Bacteriology Fungi
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Which Zygomycetes species causes abortion?
Mucor spp.
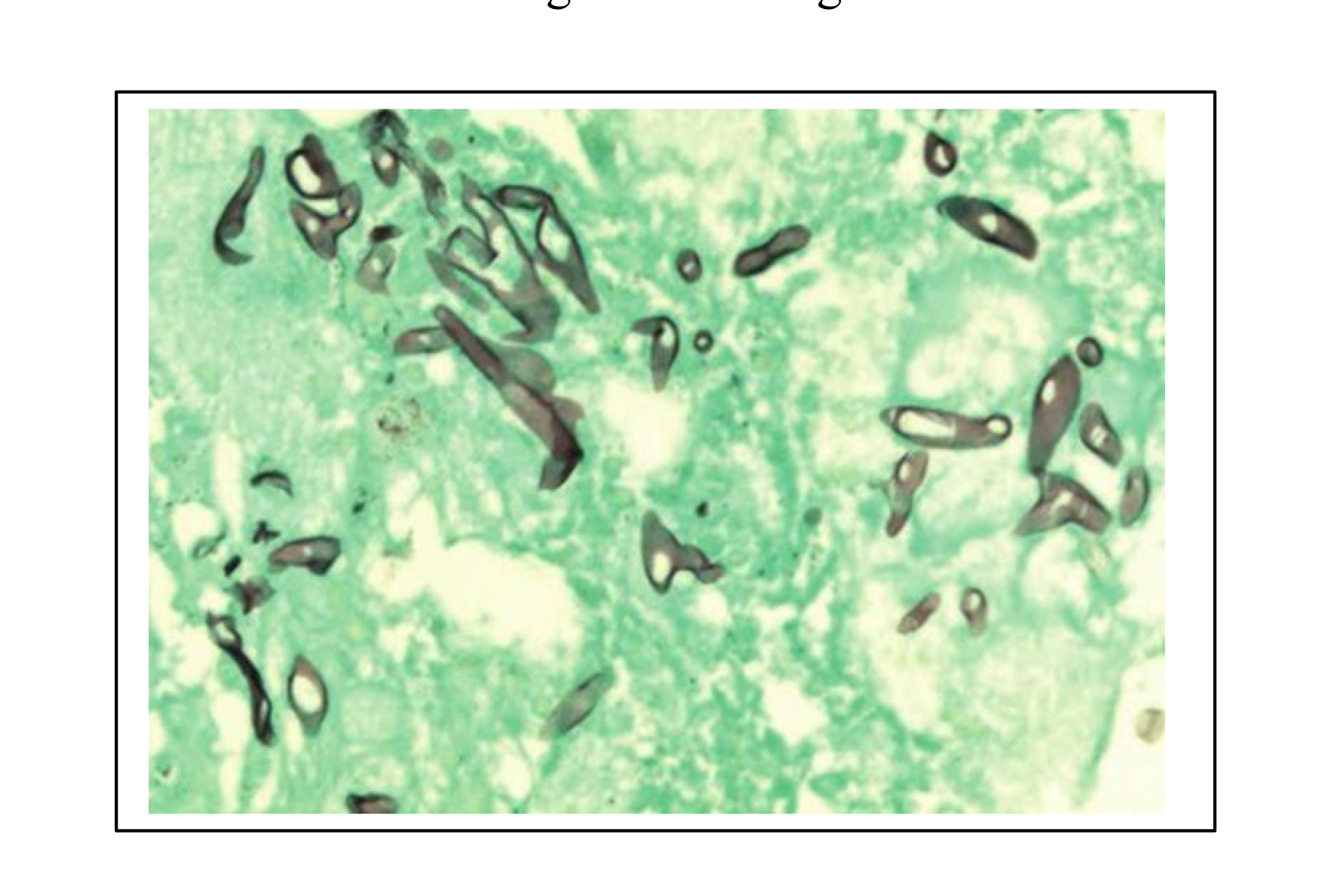
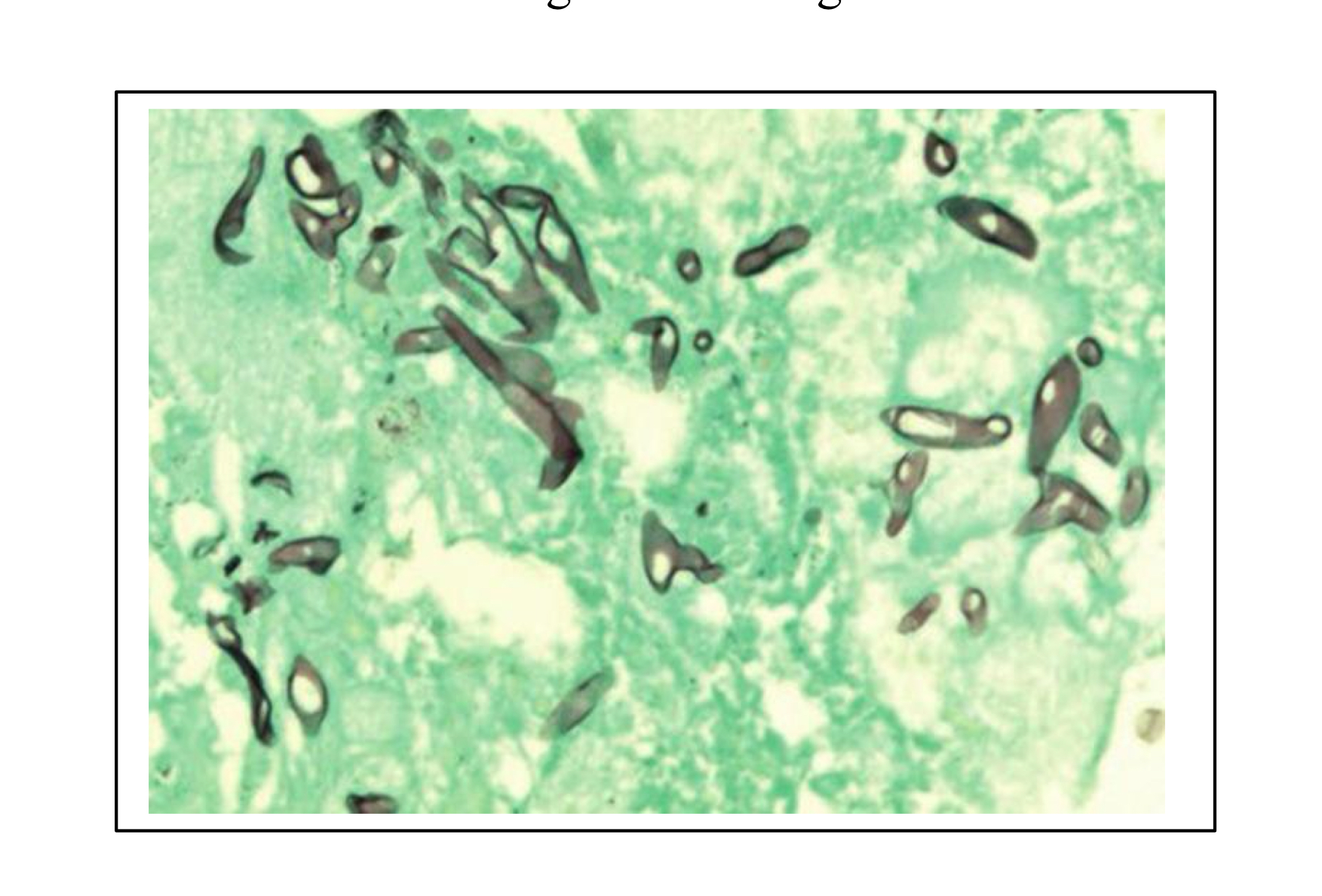
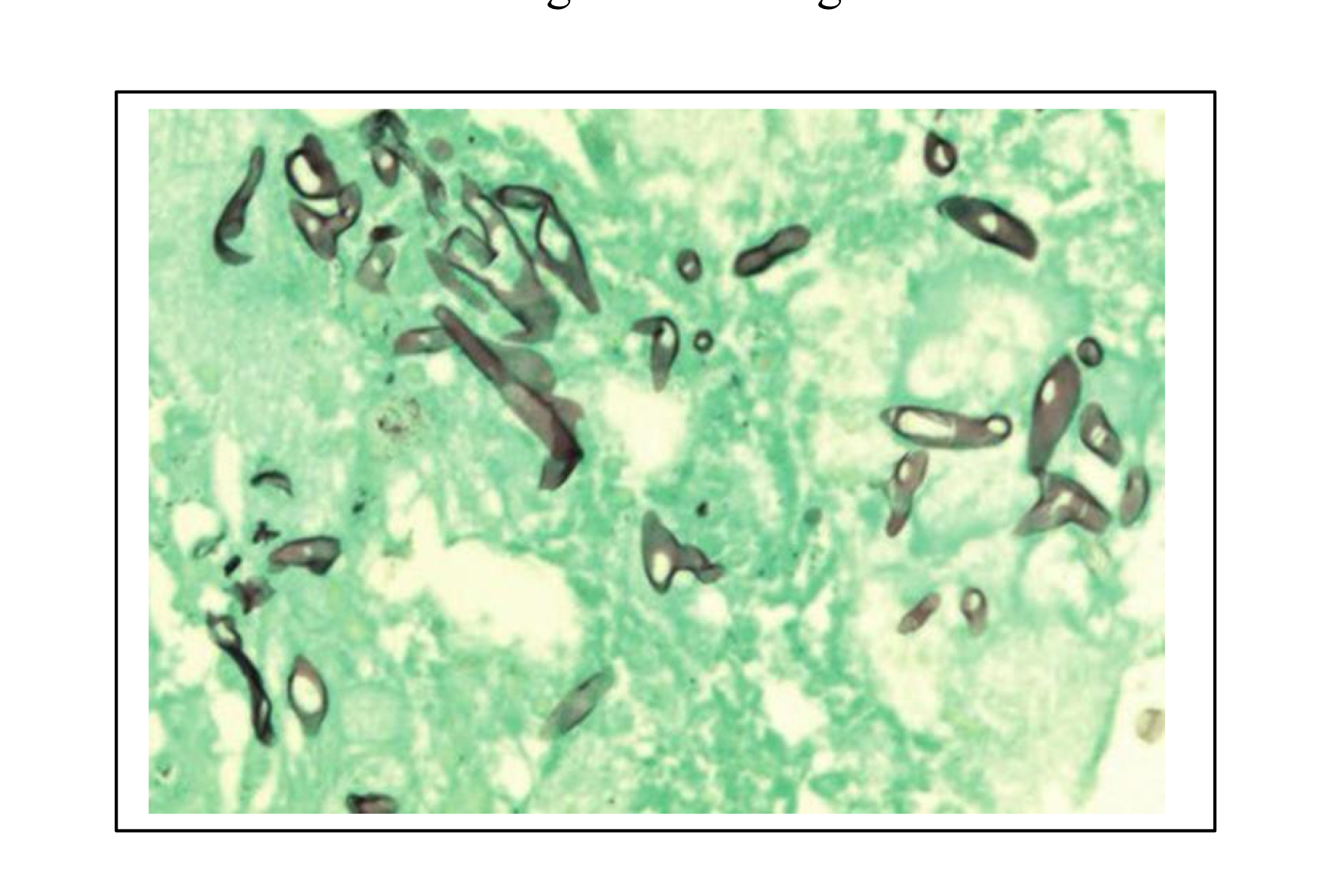
How to visualize Mucor (Zygomycetes) species?
Methenamine silver-stained histological section from the placenta of a bovine abortion caused by Mucor species (mucormycosis). Methenamine silver stains fungal elements black or brown on a light green background.
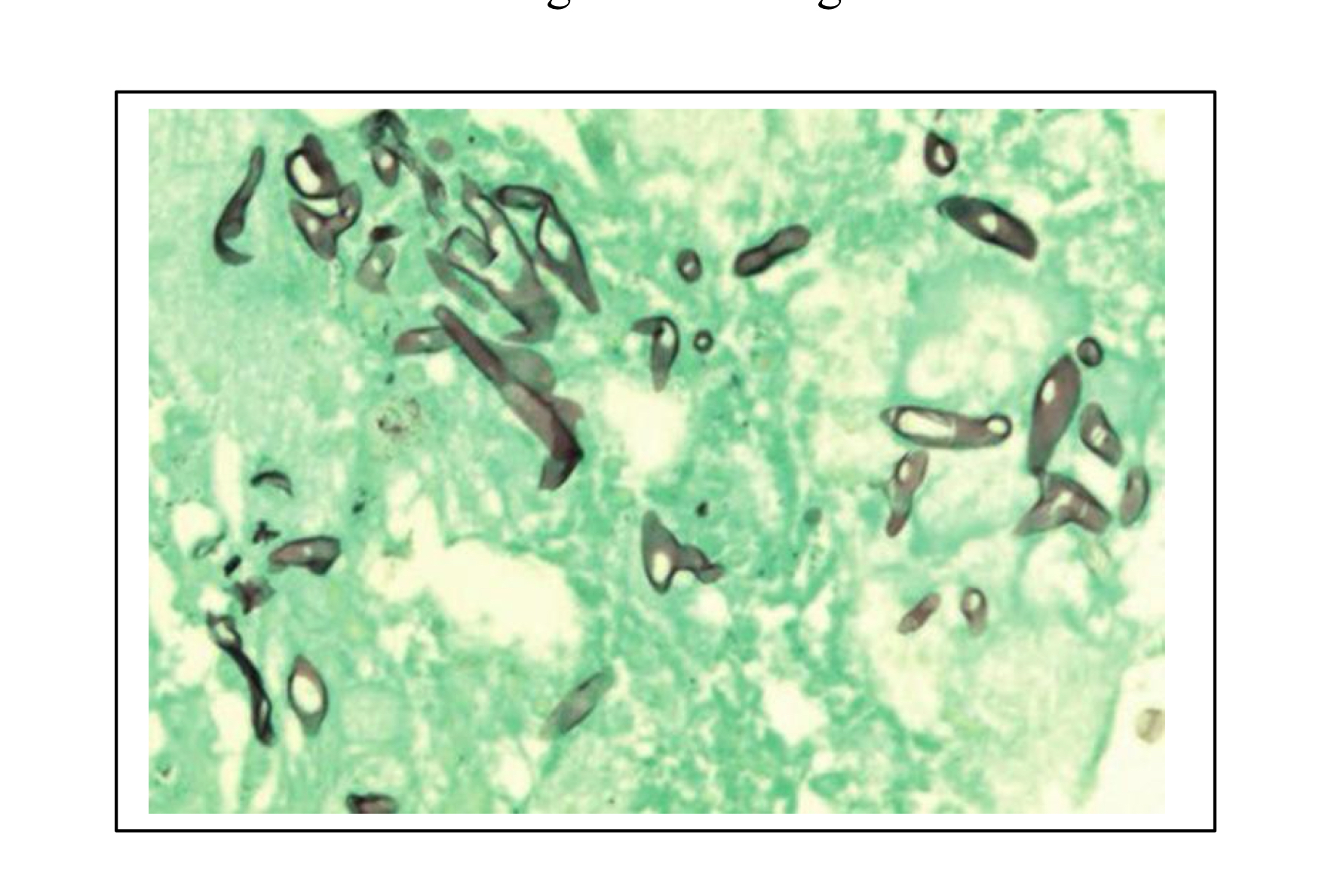
Characteristics of Mucor spp. (Zygomycetes) on Methenamine silver-stained section?
