Final Exam KNES370
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
Thelen et al. (1984) investigated the stepping reflex of infants under various conditions. Which of the following best describes their results?
Adding weight to the legs decreased the number of stepping responses. Submerging the legs in the water increased the number of stepping responses
Thelen et al. (1984) argued that their results were consistent with which of the following hypotheses?
The stepping reflex disappears during development because leg weight increases more quickly than leg weight
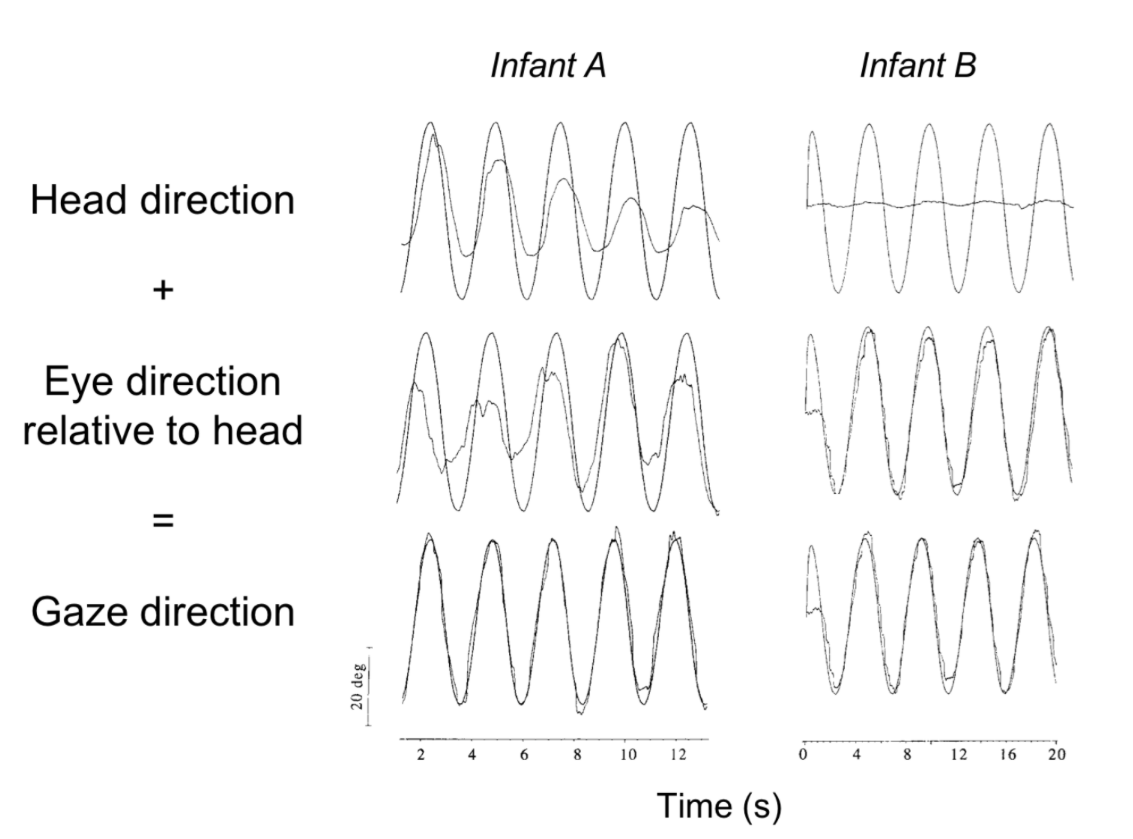
The figure below shows how two infants track a moving visual target. In each subplot, the smooth sinusoidal curve indicates how the direction of the visual target changes over time. The other curve is the infant's head direction (top row), eye direction relative to the head (middle row), or gaze direction (bottom row). Which of the following statements about the infants' ages best reflects the typical development of visual tracking?
Infant A is about 5 months old, whereas infant B is about 2 months old
What is the term for a fast short-duration (20-40ms) eye movement?
Saccade
Which of the following statements about motor redundancy is NOT true?
During the development of a motor behavior such as visual tracking, initially the individual uses all the DOF of a motor behavior. Later as more skillful behavior develops, some DOF are frozen
When is it necessary to keep the center of mass over the base of support in order to maintain balance?
For static balance
How is the concept of constraints related to the development of postural control and balance?
