Practical 4:Problem Solving Exercise (Peptic Ulcer)
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
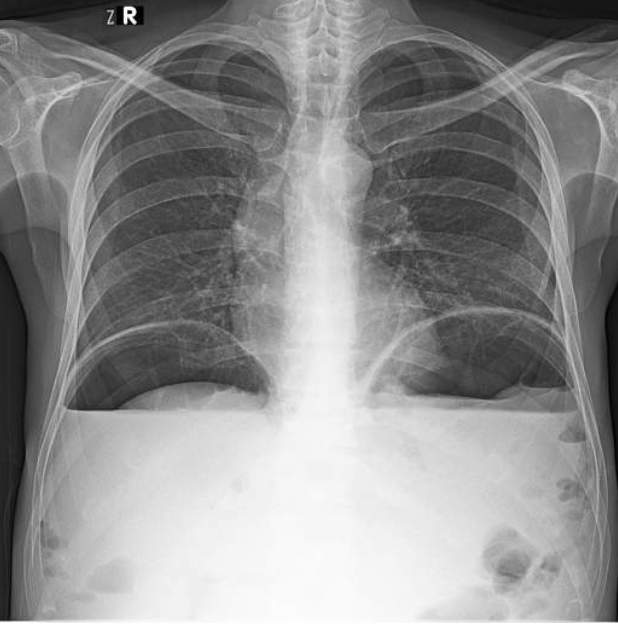
What do you think that free air under the diaphragm might indicate?
Free air under the diaphragm may suggest a possible perforation of the bowel (either stomach or gut as they hold air in these spaces) and this can lead to air leaking out and building up under the diaphragm.
There is also possible duodenal ulcers or peptic-duodenal ulcers which may also possibly be the cause of this.
Free air is example of pneuomoperitoneum.
The diagram of the X-ray shows how air build up under the diaphragm causes air to push up against arched diaphragm and flattens the muscle.
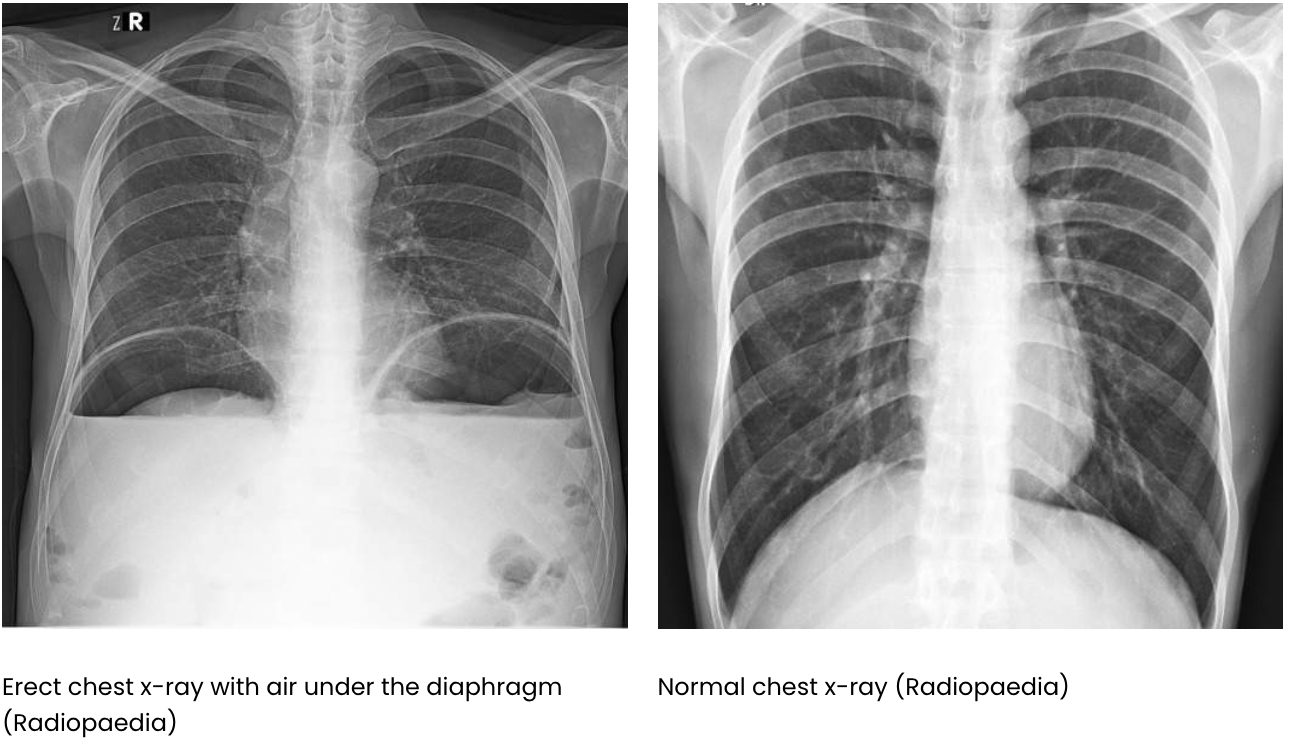
Why do we do an erect chest x-rays in humans?
This allows air to rise to top of the abdomen and the air is seen delineating the diaphragm (i.e. you can see both sides of the diaphragm where usually only one would be visible.
If the individual is too unwell to stand for a chest x-ray, a lateral decubitus film will do the same as the lateral abdominal radiograph in dogs.
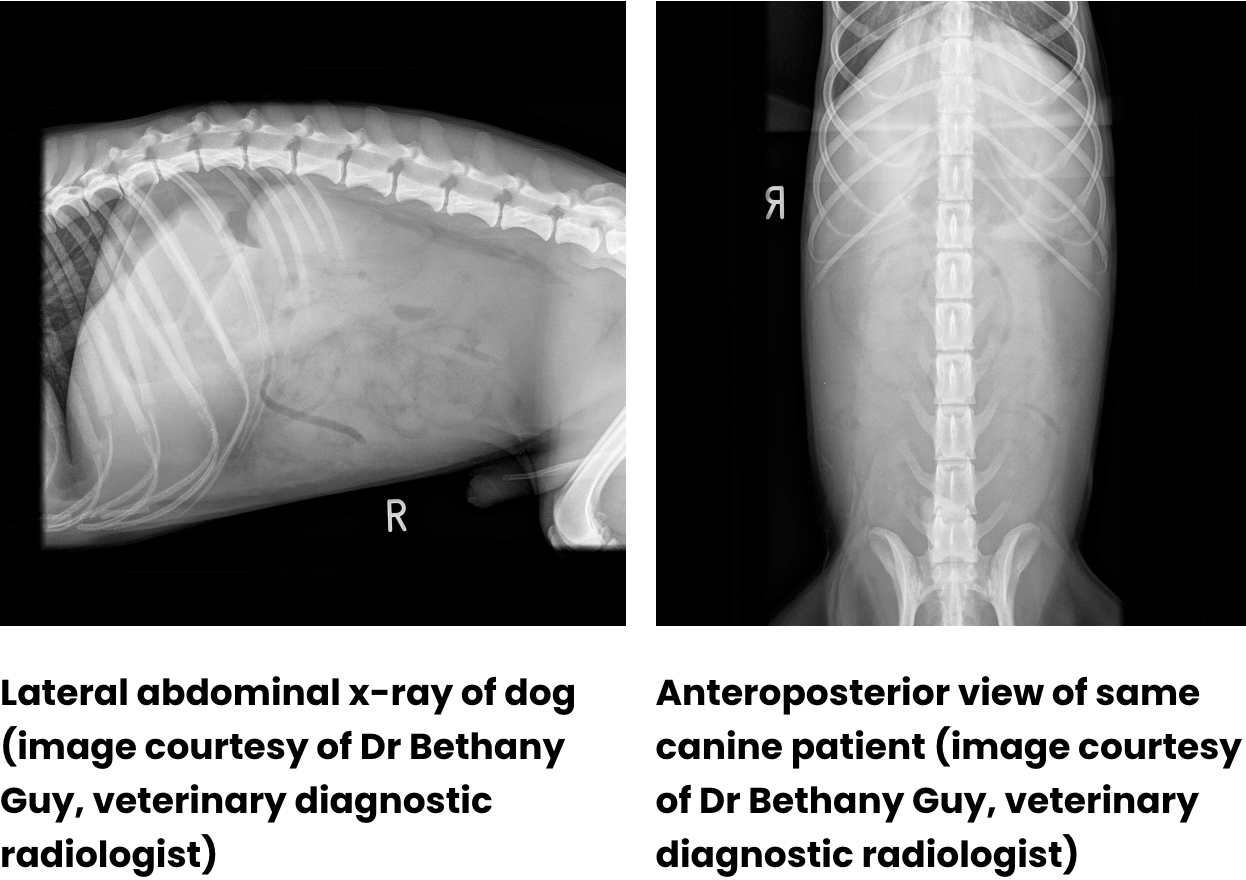
Why do we do a lateral abdominal radiograph in dogs?
This allows the air to be present at the top of the film, outlining the abdominal organs.
If a patient coughs up blood why might surgery be suggested?
Coughing up blood (haematemesis) which indicates that there is a ruptured artery somewhere that requires fixing otherwise risk of haemorrhage can contribute to blood in vomit and risk of sepsis.
