Maternal Crash Course
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Assesment/care during pregnancy or complications occurring during pregnancy
Antepartum Care
Gravidia “G”
Number of times a client is pregnant no matter what the outcome was
G1 = First time being pregnant
Para “P”
Number of deliveries that are greater than 20 weeks of gestation
TPAL stands for
Term: Greater than 37 weeks of gestation
Preterm: Less than 37 weeks of gestation but before 20 weeks.
Abortions: Miscarriage, and Elective Abortions
Living children
What does G3, P2, T1, P1 A0 L2 mean
G3 = Pregnant 3 times
P2 = Gave birth 2 times over 20 weeks
T1 = Birth over 37 weeks (term)
P1 = Birth less than 37 weeks but greater than 20 weeks
A0 = No abortions
L2 = 2 living children
Normal pregnancy discomforts are
-Blocked Nose
-Backache
-Insomnia
-Leg Cramps
-Lower Extremity edema
-Heartburn & Constipation
-Bladder problems
-Nausea & Vomiting
Naegele’s Rule → Estimating the due date of a mother
1) Due date of last menstrual period (LMP) Ex: April 14
2) Subtract 3 months
3) Add 7 days
Answer: January 21st
McDonald’s Method → Fundal Height measurement
Measuring from the pubic symphysis to the fundus, the cm correlates with the baby's gestational age.
Ex: 20cm = ~20 weeks
McDonald’s Method Key Anatomical Structures
-16 weeks: Fundus is halfway between pubic symphysis and umbilicus
-20 weeks: Fundus is found at the umbilicus
-36 weeks: The fundus is located at the xiphoid process.
Gestational age classifications
Preterm → Before 37 weeks
Early term → 37-38 weeks
Full term → 39-40 weeks
Late term → 40-41 weeks
Post term → After 42 weeks
Multisystem disorder that causes vasospasm, endothelial dysfunction & decreased organ perfusion is called
Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia key characteristics
-HTN
-Proteinuria
-Hyperactive Reflexes (+3 or +4)
-Upper Body Edema (hands & face)
Preeclampsia complication
Eclampsia → Seizures
Treatment for Preeclampsia
Magnesium sulfate & baby delivery