-The development of body systems, such as the muscular and nervous systems, are individual constraints for the development of posture; control and balance
-The development of postural control and balance constrains the development of other motor behaviors, such as reaching and grasping
Which of the following is typically true for the control of head movements in infants?
-At birth, an infant in a prone position is unable to lift their head off the floor
-During the first few months after birth, if an infant in a supine position is pulled by the arms into a sitting position, the head will lag behind the trunk
-During the first few months after birth, an important constraint on head control is the weakness of an infant’s neck muscles
Which of the following describes direction-specific responses of one-month-old infants sitting on a platform that can be moved in the horizontal direction?
None of the above
Consider the typical development of direction-specific responses for standing during the fundamental motor patterns (FMP) period. Which of the following bestdescribes responses to a forward movement of the support surface?
The tibia’s anterior and gastrocnemius muscles both respond early during the FMP period. The response of the gastrocnemius muscle becomes weaker later during the FMP period
In the study of Inglin & Woollacott (1988) on anticipatory postural adjustments, young adults and older adults were asked to push or pull on a stationary vertical structure as rapidly and strongly as possible when one of two lights turned on. Which of the following best describes observed differences between young adults and older adults when pulling?
Both young adults and older adults activated their gastrocnemius muscle before their biceps muscle. However, the time delay from gastrocnemius activation to biceps activation was greater for the older adults
When during development are anticipatory postural adjustments first observed?
During the fundamental motor patters (FMP) period
When a standing young adult is first subjected to an unexpected backwards (toes-up) rotation of the support surface, they respond by activating their gastrocnemius (and other posterior) muscles, which causes them to sway backwards. With repeated perturbations, adaptation leads to a reduction in gastrocnemius responses, which reduces their backward sway. Do children aged 1-7 years during the fundamental motor patterns (FMP) period show the same amount and consistency of adaptation as young adults?
No
Recall that in some conditions of the Sensory Organization Test, the platform that the participant is standing on is sway-referenced. Which of the following is true when the platform is sway-referenced?
-Forwards say of the participant causes the platform to rotate forwards, and backwards sway of the participant causes the platform to rotate backwards
-Proprioception is a less reliable indicator of self-motion compared to conditions without sway referencing
In the Sensory Organization Test, which of the following best describes the effect of removing vision and sway referencing the platform (Condition 5) compared to normal vision and no sway referencing (Condition 1)?
There is increased postural sway in Condition 5 compared to Condition 1 during any period of development from the FMP period to older adulthood, but the increase is greater for young children and older adults compared to young adults
Which of the following is a form of locomotion but not a form of mobility?
None of the above
Which of the following is a form of mobility but not a form of locomotion?
Pull-to-stand
Which of the following statements about crawling is both true AND suggests a cumulative aspect of development?
When an infant starts to hands-and-knees crawl, crawling will be faster, in average, if the infant had previous belly-crawling experience
Which of the following is true for the development of pull-to-stand?
Later in development of pull-to-stand, infants exhibit a clear preference for the half-kneel technique
Which of the following is thought to be the most importantrate limiter for the achievement of independent walking?
Neural and sensory aspects of dynamic balance
During the typical gait cycle for walking, the duration of which of following is substantially longer than half the total duration of the gait cycle?
Stance for the right leg
Which of following is typically seen during walking in new walkers but not in young adults?
Making initial contact with the floor flat-footed
Which of the following is an example of a new walker freezing one or more degrees of freedom during stance that will later be released?
Keeping their leg straight with their knee extended
During walking, "falling downward" into each step refers to the center of mass accelerating in the downward direction when a foot first makes contact with the support surface. Which of the following is true?
-Falling downward into each step is typically seen in new walkers
-Falling downward into each step is not typically seen in young adults
-Falling downward into each step makes walking less efficient
Which of the following best describes average changes in preferred walking speed from young adulthood to older age?
It decreases, especially after middle age
Suppose there is a pen on a table and you will use the pen to write a note. Which of the following occurs first?
Regard
Which of the following best describes hand babbling?
A young infant generating a wide variety of hand movements that have no immediate functional purpose
Which of the following is the best evidence that postural control is a rate limiter for reaching in pre-sitting infants?
