Photons and wave-particle duality
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
Light waves can behave like _____ (e.g. photons) and _____
particles
waves
What is the phenomenon called when light behave like particles and waves?
The wave-particle nature of light/ wave-particle duality
How do we know light interacts with matter (e.g. electrons) as a particle and what it is?
The photoelectric effect- phenomenon in which electrons are emitted from surface of metal upon the absorption of electromagnetic radiation
How do we also know light behaves like a wave?
As it propagates through space shown from diffraction and interference of light in Young’s double slit experiment
Electromagnetic waves carry energy in _____ called ___
discrete packets
photons
Energy of photons are quantised according to what equation?
E=hf
Although the wave theory provided good explanations for phenomena such as interference and diffraction, but _______________
it failed to explain the photoelectric effect
photons are ___________
fundamental particles which make up all forms of electromagnetic radiation
Photon definition
Massless “packet” or a “quantum” of electromagnetic energy
This means energy is not transferred continuously but as ______ of energy.
What does this mean?
discrete packets
each photon carries a specific amount of energy, and transfers this energy all in one go, rather than supplying a consistent amount of energy
How can you calculate energy of a photon (given):
E=hf
Wave equation units: E = hc/𝛌
E= energy of photon (J)
h= Planck’s constant (Js)
c= speed of light (m/s)
f= frequency (Hz)
𝛌= wavelength (m)
What does the wave equation show?
Higher the frequency of EM radiation, higher energy of photon
Energy of a photon is inversely to wavelength, E∝1/λ
A long-wavelength photon of light has a lower energy than a shorter-wavelength photon
Energy of photons is inversely proportional to what?
Wavelength
How to calculate number of photons hitting the surface every second?
Power of light source/ energy of 1 photon
What is an electronvolt?
Unit which is commonly used to express very small energies
cuz quantum energies tend to be smaller than 1 J
What equation is electronvolt derived from?
definition of pd
V= E/Q
What does this mean?
When an electrovolt travels through a potential difference, energy is transferred between 2 points in a circuit or electric field
What is an electronvolt defined as and why?
Energy gained by an electron travelling through a p.d. of 1 volt
1 eV= 1.6× 10^-19 J
cuz…
if an electron, with charge 1.6 ×10^-19, travels through a pd of 1V, E transfer is = to
E=QV = 1.6× 10^-19 X 1V = 1.6×10^-19 J
When a charged particle is accelerated through a p.d. it gains _____ ______?
Kinetic energy
How does this relate to electronvolts and what equation does this make?
If an electron accelerates from rest, an electronvolt is = to KE gained
eV= ½ mv²
What can equation be rearranged to give?
speed of electron
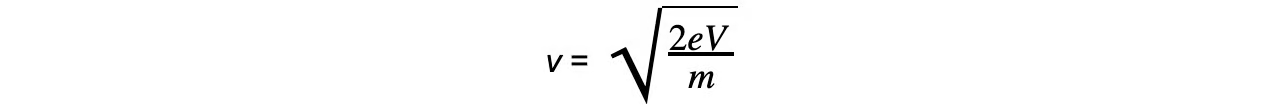
How convert between eV and J?
eV —>J: x 1.6×10^-19
J —>eV: ➗ 1.6 × 10^-19
What can be used to investigate wave properties of electrons?
