Session 6: Pathological Fractures and introduction to Radiology
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
List some types of imaging
Ultrasound
X-ray
CT
MRI
Nuclear medicine (PET)
Ultrasound
Electricity turned into sound waves (vibration) which passes through structures. Electrical current causes crystal to vibrate – generating ultrasound waves
Application = monitor fetus growth in pregnancy
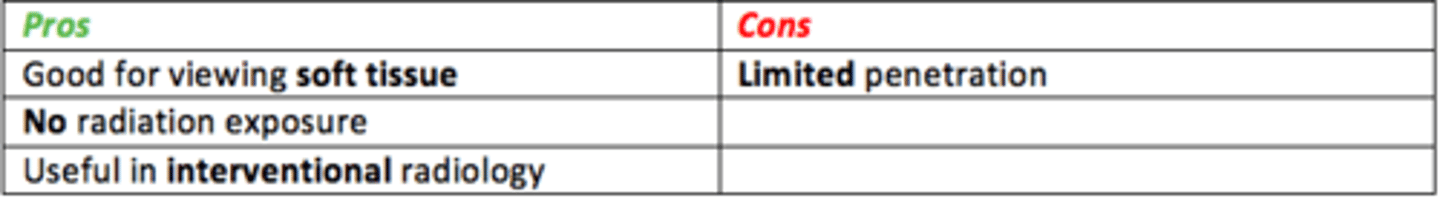
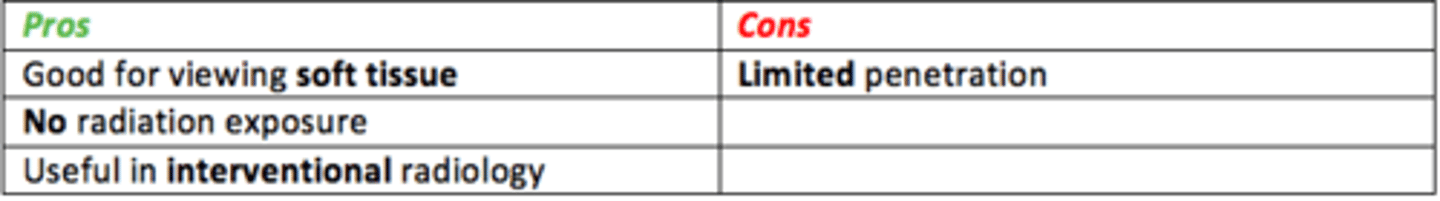
Pros/cons of ultrasound
Pros
- Good at viewing soft tissues and vessels
- Real-time imaging (dynamic)
- Portable machines (bedside)
- No radiation
- Useful in interventional radiology
- Quick, simple
Cons
- Limited penetration (excess body fat)
- Bone (poor detail)
- Dependent on skill of operator
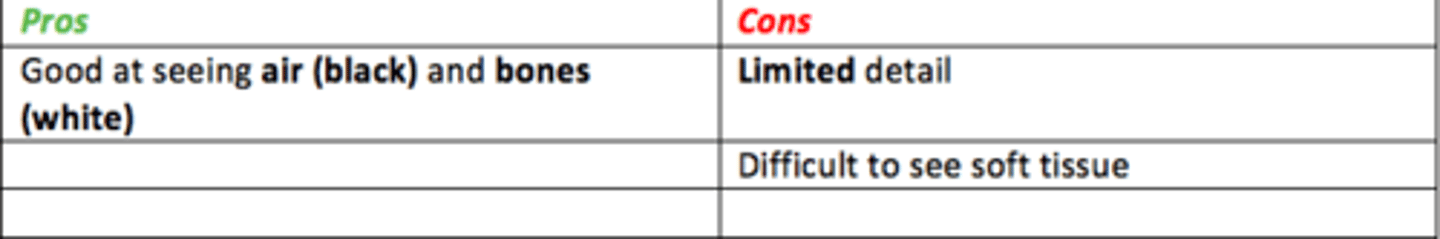
X-rays are short wavelength electromagnetic radiation
What are the pros/cons of x-rays?
Pros
- Good at seeing air (black) and bones (white)
- Can be done rapidly
- Can be portable
- Low dose of radiation compared to CT scan
Cons
- Limited detail
- Difficult to see soft tissue
- Electromagnetic radiation exposure (albeit low)
- May still require further imaging to confirm a diagnosis, low sensitivity
- 2D image only
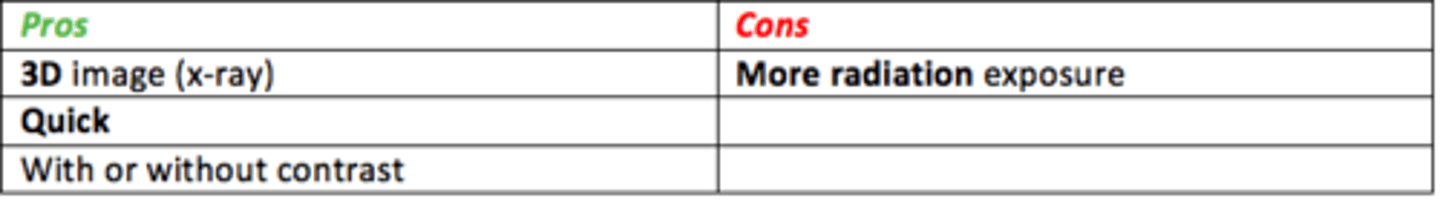
CT scans (computed tomography) are 3D x-rays (multiple x-rays pieced together in a software)
Pros/cons of 3D CT?
