CIE IGCSE Biology Unit 9: Transport in Humans
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
circulatory system
system of blood vessels with a pump and valves to ensure one-way flow of blood
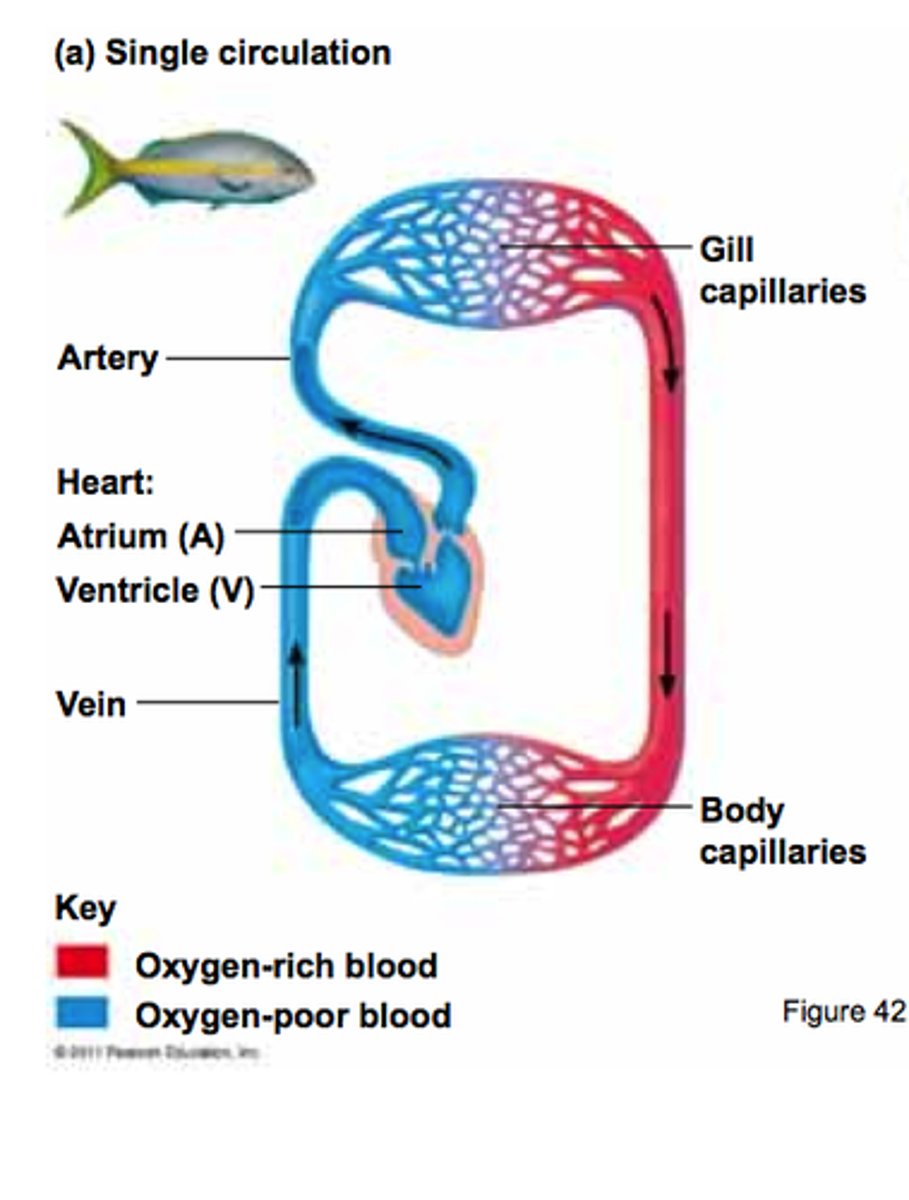
Single circulatory system
Blood only passes once through the heart
Double circulatory system
Blood completes two cycles around the heart before leaving to the rest of the body
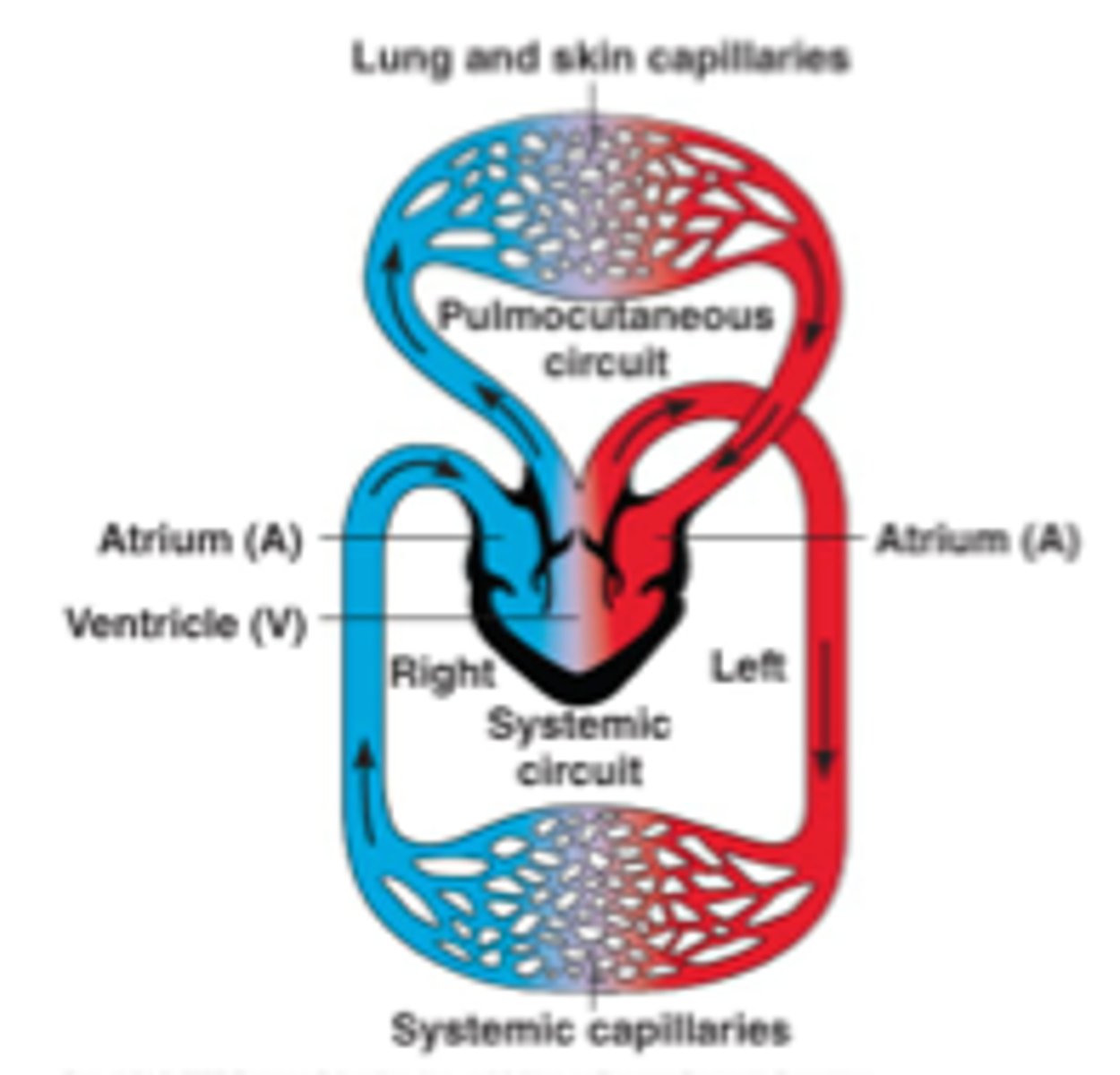
Advantages of double circulation
Deliver greater blood flow rate to tissues around body