Electron diffraction tubes
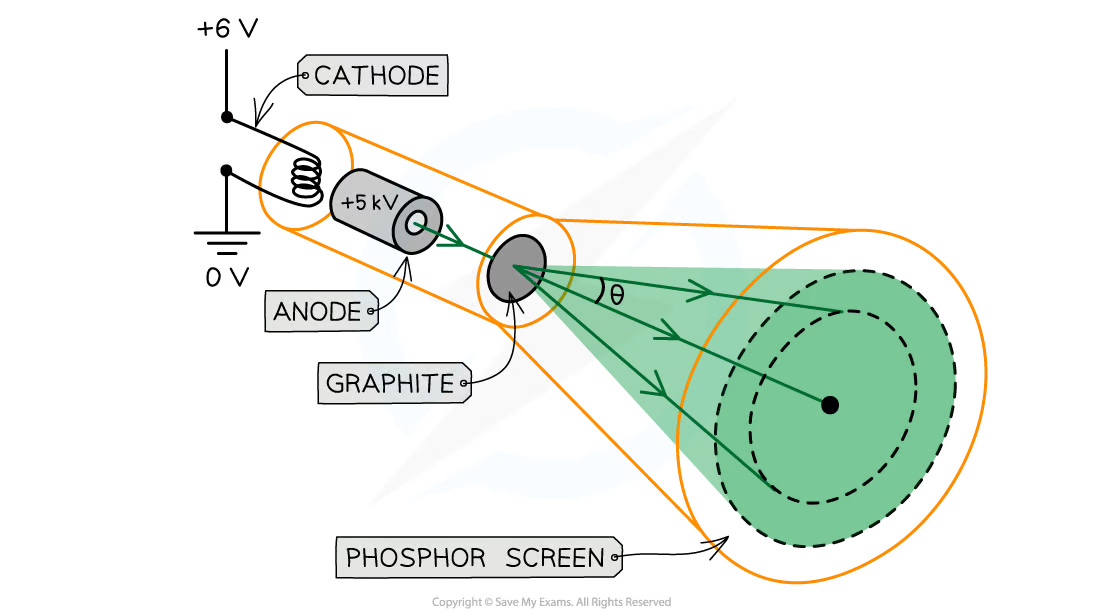
How is electron diffraction done?
Electrons are accelerated in an electron gun (produced a narrow stream of electrons from heated cathode, which is then accelerated by anode)
Accelerated to high potential
Directed through a thin film of graphite
What happens when electron diffraction is done?
Electrons diffract from gaps between carbon atoms
Produce a circular pattern on a fluorescent screen (emit light when exposed to high energy rays)
What does increasing voltage between anode and cathode do?
Causes energy and ∴ speed, of electrons to increase
What is the KE of an electron proportional to? (+equation)
Voltage across the anode-cathode
Ek = ½ mv2 = eV
What does electron diffraction show?
Evidence for wave-like behaviour of particles as they diffract which is a wave-like behaviour
Who discovered matter, such as electrons can behave as waves?
Louis de Broglie
What did De Broglie show?
A diffraction pattern is produced when a beam of electrons is directed at a thin graphite film
Diagram of experiment
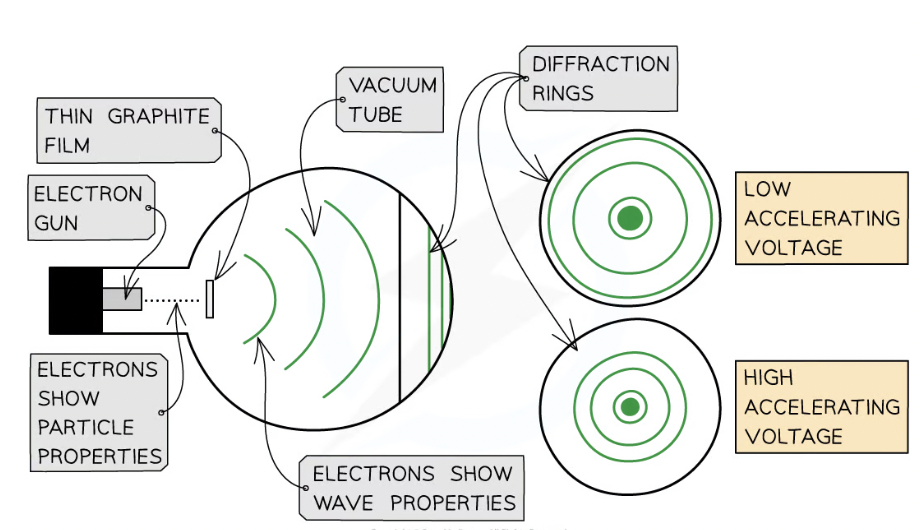
How does the diffraction rings change for low and high accelerating _____?
VOLTAGE
Low- far apart- increases diameter of rings
High- close together- reduced diameter of given ring
What must happen in order to observe the diffraction of electrons?
Must be focused through a gap similar to their size, e,g. atomic lattice
Why was graphite film ideal for the purpose of having a gap similar to size of electron?
Cuz it has crystalline structure
gaps between neighbouring planes of atoms in crystals act as slits, allowing electron waves to spread out and create a diffraction pattern
What is the diffraction pattern observed as on a screen?