Pros
- 3D X-ray (multiple x-rays pieced together in software)
- Quick
- With or without contrast
- 3D reconstruction
Cons
- Radiation hazard
- Nephrotic contrast media
- Lower resolution than MRI
- Claustrophobia
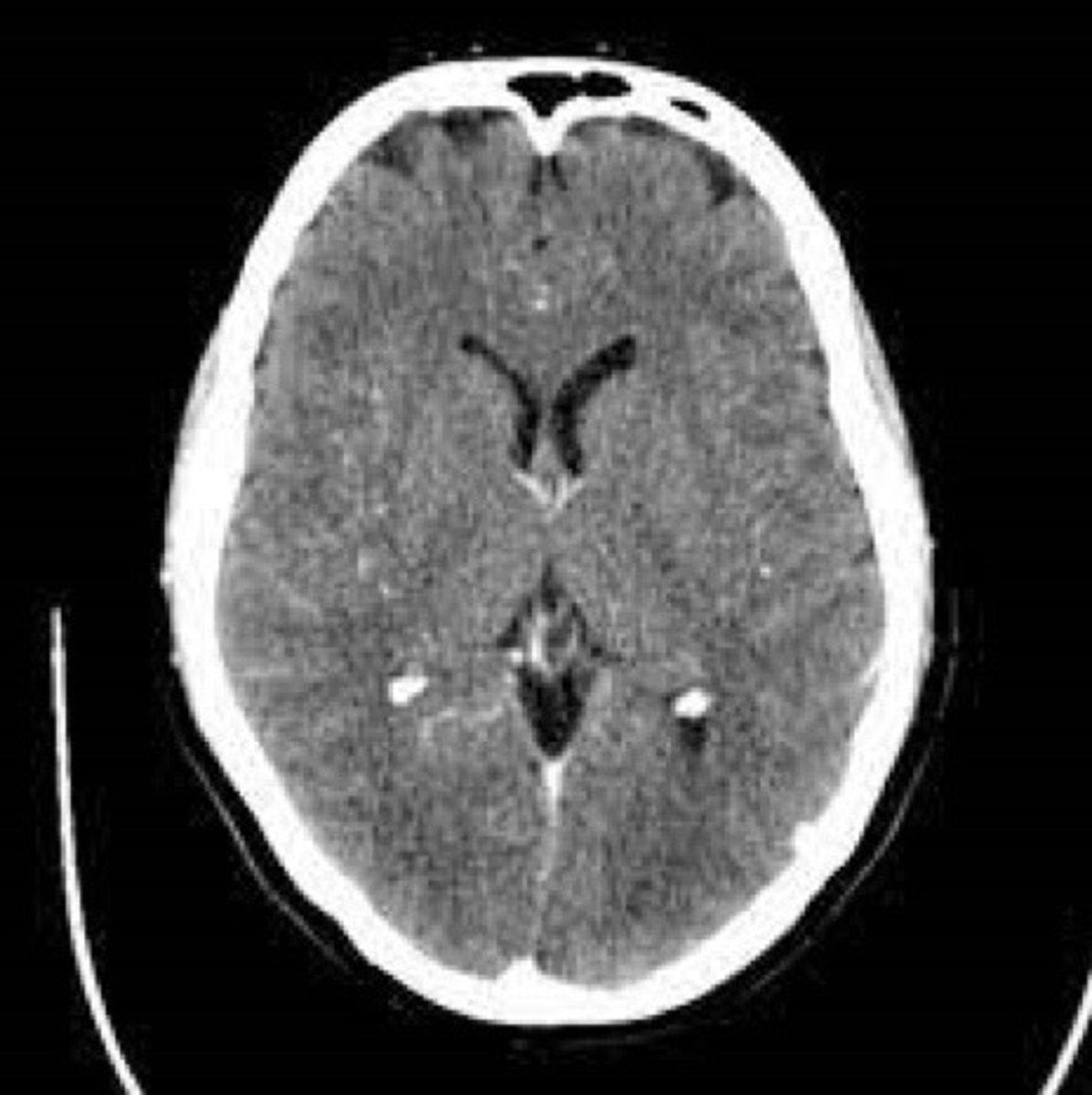
In which anatomical plane is this CT scan of the head taken
Saggital, coronal, transverse?