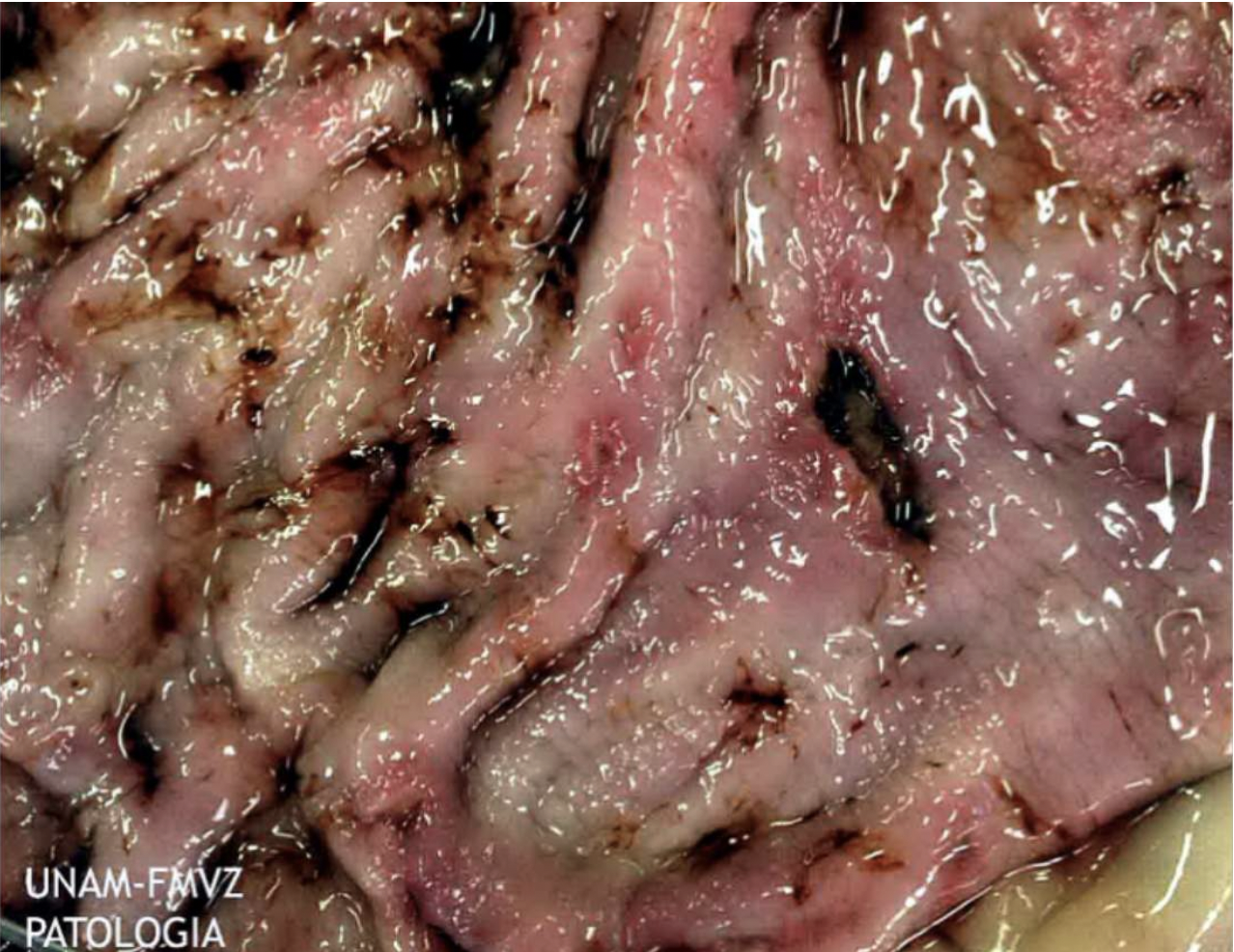
Describe what you can see in the macroscopic image of this stomach.
LHS more bumpier than RHS (around lesion:smoother and fewer folds)
Crater like + red: inflammation and rolled edge
Digested blood appears black- in humans appears as coffee ground blood
Causes of peptic ulcers
-over production of HCl- parietal cells high concentration
-Affected mucus lining the stomach which is produced by goblet cells- low levels of prostaglandins
-H.pylori
-Tumour can be ulcerated
