Practical Exam Structures
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
1
New cards
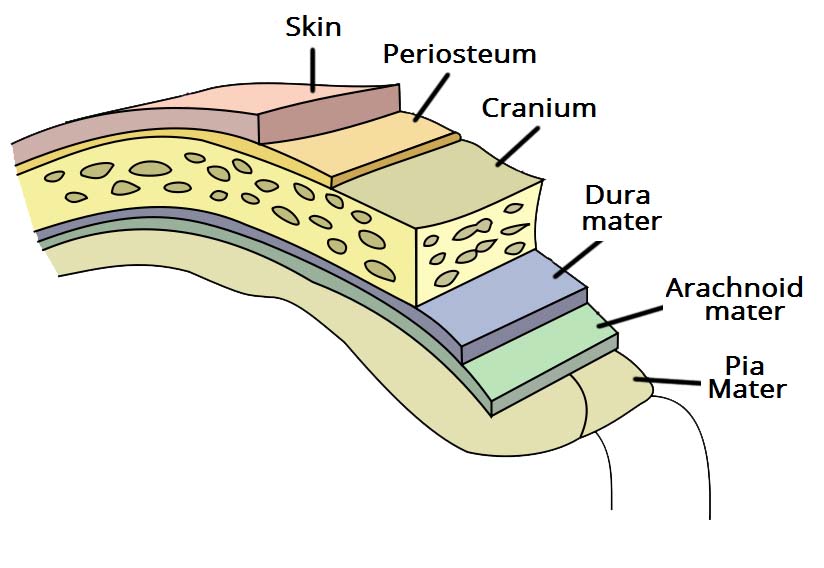
three membranes lying underneath the skull that envelop and protect the brain
meninges
2
New cards
the skull. provides protection and structure along with the surrounding meninges
cranium
3
New cards
the skin covering the head, aids in protection
scalp
4
New cards
the outermost of the 3 meninges. Leathery and thick. Provides the strongest protection for the brain underneath the skull.
dura mater
5
New cards
Located between the dura mater and pia mater. Cushions the brain.
arachnoid mater
6
New cards
