Exam 2 Review
1/86
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
place
the location in the vocal tract where the articulators forming the sound make contact
manner
how articulators relate to each other to control airflow in the oral and nasal cavities to produce a certain phoneme
voicing
whether or not the vocal folds vibrate for any given phoneme
dyspepsia
aka indigestion; a general term for discomfort in the upper abdomen, often including symptoms like pain, burning, or fullness, that can occur during or after eating
dyspnea
subjectively perceived discomfort in breathing; shortness of breath; ranges from mild to extreme
dysphonia
the generic term for any voice that sounds deviant in terms of pitch, quality, or loudness
suprahyoid
extrinsic muscles that pull the hyoid bone up
infrahyoid
extrinsic muscles that pull the hyoid bone down
inflates
When the diaphragm contracts, then the lungs (inflates/deflates).
deflates
When the diaphragm relaxes, then the lungs (inflates/deflates).
vowels
Do vowels or consonants have greater acoustic energy?
consonants
Do vowels or consonants have greater vocal tract constriction?
stops
What kind of sound would have a spectrogram with the acoustic features of a silent gap, release burst, VOT, and formant transitions?
formants
resonant frequencies of the vocal tract
hyoid bone
U-shaped bone that forms the attachment for the root of the tongue and suspends the larynx
tidal volume (TV)
the volume of air inhaled and exhaled during a cycle of respiration; varies depending on age, build, and physical activity
inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
volume of air that can be inhaled above tidal volume; further inhalation after a normal inhalation
expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
volume of air that can be exhaled below tidal volume; further exhalation after a normal exhalation
residual volume (RV)
volume of air remaining in lungs after a maximum expiration that cannot be voluntarily expelled; ensures there is always at least some volume of air
vital capacity (VC)
volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inhalation; combination of IRV (extra inhalation), tidal volume (normal inhalation and exhalation), and ERV (extra exhalation)
IRV + TV + ERV = VC
What is the formula for vital capacity?
functional residual capacity (FRC)
volume of air remaining in the lungs and airways at the end-expiratory level (at the end of a normal exhalation); made up of the ERV (extra exhalation possible) and RV (permanent air)
ERV + RV = FRC
What is the formula for FRC?
total lung capacity (TLC)
total amount of air the lungs can hold; made up of TV (normal inhale & exhale), IRV (extra inhale), ERV (extra exhale), and RV (permanent air)
TV + IRV + ERV + RV = TLC
What is the formula for TLC?
inspiratory capacity (IC)
maximum volume of air that can be inspired from end-expiratory level (end of a normal exhale); made up of TV (normal inhale & exhale) & IRV (extra inhale); deep inhale after normal exhale
TV + IRV = IC
What is the formula for inspiratory capacity?
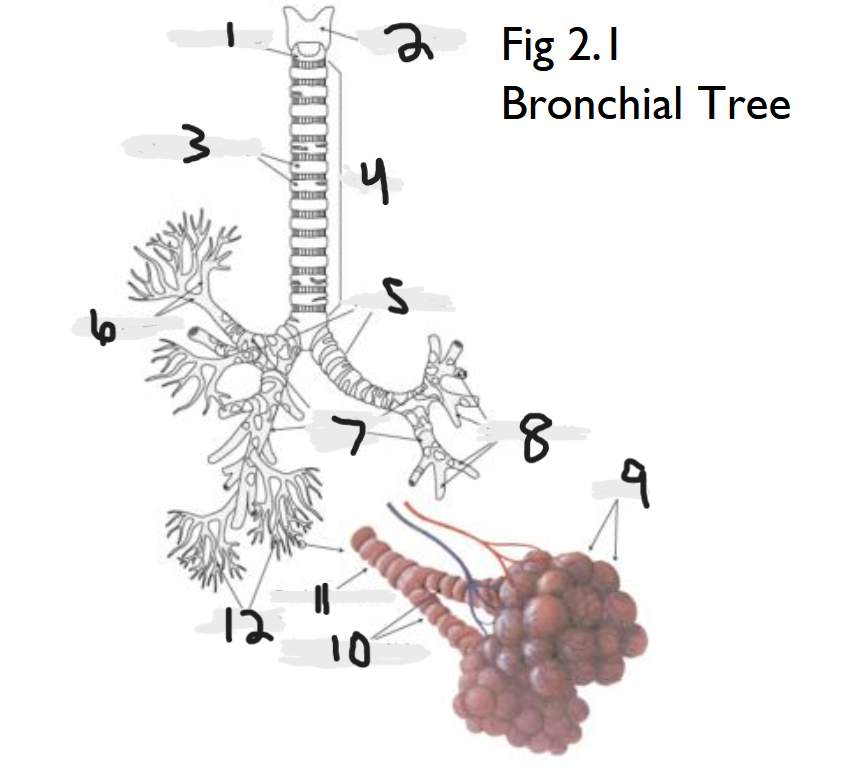
cricoid cartilage
What part of the bronchial tree is number 1?
