PDA II Osteoporosis
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Normal blood Ca level
10 mg / 100 mL
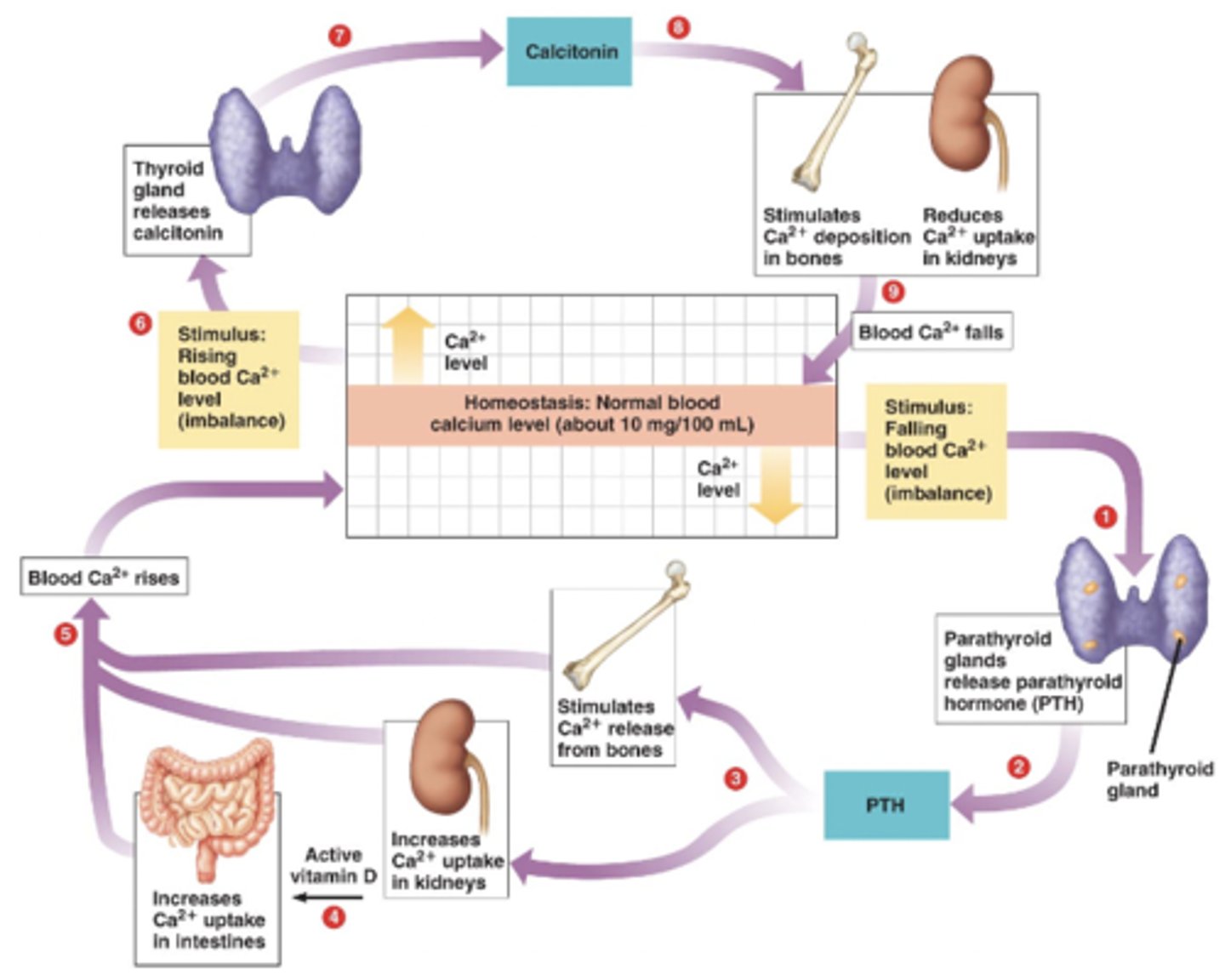
2 hormones for Ca homeostasis
-PTH
-Calcitonin
PTH
-Parathyroid hormone
-Released from parathyroid gland
-Stimulus: falling blood Ca levels
3 effects of PTH
-Stimulates Ca release from bones
-Increases Ca uptake in kidneys
-Increases Ca uptake in intestines
-All work to increase blood Ca2+ levels
Calcitonin
-Released from thyroid gland
-Stimulus: rising blood Ca levels
2 effects of calcitonin
-Stimulates Ca deposition in bones
-Reduces Ca uptake in kidneys
-Both work to reduce blood Ca levels
Osteoporosis
-Porous bone
-A condition where bone resorption exceeds bone formation
-Low bone mineral density (BMD)
-Disrupted bone architecture
-Fracture with minimal trauma
Resorption
-The process of removing or digesting old bone tissue
-Getting rid of bone
Deposition
-The process in which new bone is laid down
3 treatment strategies
-Inhibit bone resorption: decrease osteoclasts (antiresorptive)
-Promote bone formation: increase osteoblasts (anabolic agents)
