Board Exam
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
In suspected cases of hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn, what significant information can be obtained from the baby's blood smear?
presence of spherocytes (spherocytes are characteristic of ABO HDFN but not of Rh HDFN)
A urine specimen analyzed for glucose by a glucose oxidase reagent test strip may yield a falsely low or negative value in the presence of:
Ascorbic Acid
What disorder is associated with the greatest elevation in LD isoenzyme 1
pernicious anemia
Severe diarrhea causes
metabolic acidosis (due to loss of bicarb, sodium, and potassium)
broth to blood culture ratio in adult
1:10
confirmatory tests for skeletal disease
aldose and creatine kinase
germ tubes indicate
candida albicans
A weak reverse type but strong forward type indicates
child who has not fully developed (full achieved by 5-10 years old)
A gram stain of sinus shoes gram negative diplococci that is oxidase positive and carbohydrate degradation is inert
moraxella catarrhalis
A patient has a tumor that concentrates erythropoietin. He is most likely to have which of the following types of polycythemia
polycythemia associated with renal disease (Ex. renal tumor will inappropriately release erythropoietin)
What disease causes a goiter to be firm rather than rubbery
graves
an additional test to perform in a patient having a lupus work up after DRVV is
hexagonal phase
A patient is on 100 mg of aspirin/day to prevent the formation of clots caused by platelets. The mechanism in which aspirin impairs platelet function is b
inactivating cyclooxygenase which blocks thromboxane A2
what condition has a normal level of CK
Hepatitis (CK measures brain, muscle, and heart- not the liver)
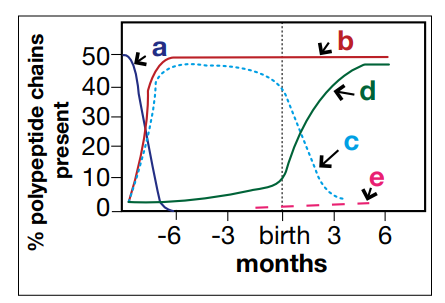
Which shows alpha
B (a is fetal, our bodies switch from fetal hemoglobin to alpha)
We can tell it’s probably a strict anaerobe if
it smells foul
What is MCHC if HCT is 20 RBC is 2.4 HBG is 5
(5/20) x 100= 25
Activated protein C (APC) resistance is associated with a mutation in
factor V (C involves cleavage of factor V. If there is a mutation on factor V or leiden a protein will cause it to be resistant to factor C, causing thrombosis)
A reagent test strip pad impregnated with a stabilized diazonium salt, such as diazotized 2,4-dichloroaniline, will yield a positive reaction in an acid medium with:
bilirubin
CD5
mature T cell
what cell produces blood group antibodies
B cells
pH in blood is determined by what electrode
glass
when are tear drops and abnormal plts seen
primary myelofibrosis
If someone is taking asprin what test is abnormal
platelet function -100
what biological sample is best measured by flow cytometry
single cell suspension
how many mL of .25 N needed to make 100 mL of .05 solution
C1V1=C2V2 so .25x=(100)(.05) solve for X = 20mL
when blood is split on the counter the first step after ppe is
absorb spill with absorbent material
highest lab professional infection from blood and body fluid
Hep B
A girl cuts her foot after swimming in the ocean. It is non-lactose fermenting, H2S pos, indole pos, and motile
Edwardsiella
A wheal and flare development in TB skin test indicates what hypersensitivity
immediate hypersensitivity
is blastomyces dermatitidis dimorphic
Yes
If a patient has all positives in IAT we need to
preform warm autoabsorption
TTP presents with symptoms..