Concentric rings (2 or more rings have same centre point)
If electrons acted as electrons in this experiment what would be observed?
partiles would be distributed uniformly across the screen
What is known as de broglie equation:
λ= h/p (given)
What are units and symbols mean in λ=h/p?
λ= de Broglie wavelength(m)
h= Planck’s constant (Js)
p= momentum (kg m s-1)
What does de Brogile equation link + what does this show?
particle-like property (momentum) to wave-like property (wavelength) demonstrating wave-particle duality for all particles
How can de Broglie wavelength be related to speed of a moving particle:
Since momentum p=mv
therefore
λ=h/mv
How to form equation that the de Broglie equation gives form relates de Broglie wavelength of particle to its KE + what is it?
Combining:
de Brogile equation - λ=h/p
KE- E= ½ mv²
—> momentum and KE relate by: p=√2mE
Gives:
λ= h/ √2mE
E- KE of particle (J)
m- mass of particle (kg)
v- speed of particle (m/s)
What are the units of λ= h/ √2mE?
E- KE of particle (J)
m- mass of particle (kg)
v- speed of particle (m/s)
What is the photoelectric effet?
Phenomena in which electrons are emitted from surface of metal upon absorption of electromagnetic radiation
Electrons removed from metal in this manner are known as _____
photoelectrons
What does the photoelectric effect provide evidence for and how this is shown?
that light is quantised/ carried in discrete packets
because…
each electron can absorb only a single photon
means only frequencies of light above threshold frequency will emit a photoelectron
What is the particle nature of light?
In classical wave theory, EM radiation is assumed to behave as a wave
Demonstrated by EM light exhibiting phenomena such as diffraction and interference
Photoelectric effect + atomic line spectra can only be explained if EM radiation is assumed to behave as particles
How to demonstrate photoelectric effect?
On gold leaf electroscope
Plate of metal, usually zinc, is attached to a gold leaf, which initially has neg charge, causing it to be repelled by central negatively charged rod
Neg charge. electrons build ip on zinc plate
UV light is shone onto metal plate, leading to emission of photoelectrons
Causes extra electrons on central rod and gold leaf to be removed, so the gold leaf begins to fall back towards central rod. Cuz they become less negatively charge hence repel less
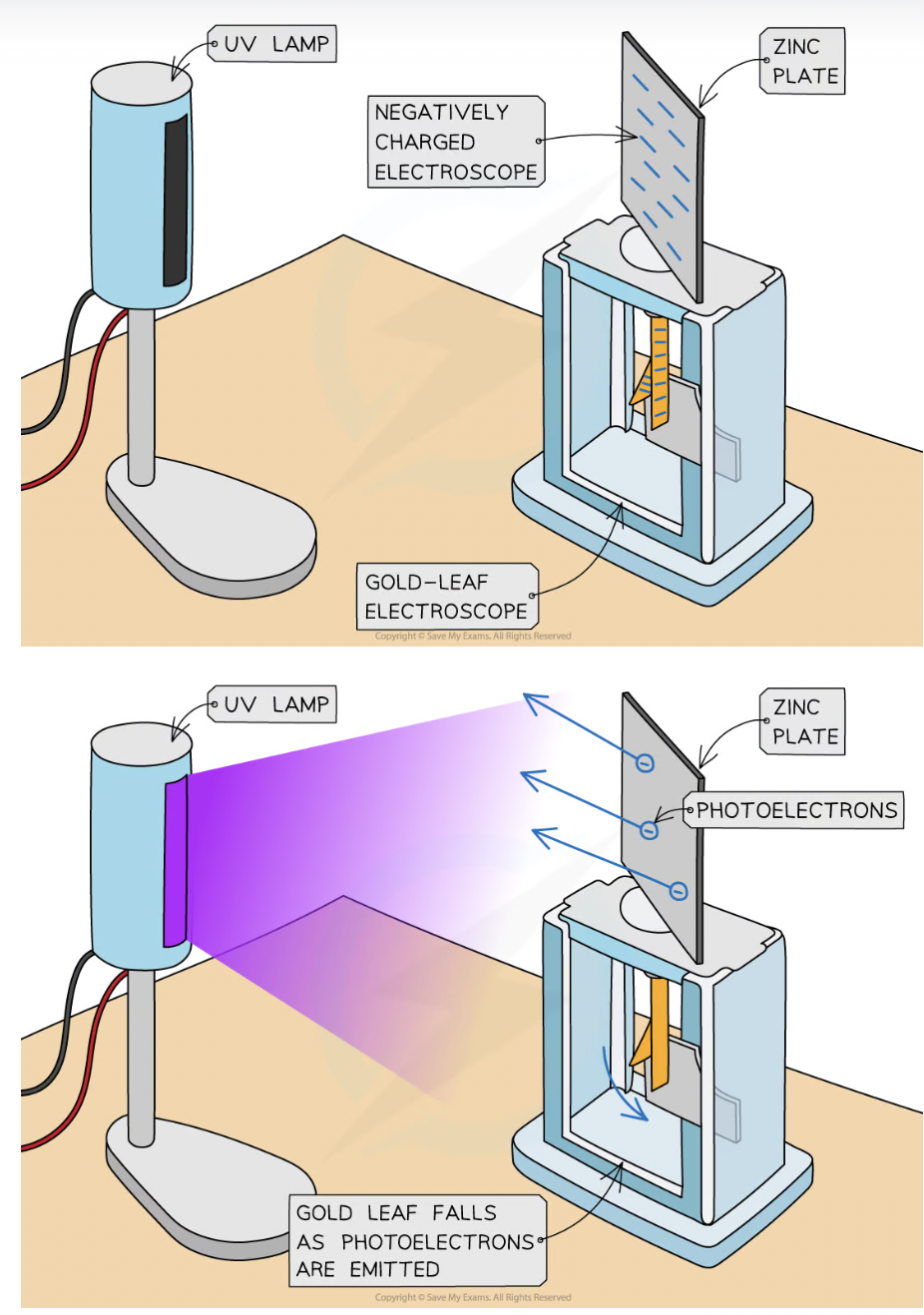
What where the observations of the gold leaf experiment?
