Chemistry Semester 1 Final
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
Accuracy
how close a measurement is to the true value of the quantity that was measured

Precision
a measure of how close a series of measurements are to one another
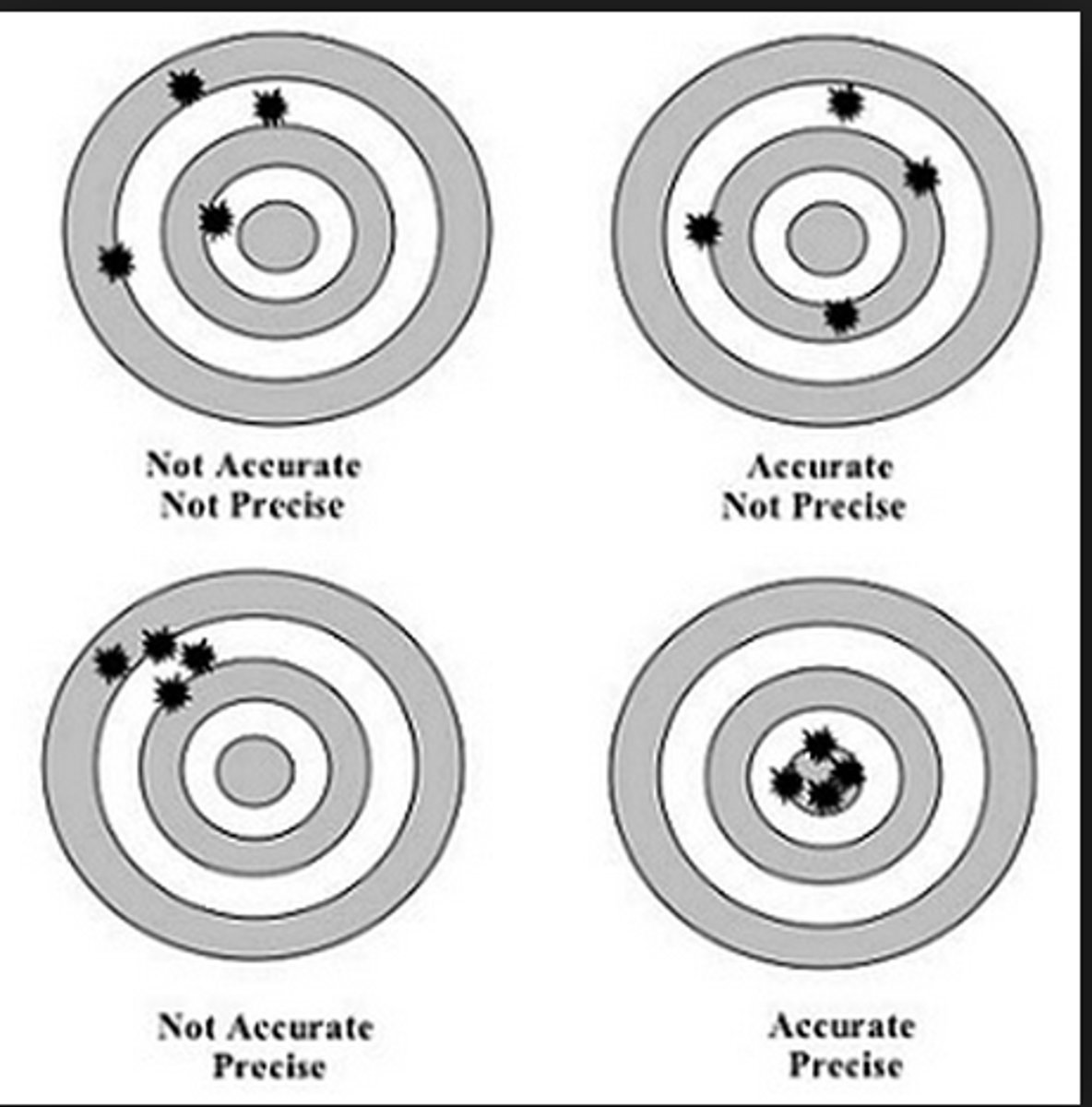
Percent Error
Accuracy ~ Tells us how close lab data is to an actual/known value
Range
the difference between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution
Significant Figures
All the digits that can be known precisely in a measurement, plus a last estimated digit
Limit of Precision
Range of possible values where the true value of the measurement lies
-where to round to
-smallest increment/10
Leading 0's
never significant
Sandiwched 0's
Always Significant
Trailing 0's
only significant if there is a decimal
SigFigs with a decimal
All zeros to the right of a non-zero digit are significant
SigFigs without a decimal
All zeros to the right of the non-zero digit are never significant
Sigfigs Addition/Subtraction
round to the least significant decimal place
SigFigs Multiplication/Divison
round to the value with the least # of sigfigs
Sigfigs with scientific notation
1. Move decimal so there is only one digit to the left of it
2. Digit term should include the correct # of SFs
3. Exponent is the # of places that the decimal jumps
Pure substances can be ________ separated.
