Ch. 10 - Anticoagulant, water treatments, and fragrances.
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Carboxylic Group
Describes the functional groups of carboxylic acids (—OH) and Ethers (-OR)
Acyl groups of the Carboxylic acid group can also attach to what? In addition to ‐OH and –OR?
A variety of electronegative atoms
(Halides, nitrogen, sulfur)
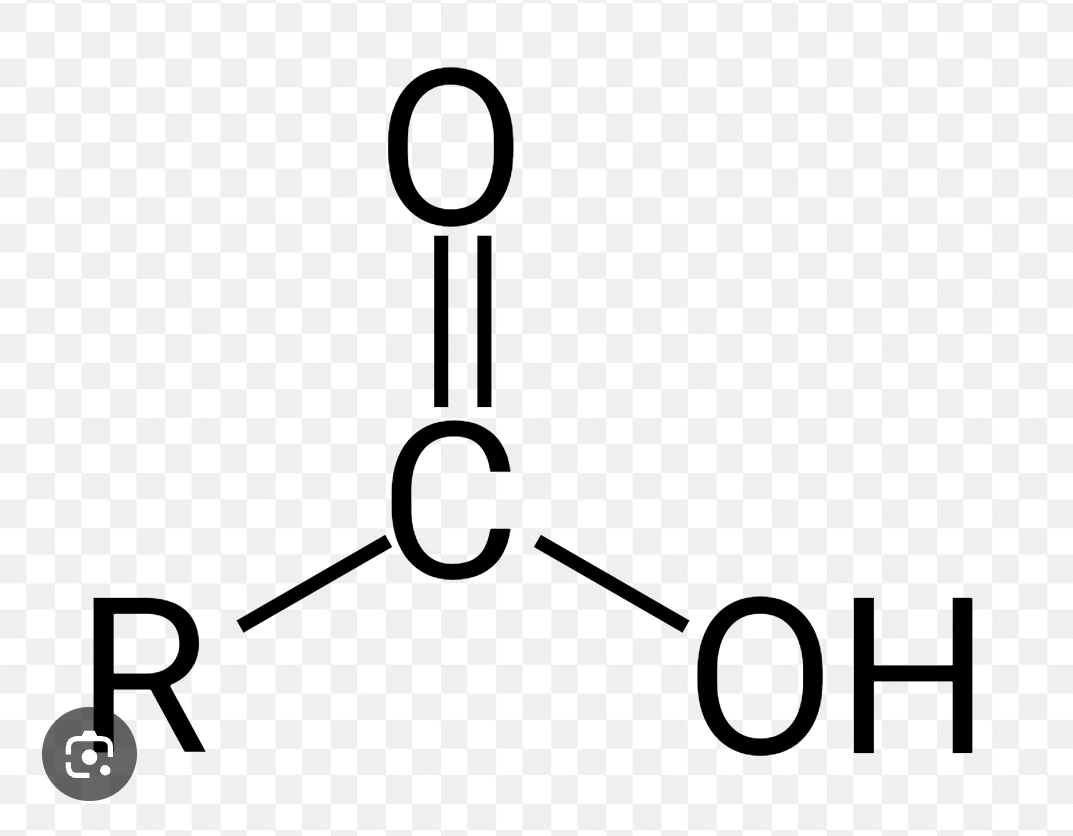
What is this structure depicting?
Carboxylic Acid
Thioesters are important to the _______ that takes place during the Krebs cycle
Acyl transfer
Carboxylic Acids
Posses at least one –COOH group
The name comes from carbonyl (–CHO) and hydroxyl (–OH)
Why are Carboxylic acids considered weak acids?