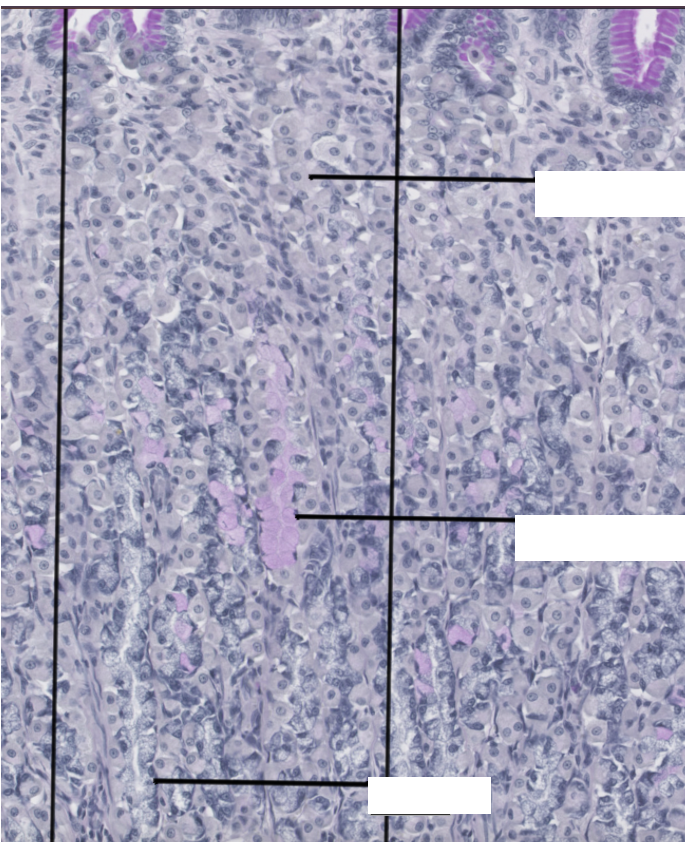
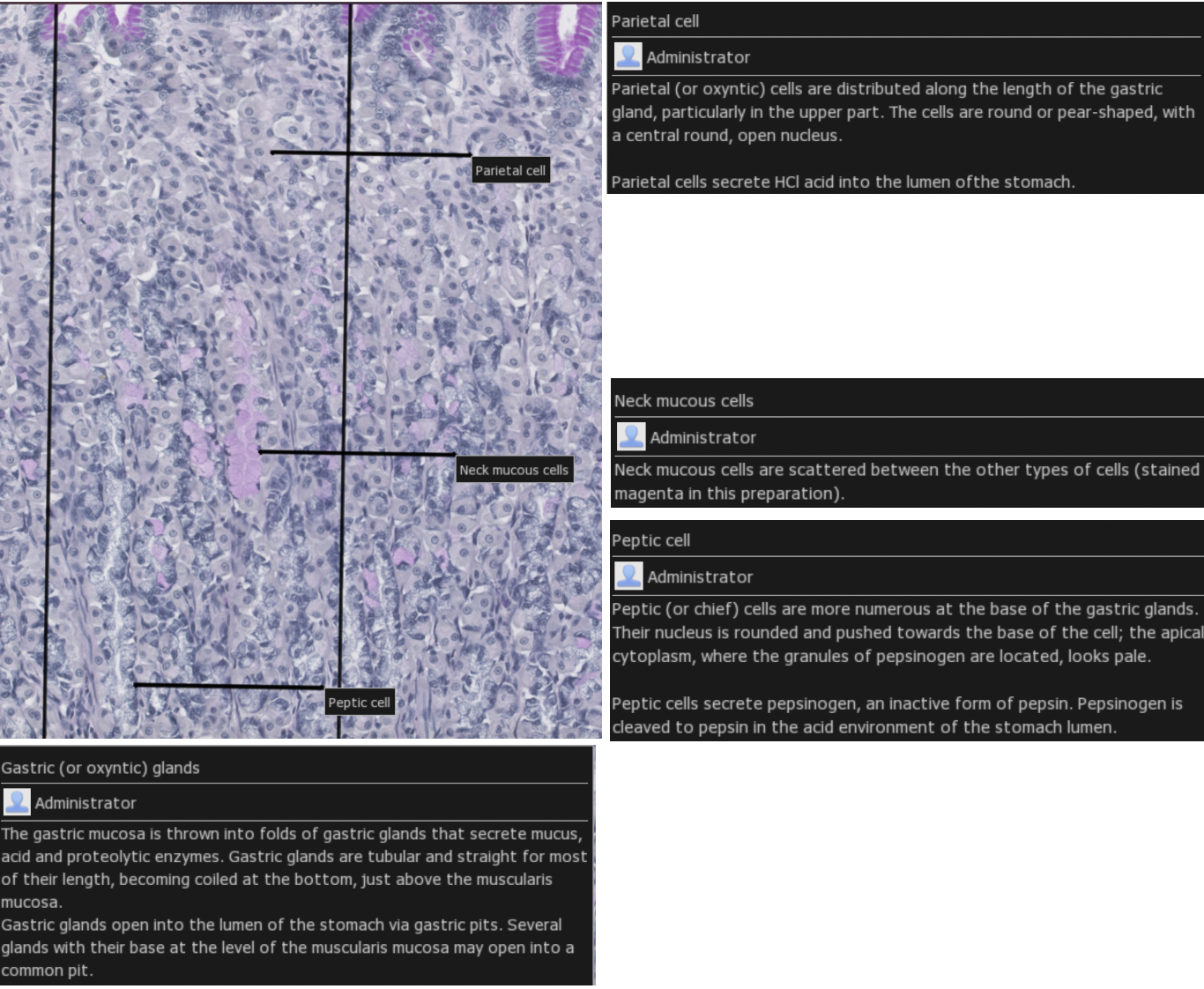
Normal stomach histology
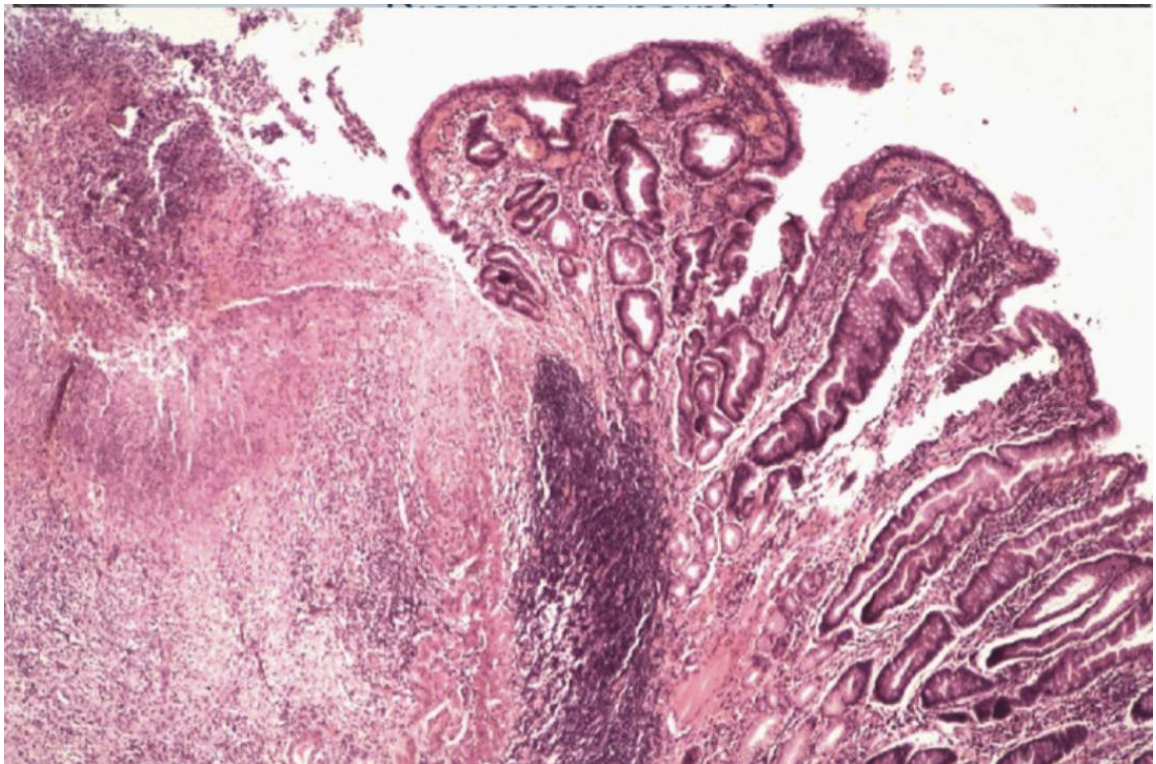
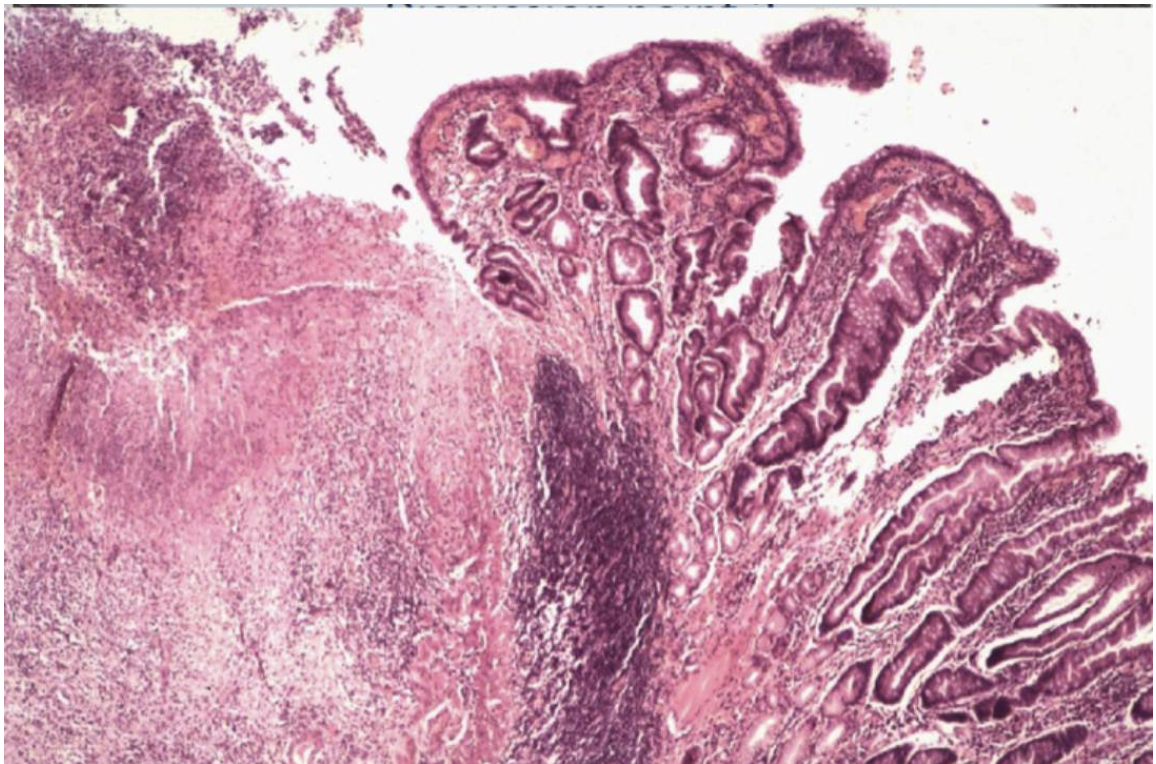
Describe what you can see in the histological images- where in the lesion does this tissue section come from?
Loss of glandular tissue on LHS
Inflammation causes hyperplastic inflammation to local tissues
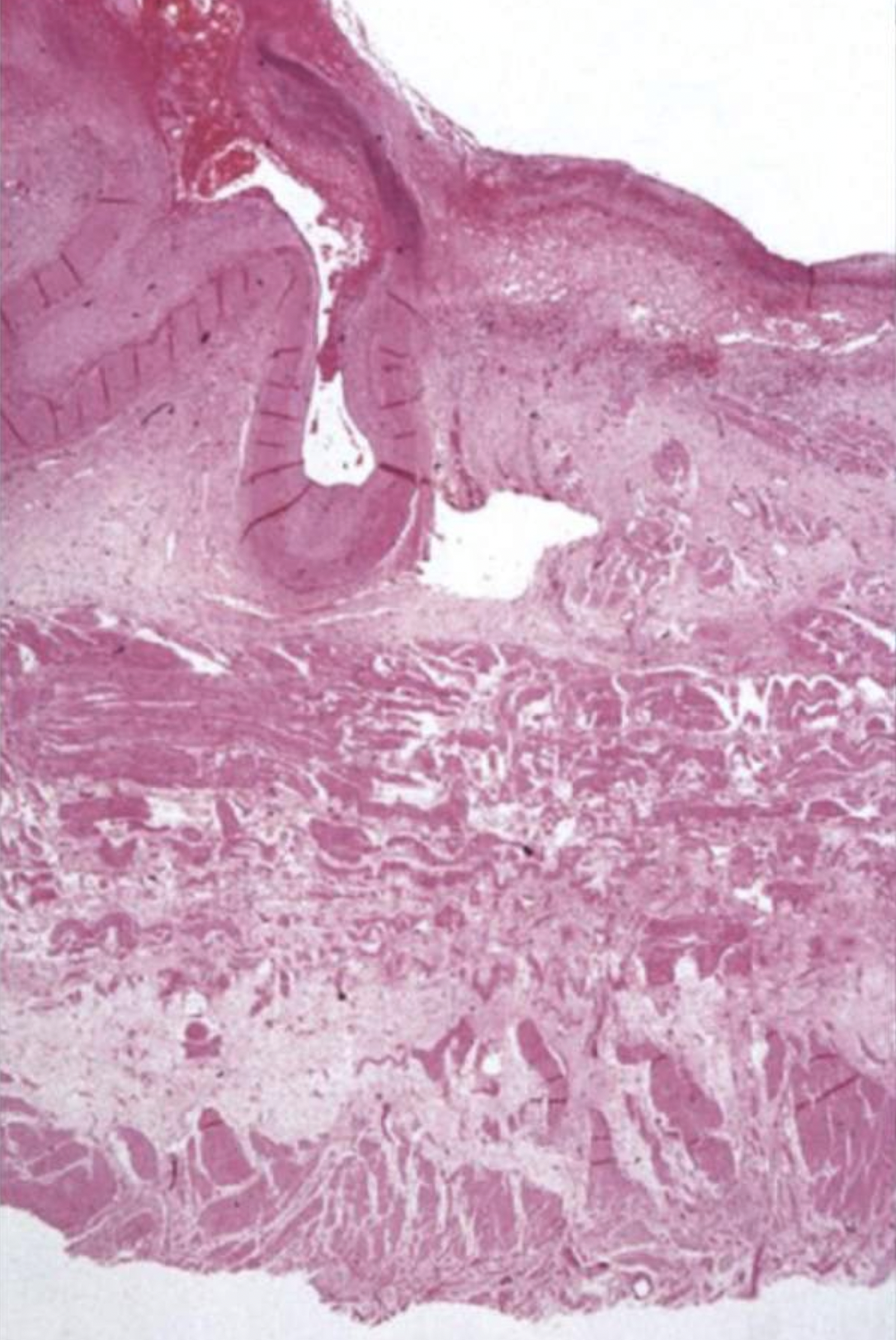
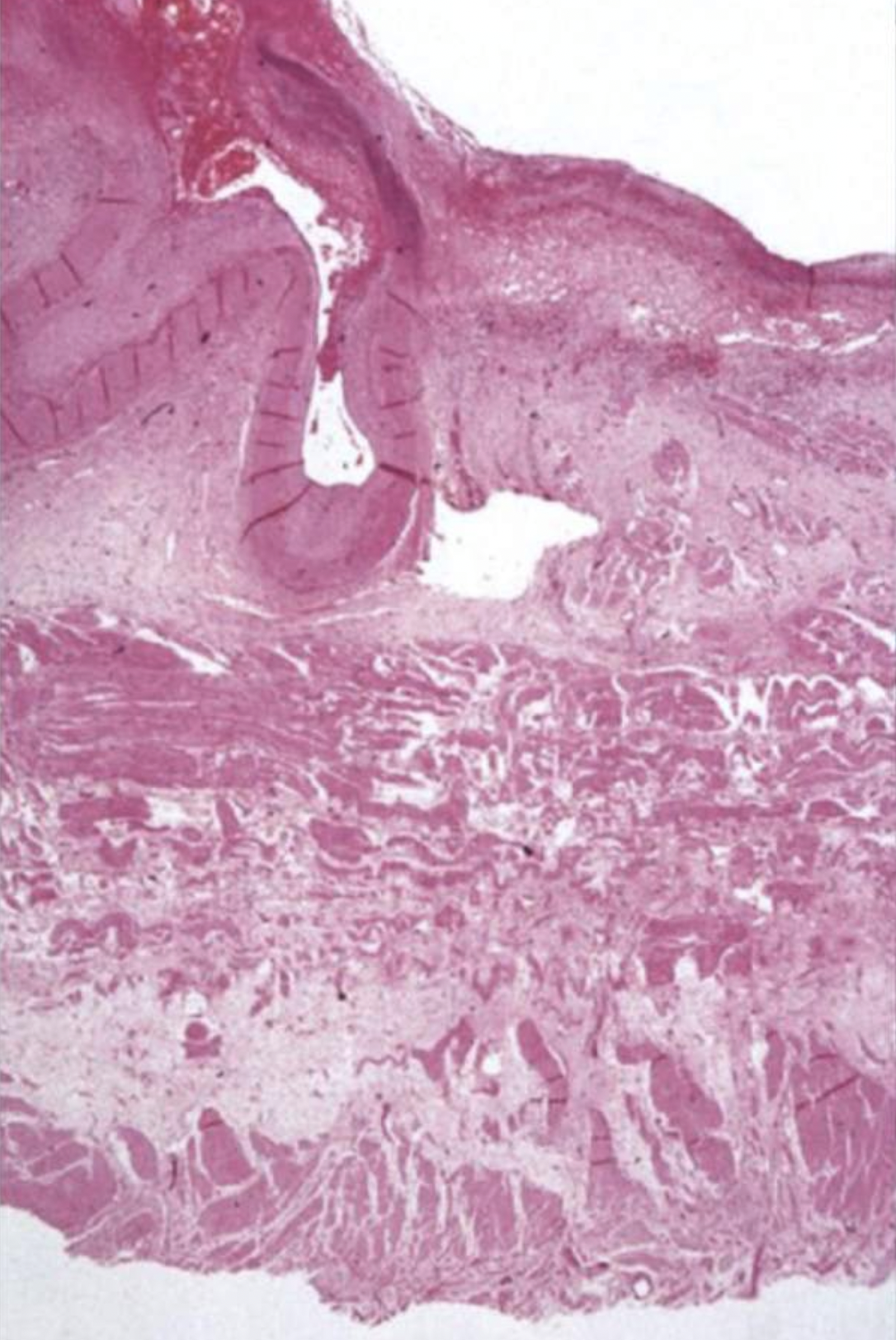
What can you see in this image?
