Gene Regulation + Biotechnology
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
New
Card Sorting
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
(Unit 8 - Ch 18 and Ch 20) Campbell Biology Version 10 Textbook
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
1
New cards
Metabolic Control in Bacteria
1\. adjusting activity of present enzymes
2\. adjusting level of certain enzymes
2\. adjusting level of certain enzymes
2
New cards
Operator
the single “on-off switch” (segment of DNA) that controls a whole cluster of functionally related genes
→ within the promoter
→ controls access of RNA Polymerase to the genes
→ within the promoter
→ controls access of RNA Polymerase to the genes
3
New cards
Operon =
operator + promoter + genes they control
4
New cards
Repressor
turns off an “always on“ operator by binding to that region
→ always specific to their operon
→ always specific to their operon
5
New cards
Regulatory Gene
genes expressed continuously at a slow rate
6
New cards
Allosteric Regulatory Protien
a protein activated by a ligand (aka an effector)
7
New cards
Corepressor
a small molecule that cooperates with a repressor or protein to switch an operon off
8
New cards
Repressible Operon
transcription is usually on but it can be “repressed“
ex: trp operon (in this case when tryptophan binds allosterically to a regulatory protein )
ex: trp operon (in this case when tryptophan binds allosterically to a regulatory protein )
9
New cards
Inducible Operon
transcription is usually off but it can be “induced“
ex: lac operon (the presence of lactose will induce this, the lactose molecules will come and bind to the repressor on the operator and hence the repressor will get removed and the RNA Polymerase can start producing the lactase enzyme)
ex: lac operon (the presence of lactose will induce this, the lactose molecules will come and bind to the repressor on the operator and hence the repressor will get removed and the RNA Polymerase can start producing the lactase enzyme)
10
New cards
Inducer
deactivates the repressor (it gone now lol) allowing the gene to be turned on
11
New cards
Negative Feedback Loop
switch is flipped, either turned on or off
ex: trp operon, lac operon
ex: trp operon, lac operon
12
New cards
Positive Feedback Loop
if the switch is on, it gets turned even more on
13
New cards
CAP
regulatory protein (catabolite activator protein)
→ is an activator
→ is an activator
14
New cards
Activator
a protein that binds to DNA and stimulates transcription of a gene
15
New cards
Differential Gene Expression
expression of different genes by cells with the same genome
ex: muscle + nerve cells are highly differentiated
ex: muscle + nerve cells are highly differentiated
16
New cards
Euchromatin
refers to any DNA that has been turned on
17
New cards
Heterochromatin
refers to any DNA that is off
18
New cards
Histone Acetylation
promotes transcription by opening up the chromatin structure by the addition of a functional group