Chemically
Mixtures can be ________ separated.
Physically
Pure substances are classified into
elements and compounds
Compounds
2 or more elements chemically combined
Elements
A molecule composed of one kind of atom; cannot be broken into simpler units by chemical reactions.
Mixtures are eiether
Heterogenous or homogenous
Heterogenous
non-uniform mixture
Homogenous
uniform composition
Definition of density
How much mass (matter) is packed into a certain amount of space (volume)
Density =
mass/volume
atomic number
number of protons
number of protons in an atom equals the:
number of electrons
Mass number =
protons + neutrons
Isotope
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
Average atomic mass
the weighted average of the atomic masses of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element
Atom with an added/subtracted proton
New element
Atom with an added or subtracted neutron
Isotope
Ion
A charged atom
Definition of an ion
An atom or group of atoms that has a positive or negative charge.
Anion
A negatively charged ion
Cation
A positively charged ion
Valenece electrons
number of electrons in outermost energy shell
Octet rule
States that atoms lose, gain or share electrons in order to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons
Energy levels
the possible energies that electrons in an atom can have
S orbital
2 electrons
P orbital
6 electrons
D orbital
10 electrons
F orbital
14 electrons
Abbreviation of electron configuration
[noble gas] + remaining
why do orbitals occur
electrons move in waves and have spin, orientations need to combine the spin pairs
Aufbau Principle
An electron occupies the lowest-energy orbital that can receive it
Hund's Rule
electrons occupy orbitals of the same energy in a way that makes the number of electrons with the same spin direction as large as possible
Pauli Exclusion Principle
An atomic orbital may describe at most two electrons, each with opposite spin direction
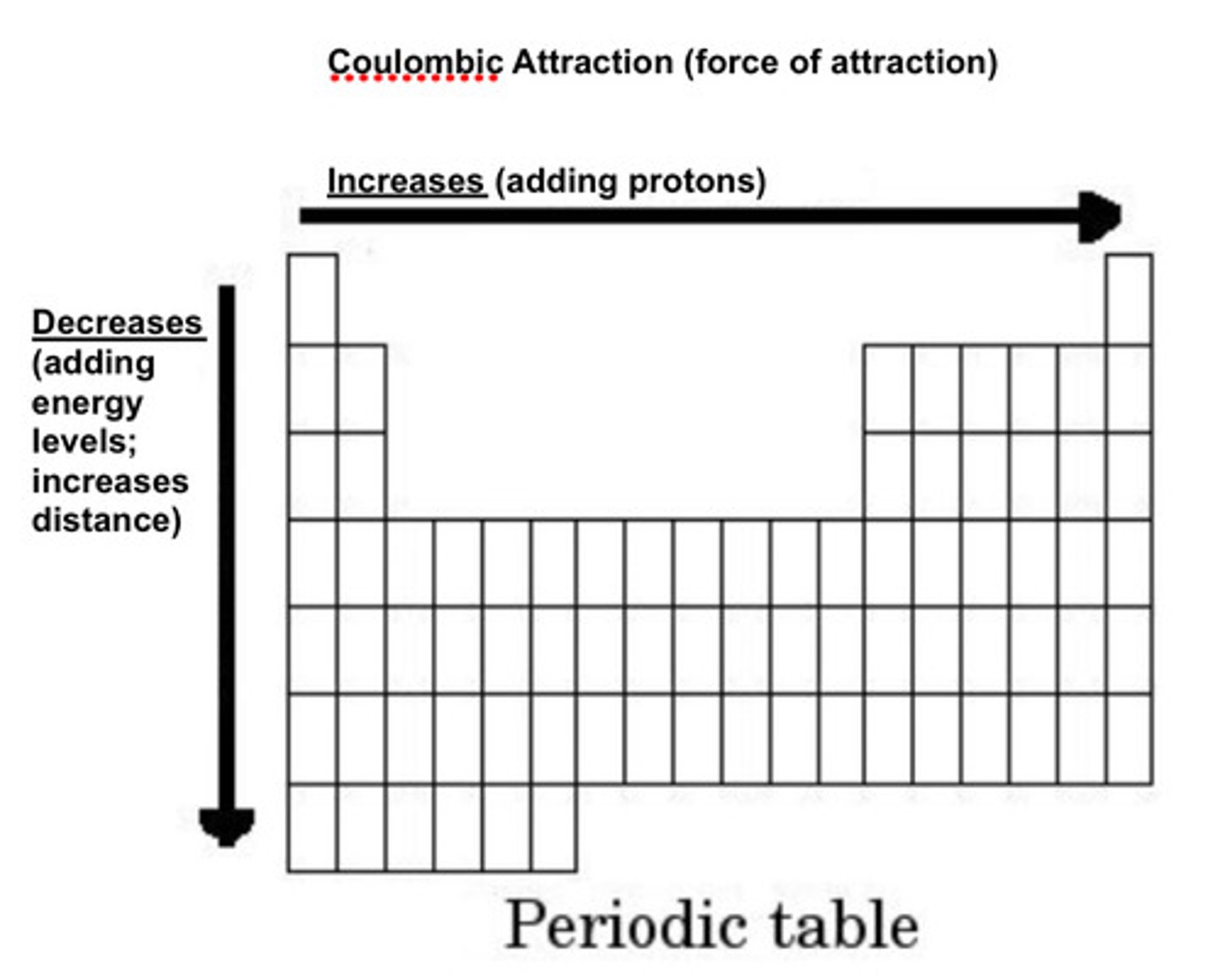
Coloumbic Attraction
The force of attraction between positive and negative charges
An increase in # of protons causes what to increase?