-Inhibit bone resorption and promote bone formation (combo agents)
2 types of antiresorptive agents
-Nutritional supplements (standard therapy)
-Prescription medications
2 types of nutritional supplements
-Calcium
-Vitamin D
Calcium medications
-Ca carbonate
-Ca citrate
-Ca phosphate
-Ca lactate
-Ca gluconate
Calcium Carbonate
-Commonly used due to higher ratio of Ca to total weight
-Requires an acidic environment for absorption
-Take with food (stimulate acid secretion) to improve absorption
Calcium carbonate drug interactions
-PPIs
-H2 blockers
-Antacids
-All decrease acid in the body (decrease absorption of calcium carbonate)
Calcium citrate
-Less dependent on acid secretion for absorption
-Useful in pts with achlorhydria, IBS, absorption disorders, or those on H2 blockers / PPIs
Achlorhydria
-Lack of hydrochloric acid in the stomach
Calcium citrate adverse effects
-GI disturbances
-Constipation
-Kidney stones (rare)
Vitamin D drugs
-Ergocalciferol (vitamin D2)
-Cholecalciferol (vitamin D3)
-Calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3)
How does vitamin D relate to calcium?
-Intake from the sun and food
-25-hydroxylase in liver converts cholecalciferol and ergocalciferol into calcifediol
-1-hydroxylase in kidney convert calcifediol to calcitriol
-Calcitriol maintains calcium balance in the body
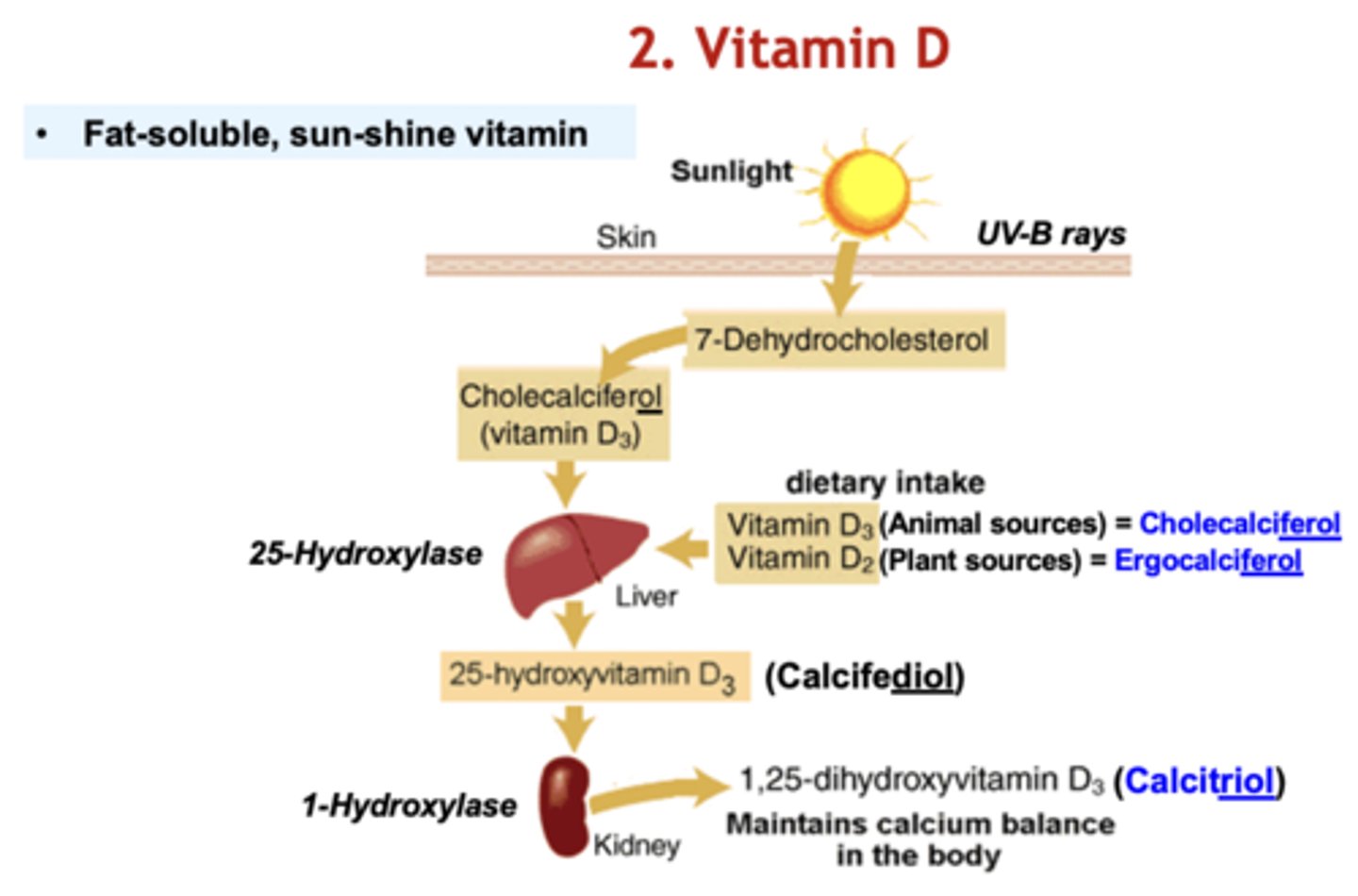
Vitamin D in combo with calcium
-Improves Ca absorption
-Improves bone mineral density
Vitamin D in pts with severe hepatic or renal disease
-Administer calcitriol
-Other forms can't be hydroxylated into active form in liver / kidney
Vitamin D adverse effects
-Hypercalcemia
-Hypercalciuria: nephrolithiasis (kidney stones)
5 classes of prescription medications
-Bisphosphonates
-RANK-L Antagonists
-Hormone replacement therapy
-Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs)
-Calcitonin
Bisphosphonates (BPs) drugs
-Alendronate (oral)
-Risedronate (oral)
-Ibandronate (oral and IV)
-Zoledronate (IV)
-Pamidronate (IV)
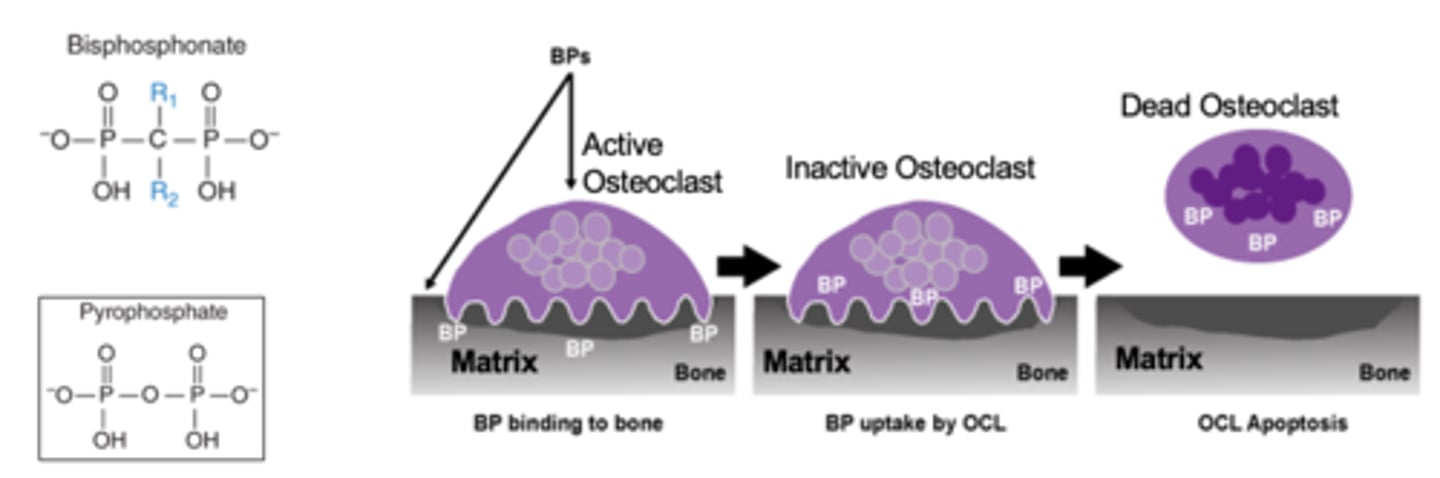
BP MOA
-Analogs of pyrophosphate
-Bind to Ca and get incorporated into bone matrix and taken up by osteoclasts