Providing additional postural support improves the straightness of hand trajectories
Which of the following best describes the typical capability of children to successfully reach and grasp an object under two conditions: (a) in a lighted room in which the child can see their arm, hand and the object; and (b) in a dark room in which the child can see a glowing object but not their arm or hand.
On average, children achieve the ability to reach and grasp in a lighted room at about age 4 months. They achieve the ability to reach and grasp in a dark room at about the same age
Newell et al. (1989a) studied the effect of task constraints on whether infants used one or both hands to grasp a cup. Which of the following best describes the results of this study?
Four-month-old and 8-month-old infants used either one or two hands to grasp the cup; two-handed grasps were more likely if the cup was large or upside down
In the study of Newell et al. (1989b), which of the following best describes how constraints affected the likelihood that a preschooler would use only one hand to grasp an object?
The likelihood of using one hand depended primarily on the relationship between task and individual constraints
Which of the following statements about grip force is true?
-On average, the maximum grip force that an individual can produce is less for older adults than for young adults
-When holding a light object, an older adult will, on average, produce more grip force than a young adult
-Both young adults and older adults use more grip force when holding an object with a slippery surface compared to an object with a rough surface
Which of the following is true for the typical development of hand velocity profiles during reaching?
-Young adults usually exhibit a hand velocity profile with a single movement unit
-During the predated period, the average number of movement units decreases more rapidly than later during development
-There is a reduction in the average number of movement units from age 1 year to young adulthood
Which of the following is true for developmental changes in the straightness of hand trajectories during reaching?
In new reachers, the length of hand trajectory is much longer than the straight-line path to the object
Recall that in the study of Posten et al. (2013), young adults and older adults were asked to move a hand-held stylus to a specified target as quickly and accurately as possible. What systematic difference was observed between the young adults and older adults?
Errors in the final position of the stylus were greater in the older adults
Consider preshaping the hand during reaching based on the size of the target object. Does this typically occur during the fundamental motor patterns (FMP) period?
Yes, but only if the child can see their hand during the reach
Recall the Tamaru et al. (2017) compared how much young and older adults open their hands while reaching to grasp either a small or large ball. Which of the following best describes the average behaviors of the two groups?
Older adults opened their hands wider while reaching compared to young adults
In a power grip, which of the following is contact with the object?
-The thumb
-Fingers (other than the thumb)
-The palm
Which of the following best describes how grip type changes during development?
Young infants most commonly use power grips. Older infants and adults use with a power grip or a precision grip depending on task constraints

The figure below illustrates three types of grasps (labelled A, B and C) used for drawing and writing. What is the typical sequence in which these grasp types first appear during development?
C,A,B
Which of the following best describes improvements in tracing and copying seen in the study by Birch & Lefford (1967) that we discussed in class?
On average, tracing and copying improved rapidly from age 5 to age 6, with more gradual improvements after age 6
Which of the following is true about the development of picture drawing?
-In Kellogg’s stages of development leading to picture drawing, the scribbling stage appears first
-In Kellogg’s stages of development leading to picture drawing, the pictorial stage appears last
-The development of picture drawing depends on the child’s home environment
Which of the following is true for declarative pointing?
An infant uses declarative pointing as part of social bonding with a caregiver
A test of balance is valid if:
The assessment of an individual yields a score that actually reflects the individual’s balance
For a measure of balance to have content validity, it must reflect:
Both static balance and dynamic balance
The study of Raîche et al. (2000) we discussed in class found that using the Tinetti test to assess fall risk has:
Some predictive validity
Suppose that a test for some condition has very high specificity. This guarantees which of the following?
Most individuals who do not have the condition will be correctly identified by the test as not having the condition
Suppose you are using a device to measure changes in children's muscle strength during development. The device breaks and starts to always give the same value for muscle strength every time it is used. This means that your assessment of muscle strength is:
Reliable but not valid
Why is the Movement Assessment Battery for Children referred to as a norm-referenced assessment tool?
It yields a percentile score that compares the child being tested to other children of the same age
Changes in motor behavior over the lifespan and the process(es) which underlie these changes are referred to as:
Motor Development
Why, according to Payne & Isaacs (2025), should we study motor development?