Force of attaction
A decrease in the distance between what causes the FoA to increase?
Outer most e- and p+
AN increase in what does not divide the FoA?
electrons
Force of Attraction periodic table
Atomic Radius
Distance between the center of the nucleus and valence electron
Atomic radius periodic trend

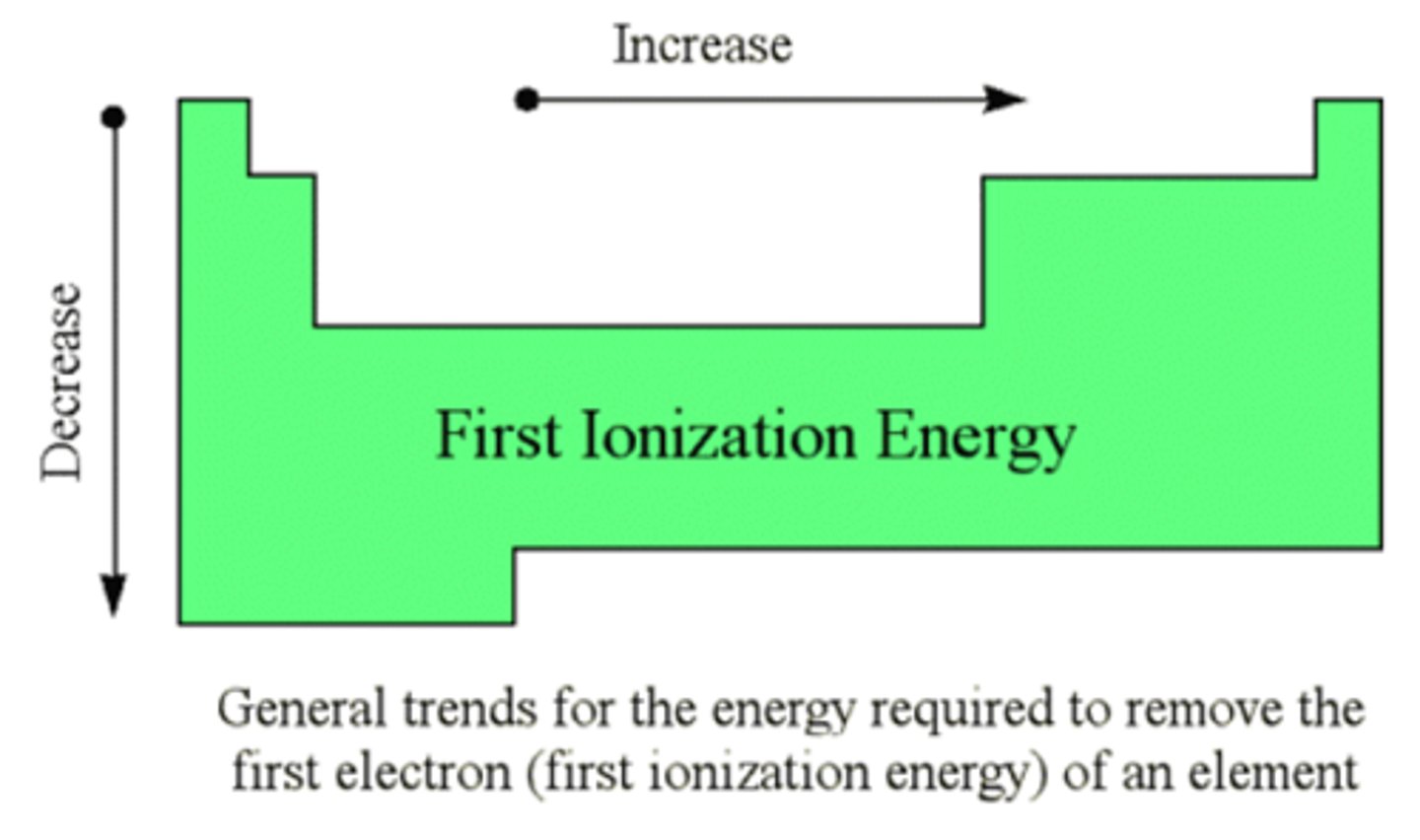
Ionization energy
The amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom
Ionization energy trend
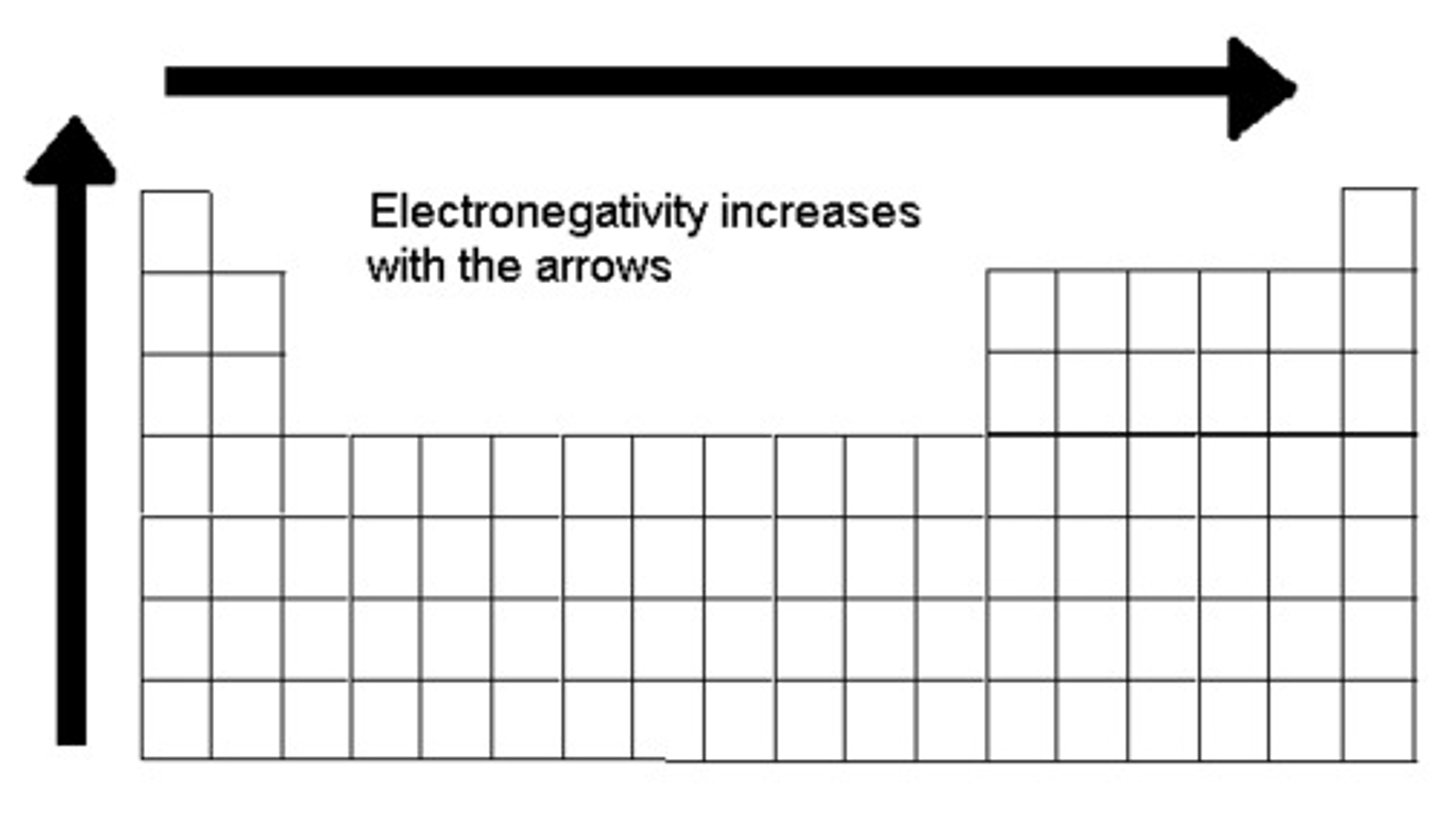
Electronegativity
A measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons
electronegativity trend
Lewis dot diagrams
diagrams that show the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
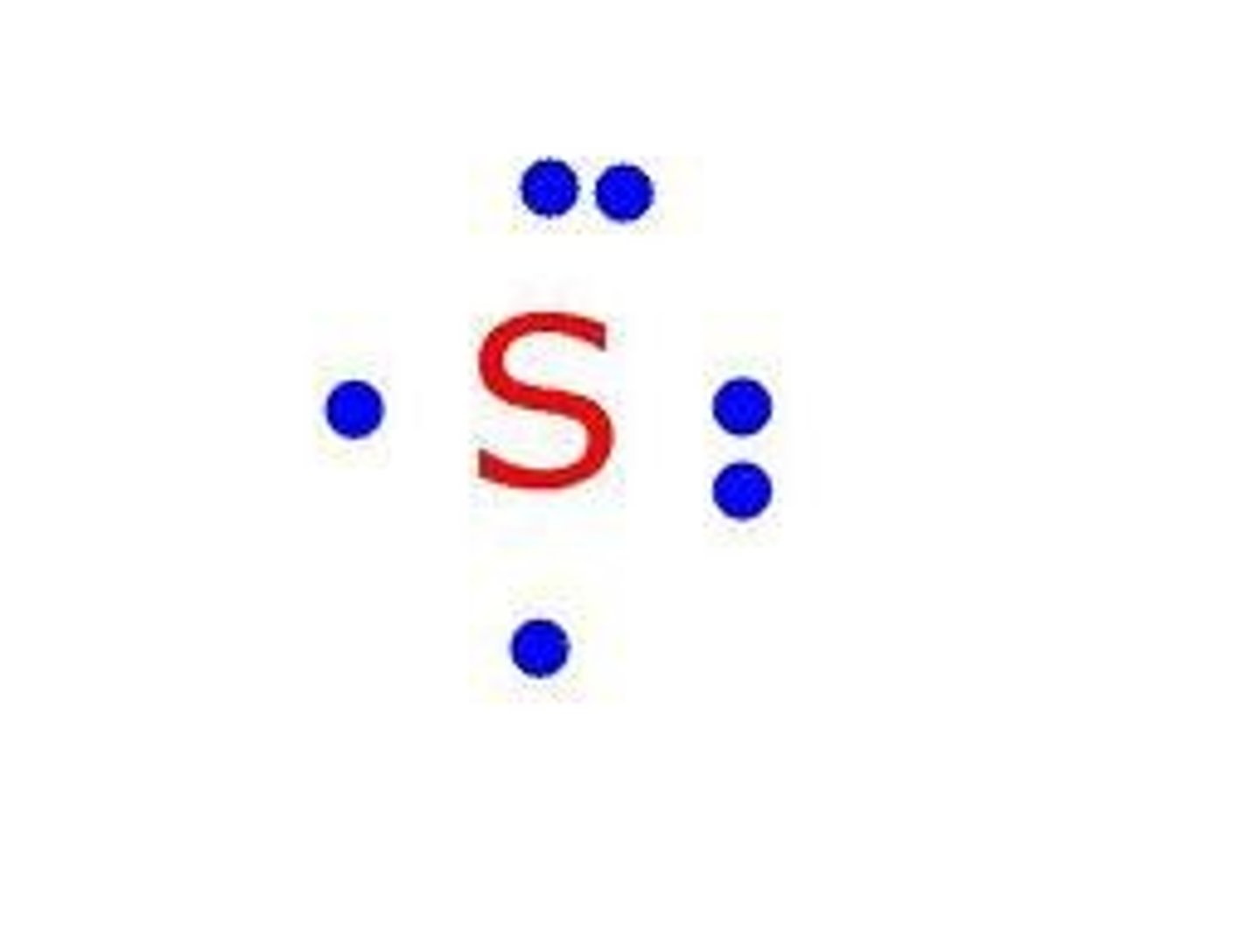
Ionic compounds form when
oppositely charged ions attract
Formulas for ionic compounds
Write the cation element symbol followed by the anion element symbol.
The number of cations and anions must be correct for their charges to sum to zero.
Properties of ionic compounds
1. Conduct electricity
2. High melting points
3. Solids at room temperature
How are covalent compounds formed
by sharing electrons
Covalent formulas
Prefixes to subscripts tell how many atoms. Ex: N3P2=Trinitrogen diphosphide
properties of covalent compounds
1. DO not conduct electricity
2. Low melting points
3. Solids, liquids, or gases at room temperature
Monatomic Ions
ions formed from a single atom
Polyatomic ions
ions that are made of more than one atom
Naming ionic compounds
The name of the metal comes first, followed by the name of the nonmetal, changing the nonmetal's ending to "ide".