-Within osteoclasts, BPs inhibit prenylation (attachment of certain lipids) to multiple proteins
-Decrease osteoclastic activity through apoptosis
-Increase bone density
BP absorption
-Poorly absorbed orally
-1-6% bioavailability
-Presence of food and beverages decreases oral bioavailability
-Must be given on an empty stomach or IV
BP half life / administration
-50% of the dose accumulates in bones and remains for months
-Long biologic half lives of up to 10 years
-Zoledronate: greatest bone absorption and longest bone retention (given as IV infusion yearly or q 2 years)
-Other BPs: administered daily, weekly, or monthly basis
-Excreted in the urine
BP clinical uses
-Mainstay agents to prevent and treat osteoporosis
-Post-menopausal and corticosteroid induced
Pamidronate clinical use
-Hypercalcemia (too much Ca in blood) that may occur in pts with some types of cancer
-Bone weakness or pain caused by myeloma or breast cancer that has spread to bones
Oral BP adverse effects
-Heartburn
-Dyspepsia
-Esophageal irritation and ulcer
-Osteonecrosis of jaw
-Take drug on empty stomach with a glassful of plain water and remain upright for 30 mins (60 mins for ibandronate)
IV BP adverse effects
-Flu like symptoms
-Musculoskeletal pain
-Injection site reactions
-Osteonecrosis of jaw
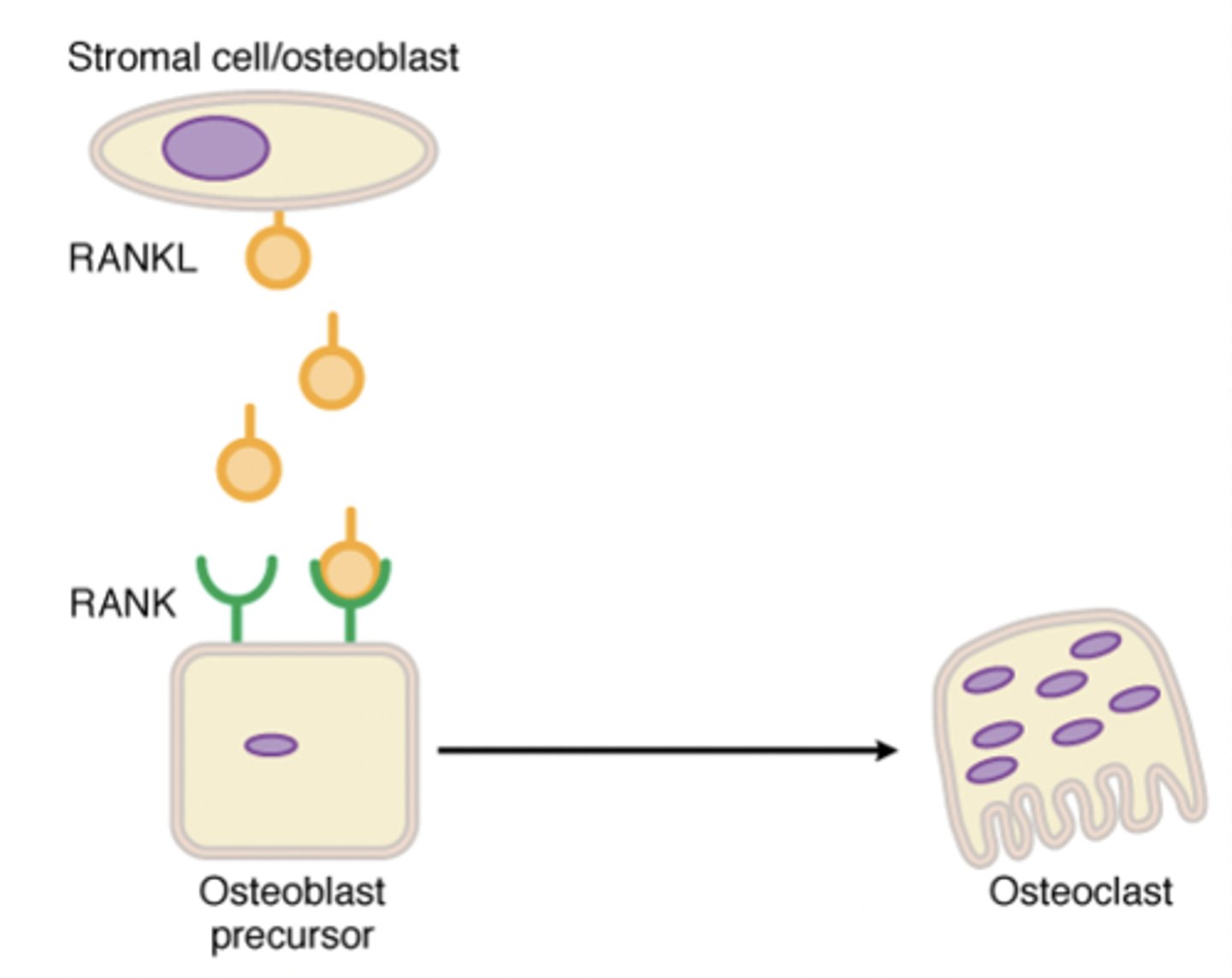
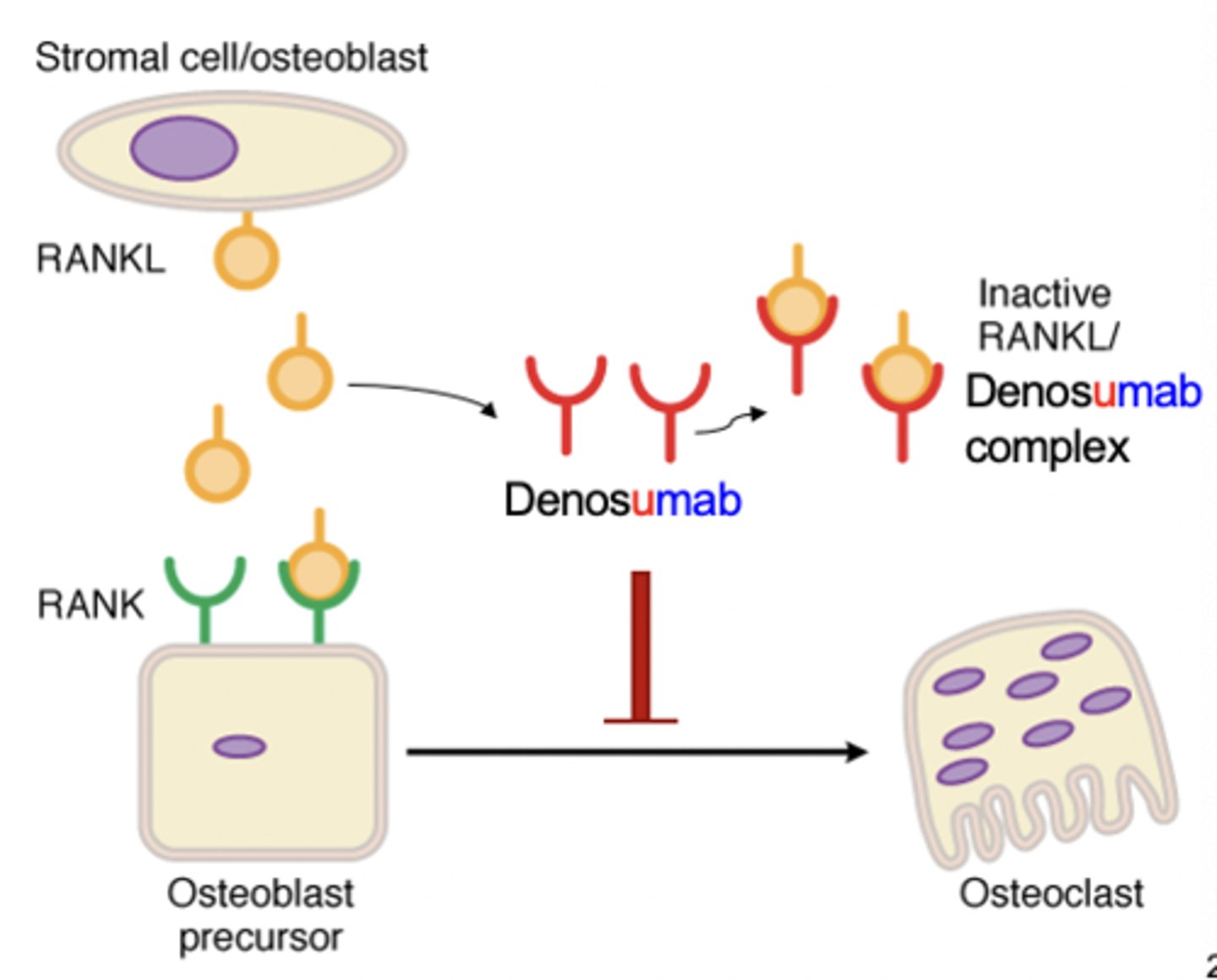
RANK ligand
-A natural ligand that acts on the receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B (RANK) present on osteoblast precursor cells
-Stimulates differentiation into osteoclasts
-Bone resorption (releases Ca into blood)
-Pro-osteoclast
RANK-L antagonist drugs
-Prolia (denosumab): human monoclonal antibody to RANK-L
RANK-L antagonist MOA
-Inhibits binding of RANKL to RANK
-Decrease osteoclast formation
-Decrease bone resorption
RANK-L antagonist clinical use
-Post-menopausal osteoporosis
-SC injection q 6 months
RANK-L antagonist adverse effects
-Hypocalcemia
-Monitor pt's plasma calcium levels
-Boxed warning: increased risk for severe hypocalcemia in pts with advanced chronic kidney disease (CKD)
SERM drugs
-Raloxifene
-Bazedoxifene
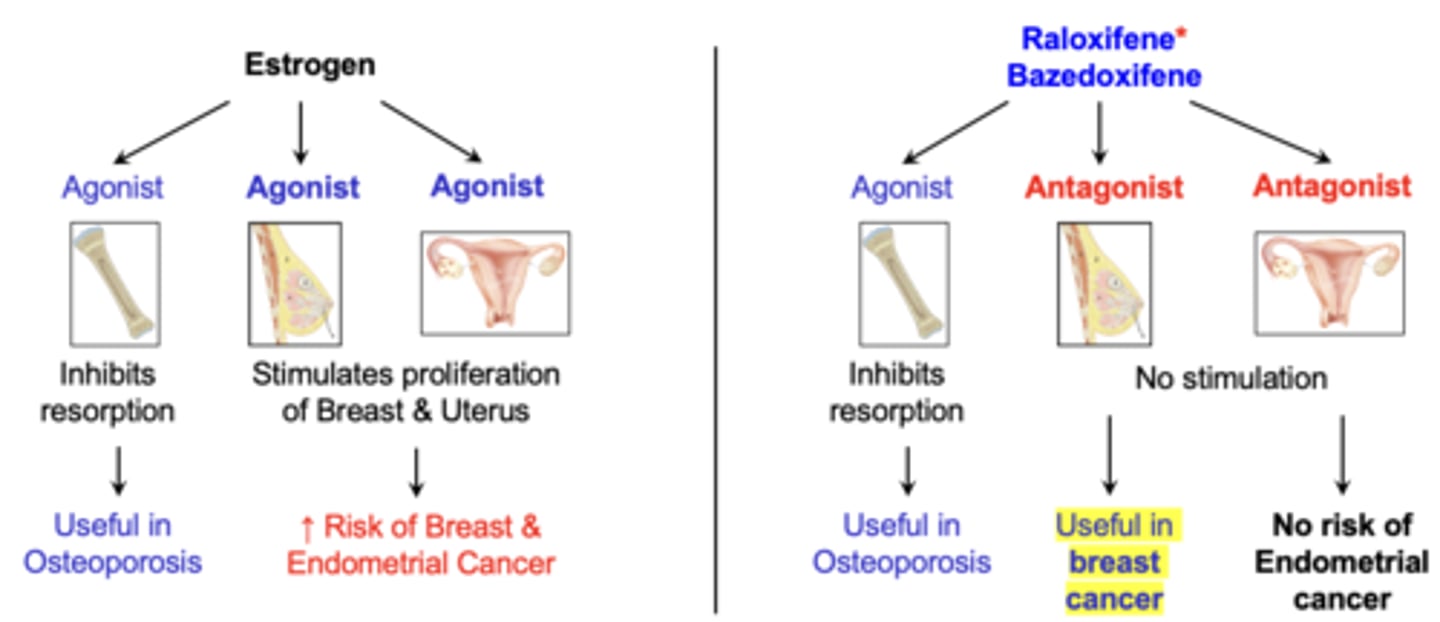