Elevated blood glucose levels due to the pregnancy hormone hPL, which causes insulin resistance and affects nutrient metabolism
Gestational Diabetes
How do you characterized Gestational Diabetes
Abnromal GTT test
Key complications of Gestational Diabetes
-Macrosomia → Large baby
-Shoulder dystocia → Baby's shoulder is stuck in mother's
Treatment for Gestational Diabetes
Diet, activity, insulin, & baby delivery
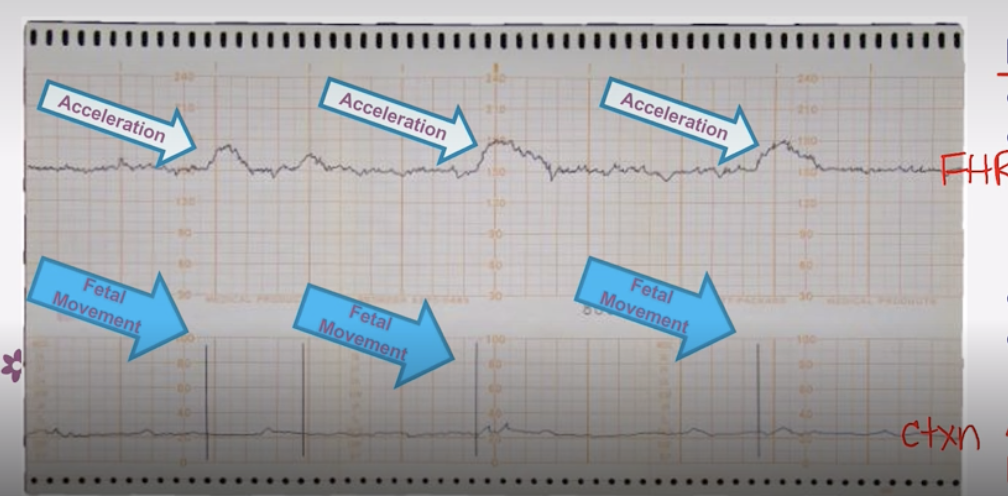
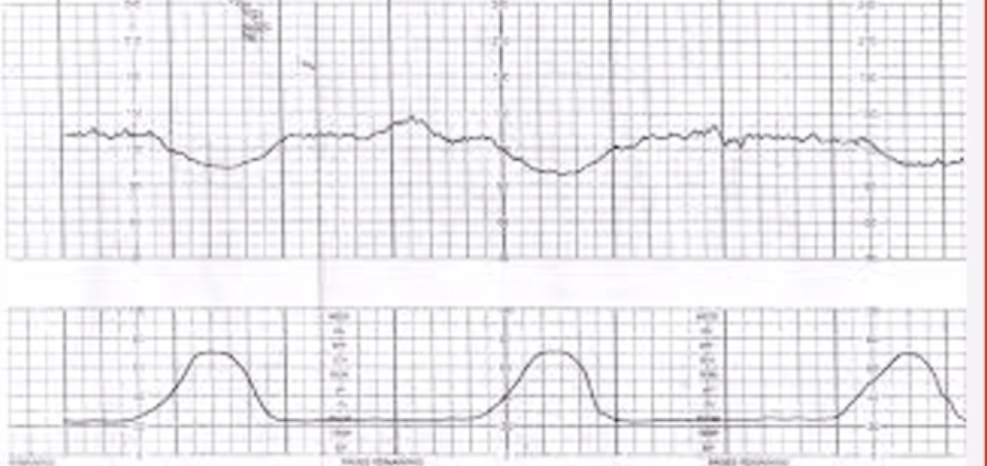
Non Stress Test Graph Orientation
Top = Fetal HR
Bottom = Uterine Contractions
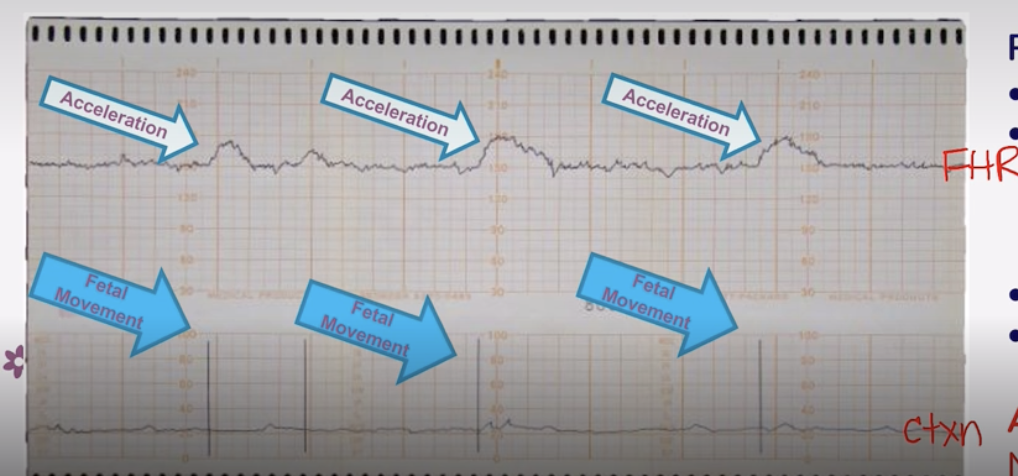
Reactive Non-Stress Test
-IS GOOD!
-Normal baseline → Fetal HR stays consistent on a line in between accelerations
-Acceleration of Fetal HR aligns with a Uterine Contraction
-Moderate Variability → Moderate Squiggles
-No decelerations noted
Non-reactive Non-stress Test
-IS BAD
-Abnormal baseline
-Absence of accelerations
-Presence of decelerations
Assessment/ care during labor and birth or complication during labor and birth
Intrapartum
Prenatal Record components
1) Gestational Age
2) Prenatal labs → Blood type, Rh, Hep B, HIV, GTT test, Group B strep status (can cause neonatal sepsis)
3) Obstetrical & Med/Surg history
4) Any other risk factors
How to determine labor status
Sterile Vaginal Exam (SVE)
Sterile Vaginal Exam Steps
1) Dilation on a scale of 0 to 10 cm
2) Effacement → Thinning of the cervix (0-100)
3) Station → Where the baby’s head (vertex or cephalic) is in relation to the ischial spine. (Above = neg ; Inline with spine = 0 ; Below = pos)
4) Presenting part → Head vs Buttocks (We want head down)
Stage 1 of labor
Early Phase: 0-5 cm cervix dilated
Active Phase: 6-10 cm cervix dilated
Stage 2 of labor
Birth of baby
Stage 3 of delivery
Delivery of Placenta
Stage 4
Body readjusts after giving birth
Greater than 5 contractions in 10 minutes is called
Tachysystole
In between contractions do we want the uterus to feel firm or soft?
