Anat Tissues Textbook
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/258
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:29 PM on 11/21/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
259 Terms
1
New cards
Histology
study of tissues and how they arranged into organs
2
New cards
Tissue
a group of similar cells and cell products that arise form the same region of an embryo and work together to perform a specific structural or physiological role in an organ
3
New cards
what are the four primary tissues
epithelial
connective
nervous
muscular
connective
nervous
muscular
4
New cards
how do the primary tissues differ from each other
types and functions of their cells, the characteristics of the matrix that surrounds the cells, and the relative amount of space occupied by cells versus matrix
5
New cards
matrix
The extracellular material of a tissue
6
New cards
Epithelial Characteristics
tissue composed of layers of closely spaced cells; covers organ surfaces, forms glands, and serves for protection, secretion, and absorption
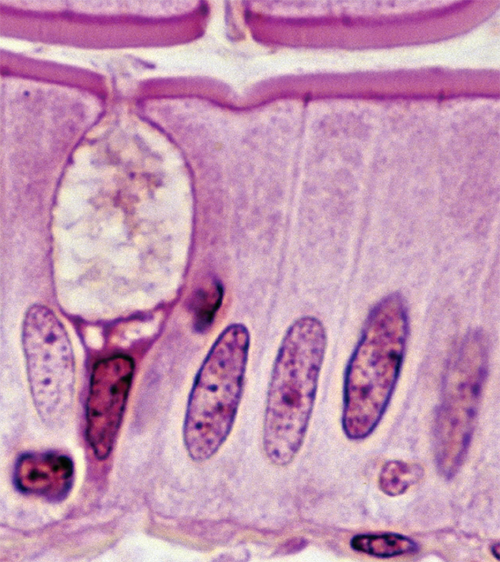
7
New cards
Epithelial Representative Locations
epidermis, lining of digestive tract, liver, and other glands
8
New cards
Connective Characteristics
Tissue with usually more matrix than cell volume; often specialized to support, bind, and protect organs
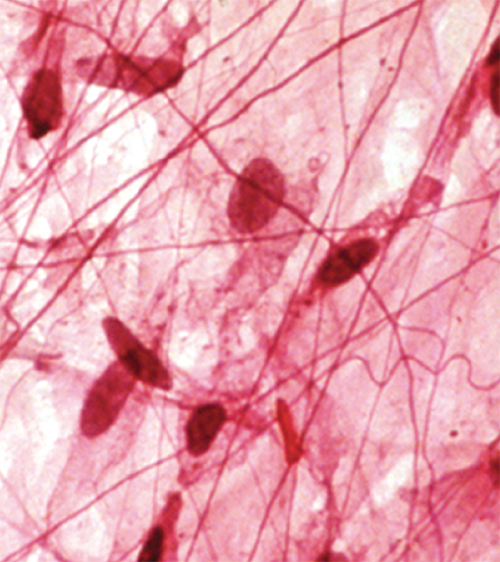
9
New cards
Connective Representative Locations
tendons, ligaments, cartilage, fat, bone, blood
10
New cards
Nervous system characteristics
tissue containing excitable cells specialized for rapid transmission of information to other cells
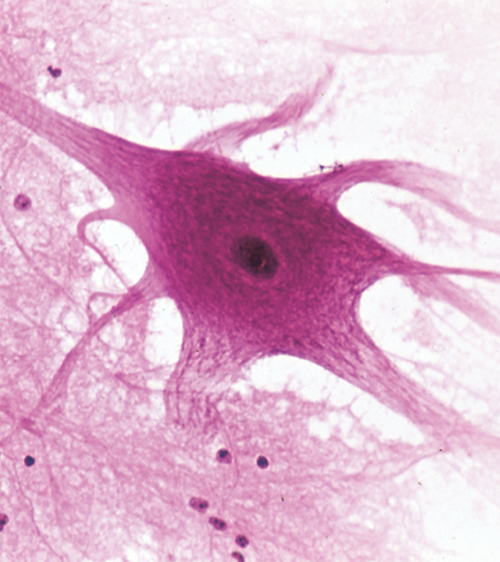
11
New cards
nervous Representative Locations
brain, spinal cord, nerves
12
New cards
Muscular characteristics
tissue composed of elongated, excitable cells specialized for contraction and movement
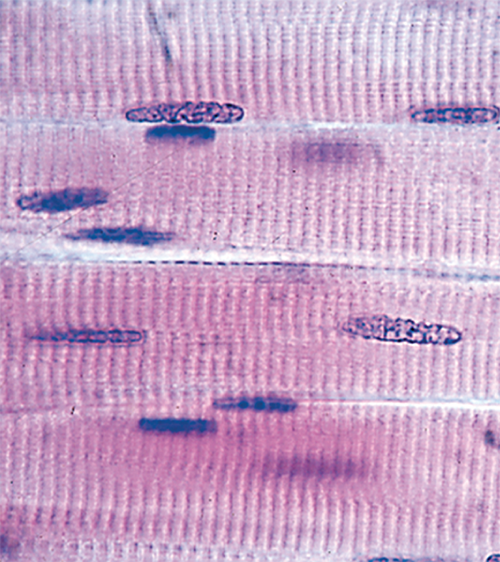
13
New cards
muscular Representative Locations
skeletal muscles; heart; walls of uterus, bladder, intestines, and other internal organs
14
New cards
nonliving matter secreted by the tissue cells
matrix
15
New cards
what is the matrix composed of
fibrous proteins, and usually clear gel known as ground substance or extracellular fluid (ECF)
16
New cards
histological sections
thin tissue slices, generally one or two cells thick that are mounted on microscope slides and dyed with various stains
17
New cards
describe microscopic images of tissue sections
shows three-dimensional object as a two-dimensional image
try to translate the microscopic image into a mental image of the whole structure
try to translate the microscopic image into a mental image of the whole structure