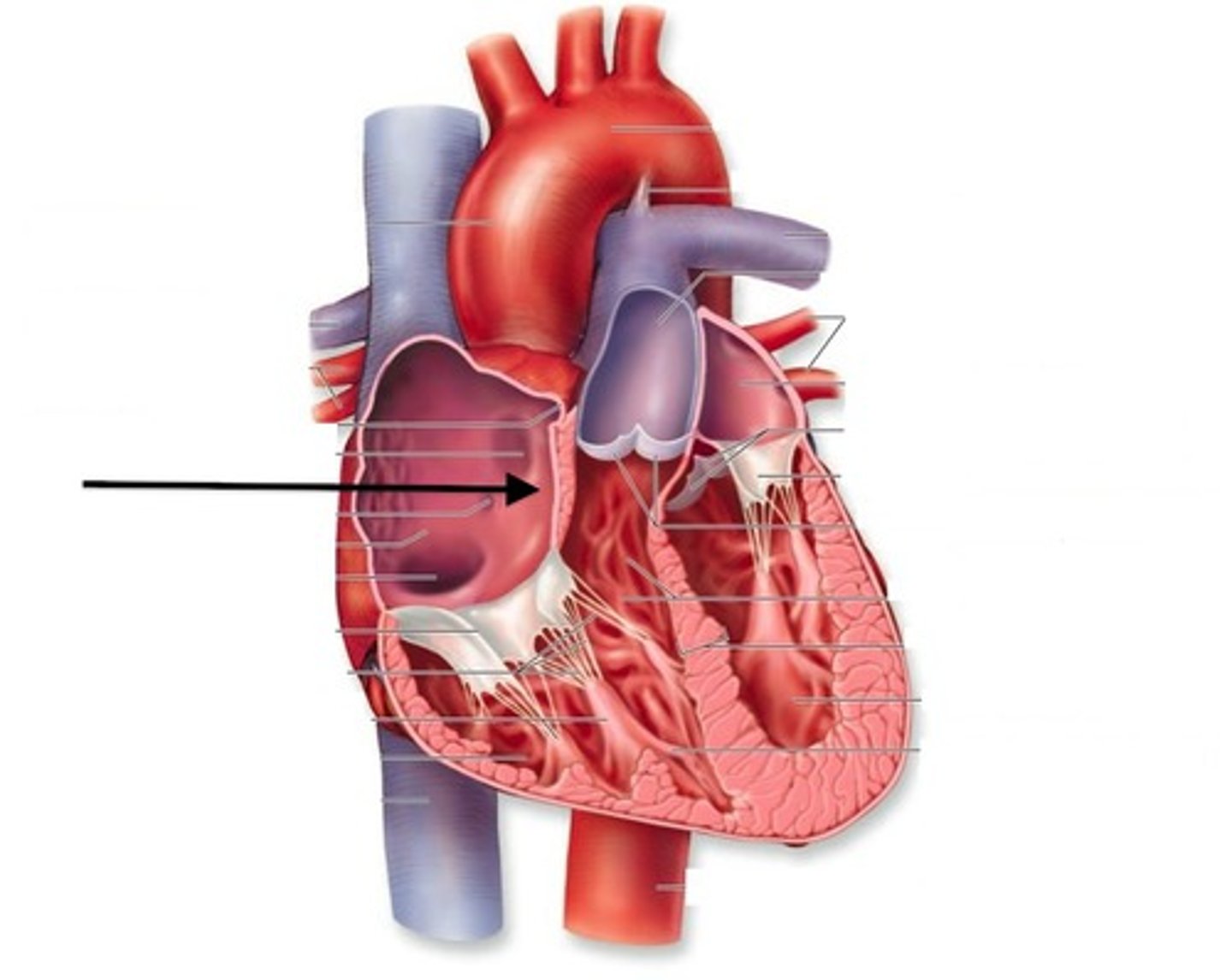
Heart structure
Divided into 4 sections:
Right atrium
Left atrium
Right ventricle
Left ventricle
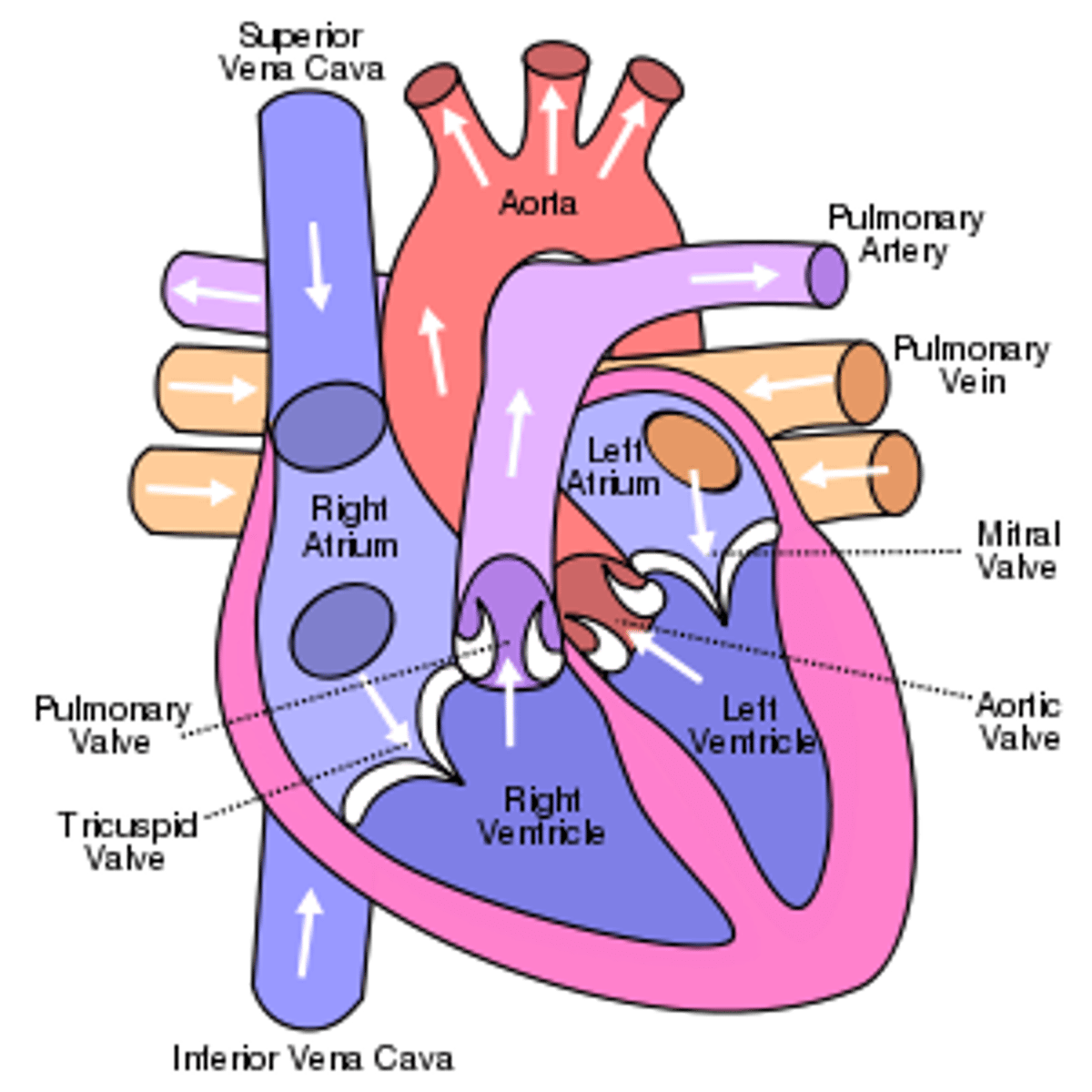
Importance of the septum
separating oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
Cardiac cycle
Consists of 3 stages:
Cardiac diastole: when chambers of heart are relaxed and filled with blood
Atrial systole: when atria contract leading to ventricular filling with blood
Ventricular systole: Contraction of ventricles to allow blood to leave heart