-If we understand the typical range of how motor behavior changes as individuals develop, we can identify atypical cases that might require intervention
-If we understand the atypical range of how motor behavior changes as individuals develop, it helps us design and implement activities to improve the motor skills of typically-developing individuals based on their ages and current levels of skillfulness
-To fully understand development, we must understand motor development and how it interacts with other domains of development such as cognitive development
Which of the following statements about motor milestones is true?
A motor milestone is the first appearance of a type of motor behavior in an individual
Which of the following best describes the reason that motor development is viewed as being cumulative
Often, early motor behaviors from the “building blocks” of motor behaviors that emerge later in life
Typically-developing infants walk independently for the first time at roughly 10-15 months of age. This illustrates that development is:
Age related
The study Atun-Einy. et al. (2012) that we discussed in class examined the attainment of four motor milestones: hand & knees crawling, independent sitting, pull to stand, and cruising. The study showed that the attainment of these milestones is:
Sequential in some respects but not strictly sequential
How does Payne & Isaacs (2025) use the terms maturation and growth?
Growth is the increases in physical size that occur with age. Maturation is the qualitative functional changes that occur with age
What term is used to describe the progression from gross, immature movement to precise, well-controlled, intentional movement?
Differentiation
Which of the following is most strongly emphasized in the neuromaturational perspective?
The orderly and sequential attainment of motor milestones
Suppose that two infants are born on the same day, one on their due date (the full term infant) and one 6 weeks before their due date (the preterm infant). Which of the following is most likely?
The full term infant will start social smiling 6 weeks before the preterm infant
Which of the following statements about standing is true for a typical young adult?
There is movement (postural sway) of the body due to errors in sensory processes, other neural processes, and force production by muscle. These movements are small because standing is a stable motor behavior
Suppose that you trip over an object while walking but are able to quickly recover and return to your normal walking pattern. This is direct evidence that:
Walking is stable
The rules of a sport are considered:
Task contraints
A rate limiter is:
An individual constraint that holds back or slows the emergence of a motor behavior
Optical illusions are due to errors in:
Perception
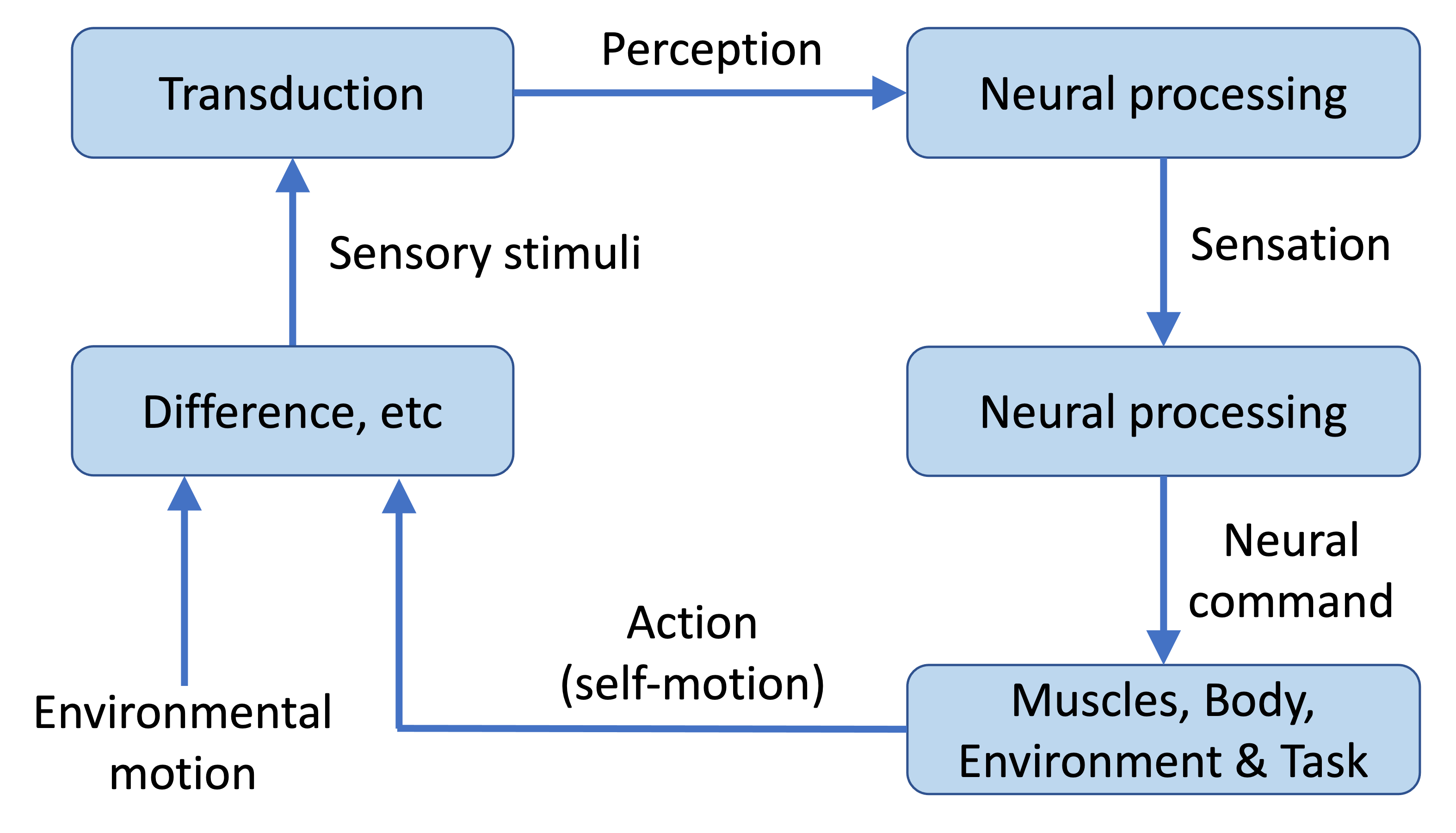
Is there anything wrong with this diagram of the perception-action cycle? If so, how would you fix it?
“perception” and “sensation” should be switched
In a “moving room” experiment, an infant who has recently started to stand and walk independently may fall over when the walls of the room move. How is this explained from the perception-action perspective?
The infant mistakenly perceives environmental motion as self-motion
