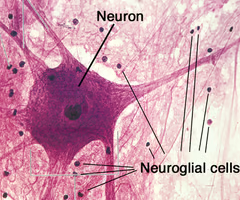
anatomy lab histolgy
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
simple squamous epithelium
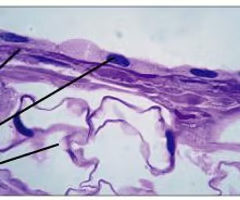
simple squamous epithelium
-composed of a single layer of flat cells
-located in lungs, blood vessels, and digestive tract
-involved in diffusion and filtration
simple cuboidal epithelium
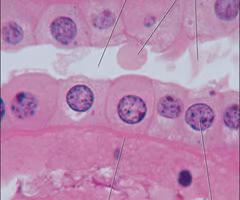
simple cuboidal epithelium
-composed of a single layer of cube-shaped cells
-located in lining of kidney tubules, ducts of salivary glands, and ovaries
-involved in secretion and absorption
simple columnar epithelium
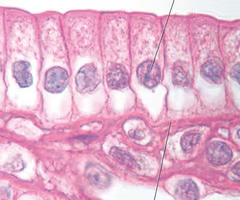
simple columnar epithelium
-composed of a single layer of rectangular-shaped cells
-located in most organs of the digestive tract, including stomach and intestines
-involved in absorption and secretion
goblet cells
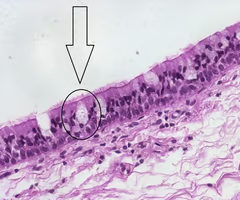
goblet cells
-produces mucus
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
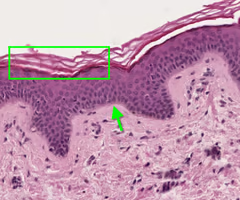
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
-makes up bulk of epidermis
-composed of 4 layers (stratum basale followed by stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, and stratum corneum)
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
-located in areas that experience high levels of wear and tear, including skin, mouth, and throat
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
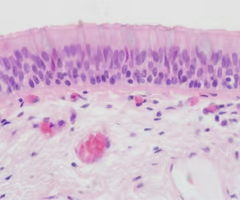
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
-composed of a single layer of cells w/ their nuclei at different levels
-located in respiratory tract, reproductive tract, and nasal cavity
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
-goblet cells and cilia help produce and move mucus along surface of epithelium
areolar tissue
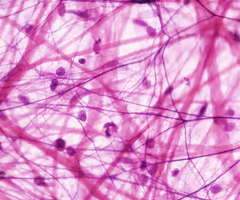
areolar tissue
-fibers in tissue are loosely arranged
-provides strength, support, and elasticity to body structures
areolar tissue
-located beneath skin, around blood vessels and organs, and between muscles
adipose tissue
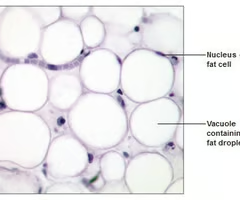
adipose tissue
-stores energy in the form of triglycerides
-adipocytes = cells that store energy as fat in adipose tissue
reticular tissue
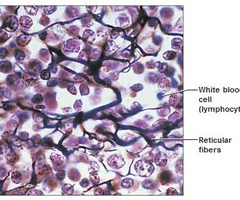
reticular tissue