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Used to test person's heart rhythm and electrical activity of the heart

Effect of exercise on heart rate
Exercise increases heart rate as the heart needs to supply more oxygen to the muscles to undergo respiration for production of energy
Effect of exercise on pulse rate
Arteries
Used to transport blood from heart
Veins
Used to transport blood from body to heart
Capillaries
One cell thick, used for diffusion of nutrients from blood to cells
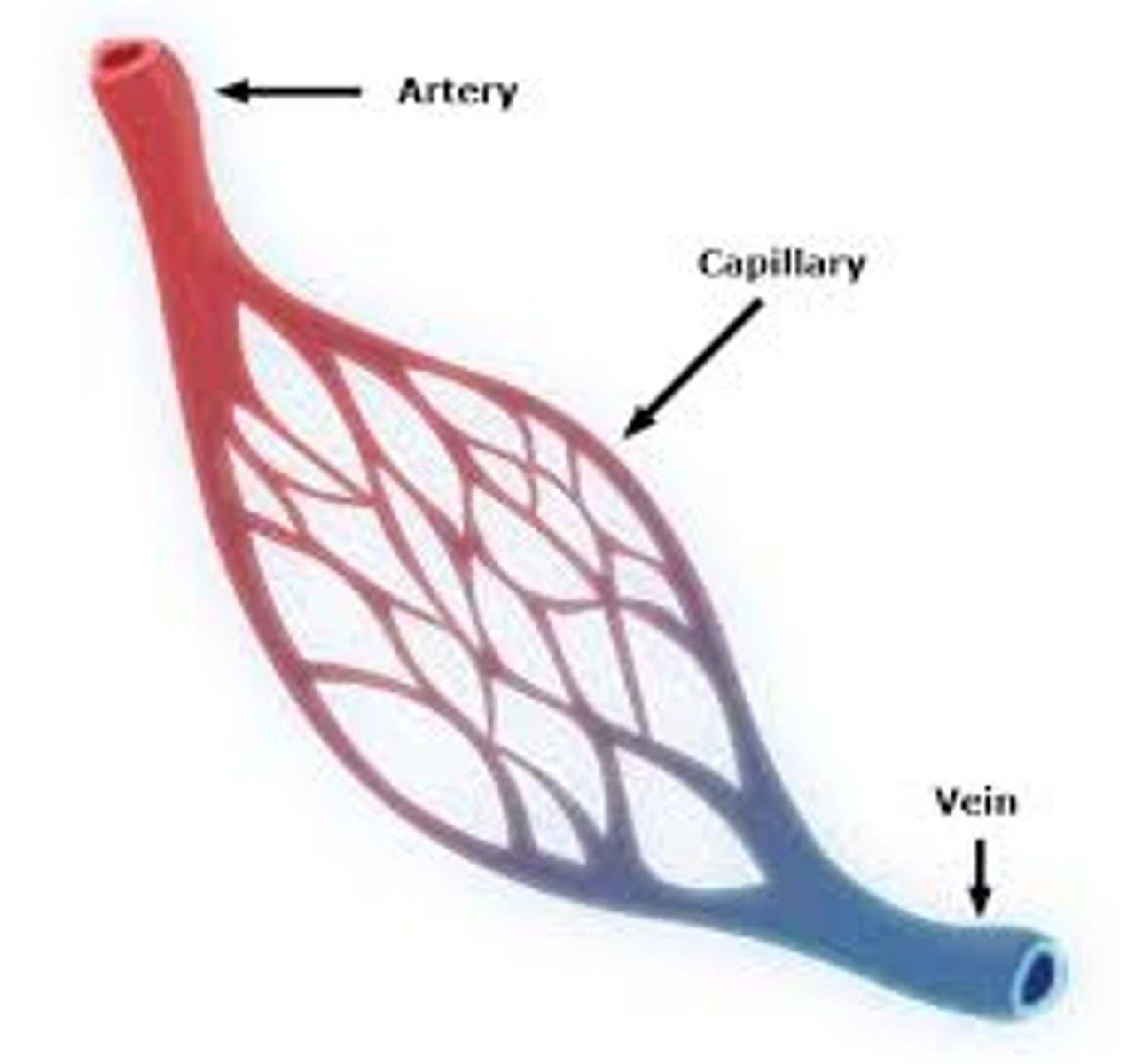