Brown stained aseptate hyphae (no segmented appearance)
Non-parallel walls
Non-dichotomous branching (two equal parts, think peace sign)
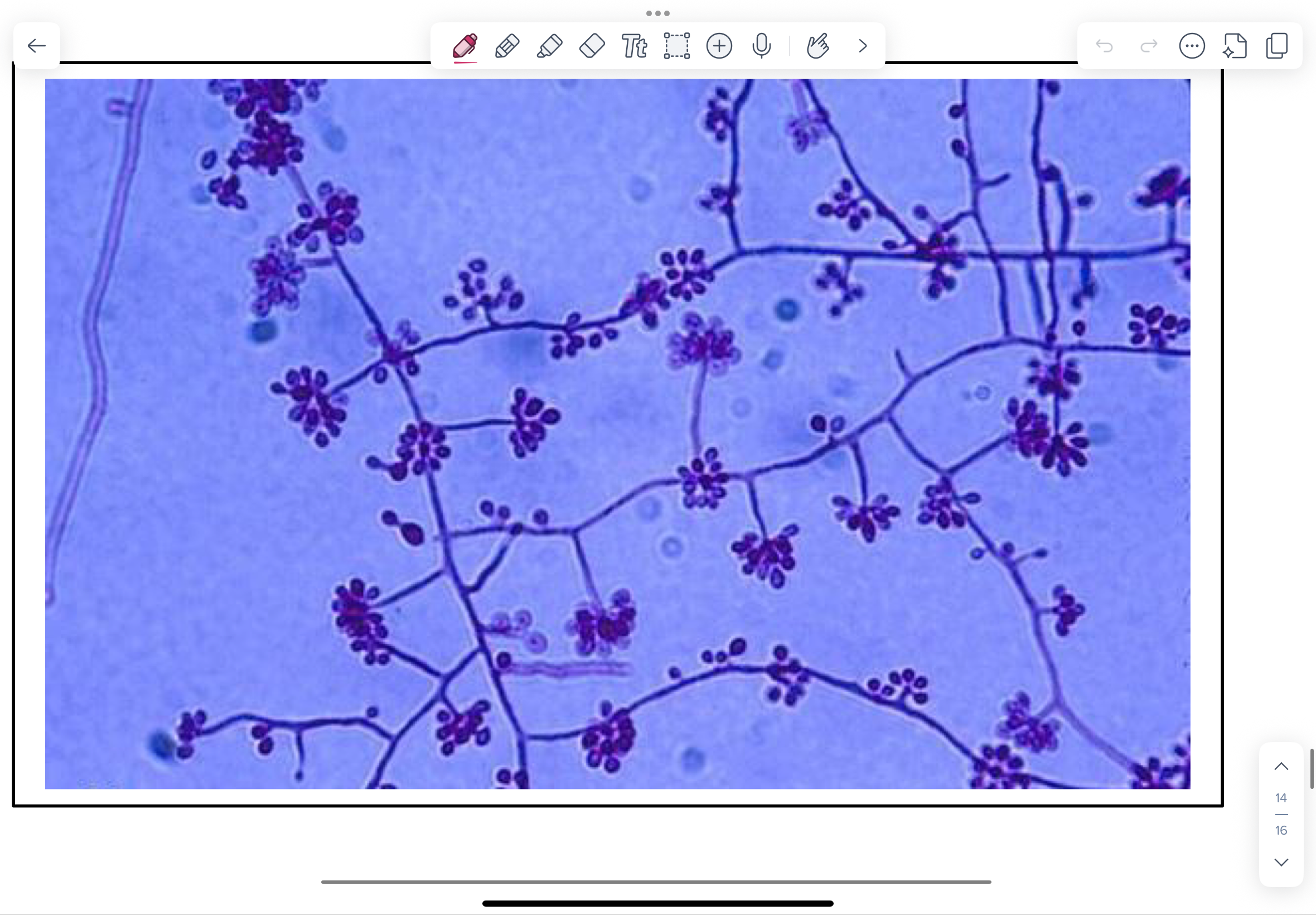
What is this?
Mucor spp. from class Zygomycetes
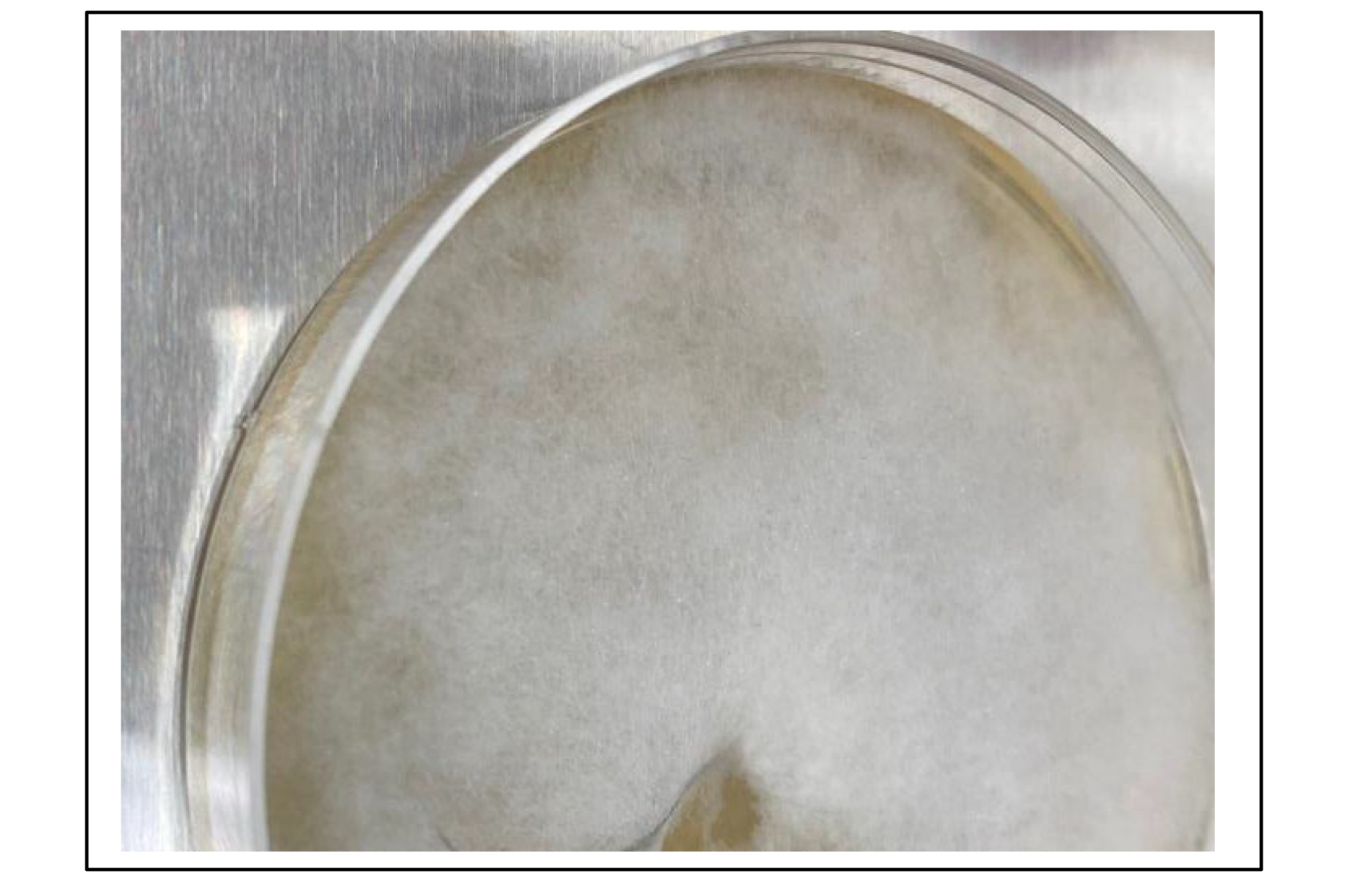

Which species is this on Sabouraud dextrose agar (SAB)?
Mucor species
What is LPCB?
Lactophenol cotton blue (LPCB)-stained scotch tape lift slide mount of culture growth. LPCB is
commonly used for the microscopic examination of fungal cultures prepared by the scotch tape method. The aniline dye component (cotton blue) lightly stains the envelope.
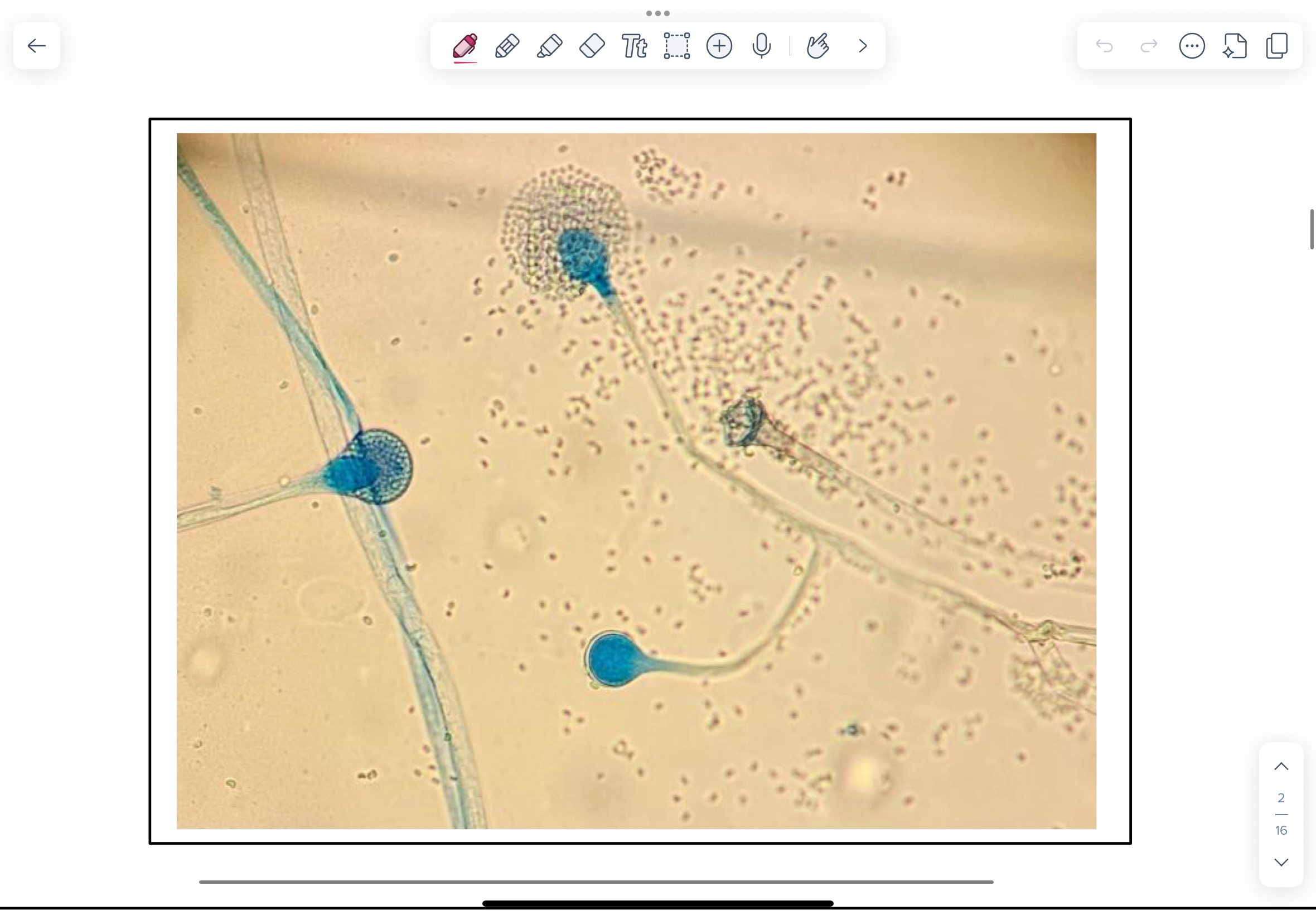
Which species is this on LPCB?
Mucor (Zygomycetes)
NOTE aseptate hyphae and characteristic sporangium filled with sporangiospores.
Which Aspergillus species causes abortion? (Aspergillosis)
Aspergillus fumigatus
Approximately 70% of mycotic (fungal) abortions in cattle occur during winter months
and arise from hay/silage contaminated with Aspergillus species.
What do we see on Methenamine silver-stained section of placenta from bovine abortion for Aspergillus fumigatus?
