Econometrics Q1
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
t-value
est / std error
Residual standard error
sqrt(MSE)
R-squared
SSR / SST
Adjusted R-squared
1 - ((MSE) / (SST / n - 1))
F-statistic
(SSR / k-1) / (SSE / df)
MSE
SSE / n-k
MSR
SSR / k-1
MST
SST / n-1
Confidence Interval
Coefficient +- (t-critical * std error)
BLUE, B
Best, smallest variance
BLUE, L
Linear, linear in the coefficients
BLUE, U
Unbiased, on average, estimator = true value
BLUE, E
Estimator, estimating population
Log-log model
Beta = elasticity. 1% change in x = beta% change in y
Log-linear model
beta = semi-elasticity. 1 unit increase in x = 100 * beta% change in y
Linear-log model
beta/100 = change in y for 1% change in x
Endogenous regressor
variable correlated with the error term
BLUE assumption violated w/ endog regressors
Estimates no longer unbiased. Expected error = zero
Causes of endogeneity
Omitted variable bias, simultaneity
Omitted variable bias
When a variable that effects both X and Y is left out
Simultaneity
When a dependent variable and 1 or more regressors affect each other at the same time
What is the purpose of the Hausman test
Check if a variable is endogenous
How does the Hausman test work?
It compares the coefficient estimates from OLS and IV (2SLS). If they differ significantly, it indicates endogeneity.
How do you interpret the Hausman test result?
Fail to reject H₀: No endogeneity → OLS is consistent.
Reject H₀: Endogeneity present → Use IV/2SLS instead.
Multicollinearity
When two or more regressors are highly correlated
How can you detect multicollinearity?
Check Variance Inflation Factors (VIFs) — values above 10 suggest serious multicollinearity.
How can you fix multicollinearity?
Combine correlated variables.
Drop one of the correlated variables.
How do you find Variance Inflation Facotrs (VIF)?
Regress each X on all the other Xs
VIF formula
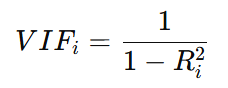
Heteroskedasticity
Variance of the error term is not consistent
Where does heteroskedasticity come from?
Data varies in scale, skewed data, group differences
BLUE assumption violated by heteroskedasticity
OLS remains unbiased, but no longer best
How do you perform the Breusch–Pagan test?
Run OLS and get residuals (u)
Regress u2 on the original X’s.
Compute nR2 and compare to χ2(k) (chi square)
How do you perform the White test?
Run OLS and get u2
Regress u2 on all X’s, their squares, and cross-products.
Compute nR2; compare to χ2 (chi square)
How to test for heteroskedasticity
Breusch-Pagan or Whites test
Autocorrelation of the Errors
Happens mainly with time-series, when the error of one period is correlated with the error of another period
OLS assumption violated with autocorrelation
OLS still unbiased, but error terms not independent across observations
How to test for autocorrelation
Durbin Watson and Breusch-Godfrey tests
How to do Durbin Watson Test
Run OLS and get residuals ui
Compute DW = Σ(ui − ui-1)2 / Σui2
How to interpret DW test
DW ≈ 2 → no autocorrelation
DW < 2 → positive autocorrelation
DW > 2 → negative autocorrelation
What is the purpose of Two-Stage Least Squares (2SLS)?
A method used to fix endogeneity by using instrumental variables—variables that are correlated with the endogenous regressor but uncorrelated with the error term.
What happens in the first stage of 2SLS?
Regress the endogenous variable on all exogenous variables (including instruments) to get predicted values of the endogenous variable (the “clean” version).
What happens in the second stage of 2SLS?
Use the predicted values from Stage 1 in place of the original endogenous variable and run the main regression.
What is a simultaneous equations system?
A set of equations (like supply and demand) where some variables are endogenous in multiple equations, meaning they influence each other across equations.
How is 2SLS used in systems of equations?
Apply 2SLS separately to each equation. For each one, use instruments that are excluded from that equation but included in others to identify it. Then run its own first-stage and second-stage regressions to get consistent estimates.
What does the Ramsey RESET test detect?
It checks for model misspecification—typically incorrect functional form or omitted variables in a regression model.
How is the Ramsey RESET test performed?
Run your original regression and save the fitted values.
Regress Y on the original X’s plus squared or cubed fitted values.
If those added terms are significant, the model is misspecified.
How do you fix model misspecification detected by the Ramsey RESET test?
Add nonlinear terms (e.g., squared or log transformations).
Include omitted variables that might explain missing variation.
What is the purpose of Difference-in-Differences?
It estimates causal effects by comparing changes over time between a treatment group and a control group — before and after a policy or event.
What is the key assumption behind DiD?
The parallel trends assumption — without the treatment, the treatment and control groups would have followed the same trend over time.
→ If violated, the DiD estimate is biased.