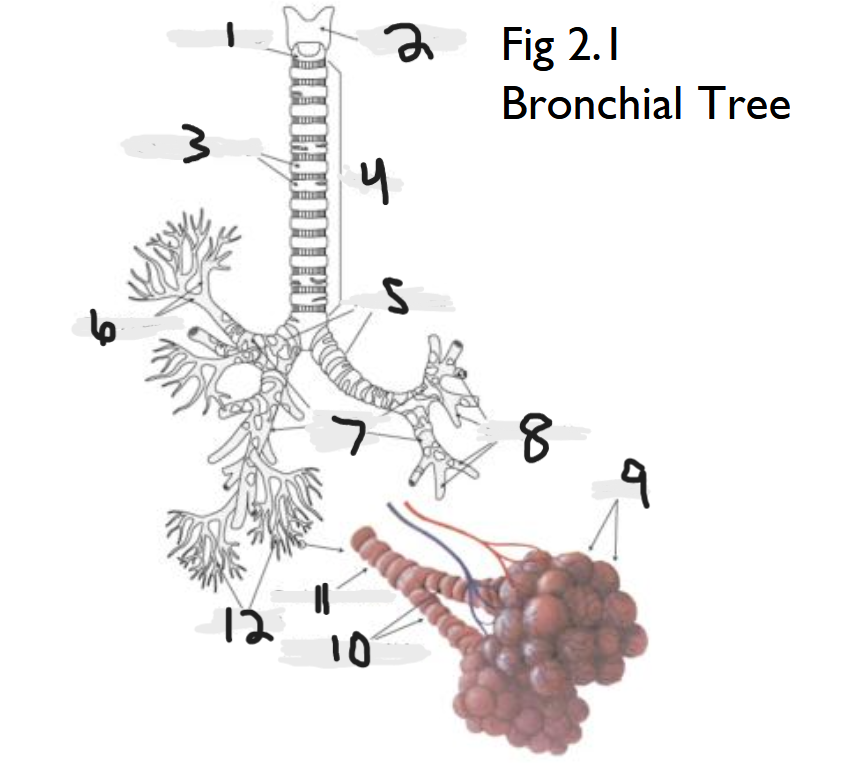
thyroid cartilage
What part of the bronchial tree is number 2?
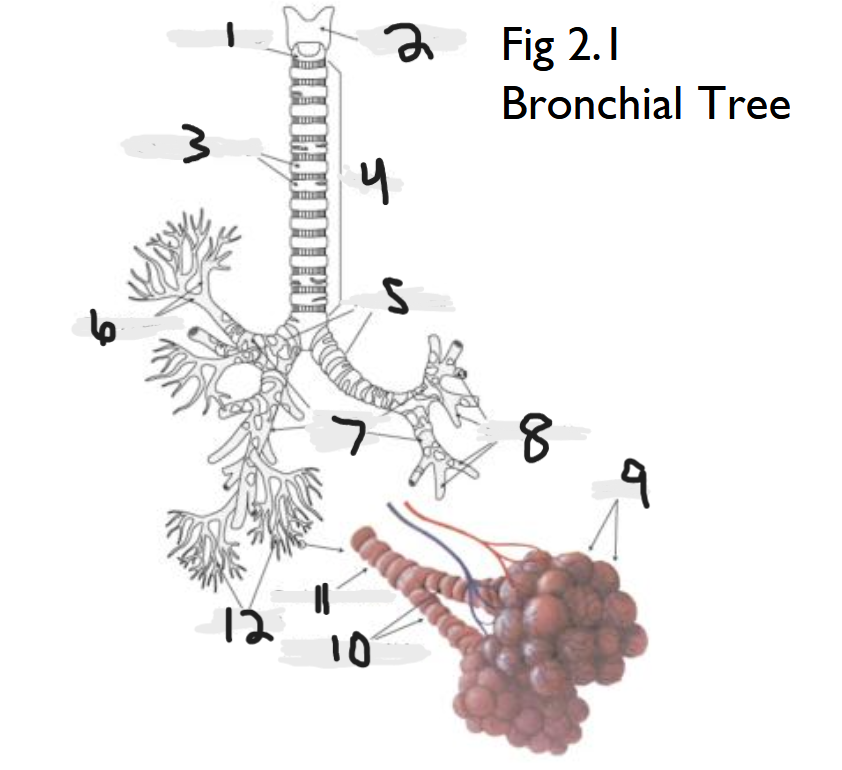
trachea
What part of the bronchial tree is number 4?