Looks like a ruptured artery-which may explain vomit
Completely ulcerated mucosa
Loss of muscularis layer
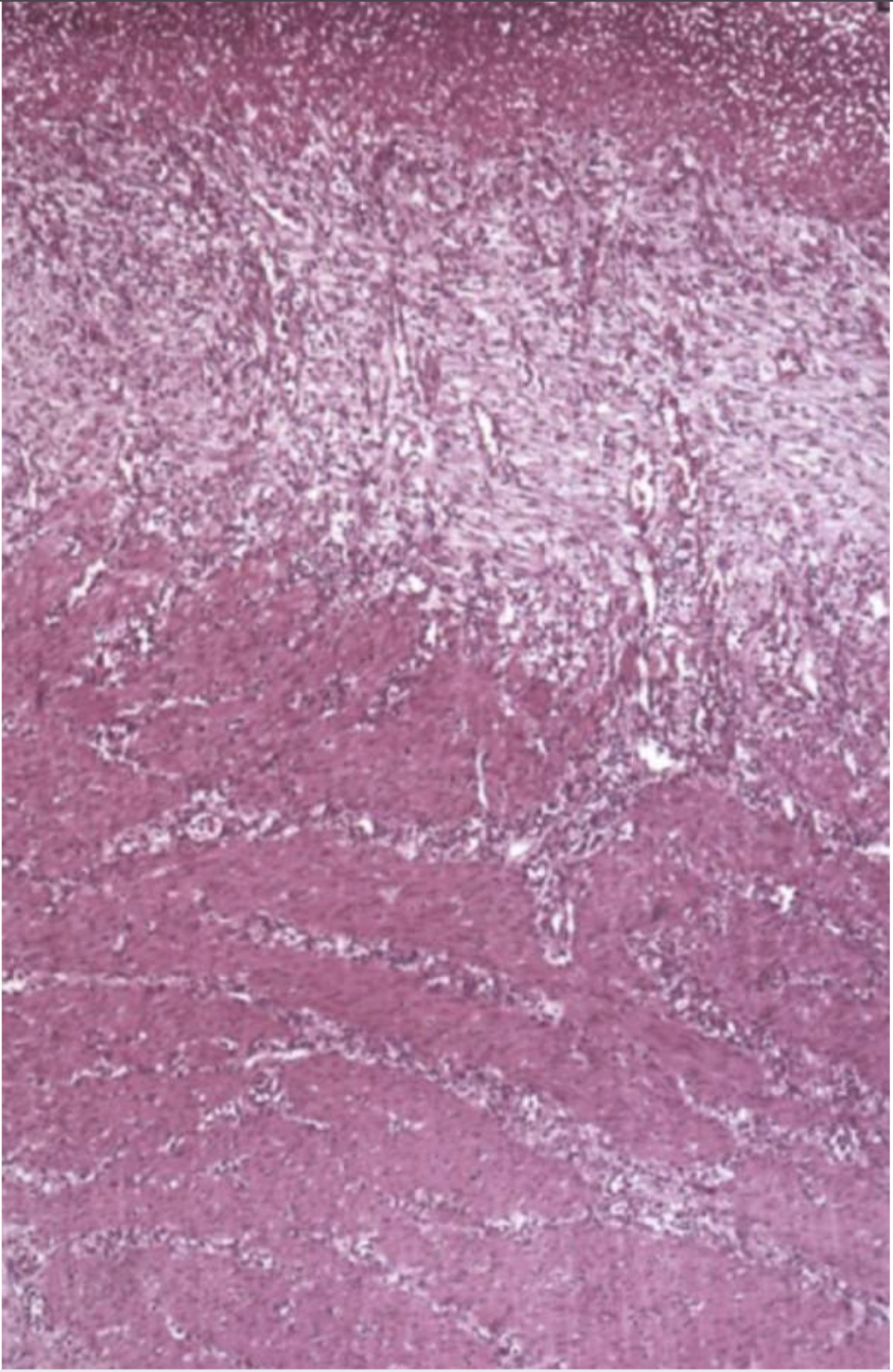
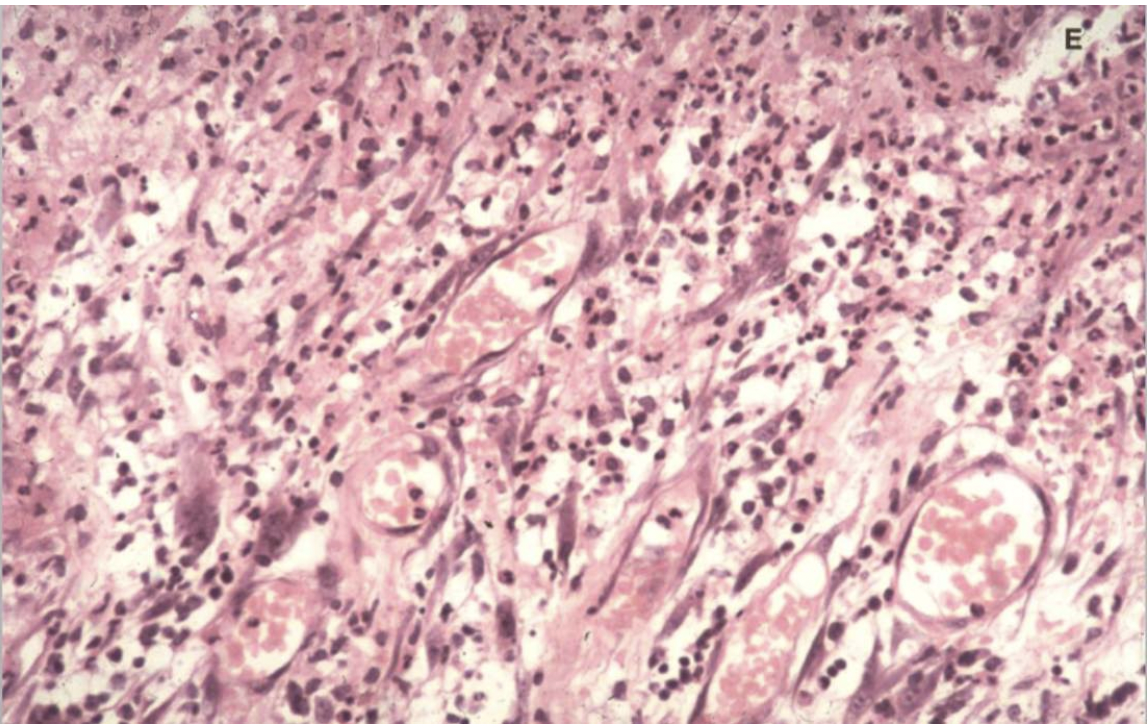
What can you see in this image?
Scar tissue- pale and pinkish
Bottom part: muscle with canals of lymphocytes and slits in the faded part are blood vessels
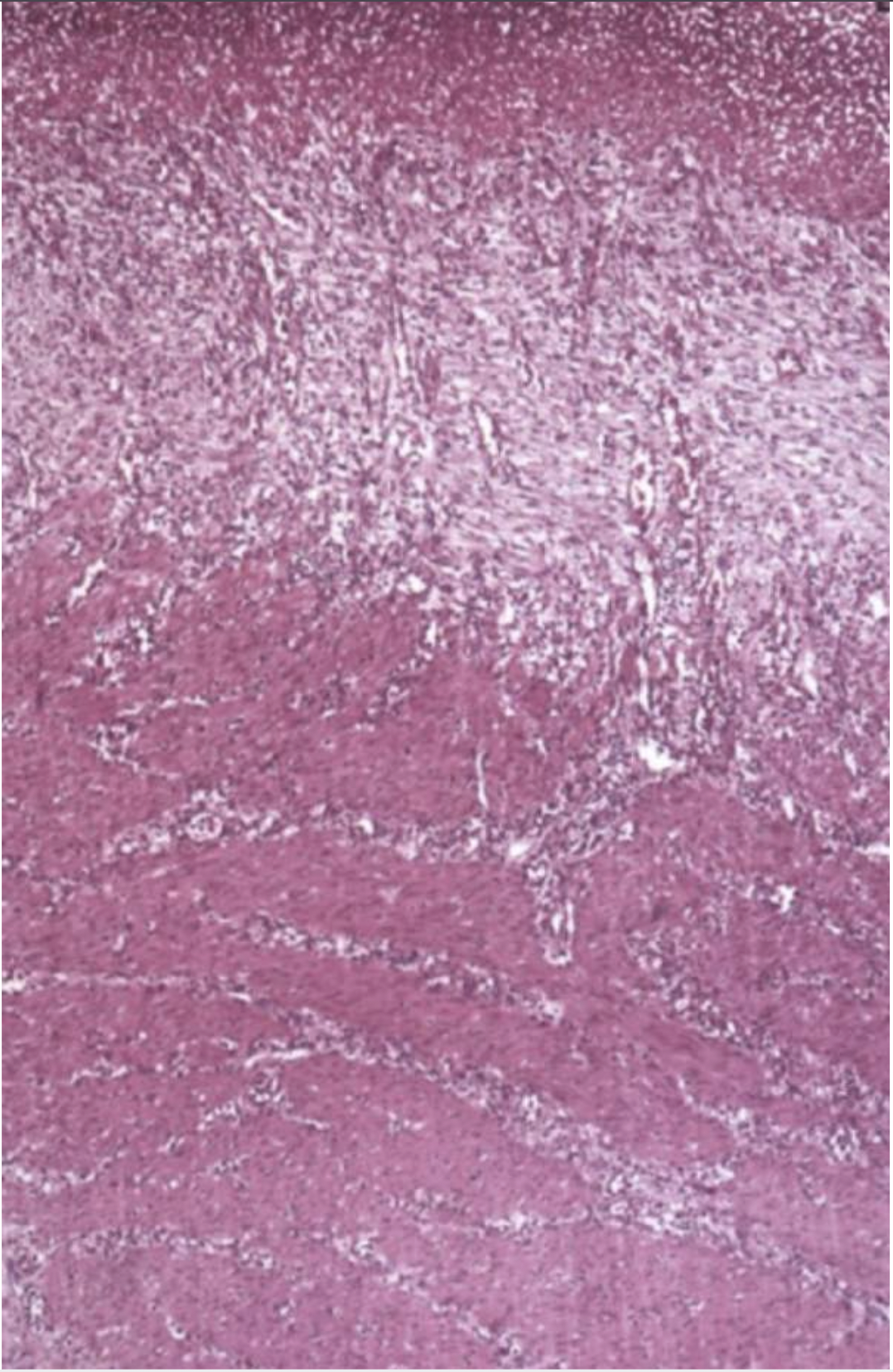
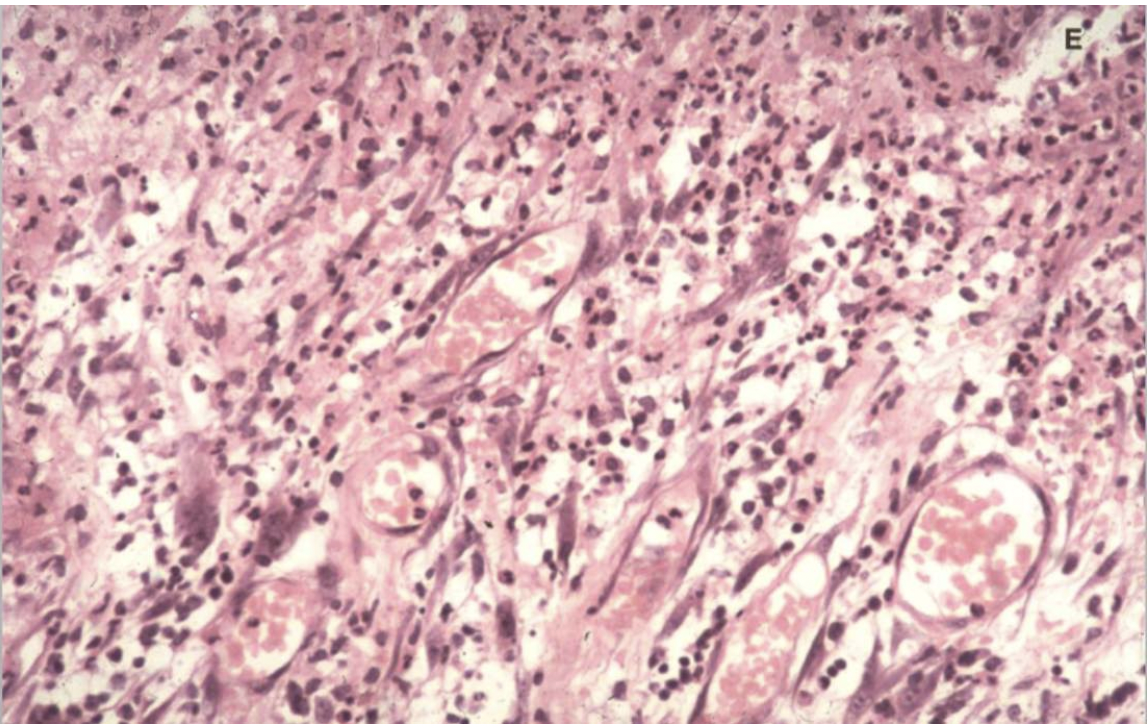
What can you see in this image?