Structure of Artery, Vein, and capillaries
Arteries: small lumen, thick muscular wall to handle pressure of blood from heart
Veins: have large lumen to transport blood back to heart, have valves to prevent backflow of blood
Capillaries: One cell thick to allow diffusion of substances
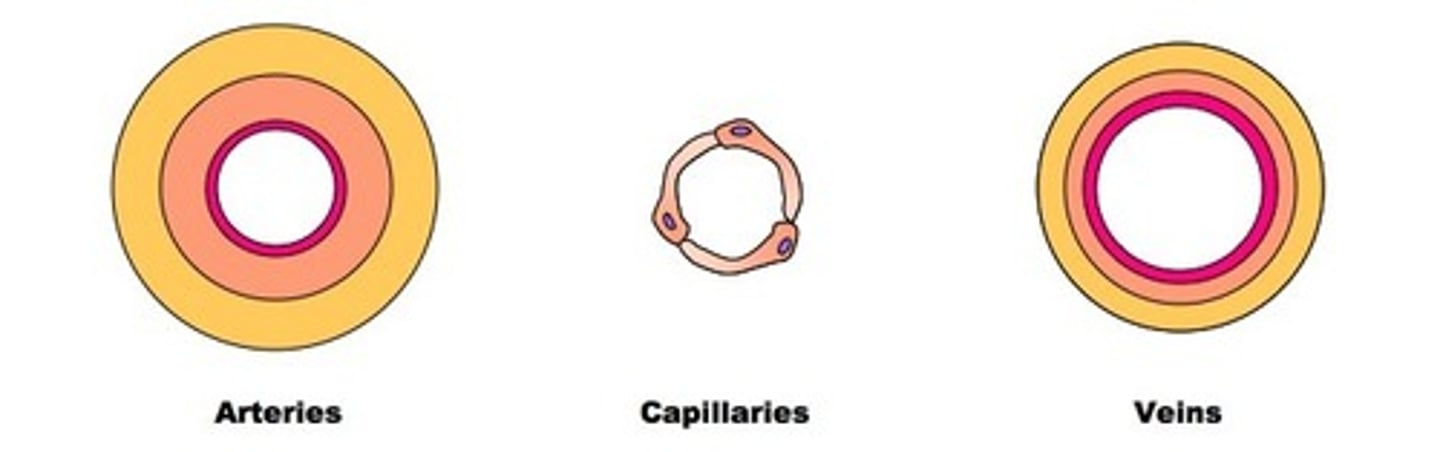
Arterioles
Arteries branch into smaller arterioles
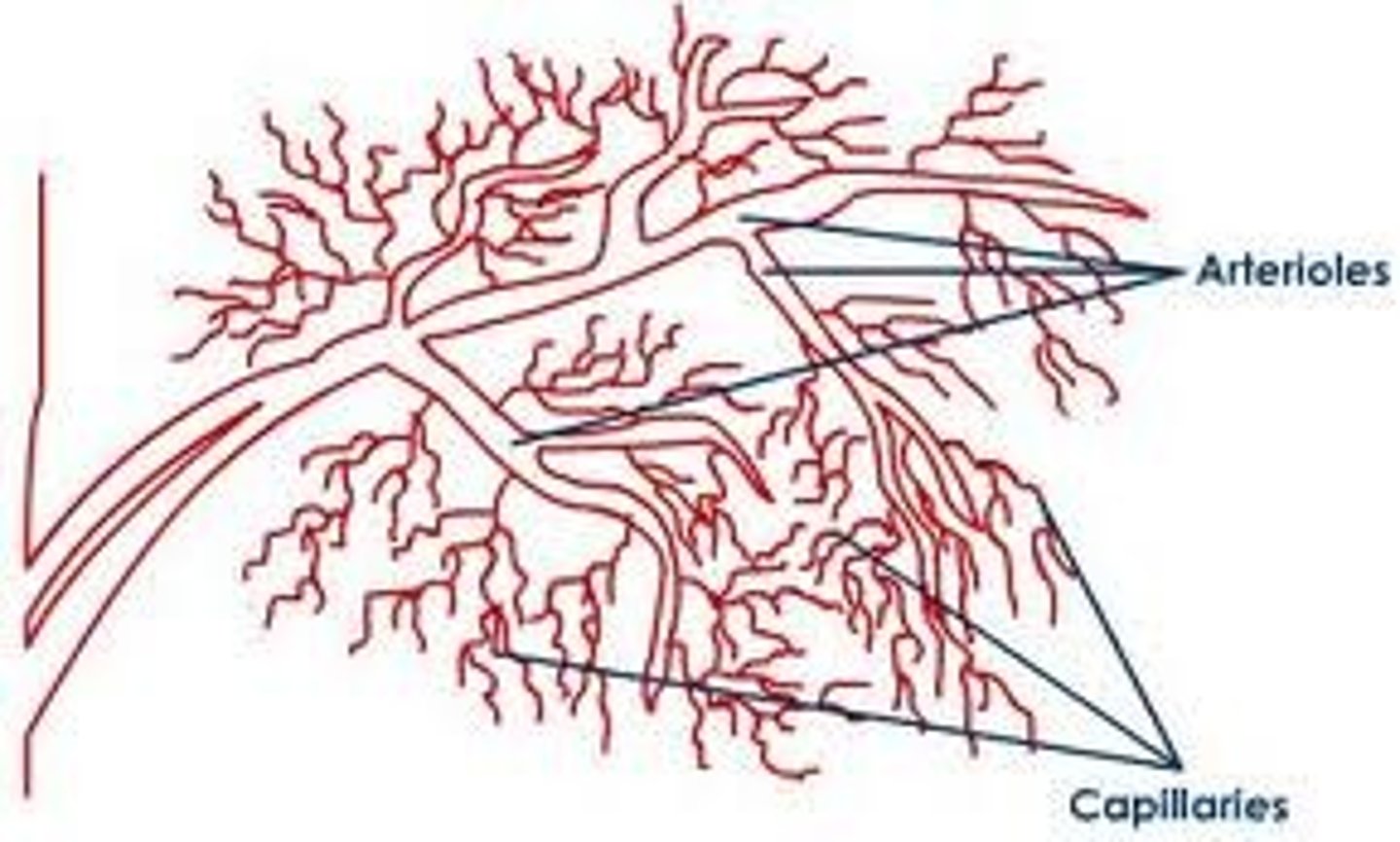
Venules
Venules allow deoxygenated blood to return to the veins to be transported back to the heart
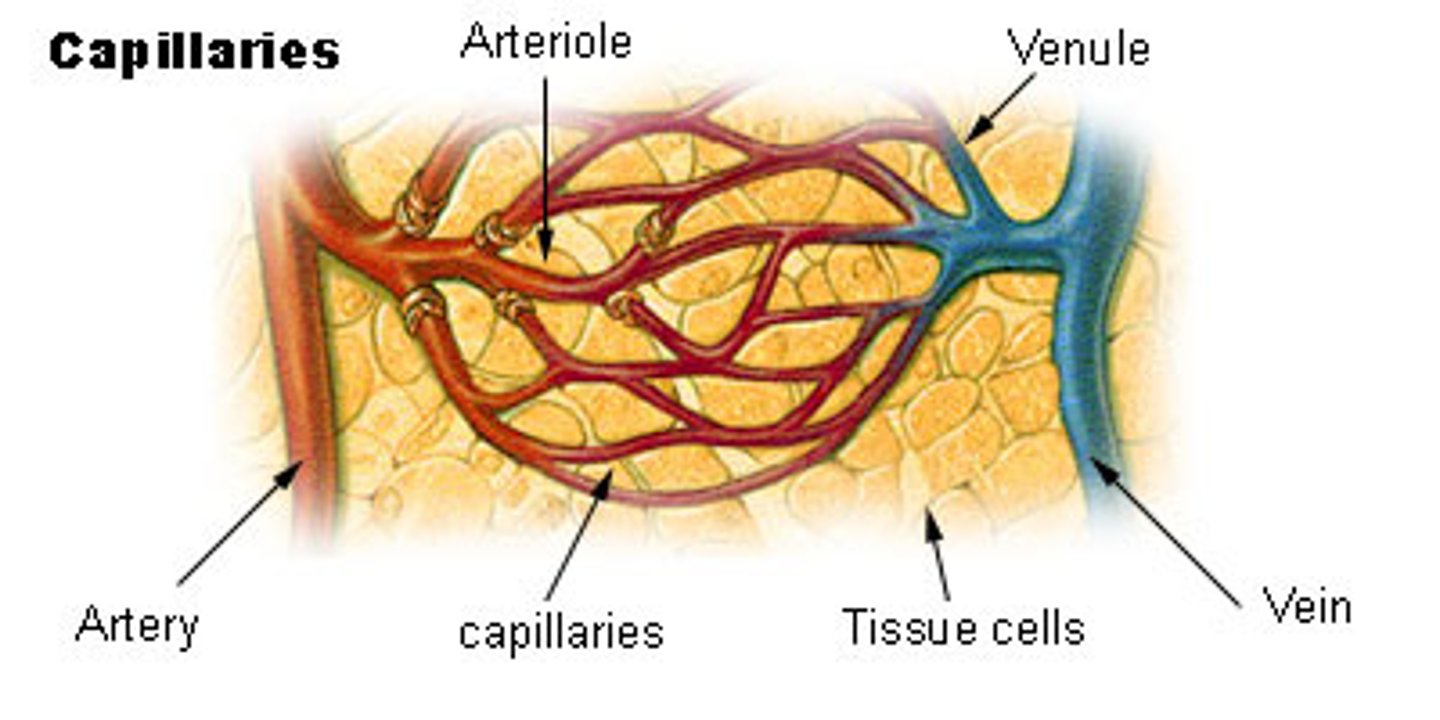