→ addition of acetyl group (-COCH3) = polar; good thing; stimulates more transcription
→ addition of methyl group = non-polar; bad; slows down transcription
→ addition of acetyl group (-COCH3) = polar; good thing; stimulates more transcription
→ addition of methyl group = non-polar; bad; slows down transcription
19
New cards
DNA Methylation
when it binds directly to DNA, that DNA is turned off
20
New cards
Genomic Imprinting
where methylation permanently regulates gene expression (of the maternal or paternal alleles) at the start of development
21
New cards
Epigenetic Inheritance
inheritance of traits transmitted by mechanisms not involving the nucleotide sequence
eg. environmental factors
→ these can be passed down to offspring
eg. environmental factors
→ these can be passed down to offspring
22
New cards
Transcription Initiation Complex
cluster of proteins that assemble at the promoter
23
New cards
Control Elements
segments of non-coding DNA for regulatory proteins to bind to
→ proximal
→ distal
→ proximal
→ distal
24
New cards
Proximal Control Elements
located close to the promoter region
25
New cards
Distal Control Elements
located distant from the promoter region
26
New cards
Enhancers
groups of distal control elements
27
New cards
General Transcription Factors
can turn on all genes, has a low rate of initiation and only produced few RNA
28
New cards
Specific Transcription Factors
can only turn on few specific genes, has a high rate of initiation and high production of RNA
29
New cards
Activator Proteins
bind to the distal control elements
30
New cards
Silencing
reduced transcription (happens when repressors recruit proteins that remove acetyl groups from histones)
31
New cards
Alternative RNA Splicing
Different mRNA molecules are produced from the same primary transcript depending on which segments are considered exons/introns
32
New cards
Non-Protein-Coding RNAs
ncRNA
→ when the central dogma (dna to rna to protein) doesn’t get to the protein stage and the RNA becomes used for other things
→ when the central dogma (dna to rna to protein) doesn’t get to the protein stage and the RNA becomes used for other things
33
New cards
microRNAs = miRNAs
→ small and single stranded
→ capable of binding to complementary sequences in mRNAs
a gene expression regulator
→ capable of binding to complementary sequences in mRNAs
a gene expression regulator
34
New cards
small-interfering RNAs = siRNAs
→ similar in size + function to the miRNAs
a gene expression inhibitor
\
RNAi = when siRNA block gene expression
a gene expression inhibitor
\
RNAi = when siRNA block gene expression
35
New cards
RNA-interference = RNAi
the blocking of gene expression by siRNA’s
36
New cards
Differentiation
process through which cells become specialized in structure and function
\
at the non-DNA level, the actual process of building a specific cell type once the instructions have been read
\
at the non-DNA level, the actual process of building a specific cell type once the instructions have been read