SERMs
-Bind to estrogen receptors and produce tissue-selective effects on target organs
-Agonist: bone (useful in osteoporosis)
-Antagonist: breast and uterus (useful in breast cancer, no risk of endometrial cancer)
SERM MOA
-Inhibit osteoclast formation and recruitment (like estrogen)
-Modestly increase bone density and decrease vertebral fractures (not as effective as estrogen)
SERM advantage and clinical use
-Reduce risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women and in women with a family history of breast cancer
-Prevent and treat osteoporosis
SERM adverse effects
-Hot flashes (anti-estrogen effects on the brain)
-Venous thromboembolism (estrogenic effects on liver)
Calcitonin drugs
-Fortical
-Miacalcin
Calcitonin MOA
-Inhibits osteoclastic bone resorption by converting active osteoclasts into resting stage
-Modest increase in bone mass
Synthetic calcitonin
-Human and salmon
-Salmon calcitonin: longer half life and 40x higher potency to human calcitonin receptor
Calcitonin clinical uses
-Intranasal spray or SC/IM injection for postmenopausal osteoporosis
-Least effective compared to other anti-resorptive drugs
Calcitonin adverse effects
-Nasal: rhinitis, epistaxis (nose bleeds)
-Injection: nausea, flushing, irritation
Anabolic agent drug class
-Parathyroid hormone (PTH) analogs
PTH analog drugs
-Teriparatide: recombinant human PTH fragment (rhPTH 1-34)
-Abaloparatide: recombinant human PTH-related peptide [rhPTHrP (1-34)]
PTH analogs
-Increase bone formation (bone mass and strength)
-Stimulate osteoblasts
-Does not just prevent bone loss (bone resorption)
PTH analog MOA
-Activate PTH1 receptors to increase osteoblast activity and number
-Increase bone mass and bone strength (opposite to PTH)
-Increase Ca absorption in GI tract and kidneys (same as PTH)
PTH analog clinical uses
-Reserved for men or women with severe osteoporosis and glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis
-Approved for only 2 years of use
-Given SC
PTH analog adverse effects
-Orthostatic hypotension
-Dizziness
-Transient hypercalcemia
-Encouraged to sit down for the first few doses to determine their response
PTH analog contraindication