Cations
metals
Anions
nonmetals
When do you use Roman numerals?
transition metals
When do you use parentheses for polyatomic ions?
When a polyatomic ion is used more than once
How do you name covalent molecules?
1. Name first nonmetal
2. Name 2nd nonmetal (ide)
When do you use prefixes?
During covalent compounds
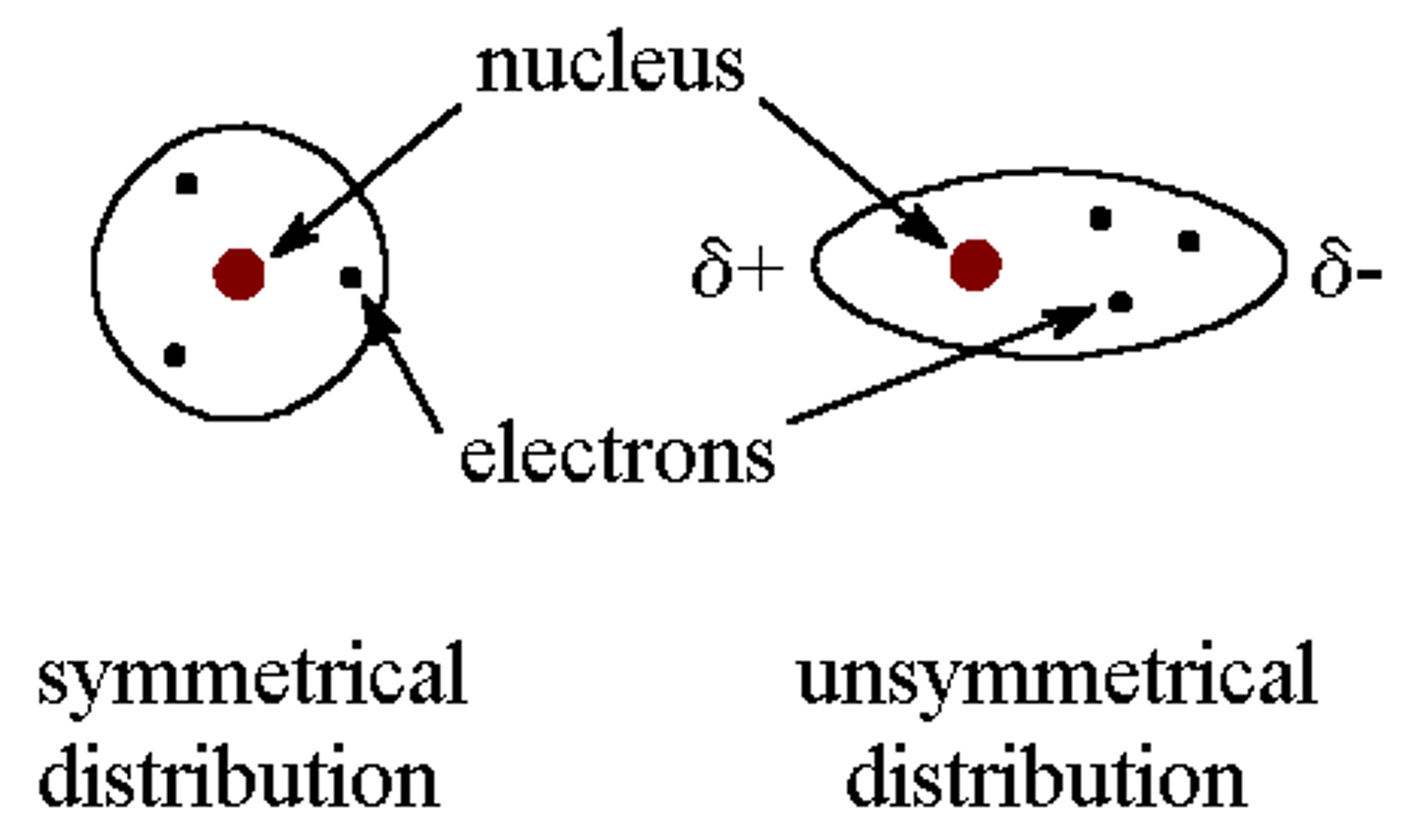
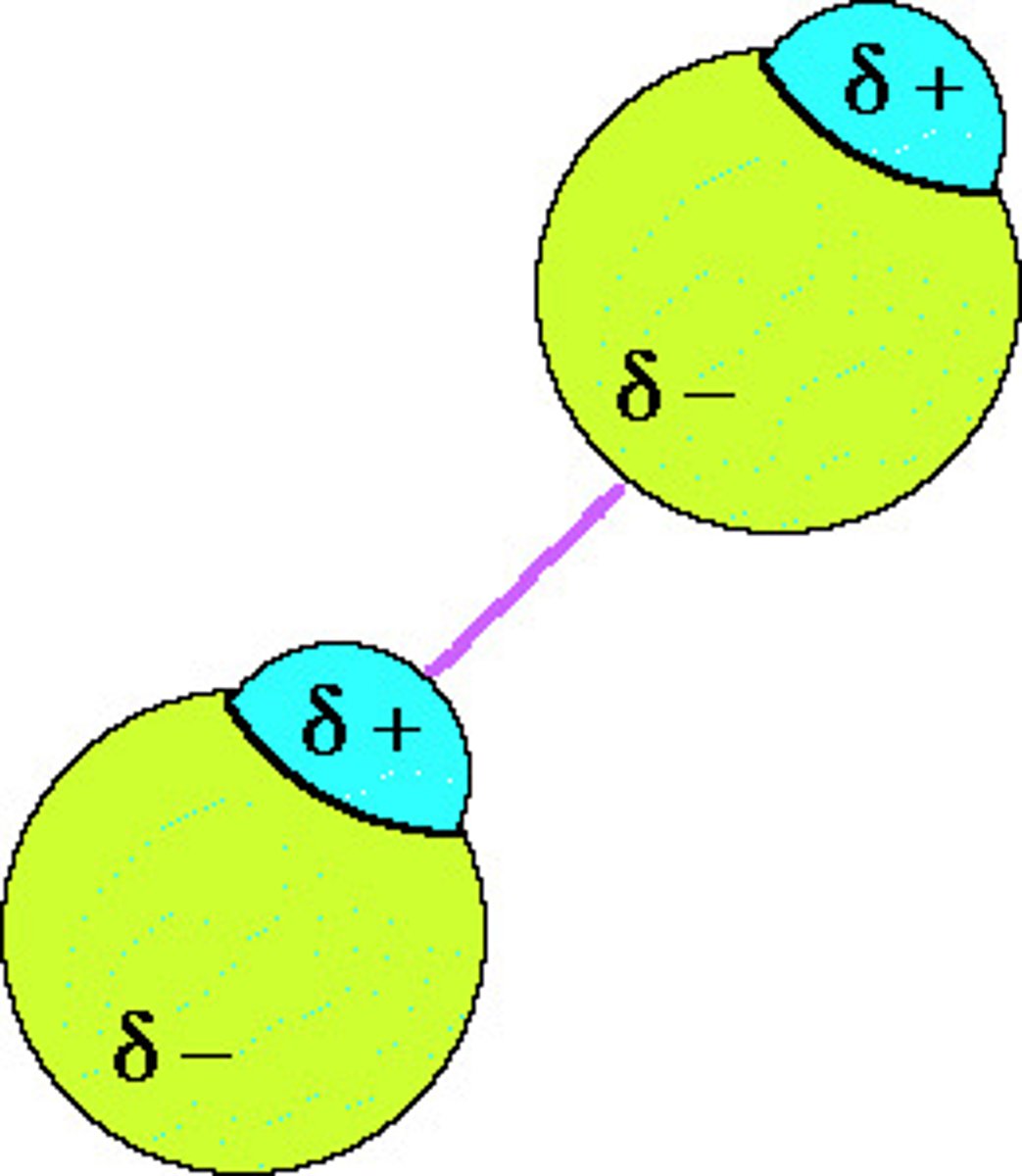
When does polarity occur?
when two atoms have a relative difference in electronegativities and share electrons unequally in a covalent bond
What does polarity create?
A dipole with slight + and - ends within a bond/molecule
What direction does a dipole arrow always point?
Toward the more electronegative atom
Change in Electronegativity <0.5
Non polar covalent
Change in Electronegativity 0.5-2
Polar covalent
Change in electronegativity >2
Ionic
What are inter molecular forces?
forces of attraction between molecules
If the IMFs are high, what is the phase of a substance
Solid
If the IMFs are medium, what is the phase of a substance
Liquid
If the IMFs are low, what is the phase of a substance
Gas
London Dispersion Forces
- occurs in all atoms/molecules
- electrons move to one side
- temporary/instantaneous divide
How to tell what has greater LDFS?
Number of electrons
Dipole Dipole
polar molecules
How to tell strength of dipole dipole?