Soft
Different Anesthesia for different births
Epidural Anesthesia → Vaginal Birth
Spinal Anesthesia → C-Section
Pudendal/Local Anesthesia→ Episiotomy Repair
What does electronic fetal monitoring measure?
1) Assess fetal well-being & uterine activity
2) Measure fetal oxygenation
Intermittent Vs Continuous External Vs Continuous Internal
Intermittent → Low risk pts
Continuous External → Low to High risk pts
Continuous Internal → High risk (usually for C-section births)
Normal Fetal HR
110-160 BPM
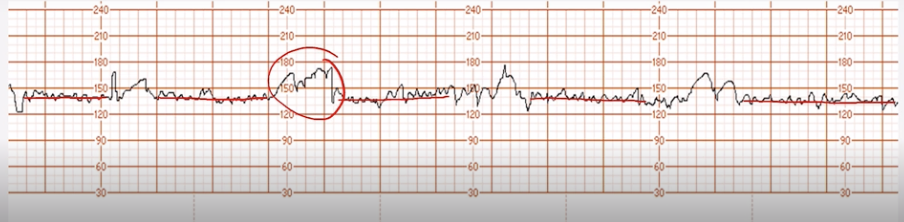
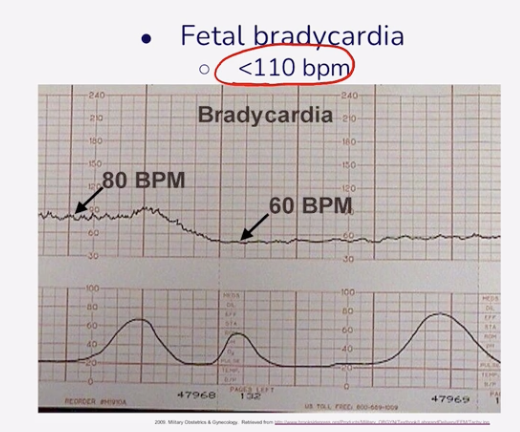
Bradycardic Fetal HR
Less than 110 BPM
Tachycardic Fetal HR
More than 160 BPM
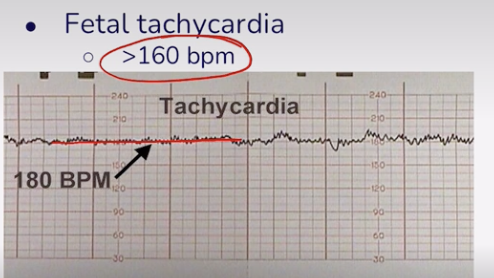
Irregular fluctuations in the FHR baseline measured as amplitude
Variability
We want moderate variability because it indicates adequate oxygenation & CNS function
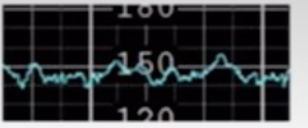
Moderate Variability
6-25 beats
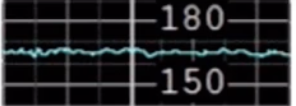
Minimal Variability
1-5 beats
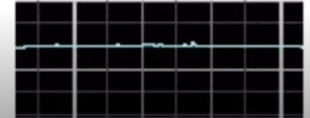
Absent Variability
0 beats
Marked Variability
Over 25 beats
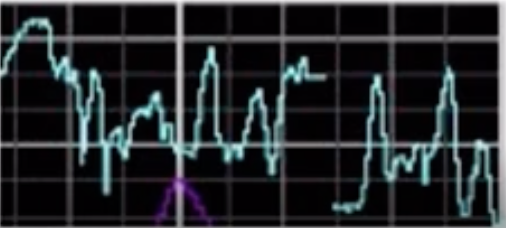
Early Decelerations
-Not a concern due to Head compression
-Slow & gradual
Causes: Active stage of labor, pushing, crowning
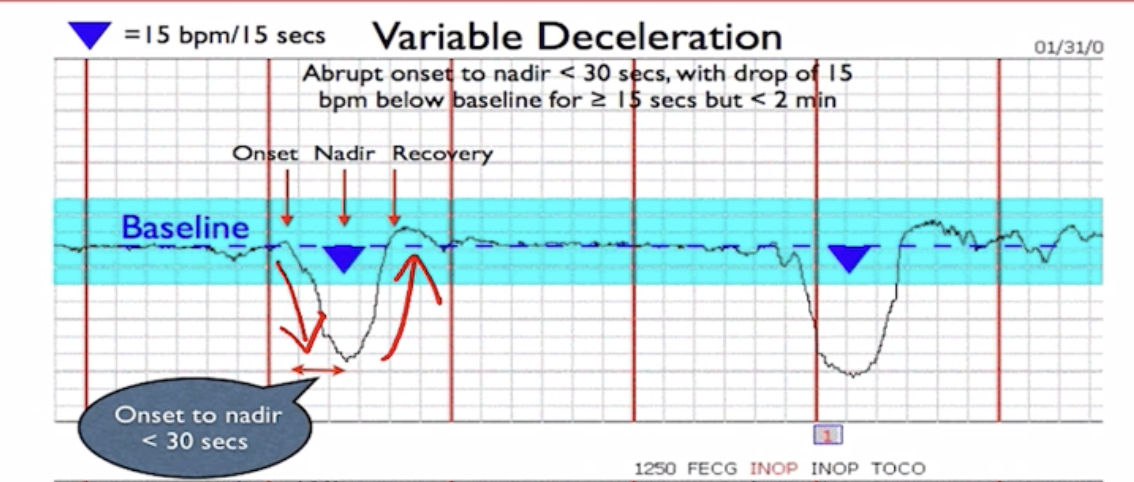
Variable Decelerations
-High levels of Concern
-Abrupt decrease and then return to baseline