It only partially dissociates in water when it forms a conjugate base and Hydronium ion
The only acidic hydrogen on an organic acid is the hydrogen associated with the ______
Oxygen atom
In carboxylic acids the ______ is much more electronegative than the hydrogen
Oxygen atom
Naming carboxylic acids
Derived from Alkanes
–e ending replaced with –Oic acid
Known as fatty acids because they occur naturally in fats
Carboxylic acids
HCOOH
Formic acid (Methanonic acid)
CH³COOH
Acetic acid (Ethanoic acid)
CH3CH2COOH
Propionic acid (propanoic acid)
CH3CH2CH2COOH
Butyric acid (Butanoic acid)
CH3CH2CH2CH2COOH
Valeric acid (pentanoic acid)
Formic acid
Occurs naturally in some ants. Formica(ant)
Acetic acid
Diluted is in household vinegar
Propionic acid
Body odor, one of the first fatty acids identified
Butyric acid
Isolated from butter
Valeric acid
Extracted from the plant valerian
In the presence of strong bases (sodium hydroxide) carboxylic acids are completely _______ in a double replacement effect style reaction
Neutralized
Metal carboxylate
Identified by naming the metal
followed by changing the —ic acid of the carboxylic acids to –ate
HCOONa
Sodium formate
CH3COONa
Sodium acetate
CH3CH2COONa
Sodium propionate
CH3CH2CH2COONa
Sodium Butanonate (butyrate)
CH3CH2CH2CH2COONa
Sodium Valerate
Sodium formate
Common Food additive
Sodium Benzoate
Preservative in acidic food
Medicine
Cosmetics
Sodium Acetate
Seasoning
_______are used as anticoagulant and water conditioners
Sodium carboxylates
Polycarbonate acids
2 or more carboxylic groups are in one molecules
Corresponding metal carboxylates used in embalming water treatments
Dicarboxylic acids
Analogous to dialcohols and Dialdehydes
Simplest dicarcoxylic acid
Oxalic Acid
HOOC-COOH
Oxalic acid
HOOC-CH2-COOH
Malonic acid
HOOC-CH2CH2-COOH
Syccinic acid
HOOC-CH2CH2CH2CH2‐COOH
Adiptic acid
Oxalic acids can be completely neutralized in the presence of a strong_____
Base
Dimetaloxalate
Product of neutralization of sodium oxalate
Role of water softening agent and anticoagulant
Sodium oxalate has the ability to _______ calcium ions
Gather together
When soluble, sodium oxalate is a _______ in embalming fluid
Modifying agent
Sodium Oxalate is classified as what kind of anticoagulant?
Precipitant anticoagulant
Precipitant anticoagulant
Removes calcium ions via precipitation. Removes calcium as a potential blood clotting initiator
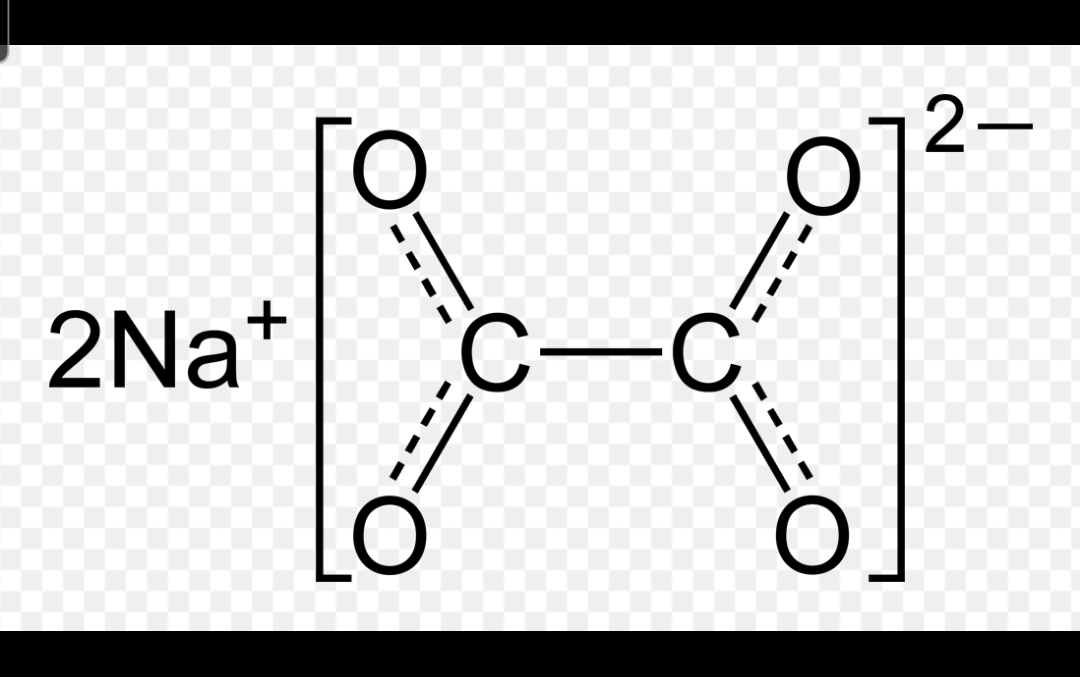
What structure is this depicting?