18
New cards
planes of section
cut at various levels
19
New cards
list of cell shapes
squamous
cuboidal
columnar
polygonal
spheroidal to ovoid
fusiform
fibrous
cuboidal
columnar
polygonal
spheroidal to ovoid
fusiform
fibrous
20
New cards
Squamous
a thin flat scaly shape
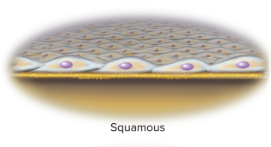
21
New cards
where are squamous cells
lining the esophagus and form the surface layer (epidermis) of the skin
22
New cards
Cuboidal
squarish and about equal in height and width
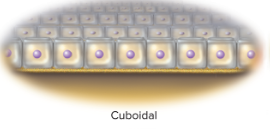
23
New cards
Examples of cuboidal cells
kidney tubules and liver
24
New cards
columnar
distinctly taller than wide
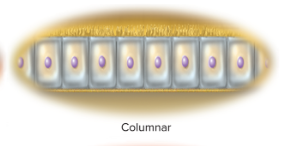
25
New cards
Columnar cells examples
inner lining cells of the stomach and intestines
26
New cards
polygonal
having irregular, angular shapes with four, five, or more sides
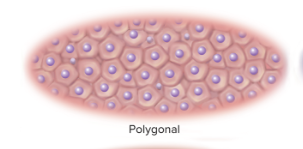
27
New cards
spheroidal to ovoid
round to oval
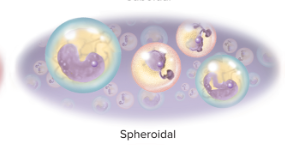
28
New cards
spheroidal examples
egg cells and white blood cells
29
New cards
Fusiform
elongated, which a thick middle and tapered ends
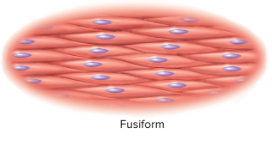
30
New cards
fusiform examples
smooth muscle cells
31
New cards
fibrous
long, slender, and threadlike
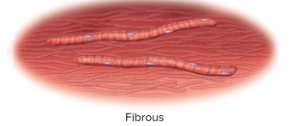
32
New cards
example of fibrous
skeletal muscle cells
33
New cards
epithelial tissue (epithelium)
consists of a flat sheet of closely spaced cells, one or more cells thick
34
New cards
where is epithelium
body surface, lines body cavities, forms the external and internal linings of many organs, and makes up most gland tissue
35
New cards
Do epithelia have blood vessels
no
36
New cards
How do epithelia get its nourishment and waste removal
it lays on a layer of loose connective tissue and depend on its blood vessels
37
New cards
List of functions of the epithelial tissues
Protection
Secretion
Excretion
Absorption
Filtration
sensation
Secretion
Excretion
Absorption
Filtration
sensation
38
New cards
Epithelial Function Protection
epithelia protect deeper tissues form invasion and injury
39
New cards
where does epithelial protect
epidermis of the skin (barrier to infection and water loss from the body)
40
New cards
Epithelial Function Secretion
epithelia produce mucus, sweat, enzymes, hormones, and most of the body's other secretions (glands)
41
New cards
Epithelial function Excretion
Epithelia removes wastes from the tissues
42
New cards
Examples of epithelial excretion
CO2 is moved across the pulmonary epithelium to be exhaled
43
New cards
Epithelial Function absorption
epithelia absorb material; nutrients
44
New cards
Epithelial function Filtration
