CONVERGENT BOUNDARIES
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
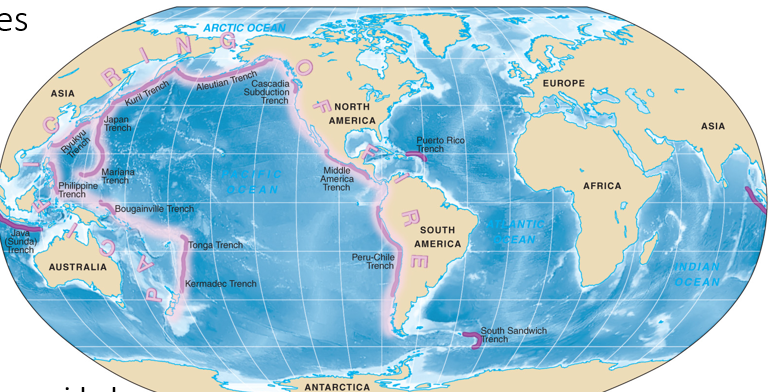
Ocean Trenches
Linear, narrow, steep-sided
Associated with subduction zones
Deepest parts of ocean
Mariana Trench, 11,022 m (36,161 ft)
Majority in Pacific Ocean
Three Plate Boundary
•East Pacific Rise – Spreading Center
•Central America Trench – Collisional Zone
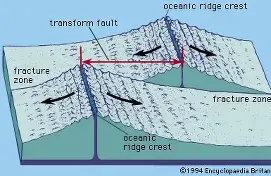
•Connectors between ridge segments are transform faults (A mid‑ocean ridge is not one straight crack but a series of ridge segments separated by offsets. A transform fault is the long fracture that links two neighboring ridge segments and lets the two sides slide sideways past each other as the plates move)
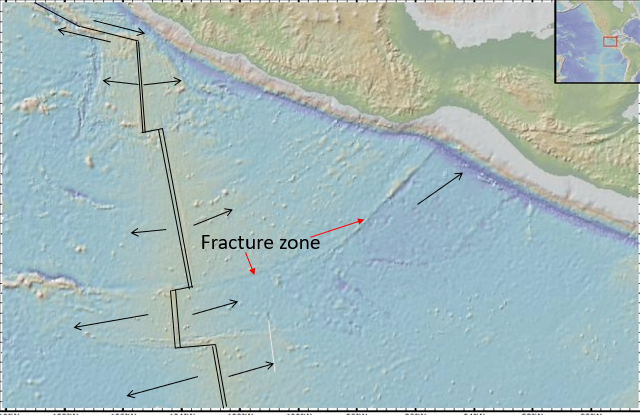
Transform Faults (PHOTO)
What a transform fault is: the active part of the break that connects two ridge segments where plates slide past each other; along the transform fault the two sides move in opposite directions so it’s a plate boundary and can produce earthquakes.
What a fracture zone is: the extended, often inactive lineation beyond the transform fault; it’s a scar in the oceanic crust that marks the offset in the ridge but beyond the ridge the two sides move in the same direction so there is no ongoing slip or earthquakes there
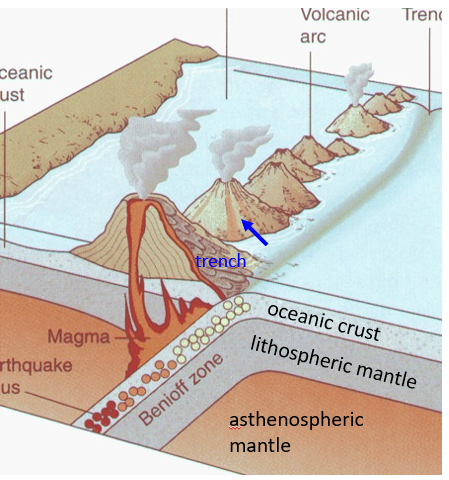
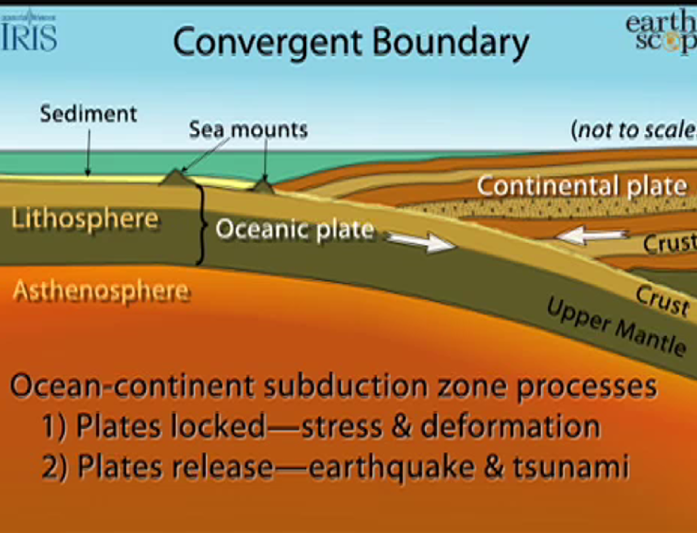
CONVERGENT BOUNDARY: SUBDUCTION OR COLLISION
Subduction: recycling of crust - a portion subsides into mantle whereas another portion returns to the surface as andesitic magma.