Which of the following best describes visual acuity for nearby objects (those 7-10 inches away) and more distant objects (those more than 20 inches away)?
None of the above
Due to the vestibular ocular reflex (VOR), when the head of a young adult is rotated to the right, their eyes rotate to the left relative to the head. Which of the following best describes average changes in the VOR during aging?
When the older adult’s head is rotated to the right, their eyes rotate to the left relative to the head, but the amount of rotation may be less than that of a young adult depending on the rate of head rotation
Which of the following occurs due to changes in tactile acuity during development?
-If you touch the fingertip of a young adult with a light amount of force, they can perceive that they are being touched. On average, older adults only perceive that they are being touched when the force becomes stronger
-Young adults can perceive a narrow gap when touching a surface with their fingertip. On average, older adults only perceive the gap when it becomes wider
Which sensory system is the first to become functional during development?
The vestibular system
Which of the following sensory systems helps us maintain balance?
-Vision
-Somatosensation
-The vestibular system
Which of the following best describes the cephalocaudal pattern of physical growth of the body during development?
The length of the head at birth is roughly half its length at maturity. The length of the legs at birth are only about one fifth to one quarter of their mature lengths
Which of the following neural structures are myelinated first during development?
-The cranial nerve that conveys vestibular information to the brain
Which of the following is true for the context-specific period of the mountain of motor development?
-The motor/movement skills that one acquires during the context-specific period are built upon the foundation of the fundamental motor skills acquired during the fundamental patterns period
-The context-specific period is characterized by different individuals acquiring different motor skills
-The motor skills acquired during the context-specific period forms the foundation for the individual achieving higher levels of skillfulness in some motor skills during the skillful period
For the compensation period of the mountain of motor development, compensation can refer to adaptation to which of the following?
-The negative effects of an injury
-The declines during aging in middle and late adulthood
In Clark and Whitall’s description of different periods in the history of the field of motor development, during which period did researchers emphasize the view that biological processes were the main influence shaping human development?
The maturational period
As humans, our developing brains anticipate certain experiences in order to develop appropriately. For example our developing brains need to hear speech sounds of our spices or encounter environmental stimuli such as the pull of gravity in order to develop typically. This type of developmental process is referred to as:
Experience-expectant development
Which of the following is true for McGraw’s Johnny and Jimmy study from the 1930s?
