Earth Systems Year 9
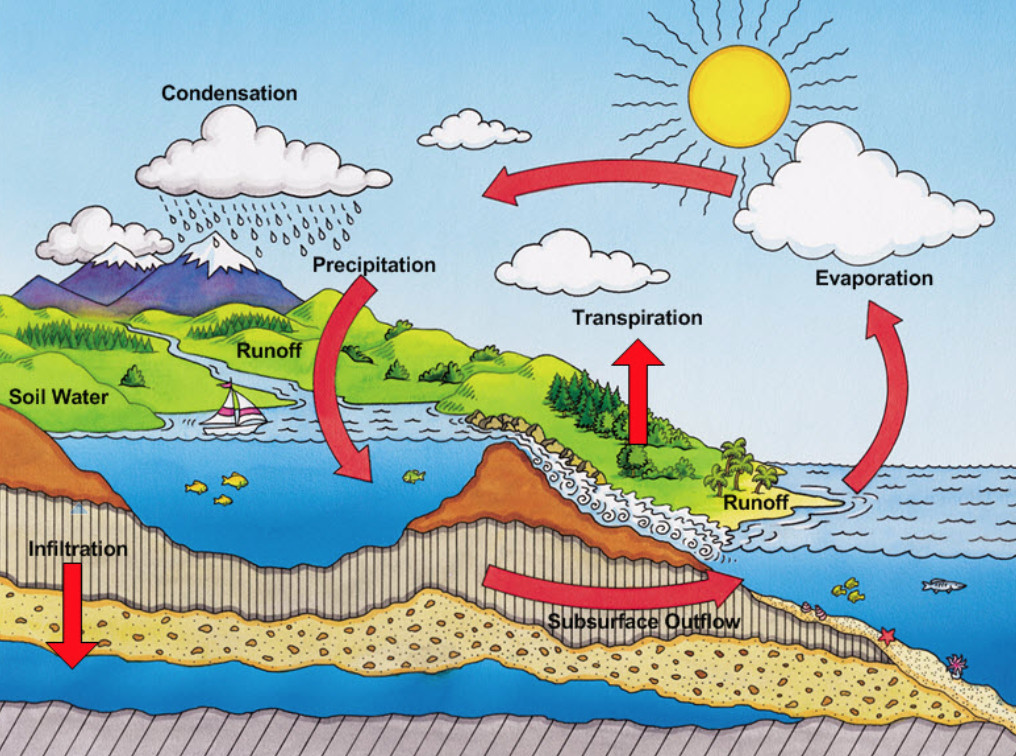
Water cycle: The continuous movement of water, on, above, or beneath the surface of the Earth. The Sun warms water on the surface of the Earth, causing it to evaporate and rise into the atmosphere. Gravity pulls water back down to the surface through precipitation.
There are 6 processes part of the water cycle:
Evaporation: Liquid water on the surface turns into gas - Liquid to Gas
Condensation: Water vapour in the air turns into liquid droplets, forming clouds and fog
Precipitation: Small droplets of water in clouds form larger droplets and fall as rain, hail or snow - Liquid to Solid
Infiltration: Rainwater soaks into the ground and flows through soil and rock layers
Runoff: Liquid water flows downhill in streams and rivers
Transpiration: Plants release water vapour from tiny pores in their leaves
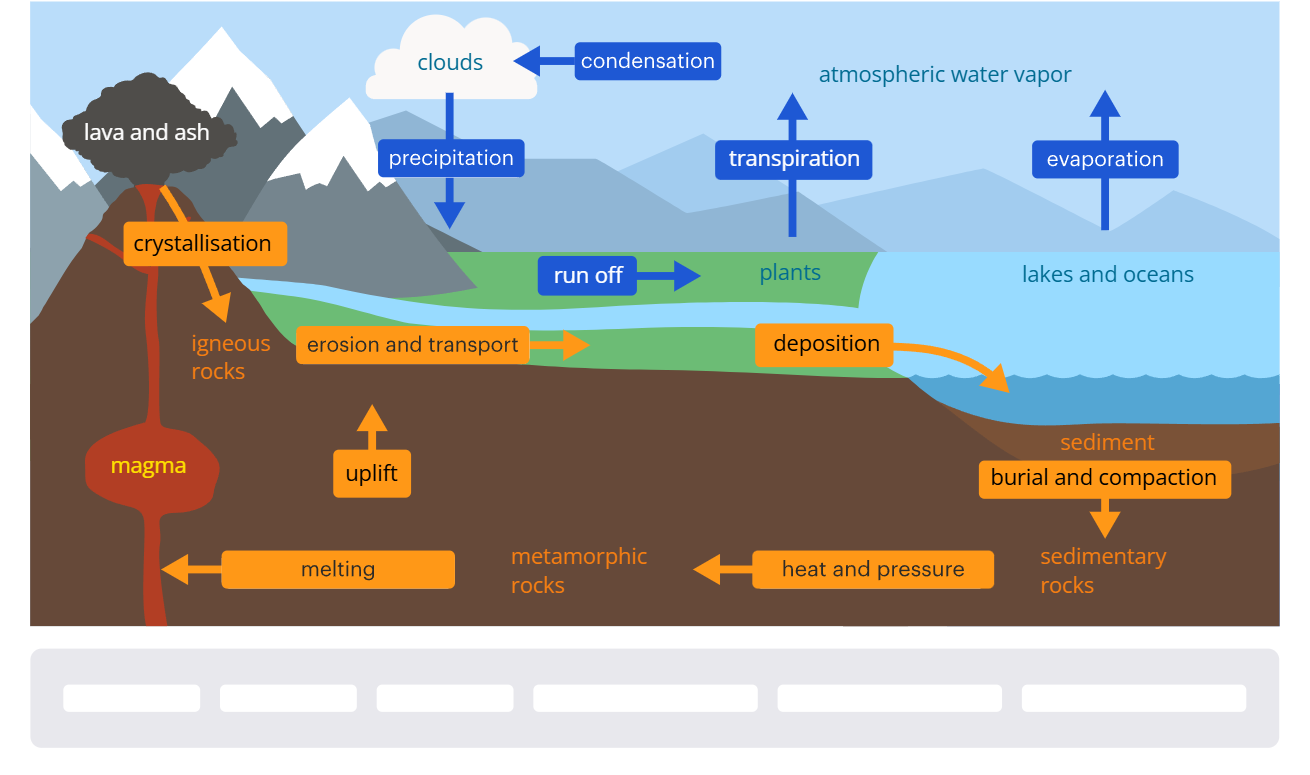
Difference between the water cycle and the rock cycle
Four of Earth’s Systems
Biosphere: living things; eg. humans, sea turtles, pine trees, bacteria
Hydrosphere: water in all its forms
Geosphere: Earth's metallic core, solid rock, molten rock, soil and sediments
Atmosphere: a mixture of gases surrounding the planet