-composed of reticular fibers, forming a mesh-like network throughout various organs and tissues
-located in lymph nodes, spleen, bone marrow, liver, kidneys, endocrine glands, and eyes
dense regular connective tissue
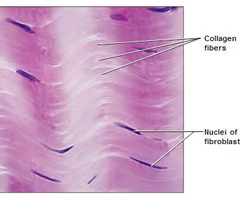
dense regular connective tissue
-provides support, protection, and connection within the body
-tendons connect muscles to bones
dense regular connective tissue
-ligaments connect bones to bones
dense irregular connective tissue
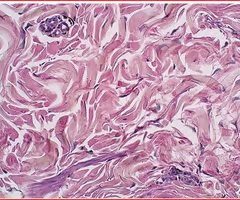
dense irregular connective tissue
-forms coverings over structures in the body
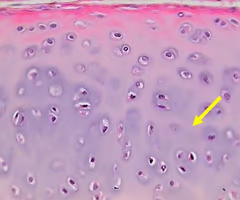
hyaline cartilage
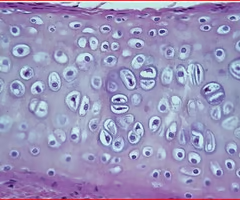
hyaline cartilage
-helps bones move smoothly past each other in joints
-located at the ends of bones that form joints
chondrocytes
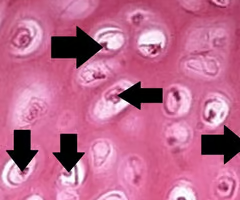
chondrocytes
-mature cartilage cells
lacunae
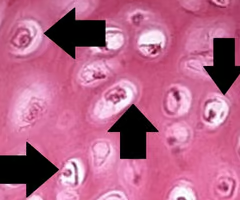
lacunae
-small cavities that contain osteocytes
matrix
matrix
-material that surrounds connective tissue cells
elastic cartilage
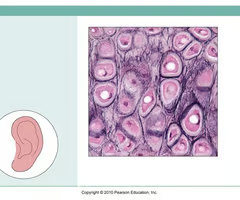
elastic cartilage
-cartilage with abundant elastic fibers; more flexible than hyaline cartilage
-located in ear, voice box, and eustachian tubes
bone tissue
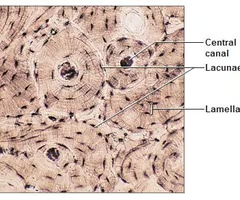
bone tissue
-hard tissue that supports and protects softer tissues and organs
osteocytes
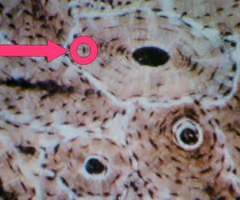
osteocytes
-bone cell formed when an osteoblast becomes embedded in the matrix it has secreted.
blood tissue
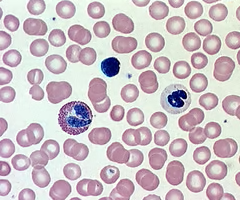
blood tissue
-transport oxygen and nutrients to cells throughout body
erythrocytes
-red blood cells that carry oxygen
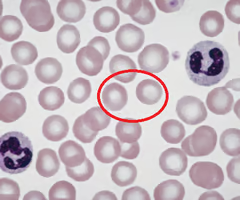
leukocytes
-white blood cells that fight infection
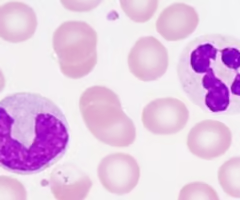
skeletal muscle tissue
-voluntary muscle pulls on bones and causes body movements
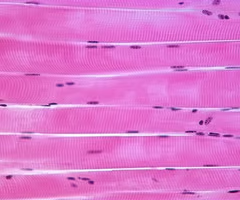
cardiac muscle tissue
-striated and involuntary, only found in heart
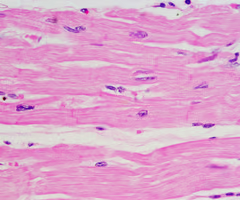
smooth muscle tissue
-involuntary muscle found in the intestines where it pushes food along the digestive tract
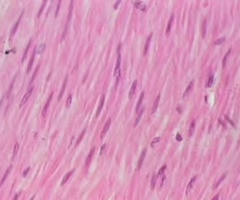
smooth muscle tissue
-also located in arteries and veins
nerve tissue
-carries messages back and forth between the brain and every other part of the body