🧪 C2
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
1
New cards
Pure substance
One single substance (properties are always the same) e.g. water, gold
2
New cards
Impure substance/mixture
Two or more substances mixed (properties vary) e.g. milk, sand
3
New cards
Element
A pure substance made for only one type of atom
4
New cards
Compound
Two or more different elements chemically bonded together
5
New cards
Mixture
Two or more different elements or compounds that are not chemically bonded together
6
New cards
Molecule
Two or more atoms chemically bonded together
7
New cards
Homogeneous mixture
Has the same composition throughout, and we cannot see the individual substances e.g. salt water, wine, steel
8
New cards
Heterogeneous mixture
Is not the same throughout, and we can see the individual substances e.g. oil and water, salt and pepper
9
New cards
Purification
Removing impurities so we are only left with the pure substance we want
10
New cards
Effect of impurities on melting points
Melting point decreases
11
New cards
Effect of impurities on boiling points
Boiling points increase
12
New cards
Can be used to measure the purity of a substance
Melting and boiling points
13
New cards
Filtration
A simple method used to separate a liquid from an insoluble solid e.g. water from sand
14
New cards
Crystallisation
A method used to separate a soluble solid from a liquid e.g. salt from water
15
New cards
Chromatography
Used to separate coloured dyes that are mixed together.
16
New cards
Chromatography process
A spot of ink is placed near the bottom of a piece of filter paper, the paper is then placed in a suitable solvent (water or ethanol), as the solvent soaks up the paper it carries the mixture with it, different components of the mixture will move at different rates - this separates the mixture out (due to differences in solubility)
17
New cards
Calculating an Rf value
Distance moved by the compound/Distance moved by the solvent
18
New cards
Rf value not
The value has to be less than 1
19
New cards
Simple distillation
A method used to separate a liquid from a soluble solid e.g. water can be separated from salt which is dissolved in the water
20
New cards
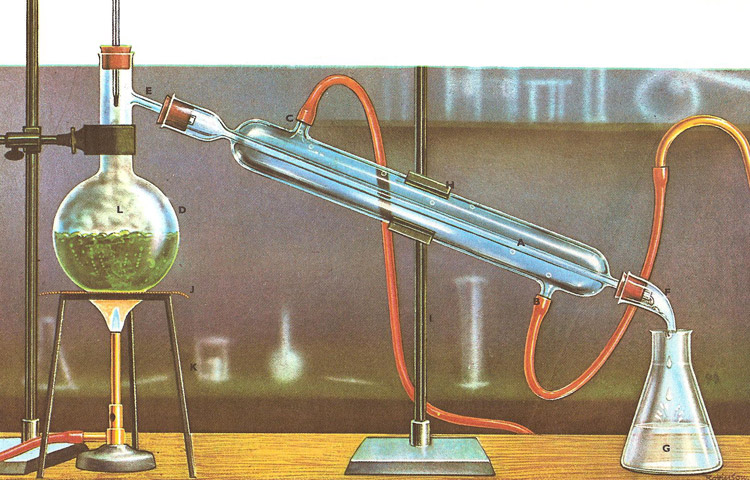
Simple distillation method
Leißig condenser cools the steam that is produced when the liquid is heated, this happens rapidly so you retrieve the distillate much quicker.
21
New cards
Fractional distillation
Method used to separate two or more miscible liquids from each other using the differences in their boiling points
22
New cards
Miscible
Liquids mix completely to form a homogeneous mixture
23
New cards
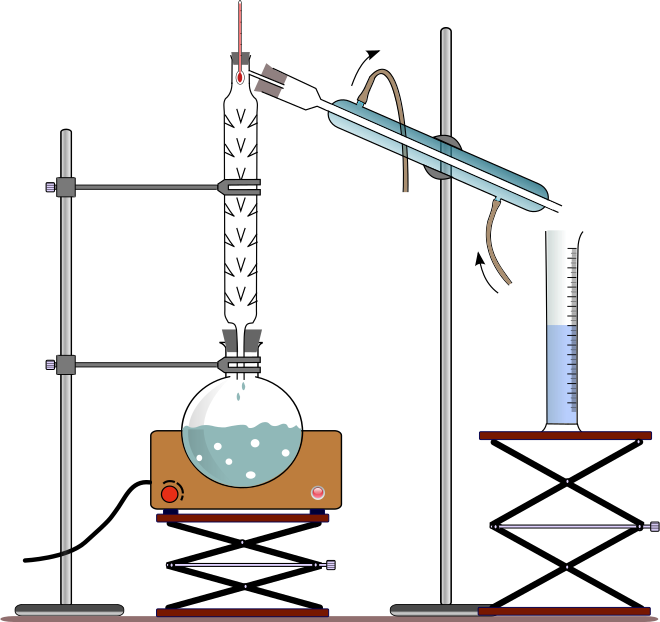
Fractional distillation method
The glass beads in the fractionating column provide a surface for condensation of the vapours to liquids. The liquid with the lower boiling point turns to vapour when it is heated and travels into the water condenser where it turns back to a liquid and is collected in a beaker
24
New cards
Diatomic molecule
A molecule containing only two atoms
25
New cards
Diatomic elements
Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine, Iodine
26
New cards
Hydrogen
H₂ Colourless, gas (at room temperature)
27
New cards
Nitrogen
N₂ Colourless, gas (at room temperature)
28
New cards
Oxygen
O₂ Colourless, gass (at room temperature)