Brown stated septate hyphae
Parallell walls
Dichotomous branching
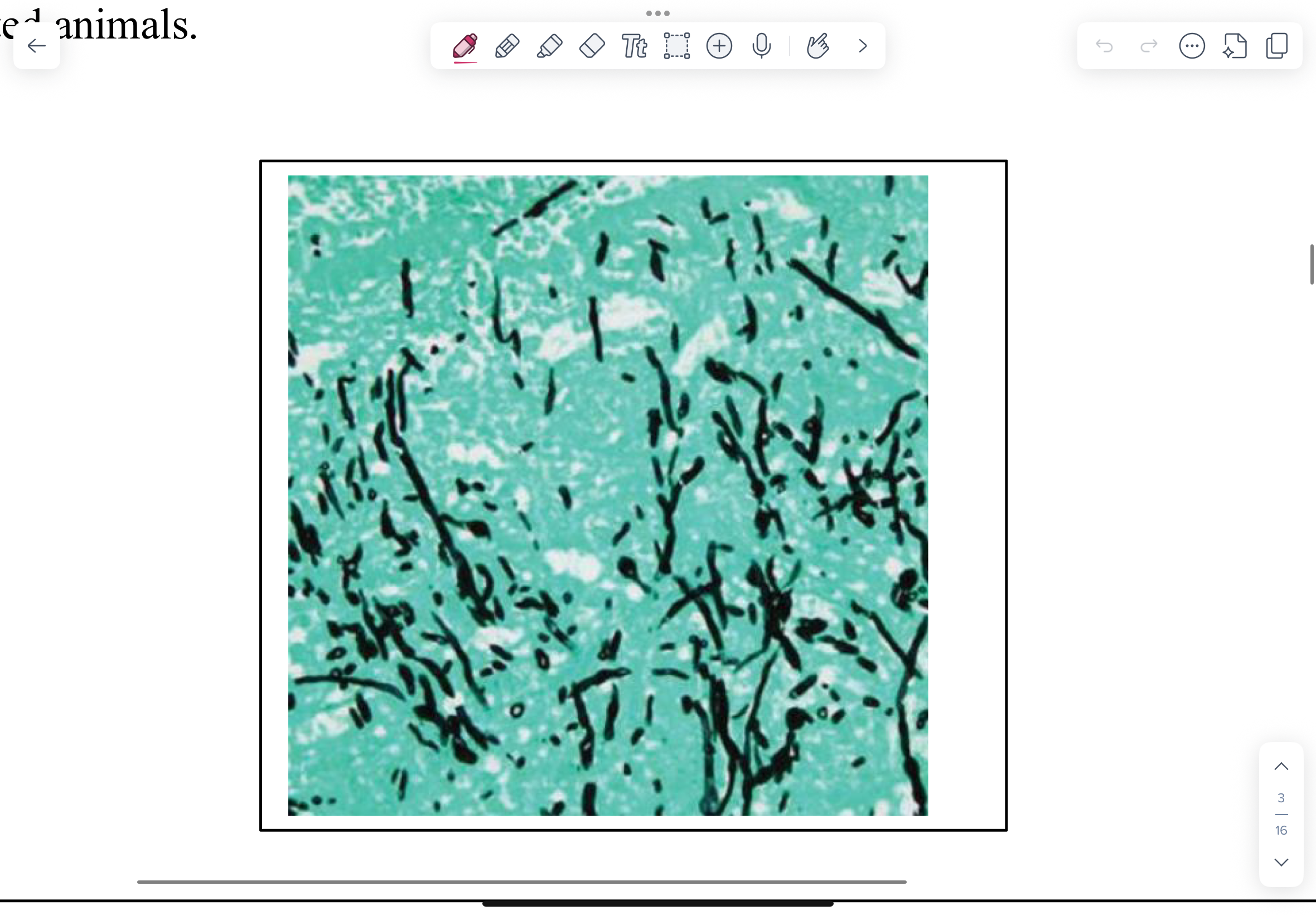
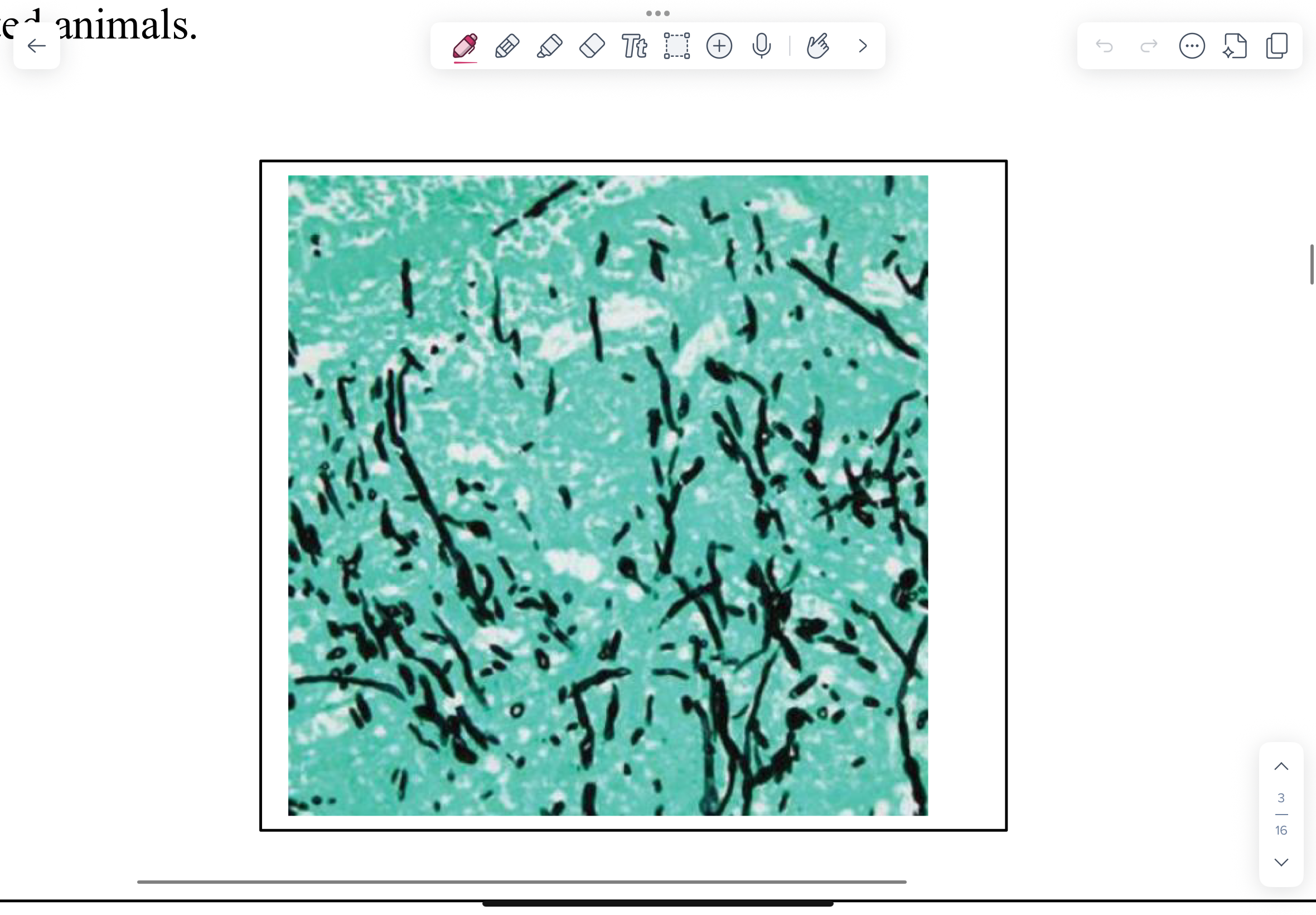
What is this?
Aspergillus fumigatus
What are Conidiophores?
Specialized fungal hyphae that produce and release asexual spores called conidia
Why do we not see conidiospores on histological tissue sections for Aspergillus fumigatus?
Because they require the presence of oxygen (air) for development. Conidiospores will form on media plates or in the respiratory tract (lungs and air sacs) of infected animals.
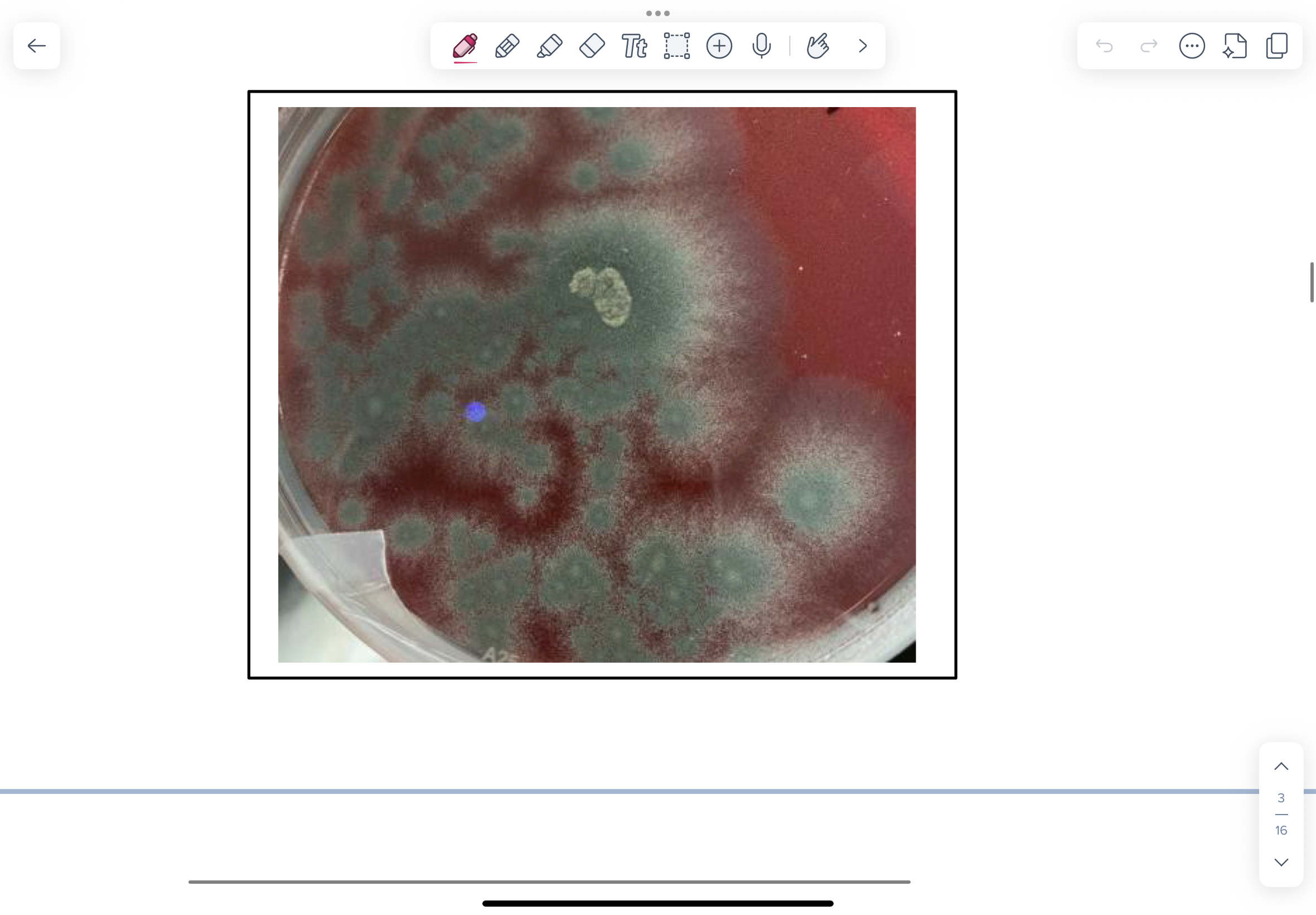
What does Aspergillus fumigatus look like on a BA plate? (From dog with chronic sinusitis)
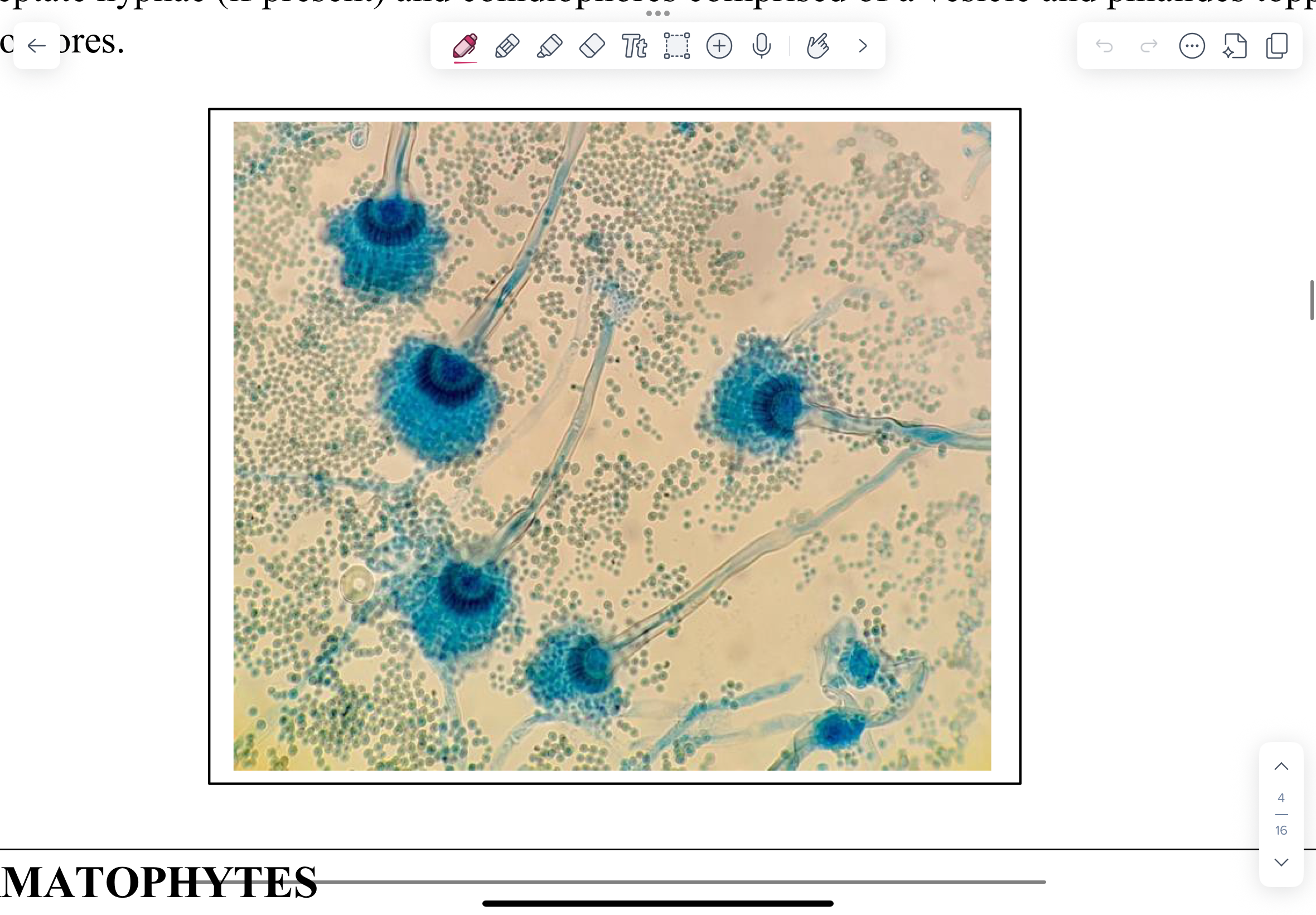
What does an LCPB-stained scotch tape mount for Aspergillus fumigatus look like?