Tender mother, innermost layer. Wraps tightly around the brain and spinal cord. Keeps cerebrospinal fluid from leaking out.
pia mater
7
New cards
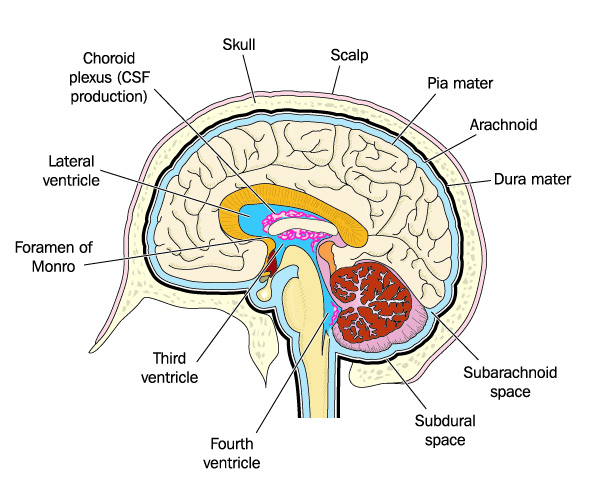
Acts as a cushion or buffer for the cortex. Located in the subarachnoid space in the brain between the skull and the cerebral cortex.
cerebrospinal fluid
8
New cards
Found in each of the brain ventricles. Produces cerebrospinal fluid.
choroid plexus
9
New cards
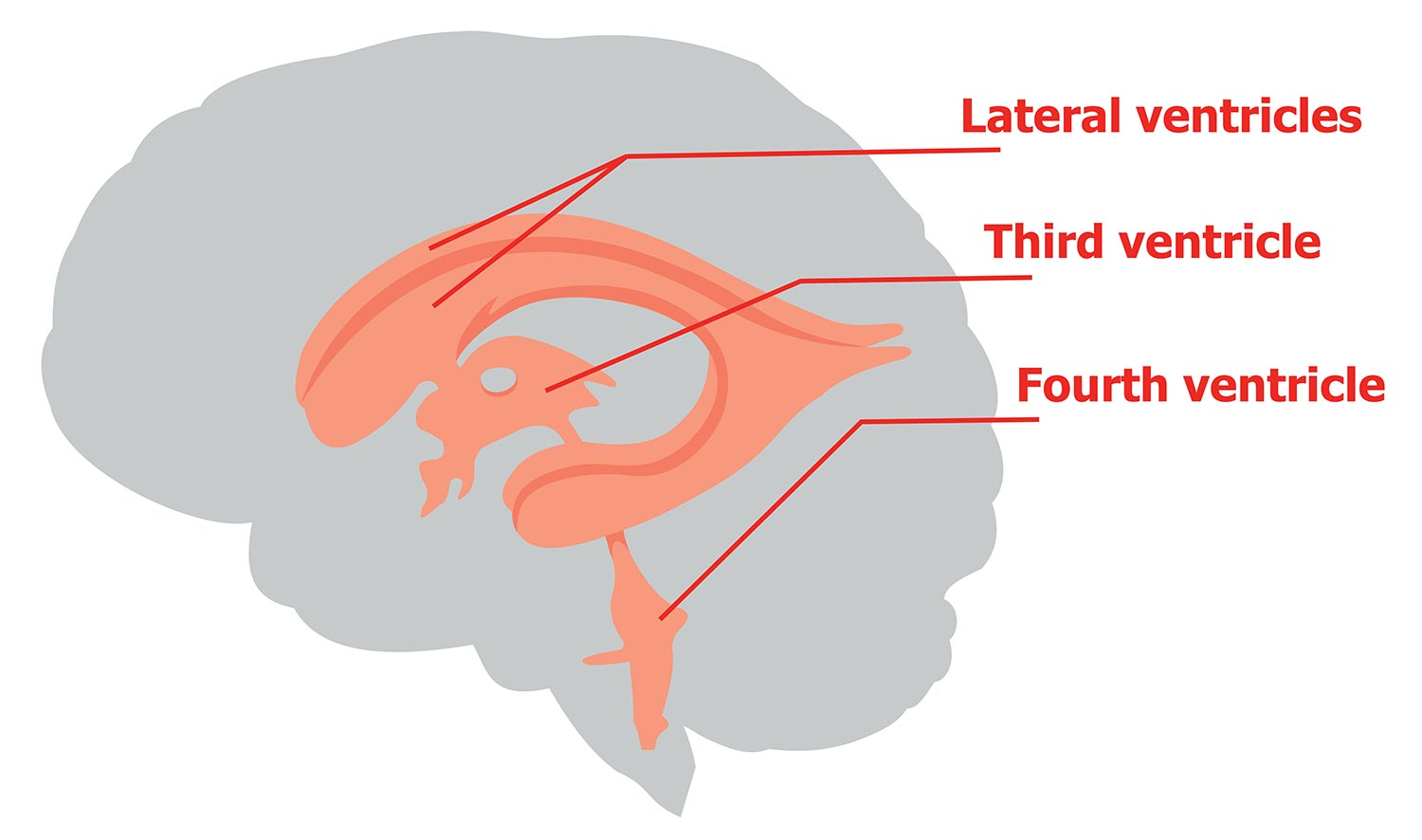
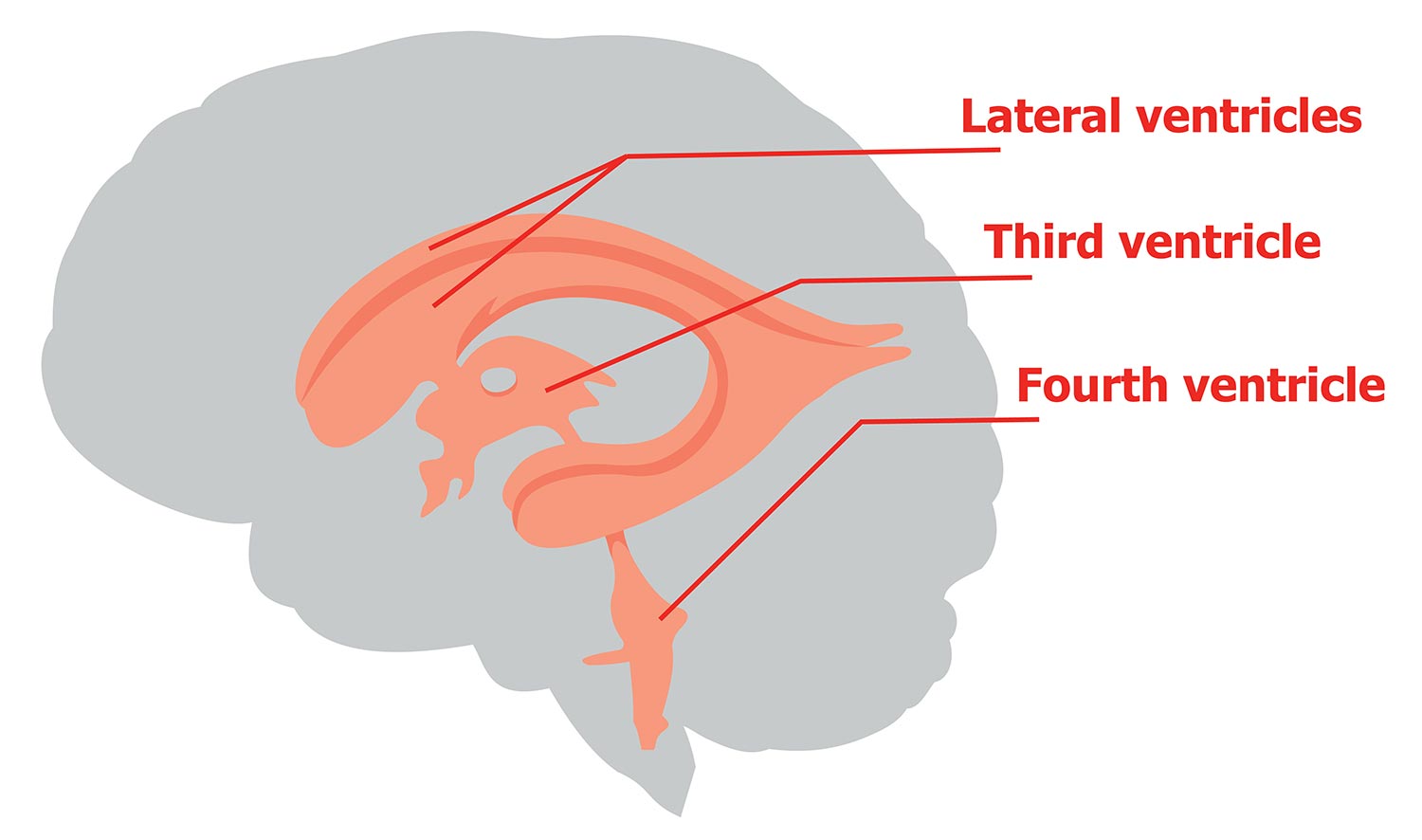
House and circulate CSF. Located deep within the cerebrum. Wraps around the thalamus. Capable of producing new neurons in adulthood.
