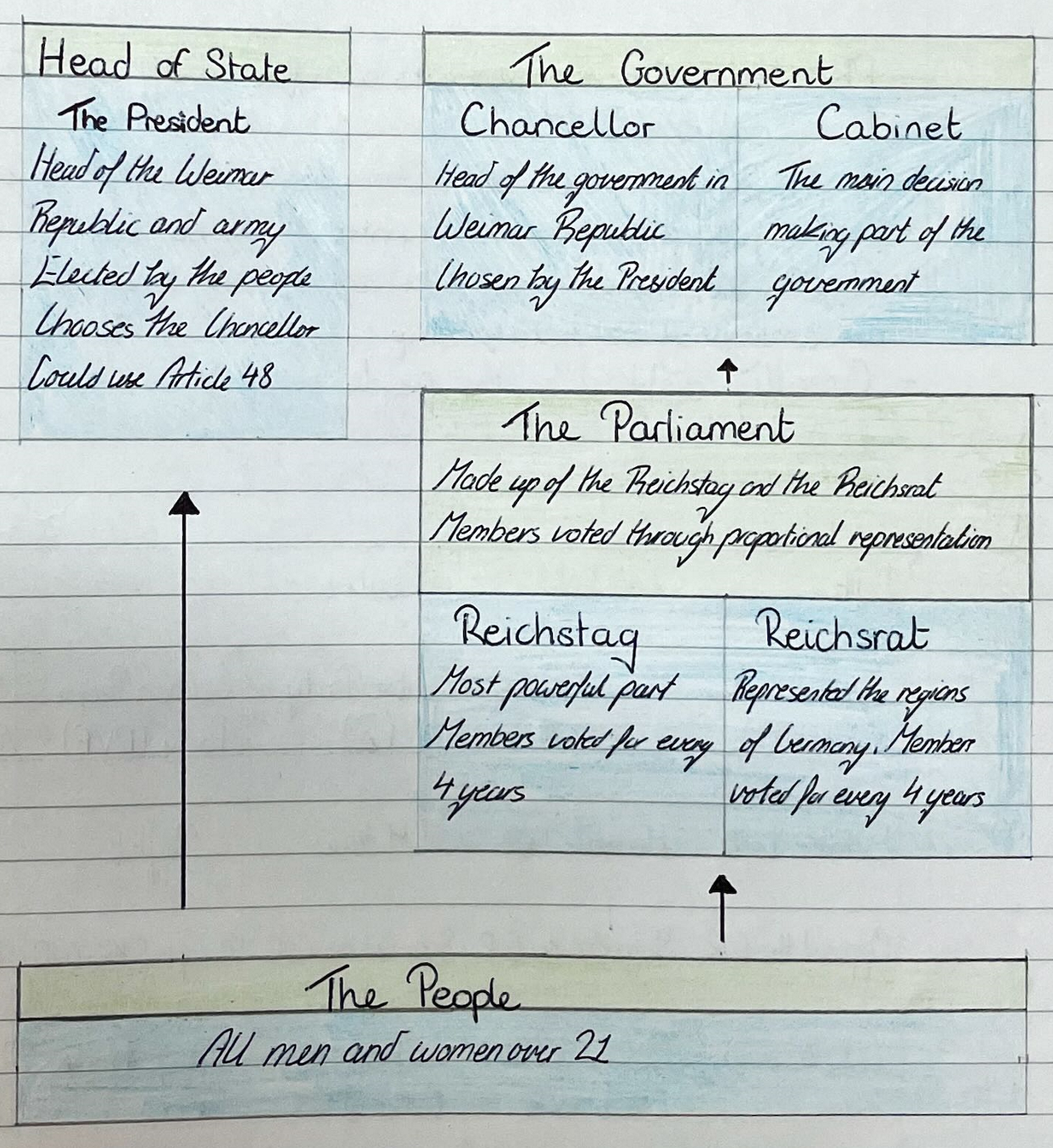
The Weimar Republic
Gave vote to all people over 21
System of proportional representation (PR) as used for elections of the Reichstag (parliament)
Elections were to take place every 4 years
Government would be run by a chancellor
Germany became a federal system o Power was shared between the central government and state (regional) governments
Strengths:
PR made sure even the smallest parties had a fair share of seats
Not one group nor person could have too much power
Most democratic country in Europe at the time o
Equal rights and votes to women
Elections for both the Reichstag and President
Freedom of speech and religion
Weaknesses:
PR led to coalition governments o Found it difficult to agree => collapse
In the 20s there were 29 parties => less chance of a majority
The army, civil servants and judges wanted the Kaiser back
Article 48 o The president could take control whenever they declared an emergency => dictatorship
Greatly disliked by the people
Communists (KDP) | Social Democrats (SDP) | Centre Party (Z) | German People’s Party (DVP) | Nationalist Socialist Party (NSDAP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Extreme Left | Moderate Left | Middle | Right | Extreme Right |
Opposed the WR | Supported the WR | Supported the WR | Accepted the WR | Opposed the WR |
Workers | Workers + Middle Class | Catholics + Conservatives | Upper Middle Class | Upper Middle Class, wealthy, ex-soldiers |