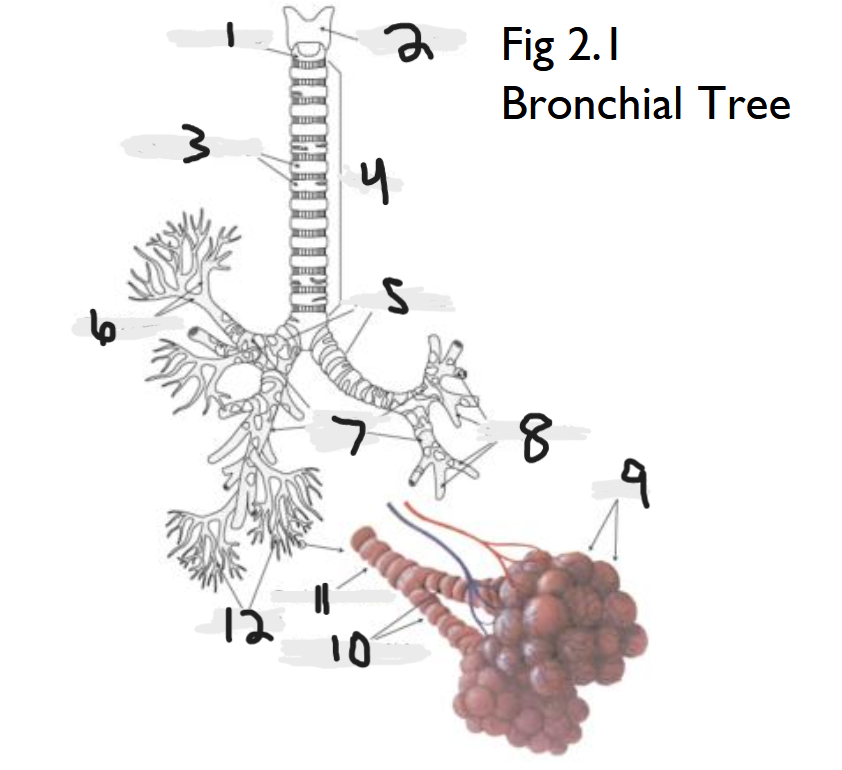
primary bronchi
What part of the bronchial tree is number 5?
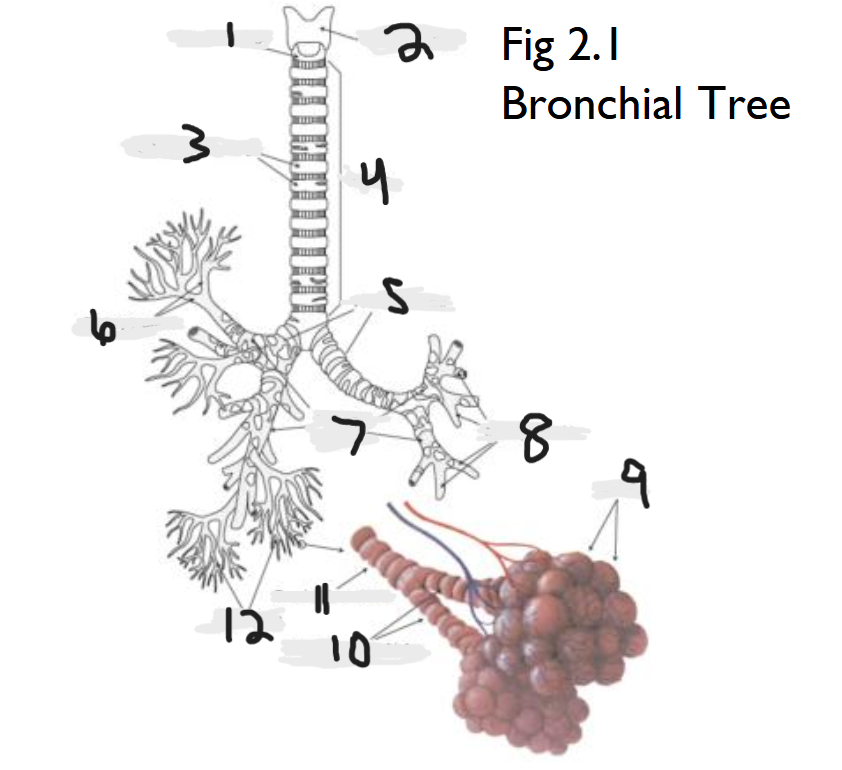
tertiary bronchi
What part of the bronchial tree is number 6 & 8?