37
New cards
Determination
refers to the point at which an embryonic cell has irreversibly committed to a particular cell type
\
at the DNA level, the instructions for becoming any cell type
\
at the DNA level, the instructions for becoming any cell type
38
New cards
Morphogenesis
the physical process that give an organism its shape
39
New cards
Cytoplasmic Determinents
maternal substances (chemicals) in the egg cell that influence the course of early development
40
New cards
Induction
when signals (such as contact with neighboring cells or growth factors secreted by neighboring cells) cause changes in the target cell
41
New cards
Pattern Formation
cytoplasmic determinants + inductive signals contributing to the development of organization in which the tissues + organs of an organism are all in their characteristic places
42
New cards
Positional Information
molecular cues that control pattern formation
43
New cards
Homeotic Genes
massive regulatory genes, control groups of genes hence also pattern formation in late embryo, larva, and adults
44
New cards
Oncogenes
cancer causing genes
45
New cards
Proto-oncogenes
normal version of oncogenes
46
New cards
3 Ways Proto-oncogenes → Oncogenes
1\. point mutation (eg. substitution mutation)
2\. gene amplification (genes are duplicated unnecessarily)
3\. translocation (when a piece of a chromosome leaves and attaches to another chromosome)
2\. gene amplification (genes are duplicated unnecessarily)
3\. translocation (when a piece of a chromosome leaves and attaches to another chromosome)
47
New cards
Epigenetic Inheritance Removal Methods
1\. meiosis (when the DNA is duplicated and re-read, many epigenetic influences are not passed on, __but some are__)
2\. chemicals
3\. wearing off by time
2\. chemicals
3\. wearing off by time
48
New cards
Biotechnology
the manipulation of organisms or their components to make useful products
49
New cards
nucleic Acid Hybridization
the base pairing of one strand of a nucleic acid to the complementary sequence on a strand from another nucleic acid molecule
50
New cards
Genetic Engineering
the direct manipulation of genes for practical purposes
51
New cards
DNA Sequencing
exploiting the principle of complementary base pairing to determine the complete nucleotide sequence of a DNA molecule
52
New cards
DNA Cloning
a method for preparing well-defined segments of DNA in multiple identical copies
53
New cards
Plasmids
small circular DNA found in bacteria
54
New cards
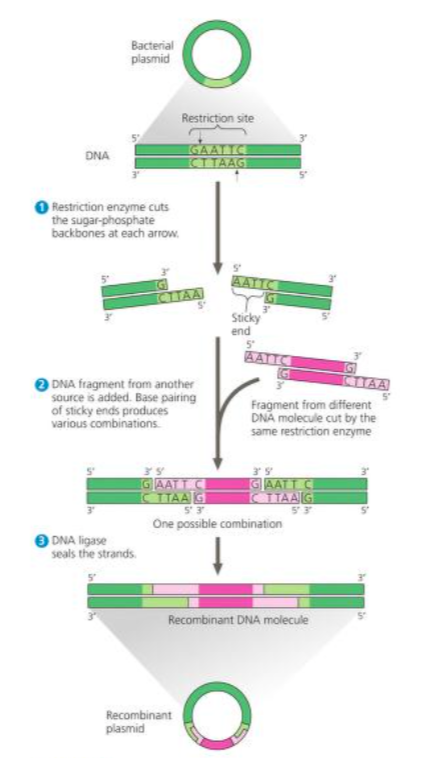
Recombinant DNA Plasmid
molecule containing DNA from two different sources, very often different species
55
New cards
Gene Cloning
the production of multiple copies of a single gene is a type of DNA cloning
56
New cards
Cloning Vector
a DNA molecule that can carry foreign DNA into a host cell and replicate there
ex: bacterial plasmids
ex: bacterial plasmids
57
New cards
Restriction Enzymes
