GEC 5 - Purposive Com. (Prelims)
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
System of Rules
Sound System
Vocabulary
What is a Language according to Linguists?
Phonology
“Sound System”
Grammar
“System of Rules”
Lexicon
“Vocabulary”
Speech Community
composed of people sharing the same set of rules in the language system
Language Acquisition
is the process where people acquire the languages used by those in the community
Language Learning
is the process where people learn languages for various reasons
First Languages
or Mother tongue, is a Language acquired while growing up
Second Languages
are languages learned by studying formally in school or informally on their own.
Language contact
occurs when people with different languages interact, communicate, and exchange ideas
Language Change
This is the result of language contact.
Communication
the exchange of ideas, thoughts, concepts, and views between and among two or more people, various contexts come into play.
Context
is the environment in circumstance or which communication takes place.
Communication Mode
Context
Purpose and Style
Classifications of Communication
Verbal-non-verbal communication
Visual Communication
2 Communication Mode Types
Verbal-non-verbal Communication
A type of communication where one cannot be separated from the other.
Visual Communication
is the type of communication that uses visuals to convey information and/or messages. Some examples are signs, symbols, imagery, maps, graphs, charts, diagrams, photos, drawings, and even forms of electronic communication.
Intrapersonal
Interpersonal
Extended
Types of Context Communication
Intrapersonal Communication
A type of communication when The Latin prefix intra- means within or inside. Means talking to oneself.
Self-verbalization or Self-statement
Other term for when one communicates with oneself as per psychologists
Interpersonal Communication
A type of communication wherein the Latin prefix inter- means between, among, and together.
Interpersonal Communication
A communication situation is _______ if it is meant to establish a deep or emotion relationship
Transactional Communication
A type of formal and profound communication wherein there is an objective to achieve something at the end of the conversation, it becomes
Extended Communication
It involves the use of electronic media. Unlike before when it only called for the use of television and radio, nowadays, the description of extended communication may be expanded to include radio or phone conferencing; video-conferencing; Skype calls; and other technological means.
Formal and Informal Communication
Types under Purpose and Style Communication
Formal Communication
employs formal language delivered orally or in written form. Lectures, public talks/speeches, research, and project proposals, reports, and business letters, among others, are all considered formal situations and writings
Formal Communication
To inform, to entertain, and to persuade are the main objectives of this type of communication.
Informal Communication:
certainly does not employ formal language. It involves personal and ordinary family conversations with friends, members, or acquaintances under the sun.
Clear, Concise, Concrete, Correct, Coherent, Complete, Courteous
7C’s of Communication
7
How many C’s are given in communication
Schreiner 2018
Who gave the process of Communication?
Creation
A communication process that is the forming of the communicative intent where the sender generates an idea.
Transmission
A communication process where it may be as simple as meeting with the intended recipient of the message, and orally sharing the message, or calling the individual to communicate orally over the phone.
Reception
A communication process wherein after transmitting the message, the communication duties change hands and fall upon the receiver of the message.
Translation
A communication process wherein once receiving the message, the recipient must translate the message into terms that s/he can easily understand.
Response
A communication process wherein this may be verbal and immediate, which is commonly the case if communication is face-to-face.
Creation > Transmission > Reception > Translation > Response
Give the 5 Process of Communication (Format: ___>___)
Sender
An element of communication: a person, group, or organization who initiates communication.. -She/He may be called the source, encoder, speaker, or communicator.
Message
An element of communication: transmitted in communication. It may consist of the idea, opinion, information, feeling, or attitude of the sender.
Channel
An element of communication: a pathway or medium through which the message travels to reach its destination. It may be oral, written, or visual.
Receiver
An element of Communication: a person who receives, analyses, understands, and interprets the message.-S/he can also be called a decoder, reader, or listener.
Feedback
An element of communication: the receiver's response that provides information to the sender.
Noise
An element of communication: a form of distortion, barrier, or obstacle that occurs in the oral communication process.
Adjustment
An element of communication: done if the message is distorted or is not clearly understood by the receiver.
Context
An element of communication: It is the situation from which the communication is done.
8
How many elements of communication are there?
5
How many communication processes are according to Schreiner
Sender, Message, Channel, Receiver, Feedback, Noise, Adjustment, Context
Give the 8 elements of communication (Format: ___,___)
Ethics of Communication:
This emphasizes that morals influence the behavior of an individual, group, or organization thereby affecting their communication.
Establish an effective value system that will pave the way for the development of your integrity as a person.
What is the first ethics of communication
Provide complete and accurate information.
Second ethics of communication
Disclose vital information adequately and appropriately.
Third ethics of communication
Communication Models
A model is an abstract. It is a representation of a real-world phenomenon applied to different forms. The interplay of variables in the model is represented graphically.
Aristotle Model
one of the oldest communication models, introduced by Aristotle, a Greek philosopher. It focuses on public speaking and persuasion.
Aristotle Model
Features of This Model:
One-way
With a passive audience
Lacks feedback and noise
Occasion = Context
Speaker is the most important element
Speaker
What element is the most important in Aristotle Model
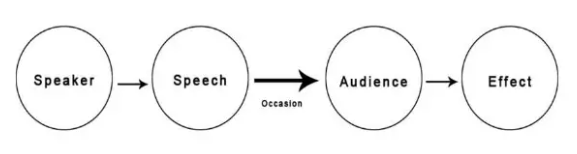
Aristotle Model
What type of Model?
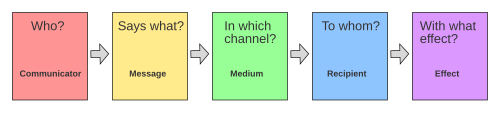
Lasswell’s Model
What type of Model?
Harold Lasswell
Who Developed Lasswell’s Model
Lasswell’s Model
Features of this model:
One-way communication
Message flows from sender to receiver only
Useful for studying mass communication (e.g. media..)
Has feedback, but not properly returned
Who, Says What, In Which Channel, To Whom, With What Effect
What are the elements of Lasswell’s Model (Format: ___,___)
Lasswell’s Model
What model is useful for studying mass communication?
Shannon–Weaver’s Model
this model explains communication as a technical process of transmitting information, originally designed for telephone and signal systems
Claude Shannon and Warren Weaver
Who developed the Shannon-Weaver’s Model?
1949
What year was Shhanon-Weaver’s model created?
Features of this Model:
Two-way communication
Acknowledges noise
Has feedback and is returned
Shannon-Weaver’s Model
Known as “mother of all models”
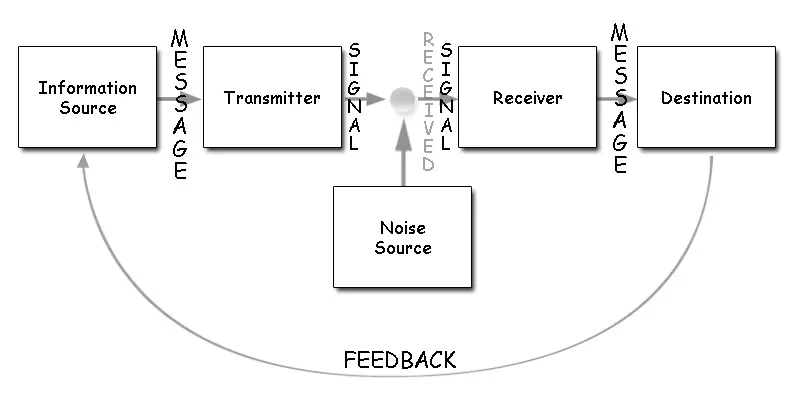
Shannon–Weaver’s Model
What model is this?
SMCR Model
Proposed by David K. Berlo in 1960, this model explains communication using four major components
David K. Berlo (1960)
Who developed the SMCR Model and in what year?
SMCR Model
Features:
One-way communication,
Highlights the importance of culture, knowledge, and attitudes in communication.
No feedback
Passive reception
SMCR Model
What model highlights culture, knowledge, and attitudes in communication
Source (Sender), Message, Channel, Reciever
What are the four components of David Berlo’s Model? (Format: ___,___)
Communication skills
Attitude
Knowledge
Social system
Culture
Components of the Source (Sender) of SMCR model
Content
Elements
Structure
Code
Treatment
Components of the Message of SMCR model
Hearing
Seeing
Touching
Smelling
Tasting
Components of the Channel of SMCR model
Communication skills
Attitude
Knowledge
Social system
Culture
Components of the Receiver of SMCR model
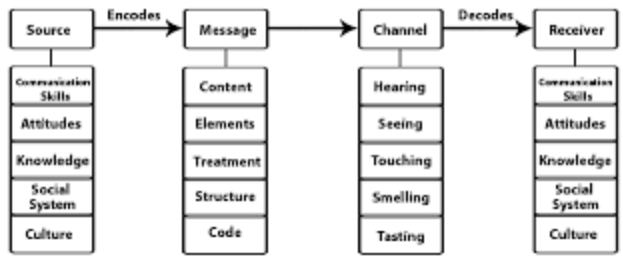
SMCR Model
What type of Model?
One-Way
What way of communication is Aristotle Model?
Two-Way
What way of communication is Shannon-Weaver’s Model?
One-way
What way of communication is Lasswel’s Model
One-Way
What way of communication is SMCR Model?