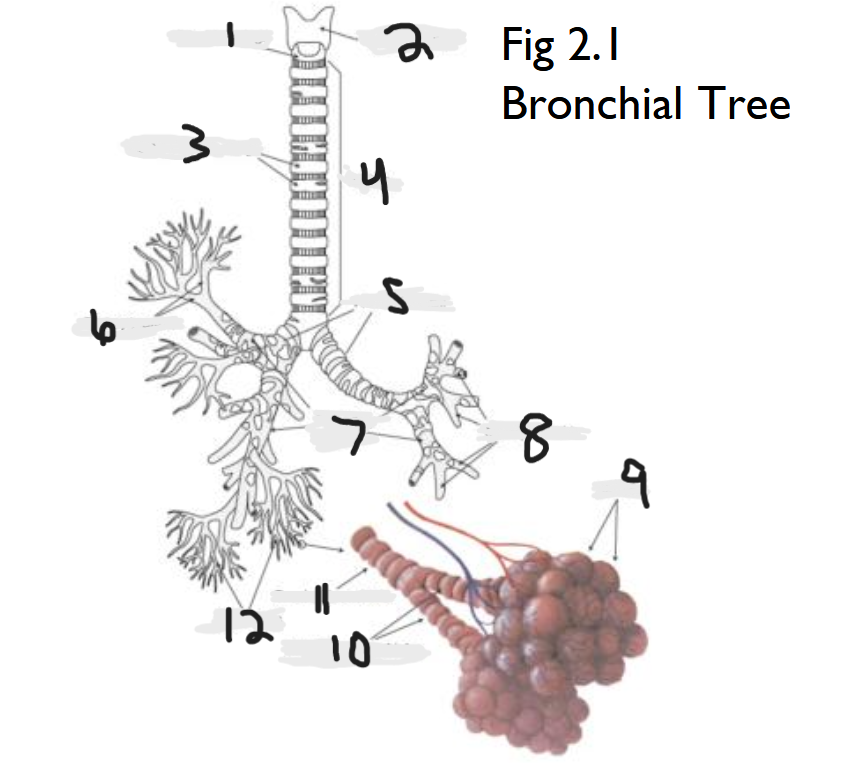
secondary bronchi
What part of the bronchial tree is number 7?
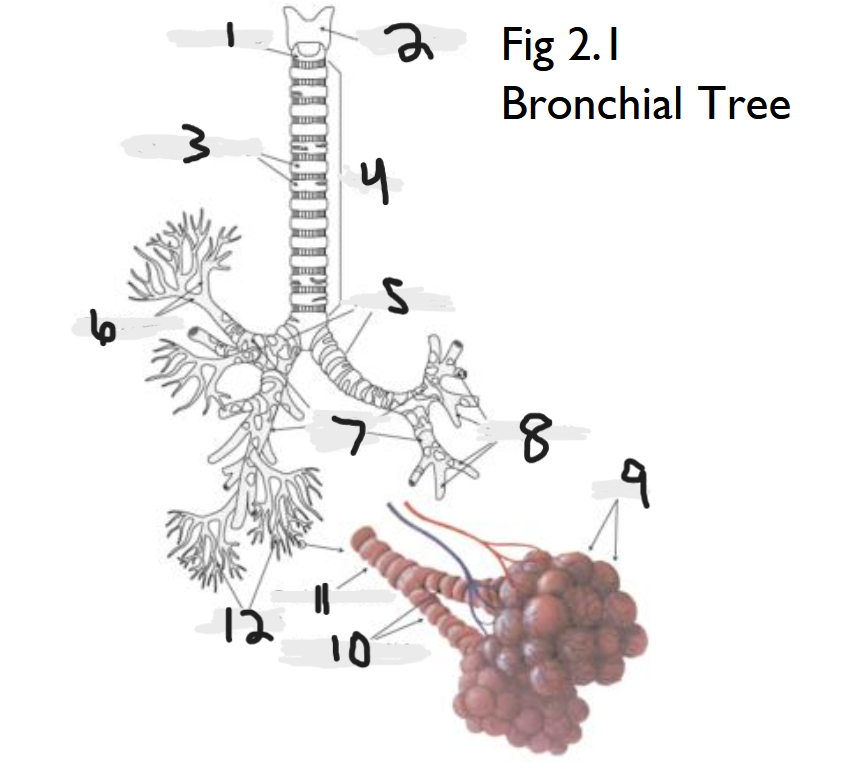
alveoli
What part of the bronchial tree is number 9?