all substances leaving the blood are selectively filtered through the epithelium that lines the blood vessels; all urinary waste is filtered through epithelia of the kidneys
45
New cards
Epithelial function Sensation
epithelia have nerve endings that sense stimulation such as touch on the skin or irritation of the stomach
46
New cards
basement Membrane
between epithelium and the underlying connective tissue and is composed mainly of protein
47
New cards
Roles of basement membrane
anchors the epithelium to the connective tissue, regulates the exchange of materials between the epithelium and the underlying tissues, and binds growth factors from below that regulate epithelial development and maintenance
48
New cards
basal surface
surface of a cell that attaches to the basement membrane
49
New cards
apical surface
upper surface that faces the body surface or the lumen of an organ
50
New cards
lumen
The internal space of a hollow organ such as a blood vessel or the esophagus, or a space surrounded by cells as in a gland acinus.
51
New cards
lateral surfaces
sides of the cell
52
New cards
epithelial cells often have
cilia, microvilli or both on their apical surface
53
New cards
2 categories of epithelia
simple and stratified
54
New cards
simple epithelium
every cell touches the basement membrane
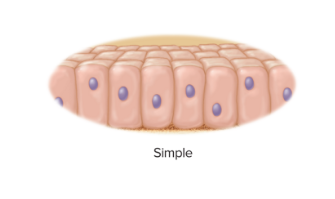
55
New cards
stratified epithelium
some cells rest on top of other cells and do not extend to the basement membrane
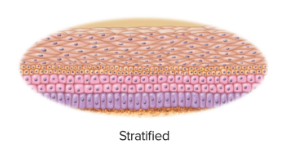
56
New cards
how many layers of cells do simple epithelium have
one
57
New cards
Four types of simple epithelium
simple squamous
simple cuboidal
simple columnar
pseudostratified columnar
simple cuboidal
simple columnar
pseudostratified columnar
58
New cards
3 types of simple epithelia named for the shapes
simple squamous (thin scaly cells)
simple cuboidal (squarish or rounded cells)
simple columnar (tall narrow cells)
simple cuboidal (squarish or rounded cells)
simple columnar (tall narrow cells)
59
New cards
pseudostratified columnar
not all cells reach the free surface; the shorter cells are covered over by the taller ones, but all of them reach the basement membrane
60
New cards
what two simple epithelium produce a mucous coating and how is it secreted
simple columnar and pseudostratified
wineglass-shaped goblet cells
wineglass-shaped goblet cells
61
New cards
goblet cells
A mucus-secreting gland cell, shaped somewhat like a wineglass, found in the epithelia of many mucous membranes
62
New cards
Simple Squamous Epithelium microscopic appearance