Shunt vessels
Artery is linked directly to vein, controls blood flow by constriction or dilation, bypasses capillaries
Coronary Heart Disease
The build up of plaque in arteries that block blood flow to rest of body
Risk Factors of Coronary Heart Disease
High cholesterol, high blood pressure, family inherited trait ,and diet are all factors that cause CHD
Treatment of Coronary Heart Disease
Coronary artery bypass: Blocked artery is bypassed by another artery taken from the patient
Coronary angioplasty: Small balloon is inflated inside the blocked artery and a stent is added to keep the artery open
Antiplatelet medicines: Aspirin, prevents blood clots from forming in arteries, risk of huge blood loss when there is cut as blood does not clot due to medication
Components of blood
red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets and plasma
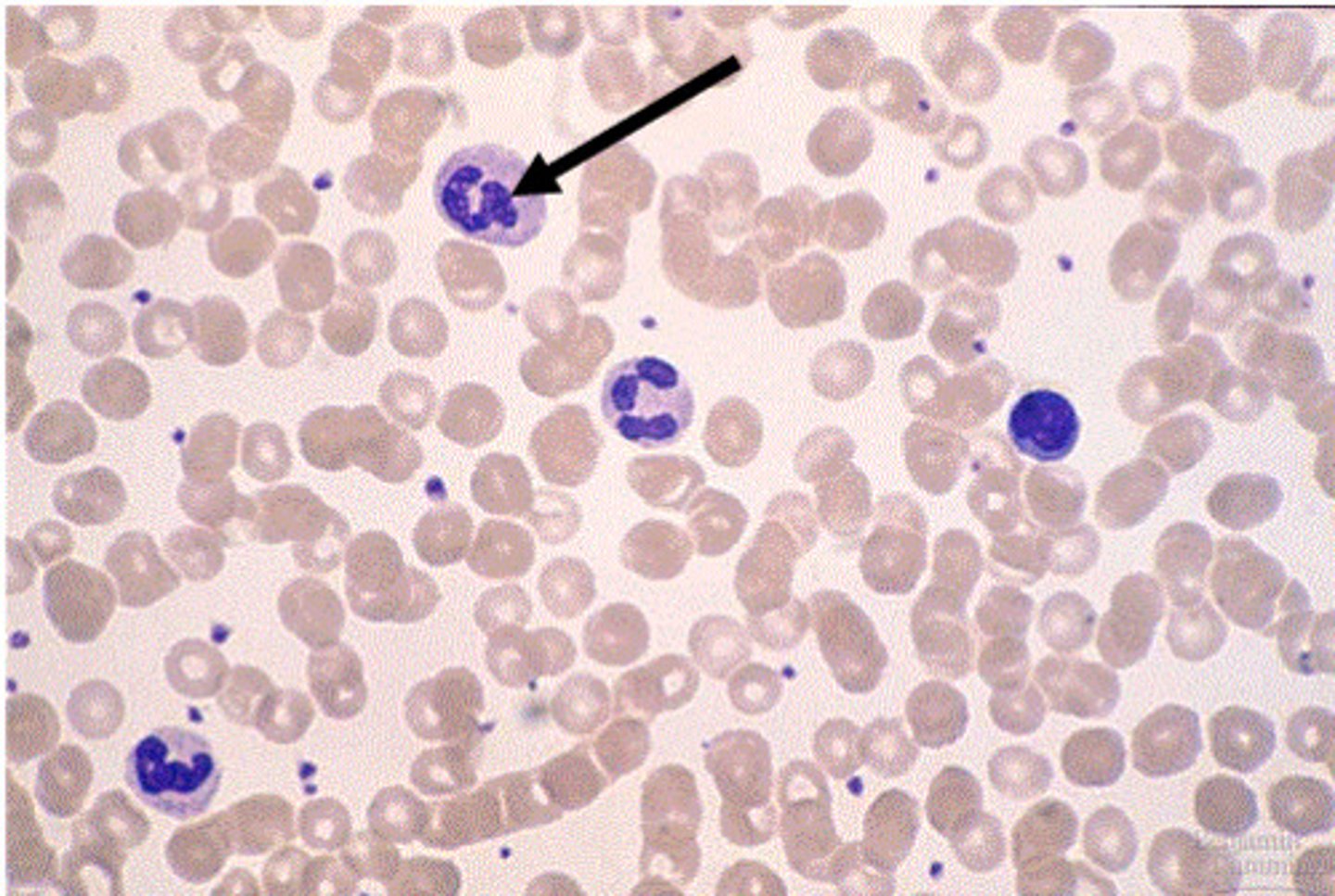
White Blood Cells
Contains lymphocytes and phagocytes used for phagocytosis and antibody production
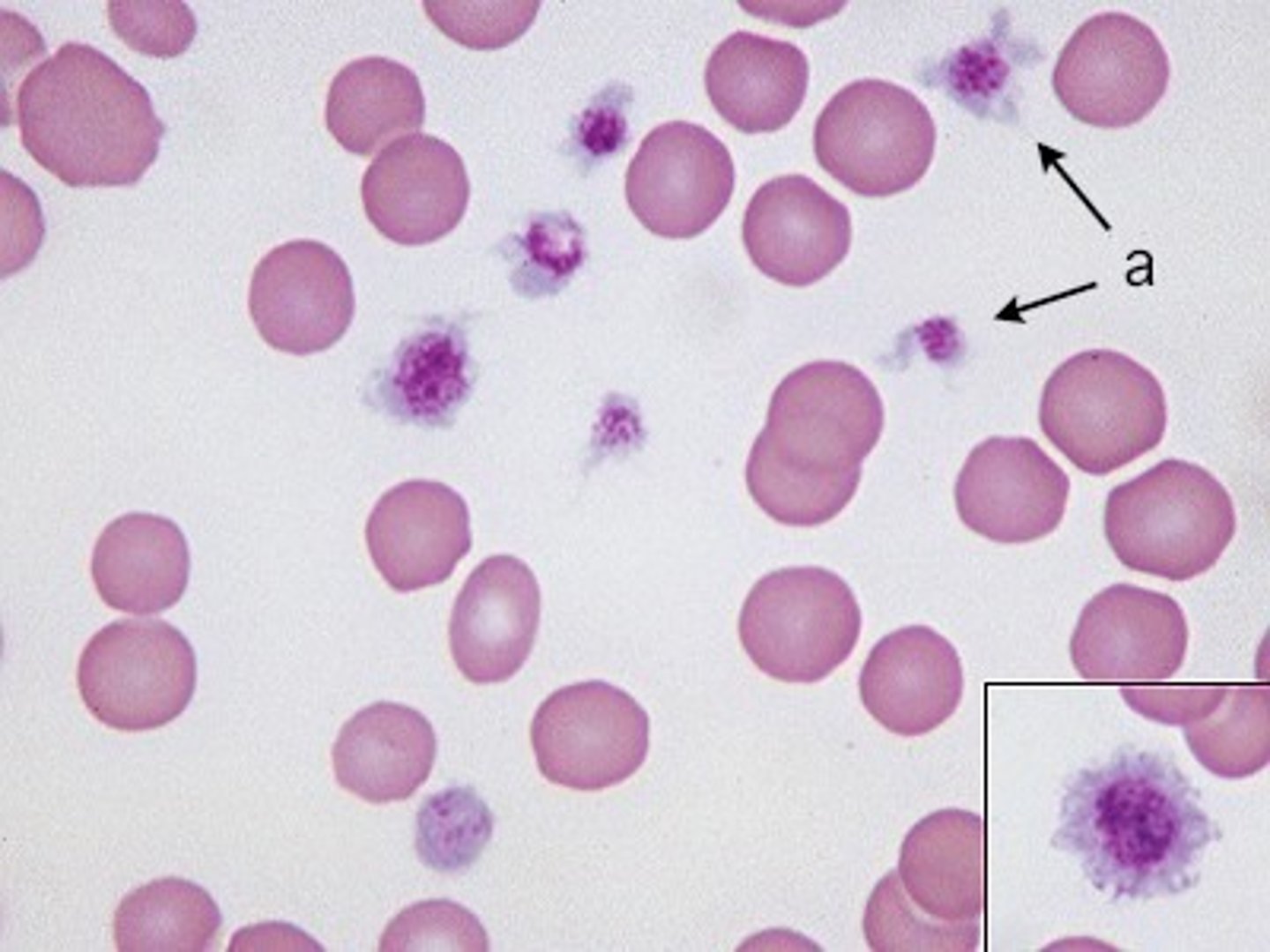
Platelets
Used for clotting
Clotting