Which bacteria causes ringworm in dogs and cats and what is the proper name?
Dermatophytosis caused by Microsporum canis
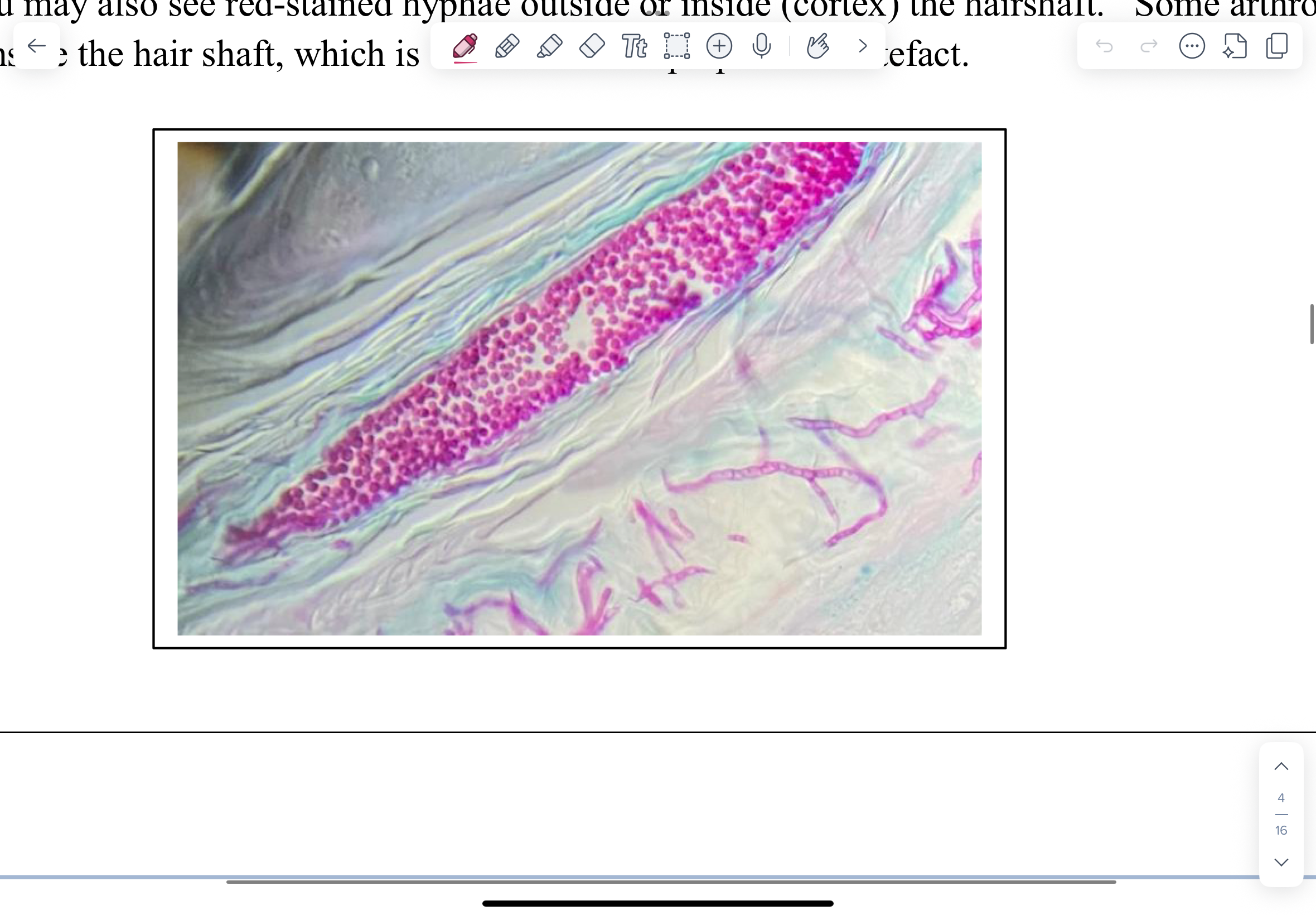
A periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)-stained section of a skin biopsy from a dog with ringworm caused by
Microsporum canis
Found in hair and hair follicles.
Bright pink/red-stained arthrospores outside the hair shafts (ectothrix infection)
How does PAS stain yeast and fungal hyphae?
PAS stains yeast and fungal hyphae bright pink or purple against a light green or orange background
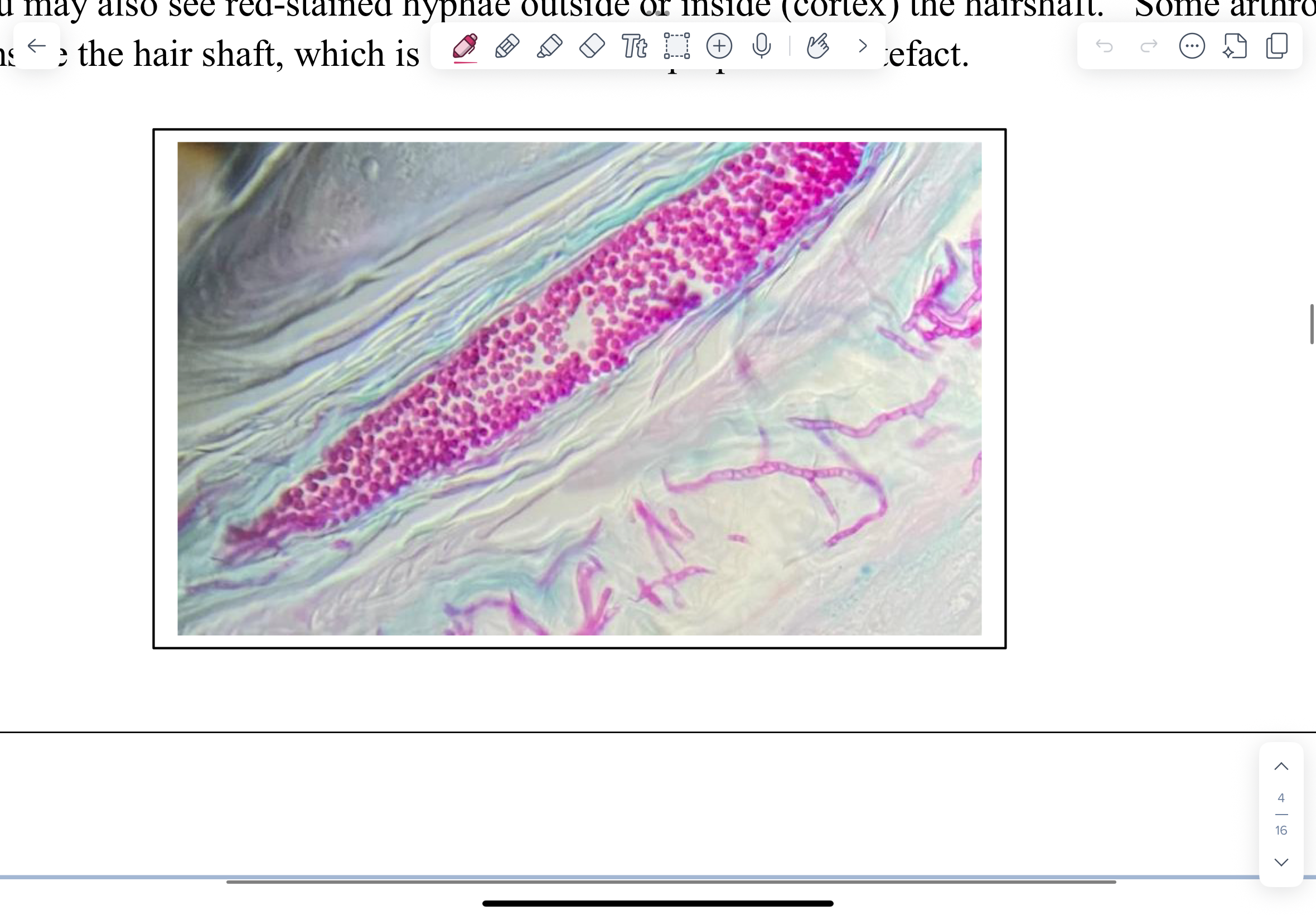
Which bacteria causes ringworm in a cow?
Trichophyton veruucosum
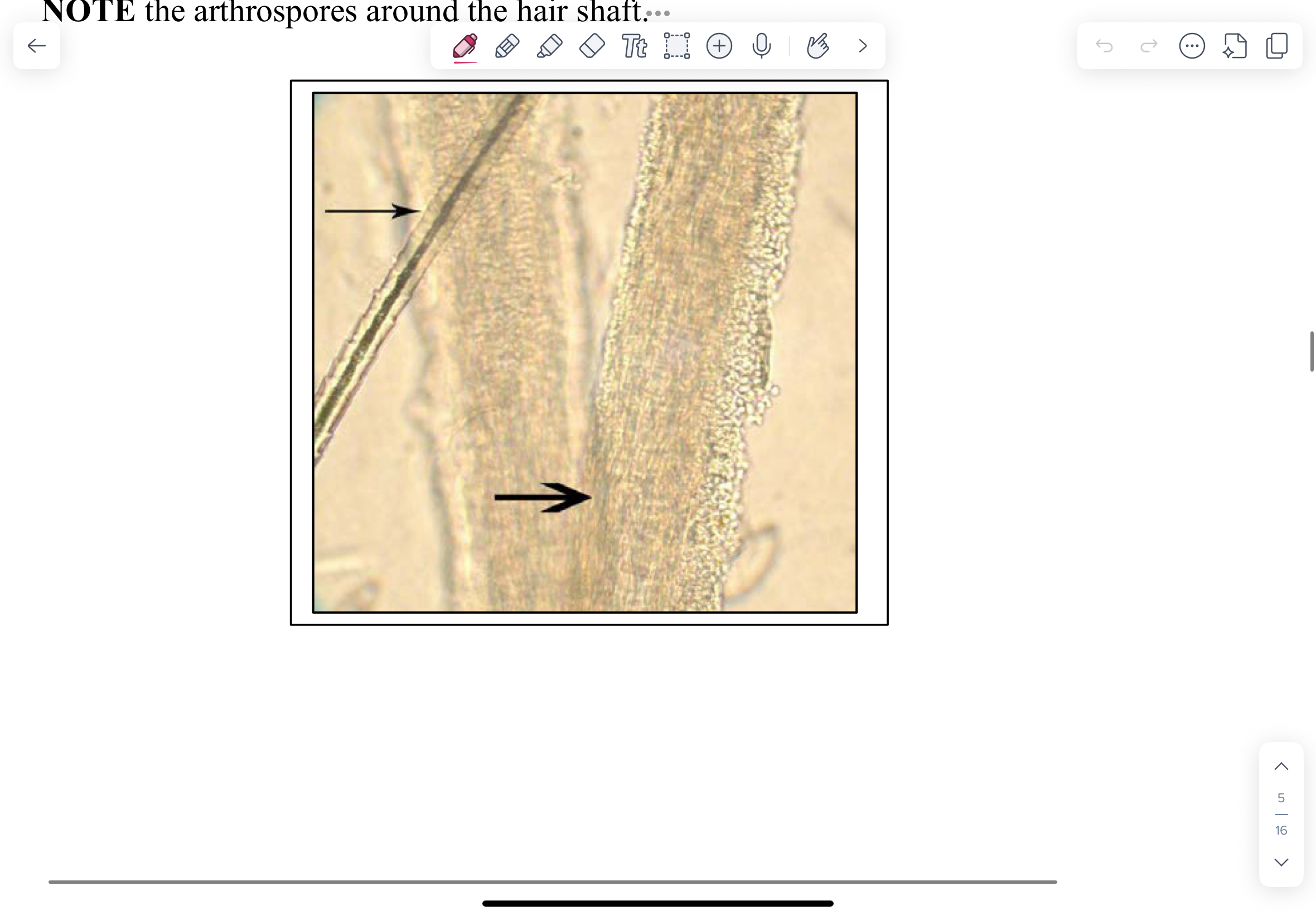
Photomicrograph of a 10% KOH wet mount of an infected hair from a case of ringworm in a cow
10% KOH can be used to clear skin, hair, mucosal scrapings, sputum and allow fungal elements to be easily visualized.
Note the arthrospores around the hair shaft.