-Pts at risk for osteosarcoma
-Pts with Paget disease of bone metastases/malignancies
Combination anabolic and antiresorptive agent drug class
-Sclerostin inhibitor
Sclerostin
-Inhibits osteoblasts and stimulates osteoclasts
Sclerostin inhibitor drug
-Evenity (romosozumab)
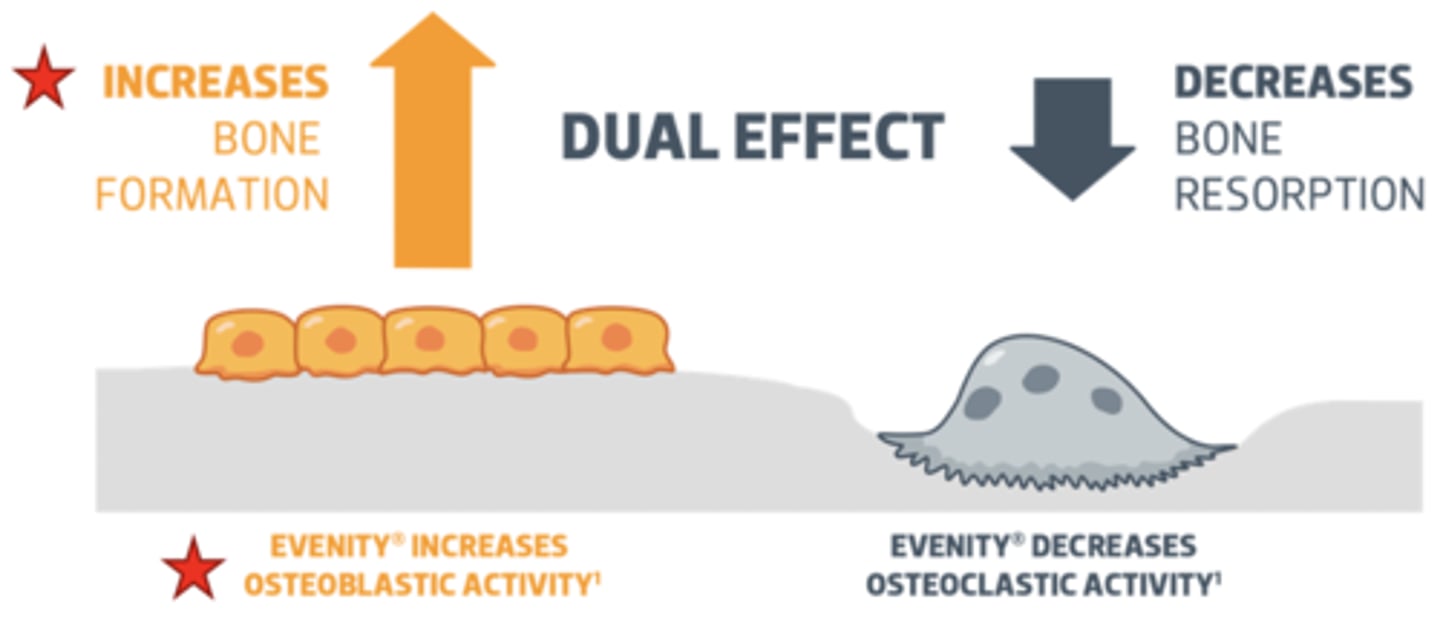
Sclerostin inhibitor MOA
-Humanized monoclonal antibody that inhibits sclerostin
-Increases bone formation and, to a lesser extent, decreases bone resorption
Sclerostin inhibitor clinical uses
-Postmenopausal women with severe osteoporosis and pts who are intolerant to or have failed other osteoporosis therapy
-Approved for only 1 year of use as anabolic effect wanes
-SC
Sclerostin inhibitor adverse effects
-Arthralgia
-Headache
-Injection site pain
-Hypocalcemia
Boxed warning for sclerostin inhibitor
-Stroke
-Heart attack
-Death from CV problems
Relative efficacy of anti-osteoporotic drugs
Romosozumab > teriparatide > denosumab > bisphosphonate > estrogen > raloxifene > calcitonin
Still learning (13)
You've started learning these terms. Keep it up!