Blood vessels and lymphocytes
What are the main physiological defence mechanisms of the gastric mucosa?
Mucus
Decreased acid production by prostaglandin activity
Increase acid pH using bicarbonates
Why might a patient develop a peptic ulcer?
NSAID’s
Alcohol
What does low HB and ferritin levels suggest?
Anaemia
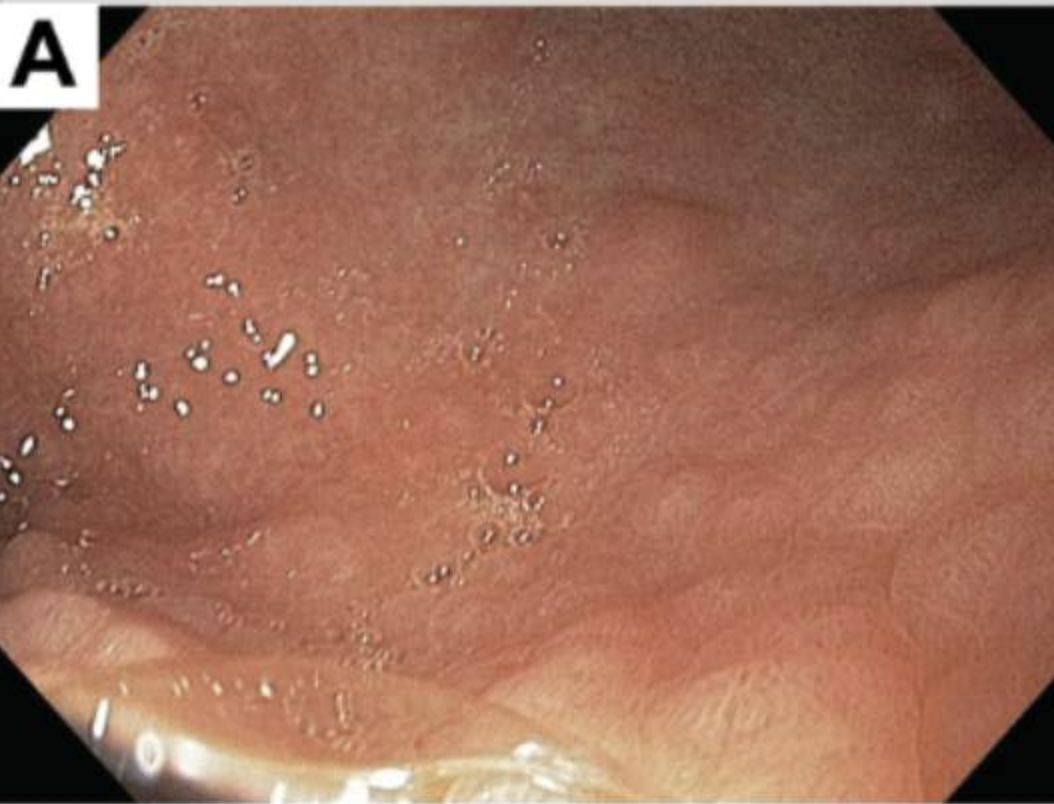
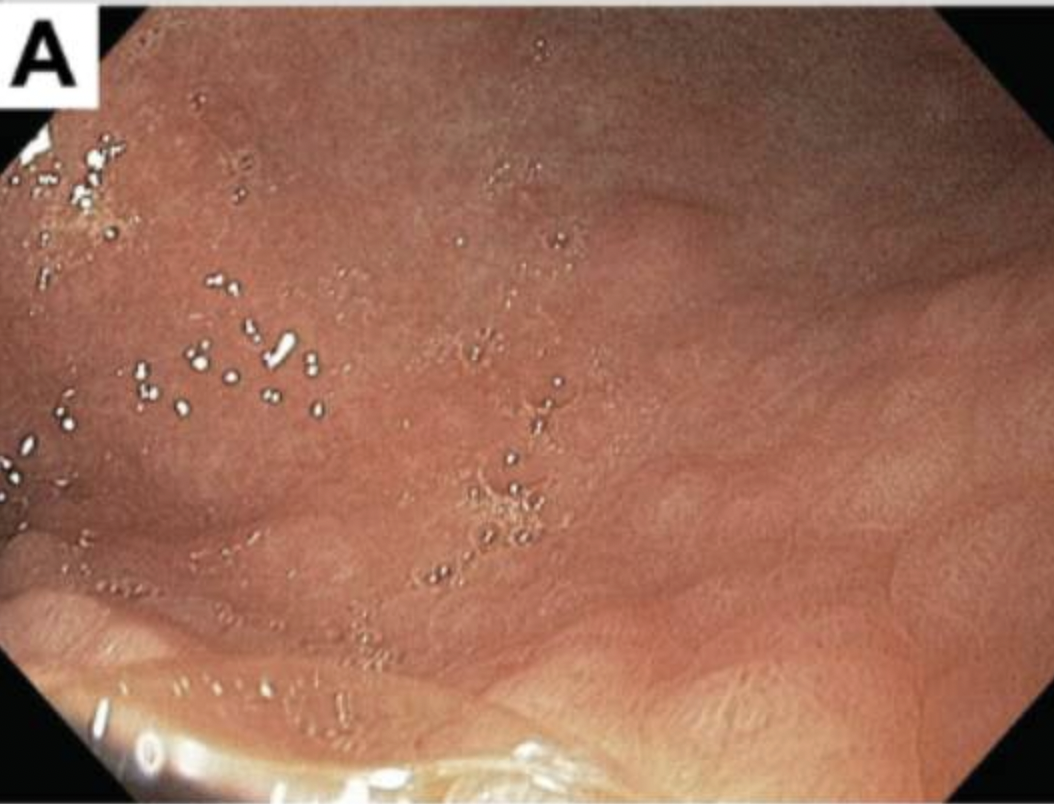
Describe the appearances of Lilly's stomach. How does this look different to Timmy's?
Little hills: diffuse nodularity
Background smooth and less of a prominent rugal folds
What is a Point of Care Test (POCT)?
A medical diagnostic test performed at or near the patient's bedside, rather than in a traditional laboratory. These tests are designed to provide rapid results, enabling healthcare professionals to make quicker clinical decisions about diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring.
Examples of POCT
Blood glucose meters for diabetes management
Urine analysis dipsticks
Blood gas analyzers
Tests for conditions like deep vein thrombosis (DVT) using a D-dimer test
What is a Urease Test? What does it indicate and how does it work?
Detects the presence of the urease enzyme that converts urea to ammonia and …, which indicates the presence of bacteria that produce it, such as H. pylori or Proteea.
The test works by placing a sample (like a stomach biopsy or a pure bacterial culture) in a medium containing urea and a pH indicator, such as phenol red. If urease is present, it converts urea to ammonia and carbon dioxide, which raises the pH and causes the color indicator to change, typically from yellow to pink or red
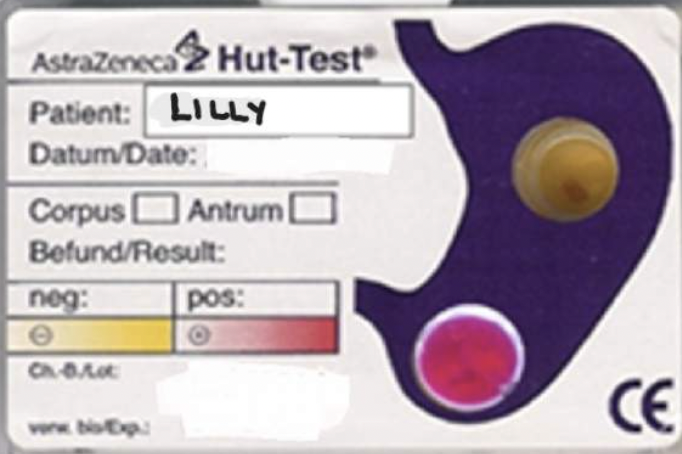
Have a look at Lilly's Urease Test result - what does this show?