Volcanic arcs: stratovolcanoes
•Island arc; chain of islands, e.g., Japan
•Continental arc; volcanic mountain range, e.g., Andes Mountains
Earthquakes cluster along Benioff zone.
Volatile
“Short-tempered”, readily wants to be a gas; not explode.
Ex: alcohol (evaporates readily)
Convergent Boundary (PHOTO)
collisions associated with uplifts
→stress builds, potential earthquakes
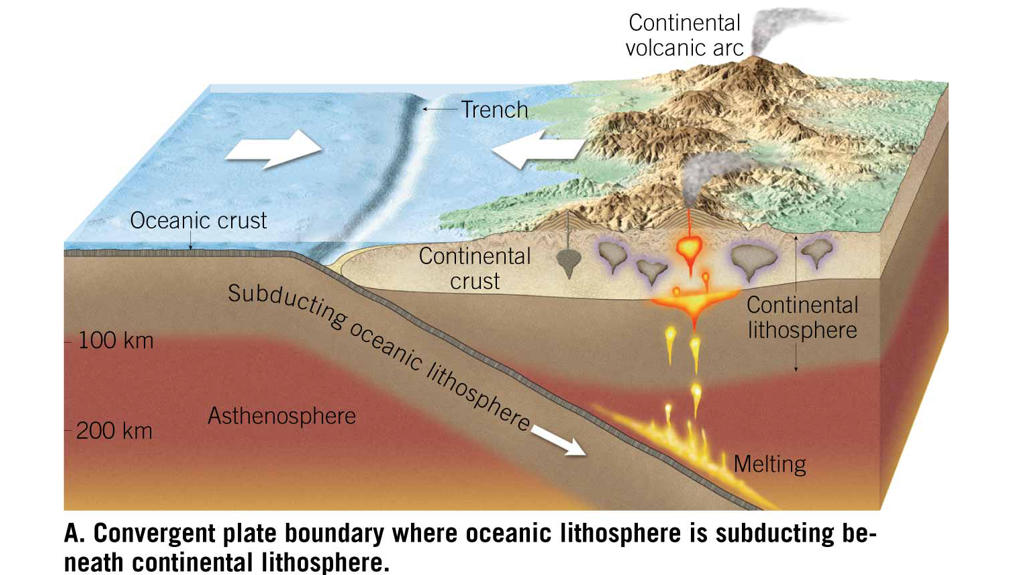
Convergent Plate Boundary where Oceanic Lithosphere is Subducting Beneath Continental Lithosphere (PHOTO)
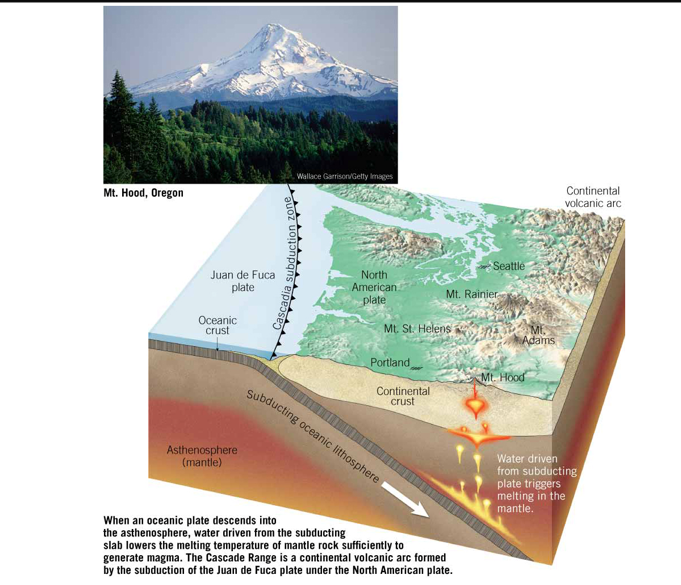
MT Hood