Placing UV source closer to metal plate causes gold leaf to fall more quickly
Using higher f light source does not change how quickly gold leaf falls
Using filament light source causes no change in gold leaf’s position
Using pos charged plater causes no change in gold leaf’s position
Emission of photoelectrons happens as soon as the radiation is incident on surface of metal
Why does placing the UV light source closer to metal plate cause gold leaf to fall more quickly?
Placing UV source closer to plate increases intensity incident on the surface of the metal
Increasing intensity/ brightness of incident radiation increases n. of photoelectrons emitted per second
∴ gold leaf loses neg charge more rapidly
Why does using a higher frequency light source not change how quick the gold leaf falls?
Max KE of emitted electrons increases w. the frequency of the incident radiation
In the case of the photoelectric effect, energy and frequency are independent of intensity of radiation
So, intensity of incident radiation affects how quickly the gold leaf falls, not the frequency
Why does using a filament light source cause no change in the gold leaf’s position?
If the incident f is below certain threshold frequency, no electrons are emitted, no matter the intensity of the radiation
Filament light source has frequency below the threshold frequency of the metal, so no photoelectrons are released
Why does using a pos charged plate cause no change in gold leafs position?
If plate is pos charged, means there is an excess of pos charge on surface of metal plate
Electrons are neg charged, so will not be emitted unless they are on surface of metal
Any electrons emitted will be attracted back by pos charges on surface of metal
Why does emission of photoelectrons happen as soon as radiation is incident on surface of the metal?
A single photon interacts with a single electron
If energy of photon is equal to the work function of metal, photoelectrons will be released instantaneously
number of photoelectrons emitted is ____ to the number of photons incident on the surface in which the photoelectric effect is taking place
equal
Since energy is always conserved, energy of an incident photon is equal to:
Work function + max KE of photoelectron
Energy of a photon, hf, is transferred to electron to release it from material (work function) and remaining amount is given as KE to emit photoelectron
What is photoelectric equation + what units mean?