Transverse/axial
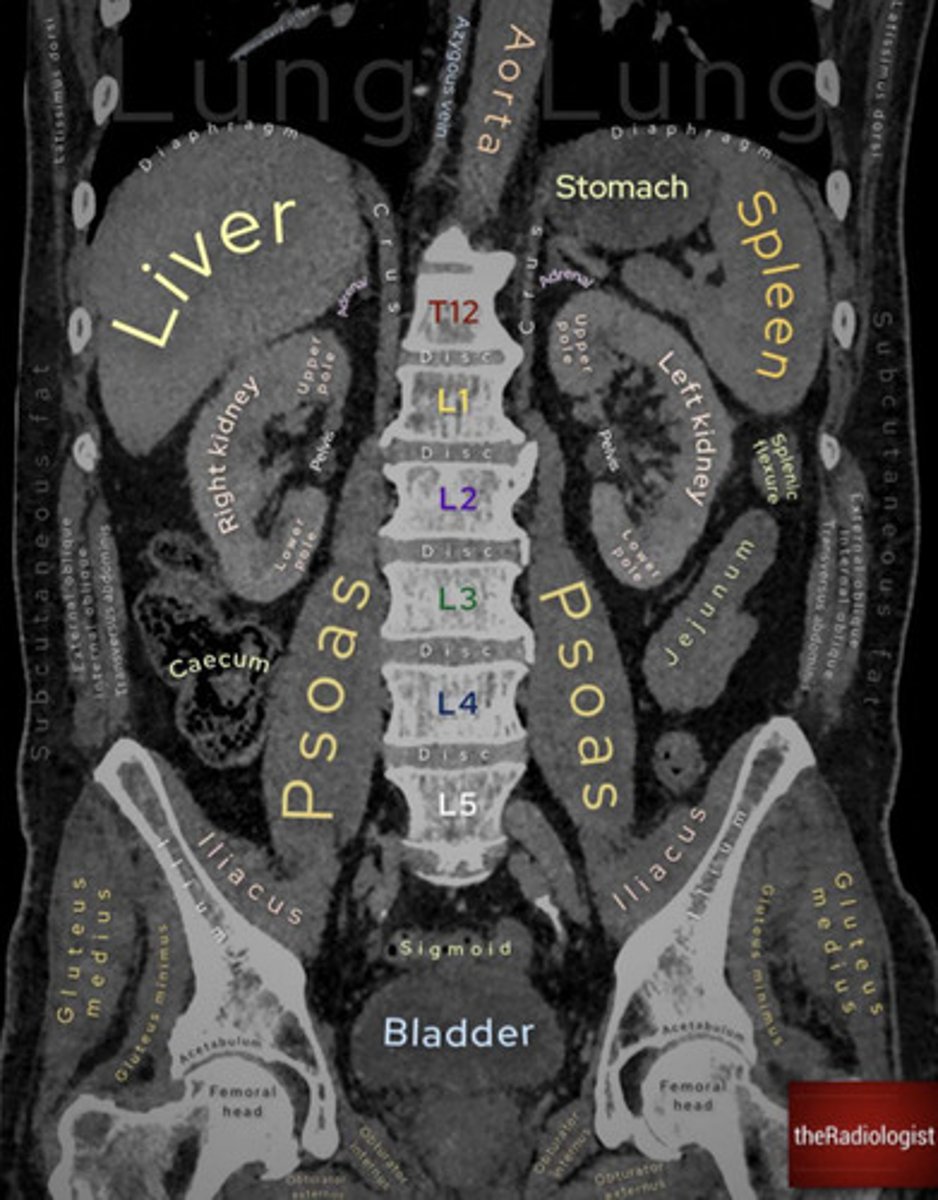
In which anatomical plane is this CT scan of the abdomen taken
Saggital, coronal, transverse?
Coronal
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
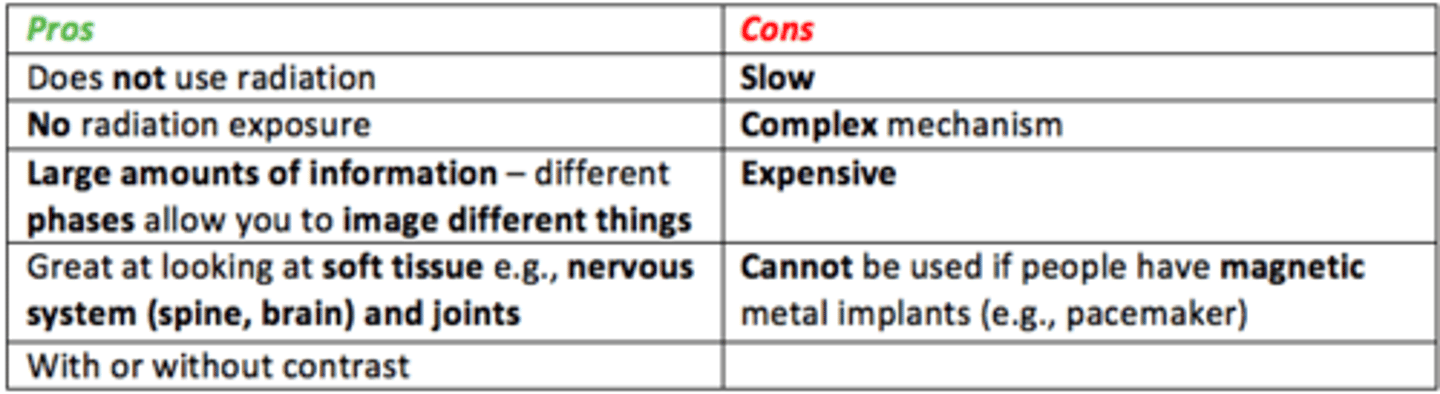
Pros/cons of MRI?
