C6: Multivariate correlational research
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What are the criteria for causality?
Covariance
a relationship between X & Y
Temporal precedence
X comes before Y
No alternative explanations
no third variable Z
How do bivariate correlations meet or not meet the criteria for causality? What are the solutions?
Covariance
bivariate correlations form evidence for covariance
Temporal precedence
bivariate correlations don’t necessarily prove temporal precedence, because you measure them at the same time
sometimes you can logically figure out which came first, ex. meeting partner & marriage satisfaction
solution: longitudinal designs (separate points in time)→ automatically multivariate correlation
No alternative explanations
bivariate correlations can’t rule out alternative explanations
solution: controlling for 3rd variables
What is a longitudinal design?
Same variables measured at multiple points in time in sample
you measure both X & Y at all measure moments
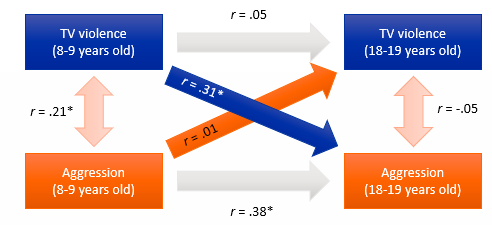
Based on which 3 types of correlations can you interpret the results of longitudinal designs?
Cross-sectional correlations
Auto-correlations
Cross-lag correlations
What are cross-sectional correlations (interpretating results of longitudinal designs)?
Correlation X & Y at the same measurement moments
X & Y at T1
X & Y at T2
What are auto-correlations (interpretating results of longitudinal designs)?
Correlation of same variables at different measurement moments,
X at T1 & T2
Y at T1 & T2
What are cross-lag correlations (interpretating results of longitudinal designs)?
Correlation of X at 1st measurement with Y at 2nd measurement moment & vice versa
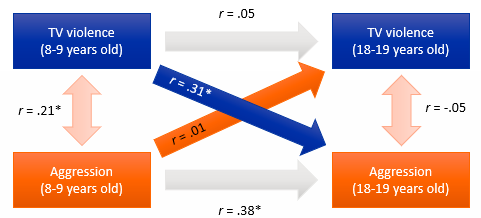
What are the limitations of a longitudinal design if we want to prove causality? Tip: think of the 3 correlations.
Cross-sectional correlations show a relationship between variables (covariance), but don’t say anything about temporal precedence
ex. + relationship between tv violence & aggression at 8, but you don’t know which causes which
Auto-correlations don’t tell us anything about temporal precedence & covariance
ex. just tells us that there is a relationship between aggression at 8 vs 18
Cross-lag correlations do tell us something about temporal precedence
BUT we can’t rule out alternative explanations, there could be many other variables (SES, parenting style…)
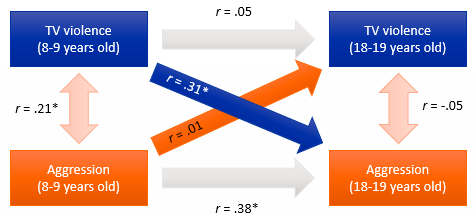
What does it mean when auto-correlations are significant?
There’s stability between the variables
ex. + correlation between narcissism at T1 & T2 means narcissism is stable
Which type of correlation meets the most criteria for causality?
Cross-lag correlation, but we still can’t rule out other explanations
Why are longitudinal designs sometimes used instead of experiments?
Due to ethical & practical reasons
How does a multiple regression try to solve the limitations of bivariate correlations & longitudinal designs?
+2 measured variables
Controlling for 3rd variables to rule out alternative explanations
Adding control variables to regression
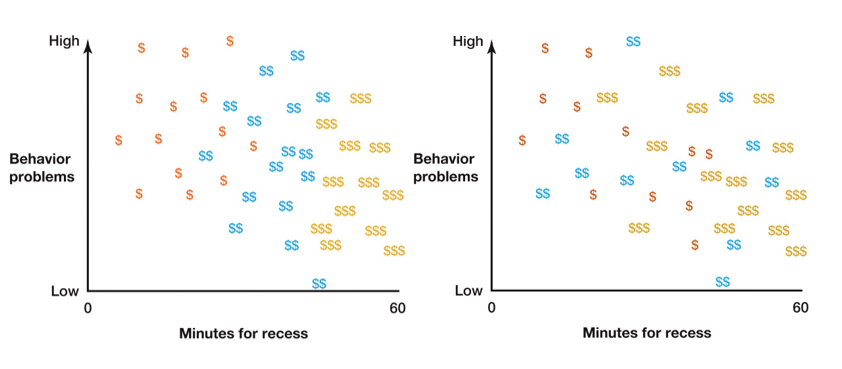
In which of these graphics is SES third variable & how can you see this with a multiple regression?
Prediction using multiple measured variables
Right: If you take SES into account & look at relationship between the 2 variables, you always have a negative correlation still
→ SES is NOT a 3rd variable
Left: If you don’t take SES into account, you have a negative correlation, BUT if you do take SES into account, the relationship disappears
→ SES IS a 3rd variable
What do Beta (β) & b mean in a multiple regression?