E= hf= Φ + ½ mv2max
h= plancks constant (Js)
f= frequency of incident radiation (Hz)
Φ= work function of the material (J)
KE max= max KE of photoelectrons (J)
What does photoelectric equation demonstrate:
If the incident photons do not have a high enough frequency and energy to overcome the work function (Φ), then no electrons will be emitted
hf0 = Φ, where f0 = threshold frequency, photoelectric emission only just occurs
KEmax depends only on the frequency of the incident photon, and not the intensity of the radiation
The majority of photoelectrons will have kinetic energies less than KEmax
How can photoelectric equation be rearranged into straight line equation:
y = mx + c
KEmax = hf - Φ
if graph of max KE against f, what are the key elements:
The work function Φ is the y-intercept
The threshold frequency f0 is the x-intercept
The gradient is equal to Planck's constant h
There are no electrons emitted below the threshold frequency f0
Threshold frequency definition:
The minimum frequency of incident electromagnetic radiation required to remove a photoelectron from the surface of a metal
Threshold wavelength definition:
The longest wavelength of incident electromagnetic radiation that would remove a photoelectron from the surface of a metal
work function Φ/ threshold energy, of a material definition:
The minimum energy required to release a photoelectron from the surface of a metal
an electron can only escape from the surface of the metal if it absorbs a photon which has an energy equal to __ or higher
Φ
What is KE related to?
Independent of intensity
Dependent of frequency
What is photoelectric current?
rate of emission of photoelectrons emitted per second
What is photoelectric current proportional to and why?
intensity of radiation incidence to metal
because intensity is proportional to number of photons striking the metal per second, since each photoelectron absorbs a single photon, the photoelectric current must be proportional to intensity of incident radiation
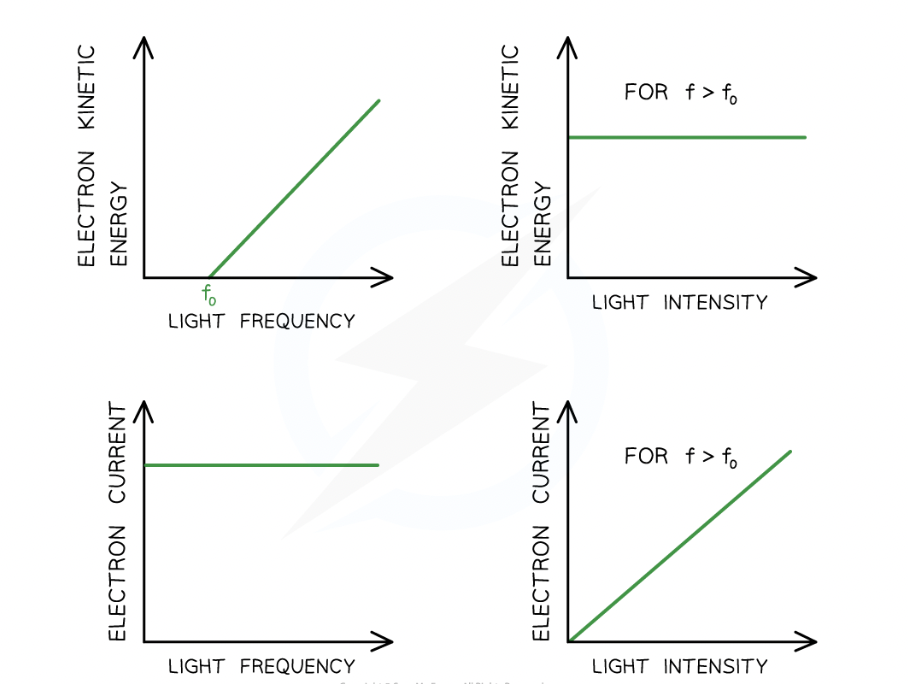
work function is = to
Φ=hf0
Wave theory and particle theory: No electrons are emitted if the incident radiation frequency f0
Wave theory: E spreads out evenly over wavefront, each wave would add more E to electron. eventually electron would emit, at any f
Particle theory: Each photon has energy E=hf. If f of photon is greater than f0, then the energy of photon is great enough to eject an electron
Wave theory and particle theory: speed of emitted electrons depends only on the f
Wave theory: E is proportional to I for wave. ∴ more I light would pass more energy to the electrons. they would emit faster
Particle theory: E=hf ∴ greater f meant greater energy of photon and greater emitted speed of electrons
Wave theory and particle theory: electron emission was instantaneous
Wave theory: If wave was incident for long enough, enough energy would eventually transfer and an electron would emit with a time delay
Particle theory: above a certain f, one photon interacts with one electron and is emitted immediately
How experiment to find planck’s constant works?
Using LEDs by considering the energies of the photons they emit
LEDs convert electrical energy into light energy
Emit visible photons when p.d. across them is above critical value (threshold p.d)
When this happens it emits photons of specific wavelength
at this p.d work done is given by W=VQ
Energy is same as energy of the emitted photon
Threshold p.d X charge on electron = energy of emitted photon
Ve= hf
Expressing this in terms of wavelength of emitted photon wavelength gives
eV= hc/λ
From de Broglie equation what is wavelength inversely proportional to?