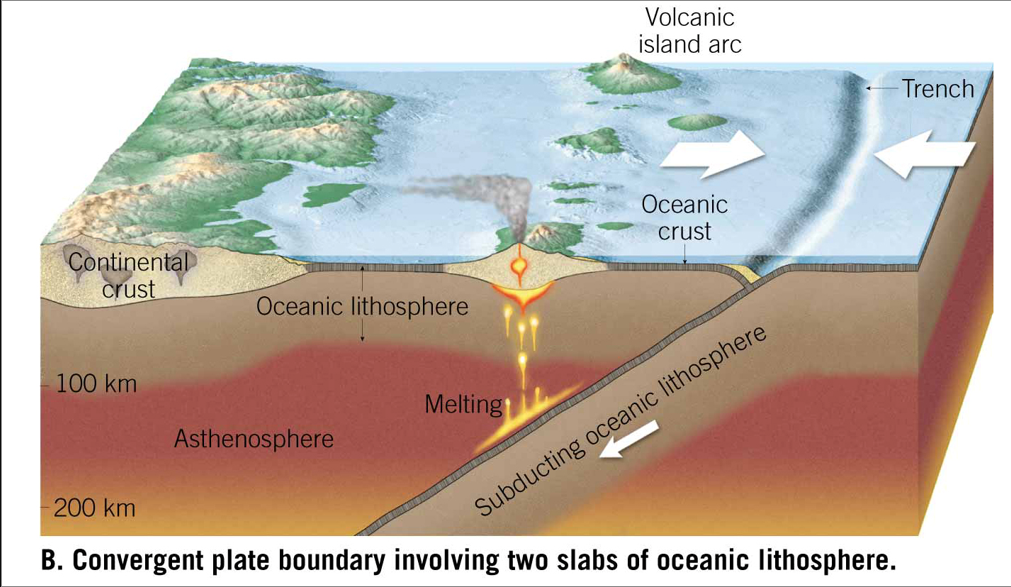
Convergent Plate Boundary Involving Two Slabs of Oceanic Lithosphere
Converging plates
-> o vs o: Subduction, one will win. Top Plate will have volcanism and island arcs. ANDESITE produced
Mid-ocean rides: make basalt (MORB)
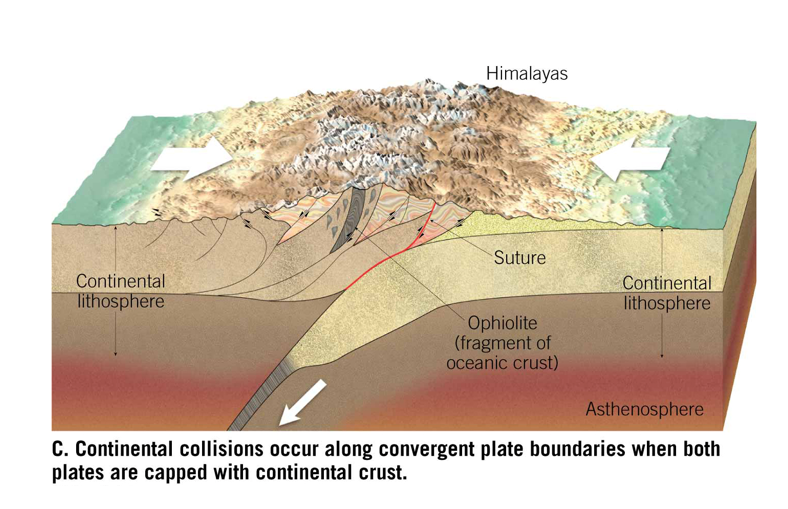
Continental Collisions Occur Along Convergent Plate Boundaries When Both Plates are Capped with Continental Crust
Out of oceanic crust (ran out of subduction, no mor volcanoes), so it’s getting stitched up and creates a continental crust that can’t be breached and so not volcanoes but maybe hot spring.