lateral ventricles
10
New cards
A narrow cleft below the corpus callosum, between the 2 thalami. Produces, secretes, and circulates CSF.
3rd ventricle
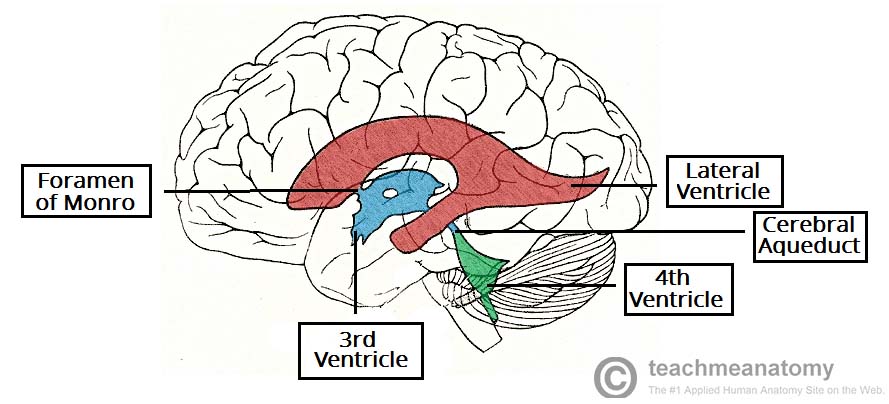
11
New cards
Produces and circulates CSF. Inferior to the 3rd ventricle.
4th ventricle
12
New cards
the two hemispheres of the cerebral cortex, joined by the corpus callosum
cerebral hemispheres
13
New cards
Largest lobe of the cerebral cortex. Executive function, information processing, higher cognition. Located superior to the temporal lobe and anterior to the parietal lobe.
frontal lobe
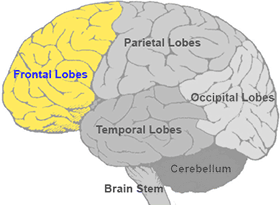
14
New cards
Located posterior to the frontal lobe and anterior to the occipital lobe. Information integration, somatosensation, proprioception.
parietal lobe
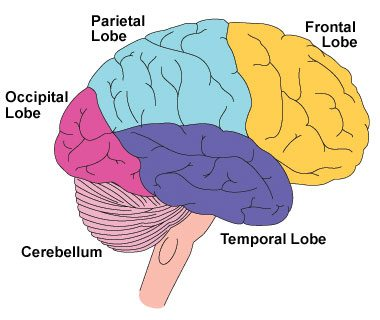
15
New cards
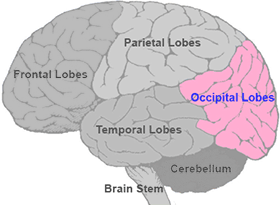
Located at the back of the head. Decodes visual signals.