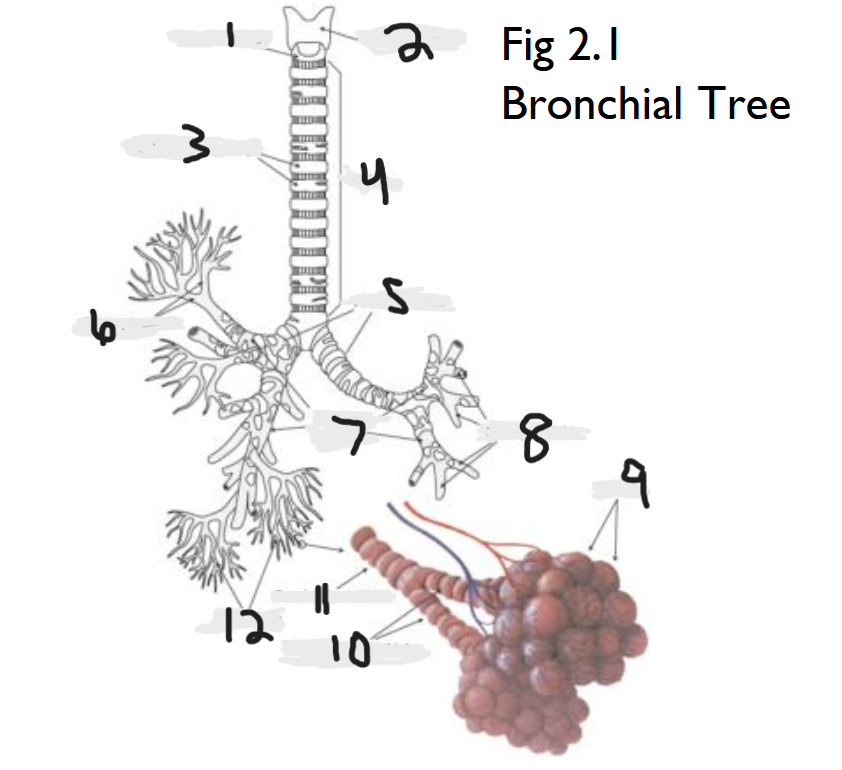
bronchioles
What is number 12?
glottal sound, vocal tract resonator, radiated sound at the lips
What are the three components of the source filter theory of vowel production?
labial, lingual, velopharyngeal, laryngeal
What are the four valves of the vocal tract?
Epiglottis, cricoid, thyroid
What are the three unpaired cartilages?
arytenoid, corniculate, cuneiform
What are the three paired cartilages?
extrinsic muscles
The large up-and-down movements of the larynx that occur mainly during swallowing are done by the _______.
extrinsic
muscles that are attached to two different structures at its end; usually serves to bring the two structures closer together or further apart
intrinsic
muscles that are attached at both ends within the same structure
modal register
vocal register used in conversational speech; the normal range of pitches
glottal fry
the lowest vocal register, often sounded crackly or hoarse; can be caused by voice disorder or may be a conscious or unconscious choice by the individual
falsetto
the highest vocal register, think soprano pitches
4x
The first resonant frequency (first formant) occurs at a wavelength who frequency is _____ the length of the tube.
open
During the production of nasal sounds (/m/, /n/, /ŋ/), the velopharyngeal port is (open/closed).
myoelastic aerodynamic theory of phonation
theory that voice is produced through the interaction of muscle force and airflow (essay question alert)
voiceless sounds
sounds in which there is no vocal fold vibartion
voiced sounds
sounds in which there is vocal fold vibration
voiced
All vowels are ________.
intonation
the rise and fall of the voice during speaking that helps communicate emotions and attitude during speech
wavelength = (tube length) x 4
What is the formula for calculating wavelength if given the tube length?
F1 = (34,400 cm/s) / wavelength
What is the formula for the first resonant frequency (first formant) of a tube if given the wavelength of the tube?
F2 = F1 × 3
What is the formula for the second resonant frequency (second formant) of a tube if given the first resonant frequency (first formant) of the tube?