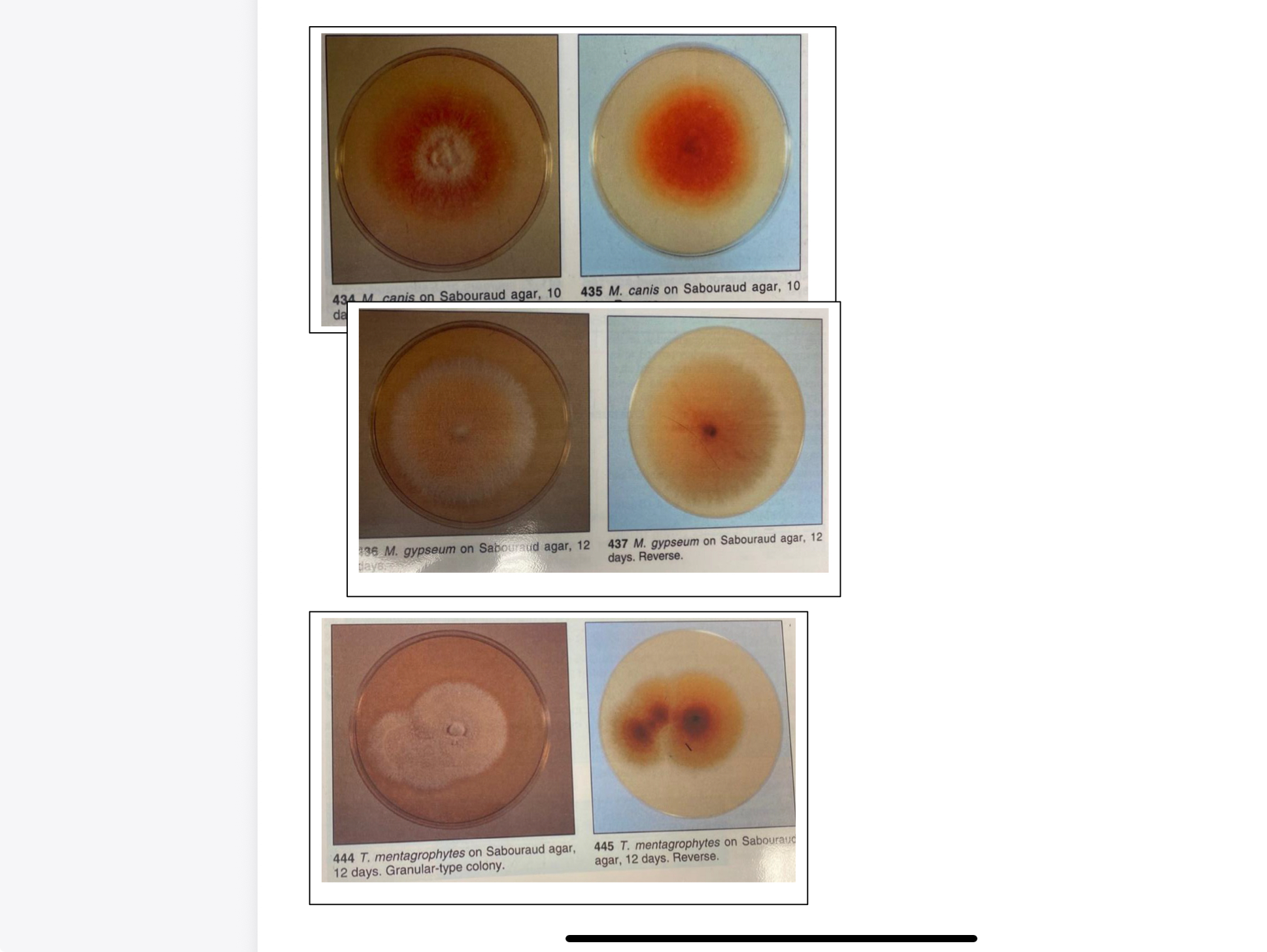
Dermatophyte cultures and/or photographs of Microsporum canis, M. gypseum, and Trichophyton
mentagrophytes.
SAB dextrose agar with the addition of chloramphenicol and cycloheximide (SAB CC) is a highly selective medium for the isolation of dermatophytes from cutaneous specimens. This agar inhibits the growth of saprophytic bacteria and fungi present on the animal’s skin and hair.
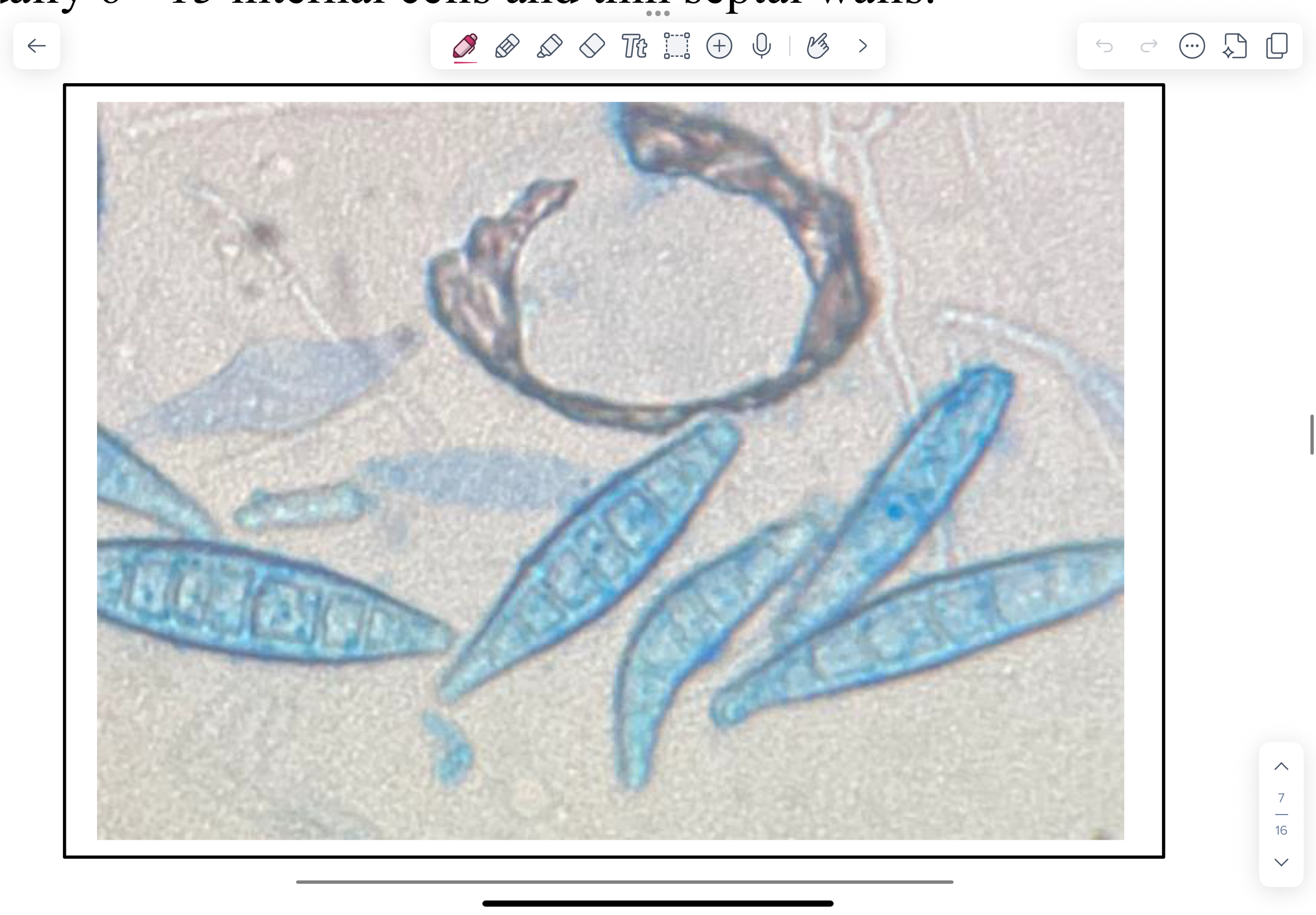
LPCB-stained slide mount of Microsporum canis culture showing macroconidia.
M. canis macroconidia are spindle-shaped, long, rough, with a terminal knob, and thick outer cell
walls. There are usually 6 - 15 internal cells and thin septal walls.
Green algae
Prototheca
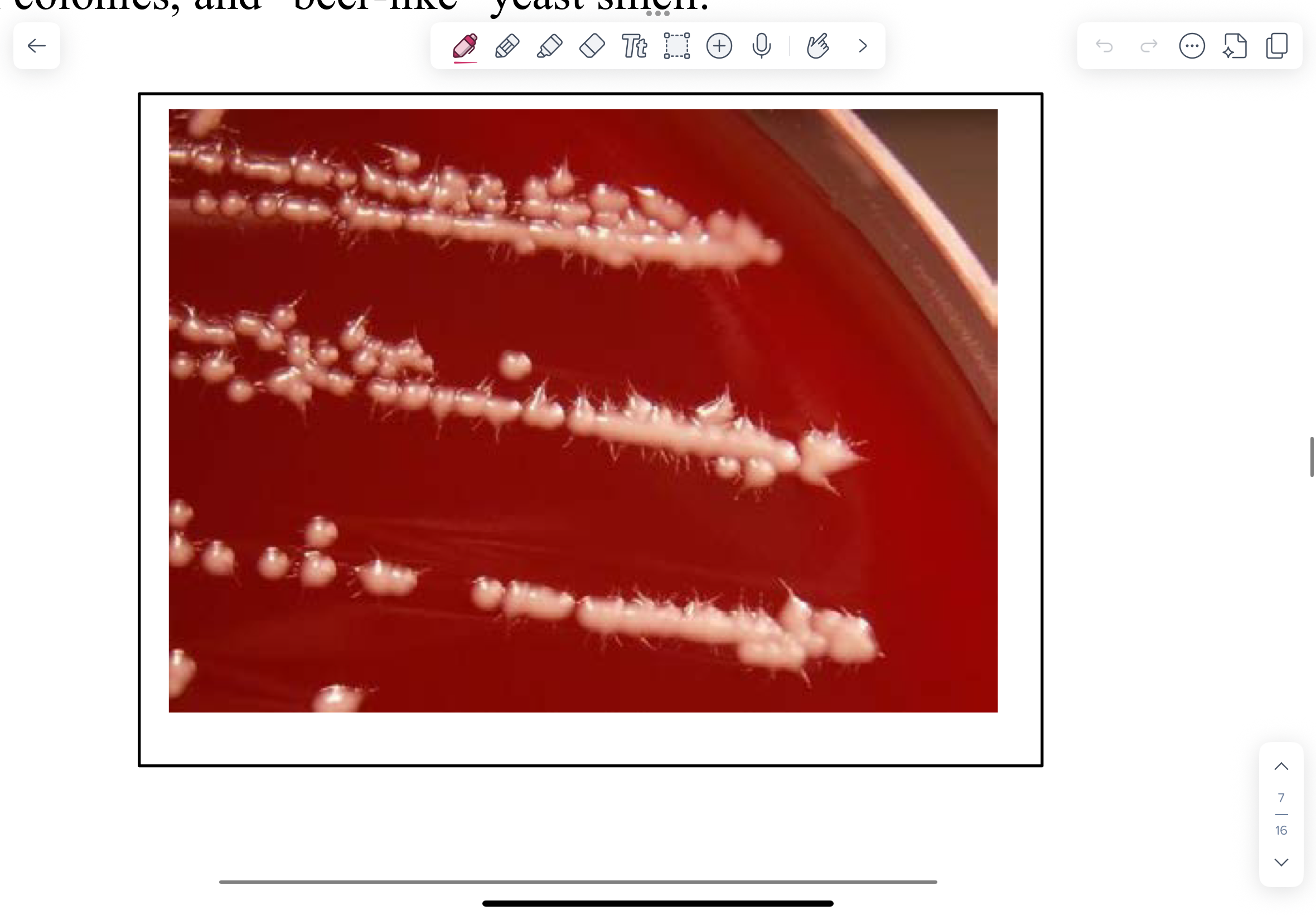
Candida species - Candida albicans (this is a YEAST)
They grow readily on BA or Sabouraud agar (SAB)
Cream coloured, shiny, bacterial-like colonies. Has a beer-like yeast smell. Do not mix up with staphylococcus.
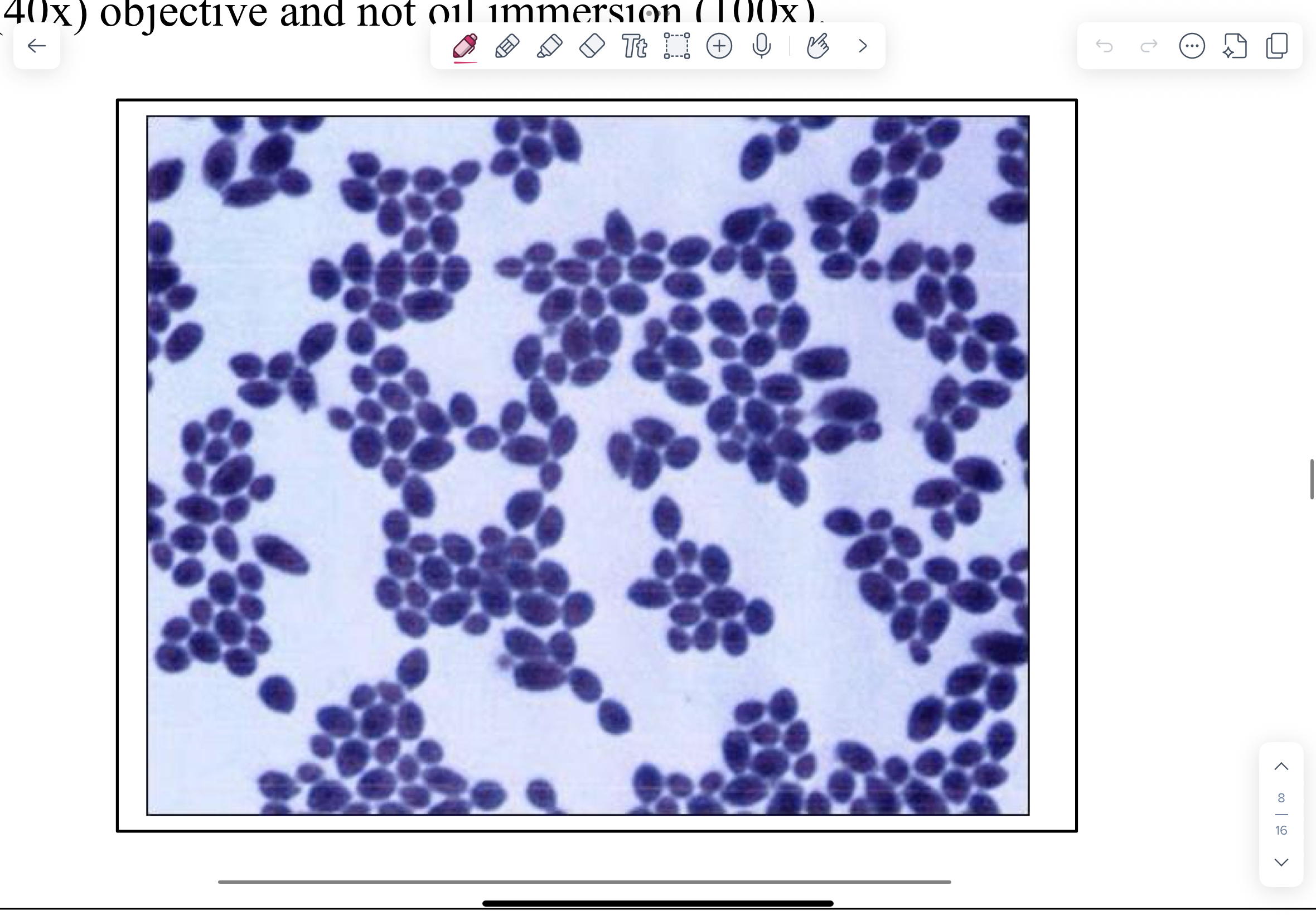
Gram-stained smear of C. albicans colony.