Lilly is negative for a ulcer at the body of the stomach just under the antrum however is positive for ulcer at the base of the stomach just before the pylorus.
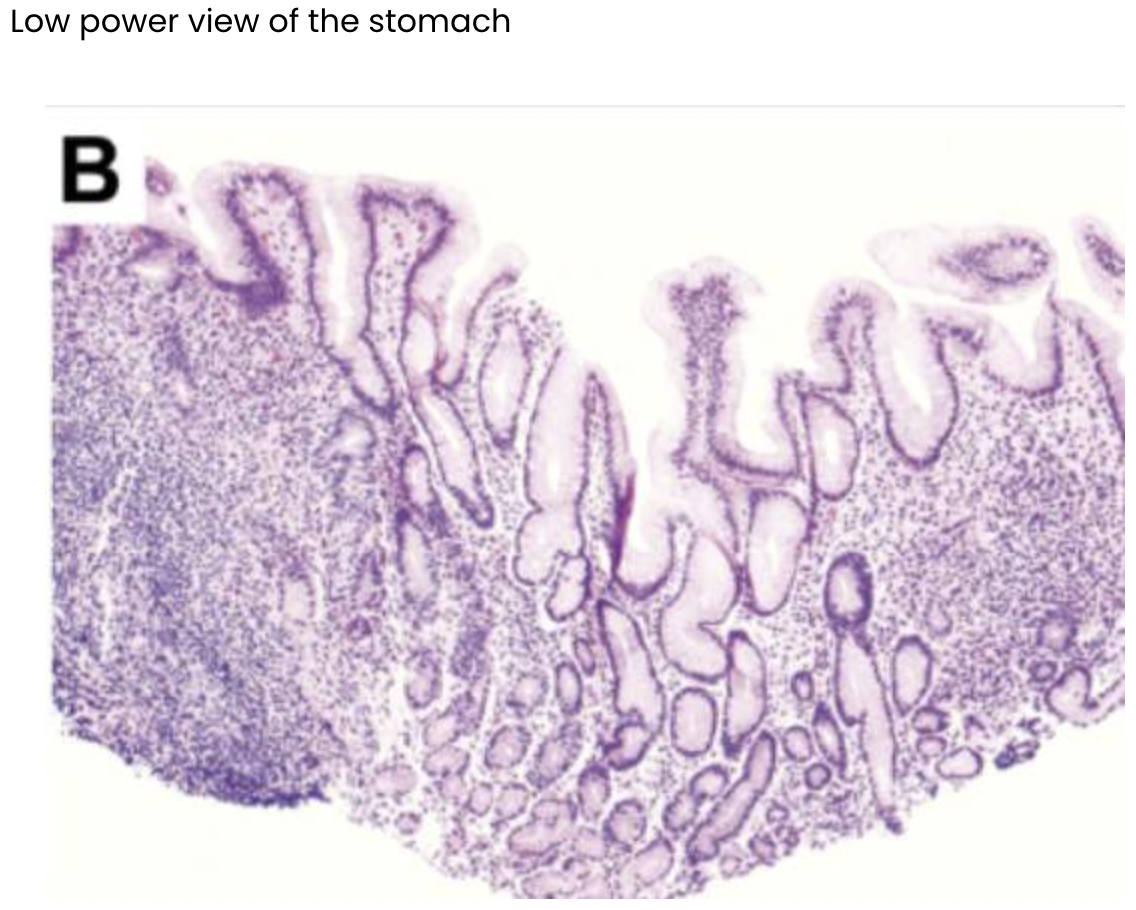
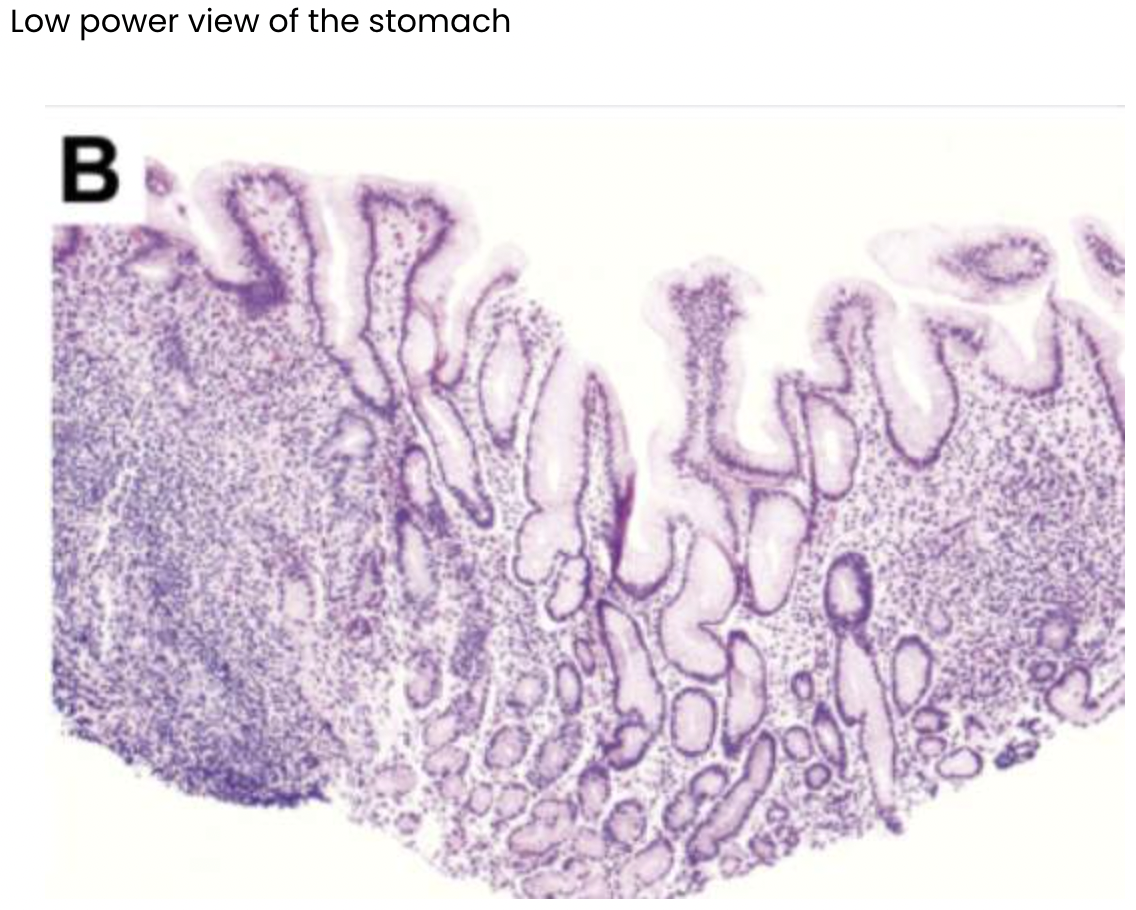
Describe what you can see in the images below.
Loss of folds
Inflammation
Lymphocytes
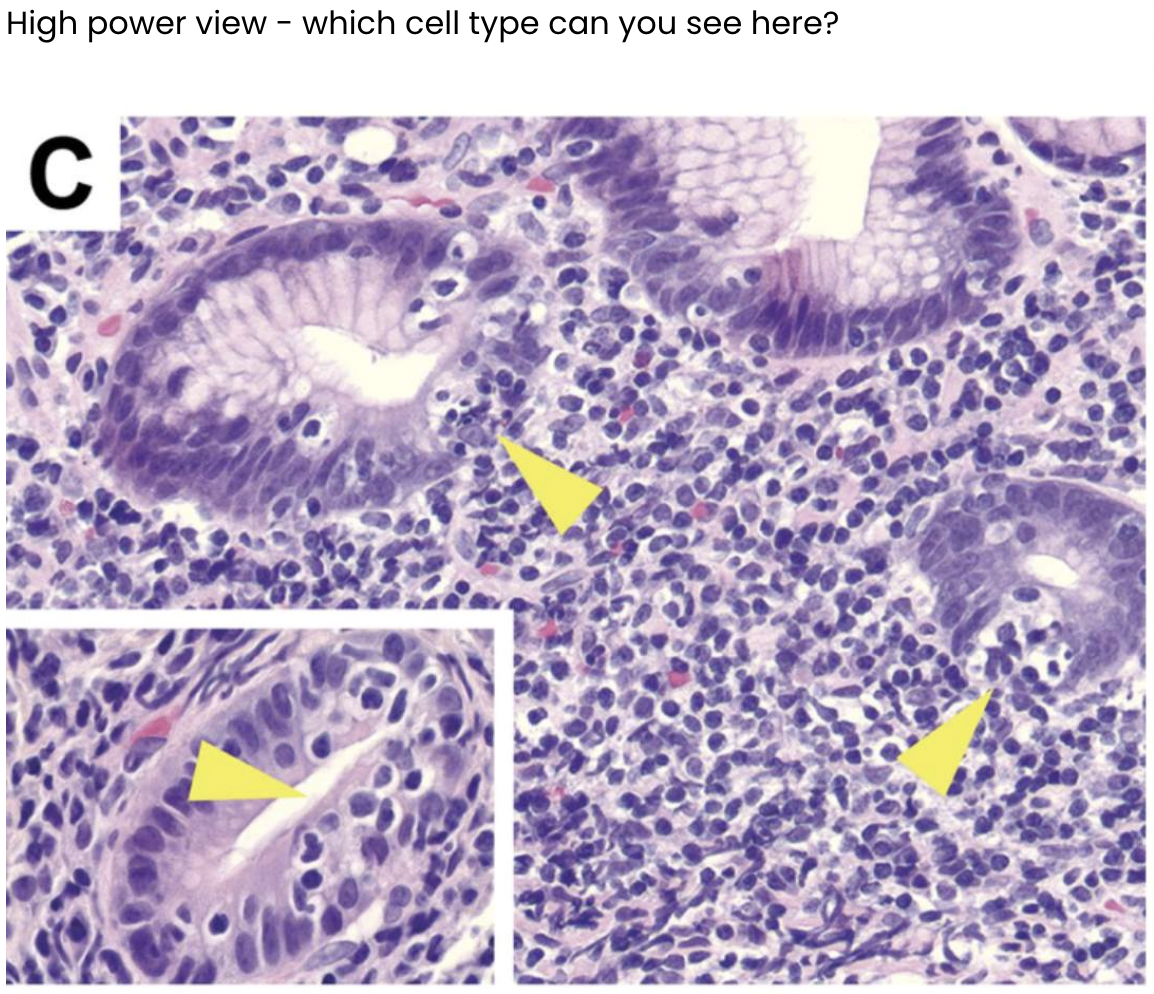
Describe what you can see in the images below.