Pros
- Does not use radiation
- Very high resolution
- 3D imaging
- High sensitivity (excellent soft tissue differentiation)
- Multiplanar
- Provides full section imaging (compared to ultrasound which is limited by window)
Cons
- Cannot be used if people have magnetic metal implants (e.g., pacemakers)
- Slow/lengthy exam
- Expensive
- Complex mechanism
- Motion artefact, claustrophobia
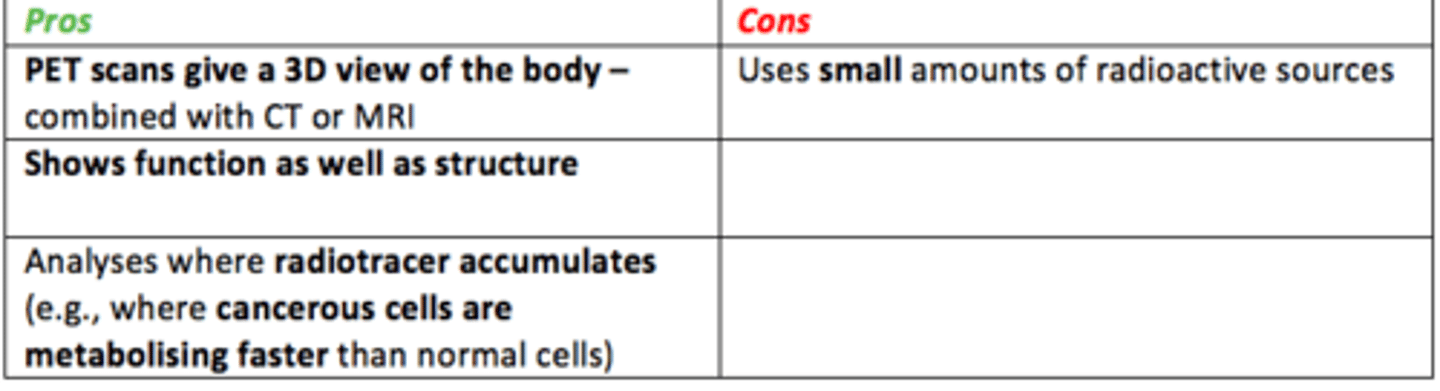
Pros/cons of nuclear medicine
Pros
- Gives 3D view of the body combined with CT/MRI
- Shows function & structure
- Analyses areas where radio-tracer accumulates (e.g., cancerous cells metabolising faster than normal cells)
Cons
- Uses small amount of radioactive sources
- Expensive
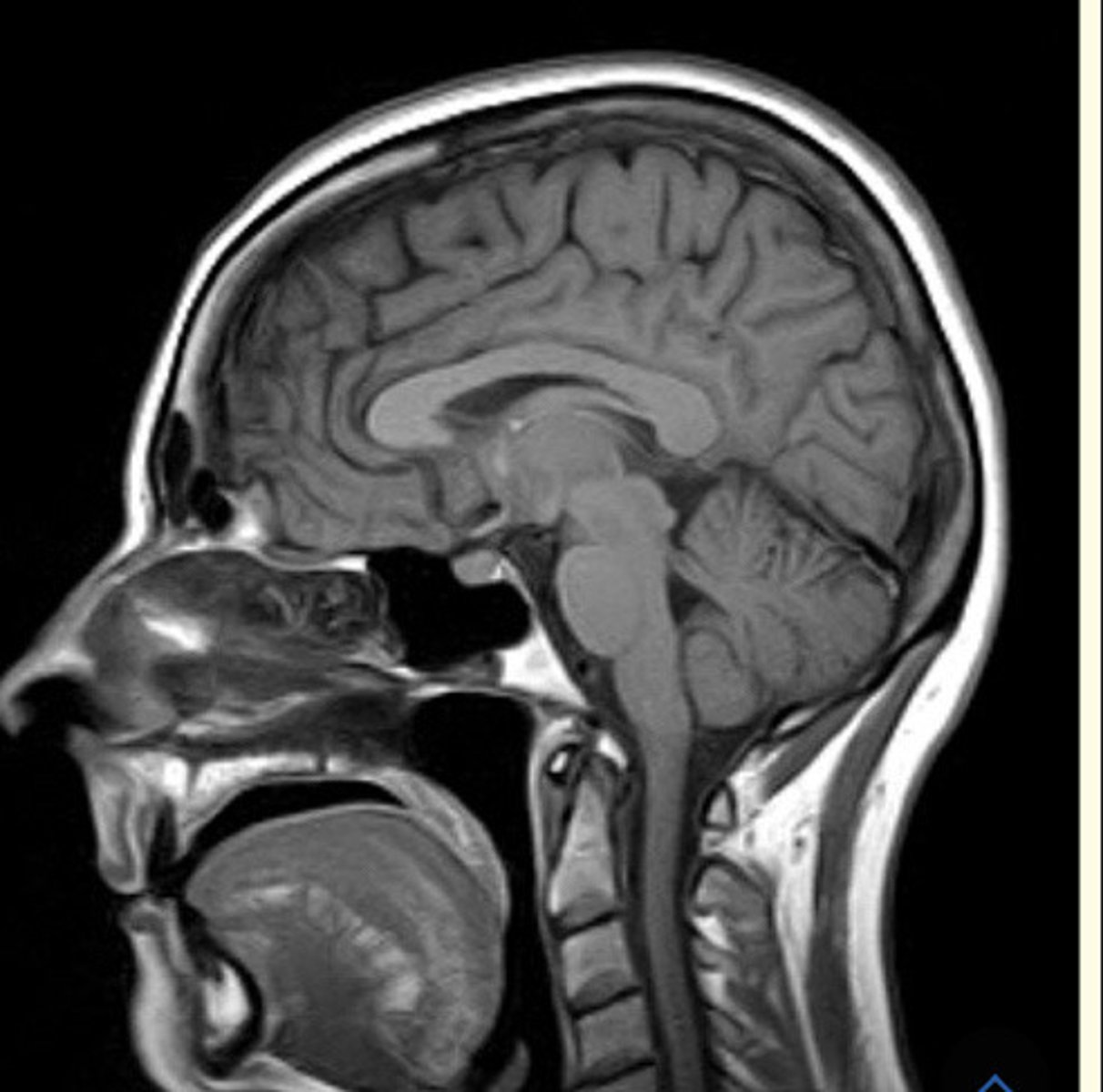
What anatomical plane is this MRI scan of the head taken?