F3 = F1 x 5
What is the formula for the third resonant frequency (third formant) of a tube if given the first resonant frequency (first formant) of the tube?
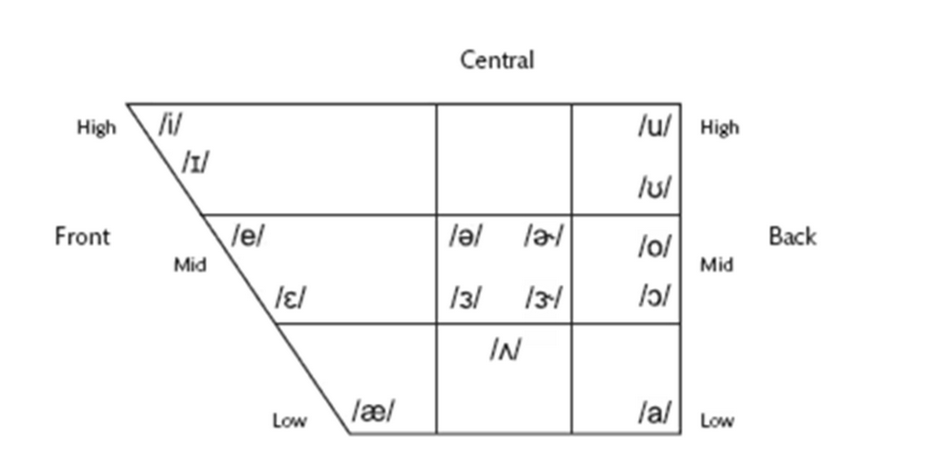
vowel quadralateral
What is this an image of?
labial valve
a valve of the vocal tract made up of the lips, their movement and contact with other articulators
lingual valve
a valve of the vocal tract made up of the tongue interacting with other articulators
velopharngeal valve
a valve of the vocal tract at the back of the throat that can move to open or block the area connecting the oral and nasal cavities to produce various phonemes
nasal, oral, pharyngeal
What are the three vocal tract cavities?
laryngopharynx, oropharynx, nasopharynx
What are the three portions of the pharynx?
levator veli palatini
Which muscle elevates the velum?
hypernasality
nasally sounding voice caused when air escapes through the nasal cavity rather than the oral cavity
hyponasality
stuffy sounding voice caused when air is completely prevented from escaping through the nasal cavity
broadly tuned resonator
The vocal tract’s irregular shape makes it a _______________ that transmits a wide range of frequencies.
stop gap
acoustic cue of stops that involves a brief silence as pressure is built up
release burst
acoustic cue of stops that involves a burst noise upon release
aspiration
acoustic cue of stops that involves a brief hiss of air
voice onset time (VOT)
the time between the release of a stop consonant and the onset of vocal fold vibration
voicing lead
type of voice onset time that begins before a stop release; vocal folds approximate throughout stop closure
found in voiced stops
short-lag
type of voice onset time that involves the vocal folds being adducted by the time the stop is released; creates a silent closure, with voicing beginning on the release or just after
found in voiceless unaspirated stops
long-lag
type of voice onset time that invovles the vocal folds adducting after the stop is released
found in voicless aspirated
higher, lower
In general, vowels are ________ in intensity and _______ in frequency than consonants.
coarticulation
the articulation of three or more speech sounds together so that they influence each other
increases
The vowel’s first formant (decreases/increases) as you move from top to bottom of the vowel quadralateral.
decreases
The vowel’s second formant (decreases/increases) as you move from left to right of the vowel quadralateral.
vocal folds
The fundamental frequency of your voice is determined by their source which is the
vocal tract
Formants of your voice are determined by their filter which is the
3
The right lung has _____ lobes.
2
The left lung has _____ lobes.
vocalists
Who might use a large portion of their expiratory reserve volume to sustain a long phrase without inhaling?
epiglottis
a broad cartilage that is shaped like a leaf
medial compression of the vocal folds
According to the myoelastic aerodynamic theory of phonation, what causes subglottal air pressure to increase during phonation?
pleural linkage
negative pressure in the pleural space that keeps the thorax and lungs connected (but protected and with a smooth moving surface by the pleura)
lamina propria
The mucous membrane of the true vocal folds is called the ________ and is composed of three layers.
squamous epithelium, superficial lamina propria, intermediate lamina propria, deep lamina propria, thyroarytenoid muscle
What are the five layers of the vocal folds, from most superficial to most deep?