chapter 13-15
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What are the 2 anatomical subdivisions of the nervous system.
CNS & PNS
CNS
Consists of brain and spinal chord
integrating, processing and coordinating
Intelligence, memory, learning, and emotion.
NOTE: There are no nerves at the brain or spinal chord
PNS
Neural tissue outside the PNS
Provides sensory info to the CNS
Carries motor commands to peripheral tissues
2 divisions (afferent and efferent)
Ending to the spinal chord:
ends at L1/L2
Has carrot-tip like end (Conus medullaris)
The horse tail of nerves (caudal equina) —> enter or exit through the anterior and posterior sacral foramina
Afferent vs. efferent
Afferent: Sensory information INTO the CNS.
Efferent: motor commands OUT to muscle and glands.
(SAME DAVE)
Is there more neurons or neuroglia within neural tissue?
there is more neural glial
Main functions of neuroglial
provides framework for neural tissue
Maintain the intercellular environment
Acts as phagocytes
Neuroglial found in PNS vs CNS
PNS:
Satellite cells
Schwann Cells
CNS:
Ependymal cells
oligodendrocytes
astrocytes
microglial (macrophages)
Schwann Cells
surrounds ALL axons of PNS regardless of being unmyelinated or not
participates in repair processes after injury —> in deep injury to a nerve, Schwann cells that remain can form a structure described as a "tube" like a straw and this tube allows an axonal bud to grow down it, guided by chemotaxis (a chemical information flow from the target)
PNS
Satellite cells
regulates O2, CO2, nutrient, and NT levels in the ganglia
PNS
If one were to put a pin through the PNS and hit Schwann cells, would they be able to hit both myelinated and unmyelinated axons
YES!!!
Astrocytes
Largest and most numerous glial cells
located in CNS
maintain the BBB
form scar tissue after injury
Microglia
removes cell debris, wastes and pathogens via phagocytosis. (CNS)
Ependymal cells
line the ventricles and the central canal of the spinal chord
assist in the production, circulation, and monitoring of CSF
Name the 3 receptors monitored by the sensory neurons
exteroceptors
proprioceptors
interoceptors
exteroceptors
receives info from external environment
touch, temp, and pressure sensations
special senses of sight, smell, and hearing
proprioceptors
receives info from internal environment
position and movement of skeletal muscles and joints
information carried into somatic sensory neurons
interoceptors
receives info from internal environment
digestive, respiratory, cardiovascular, urinary, and reproductive systems
sensations of deep pressure as well as taste.
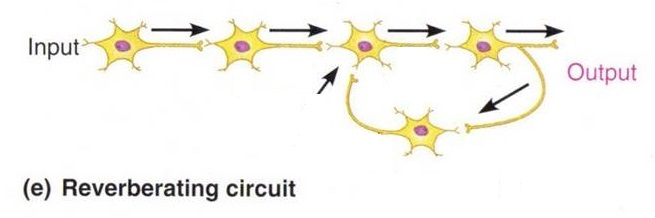
What type of pathway of neural circuits regulates homeostasis?
reverberation
Neural cortex
Gray matter on the surface of the brain
Centers
collections of the neuron cell bodies in the CNS; each have specific function
Gray matter org
Higher Centers
the most complex centers of the brain
(gray matter org)
nuclei
collection of neuron cell bodies in the interior of the CNS
(gray matter org)
Tracts
Bundles of CNS axons that share a common origin and destination (white matter org)
Columns
white matter org
several tracts that forms an anatomically distinct mass (think of white columns in the spinal cord.
T or F: does the spinal chord and the brain have functional independence
T
Which part of the spinal chord are lateral horns present?
T1 - L2
Filum Terminale
is a pia mater structure
keeps the spinal cord in its dural sac
What does Filum Terminale and denticulate ligament have in common
the both originate from the pia mater
Name the 3 meningeal layers
dura mater (tough mother)
arachnoid mater
pia mater (innermost layer)
Which structures in the spinal cord include CSF
Subarachnoid area
Central canal
What do the lateral gray horns of the spinal cord include
Visceral motor neurons
Ascending vs Descending tracts
Ascending: relays info from spinal cord to the brain
Descending: relays info from the brain to spinal cord
The brachial plexus separates what two structures?
the anterior and middle scalenes (muscle)
Name nerves from lateral to medial that make up the brachial plexus.
musculocutaneous, axillary, radial, median, and ulnar nerves
“my aunt raced my uncle)
Sciatic Nerve
huge nerve located inferiorly
for most people, exits from the inferior border of the piriformis muscle
General steps for a reflex arc
stimulus. stretching of muscle stimulates muscle spindles
activation of a sensory neuron
information processing at moter neuron
activation of motor neuron
response. contraction of muscle
Cingulate Gyrus
the emotional gyrus (overwhelming emotion)
note that our most powerful visceral memories come from smell: olfaction goes directly into the cingulate gyrus rather than the thalamus
What to remember about the ventricles
in a midsagittal cut, the 3rd ventricle would be destroyed
if you put a pin through the 3rd ventricle; you are in the thalamic nuclei
on either side of the 3rd ventricle, you have the thalamus
FILLED WITH CSF
Choroid Plexus
includes epitomal cells
main function is to produce CSF
Define anastomosis:
natural connection between structures that create alternate ways to get blood to go where it needs to go. (think of circle of willis)
Claustrum
a structure involved in subconscious processing
act like a conductor of an orchestra, letting things happen at certain times
associated with when time seems to move slowly during a state of emergency, gives person time to think and do things that may not be possible in a regular time frame
Lentiform nucleus
includes putamen and globus pallidus
DA-ergic
What is the amygdala’s function centered around?
sex, fear and aggression
Brain regions (5)
telencephalon (cerebrum)
Diencephalon
Mesencephalon
Metencephalon (cerebellum and pons)
myelencephalon (medulla oblongata)
Telencephalon
cerebrum
It is primarily associated with consciousness
Diencephalon
connects the cerebrum to the brain stem (both functionally and structurally)
functions are almost exclusively subconscious
Includes: epithalamus, thalamus, and hypothalamus
Epithalamus
includes pineal body
responsible for converting serotonin into melatonin
Thalamus
the relay center or all sensory and motor information flowing through the brain. —> only exception is olfactions (goes through the cingulate gyrus)
Located on either side of the 3rd ventricle
Hypothalamus
center for satiety
This refers to the control of the four biological imperatives: eating, sleeping, drinking, and sexual behavior
Suprachiasmatic Nucleus or SCN: Located above optic chiasm, responsible for generating our circadian rhythm
What to know on exam about the SCN
Suprachiasmatic Nucleus
generation of the circadian rhythm.
Mesencephalon
also known as the midbrain
Corpora quadrigemina: superior and inferior colliculi (visual and auditory)
Reticular Formation: automatic processing of incoming sensations and outgoing motor commands; can initiate motor responses responses to stimuli; helps maintain consciousness
Metencephalon
pons: respiratory activities —> within gray matter
cerebellum: coordinating movement beneath the level of consciousness —> adjusts postural muscles of the muscle to maintain balance + programs and fine-tunes voluntary and involuntary movements
myelencephalon
medulla oblongata
connects the brain with the spinal cord
relation station, house for cranial nerve nuclei and controls visceral functions like blood pressure, and heart rate.