Gland: columnar epithelium + infiltration of lymphocytes
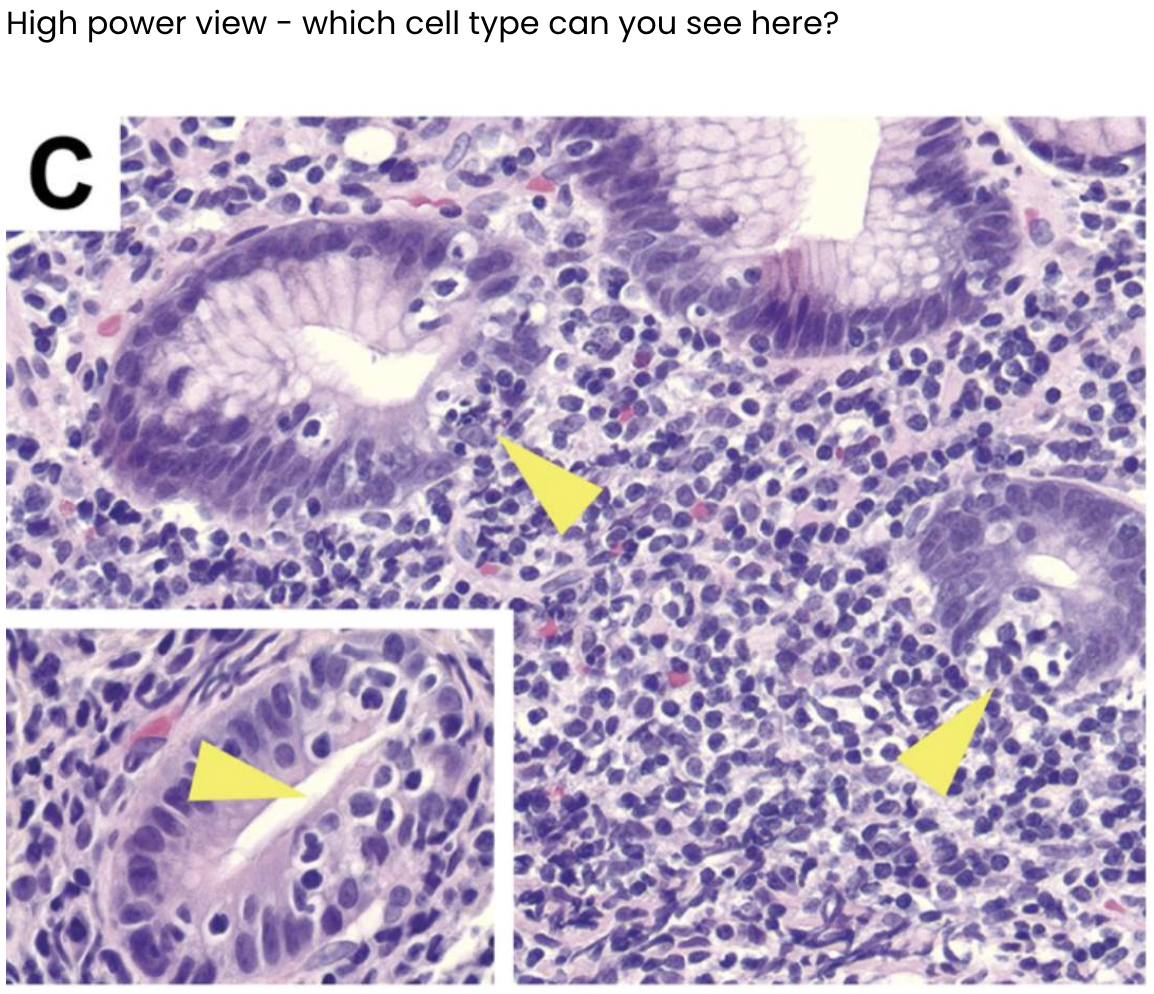
Describe what you can see in the images below.
Appears to be some microorganism- bacteria in lumen
Possible infiltration of lymphocytes into gastric cells
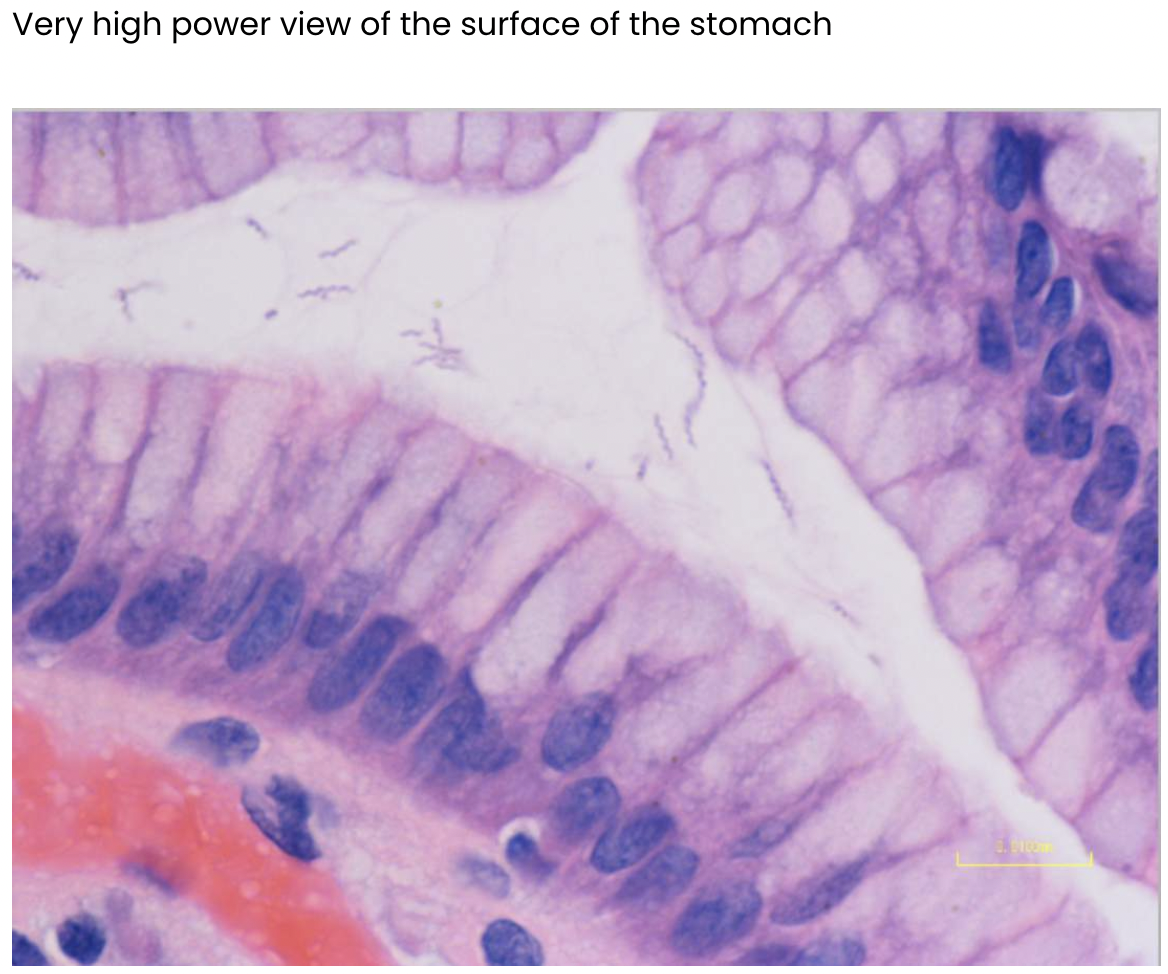
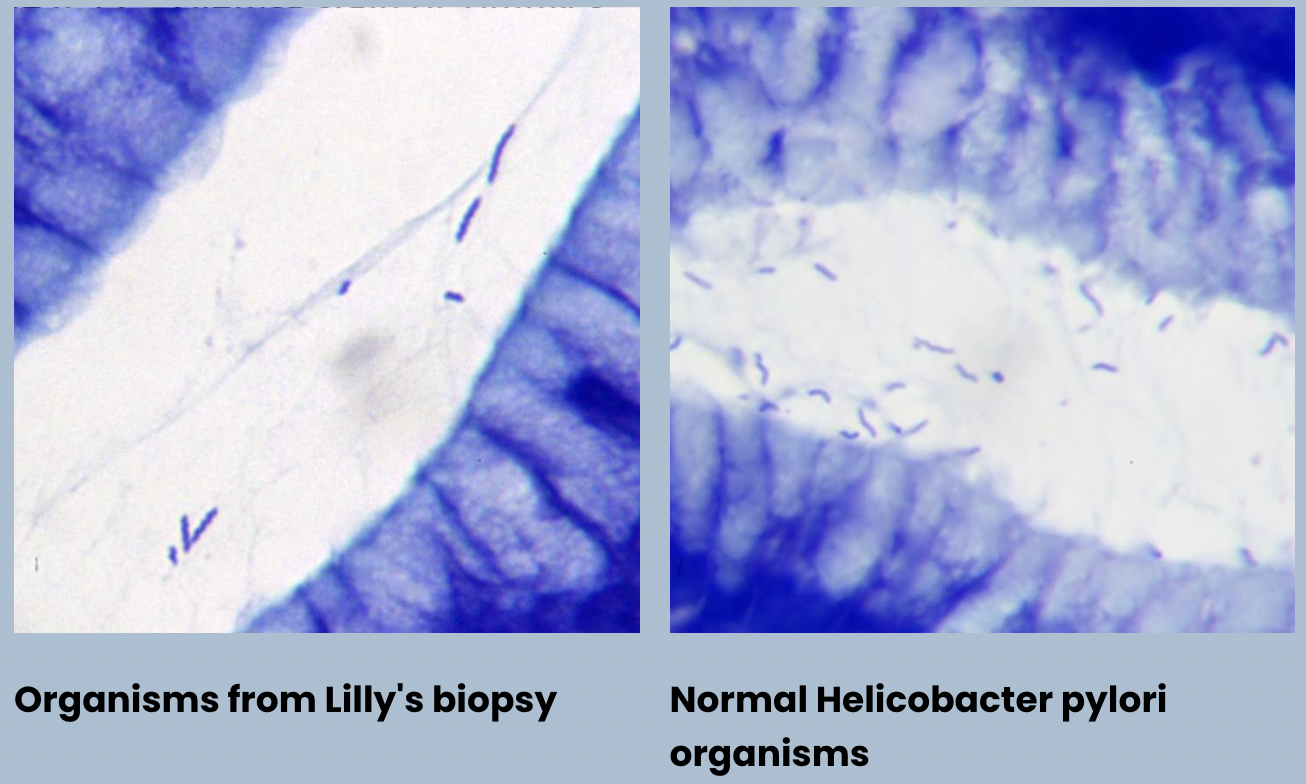
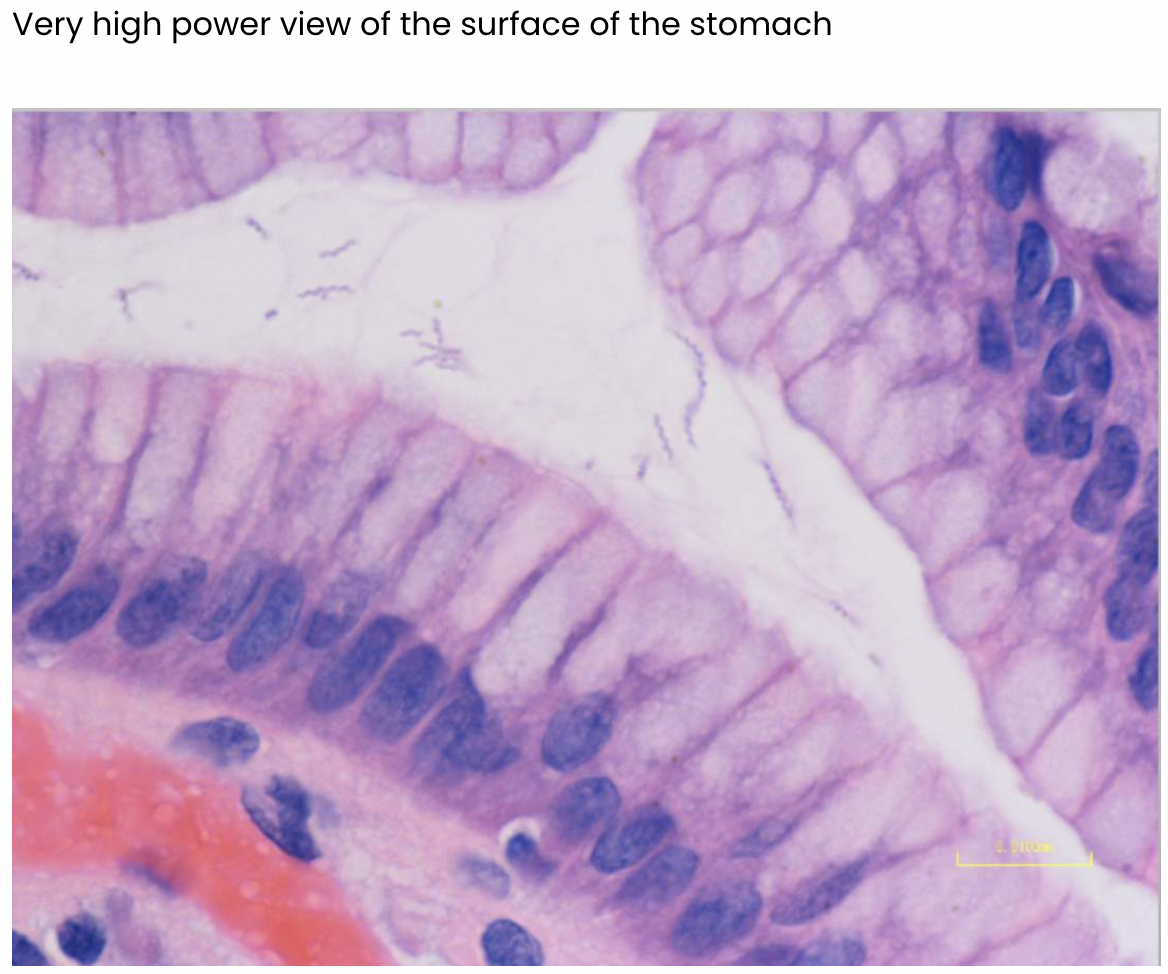
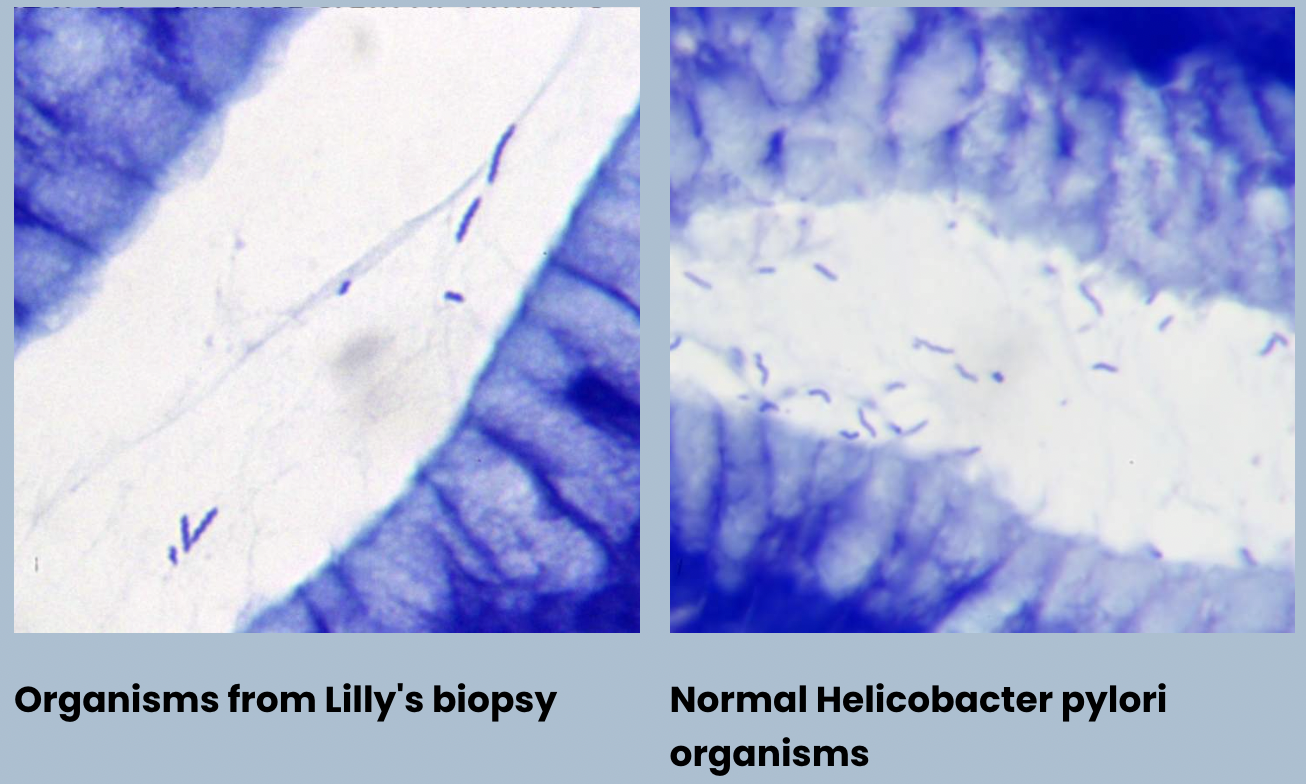
H.pylori infection
H.pylori infection - H.pylori normally V-shaped: seagull shape and more bendy and curvy
