Communication and Motivational Interviewing Recording
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Motivational interviewing is a what technique?
Behavioural change technique
what is a model that is commonly used for behavioural change?
COM-B model
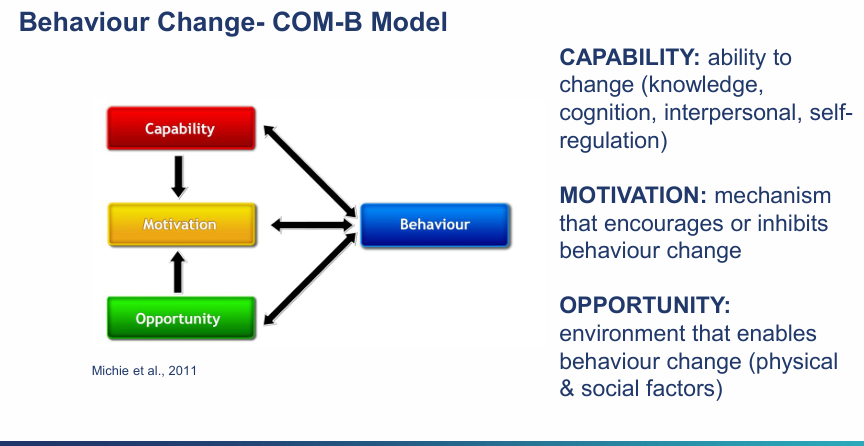
Explain the COM-B model?
Capability: Ability to change (knowledge, cognition, interpersonal, self-regulation)
Motivational: Mechanisms that encourage or inhibits behavioural change
Opportunity: Environment that enables behavioural change (physical and social factors)
What are questions to ask and the process with trying to address behaviour change? (3 main steps)
Individual factors: knowledge, motivation, confidence, mental or physical health constraints stopping them from making that change,
The environment/social factors, family influence, stigma attached, family norms , cultural expectations and roles,
wider environmental factors: cost, living and working conditions, availability of healthy food,
Systemic: digital access, policies, professional practices and incentives
Barriers: Misinformation, lack of understanding, low literacy, language barrier, competing schedules
facilitators: trusted relationship with professionals, peers, family, social support, community network that can facilitate behavioural change, access to services

What were some traditional approaches to delivering health advice

What is MI?
Collaborative person-centred form of guiding to elicit and strengthen motivation for change
Collaborative conversation to strengthen a person’s motivation and commitment to change
Eliciting and exploring the persons own reason for change within an environment of acceptance, compassion and empathy
Patient is responsible for making decision to make a change
more about listening to and supporting the patient

Is motivation a personality trait and static state?
no its a state of readiness to change, cant say a person is not motivated - they could be motivated tomorrow but not today,
motivation can fluctuate over time and is amenable to change
the primary focus is to resolve ambivalence about behavioural change

Does MI work?

What do you not do during MI?
You don’t tell the patient that they need to make a change in their health behaviour - the patient decides
Or try to coerce a patient to make a change
Instead, you guide them by resolving their ambivalence to strengthen motivation to change
What is MI spirit? (4 main)
Partnership: Spirit of partnership: working together with equal input from Pt and Clinician, respecting pt autonomy
Acceptance: Understanding Pts perspective and not being judgemental; ensuring that we support them with their self-efficacy to change
Compassion: Supporting Pts who may be struggling with behaviour change, showing real compassion and empathy words them
Evocation: To explore what is important to the pt and how they would like to make a change

MI spirit is about resolving what A?
you must express E?
Avoid?
Support the pts what?
Resolve their ambivalence
Express empathy
Avoid argumentation
Support self-efficacy
-Step away from being the expert-
How to show empathy?
Listen and reflect on what the patient is saying
Who should present the arguments for change?
The patient rather than the clinician
therefore take the opportunity to work with ambivalence
What is resolving ambivalence?
Support the patient in balancing the Pros/Cons
Remember that readiness to change is not static status but can fluctuate over time

How to avoid argumentation?
Explore pros and cons of change
Don’t lecture the pt
Disagree or judge them
How to support self-efficacy?
Explore with participant a time when they were successful
Strengthen beliefs about possibility for change
A persons belief in the possibility of change is an important motivator
Acknowledge and praise the patient for previous attempts
What is OARS - which can be used for MI?
O=open ended questions
A=affirmation - support and encouragement
R - reflect on what you have heard from the pt - what they say and mean
Summarise - use summaries to communicate understanding e.g “I think if I have got this right, you have told me you would like to reduce amount of sugar and that you would go and think about perhaps reducing sugar intake”

What are the steps in Motivational interviewing?