fever, anemia, and thrombocytopenia (NOT liver failure)
A blood gas exposed to air causes
elevated oxygen, decrease CO2, and elevated pH
The reason that group O individuals have the most amount of H antigen on their red cells compared to other ABO phenotypes is
H antigen is left unchanged by the absence of A and/or B transferase enzymes
In comparison to malignant lymphocytes, reactive lymphocytes
are morphologically more variable throughout a smear
A wound specimen grows 2 colony types on sheep blood agar and 1 clear colony type on MacConkey agar. Sheep blood agar growth is documented as:

Colony 2 should be put on CNA or PEA cause its a gram positive and we want to remove the swarming GNR (CNA and PEA for gram positive)
The protein portion of an enzyme complex is called the
Apoenzyme (holoenzyme is active system formed by apoenzyme and a cofactor)
How does the bone marrow respond to anemic stress
Wanna produce more RBCs (NRBS come out cause they’re premature)
Best method to diagnose lactase deficiency
H2 breath test (based on bacteria reacting with lactase)
A very high PSA level is expected; however, a low level is obtained. The explanation could be
Hook effect (PSA can be higher if it was a recent rectal exam or african american population)
Organism that has satellite phenomenon around S. aureus
H. influenzae
If a cell looks mononuclear with ruffled edges its prob
a hairy cell
The data in this table is obtained from a cellulose acetate protein electrophoresis scan:

(γ globulin/total area) × TP = 30 units/180 units × 6.5 = 1.1 g/dL.
A blood gas sample is sent to the lab on ice, and a bubble is present in the syringe. The blood had been exposed to room air for at least 30 minutes. The following change in blood gases will occur
Increase oxygen and decrease HCO3
Cocaine is metabolized to:
benzoylecgonine
If there is a bleeding problem but PT PTT fibrinogen and plts are normal whats the problem
XIII since its absorbed into a clot and can only be measured by 5M urea
An obstetrical patient has had 3 previous pregnancies. Her first baby was healthy, the second was jaundiced at birth and required an exchange transfusion, while the third was stillborn. Which of the following is the most likely cause?
Rh incompatibility (ABO first preg, Rh later preg)
A 4-year-old boy presents with chronic ear infections and is on prophylactic antibiotics. He also presents with a bleeding diathesis. Factor assay results are shown in this table:

vitamin K dependant (II, VII, IX, and X)
In most compound light microscopes, the ocular lens has a magnification of
10X
relapsing fever in humans caused by
borrelia recurrentis
what RBC inclusion is made of residual nuclear fragments
cabot ring (seen in megaloblastic anemia)
Which of the following procedures is recommended to confirm that an unknown mold is one of the pathogenic dimorphic fungi
Molecular testing
Hepatitis B, a disease arising from a DNA virus, is diagnosed in its acute phase via serology for HBsAg, HBcIgM and total alpha-HBc. Once a patient reaches chronic HBV infection, effectiveness of therapy may be evaluated using
HBV DNA testing with realtime PCR
S. pneumoniae differentiated from viridans strep by
bile solubility (S. pneumoniae is soluble)
The drug cephalosporin can cause a positive direct antiglobulin test due to modification of the RBC membrane by the drug, which is independent of antibody production. This mechanism related to the drug cephalosporin is best described as
nonimmunologic protein adsorption
What are the 3 steps of an individualized quality control plan (IQCP)
risk assessment, quality control plan, quality assessment
Sometimes confused for N. gonorrhorae
Moraxella osloensis
Measurement of which of the following may be performed to account for the patient's hydration status and renal function
Creatinine
Several hours after birth an infant develops petechiae, purpuric hemorrhages and a platelet count of 21 × 103/µL (21 × 109/L). The most likely diagnosis is
autoimmune neonatal thrombocytopenia
E. coli 0157 H7 isolated on
MAC w sorbitol
Occasional spontaneous bleeding may occur in a hemophiliac who is classified as
moderate (frequent bleeding is severe)
Which one of the following provides a presumptive identification of a viral infection
cytopathic effect on cell cultures
The best way to lower the light intensity of the microscope is to
lower rheostat
A 70-kg patient is transfused with 1 unit of Apheresis Platelets. What is the expected increase in the patient's platelet count
When a 70-kg individual is transfused with 1 unit of Apheresis Platelets, the expected increase is approximately 30-50,000 platelets/μL for each unit