occipital lobe
16
New cards
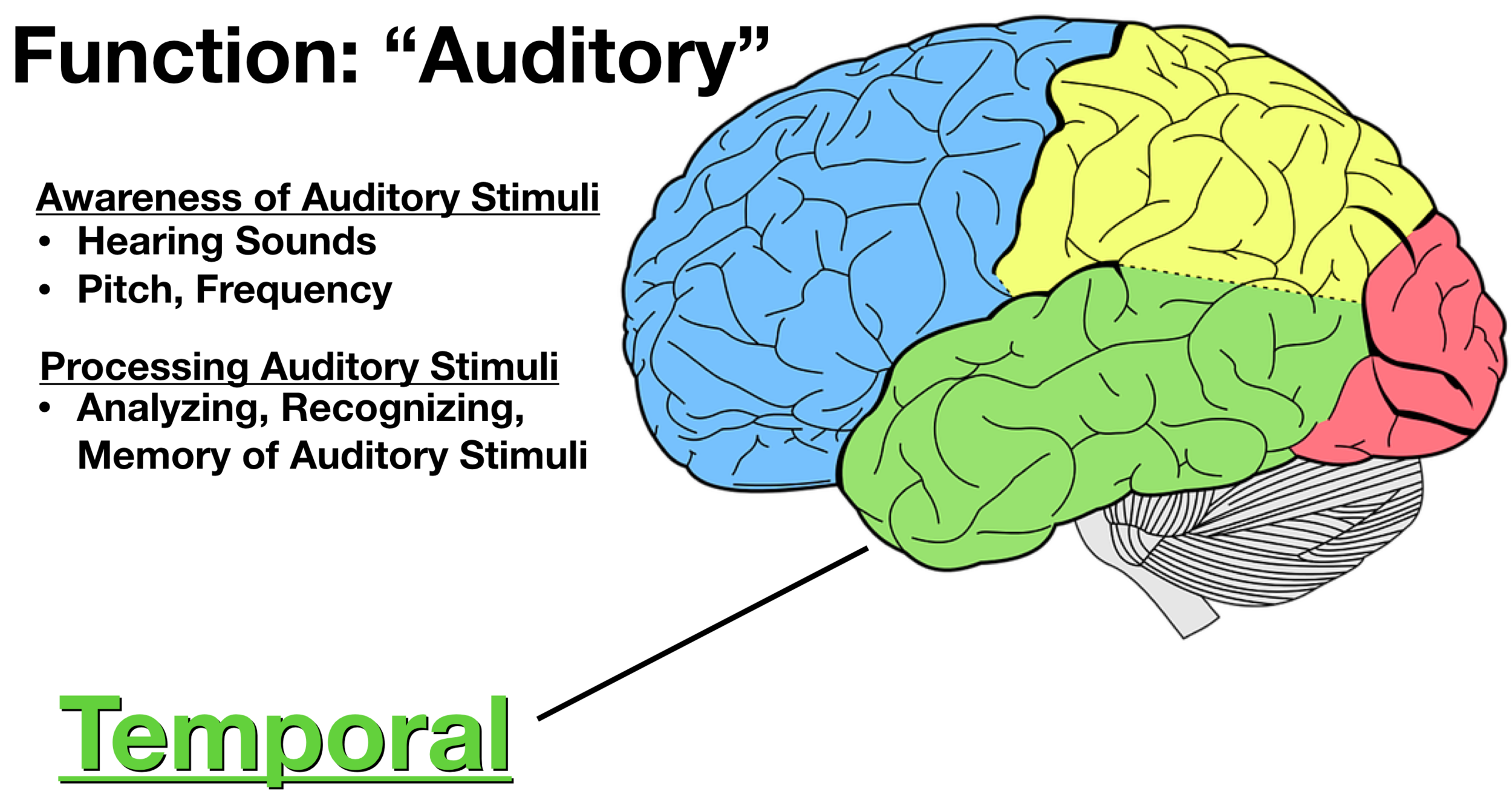
Sits behind the ears/temples. Houses memories, emotion, and language comprehension. Houses the hippocampus, the primary auditory cortex, and Wernicke's area.
temporal lobe
17
New cards
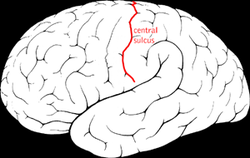
Forms the boundary between the frontal and parietal lobes on the lateral and medial surfaces of the cerebral hemispheres. This separates the primary motor cortex from the primary somatosensory cortex.
central sulcus
18
New cards
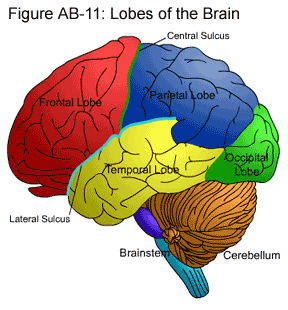
Separates the temporal lobe from the frontal and parietal lobes.
lateral sulcus/sylvian fissure
19
New cards
A deep groove that divides the left and right hemispheres of the brain.
longitudinal fissure
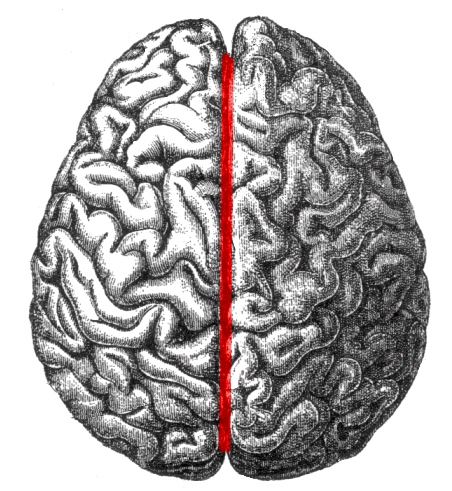
20
New cards
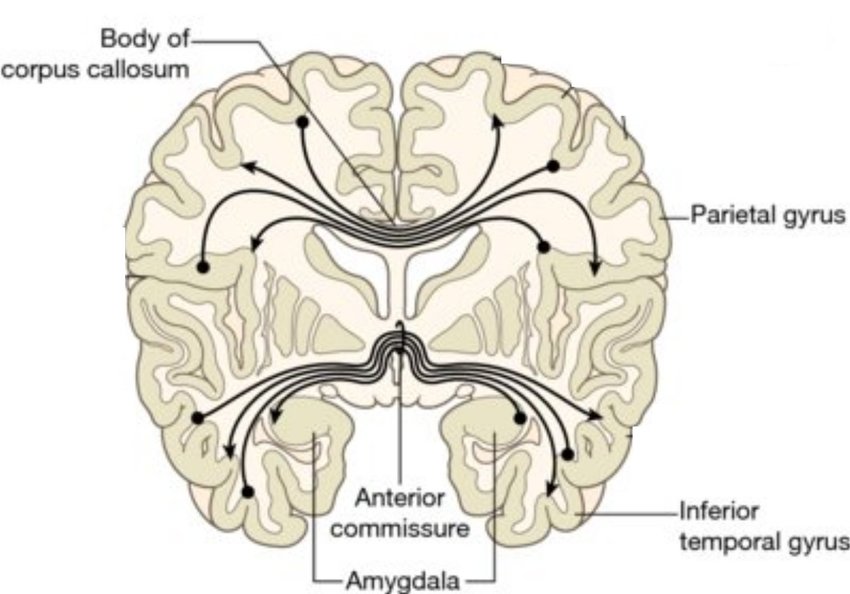
A bundles of axons that connects the two temporal lobes across the midline. Connects the olfactory bulb and parts of the cerebrum to the same areas on the opposite side.