Sodium Oxalate
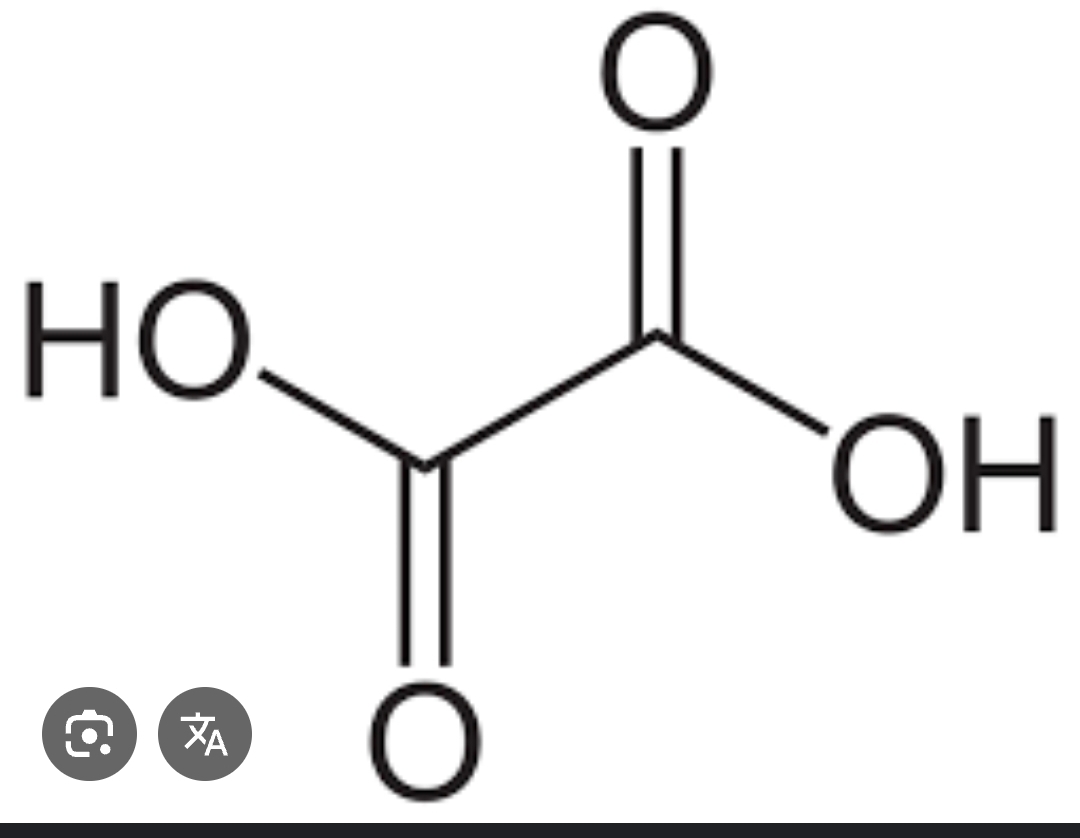
What structure is this showing?
Oxalic acid
Tricarboxylic acid
3 carboxylic acids groups and Hydroxyl group
Common way to remove solid water deposits is to add vinegar (a tricarboxylic acid)
Sequestrant anticoagulant
Cages in the calcium ions making it unavailable to coagulate blood
Types of tricarboxylic acids
Citric acid
Potassium citrate
Sodium citrate
What tricarboxylic acids are sequestrant?
Potassium cirate and sodium cirate.
Why have potassium citrate and sodium cirate gone out of favor for anticoagulation?
They can actually increase clotting by promoting bacteria
EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid)
"Colorless, water soluble, poly carboxylic acids
Ability to sequester metal ions
Hexadentate ligand
Great sequestrant anticoagulant
Important ingredient in embalming fluid
Cleating agent
Chelation
The formation of at least two coordinate bonds between a central metal and an organic ligand
After being bound by EDTA metal ions remain in solution but have little to no ______
Reactivity
What organic molecule is used as anticoagulant and water conditioners today?