The persistence of which marker is the best evidence of chronic HBV infection
HBsAg
Chlamydia trachomatis infections have been implicated in
LGV and conjunctivitis
If all liver enzymes are slightly increased
chronic hepatitis
Glycosylated Hb in a hemolytic anemia will
decrease
In order to be a plateletpheresis donor, the platelet count must be at least
150,000/µL
urobilinogen formed in what organ
intestine
Unless blood gas measurements are made immediately after sampling, in vitro glycolysis of the blood causes a
fall in pH and a rise in pCO2
2,3-DPG's role in RBC metabolism is to
increase the release of O2 from oxyhemoglobin to the tissues
how do antihistamines work
block H1 histamine receptors
The buffering capacity of blood is maintained by a reversible exchange process between bicarbonate and
chloride
Which of the following genes is analyzed with molecular assays to distinguish weak D from partial D
RHD
Macrophages and monocytes have Fc receptors for which of the following immunoglobulins
IgG
A 22-year-old patient has trace urinary protein by dipstick method and a urine albumin excretion rate of 50 µg/min (normal is < 20). This correlates with the term
microalbuminuria/albuminuria
Which of the following phenotypes will react with anti-f? fisher race
rr (dce/dce)
Antibody class/isotype and antibody subclass are determined by major physiochemical differences and antigenic variation found primarily in the
The constant region of the heavy chain determines the biological function of the immunoglobulin and defines the immunoglobulin into 1 of 5 subclasses
A massive transfusion event can result in what type of complication(s)
citrate toxicity and hypocalcemia
Group of antibodies that show enhanced reactivity with enzyme treated cells
Rh antibodies
Antigen most likely to be involved in HDFN
K
Intraoperative strategies for blood management include
reinfusing shed blood recovered during surgery that has been washed with normal saline
is anti-P1 significant
no
Out of 2000 cells that are counted, 30 of them appear to contain fetal hemoglobin how much RhIG should be given
30/2000 × 5000= mL/30 2.5 vials are needed, and this is rounded up to 3 since the number following the decimal is ≥5. To these 3 vials, 1 additional vial will be added, giving 4 vials of RhIG for administration.
The Rh-negative phenotype results from the complete deletion of what gene(s)?
RHD
A blood donor has the genotype: hh, AB. Using anti-A and anti-B antisera, the donor's red cells will type as group
O (The blood donor lacks the Hgene so there is no H precursor substance. In the absence of H antigen, no A or B antigens are expressed. These red cells appear to type as group O as they do not react with anti-A or anti-B.)
A 10-year-old girl is hospitalized because her urine has a distinct red color. The patient has recently recovered from an upper respiratory infection and appears very pale and lethargic. Tests are performed with the results show in this table:

Paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria (donath landsteiner positive)
What percent of group O donors would be compatible with a serum sample that contained anti-X and anti-Y if X antigen is present on red cells of 5 of 20 donors, and Y antigen is present on red cells of 1 of 10 donors
68 (75% of donors would be compatible with anti-X and 90% with anti-Y. The frequency of compatibility for both antigens is determined by multiplying the 2 compatibility percentages: 0.75 × 0.90 = 0.675 or 68%.)
Which of the following is the preferred specimen for the initial compatibility testing in exchange transfusion therapy
Maternal serum
What information related to receiving a blood transfusion needs to be documented in a patient's medical record
signed consent
A sample of blood from each donation is tested for what infectious disease agents
HIV-1/2, HTLV-I/II, WNV, HCV (and syphilis, plasmodium and babesia depends on location)
are high prevalence antigens clinically significant
yes
A trauma patient who has just received 10 units of blood may develop
thrombocytopenia (no platelets are being given in rbcs)
Which of the following transfusion reactions is characterized by high fever, shock, hemoglobinuria, DIC and renal failure
bacterial contamination
Fetal and neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia (FNAIT) is caused by which of the following maternal antibodies
IgG alloantibodies against HPA antigens
Red Blood Cells Leukocytes Reduced must be prepared by a method known to reduce the leukocyte count to
<5.0×10^6
What is linkage disequilibrium in reference to HLA haplotypes
occurrence of HLA genes in the same haplotype more often than would be expected based on the gene frequencies
Wra is a
low prevalence antigen