single layer of thin cells, shaped like fried eggs with a bulge where the nucleus is located; nucleus somewhat flattened in the plane of the cell, like an egg yolk; cytoplasm may be so thin it is hard to see in tissue sections; in surface view, cells have angular contours and nuclei appear
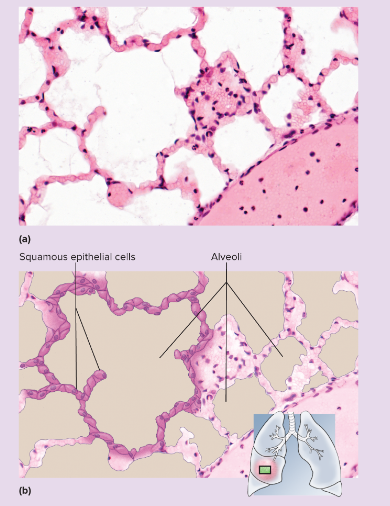
63
New cards
Simple Squamous Epithelium representative locations
air sacs (alveoli) of lungs; glomerular capsules of kidneys; some kidney tubules; inner lining (endothelium) of heart and blood vessels; serous membranes of stomach, intestines, and some other viscera; surface layer (mesothelium) of pleurae, pericardium, peritoneum, and mesenteries
64
New cards
Simple Squamous Epithelium functions
allows rapid diffusion of transport of substances through membranes; secretes lubricating serous fluid
65
New cards
simple cuboidal epithelium microscopic appearance
single layer of squarish or rounded cells; in glands, cells often pyramidal and arranged like segments of an orange around a central space; spherical, centrally placed nuclei; often with a brush border of microvilli in some kidney tubules; ciliated in bronchioles of lung
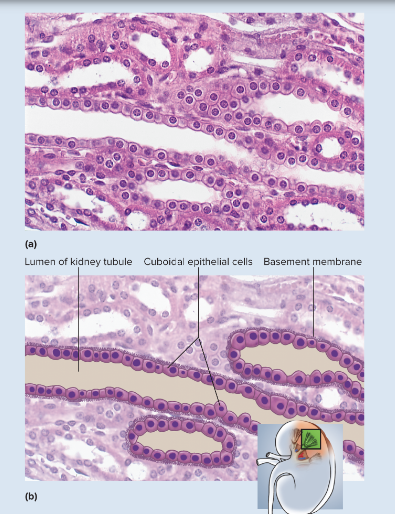
66
New cards
simple cuboidal epithelium representative location
liver, thyroid, mammary, salivary, and other glands; many gland ducts; most kidney tubules; bronchioles
67
New cards
simple cuboidal epithelium functions
absorption and secretion; production of protective mucous coat; movement of respiratory mucus
68
New cards
simple columnar epithelium microscopic appearance
single layer of tall, narrow cells; oval or sausage-shaped nuclei, vertically oriented, usually in basal half of cell; apical portion of cell often shows secretory vesicles visible with TEM; often shows a brush border of microvilli; ciliated in some organs; may possess goblet cells
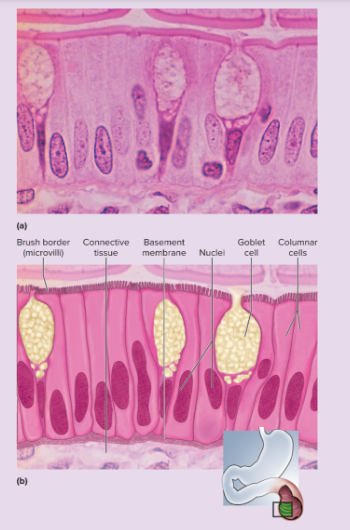
69
New cards
simple columnar epithelium representative locations
inner lining of stomach, intestines, gallbladder, uterus, and uterine tubes; some kidney tubules
70
New cards
simple columnar epithelium functions
absorption and secretion; movement of egg and embryo in uterine tube; secretion of mucus
71
New cards
pseudostratified columnar epithelium microscopic appearance
looks multilayered; some cells do not reach free surface but all cells reach basement membrane; nuclei at several levels in deeper half of epithelium; often with goblet cells; often ciliated
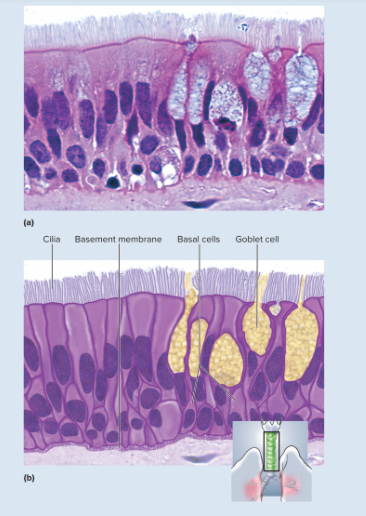
72
New cards
pseudostratified columnar epithelium representative locations
respiratory tract from nasal cavity to bronchi; portions of male reproductive tract
73
New cards
pseudostratified columnar epithelium functions