-Unpredictable shape
-Caused by cord compression
Late Deceleration
-Most Concerning effect
-Gradual, but NADIR (lowest point of bubble) happens AFTER contraction
-Indicates not enough oxygen to the baby
-Causes: HTN, Vascular damage, Uterine tachysystole
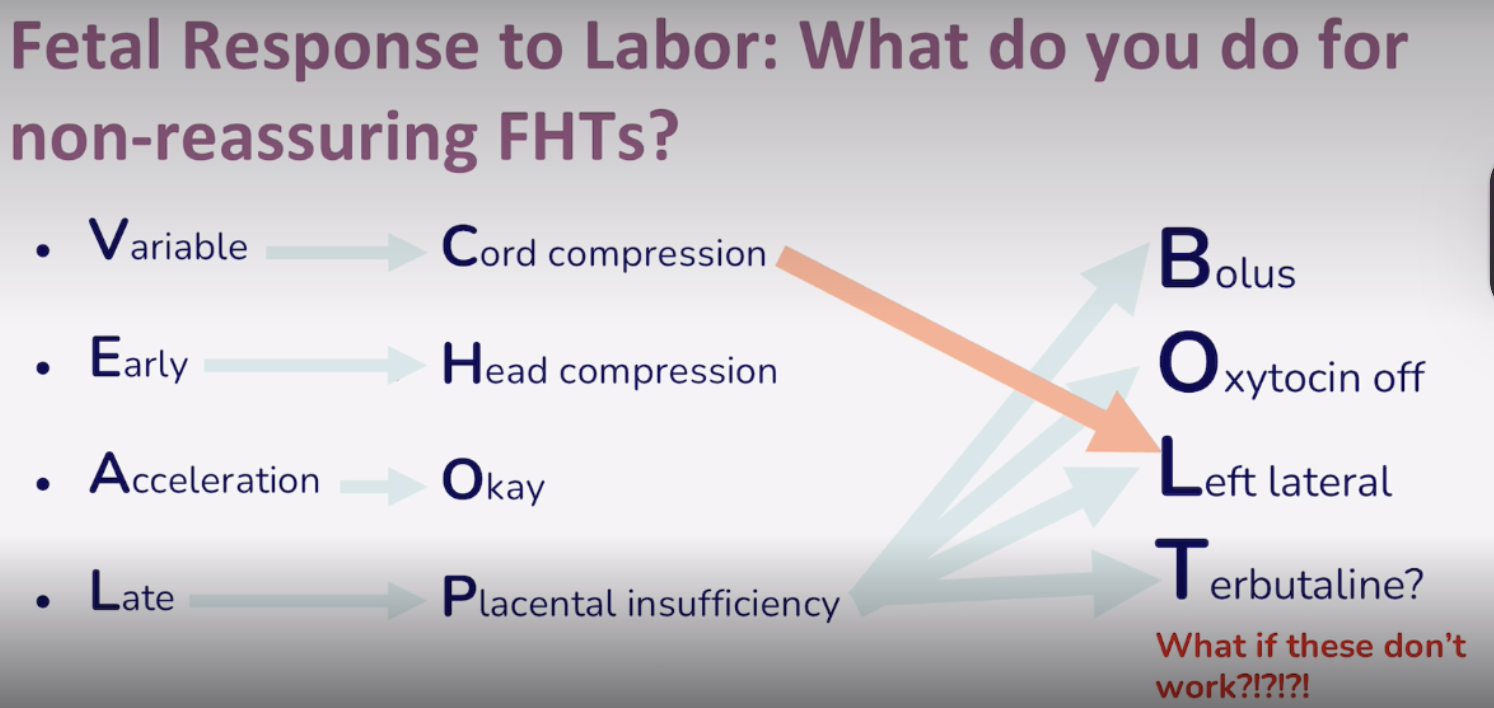
BOLT Pneumonic
If these do not work, we will have to do an emergency C section
External manipulation of the fetus to a vertex presentation is called
External Cephalic Version
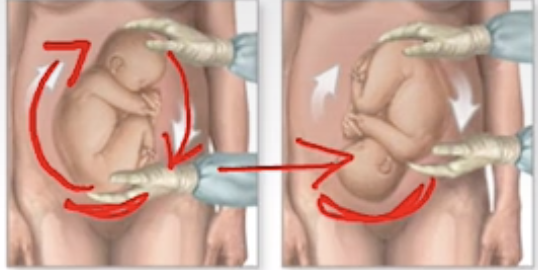
Artificial rupture of membranes is called
Amniotomy
Incision between the vaginal opening and butt
Episiotomy
What is the most common medication to induce labor
Oxytocin
What complication causes the most emergency c sections for pregnant women
Non-reassuring Fetal Heart Tracking (FHT’s)
Assessment/care after birth or complications occuring after birth
Postpartum
Fundus assessment postpartum
Constituency → Firm
Location → 1st day it is usually around Umbilicius. (Above = + ; Below = -)
Position → Midline in stomach (deviation occurs due to a pts full bladder)
Vaginal bleeding that happens after birth is called
Lochia
Normal vs Not normal Lochia
Scant, Small, Moderate = Normal
Large = Not normal
What medication is given to prevent postpartum hemorrhage
Prophylactic Oxytocin
Pain medication for pts who have had a C section
Ketorolac
What is the most common complication for postpartum mothers