enzymes that cut DNA molecules at a limited number of specific locations
ex: Hind111, EcoR1
ex: Hind111, EcoR1
58
New cards
Restriction Site
the short particular DNA sequence that the restriction enzyme recognizes
59
New cards
Restriction Fragments
restriction enzymes will make many cuts in a DNA molecule, yielding a set of restriction fragments
60
New cards
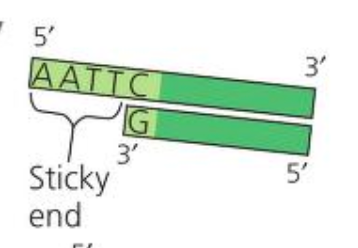
Sticky End
not a blunt end,
\
\
61
New cards
Blunt End
not a stick end
look like that → |
|
look like that → |
|
62
New cards
DNA Ligase
joins the sugar-phosphate backbone with covalent bonds
63
New cards
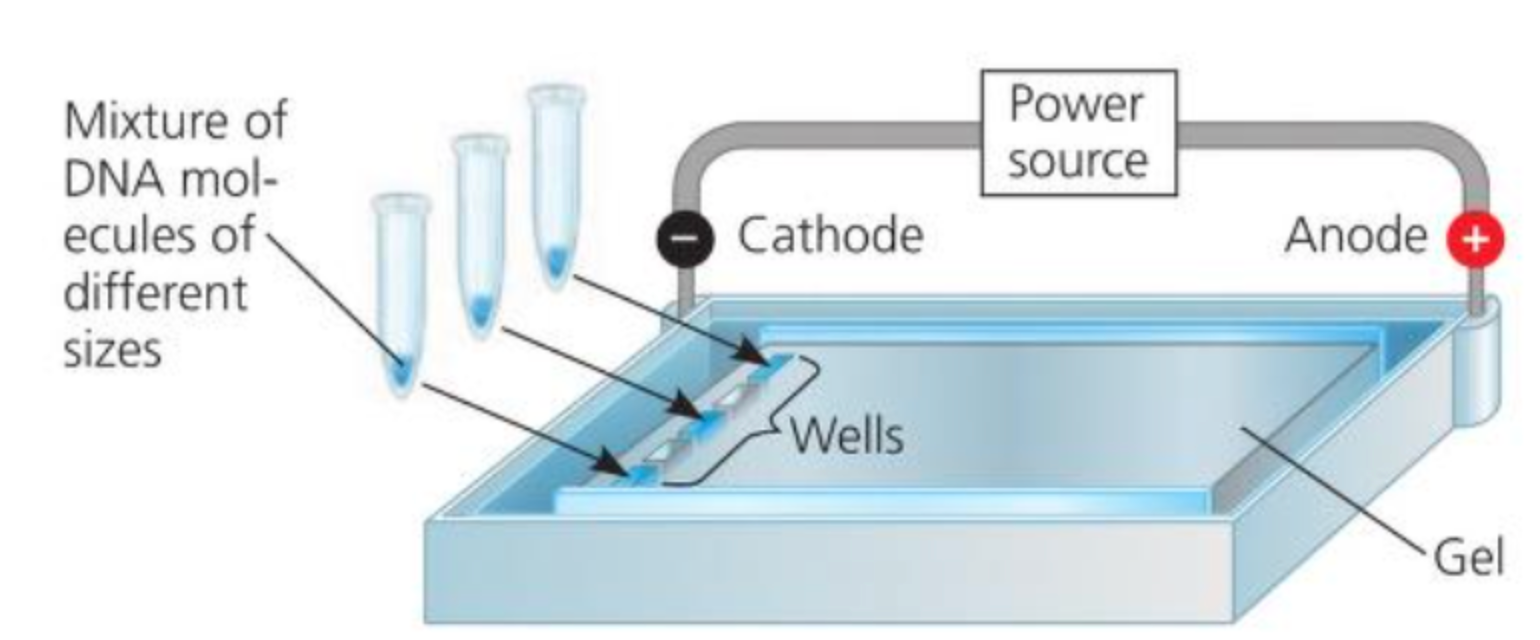
Gel Electrophoresis
a technique used to separate and visualize DNA fragments of different lengths
→ this technique uses a gel made of a polymer as a molecular sieve to separate out a mixture of nucleic acids (or proteins) on the basis of size, electrical charge, and other physical properties
→ this technique uses a gel made of a polymer as a molecular sieve to separate out a mixture of nucleic acids (or proteins) on the basis of size, electrical charge, and other physical properties
64
New cards
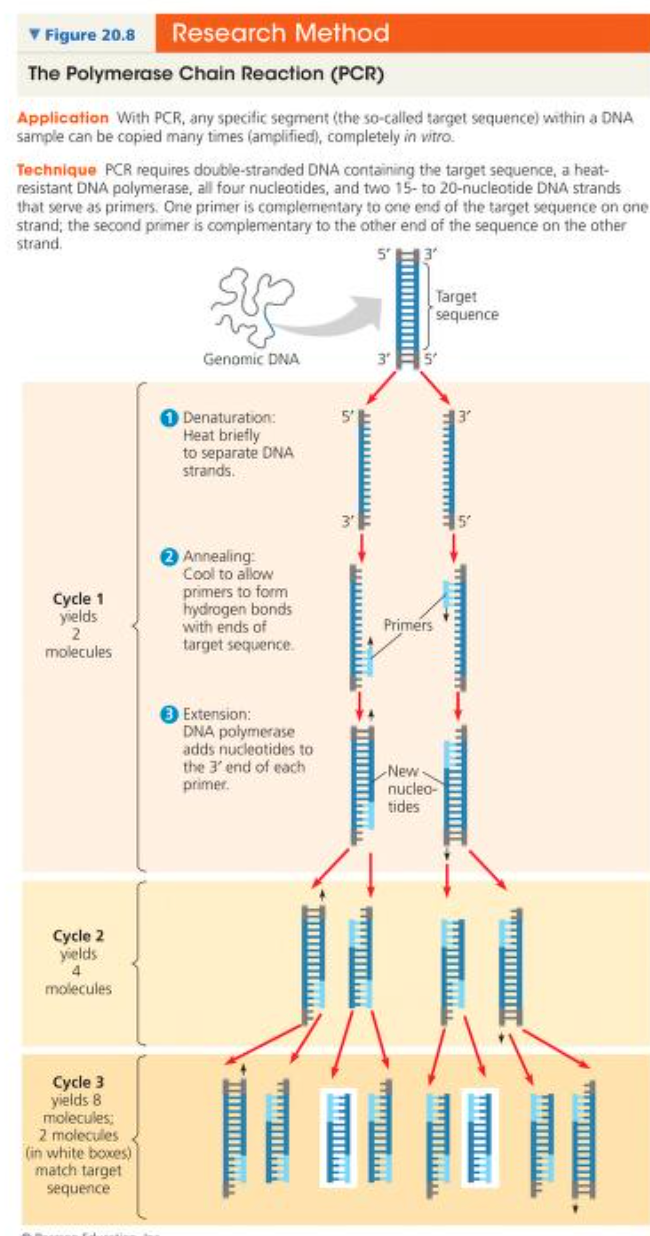
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
a technique used to obtain many copies of one gene
65
New cards
Stem Cells
cells found in the embryo, are cells that have the most genes turned on as compared to other cells in the body
\
analogy: library is fully open with all books accessible
\
analogy: library is fully open with all books accessible
66
New cards
Totipotent
cells that can become any other kind of cell in the body if they are in the correct environment
\
analogy: can read any book you want
\
analogy: can read any book you want
67
New cards
Pluripotent
cells that can become **almost** any other kind of cell in the body if they are in the correct environment
\
analogy: can read any book you want but the “r-rated“
\
analogy: can read any book you want but the “r-rated“
68
New cards
Multipotent
cells that can become **some other kinds of cells** in the body if they are in the correct environment
\
analogy: can read any book you want but the “r-rated“ and “tv-14“
\
analogy: can read any book you want but the “r-rated“ and “tv-14“
69
New cards
Unipotent
cells that can become **only that cell**
\
analogy: can read any book you want but the “r-rated“, “tv-14“, and “pg-13“ so basically you can only read the “pg“
\
analogy: can read any book you want but the “r-rated“, “tv-14“, and “pg-13“ so basically you can only read the “pg“
70
New cards
Germ Layers
groups of cells in the zygote (baby forming)
→ three types: endoderm (skin + nervous system), ectoderm (linings in digestive + liver), mesoderm (bone + muscle + tissue)
→ three types: endoderm (skin + nervous system), ectoderm (linings in digestive + liver), mesoderm (bone + muscle + tissue)
71
New cards
Induced Pluripotent Cell (IPC)
a cell that is already differentiated (skin or rbc) and is turned back into pluripotent