Saggital
What is a fracture
A break or crack in a bone
What is a pathological fracture
Normal (minor) stress placed on a bone breaks it due to it being weakened by disease
Morbidity
Refers to ill health in an individual and the levels of ill health in a population or group.
Mortality
The number of deaths in a population from a particular cause
Normal bone is made up of ___ and ___ phosphate
collagen and calcium phosphate
Osteoblasts ___ bone
build
Osteoclasts ___ bone
Osteoclasts cut/claw away bone
Calcium absorbed in the small intestine and kidney using vitamin ___
vitamin D
Calcium levels and osteoclast activity modulated by ___
PTH (parathyroid hormone)
What are some causes of weak bones in children
Bone cysts, rickets, osteogenesis imperfecta, infection, cancer
What are some causes of weak bones in adults
Osteoporosis, osteomalacia, Paget's disease, infection, cancer
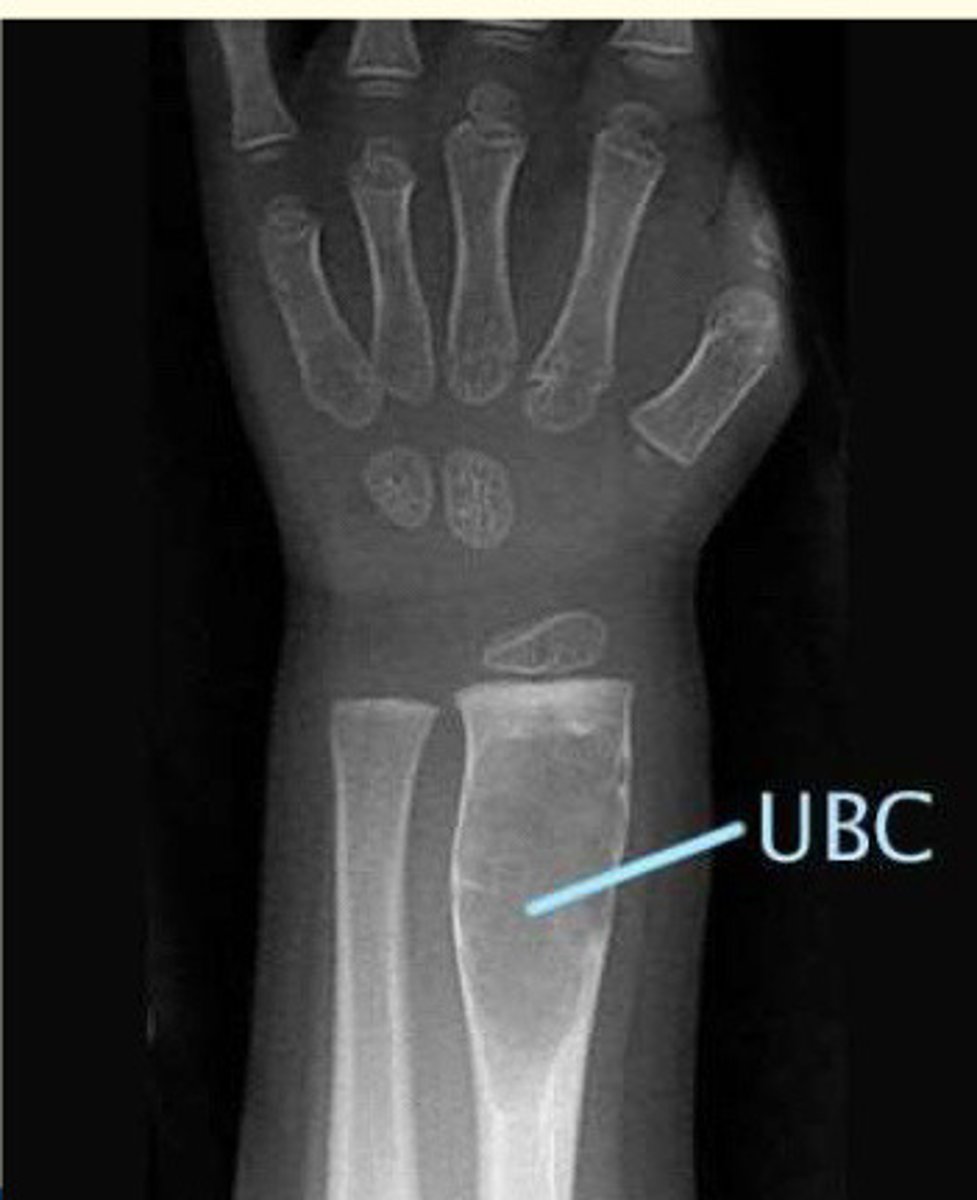
What are bone cysts
Fluid filled spots inside bones which develop during growth of bones
These usually do not cause issues but can occasionally weaken bones enough to break
Rickets and osteomalacia are caused by...
