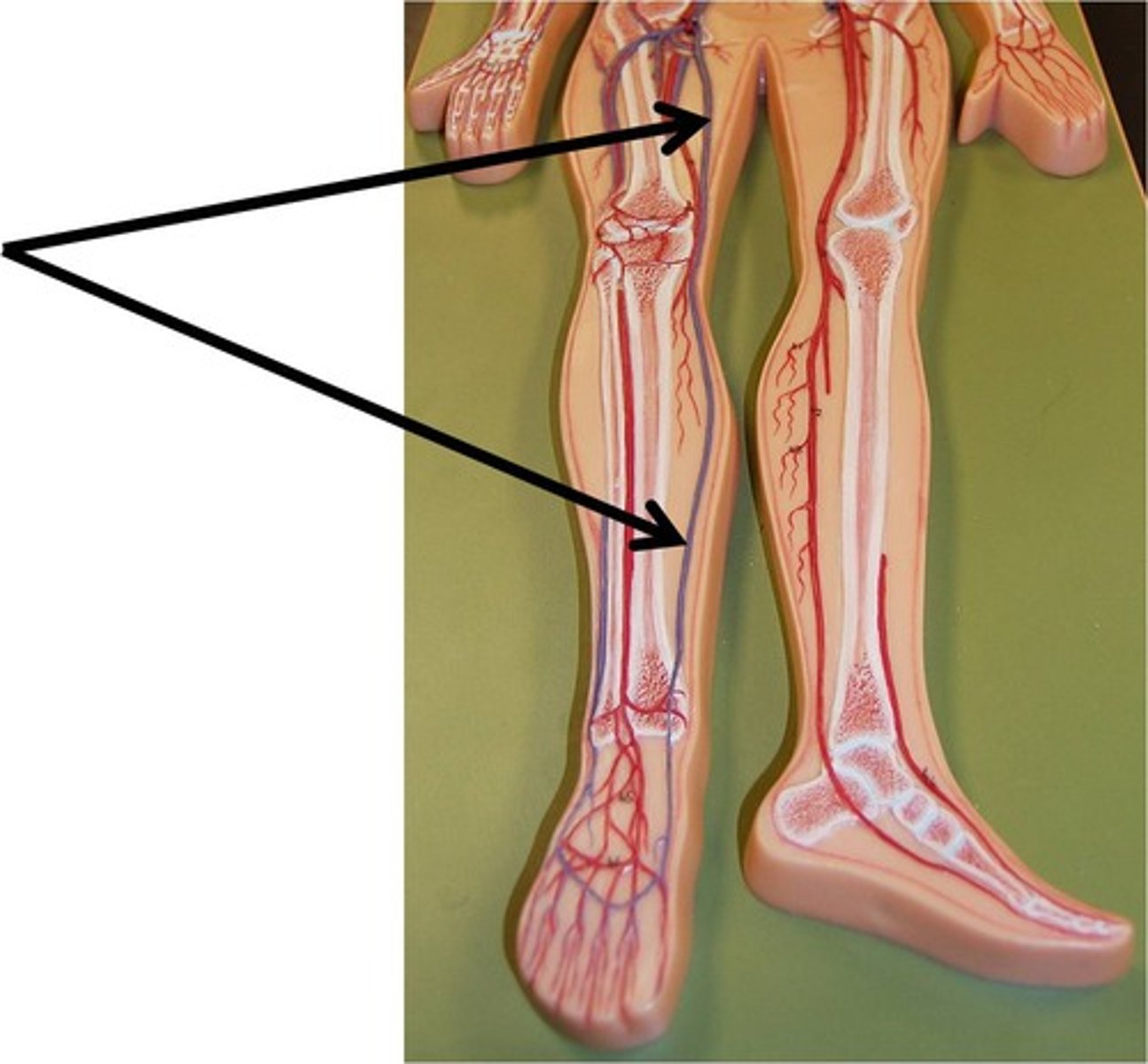
Which veins of the pelvis and lower limb are deep?
femoral, popliteal, anterior tibial, and posterior tibial veins
Which veins of the pelvis and lower limb are superficial?