Overlapping Systems: It's water, so is part of the hydrosphere, but being in a gaseous state it mixes with other gases surrounding the planet, so is part of the atmosphere as well. Clouds are made of water droplets or tiny ice particles. They're not gases, but we can still think of them as part of the atmosphere, as well as of the hydrosphere.
Movement of Energy:
Most of the energy on the Earth's surface comes from the Sun, as electromagnetic radiation. Only a little energy comes up from inside the Earth, as heat.
Of all the Sun's radiation that strikes the planet, about:
30% reflects straight back out again
20% is absorbed by the atmosphere
50% is absorbed by land and sea
The radiation that reflects back out into space has no effect on the planet. The radiation that is absorbed transforms to heat, increasing the temperature of the air, land or water that absorbs it.
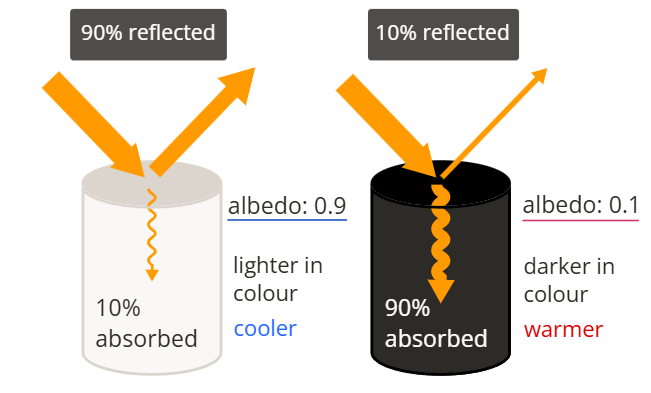
Albedo Effect: This is the amount of radiation of all wavelengths that different surfaces reflect. A surface that reflects no radiation at all has an albedo of 0, something that reflects all radiation has an albedo of 1, and something that reflects half of the radiation it is exposed to has an albedo of 0.5.
White Surfaces: These surfaces reflect most of the light, which means that due to less light being absorbed, it won’t make the surface as hot.
Black Surfaces: Dark objects reflect light poorly, meaning that most of the light is absorbed into the objects as heat.