29
New cards
Fluorine
F₂ Pale yellow, gas (at room temperature)
30
New cards
Chlorine
Cl₂ Pale green, gas (at room temperature)
31
New cards
Bromine
Br₂ Red/brown, liquid (at room temperature)
32
New cards
Iodine
I₂ Purple, solid (at room temperature)
33
New cards
The metallic elements
Shiny, dense, high melting point solids which are excellent conductors of heat and electricity. They are highly malleable and ductile. Tend to form positively charged ions. e.g. Lead (Pb), Mercury (Hg)
34
New cards
Ductile
Can be drawn into wires
35
New cards
Malleable
Can be bent and shaped
36
New cards
The non-metals
Non-shiny and volatile with low density. They are poor conductors of heat and electricity and are not malleable or ductile. e.g. Carbon (C), Bromine (Br)
37
New cards
The metalloids (semi-metals)
Difficult to categorise as metals or nonmetals because they show properties of both e.g. Silicon is hard and shiny with some conductivity but is brittle with low density
38
New cards
Group 1
The alkali metals
39
New cards
Group 2
The alkali earth metals
40
New cards
Group 7
The halogens
41
New cards
Group 0 (8)
Noble gases
42
New cards
Between groups 2&3
The transition metals
43
New cards
Number of shells
Period number
44
New cards
Number of electrons in outer shell
Group number
45
New cards
Makeup of an atom
Atoms are made of even smaller particles called subatomic particles
46
New cards
Subatomic particles
Proton, Neutron, Electron
47
New cards
Proton
Positive charge
48
New cards
Neutron
No electrical charge
49
New cards
Electron
Negative charge
50
New cards
Where protons and neutrons are found
Exist in a dense core at the centre of the atom, called the nucleus
51
New cards
Where electrons are found
Spread out around the edge of the atom. They orbit the nucleus in layers called shells.
52
New cards
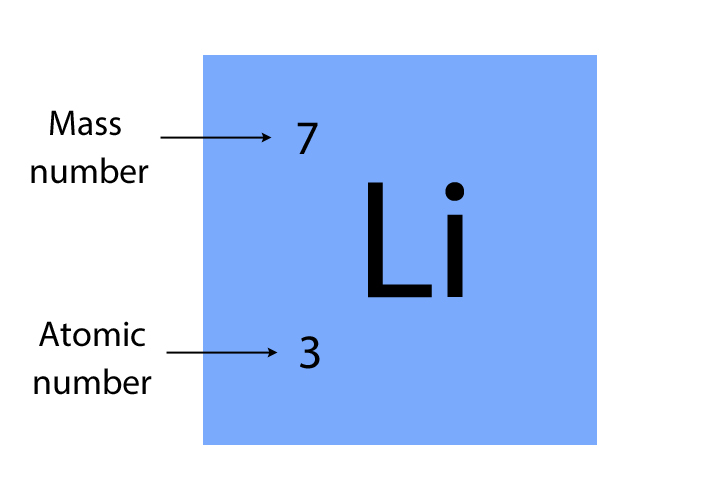
Relative atomic mass (mass number)
The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus
53
New cards
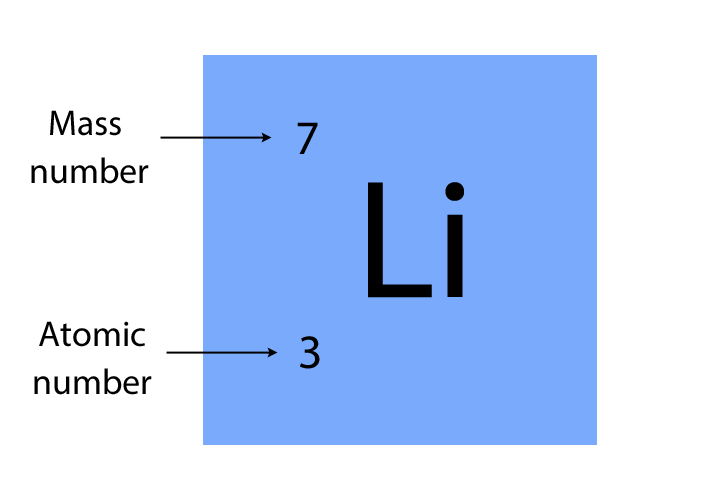
Atomic number
The number of protons in the nucleus
54
New cards
Isotope
Atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons (same atomic number, different mass number)
55
New cards
pH scale
Tells you how acid or alkali something is
56
New cards
1-6
Acid
57
New cards
8-14
Alkali
58
New cards
7
Neutral
59
New cards
1
Strong acid
60
New cards
6
Weak acid
61
New cards
9
Weak alkali
62
New cards
14
Strong alkali
63
New cards
Alkali metals
Lithium, Sodium, Potassium, Rubidium, Caesium, Francium
64
New cards
Properties of Alkali metals
Softness, density and reactivity increase as you go down the group, all have 1 electron in their valance (outer) shell, the shine will tarnish quickly in air due to the reaction with oxygen, all react vigorously with water
65
New cards
The Halogens
Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine, Iodine
66
New cards
Properties of Halogens
All have 7 valence electrons, non-metals, diatomic molecules, reactivity and volatility decreases down the group, density and melting points increase down the group
67
New cards
Displacement
When a halogen is added to a solution of a compound containing a less reactive halogen, it reacts with the compound to form a new one
e.g. fluorine + sodium chloride → sodium fluoride + chlorine
e.g. fluorine + sodium chloride → sodium fluoride + chlorine