Can find andesite before the suture happened. Won’t sink in subduction because the crust is too thick.
IT EVENUTALLY CONPRESSES AND UPFLIFTS ( → ←)
Active Volcanoes in… (Based on PowerPoint)
In Aleutian Chain, Alaska
ALSO, Maug Volcano (Izu-Bonin Mariana Subduction zone)
→ MAIRIANA TRENCH: DEEPEST PART OF THE OCEAN.
Fundamental Silica CYcle
•Basalt rises from the mantle (MORB- Mid-Ocean Ridge Basalt)
•Horizontal transport picks up silica
•Subduction results in generation of two fractions:
•one that sinks back into the mantle, and
•one that becomes produces magma at volcanic arcs.
Mantle rocks contain about 44% silica.
MORB ~ 50% silica.
Think layer of sediment ~ 80% silica
Andesite (strato)volcano ~ 60% silica.
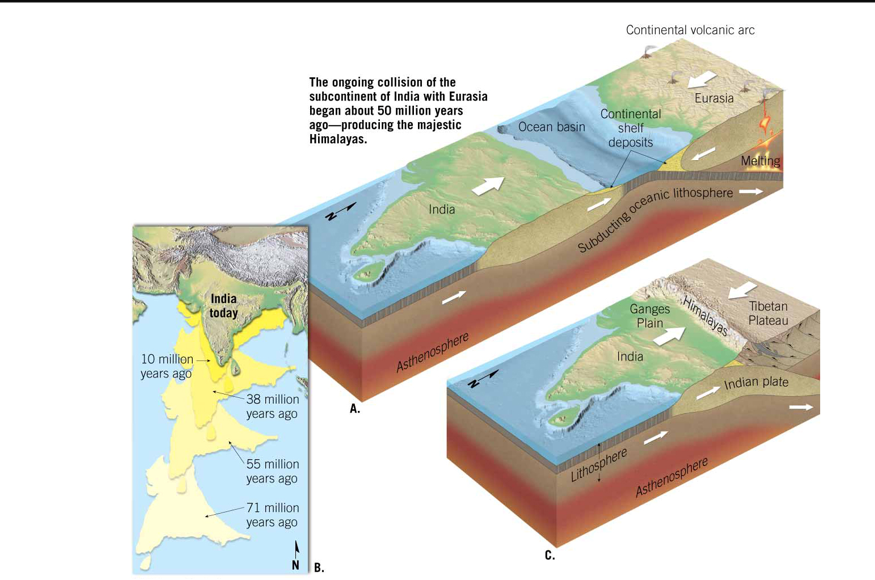
Himalayas (Photo)
Collisions of continental masses, causes uplift for formation of mountains
→ Collions make andesite; SPREADGIN CENTERS make basalt (ALL MORB)
→ other examples of collisions are Swiss Alps and Rocky Mountains,
BASALT (COMPOSITION CHEMICALLY)
Rich in Fe, Mg and 50% SiO2. 3 things make it mafic.
→ 50% pyroxene, 50% plagioclase
70% of Earth is basaltic crust
MOST OF THE EARTH IS COVERED IN PRYOZENE AND PLAGIOCLASE
ASSOIACTED IN SPREADING CENTER AND DIVEGRENT BOUNDARIES
MINERALS (COMPOSITION CHEMICALLY)
Pyroxene: (Ca Mg Fe)2 SiO6
Plagioclase Feldspar: (Ca Na) Aluminosilicate: regulates atmosphere through weathering
K-Feldspar: Found in granitite (K-aluminosilicate)
→ Al2SiO6
Andesite (COMPOSITION CHEMICALLY)
Associated with convergent, even in island and continental arcs; Ring of fire (Phillipines, Japan and South America)
Transforms Assoiated With.. (Class Notes)
It’s a type of motion
→NO volcanism
→BIG earthquakes