Electronegativity
Hydrogen Bonding
Occurs in polar molecules with FON bonds
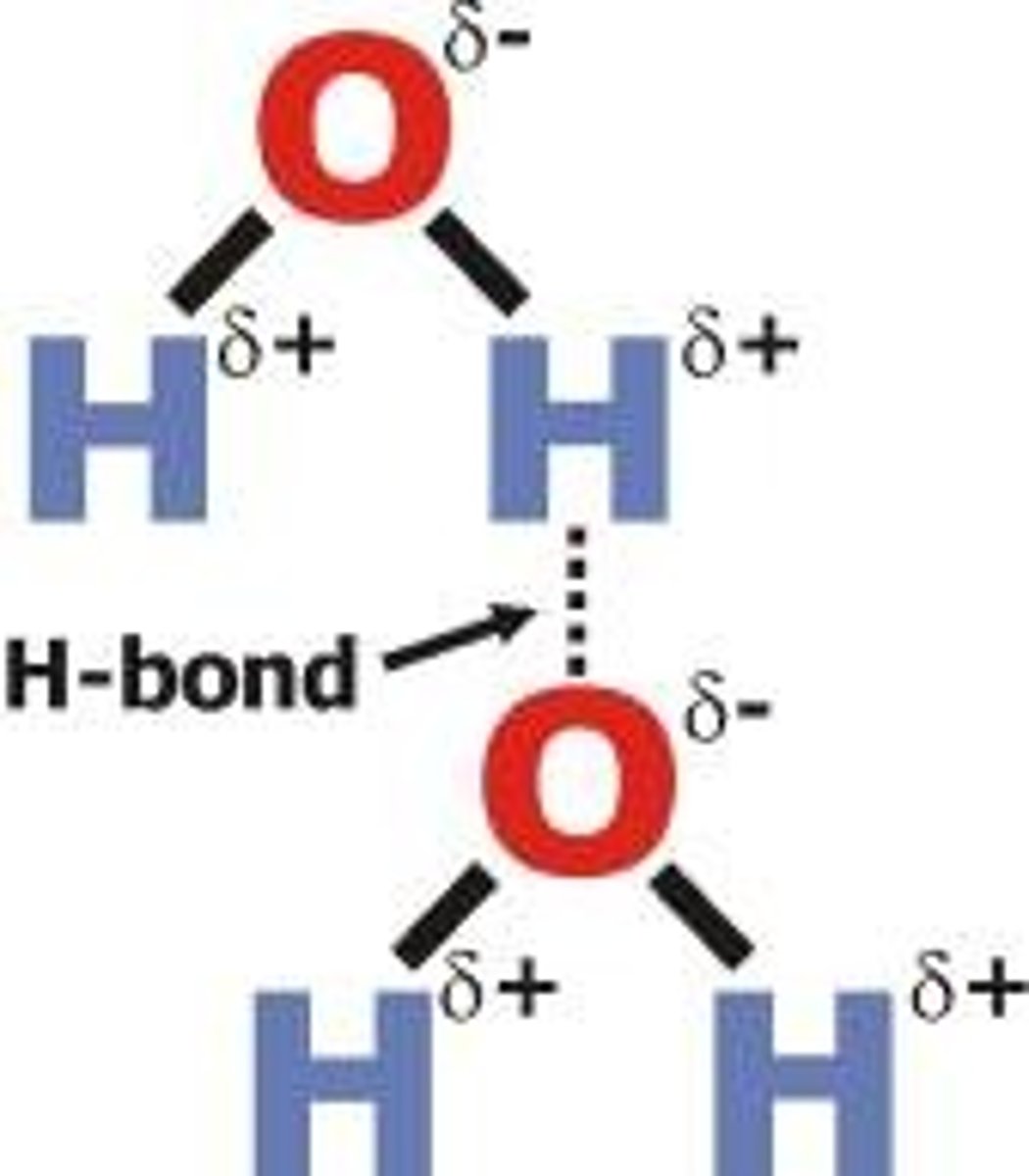
How to tell strength of HBs?
Number of FON bonds
Phase energy
The amount of energy needed to change the phase of a substance
Formula for phase energy
q=mH
Heat of fusion
Amount of energy required to change a substance from the solid phase to the liquid phase.
Heat of vaporization
The amount of energy required for the liquid at its boiling point to become a gas
Thermal energy
The amount of energy stored in moving particles
Formula for thermal energy
q=mcat

Specific heat energy
the amount of heat energy required to increase the temperature of one gram of a substance by one degree Celsius
Temperature
A measure of the average energy of motion of the particles of a substance.
Which direction does energy flow in?
hot to cold
Smaller specific heat means:
More mass needed for energy transfer