anterior commissure
21
New cards
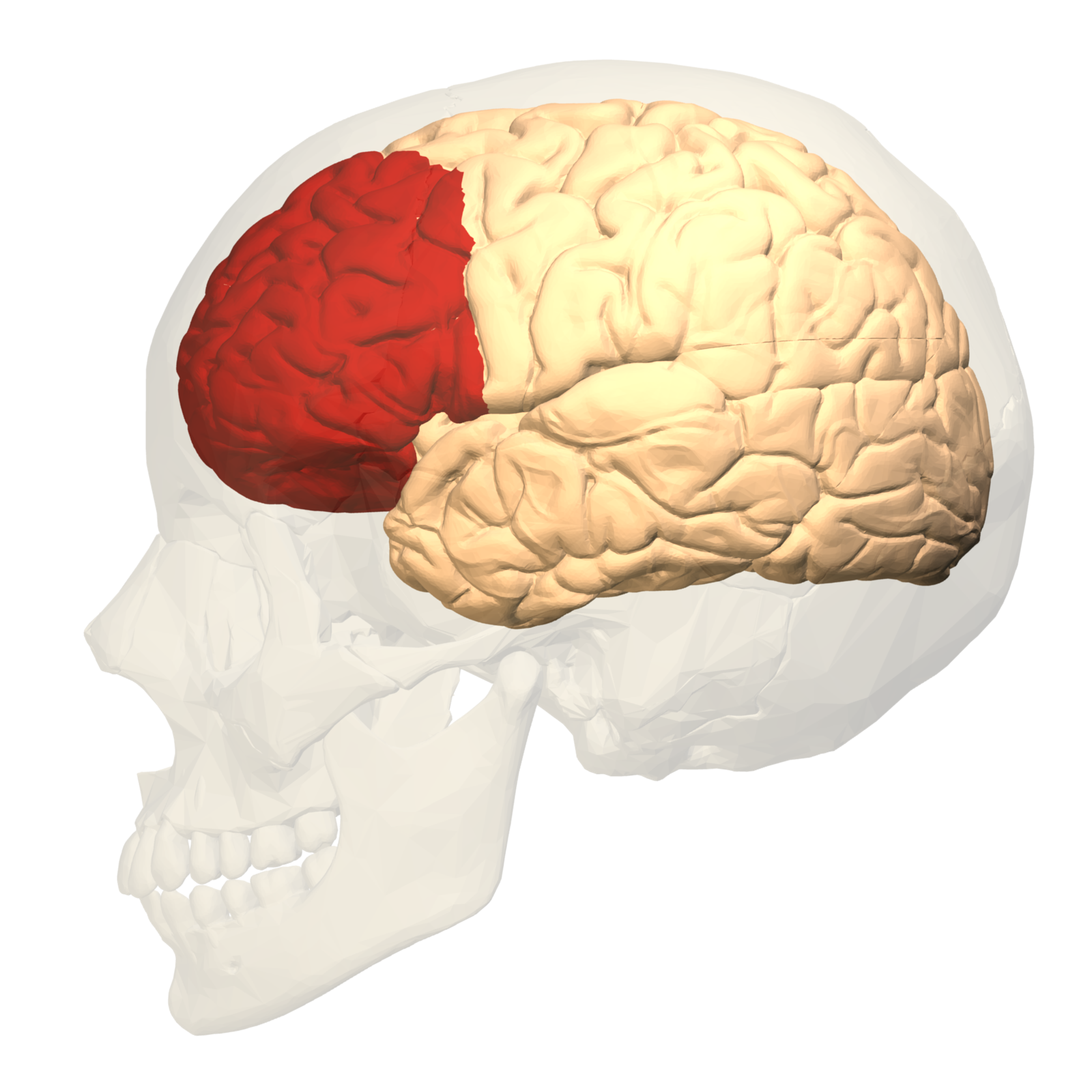
Left hemisphere. Anterior part of the brain. Involved in functions of cognitive control such as decision making. Influences personality traits.
