Environmental Biology Quiz
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Environmental Literacy
demonstrate knowledge and understanding of the affect the environment had on humans and the effects that humans have on the environment
Ecosystem Services
human dependence on ecosystems
ex. water purification, biogeochemical cycling, natural resources such as firewood and food
Ecological Footprint
human domination of ecosystems
ex. deforestation, freshwater salinization syndrome, climate change/global warming, agricultural runoff
Sustainability
human stewardship of ecosystems
sustainable societies must live within regenerative capacity of the Earth
meet present needs without compromising future generations
Sustainable Development
development meets present and future human needs without damaging environment biodiversity
Habitat Destruction
the single greatest cause of modern extinction
affecting nearly 75% of all species designated as extinct, endangered, vulnerable, or rare
greater than 90% of world’s coral reefs have been damaged
Habitat Fragmentation
habitats are broken up into fragments mostly too small to support populations
Wildlife Corridors
connect habitat fragments
Invasive Species
introduced species are accidentally or intentionally moved from native locations to new geographic regions
ex. Nile Perch in Lake Victoria, led to the extinction of many native Cichlid species
Overexploitation
humans harvesting plants and animals too fast to replace
ex. Atlantic Cod, Minke Whale, Bison
Disruption of Food Chains
the extinction of one species can doom other members of its trophic chain
Acid Rain
when coal is burned, Sulfur and Nitrogen are released
these react with air and water vapor in the atmosphere to form Sulfuric Acid and Nitric Acid that are picked up by falling rain/snow
Freshwater Salinization Syndrome
the accumulation of salts in freshwater ecosystems due to human activities, primarily road salt, sewage, and irrigation
Global Warming
the Greenhouse Effect is caused when gases in the Earth’s atmosphere trap the suns daily heat and prevent it from being released into space at night
Tragedy of the Commons
when a common resource is used below its carrying capacity, all users can benefit from the resource
if one or a few individuals use the resource beyond its carrying capacity, the resource will degrade and become unavailable to all users
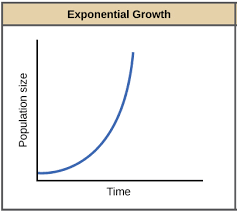
Exponential Population Growth
maximum growth rate under ideal conditions
Logistic Population Growth
population growth is limited by carrying capacity (K)
fits the growth of real populations
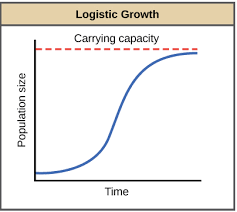
Carrying Capacity (K)
the maximum population size an environment can support
Maximum Sustainable Yield (MSY)
maximum number of individuals that can be sustainably harvested from a species
found at half the maximum effective population size MSY = (K x r)/2
Normal rain typically has a pH of around ___ and is slightly acidic due to dissolved ___
5.6 and CO2
pH Scale
way to rank a solution’s acidity relative to neutral pure water and is a measure of how many free protons (Hydrogen ion) there are in a solution
0-7 acidic, 7-14 basic, 7 neutral
logarithmic - moving one number means the solution is ten times more acidic and has ten times more free protons
Atmospheric fall out of acid can occur in 3 ways...
Acid rain = precipitation
Acid fog that hangs over high peaks
Dry deposition of acidic particles settling during dry weather
In Freshwater systems, Phosphorus (P) is a limiting resource for the following reasons…
Naturally low in abundance
Less soluble in water
Reacts with soil particles and metals making it unavailable to living organisms
Collects at the ocean bottom due to sedimentation and is not easily brought back to terrestrial environments
What leads to over-fertilization of freshwater systems…
pollution in the form of agricultural fertilizer and untreated sewage due to rainstorms can deliver large amounts of Phosphate
Eutrophication
harmful over-fertilization of water due to excessive nutrient input
ex. N, P, K
Stage 1 of Eutrophication
Nutrient Overload - too much N, P, or K
Stage 2 of Eutrophication
Algal Blooms - algal population explosion blocks sunlight from reaching below
Stage 3 of Eutrophication
Hypoxia/Anoxia - heterotrophs use all dissolved O2 in decomposing dead algae
Stage 4 of Eutrophication
Dead Zones - death of fish and other species that need oxygen