Low vitamin D
Leading to reduced calcium absorption
Leading to impaired mineralisation of bone
In children - rickets and osteomalacia cause bones to…
Grow without mineralisation
In adults - rickets and osteomalacia cause…
Impaired bone remodelling
Soft/weak bones
What are other causes of weak bones?
Osteomyelitis
Osteogenesis imperfecta
Paget's disease
Cancer

Osteomyelitis
Infection - causes area of bone breakdown due to bacterial infection
Osteogenesis imperfecta
Autosomal dominant inherited condition - brittle bone disease
Paget's disease
High turnover of bone - leads to area of high and low density
Osteoporosis approximately affects ___% people at age 50 and almost ___% of people at 80
Osteoporosis approximately affects 2% of people at age 50 and almost 50% of people at 80
___ is the most common cause of pathological fractures
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis mainly affects ___ bones
Osteoporosis mainly affects cancellous (spongy) bones
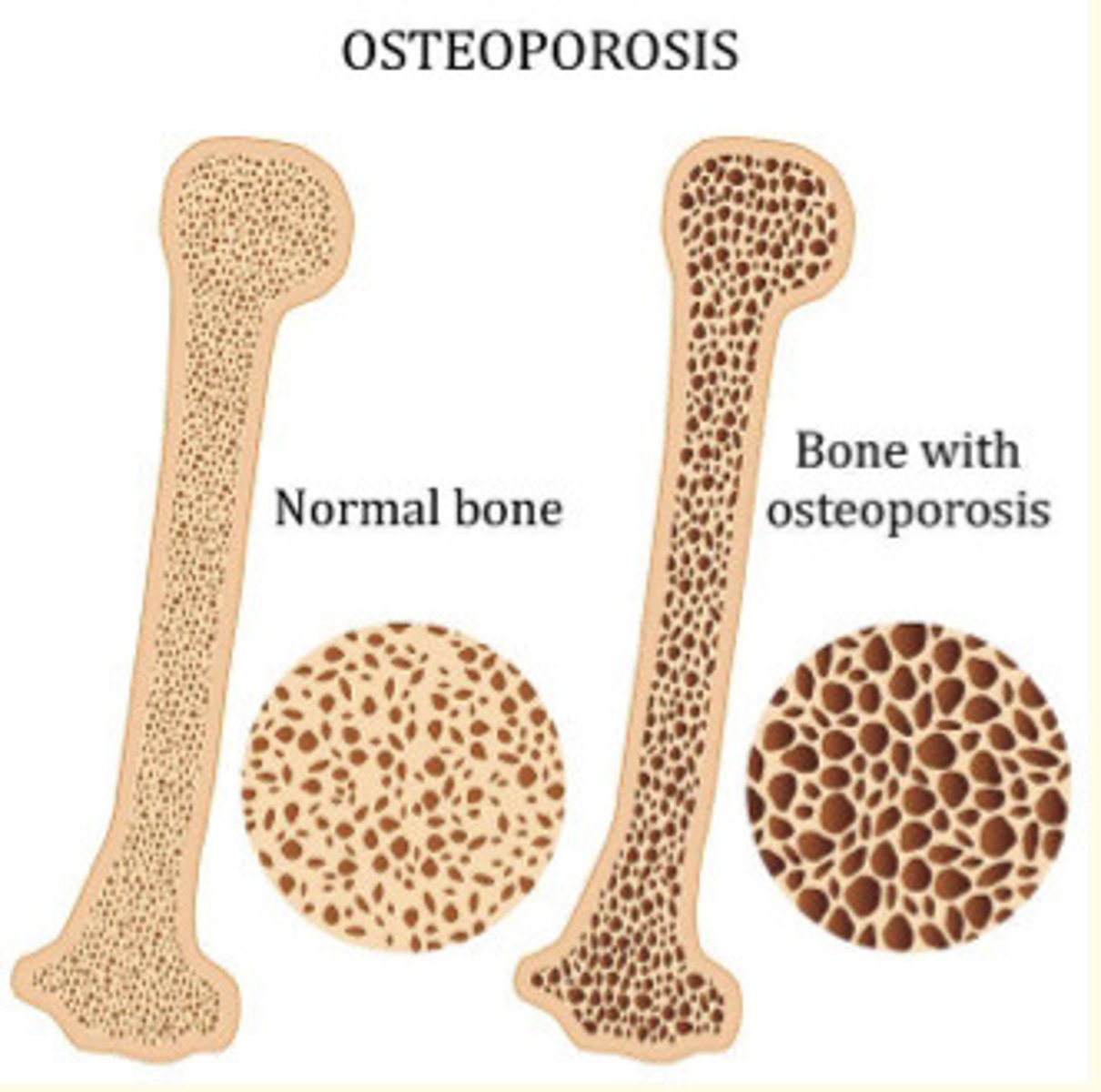
What is the effect of osteoporosis on the bone?