prefrontal cortex (frontal lobe)
22
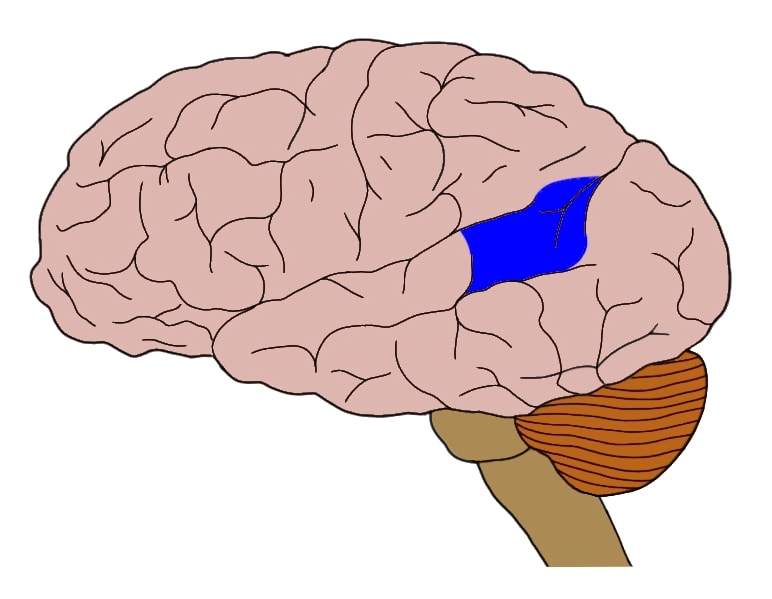
New cards
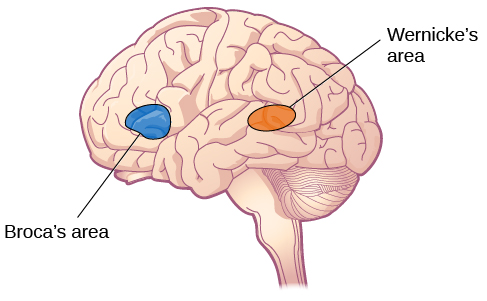
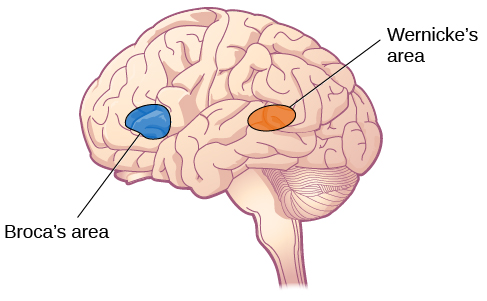
Left hemisphere, located in the frontal lobe in the inferior frontal gyrus. Inferior to the motor cortex. Controls response inhibition which stops an action when cued. Controls language production.
Broca's area/inferior frontal gyrus (frontal lobe)
23
New cards
Right hemisphere. Superior part of the brain, posterior to the somatosensory cortex. Reconciles visual information from the occipital lobe, identifies objects by touch, sifts through information in the memory.
superior parietal lobule
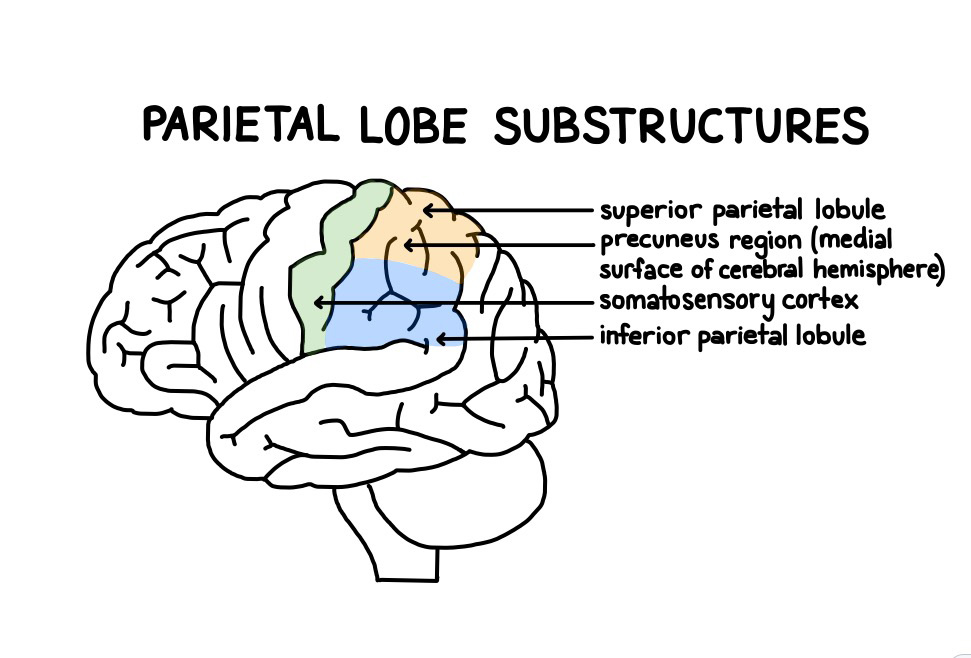
24
New cards
Left hemisphere. Anterior part of the parietal lobe. Where sense of touch is processed.