Momentum, p
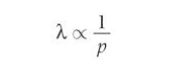
What is the change to a line in graph for photoelectric effect if the metal has work function energy greater than previous one?
Shifted to the right threshold frequency is greater
EQ: Describe + explain photoelectric effect in terms of photons interacting with the surface of a metal?
Is removal of electrons if exposed to em rad
Surface electrons are released
Single photon interacts single electron
E is conserved
E of photon= hf
Einsteins photoelectric equation: hf= φ + KE
Electrons released when hf>φ/ f is greater than threshold f, none is opposite
KE is independent if I when electrons r emitted
I increases rate of electrons released
I has no effect when there is no emission of electrons
EQ: Explain what energy levels are + how they can be used to explain the emission of photons from atoms
Electrons have discrete energies in atom
each photon produced by electron moving between levels
photon E = to E difference between levels
E1-E2= hf
Electron loses energy
EQ: If 2 laser have same power but 2nd has higher f, explain why laser emitting 2nd light emits fewer photons per second compared to 1
2 has higher f ∴ energy per photon is higher so fewer needed to produce same power
How to work out current ?
Electrons emitted per second X 1.6×10^-19 (elementary charge)
Reasons photoelectron emission is not 100 per cent
-Reflection/ absorption at top layer
- Photons below threshold e/ photons absorbed by electrons wo being released
- recombination of ion pairs in insulating layer
-scattering of light/photons out of insulating layer
How to calculate p.d.
eV= ½ mv²
V= ½ mv² / e
what is speed of photons?
speed of light
photons
particles of light
Sometimes referred to as a quantum of energy of EM radiation. A quantum in this context just means a set finite amount
What is plancks constant measured in?
Js
What quantity can be measured in eV?
energy
What is de broglies equation and what does it do?
λ= h/p
relates wave and particle properties wavelength wave-property and momentum a particle property
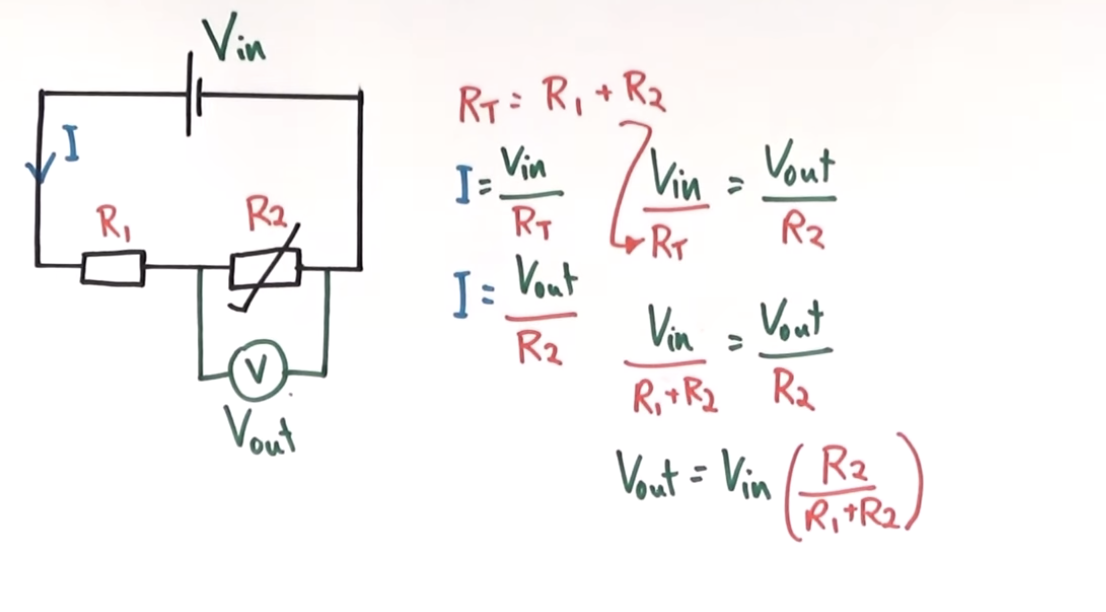
potential divider curcuit equation