the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin to form a mesh to prevent blood loss and the entry of pathogen

Plasma
Used for transport of blood cells, ions,
soluble nutrients, hormones and carbon
dioxide
Lymphocyte
Used to produce antibodies to protect against pathogens in the body

Phagocyte
used for phagocytosis
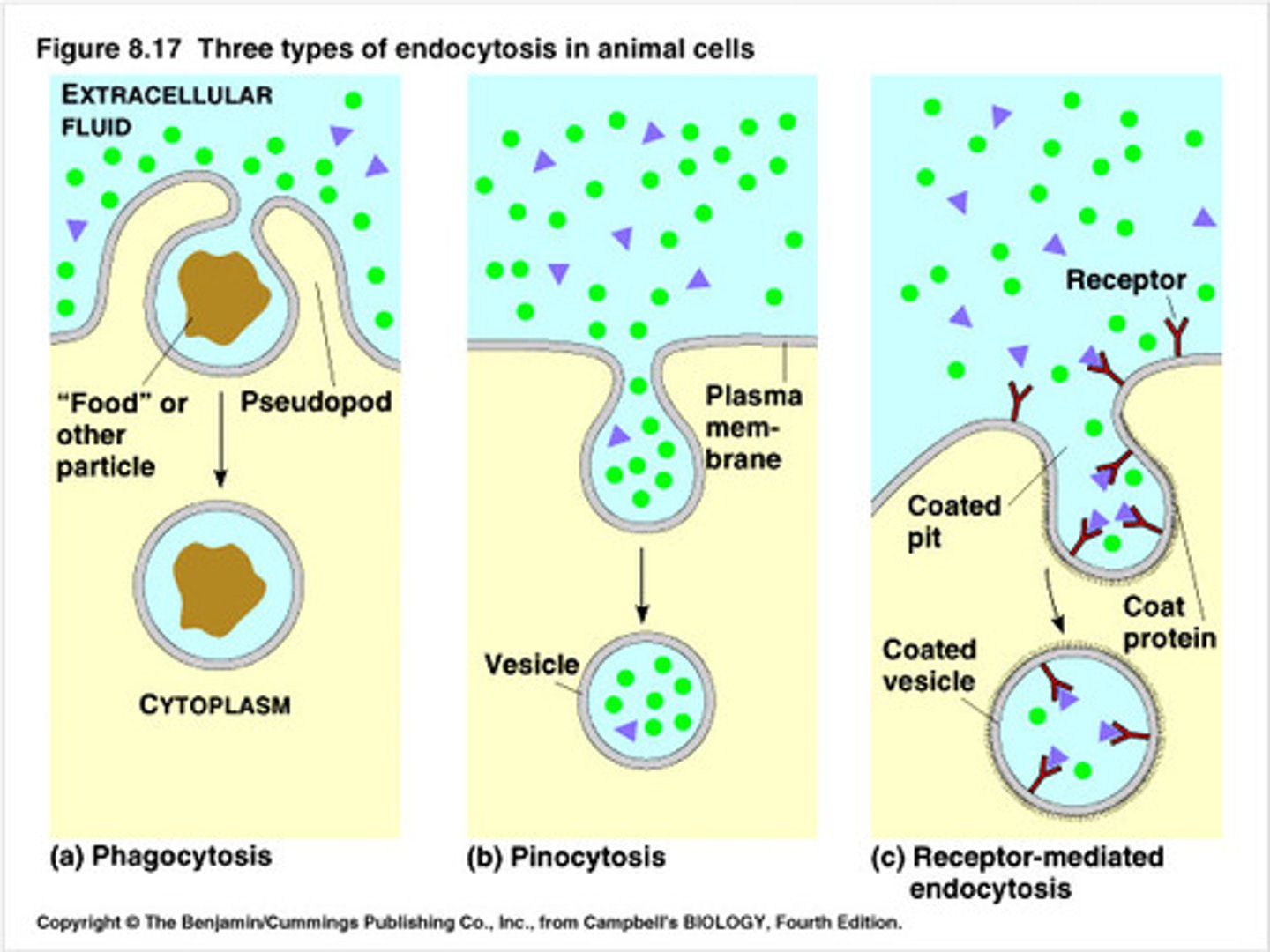
Phagocytosis
-Antibodies released to agglutinate pathogens
-Phagocytes engulf pathogens
-Enzymes released inside phagocytes that kill pathogen and make it a food source for the phagocyte
