Antigens
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
What is shorthand for antigen?
Ag
What kind of substance is an antigen?
Any (Usually protein, glycolipid, or polysaccharide.
What do antigens trigger?
Immune response to produce antibodies
Where are antibodies typically found?
on pathogens or parts of foreign substances
What is a pathogen?
Living organism or Virus that causes disease
What are pathogens also called?
Germs
What is an Epitope?
small, specific region on an antigen that recognized and bound by immune receptors like antibodies or T-cell receptors
What is a ‘Neutralizing Epitope’?
One that kills things off
What do these descriptions best match?
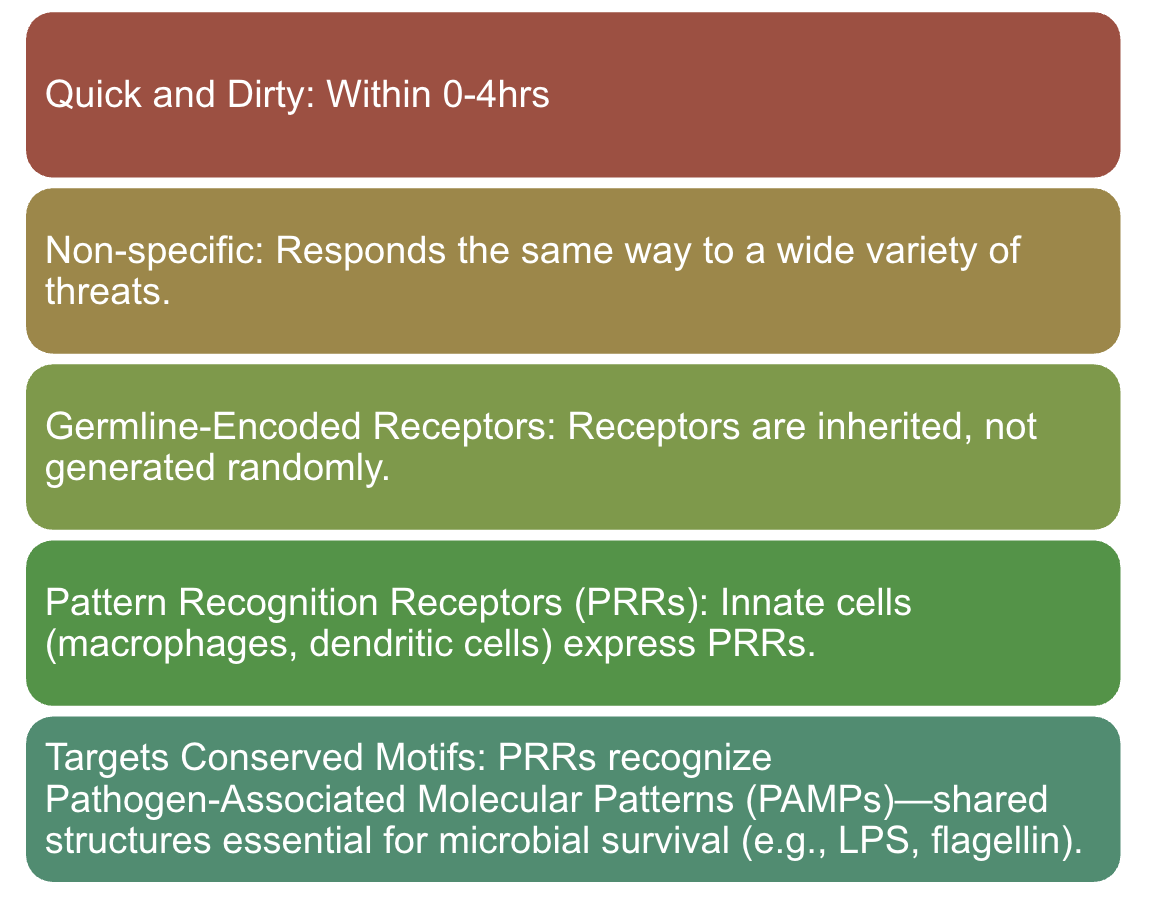
Innate Antigen Recognition: Pattern Detection

What best describes ‘highly specific’?
Recognizes individual, unique epitopes with extreme precision.

What best describes ‘Somatic Recombination’?
Receptors are generated through random genetic rearrangement, creating a massive, diverse repertoire.

What best describes ‘clonally distributed’?
Each B or T cell expresses only one type of receptor specific to a single antigen

Regarding Key Receptors:
What do B-cell Receptors (BCRs) / Antibodies do?
Bind directly to native antigens

Regarding Key Receptors:
What do T-cell Receptors (TCRs) do?
Recognize processed antigen fragments (peptides) presented on Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) molecules.