= What is relationship between variables? how will outcome change if independent variable changes?
Beta (β) = standardized beta
can be compared to each other
b = unstandardized beta
can’t be compared to each other
How does a multiple regression rule out third variables? Tip: think of the 3 cases in which you predict dependent variable with 1 or 2 independents. Use the example of predicting teen pregnancies with temperature, while seeing if income is a third variable.
Case 1: When predicting teen pregnancies with both income & temperature, then only income predicts teen pregnancies while controlling for temperature.
effect of temperature disappeared when controlling for income → income = 3rd variable
Case 2: When predicting teen pregnancies with both income & temperature, income predicts teen pregnancies while controlling for temperature & temperature predicts pregnancies while controlling for income.
so even while controlling for income, temperature still has an effect
both seem to predict teen pregnancies
→ income NOT 3rd variable
Case 3: When predicting teen pregnancies with both income & temperature, then only temperature predicts teen pregnancies while controlling for income.
even while controlling for income, temperature still has an effect
income unrelated
temperature might be alternative explanation for the relationship we observe between income & teen pregnancies
So a multiple regression model is able to tell us which predictors are significant, while controlling for other variables. However, there is still a problem, which one?
We can only rule out third variables that we measured & included in the multiple regression model, but you can come up with more alternative explanations
How does a multiple regression meet the criteria for causality?
Covariance? Yes
Temporal precedence? If you combine multiple multiple regressions with longitudinal studies
Rule out all alternative explanations? To some extent
→ Multiple regression cannot offer definitive evidence for causal effects!
Can patterns & parsimony (simple explanation) prove causality? If so, in what way? Tip: think of the effect of smoking on cancer.
You can form conclusions on causality based on a pattern you observe in literature
ex. there’s an abundance of correlational research on smoking & lung cancer that show a high correlation, the simplest explanation is that cigarette smoke is a carcinogen, so even if the researches were correlational, you can still conclude its causal effect
there are also effects of second-hand smoking & filtered vs unfiltered smoking
What is a mediator?
Mediator (M) explains why there’s a relationship between X & Y
mediation hypothesis → causal claims
describe causal chain, process or mechanism
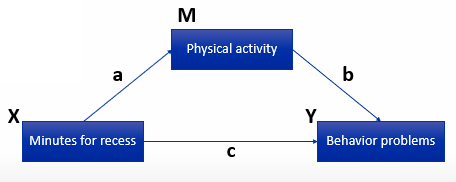
Explain the steps to demonstrate mediation. When can we speak about a mediator?
Predict Y with X (c path)
Predict M with X (a path)
Predict Y with M (b path)
Predict Y with X & M. If c is smaller then in step 1 → mediation
physical activity predicts behavior problems, but effect of minutes for recess decreases, not as large as what we found in step 1
Longer recess, more physical activity, more tired, less behavioral problems
What is the difference between mediators & confounders?
= 3rd variables
Confounder relates to both variables
If you control for it, relationship between X & Y disappears
See slide 34!!!!

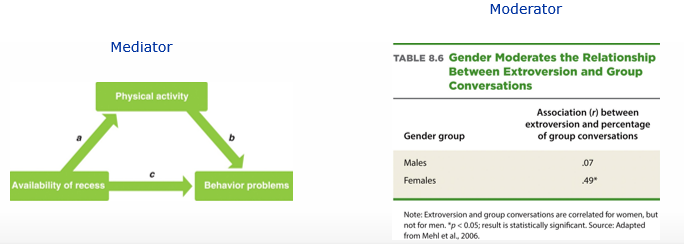
What is the difference between mediators & moderators?
Moderators tell us for which groups, individuals, contexts we find certain effect
ex. relationship between extroversion & group conversations is different for sexes → measured separately → relationship depends on sex (= moderator)
See slide 34!!!
In which 3 ways can we control for confounders?
Control by design
Control by randomization
Statistical control
How can we control for confounders by design? Illustrate with an example: study on relationship between physical activity & heart rate.
Confounders: frequency of exercising, so for people who don’t exercise a lot they have to run 1 km, people who exercise a lot 10 km so both groups will reach similar levels of heart rates
How can we statistically control for confounders?
Control for alternative explanations in statistical tests, statistical analysis, ex. using multiple regression
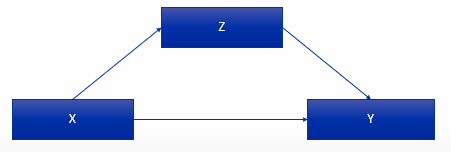
Look at this example. Did we or did we not control for Z? What is Z in this case?
No, we did NOT control for Z
Z = mediator
arrow goes from X → Z → Y
Z explains why there’s a relationship between X & Y
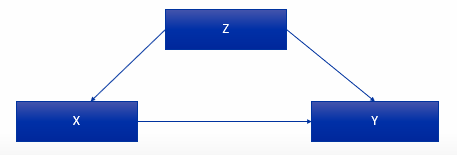
Look at this example. Did we or did we not control for Z? What is Z in this case?
Yes, we did control for Z
By relating it to both X & Y → do we still observe a relationship between X & Y or does it disappear?