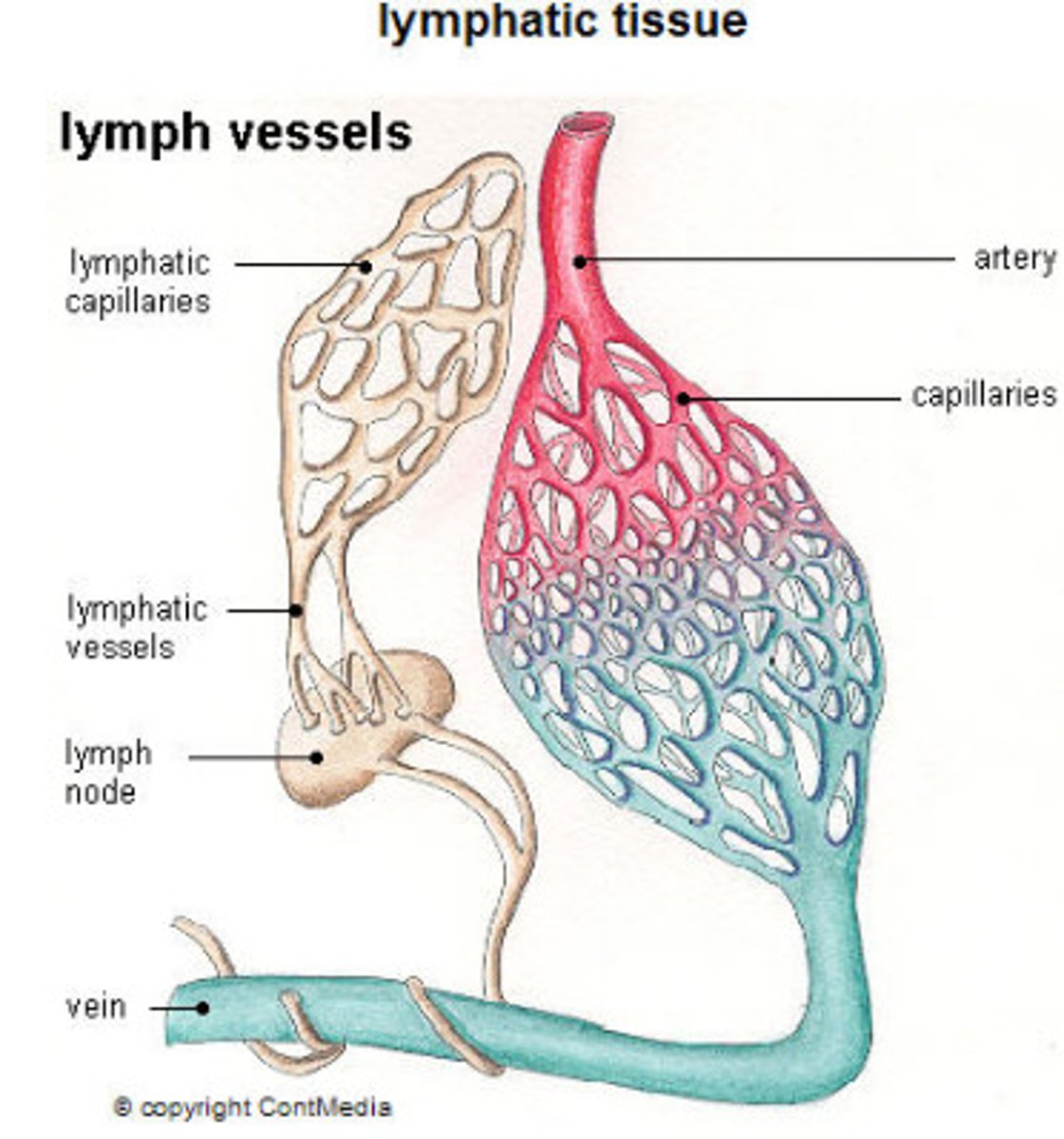
Lymphatic System
Network of tissues and organs that rid the body of toxins, waste and unwanted substances
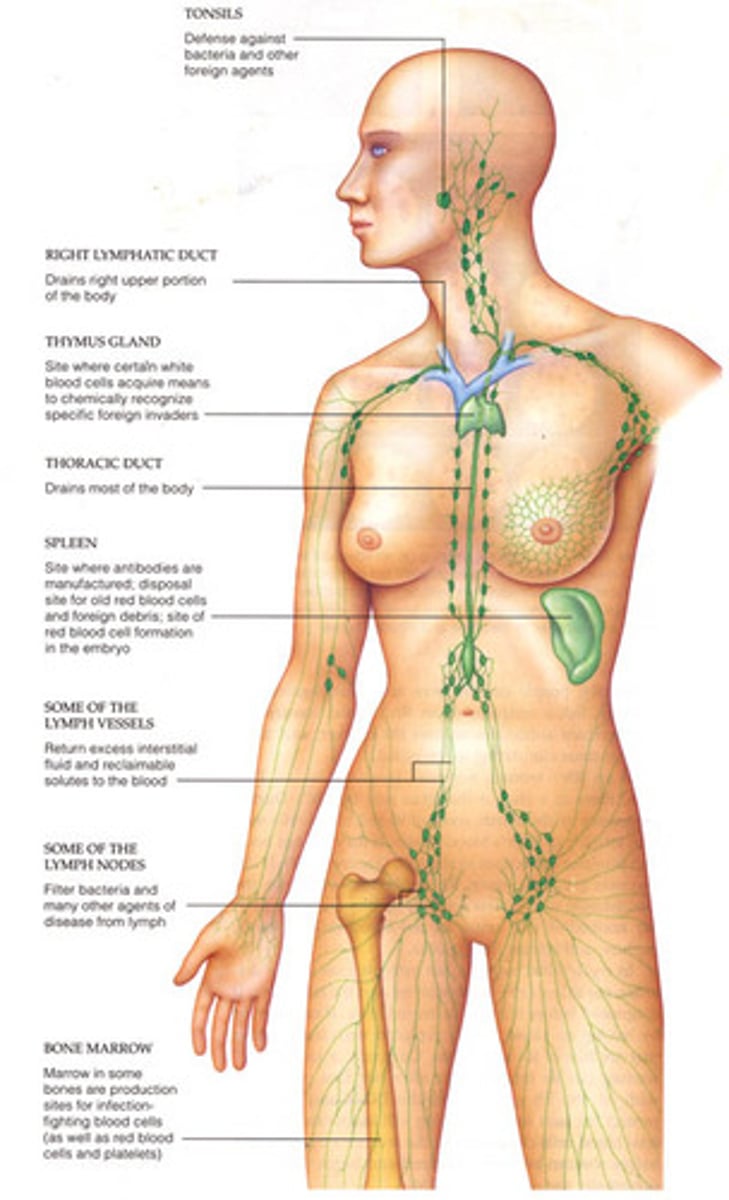
Lymphatic vessels
Transport lymph(tissue fluid) to subclavian veins, have valves to prevent backflow, slow and rely on peristalsis to move
Lymph nodes
Contain lymphocytes that make antibodies
Exchange of materials between capillaries and tissue fluid
-Proteins are transported in lymph vessel
-Bacteria may be picked up and destroyed in lymph nodes by lymphocytes