NOTE blue budding yeast (3.0-5.0 µm) with daughter cell connected by a narrow base. The occasional short hyphae may be present. You might mistake these for large gram-positive cocci. Keep in mind that you are on the high-dry (40x) objective and not oil immersion (100x).
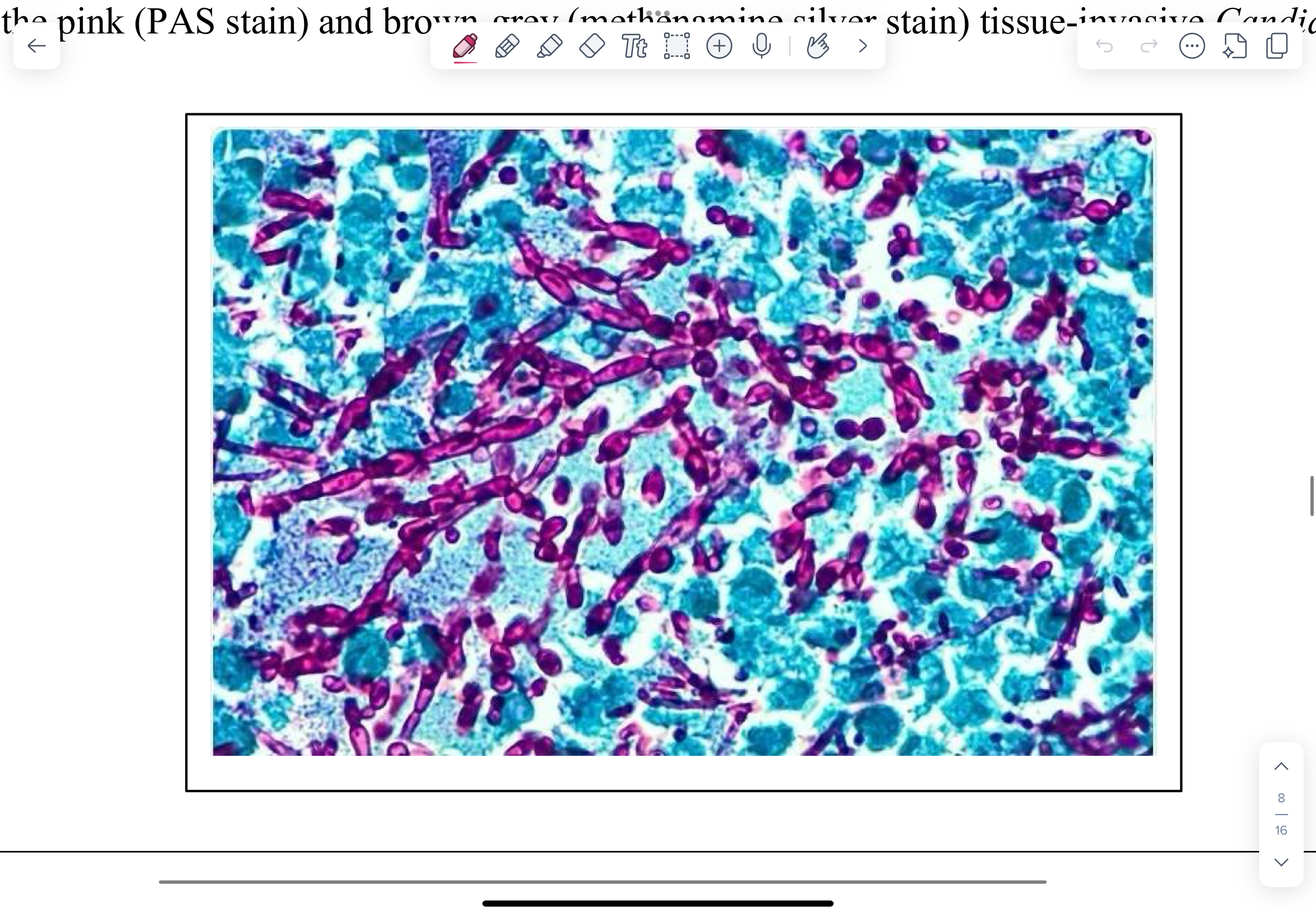
Photos of PAS (top) and Methenamine silver (bottom)-stained histological sections of tissue-invasive Candida infections.
Pink (PAS stain) and brown-grey (methenamine silver stain) tissue-invasive Candida hyphae.
Malassezia pachydermatis (YEAST)
Often from dog ear infections.
Gram-stained smear of a case of chronic otitis externa in a dog.
Malassezia pachydermatis (YEAST)
NOTE the peanut-shaped (also described as “boot print” or bottle-shaped)

Cryptococcus neoformans and Cryptococcus gatii (YEAST)
Infections in cats and humans arise from inhalation of infectious environmental forms in endemic parts of North America (Cryptococcus var. neoformans - pigeon feces in particular; Cryptococcus gatii - aerosols from certain species of aromatic trees).
Cryptococcosis is the most common systemic fungal pathogen in cats
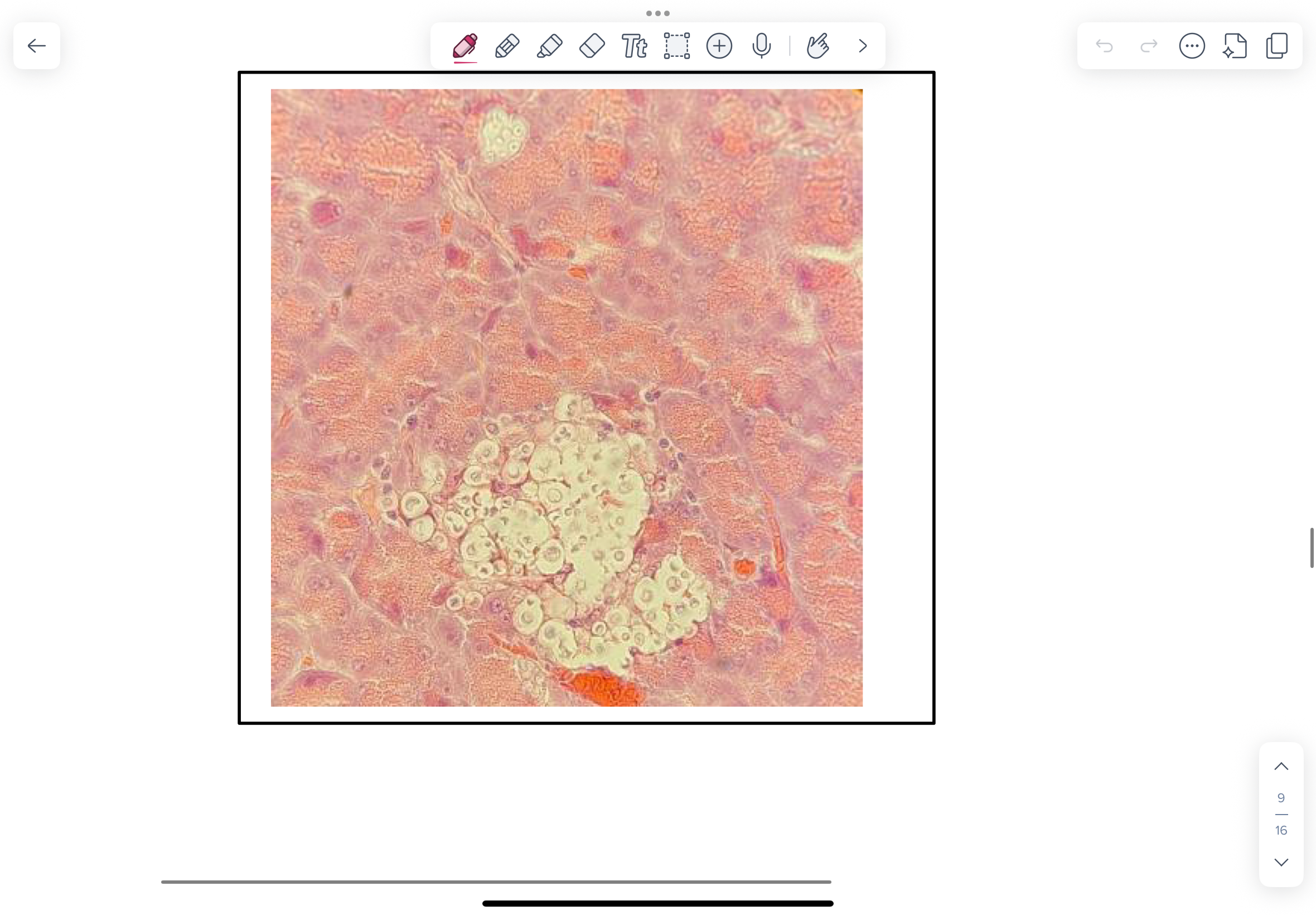
H&E-stained preparation from a cat which showed pneumonia and mediastinal lymphadenopathy at post mortem caused by Cryptococcus neoformans infection.
NOTE Cryptococci are typically round (3-15 µm) with daughter cells budding on a narrow base.
To locate yeast in this histological section, look for clusters of “empty-spaces” or “soap-bubbles” within inflammatory cell infiltrates. These are a result of yeast bodies surrounded by a wide capsular space that does not take up stain. If you look closely you will see bluish-grey yeast bodies.
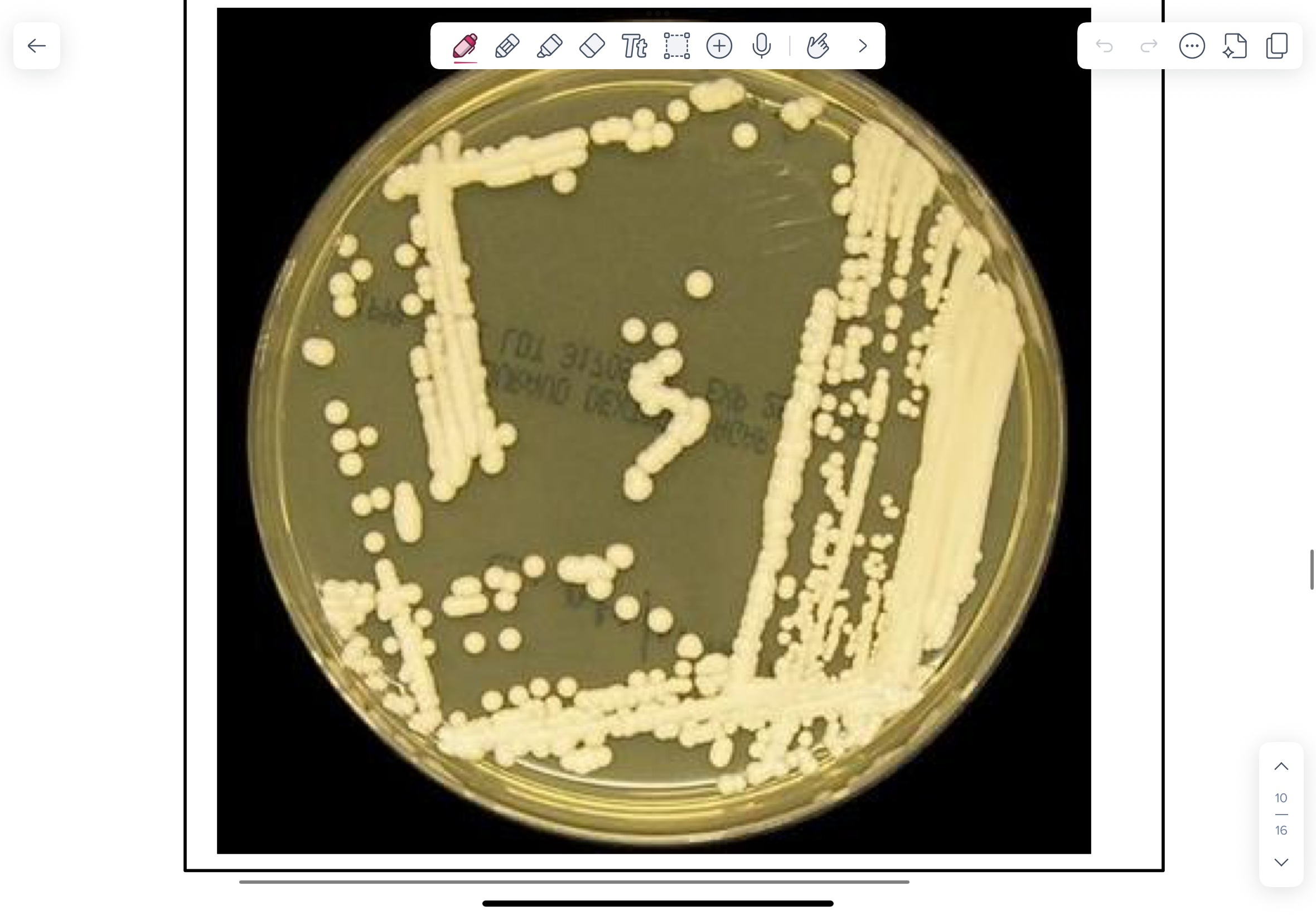
SAB culture of Cryptococcus neoformans incubated at 350C. Cryptococcus neoformans grows well on BA or SAB.
Small, mucoid, cream-coloured colonies.
India ink negative stain wet mount of Cryptococcus neoformans to demonstrate capsule.
NOTE the characteristic thick capsule and asymmetrically dividing yeast.
THERMALLY DIMORPHIC FUNGI
These are fungi that have two forms: a yeast (Sporothrix schenckii, Histoplasma capsulatum, Blastomyces dermatitidis) or spherule (sporangium) (Coccidioides immitis) in tissue/or culture carried out at 35C (i.e. - at body temperature), and a mould form at environmental temperatures (20C)
Histoplasma capsulatum
Thermally dimorphic fungi!