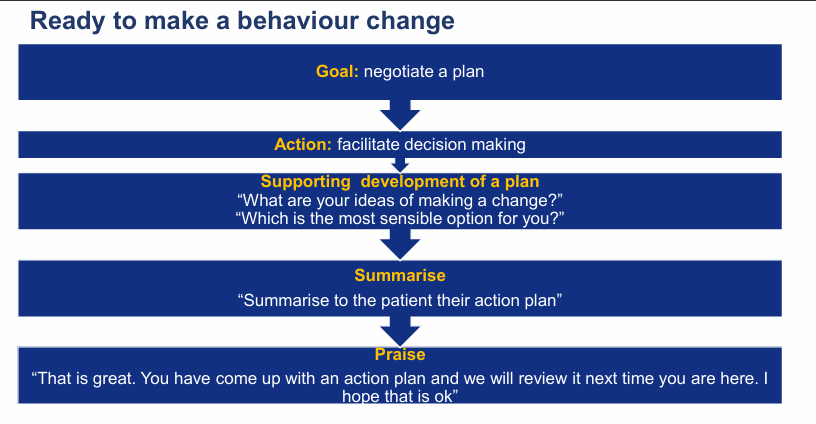
If the patient is ready to make a behavioural change?
the goal is to negotiate a ?
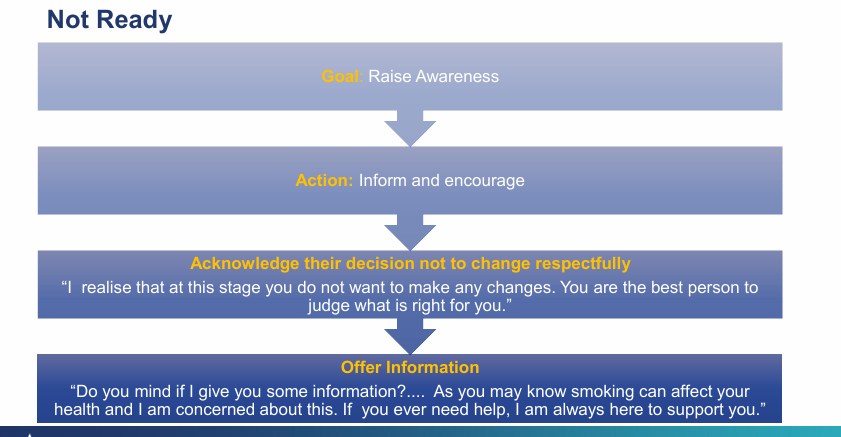
What if the patient is not ready?
what is the goal now?
Raise awareness
inform them about the consequences and enourage positive behavioural change
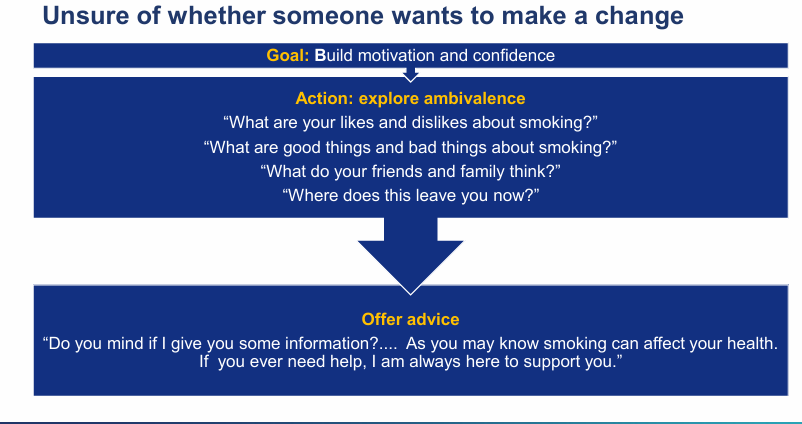
What if the patient is unsure of whether someone wants to make a change?
the goal is now what?
Build motivation and confidence?
use MI - explore the ambivalence
The overall principle of MI?