secretes and propels respiratory mucus; absorbs excess fluid from parts of the male reproductive tract
74
New cards
stratified epithelia
range from 2 cell layers to 20 or more
75
New cards
4 types of stratified epithelia
stratified squamous
stratified cuboidal
stratified columnar epithelia
transitional epithelium
stratified cuboidal
stratified columnar epithelia
transitional epithelium
76
New cards
3 types of stratified epithelia based on shape
stratified squamous
stratified cuboidal
stratified columnar epithelia
stratified cuboidal
stratified columnar epithelia
77
New cards
how was the transitional epithelium originally named
thought to represent a transitional stage between stratified squamous and stratified columnar epithelium- proven untrue
78
New cards
stratified columnar is
rare (occurring in short transitional zones where one epithelium type grades into another)
79
New cards
stratified squamous epithelium-keratinized microscopic appearance
multiple cell layers with cells becoming increasingly flat and scaly toward surface; surface covered with a layer of compact dead cells without nuclei; basal cells may be cuboidal to columnar
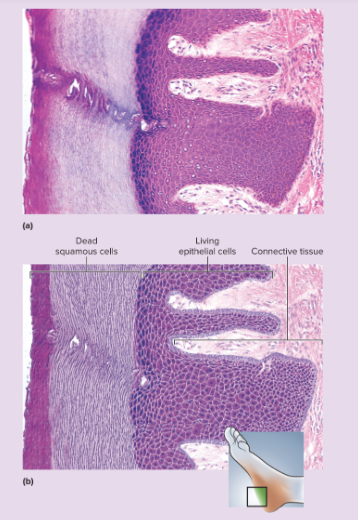
80
New cards
stratified squamous epithelium-keratinized representative locations
epidermis; palms and soles are especially heavily keratinized
81
New cards
stratified squamous epithelium-keratinized functions
resists abrasion; retards water loss through skim; resists penetration by pathogenic organisms
82
New cards
Stratified squamous epithelium-nonkeratinized microscopic appearance
same as keratinized epithelium but without the surface layer of dead cells
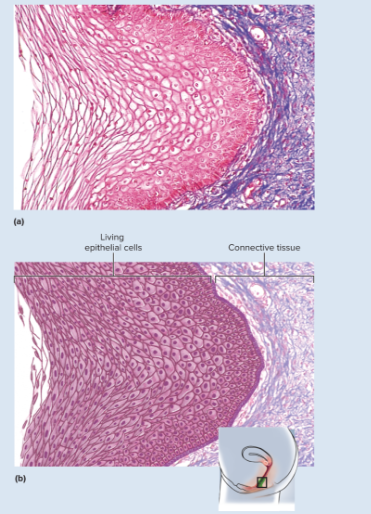
83
New cards
Stratified squamous epithelium-nonkeratinized representative locations
tongue, oral, mucosa, esophagus, anal canal, vagina
84
New cards
Stratified squamous epithelium-nonkeratinized functions
resists abrasions and penetration by pathogenic organisms while providing a moist slippery surface
85
New cards
stratified cuboidal epithelium microscopic appearance
Two or more layers of cells; surface cells squarish or rounded
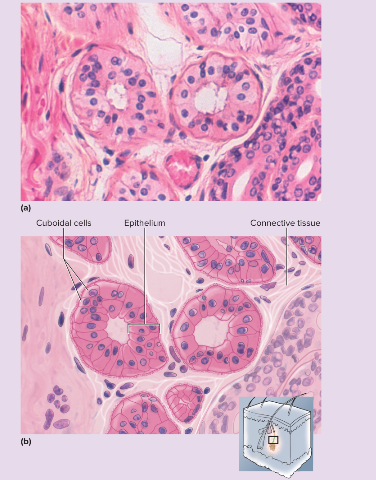
86
New cards
stratified cuboidal epithelium representative functions
sweat gland ducts; egg-producing vesicles (follicles) of ovaries; sperm-producing ducts (seminiferous tubules) of testes
87
New cards
stratified cuboidal epithelium functions
contributes to sweat secretion; secretes ovarian hormones; produces sperm
88
New cards
Transitional epithelium microscopic appearance
Somewhat resembles stratified squamous epithelium, but surface cells are rounded, not flattened, and often bulge above surface, typically five or six cells thick when relaxed, two or three cells thick when stretched; cells may be flatter and thinner when epithelium is stretched (as in a distended bladder); some cells have two nuclei