-Johnny, the twin who was given extra opportunities to learn motor skills, was able to learn some motor skills, such as roller skating, at an usually young age
-The study was important as an early study on the effects of nature and nurture on motor development that influenced later studies
-The study had important limitations such as including only one pair of twins and the fact that they were fraternal twins rather than identical twins
The study of Fraiberg & Addison (1974) compared the ages at which blind and sighted infants attained motor milestones. The study found that:
-Blind infants tended to attain motor milestones at an older age than sighted infants
Which of the following best describes the Maurer et al. (1999) study on infants born with cataracts?
Immediately after surgery to remove the cataracts, the visual acuity of the infants was similar to that of newborns. This demonstrated that the development of visual acuity is experience-expectant
Which of the following refers to a period of time during development when specific conditions or stimuli are required for optimal, or even typical, development to occur?
A sensitive period
Maurer and colleagues observed a “sleeper” effect in children born with cataracts who had their cataracts surgically removed during the first year after birth. Which of the following was observed?
At age 5-6 years the children’s visual acuity was noticeably worse than typical infants of the same age
Hopkins & Westra (1990) compared three groups of infants born in the same hospital and raised in the same neighborhood in England. Infants in the Jamaican A group were raised with culturally Jamaican caregiver practices that included “formal handling.” Infants in the so-called English group were raised in families that were not culturally Jamaican and did not received formal handling. Which of the following is true about this study?
On average, infants in the Jamaican A group sat independently at a younger age than those in the English group
In the study of Zelazo et al. (1972), infants were randomly assigned to different groups, each group of infants underwent a different groups were observed. What was the advantage of assigning infants to different groups randomly?
There were no systematic differences in nature among the groups, so any systematic differences in outcomes among the groups provided evidence of how nurture affects motor development
In the study of Zelazo et al. (1972) described in the previous question infants in the active exercise group received seven weeks (from age 1 week to age 8 weeks) of daily stimulation of the placing and stepping reflexes, and infants in the passive exercise group received seven weeks of daily passive exercise. Which of the following best describes the average outcomes of these two groups?
-The strength of the stepping reflex systematically increased over the seven weeks for the active exercise group
-There was no systematic increase in the strength of the stepping relfex over the seven weeks for the passive exercise group
-The active exercise group attained the motor milestone of independent walking at a younger age than the passive exercise group
Which of the following provides the strongest evidence the aging is universal?
The masters records for the 100-m dash are slower for older age groups than for younger age groups
Which of the following is an effect of aging?
-Increased vulnerability to injury and disease
-Decreased function of body systems, even those not affected by injury or disease
Which of the following is change in individual constraints during the reflexive and predated periods of motor development?
-Body growth
-Increasing muscular strength
-Increasing function of sensory systems
Which of the following is an example of a dramatic change in an environmental constrain at the time of birth?
-The force of gravity on the body is no longer counteracted by buoyancy from amniotic fluid
Which of the following is true for rhythmic stereotypies?
-They are spontaneous rhythmic movement stereotypic in form and timing
-They are very common during the first year after birth
-If exhibited later during development, they may be a symptom of a pathological condition
-Which of the following best describes when humans first exhibit spontaneous and reflexive movements?
-Both spontaneous and reflexive movements occur prenatally
Which of the following is not an infantile reflex?
The patellar tendon reflex
Which of the following is true for the asymmetric tonic neck reflex?
If infant’s head is rotated rot the right, the right arm extends and the left arm flexes
Suppose you are supporting an 8-month-old infant off the ground in a prone position by placing your hand under the infant’s belly. Which of the following do you expect?
-The infant will raise their head
-The infant will raise their legs
-if you push the infant’s head down, the infant will lower their legs
If resistance to passive movement at a joint is greater if the movement is fast, this is direct evidence of:
Spasticity
Which of the following statements about clonus is NOT true?
Clonus is due to a weakened tonic stretch reflex
Which of the following statements about muscular dystrophy (MD) is true?
Most individuals with MD use a wheelchair by the time they reach adulthood
Gowers’ sign is typically seen in children with which of the following conditions?
Muscular dystrophy
Which of the following statements about sensory reweighing is true?
-In the moving room paradigm, when the walls of the room start to move, young adults will decrease their reliance on vision, which reduces the risk of losing balance
Which of the following is nOT a diagnostic criterion for development coordination disorder according to the most recent version of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5)?
The child does not have a diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder