Pathogens
Germ Theory
Diseases are caused by microorganisms
Biohazards
biological substances is a threat to human health
Epidemiology
branch of medicine wich deals with diseases
Public health
protects health of people and their communites
Epidemics
widespreas disease in community with large part of them infected at one time
Pandemics
Widespread disease in a country with a large part effected at one time
Viruses
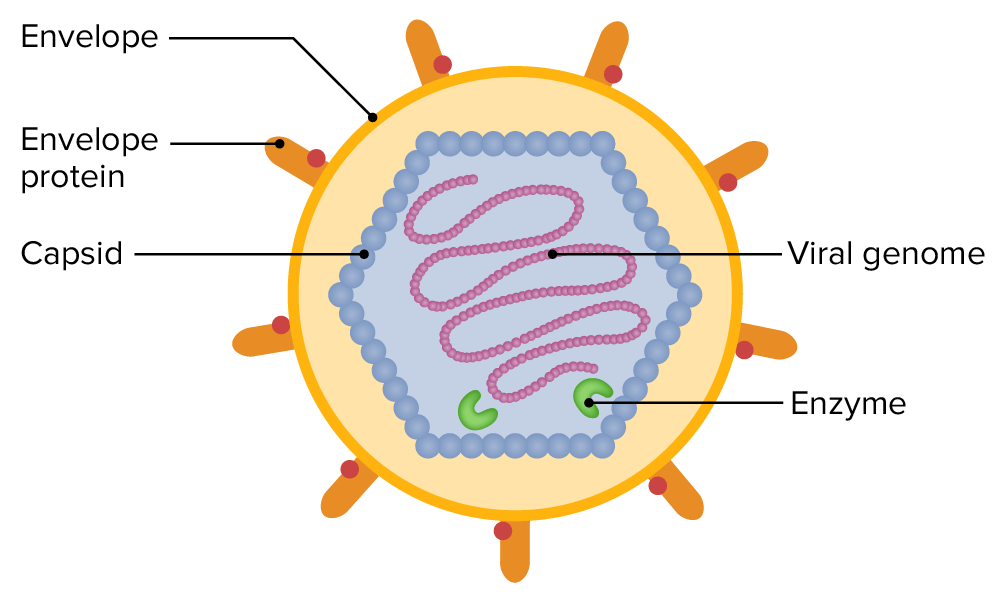
genome
the dna or rna housing center
Capsid
protien coat around genome
compased of protiens
has enzymes need for replication
Enveolpe
covers capsid
made of protiens and lippids
has protiens needed to attach to host cell
Virus life cycle
attaches, enters host cell, starts replicating, exit cells
Attached via keys
Naked:
no envelope
receptors attached to capsid
How they enter host cells 2 ways
Punch hole in host cell
enter via endocytosis then punch through endosome membrane
How they exit host cell
Fills cell with bacteria then burst
Enveloped:
envelope
How they enter the cell 2 ways
Fuse with membrane
Taken by enocytosis then fuse with endosome membrane
How they exit
Forms and buds off of cell, taking some cell membrane with it
can destroy host cell receptor
Aseptic Tequnice
procedures to avoide contamination
prevents extra stuff on petridish
Gloves
prevent contamination from hands
Petri dish
keeps bacteria contained
needs to be placed upside down in incubator
Enoculation loop
collect bacteria
LB nutrient Agar
growth medium for bacteria
Incubator
maintains constant optiomal tempature
Petri dish labeling
on bottom
Streaking
so you can see individual colonies
Shape of colonies
circular
irregual,
filamentous
rhizoid
Elevation
raised
convex
flat
umbonate
cratiform
Margin
entire
undulate
filaform
curled
lobate
Coloney Morphologies and Arrangments
Bacillus
Rod shaped
Coccus
circle
Spirialla
curcled ribbion
Diplo
clump to only one other, pair
Straphylo
large mulriply culmp
Stepto
straight line
Agents of Disease
Viruses
nonliving particles with DNA or RNA that infect cells and replicate
Bacteira
prokaryote that can be both beneficial or harmful
Fungi
eukayotes related to mushrooms some cause infections
Protozoa
single celled microscopic animals wich act as para sits
Prions
infectious protien
helminths
multicellurla parasitic worms that use humans as hosts
Reservoir
habitats where infectious agents live, grow, and multiply\
Portals of exit
how it leaves the host
Modes of transmisison
direct
transfer immediately between hosts
indirect
can be housed temporaly
ex: contaminated surfaces
Portals of entry
how it enters the body
immune system is made up of many cells, organs, and tissues. Some prevent pathogens from entering the body, and some attack pathogens already inside the body.
Most immune cells develop from stem cells in the bone marrow.
The immune system responds to pathogens in two main ways:
innate and adaptive immune responses.
These types of responses communicate with and complement each other.
The innate immune response is the body’s first line of defense.
barriers to infection
Skin
Mucus
phagocytes
Eats disease
mast cells
alarm system
inflammation
Raises temp
helps to raise defense
The adaptive immune response takes longer to mount but provides more specific protection against pathogens.
T cells
Helper
has the neccasy receptor to bind to antigen
Killer
kills it
They stick around to remeber the infection
B cells
Create antibodies
antibodies.
The immune system reacts to antigens, small molecules recognized by immune cells
After the first infection by a specific pathogen, the adaptive immune response can mount a greater and faster response to subsequent infections.
Vaccines stimulate an immune response to a weakened or partial pathogen so that the secondary immune response can occur when the real pathogen is encountered