somatosensory cortex/postcentral gyrus (parietal lobe)
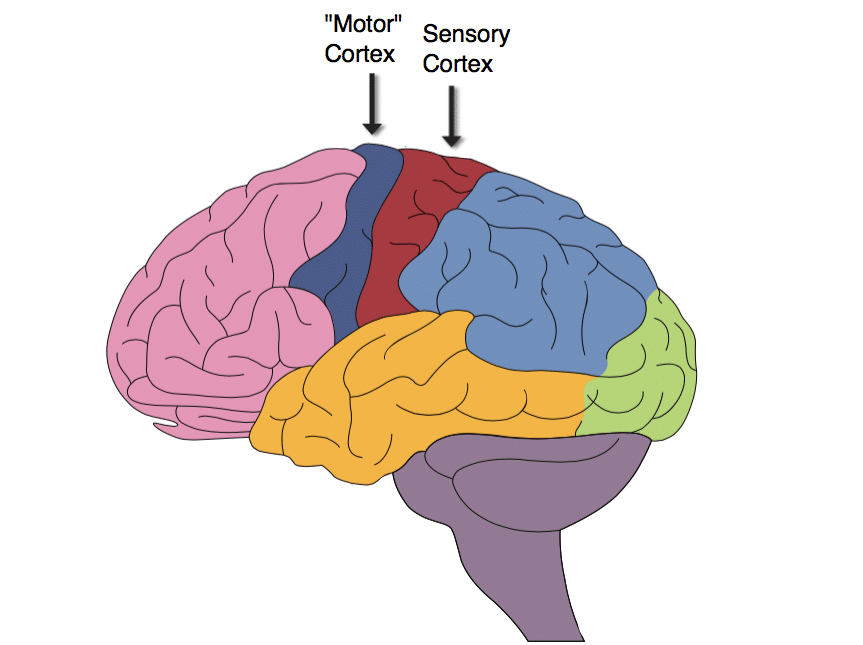
25
New cards
Located on the superior temporal gyrus in the temporal lobe. Interprets sounds, enables identification of unique sounds and the origin of sounds.
primary auditory cortex (temporal lobe)
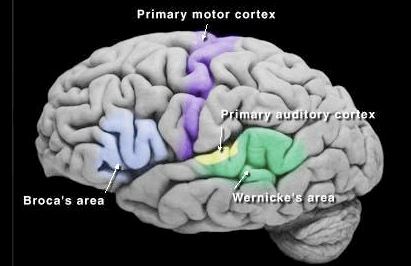
26
New cards
Contains motor neurons involved in the comprehension of speech. Located near the posterior part of the temporal lobe in the left hemisphere.
Wernicke's area (temporal lobe)
27
New cards
The superior part of the temporal lobe. Lies inferior to the lateral sulcus and superior to the superior temporal sulcus. Contains part of the auditory cortex. Involved in auditory processing, including language.
superior temporal gyrus
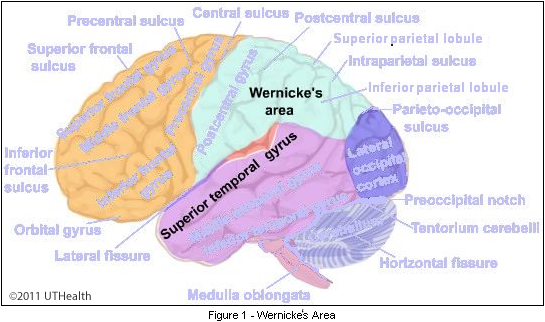
28
New cards
Comprehension of speech. Located in the left hemisphere near the back of the temporal lobe, in the posterior part of the superior temporal gyrus.
Wernicke's area
29
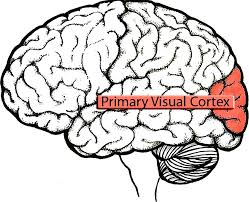
New cards
posterior part of the occipital lobe. The first part of the occipital lobe to receive visual information, which is relayed to other areas in the occipital, parietal, and temporal lobes for further processing.