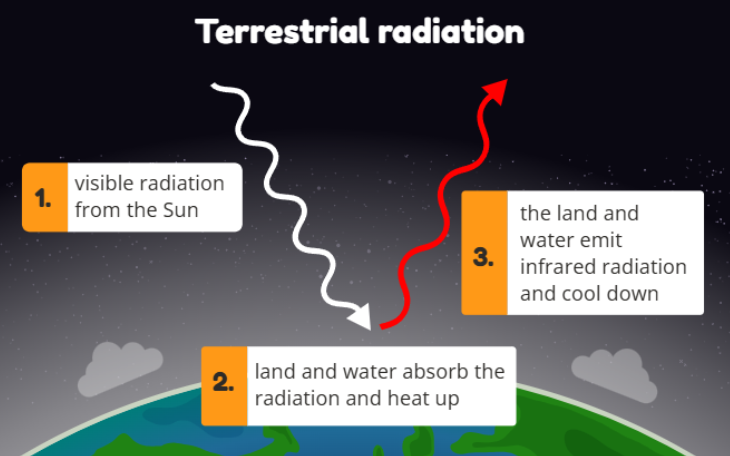
Terrestrial Radiation: When electromagnetic radiation from the sun enters the Earth, some of it gets absorbed by the Earth’s water, land and atmosphere. This means that due to the heat, some of the water evaporates into the atmosphere, forming clouds. The clouds than reflect the radiation coming towards Earth back into space - (infrared radiation)
idk which one it is: Air, land and water heat up by absorbing electromagnetic radiation from the Sun. This is short-wavelength, high-energy visible radiation. When these materials absorb the radiation, they transform the energy into heat.
The air, land and water then transform the heat back into electromagnetic radiation, but because they are not very hot the radiation is lower-energy long-wavelength infrared radiation. This is called terrestrial radiation because it comes from the Earth's air, land and water.
Sequence: Visible light from Sun → energy absorbed as heat → energy emitted as infrared radiation
Conduction is another means of energy transfer. It doesn't involve the movement of matter – heat simply moves through matter from areas of higher temperature to areas of lower temperature, when they are touching .
Another way that heat moves is convection. Air and water are both fluids, which means that they can flow. If they heat up, they rise, and then cooler parts of the air or water move in to fill the space that the warm fluid has moved from. For example, wind is air coming in to replace warmed air that has risen.
Finally, water also transports energy due to evaporation. It takes energy to change liquid water into water vapour, even if the temperature stays the same. So whenever water evaporates, energy transfers into the atmosphere.
Endothermic reactions absorb heat from their surroundings
Exothermic reactions release heat to its surroundings.
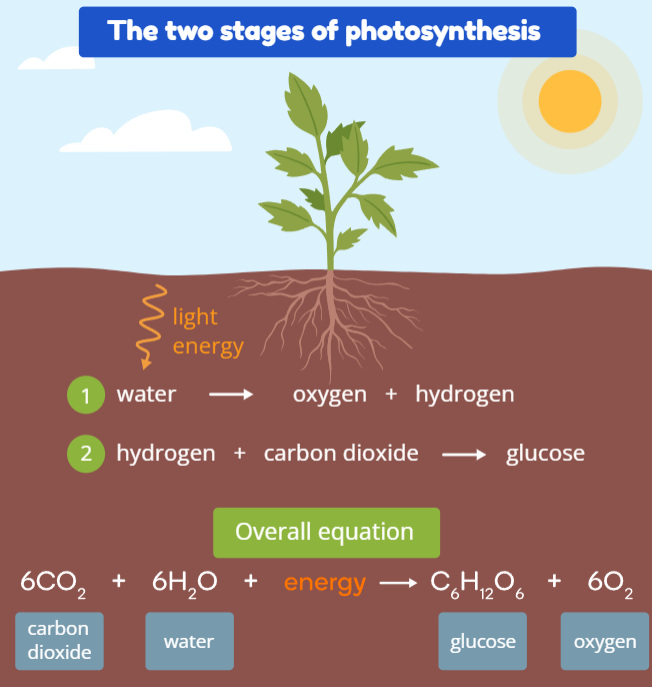
Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis is when plants use energy (sunlight) to make their own food, this is used through the help of carbon dioxide, water and light. When the plants take in these substances, it produces glucose and oxygen. It is an endothermic process.
It turns light energy to chemical energy
Word Equation: Carbon dioxide + water + energy - glucose + oxygen
Chemical Equation: CO2 + H2O + energy - C6 H12 O2 + O2
Cellular Respiration: Respiration is the reaction that releases the chemical energy in glucose for use in life processes. Most plants and animals use this reaction to release energy in cells, essential for growth, repair and reproduction. It is an exothermic reaction as it releases energy.
Word Equation: Glucose + oxygen - carbon dioxide + water + energy
Chemical Equation: 6 C6 H12 O6 - 6 CO2 +6 H2O +energy