Postpartum Hemorrhage
What are the five Ts of Postpartum Hemorrhage
Tone → Uterine Atony “Boggy Uterus”
Tissue → Retained Placenta
Trauma → Lacerations/hematoma
Thrombin → Coagulation
Traction → Inverted uterus
Other complications for postpartum mothers
-DVT’s
-Infection → UTI, mastitis
-Alterations in emotional status
Discharge Planning for postpartum patients
Vaginal Birth → 1 to 2 days
C-section → 3 to 4 days
-Stable VS
-Able to perform self & neonatal care
-Address emotional status
Seconds after birth, what is the nurse’s job
To dry and stimulate the baby to make sure it clears its airways.
What 3 medications are administered to the baby right after birth
1) Erythromycin eye ointment
2) Vitamin K injection
3) Hepatitis B vaccine
APGAR Scoring
1 Minute after birth
5 minutes after birth
APGAR between 7-10 is Good
HR → 0 Absent ; 1 Below 100 ; 2 Above 100
Respiratory Effort → 0 Absent ; 1 Irregular → 2 Crying
Muscle Tone → 0 Flaccid ; 1 Some flexion ; 2 Active motion
Reflex irritability → 0 No Reaction ; 1 Grimace ; 2 Vigorous Crying
Color → 0 Pale Blue ; 1 Body pink with blue extremities ; 2 Pink
Breastfeeding vs Bottle feeding babies
Breast Feeding → Every 2-3 hours
Bottle Feeding → Every 3-4 hours
What are the 2 most common neonate complications
Hypoglycemia → Less than 40 mg/hr before 4 hr or less than 45 mg/hr after 4 hr
Jaundice → Less than 5 mg/dL