primary visual cortex (occipital lobe)
30
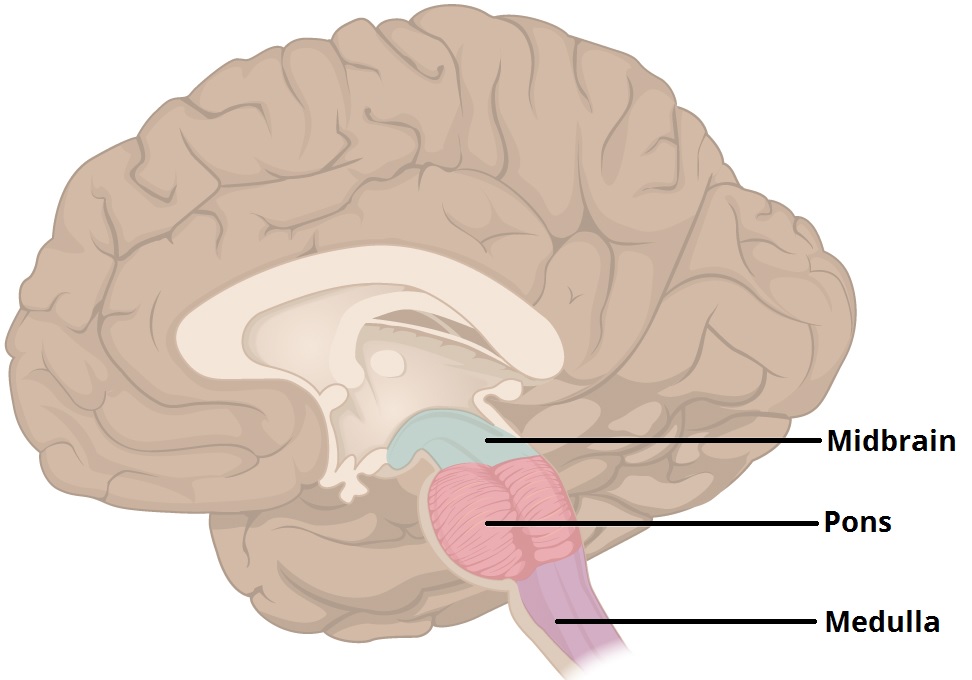
New cards
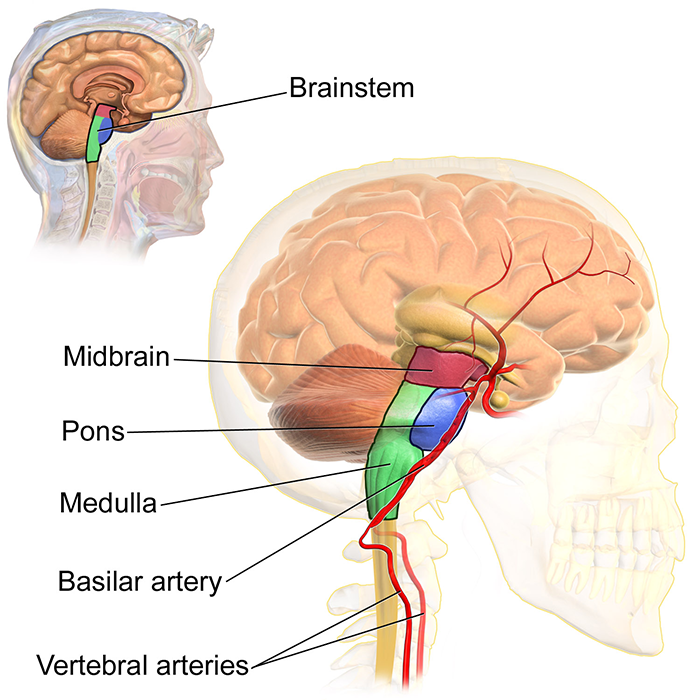
Located inferior to the cerebral cortex at the topmost part of the brainstem. Connects the brain to the spinal cord. Regulates movement and plays a role in visual and auditory processing.
midbrain (brainstem)
31
New cards
Inferior to the midbrain, connected to the spinal cord. Links the brain to the spinal cord and handles involuntary processes such as respiration, sleep cycles, and bladder control.
pons (brainstem)
32
New cards
Lower or hindmost part of the brain; continuous with spinal cord. Controls functions such as breathing, heartbeat, and blood pressure.
medulla oblongata
33
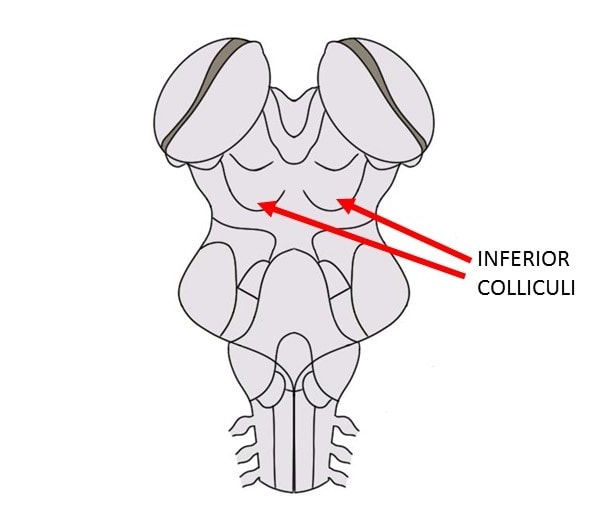
New cards
Located in the midbrain caudal to the superior colliculus. Acts as a relay point for auditory information.
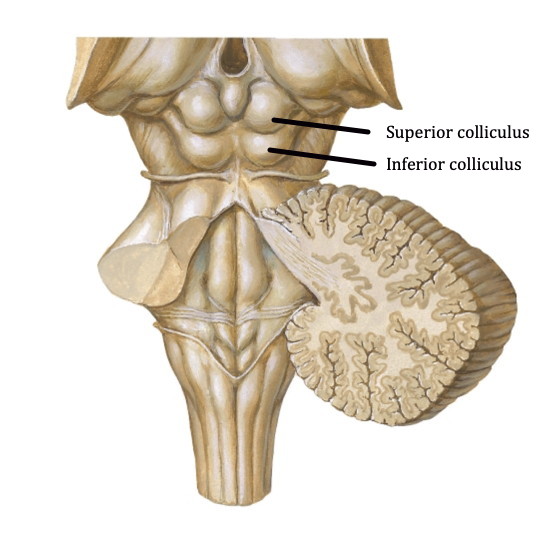
inferior colliculus
34
New cards
Located on the posterior midbrain, rostral to the inferior colliculus. Helps orient us, particularly using eye movements. Multisensory; integrates visual, auditory, and somatosensory spatial information.
superior colliculus