Deterioration in trabecular bone matrix
Reduction in bone mass
Risk factors of osteoporosis
ACCESS
- Age/alcohol
- Corticosteroid use (prednisolone)
- Calcium (low)
- Estrogen (low) - post-menopausal, women
- Smoking
- Sedentary lifestyle
Some risk factors of osteoporosis
Older age
F > M
Calcium deficiency
Smoking
Alcohol intake high
Sedentary lifestyle
What tools is used to assess risk of osteoporosis?
FRAX - tool that puts risk factors together to determine risk of osteoporosis. This calculates the risk of major osteoporotic fracture (MOF)
INPUT
- Sex
- Weight/height
- Previous fractures
- Currently smoking
- Glucocorticoids
- Rheumatoid arthritis
What tool is used if someone is at significant risk of osteoporosis (used to guide treatment)?
DEXA scan - bone density scanning through x-ray
___ have a higher peak bone mass
Men have a higher peak bone mass
What is a fragility fracture
A fracture resulting from a force that would not ordinarily result in fracture
Secondary to osteoporosis
What is a common site of fragility fracture?
- Hip and vertebrae
- Wrist fractures
Fragility fractures are fractures after a fall from ___ height
standing height
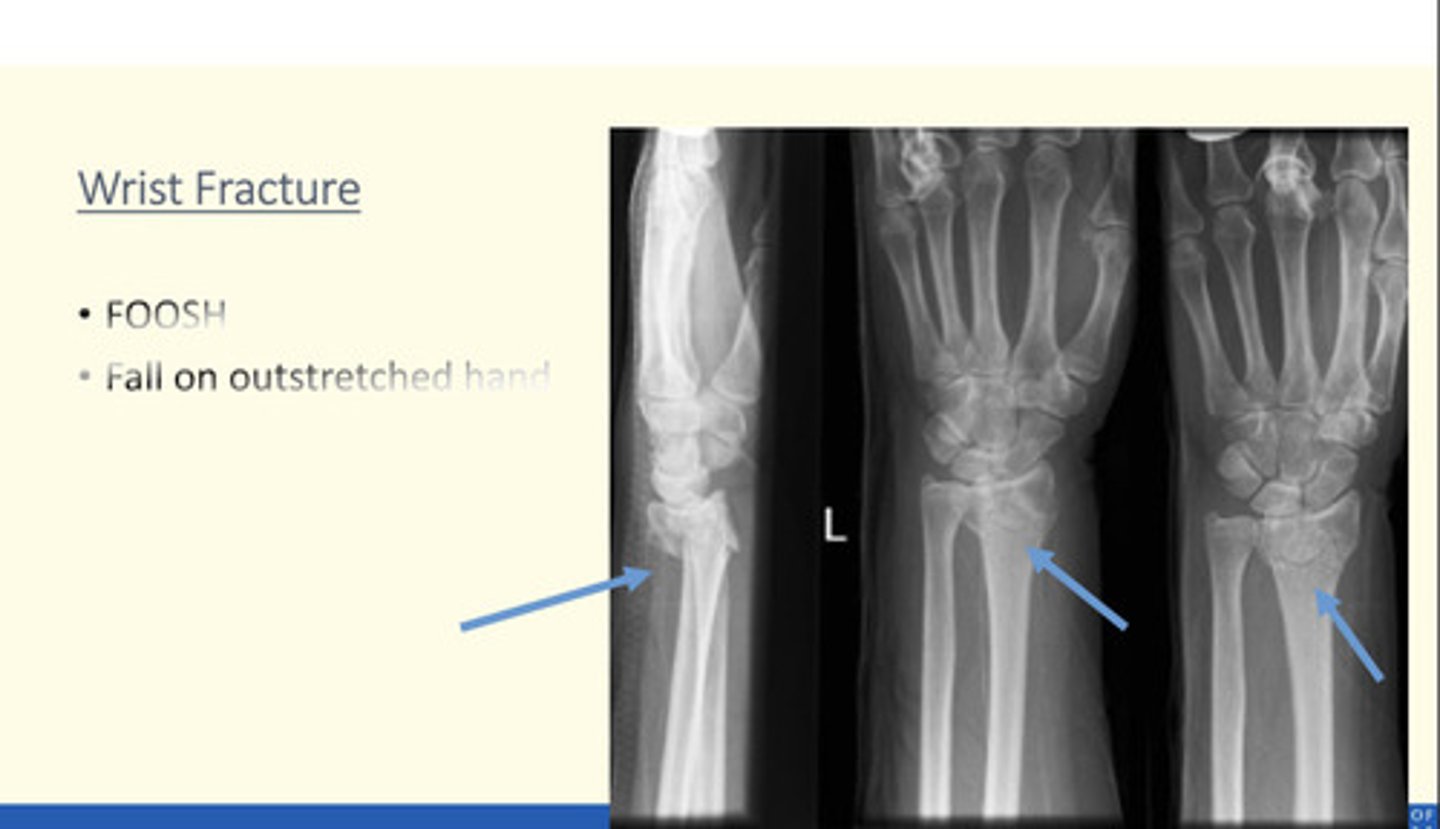
Wrist fracture (FOOSH)
Fall on outstretched hand
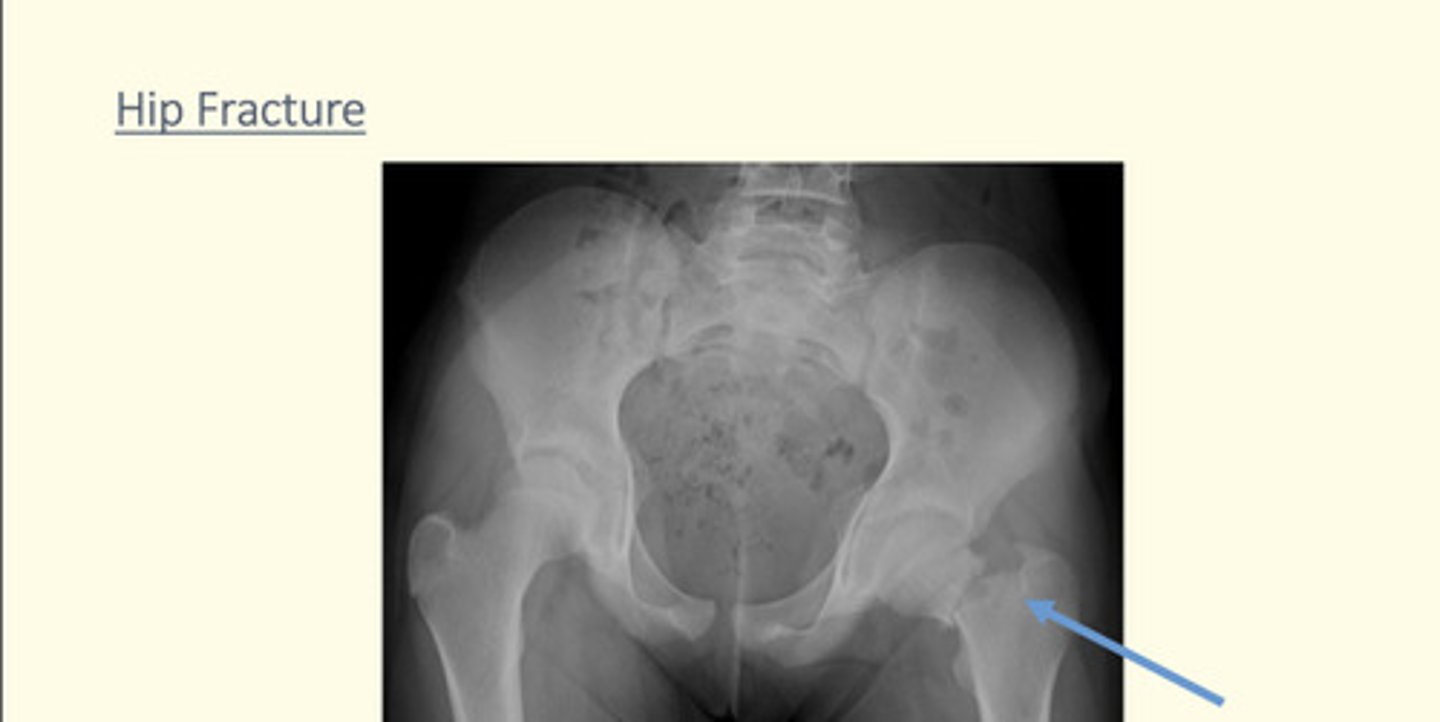
Hip fracture
What is management of osteoporosis?
- Calcium & Vitamin D supplements
- Bisphosphonates
- Acute management of any fractures
What are some preventative measures against osteoporosis?
Early identification and intervention for risk factors
- HRT, careful use of steroid prescribing (prednisolone)
- Cessation of smoking/alcohol
- Medication review
Falls prevention
- Strength training & physio
- Home assessment

What type of molecules are temporarily realigned by magnets of an MRI machine?