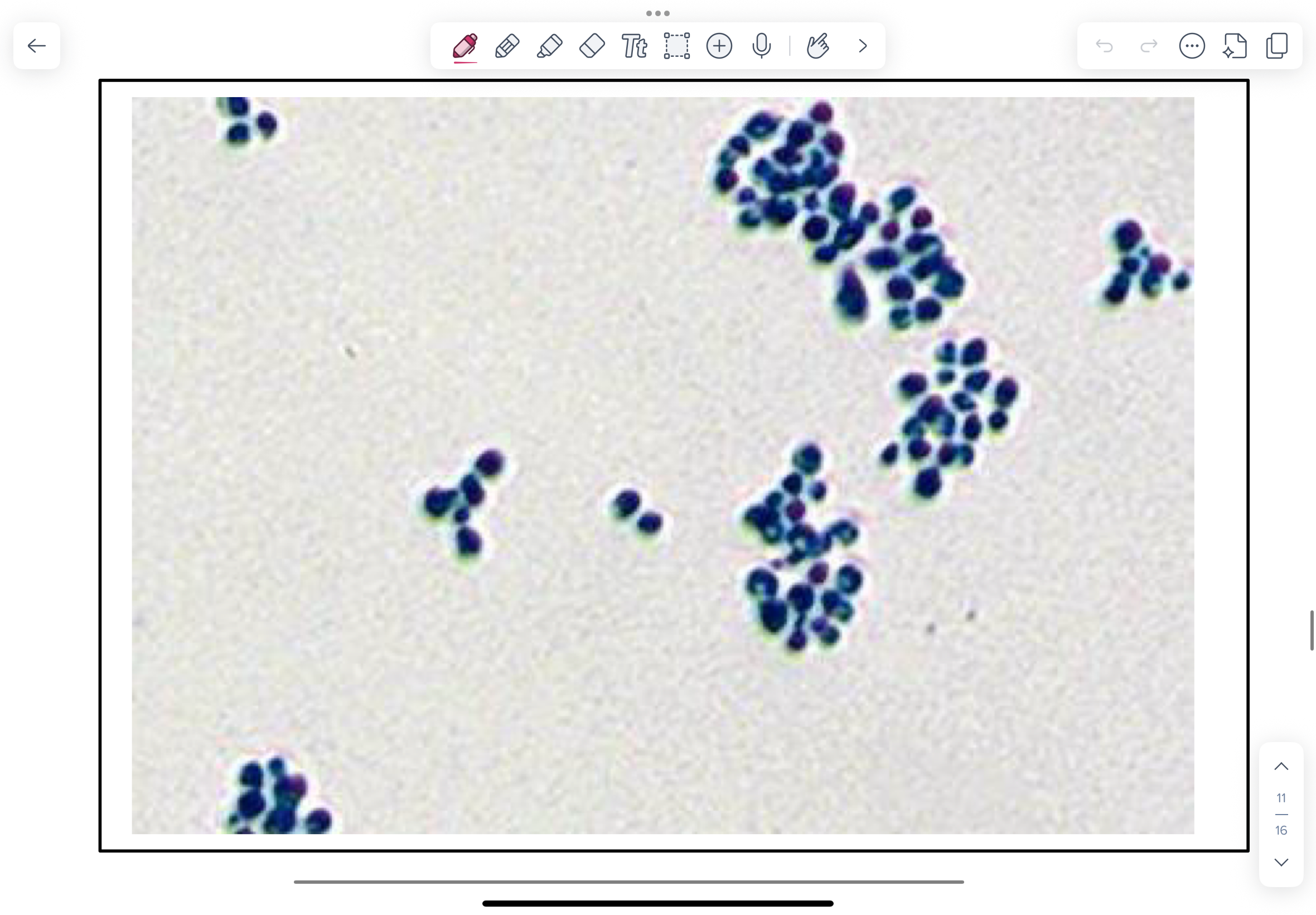
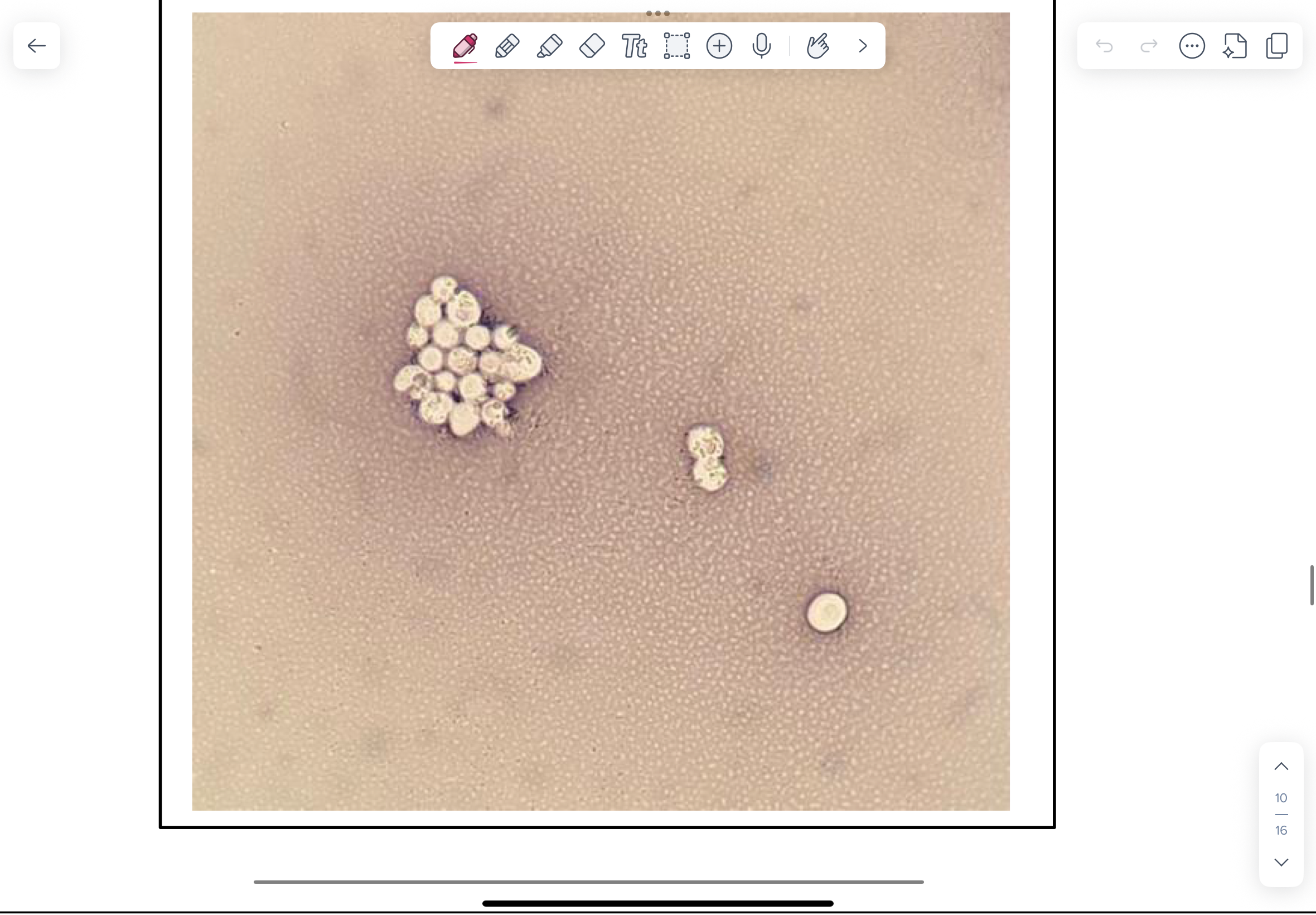
Photomicrographs of LPCB-stained Histoplasma capsulatum prepared from colonies grown at 200C and 350C.
NOTE septate hyphae and characteristic large tuberculate chlamydospores in the culture grown at 20C. Smaller microconidia attached directly to the hyphae may be present.
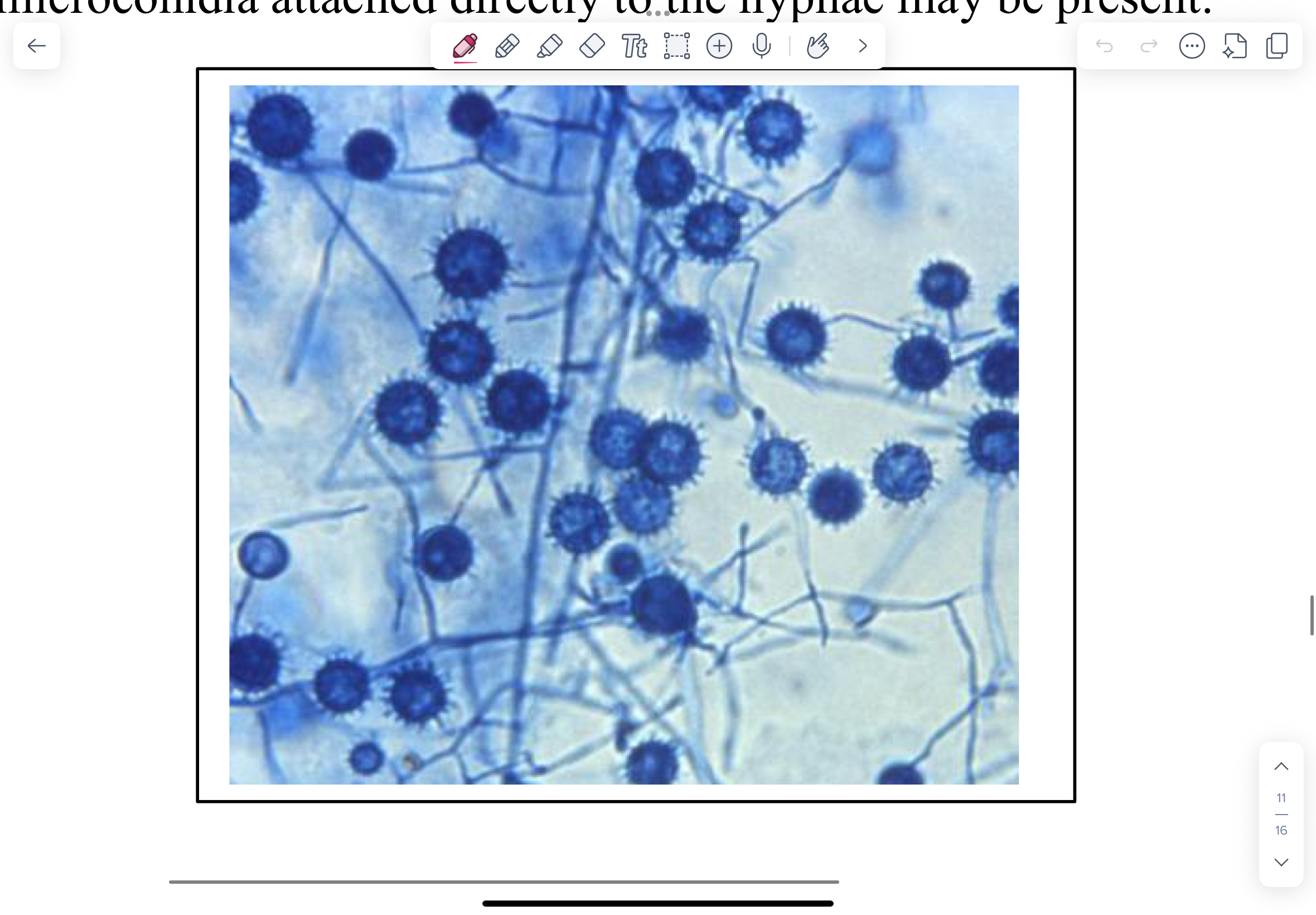
PAS-stained tissue section from an animal that died from histoplasmosis.
In this case it is often useful to go to the oil-immersion objective in order to visualize these small intracellular yeast.
NOTE small, light stained (red-purple) intracellular, budding yeast (2.0-4.0 μm).
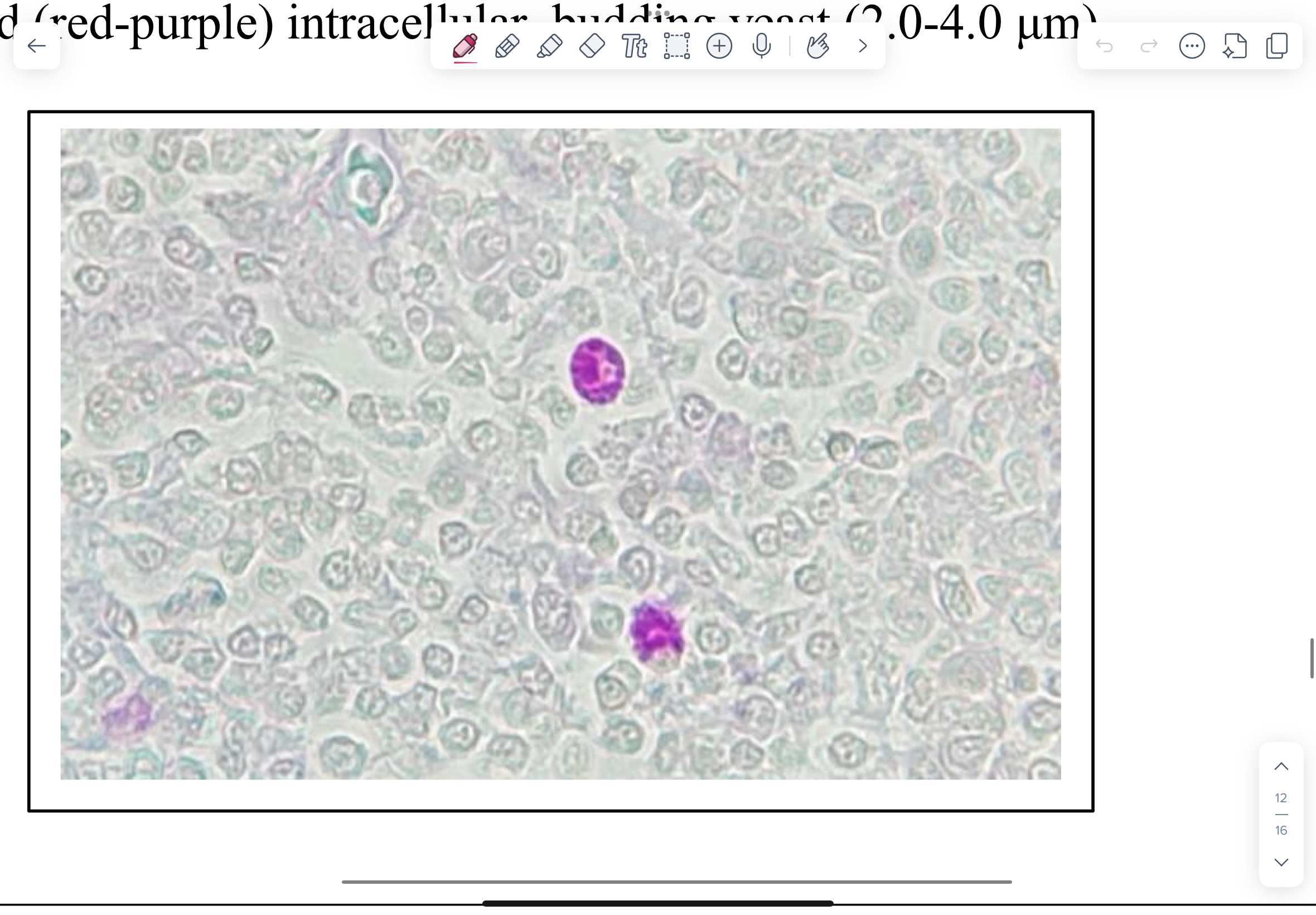
Blastomyces dermatitidis (Thermally)
Lungs (transtracheal aspirates), skin (exudates/aspirates), and brain (CSF) are sites where lesions commonly develop and would demonstrate Blastomyces dermatitidis yeast.