great saphenous vein
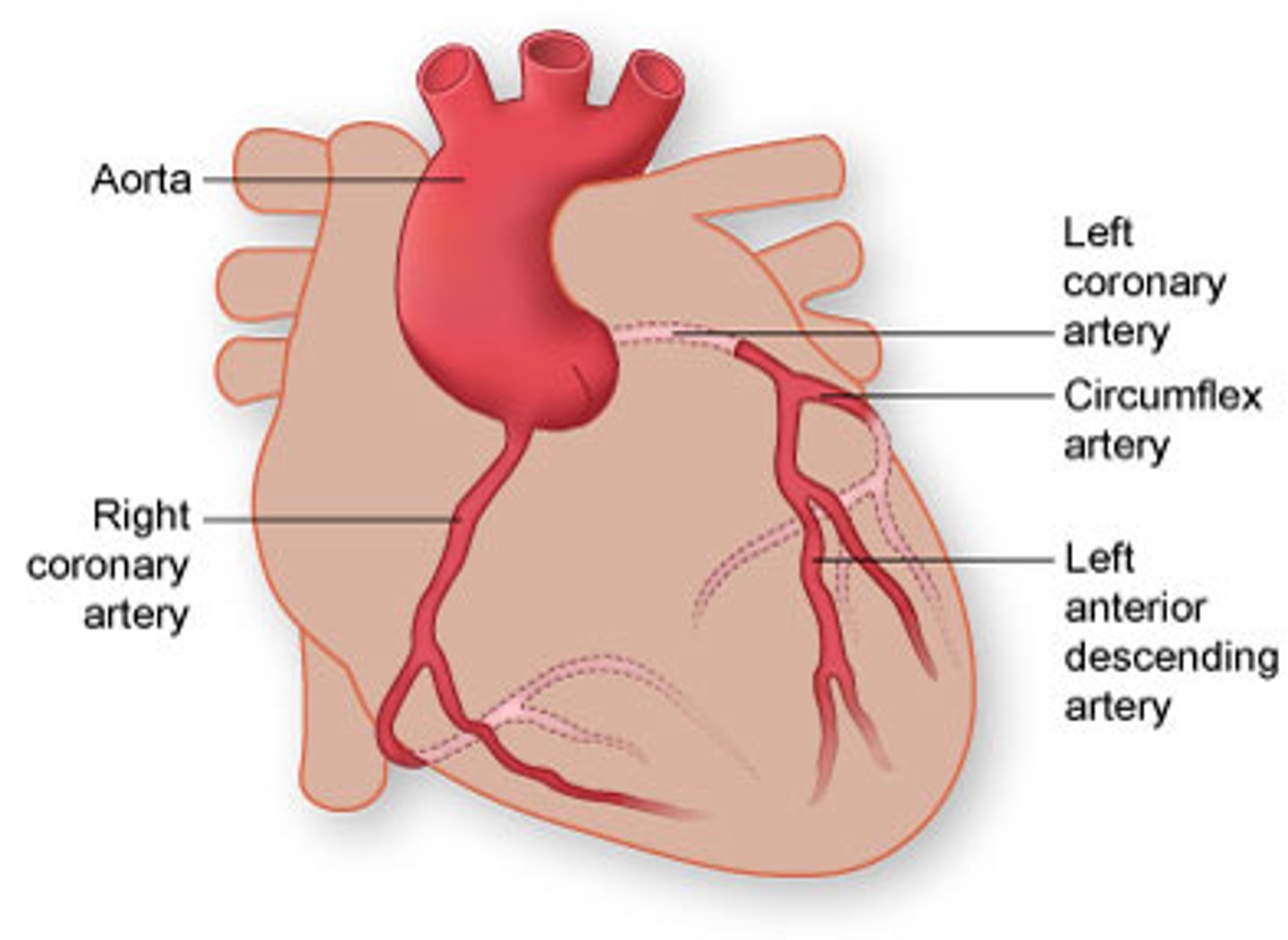
coronary arteries
great cardiac veins
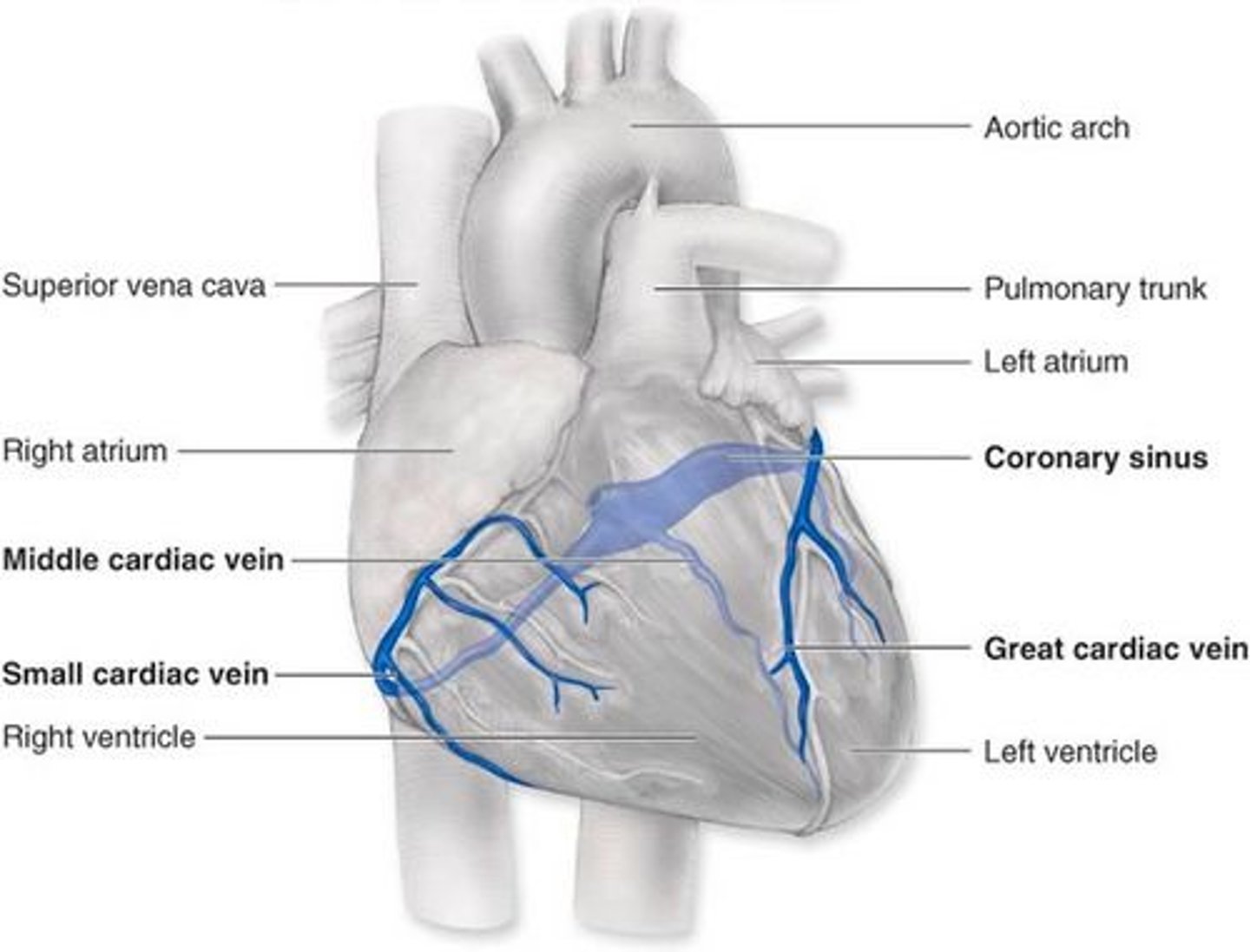
small cardiac veins
Respitory system functions
Gas exchange
Regulation of blood pH
Voice Production
Olfaction
protection
What makes up the upper respiratory tract
nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx
What makes up the lower respiratory system
trachea, bronchi, lungs
What functions as a passageway for air and food, and also houses the tonsils?