Water molecules
What colour is fluid on an USS (ultrasound scan)?
Black
What is the indications for x-ray?
- Imaging of the skeletal system
- Can be used for detecting some disease processes in soft tissues
Chest x-ray indications
Used for identifying lung pathologies
- Pneumonias
- Infections
- Heart failure
- Cancer
Abdominal x-ray indications
Used for identifying obstruction, free air from visceral perforation
What is the indications for ultrasound?
- Transthoracic imaging = heart, echocardiogram
- Trans-abdominal = review swelling/masses
- Foetal scans = monitor foetal growth
- Soft tissue swellings = cysts, lymph nodes
- Assist biopsies, needle placement in central line insertion
Doppler ultrasounds are used for
Looking for clots
What is the indications for CT?
- Acute trauma
- Head injury/initial imaging for stroke/haemorrhage
- Cancer staging
- Abdominal imaging e.g., acute appendicitis
- Facial bones
What is the indications for MRI?
- Neuroimaging = demyelinating disease, dementia, cerebrovascular disease
- Cardiovascular = myocardial ischeamia, myocarditis, cardiomyopathies
- MSK = spinal, soft tissue tumours
- GI = liver, pancreas, bile duct
- Angiography = stenosis, aneurysm
Contraindications of MRI (absolute and relative?
Absolute = some metal implants (e.g, aneurysm clips), pacemakers, some stents, cochlear implants
Relative (mostly due to contrast agent used) = pregnancy, allergies, kidney disease
What does x-rays image?
Bone
What does ultrasounds image?
Soft tissues/vessels
What does CT scans image?
- Bones
- Soft tissue
- Calcium containing deposits
- Blood vessels (angiography)
What does MRI image?
Most tissues visualised well
High calcium and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) enzyme in blood test
Bone cancer