EDTA. No harmful effects. Used in medicine for chelation therapy for treating for treatment of mercury and least poisoning
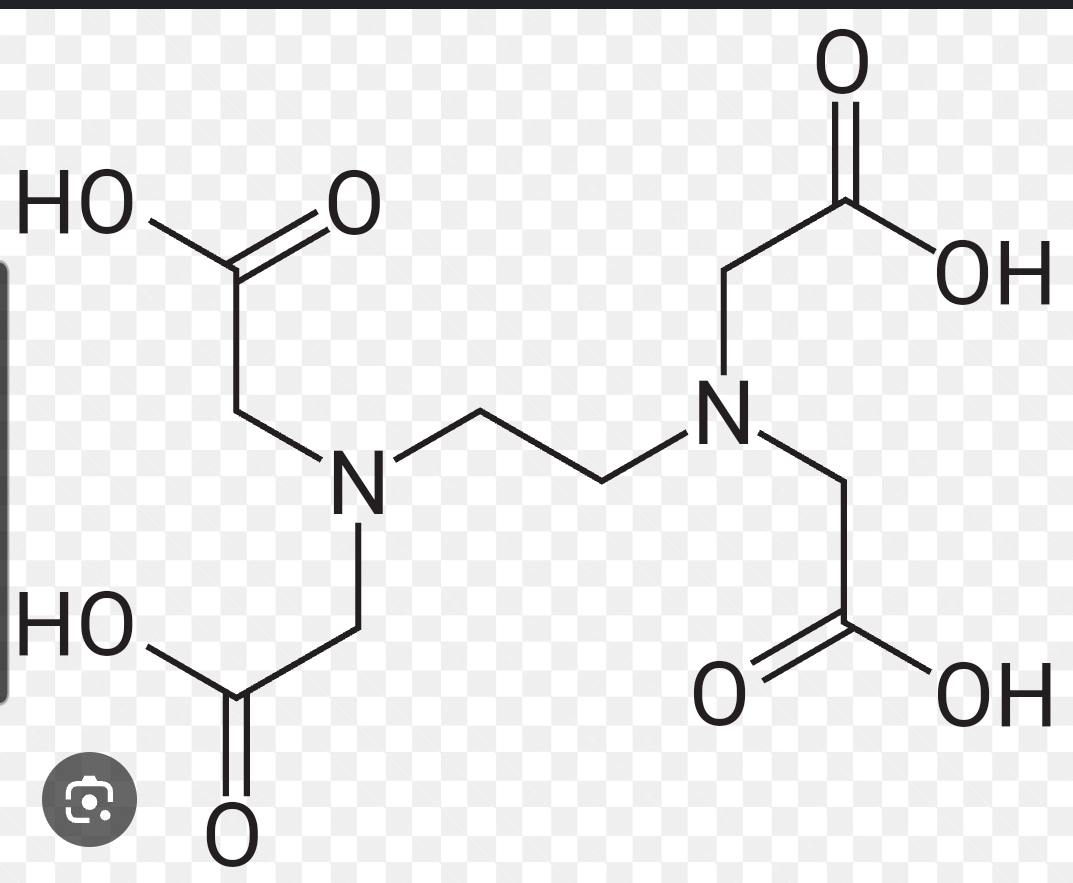
What structure is this showing?
EDTA
Esters
Formed by combining a carboxylic acid with an alcohol (esterfication reaction)
High molecular Mass esters (glycerides)
Make up main class
Animal fats, veg oils
Lower molecular weight esters
Pheromones
Naming esters
Name alkyl group attached to oxygen
Change -ic acid to ate
Methyl Salicylate (fragrance)
Possess both phenol and esters function
Wintergreen scent
Precipiant anticoagulant
Thioester
Linking oxygen replaced by sulfur (Sulfur has same number of valence electrons as oxygen)
Naming thioesters
Named as if the alkyl chain from the alcohol is a substitutent
No number assigned to alkyl chain
Followed by the name of the parent chain (acetate)
Named as alkane w/Thioate
Prepared by reaction of a carboxylic acid with a thioalcohol (mercaptan)
Thioesters
How are thioesters important?
They are important biologically. Krebs cycle. Acetyl-CoA and how we get ATP