pharynx
What is the site of gas exchange
alveoli
What connects the laryngopharynx with the trachea and houses the vocal cords?
larynx
What functions in warming, moistening, and filtering air: receives olfactory stimuli: and acts as a resonating chamber for sound?
nasal cavity
What is the tubular passageway for air connceting the larynx to the bronchi?
trachea
What prevents food or fluid from entering the airways?
epiglottis
What is the air passageway entering the lungs?
primary bronchi
What is the site of the cough refelx?
carina
What provides additional space for warming and humidifying air?
paranasal sinuses
What branches from the terminal bronchioles?
respitoray bronchioles
Following removal of the larynx, an individual would
a) be unable to speak
b) be unable to cough
c) have difficulty swallowing
d) be in respiratory difficulty
e) be unable to breathe through the nose
a) be unable to speak
The Eustachian tubes open into the
a) oropharynx
b) laryngopharynx
c) nasal cavity
d) mouth
e) nasopharynx
c) nasal cavity
Which of the following would be fewest in number, but largest in diameter?
a) primary (main) bronchi
b) terminal bronchioles
c) alveoli
d) respiratory bronchioles
a) primary (main) bronchi
The choana open into the
a) mouth
b) larynx
c) nasopharynx
d) oropharynx
e) laryngopharynx
c) nasopharynx
The three folds on the walls of the nasal cavity are called...
nasal conchae
Although the cartilage rings maintain the passageway for air through the trachea, the _____________________ muscle can constrict the diameter of the passageway.
trachealis
The largest cartilage of the larynx is the....
thyroid
Ingestion
Intake of food
mastication
the process of chewing
secretion
The release of biosynthesized substances.
digestion
Breakdown of food substances into simpler forms that can be absorbed and used
absorption
The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of the digestive system into the blood
elimination
Act of removal of materials from the body
propulsion
movement of food along the digestive tract
peristalsis
Involuntary waves of muscle contraction that keep food moving along in one direction through the digestive system.
mass movements
Powerful peristaltic contractions that occur a few times each day in the colon
Segmentation in intestines
non-adjacent segments contract and relax to mix food
What makes up the hard palate?
maxilla and palatine bones
What makes up the soft palate?
skeletal muscle, nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium
palatine tonsils
at posterior end of oral cavity
What is the function of saliva?
Cleanses the mouth, moistens and dissolves food chemicals, aids in bolus formation, and contains enzymes that break down starch.
parotid salivary gland
lies under the skin covering the lateral and posterior surface of the mandible
submandibular salivary gland
a salivary gland inside the lower jaw on either side that produces most of the nocturnal saliva
sublingual salivary gland
below the tongue
Esophageal hiatus
where the esophagus passes through the diaphragm
Hiatal hernia
protrusion of a part of the stomach upward through the opening in the diaphragm
Superior esophageal sphincter
at the junction of the pharynx and the esophagus; closes during inhalation preventing air from entering the GI tract
inferior esophageal sphincter
At the junction of the esophagus and the stomach; prevents materials from regurgitating from the stomach into the esophagus
cardiac orifice
opening of the esophagus into the stomach
pyloric orifice
opening between stomach and small intestine
What are the muscle layers of the stomach?
Longitudinal (outer)
Circular (middle)
Oblique (inner)
What is the purpose of rugae?
allow stomach to expand and increase surface area
What do parietal cells produce?
HCl (hydrochloric acid)
What do chief cells produce?
pepsinogen (pepsin)
duodenum
first part of the small intestine
jejunum
second part of the small intestine
ileum
third part of the small intestine
circular folds
deep folds of the mucosa and submucosa that extend completely or partially around the circumference of the small intestine
vili
fingerlike projections that absorb nutrients
microvili
increase surface area for absorption
lacteal
a lymph tubule located in the villus that absorbs fatty acids
How many lobes does the liver have?
4 lobes
What are the functions of the liver?
-Detoxification of blood including the breakdown of alcohol
-Phagocytosis
-Production of bile
biliary apparatus
network of thin ducts that transport bile from liver and gall bladder to duodenum