Infection: lot straighter and coiled tighter and thicker
Can you think of 5 complications of a peptic ulcer?
Perforation —> sepsis —> death
Scar tissue
Anaemia
Haemoptysis
What is a PPI?
Affects proton movement so it stays in stomach so reduces acidity and increases pH and this affects parietal cells in the fundus of the stomach?
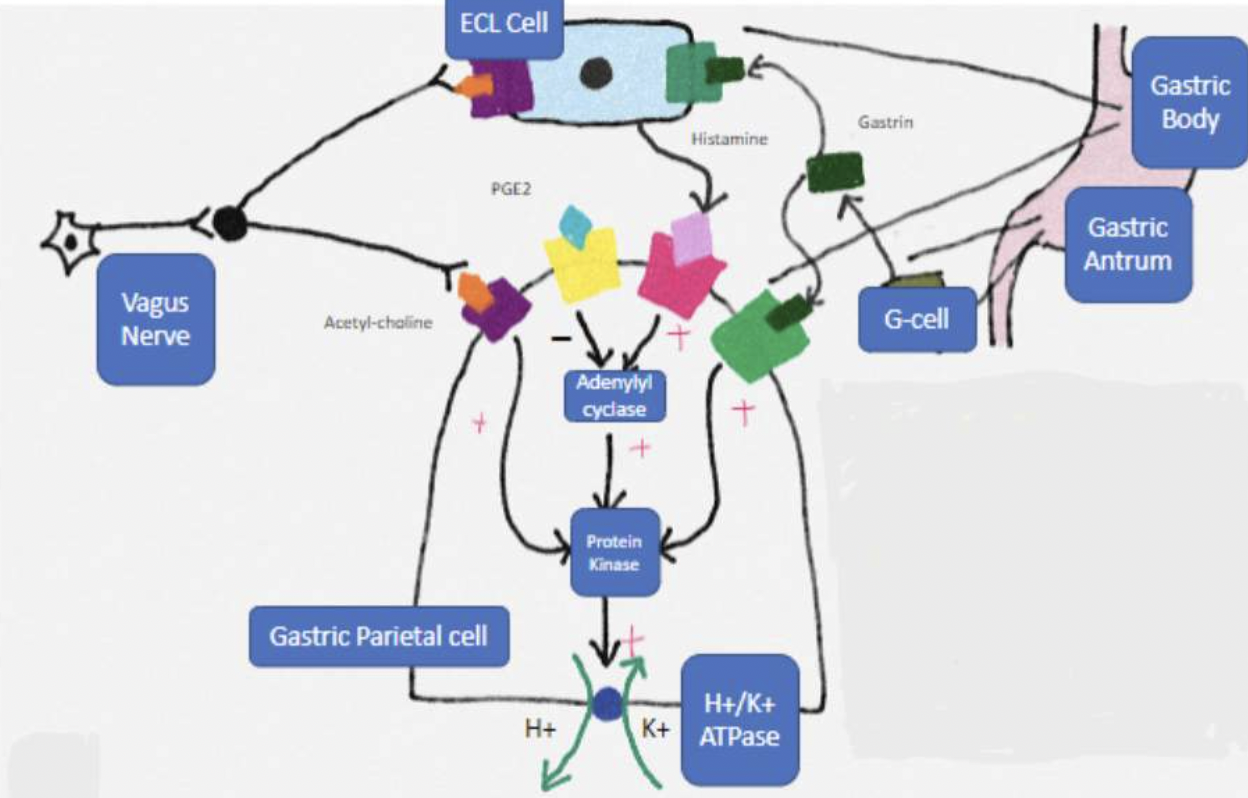
Zollinger Ellison syndrome
Gastrinoma (tumour)
Increased gastrin production
Increased acid production