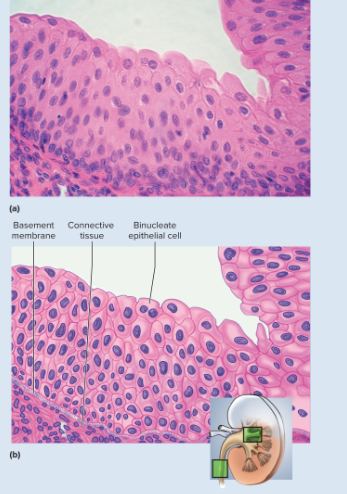
89
New cards
Transitional epithelium representative locations
limited to urinary tract- part of kidney, ureter, bladder, part of urethra
90
New cards
Transitional epithelium functions
stretches to allow filling of urinary tract; protects deeper cells and tissues form damage by acidic and hypertonic urine
91
New cards
what is the most widespread epithelium
stratified squamous epithelium
92
New cards
Describe squamous epithelium cells
deepest cells are cuboidal to columnar and undergo continual mitosis
daughter cells push toward the surface and becomes flatter (squamous) as the migrate farther upward until the die and flake of (exfoliation)
daughter cells push toward the surface and becomes flatter (squamous) as the migrate farther upward until the die and flake of (exfoliation)
93
New cards
exfoliation
the peeling off in flakes or scales of bark or dead skin
94
New cards
exfoliate cytology
study of exfoliated cells
95
New cards
2 kinds of stratified squamous epithelia
keratinized and nonkeratinized
96
New cards
keratinized epithelium
found in the epidermis, is cover with a layer of compact, dead, squamous cells. These cells are packed with durable protein keratin and coated with a water repellant (retards water loss from the body and resists penetration by disease organisms)
97
New cards
nonkeratinized
lacks the surface layer of dead cells
located in tongue, oral mucosa, esophagus, vagina, and other internal surfaces.
provides a surface that is abrasion resistant but also moist and slippery. Resists stress produced by chewing, swallowing, sexual intercourse, and birth
located in tongue, oral mucosa, esophagus, vagina, and other internal surfaces.
provides a surface that is abrasion resistant but also moist and slippery. Resists stress produced by chewing, swallowing, sexual intercourse, and birth
98
New cards
Transitional epithelium (urothelium)
found only in the urinary tract
protects the cells from the acidic and hypertonic urine. Umbrella cells- at the surface protect the deeper cells from urine
protects the cells from the acidic and hypertonic urine. Umbrella cells- at the surface protect the deeper cells from urine
99
New cards
what is the most abundant primary tissue
connective tissues
100
New cards
functions of connective tissue list
Binding organs
support
physical protection
immune protection
movement
storage
heat production
transport
support
physical protection
immune protection
movement
storage
heat production
transport