Methenamine silver-stained lung section from a dog with blastomycosis
NOTE large (8.0-15.0 µm), double-layered, envelope, budding yeast with a wide-base between mother and daughter cells.
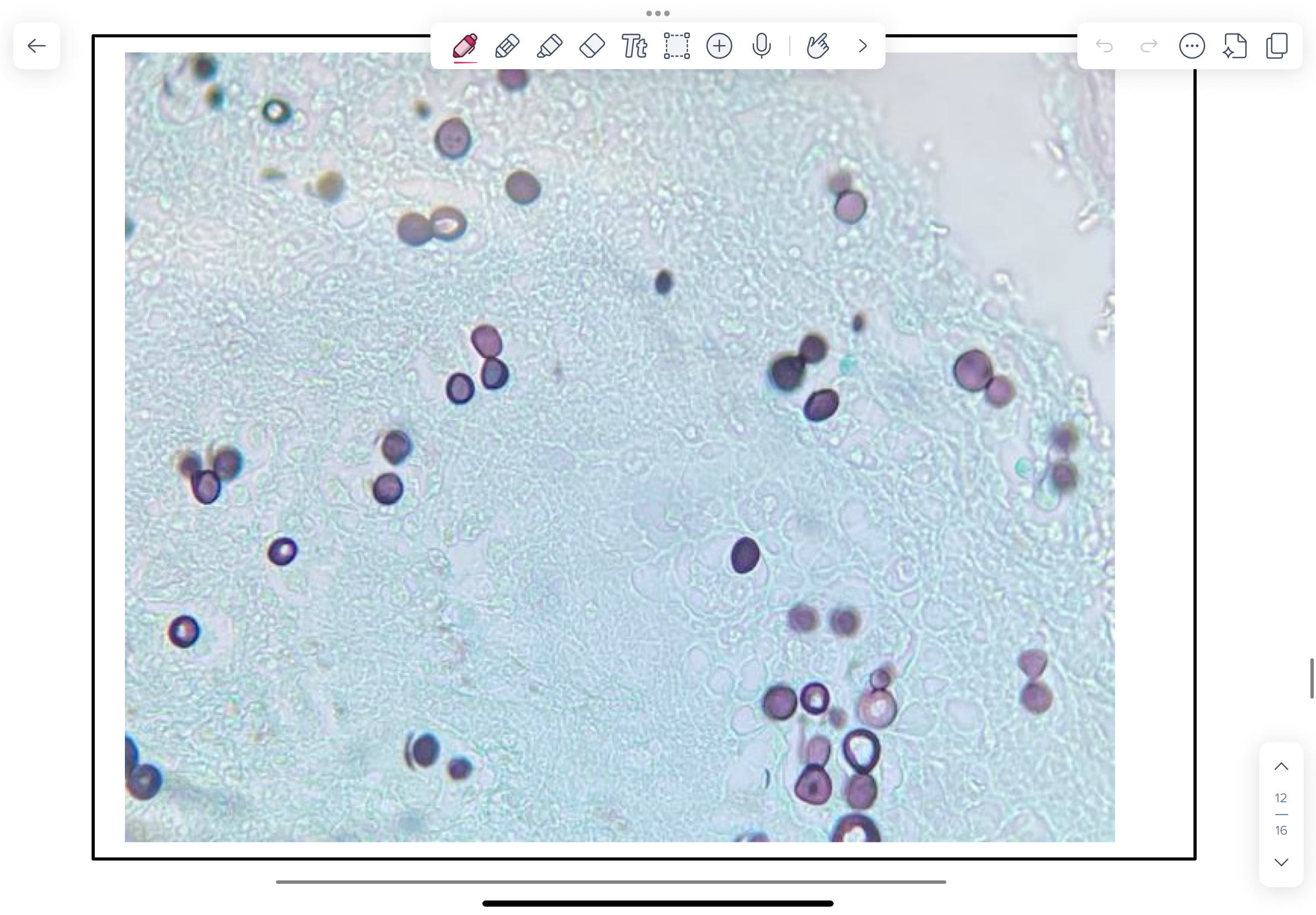
Coccidioides immitis (Thermally)
North American dogs with coccidiodomycosis will have a history of travel to south western United States (Arizona, Utah, New Mexico, California) or Mexico where Coccidioides spp. are endemic.
PAS-stained histological lung preparation from a dog with coccidioidomycosis.
NOTE endosporangia (called spherules) varying from 20µm (immature) to 200µm (mature and filled with infectious endospores) in diameter and surrounded by inflammatory cells.
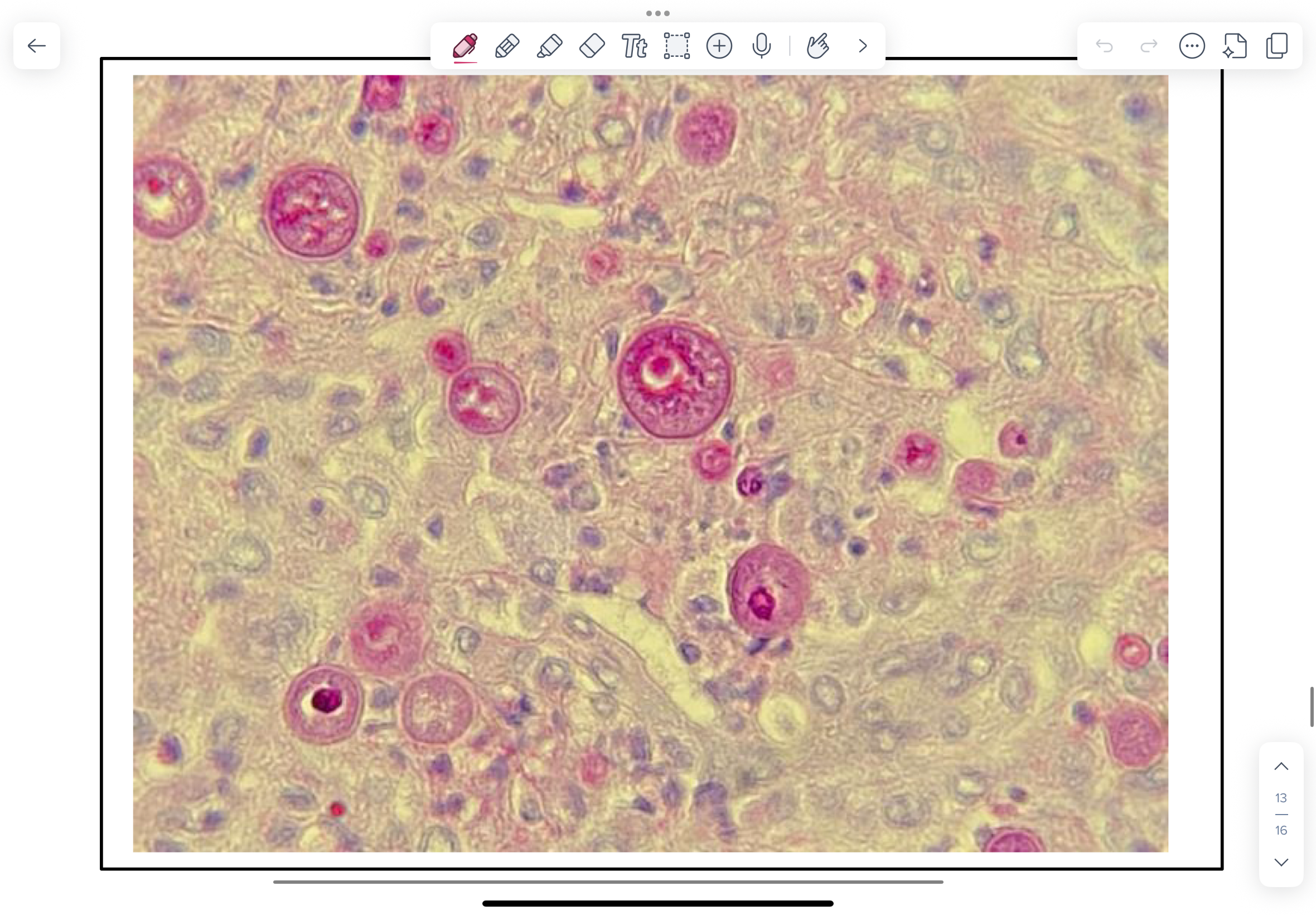
Sporothrix schenckii (thermally)
Sporothrix schenckii causes sporotrichosis (lymphocutaneous and disseminated disease) mainly in humans, horses, dogs and cats.
SAB cultures of Sporothrix schenckii incubated at 200C and 350C.
NOTE fuzzy, mold-like colonies on the SAB plate incubated at 200C
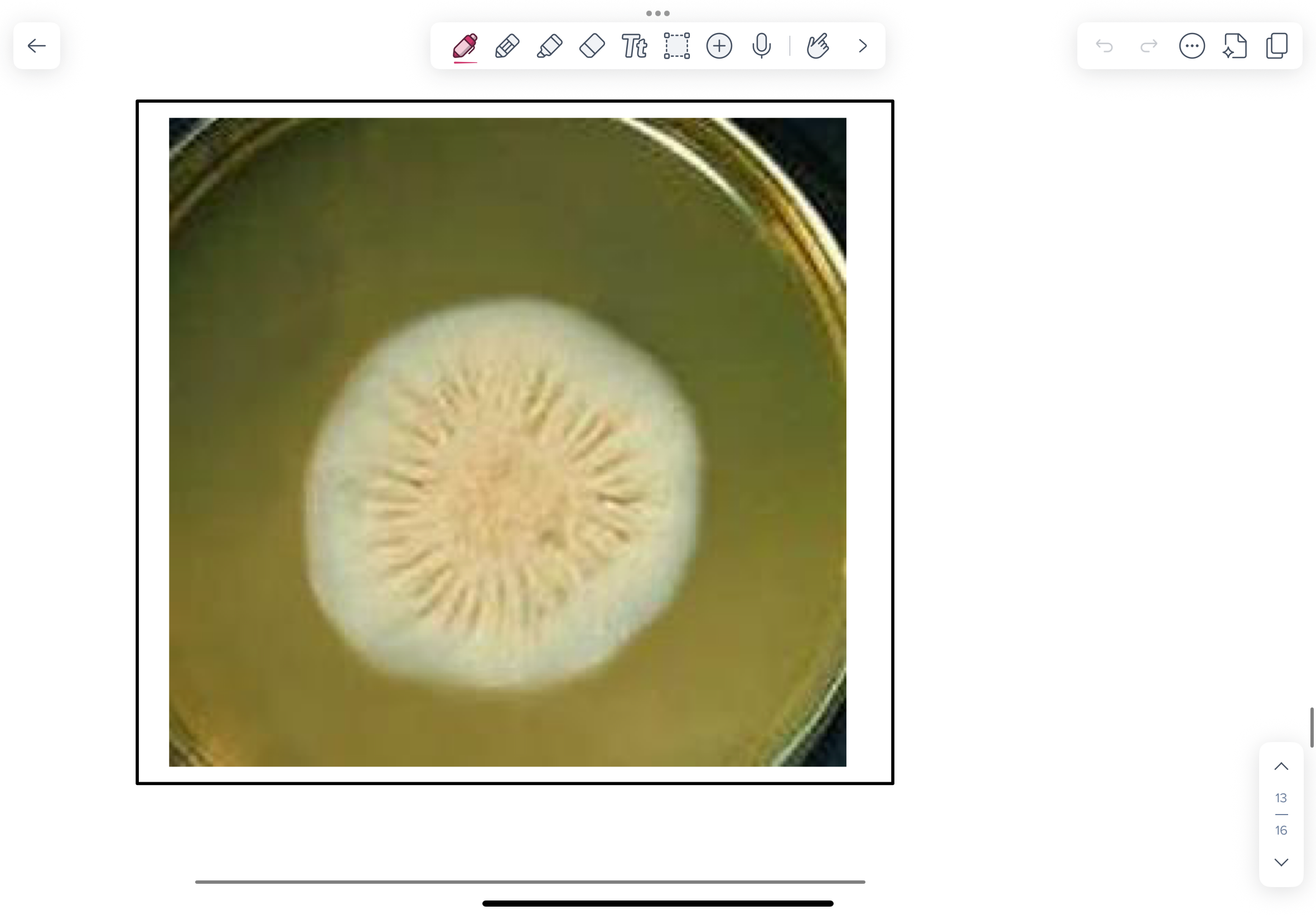
Sporothrix schenckii
A LPCB scotch-tape slide prepared from colonies taken from the 200C culture.
NOTE fine (1.0 -2.0 µm thick) branching, septate hyphae and flowerettes of pyriform conidia on short conidiophores. Typically these flowerettes fragment during preparation and conidia are often scattered.